Abstract
Fishery processing by-products have been of great interest to researchers due to their beneficial applications in many fields. In this study, five types of marine by-products, including demineralized crab shell, demineralized shrimp shell, shrimp head, shrimp shell, and squid pen, provided sources of carbon and nitrogen nutrition by producing a protease from Paenibacillus sp. TKU047. Strain TKU047 demonstrated the highest protease productivity (2.98 U/mL) when cultured for two days on a medium containing 0.5% of shrimp head powder (SHP). The mass of TKU047 protease was determined to be 32 kDa (approximately). TKU047 protease displayed optimal activity at 70–80 °C and pH 9, with a pH range of stability from 6 to 11. TKU047 protease also showed stability in solutions containing surfactants and detergents. Based on its excellent properties, Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease may be a feasible candidate for inclusion in laundry detergents.
1. Introduction
Every year, the seafood processing industry discards a large amount of by-products, including viscera, shells, heads, squid pens, fins, and bones, even though they could be recycled to produce bioactive compounds like gelatin [1,2,3,4], enzymes [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], chitin [8,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26], chitin oligomers [7,11,12], α-glucosidase inhibitors (aGI) [27,28,29,30,31], carotenoids [32,33], and bioactive peptides [34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. Consequently, much research has gone into converting these by-products into bioactive products that have potential applications in biotechnological, agricultural, nutritional, pharmaceutical, and biomedical industries [1,4,5,17]. Marine chitinous byproducts, such as shells of crabs and shrimps, and pens (gladius) of squids, are a great source of chitin. However, these materials also contain a significant amount of mineral salts and proteins [4,8,17]. As a result, strong alkalis and acids are typically used for deproteinization and demineralization during the production of chitin and chitosan. However, there are several drawbacks to the use of chemical procedures. With a more environmentally friendly production process, these marine byproducts could be used as carbon/nitrogen sources for microorganism bioconversion to various high-value products, including chitinase/chitosanase [6,11,12,13,15,16,20], proteases [13,14], exopolysaccharides [41,42,43], and tyrosinase inhibitors [44].
Proteases break down proteins to release peptides and amino acid bases upon catalyzing the hydrolytic reaction [45]. Since there is a huge demand for proteases in many fields, including detergent, brewing, meat, photography, leather, and dairy industries, research on the production and application of proteases is ongoing [46,47]. Compared to plant and animal sources, proteases from microorganisms have more advantages as they can be cultured at an industrial scale, have a short fermentation period, and are easy to obtain [45]. In addition, microorganisms could utilize a wide range of C/N sources, including various types of fishery by-products, to produce proteases [45], which would help reduce the cost of protease production and make their application more attractive.
Paenibacillus is a useful bacterial family employed in the medical, industrial, and agricultural fields [48]. Recently, when fishery processing by-products were used as the nutrition source (carbon and nitrogen), several strains of Paenibacillus exhibited excellent abilities in the production of bioactive compounds, including α-glucosidase inhibitors [49], exopolysaccharides [43], anti-inflammatory medication [50,51], antioxidants [30], and chitosanases [11,12,13]. However, few reports have examined proteases derived from Paenibacillus, especially using shrimp heads. While several Paenibacillus strains demonstrated protease productivity on media containing squid pen or demineralized crab shell, the properties of their proteases were not explored [13].
In the current study, a proteolytic strain screened from soil samples at Tamkang University, Paenibacillus sp. TKU047, used squid pen powder (SPP) as the main source for providing carbon, as well as nitrogen. The optimal conditions for protease production on five types of fishery processing by-products including SPP, shrimp shell powder (SSP), demineralized crab shell powder (deCSP), shrimp head powder (SHP), and demineralized shrimp shell powder (deSSP), as well as the enzyme characteristics were investigated. In order to determine its industrial potential, the detergent compatibility of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 was also explored.
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Screening of a Proteolytic Strain
More than 60 bacterial strains were obtained from soil samples using a medium containing 1% SPP. Among them, TKU047 showed the highest protease activity (1.97 U/mL). In studies aimed to find a bacterial strain which efficiently converted fishery processing by-products into worthwhile bioactive compounds, TKU047 showed good potential for protease production. Thus, TKU047 was selected for further experiments. TKU047 was proven to be a member of Paenibacillus by morphological, biochemical, and 16S rDNA sequencing methods. However, its identified profile using the API 50 CHB/E kit did not match with any specific Paenibacillus species. As such, TKU047 was simply identified as Paenibacillus sp. The biosynthesis of proteases by Paenibacillus have rarely been reported [52,53,54], especially on fishery processing by-products [13], therefore the current study shows promise in seeking to discover a novel protease.
