Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Elemental Analysis
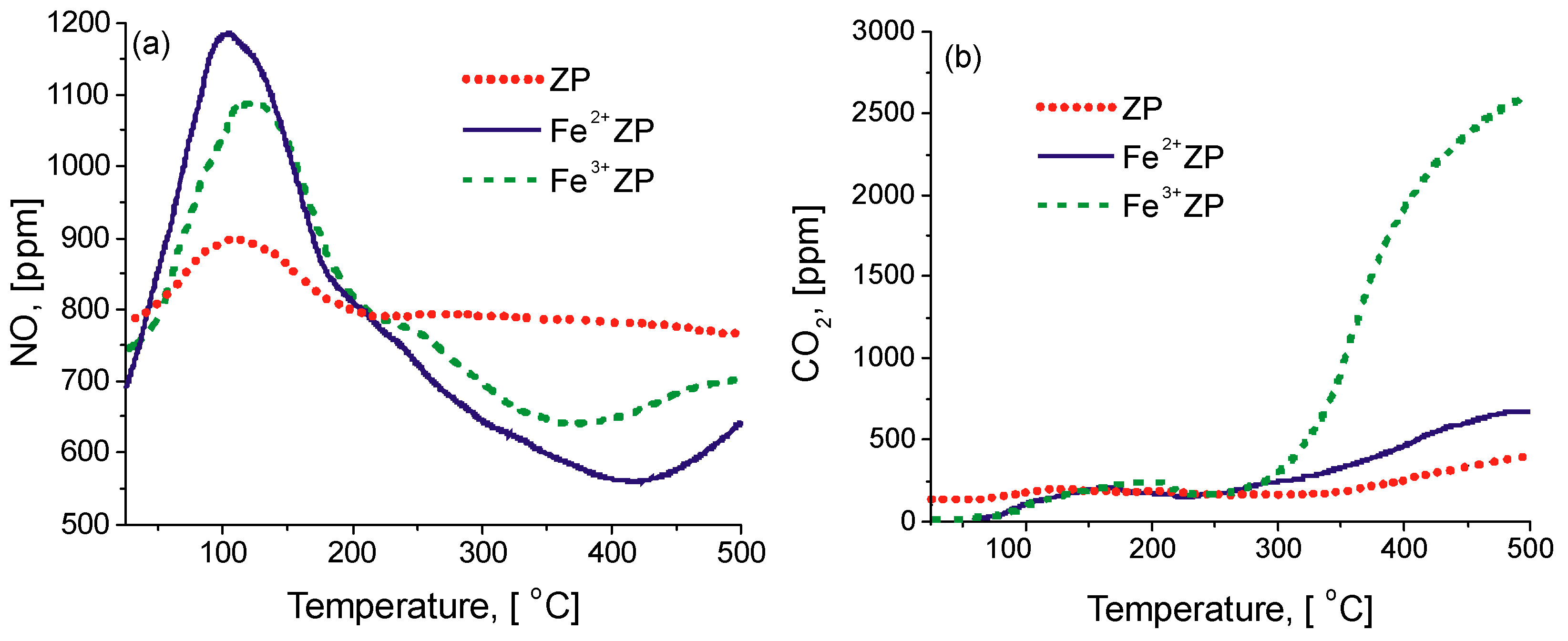
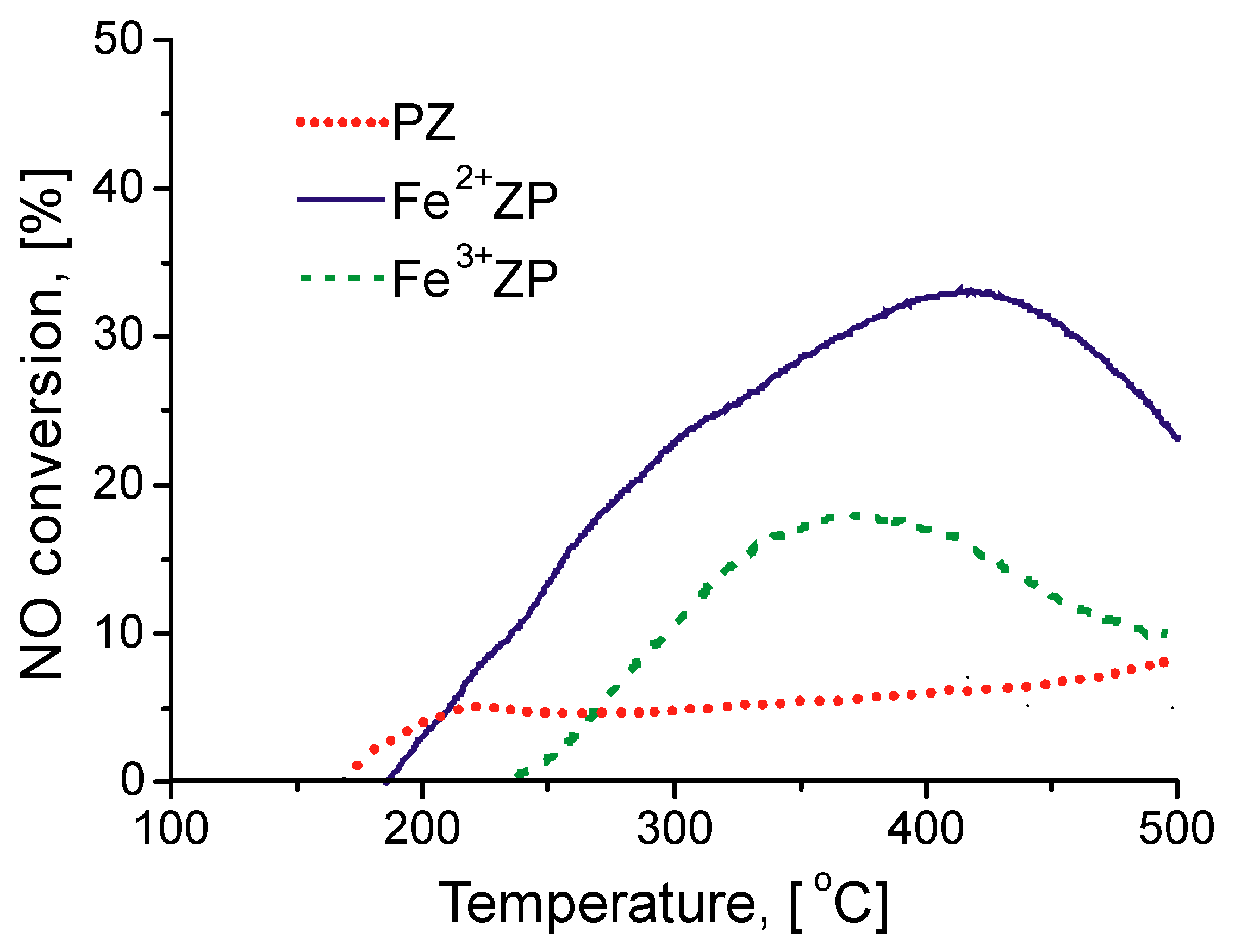
2.2. Catalytic Activity in HC-SCR
2.3. XRD Analysis
2.4. Textural Properties
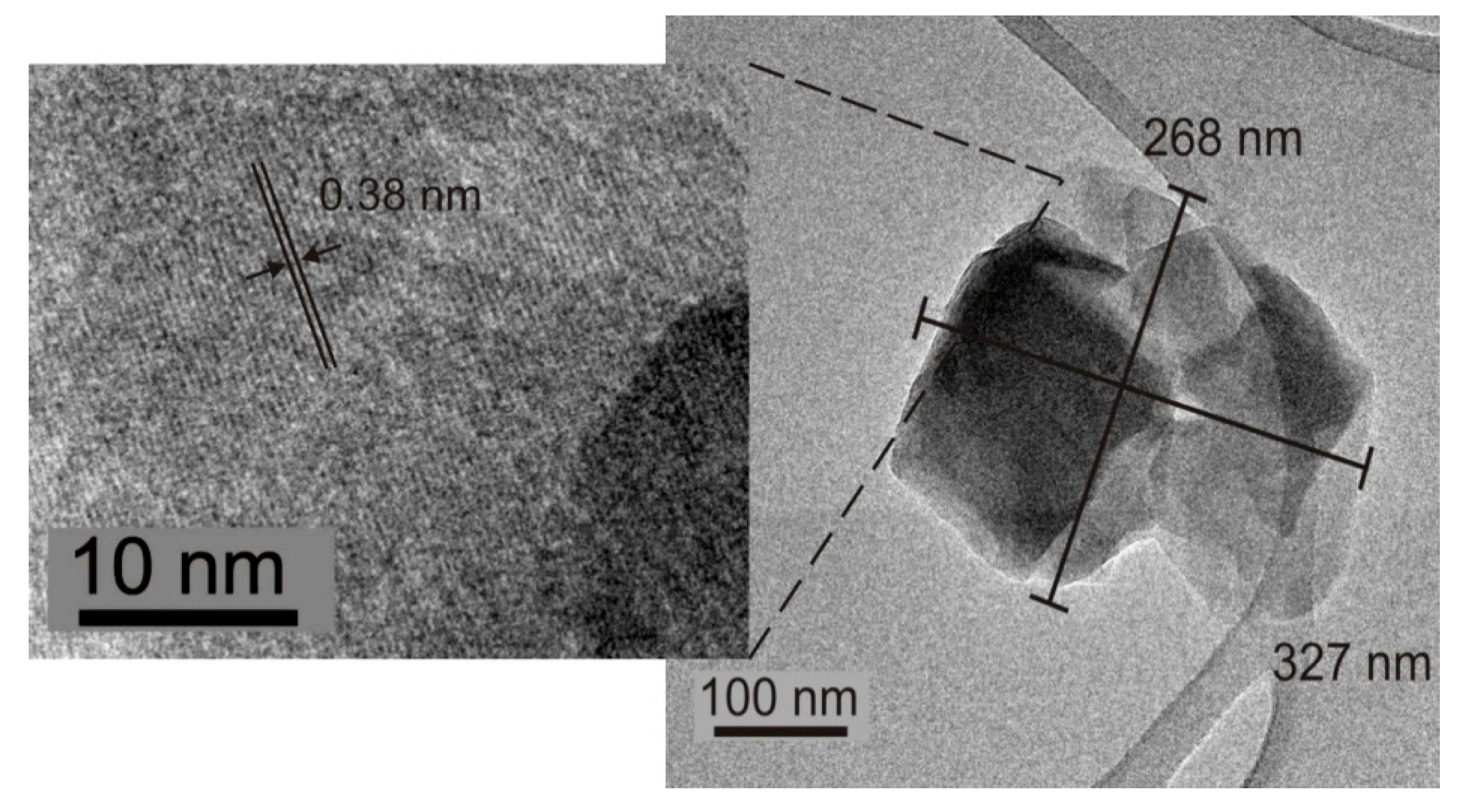
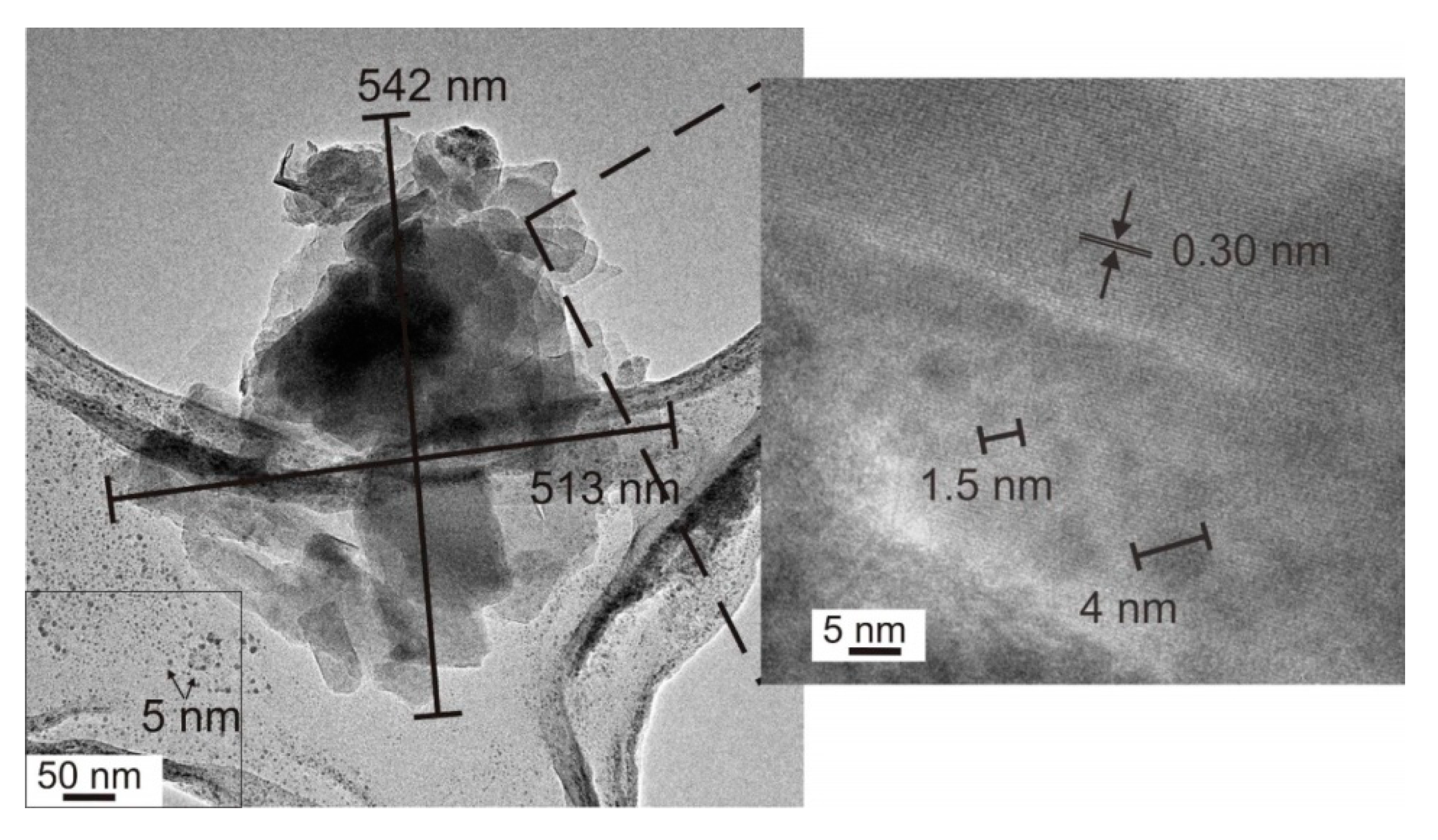
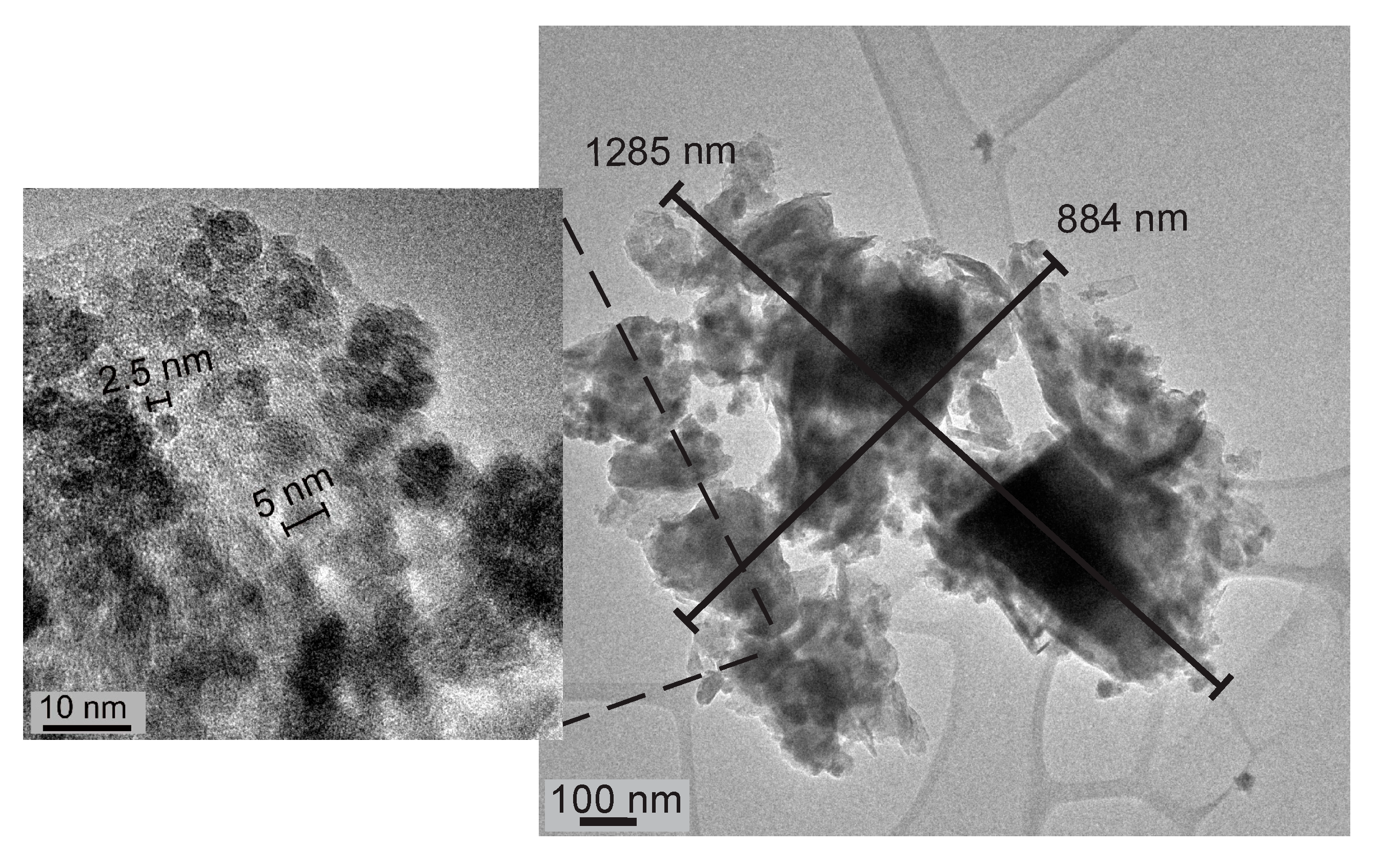
2.5. HRTEM Analysis
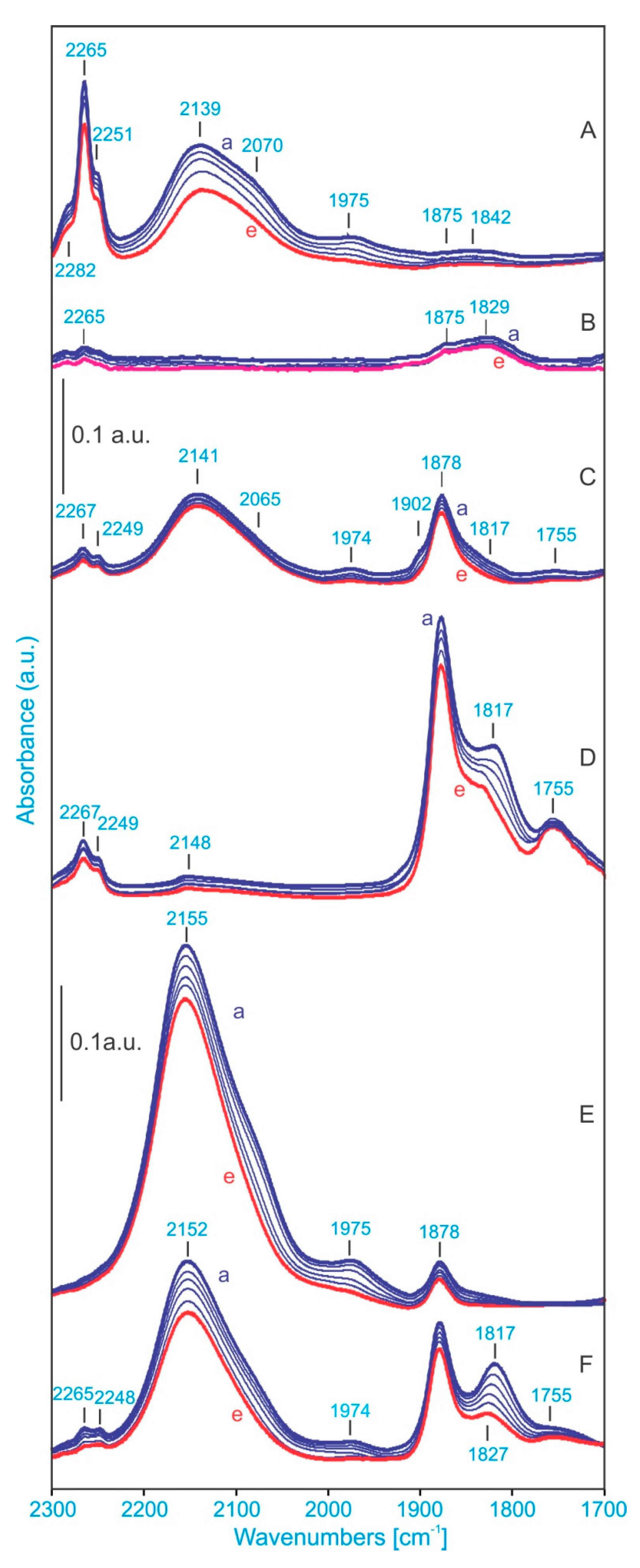
2.6. NO Adsorption Studies Followed by FTIR
2.6.1. ZP Sample
2.6.2. Fe2+ZP and Fe3+ZP Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinrich, F.; Schmidt, C.; Löffler, E.; Grünert, W. A highly active intra-zeolite iron site for the selective catalytic reduction of NO by isobutene. Catal. Commun. 2001, 2, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, A.M.; Mert, S.; Due-Hansen, J.; Fehrmann, R.; Christensen, C.H. Fe-BEA Zeolite Catalysts for NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Lett. 2009, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.; Makkee, M. Preparation of Fe-ZSM-5 with enhanced activity and stability for SCR of NOx. Catal. Today 2006, 114, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, S.; Kröcher, O.; Tissler, A.; Althoff, R. The determination of the activities of different iron species in Fe-ZSM-5 for SCRof NO by NH3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. A comparative study of the NH3-SCR reactions over a Cu-zeoliteand a Fe-zeolite catalys. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Millington, P.J.; Bailie, J.E.; Rajaram, R.R.; Anderson, J.A. A comparative study of the role of the support on the behaviourof iron based ammonia SCR catalysts. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 104, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høj, M.; Beier, M.J.; Grunwaldt, J.D.; Dahl, S. The role of monomeric iron during the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3 over Fe-BEA zeolite catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 93, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, R.H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Lambert, C.K.; Yang, R.T. Mechanism of Propene Poisoning on Fe-ZSM-5 for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucherov, A.; Montreuil, C.; Kucherova, T.; Shelef, M. In situ high-temperature ESR characterization of FeZSM-5 and FeSAPO-34 catalysts in flowing mixtures of NO, C3H6, aand O2. Catal. Lett. 1998, 56, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosius, R.; Martens, J.A. Reaction Mechanisms of Lean-Burn Hydrocarbon SCR over Zeolite Catalysts. Top. Catal. 2004, 28, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosius, R.; Martens, J.A. Analysis of the structural parameters controlling the temperature window of the process of SCR-NOx by low paraffins over metal-exchanged zeolites. Catal. Today 2002, 75, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Y.; Wang, X.; Sachtler, W.M.H. Reduction of NOx over zeolite MFI supported iron catalysts: Nature of active sites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, J.; Gurgul, J.; Socha, R.P.; Shishido, T.; Che, M.; Dzwigaj, S. Selective catalytic reduction of NO by ethanol: Speciation of iron and “structure–properties” relationship in FeSiBEA zeolite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 91, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, R.; Aissat, A.; Cousin, R.; Courcot, D.; Siffert, S. Catalysts for NOx selective catalytic reduction by hydrocarbons (HC-SCR). Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 504, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, M.A.; Pitchon, V.; Kiennemann, A. Pollution by nitrogen oxides: An approach to NO(x) abatement by using sorbing catalytic materials. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 445–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowskaa, M.; Chmielarz, L.; Macina, D.; Piwowarska, Z.; Dudek, B.; Adamski, A.; Witkowski, S.; Sojka, Z.; Obalová, L.; van Oers, C.J.; et al. Catalytic decomposition and reduction of N2O over micro-mesoporous materials containing Beta zeolite nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 146, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Park, J.H.; Shin, C.H.; Lee, J.; Seo, G. Catalytic decomposition of nitrous oxide over Fe-BEA zeolites:Essential components of iron active sites. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.G.; Chen, F.; Zhan, X. Characterization of iron-containing AlPO-5 as a stable catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of N2O with CH4 in the presence of steam. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 435, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Guo, Y.; Bi, H.T. NOx adsorption and reduction with C3H6 over Fe/zeolite catalysts: Effect of catalyst support. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchina, A.; Rivallan, M.; Berlier, G.; Lamberti, C.; Ricchiardi, G. Structure and nuclearity of active sites in Fe-zeolites: Comparison with iron sites in enzymes and homogeneous catalysts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 3483–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tito-Ferro, D.; Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Concepción-Rosabal, B.; Berlier, G.; Chávez-Rivas, F.; Penton-Madrigal, A.; Castillón-Barraza, F.; Petranovskii, V. Iron exchanged natural mordenite: UV–Vis diffuse reflectance and Mössbauer spectroscopy characterisation. Int. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Gelves, J.F.; Dorkis, L.; Márquez, M.A.; Álvarez, A.C.; González, L.M.; Villa, A.L. Activity of an iron Colombian natural zeolite as potential geo-catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Today 2019, 320, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, A.; Reitzmann, A.; Hardacre, C.; Yalcin, H. Abatement of nitrous oxide over natural and iron modified natural zeolites. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 407, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisuradze, G.; Sidamonidze, S.; Akhalbedashvili, L.; Kvatashidze, R. Modified Natural Zeolites as Catalysts for Catalytic Reduction of NO with CO—Main Components of Exhaust Gases. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. B 2015, 4, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Tost, R.; Santamaría-González, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Jiménez-López, A.; Autié, M.A.; Carreras-Glacial, M.; Autié-Castro, G.; Guerra, M. Selective Catalytic Reduction of Nitric Oxide by Ammonia over Ag and Zn-Exchanged Cuban Natural Zeolites. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2005, 631, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiro, H.; Iwamoto, M. Copper ion-exchanged zeolite catalysts in deNOx reaction. Appl. Catal. A 2001, 222, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Petranovskii, V.; Castillón-Barraza, F.; Concepción-Rosabal, B. Copper-Silver Bimetallic System on Natural Clinoptilolite: Thermal Reduction of Cu2+ and Ag+ Exchanged. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, O.E. Natural Zeolites 93: Occurrence, Properties, Use; Ming, D.W., Mumpton, F.A., Eds.; ICNZ: Brockport, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Ivanova, E.; Kefirov, R.; Janas, J.; Plesniar, A.; Dzwigaj, S.; Che, M. Adsorption properties of Fe-containing dealuminated BEA zeolites as revealed by FTIR spectroscopy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 131, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjar, R.; Millot, Y.; Man, P.P.; Che, M.; Dzwigaj, S. Two Kinds of Framework Al Sites Studied in BEA Zeolite by X-ray Diffraction, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, NMR Techniques, and V Probe. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 20167–20175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Fuentes, G.R.; Aguilar, A.B. The role of carbonate ions in the ion-exchange Ni2+=2NH4+ in natural clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2000, 41, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Gómez, A.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G.; Aguilar, A.B.; Ballan, J.S. Natural clinoptilolite as an exchanger of Ni2+ and NH4+ ions under hydrothermal conditions and high ammonia concentration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2002, 53, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breck, D.W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves: Structure, Chemistry and Use; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Zorpas, A.A.; Loizidou, M.D.; Grigoropoulou, H.P. Simultaneous removal of metals Cu2+, Fe3+ and Cr3+ with anions SO42- and HPO42- using clinoptilolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Sugiyama, S.; Matsuoka, O.; Honda, T.; Banno, Y.; Nosoye, H. AFM imaging of the surface of natural heulandite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J. Inorganic Chemistry in Aqueous Solutions; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G.; Murrillo, C.A.; Bochmann, M. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ugurlu, O.; Haus, J.; Gunawan, A.A.; Thomas, M.G.; Maheshwari, S.; Tsapatsis, M.; Mkhoyan, K.A. Radiolysis to knock-on damage transition in zeolites under electron beam irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 113408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; Meier, W.M.; Olson, D.H. Framework Type MOR (Material: Mordenite), Database of Zeolite Structures. 2013. Available online: http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 3 April 2019).