2.2. Screening the C/N Source for Protease Production
Finding the best carbon/nitrogen (C/N) source was a necessary step for protease production in numerous reports [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. In the current study, five kinds of fishery processing byproducts were used to grow Paenbacillus sp. TKU047, including SHP, SPP, SSP, deSSP, and deCSP. Each material was added to a medium containing only basal mineral salts (0.05% MgSO4 and 0.1% K2HPO4) at 1% concentration. As shown in Figure 1, protease productivity achieved the highest value at days 4 and 5, with the exception of SHP (only 3–4 days). The greatest production was found with SHP (2.93 U/mL on day 3 and 2.94 on day 4) and SPP (2.90 U/mL on day 5), followed by deCSP (2.63 U/mL on day 4), deSSP (2.16 U/mL on day 5), and SSP (0.95 U/mL on day 4). Although there was no significant difference between SHP and SPP in maximum protease productivity, TKU047 required a shorter incubation period with SHP than SPP (3 versus 5 days). As a result, SHP was chosen as the best source for producing protease by TKU047. Compared to other bacterial strains producing protease, TKU047 had higher protease productivity than Bacillus, Paenibacillus, and Serratia [13]. This suggested that Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 had potential for the conversion of fishery processing by-products for protease production.
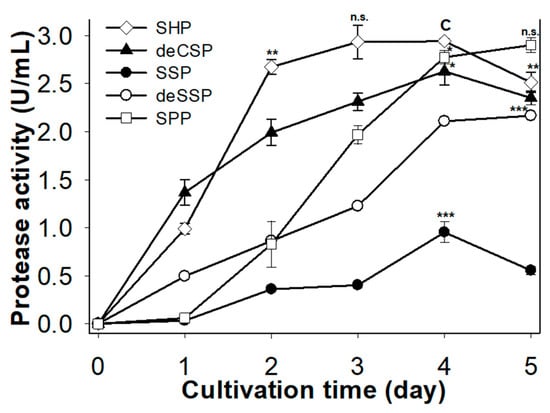
Figure 1.
Screening of fishery processing byproducts as the C/N source for protease production in Paenibacillus sp. TKU047. All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). The letters n.s., *, **, and *** indicate not significantly different or significantly different at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, or p < 0.001, respectively, in comparison with the control group (C) based on one-way ANOVA analysis. The data point of SHP at day 4 was used to denote the control group.
In many reports, protease production required extra sources, such as glucose [55], lactose [56], beef extract [57], peptone [58], or yeast extract [44]. Due to their higher costs, these chemicals would increase the price of enzyme production. By-products from agriculture and fishery processing could overcome this drawback by providing the sole C/N source for the microorganisms [8,13,14,45]. Among these, shrimp heads contain a high ratio of protein and chitin [13], which makes them a good C/N source for producing various bioactive compounds via microbial fermentation [11,27,29].
2.3. Effect of Shrimp Head Powder Concentration
The effect of SHP concentration on producing protease was investigated herein. Different SHP concentrations (0.1%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%, and 2%) were added to the basal medium (0.05% MgSO4, and 0.1% K2HPO4) to determine optimal concentration. As shown in Figure 2, maximum protease activity was found on days 2–4, but lower SHP concentrations achieved maximum protease activity in a shorter period of time than higher concentrations of SHP (2 days with 0.1% SHP and 0.5% SHP, 3 days with 1% SHP and 1.5% SHP, and 4 days with 2% SHP). The highest protease activity was generated with 0.5% SHP (2.98 U/mL, 2 days) and 1% SHP (2.97 U/mL on day 3 and 2.96 U/mL on day 4). This result suggests that lower SHP concentrations may achieve a better result than higher concentrations. Similarly, it was found that Paenibacillus sp. TKU042 expressed its highest protease activity at lower SPP concentrations of 0.5–2% [13]. Due to its shorter cultivation time and the lack of significant difference in protease activity compared to 1% SHP, 0.5% (w/v) was chosen as the best SHP concentration for producing protease.