- Skarlis, S.A.; Berthout, D.; Nicolle, A.; Dujardin, C.; Granger, P. Combined IR spectroscopy and kinetic modeling of NOx storage and NO oxidation on Fe-BEA SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 148, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, M.; Marie, O.; Bazin, P.; Daturi, M. Fe-H-BEA and Fe-H-ZSM-5 for NO2 removal from ambient air —A detailed in situ and operando FTIR study revealing an unexpected positive water-effect. J. Catal. 2010, 271, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivallan, M.; Ricchiardi, G.; Bordiga, S.; Zecchina, A. Adsorption and reactivity of nitrogen oxides (NO2, NO, N2O) on Fe–zeolites. J. Catal. 2009, 264, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlier, G.; Lamberti, C.; Rivallan, M.; Mul, G. Characterization of Fe sites in Fe-zeolites by FTIR spectroscopy of adsorbed NO: Are the spectra obtained in static vacuum and dynamic flow set-ups comparable? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlier, G.; Pourny, M.; Bordiga, S.; Spoto, G.; Zecchina, A.; Lamberti, C. Coordination and oxidation changes undergone by iron species in Fe-MCM-22 upon template removal, activation and red–ox treatments: An in situ IR, EXAFS and XANES study. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Tsyntsarski, B.; Nikolova, T. Stability and reactivity of the nitrogen-oxo species formed after NO adsorption and NO+O2 coadsorption on Co-ZSM-5: An FTIR spectroscopic study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 4521–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gankanda, A.; Grassian, V.H. Nitrate Photochemistry in NaY Zeolite: Product Formation and Product Stability under Different Environmental Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 2205–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacław, A.; Nowinska, K.; Schwieger, W.; Zielinska, A. N2O decomposition over iron modified zeolites ZSM-5. Catal. Today 2004, 90, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Penkova, A.; Daturi, M.; Saussey, J.; Lavalley, J.C. FTIR spectroscopic study of low-temperature co-adsorption of NO and O2 on H-ZSM-5: Evidence of formation of [ONNO]+ species. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2003, 377, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiivanov, K.; Saussey, J.; Freysz, J.L.; Lavalley, J.C. FT-IR study of NO + O2 co-adsorption on H-ZSM-5: Re-assignment of the 2133 cm-1 band to NO+ species. Catal. Lett. 1998, 52, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Bi, R.; Zhao, Z.; He, H. Defect of HY as catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO in comparison with the pentasil zeolites. J. Mol. Catal. A 2009, 303, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, C.; Marie, O.; Thibault-Starzyk, F.; Lavalley, J.C. NO+ ions as IR probes for the location of OH groups and Na+ ions in main channels and side pockets of mordenite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 50, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, G.B.G.; Bordiga, S.; Richiardi, G.; Fisicaro, P.; Zecchina, A.; Rossetti, I.; Selli, E.; Forni, L.; Giamello, E.; Lamberti, C. Evolution of Extraframework Iron Species in Fe Silicalite; 1. Effect of Fe Content, Activation Temperature, and Interaction with Redox Agents. J. Catal. 2002, 208, 64–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lezcano, M.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; d′Itri, J.L. FTIR Study of the Interaction of Nitric Oxide with Fe-ZSM-51. Kinet. Catal. 