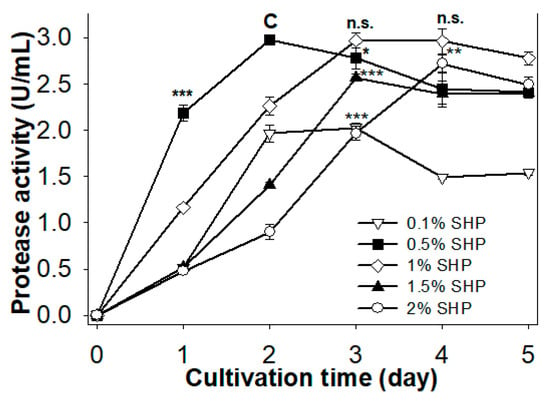
Figure 2.
Effect of SHP concentration on protease production in Paenibacillus sp. TKU047. All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). The letters n.s., *, **, and *** indicate not significantly different or significantly different at p < 0.05, p < 0.01, or p < 0.001 (respectively) in comparison with the control group (C), based on one-way ANOVA analysis. Data point of 0.5% SHP on day 2 was used to signify the control group.
2.4. Isolation of TKU047 Protease
TKU047 protease was purified from culture broth by the following steps: EtOH precipitation, ion chromatography, and size-exclusion chromatography. Table 1 shows the purification profile. The enzyme was efficiently concentrated by EtOH with 96.44% of activity retained and eluted on a Macro-Prep High S column using a NaCl gradient from 0 M to 1 M. As shown in Figure 3, only one activity peak appeared at the elution stage. The activity fractions were concentrated by lyophilization for later use. A high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system with KW802.5 column was used to purify TKU047 protease, and 7.83 g of TKU047 protease was collected with a recovery yield of 34.70% and a specific activity of 16.18 U/mg. It had been reported that Paenibacillus sp. TKU042 and P. tezpurensis sp. nov. AS-S24-II had higher values of specific activity than the TKU047 protease. However, the enzyme from TKU047 had the best recovery yield among the three [13,52].

Table 1.
Purification of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease.
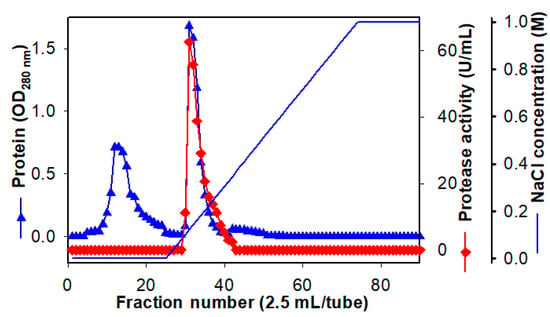
Figure 3.
A typical chromatogram of Macro-prep High S column of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease.
The purification of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 was also analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). As shown in Figure 4, the band of TKU047 protease clearly appears at the line of the culture supernatant, indicating that TKU047 may release protease into the medium as one of its main products in the presence of SHP. According to protein markers, the mass of TKU047 protease was 32 kDa, which was very similar to Paenibacillus sp. TKU042 protease (35 kDa) [13], but different from other Paenibacillus proteases, such as P. tezpurensis sp. nov. AS-S24-II (43 kDa) [52], P. larvae strain 44 (59 kDa) [53], and P. lautus CHN26 (52 kDa) [54].
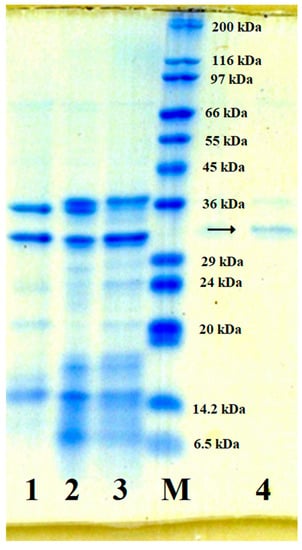
Figure 4.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) profile of the TKU047 protease. M: Protein markers. 1 and 2: Crude enzyme after EtOH precipitation. 3: Adsorbed on Macro-prep High S column. 4: Purified enzyme after HPLC analysis on KW802.5 column. →: Purified enzyme.
2.5. Effects of Temperature and pH on TKU047 Protease
As shown in Figure 5, TKU047 protease displayed optimal activity between 70–80 °C. TKU047 protease also expressed thermal stability, while retaining over 80% of its activity at 60 °C. These results suggest that TKU047 protease is a thermostable enzyme. Compared to other reports, TKU047 showed a higher optimal temperature than P. tezpurensis sp. nov. AS-S24-II protease (45–50 °C) [52] or P. lautus protease (20–30 °C) [54], and could be comparable with thermostable proteases from Bacillus strains [45]. A higher optimal temperature and thermostability are important factors for industrial applications; therefore, Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease has a great advantage over other proteases.