2001, 42, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traa, Y.; Burger, B.; Weitkamp, J. Zeolite-based materials for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with hydrocarbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 30, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Z.; Ruan, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Infrared Study of the NO Reduction by Hydrocarbons over Iron Sites with Low Nuclearity: Some New Insight into the Reaction Pathway. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 15713–15727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, A.A.; Bitter, J.H.; Koningsberger, D.C. Reactivity of binuclear Fe complexes in over-exchanged Fe/ZSM5, studied by in situ XAFS spectroscopy 2. Selective catalytic reduction of NO with isobutene. J. Catal. 2003, 218, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, T.; Liang, D.; Xu, C.; Tang, J.; Lin, L. Effect of addition of Zn on the catalytic activity of a Co/HZSM-5 catalyst for the SCR of NOx with CH4. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 35, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.L.M.; Silva, C.M.; Moreno-Tost, R.; Lopes-Farias, T.; Jiménez-López, A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. A study of copper-exchanged mordenite natural and ZSM-5 zeolites as SCR–NOx catalysts for diesel road vehicles: Simulation by neural networks approach. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 88, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglino, D.; Li, H.; Erickson, R.; Lund, A.; Yahiro, H.; Shiotani, M. EPR and ENDOR studies of NOx and Cu2+ in zeolites: Bonding and diffusion. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 2887–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tito-Ferro, D.; Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Concepción-Rosabal, B.; Chávez-Rivas, F. El hierro en la roca zeolitizada del yacimiento de Palmarito de Cauto: Separación y caracterización de fases magnéticas, V. Córdova-Rodríguez, R. Rizo-Beyra. Rev. Min. Y Geol. 2011, 27, 22–37. [Google Scholar]
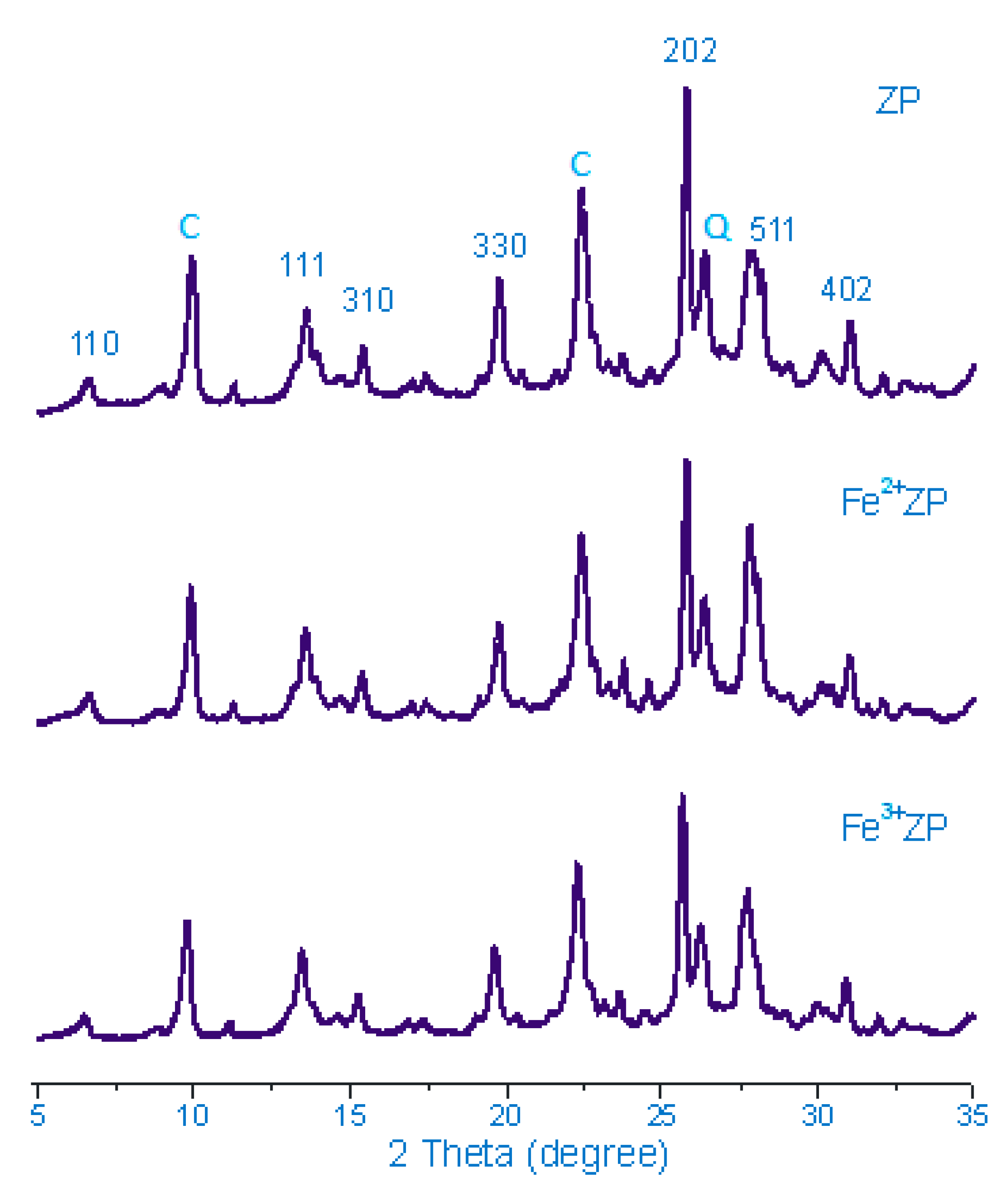
| Plane | Peak Position (Shift) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ZP | Fe2+ZP | Fe3+ZP | |
| 111 | 13.57 | 13.55 (0.02) | 13.44 (0.11) |
| 310 | 15.41 | 15.40 (0.01) | 15.27 (0.13) |
| 330 | 19.77 | 19.74 (0.03) | 19.59 (0.15) |
| 202 | 25.76 | 25.76 | 25.63 (0.13) |
| 402 | 31.06 | 31.04 (0.02) | 30.89 (0.15) |
| Sample | SSABET (m2/g) | SSALang (m2/g) | SSAext (m2/g) | Vmic (cm3/g) | Amic (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZP | 244 | 312 | 3 | 0.109 | 241 |
| Fe2+ZP | 259 | 331 | 26 | 0.105 | 233 |
| Fe3+ZP | 256 | 328 | 26 | 0.104 | 230 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chávez Rivas, F.; Rodríguez-Iznaga, I.; Berlier, G.; Tito Ferro, D.; Concepción-Rosabal, B.; Petranovskii, V. Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts. Catalysts 2019, 9, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100866
Chávez Rivas F, Rodríguez-Iznaga I, Berlier G, Tito Ferro D, Concepción-Rosabal B, Petranovskii V. Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts. Catalysts. 2019; 9(10):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100866
Chicago/Turabian StyleChávez Rivas, Fernando, Inocente Rodríguez-Iznaga, Gloria Berlier, Daria Tito Ferro, Beatriz Concepción-Rosabal, and Vitalii Petranovskii. 2019. "Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts" Catalysts 9, no. 10: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100866
APA StyleChávez Rivas, F., Rodríguez-Iznaga, I., Berlier, G., Tito Ferro, D., Concepción-Rosabal, B., & Petranovskii, V. (2019). Fe Speciation in Iron Modified Natural Zeolites as Sustainable Environmental Catalysts. Catalysts, 9(10), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9100866