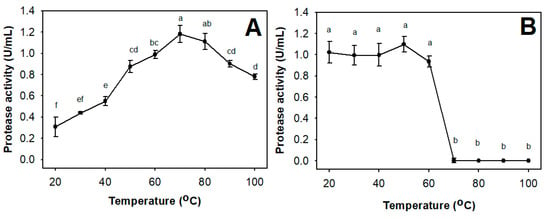
Figure 5.
Effect of temperature on the activity (A) and stability (B) of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease. All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). Different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) indicate significant difference based on Tukey’s test with p < 0.05.
The effect of pH on the activity and stability of TKU047 protease was also investigated. The optimal pH of TKU047 was 9 and the enzyme was stable in a pH range of 6–11 (Figure 6). With over 80% of enzyme activity retained at alkaline pH range (7–11), TKU047 protease was consequently defined as an alkaline protease. The vast majority of Paenibacillus proteases express higher activity under alkaline conditions; the optimal pH is approximately 9 [52,54]. Alkaline proteases have received much attention due to their many applications in the detergent, food, pharmaceutical, and leather industries [45]. It is therefore worthwhile to investigate Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease for other valuable properties.
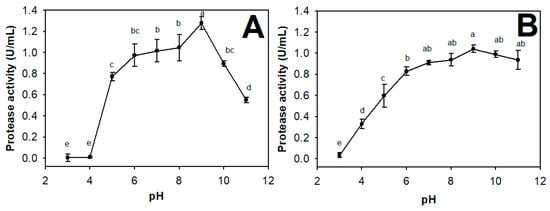
Figure 6.
Effect of pH on activity (A) and stability (B) of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease. All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). Different letters (a, b, c, d, and e) indicate significant difference based on Tukey’s test with p < 0.05.
2.6. Substrate Specificity
As shown in Figure 7, TKU047 protease expressed the greatest activity in order of casein > fibrinogen > keratin > albumin > gelatin > elastin > collagen. It suggested that TKU047 could exhibit good caseinolytic and fibrinolytic ability compared to other activities. This result is different from the protease produced by P. tezpurensis sp. nov. AS-S24-II strain, which demonstrated its best activity on keratin [52].
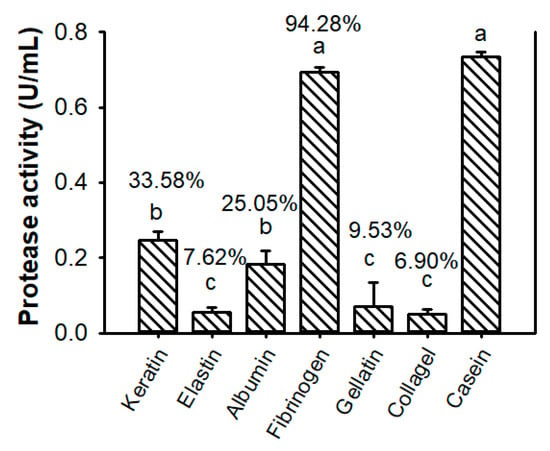
Figure 7.
Substrate specificity of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease. All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). Different letters (a, b, c, and d) indicate significant difference based on Tukey’s test with p < 0.05. The values on top of the bars (%) are the ratios of the activities of TKU047 protease on different substrates to those on casein.
2.7. Effect of Metal Ions, Protease Inhibitors, and Surfactants
Among the tested ion metals, Fe2+, Na+, and Ba2+ significantly increased the activity of TKU047 protease by 25%, 44%, and 56%, respectively; other metal ions showed only a slight effect on enzyme activity (Figure 8). Na+ has been reported as a factor that enhances protease activity [8]; however, the results for Fe2+ and Ba2+ were different in other reports, which suggests that those metal ions inhibited protease activity [45,54]. In the presence of surfactants, TKU047 protease showed good resistance, with the retained activity higher than the control group (112% on tween 40, 116% on tween 20, and 161% on SDS) with only Triton X-100 being the exception (retaining 54% of initial activity). Since no activity was lost after incubating with 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME), the thiol group may not contribute to the activity of the TKU047 protease. In addition, the results of adding ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) revealed that TKU047 was only strongly inhibited by EDTA. This indicates that TKU047 protease is part of the metallo-protease family. This is consistent with reports that proteases from Paenibacillus strains are metallo- or serine-proteases [52,53].
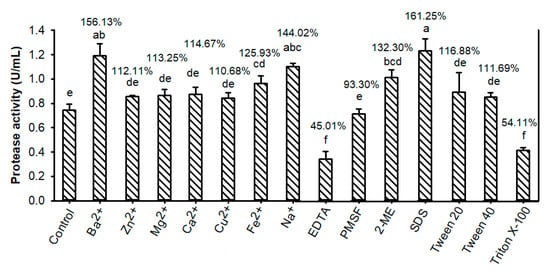
Figure 8.
Effect of metal ions, protease inhibitors, and surfactants on Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease. All points on the graph indicated the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). Different letters (a, b, c, d, e, and f) indicate significant difference based on Tukey’s test with p < 0.05. The values on top of the bars (%) are the ratios of the residual activities to the protease activity of the enzyme in the phosphate buffer (control).
2.8. Compatibility with Commercial Detergents
According to the above results, Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease expressed several valuable properties, such as high productivity when converting shrimp heads, thermal stability, alkaline tolerance, and resistance to surfactants. As such, TKU047 protease could be considered a good candidate for a detergent additive. However, the detergent stability of this protease needed to be investigated before any further steps were taken. To explore the compatibility of TKU047 protease with detergent, four kinds of commercially available Taiwanese detergents: EKOS, Yigan Sanjing (YGSJ), AMAH concentrated lavender laundry detergent (AMAH), and YEUHYANG eco-friendly laundry powder (YEUHYANG), were used at 1% concentration. Before testing, all the detergents were examined for protease activity, but none exhibited proteolytic ability on casein. As shown in Figure 9, TKU047 protease had excellent compatibility with YEUHYANG detergent, with no protease activity lost after treatment. The compatibility of TKU047 protease with EKOS, YGSJ, and AMAH detergents was also acceptable, with over 70% of residual activity observed. It has been reported that some alkaline proteases from bacteria express good detergent compatibility. For instance, Sardinella longiceps protease retained over 90% of activity with Arial, Bahar, Tide, and Bonux detergents [59], while B. licheniformis RP1 retained over 93% of activity with Axion and Dixan detergents [60] and Bacillus sp. SSR1 exhibited over 70% of activity with tested detergents [61]. Due to its high detergent compatibility, TKU047 protease has potential as a detergent additive.
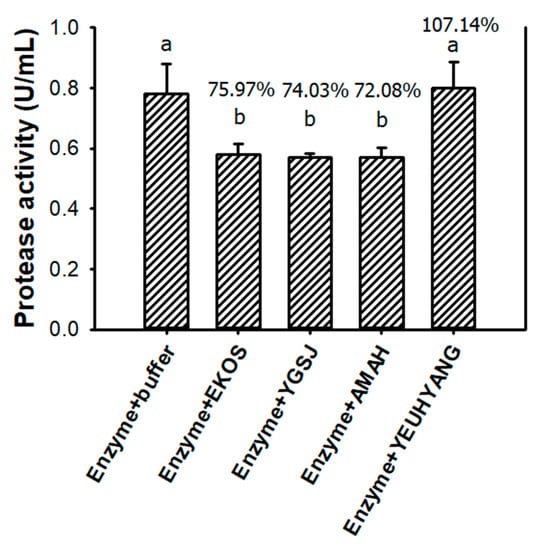
Figure 9.
Compatibility of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease with some commercial detergents (0.5%, w/v). All points on the graph indicate the mean of each experiment (with n = 3) and standard deviation (error bar). Different letters (a and b) indicate significant difference based on Turkey’s test with p < 0.05. The values on top of the bars (%) are the ratios of the residual activities to the protease activity of the enzyme in the phosphate buffer.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Fishery processing byproducts, excepting shrimp heads (from Fwu-Sow Industry, Taichun, Taiwan), were from Shin-Ma Frozen Food Co. (I-Lan, Taiwan) [7]. Crab shells and shrimp shells were treated by acid to remove the mineral contents [11]. The resin of ion chromatography (Macro-prep High S) was bought from BioRad (Hercules, CA, USA). HPLC columns (KW-802.5) were bought from Showa Denko K. K (Tokyo, Japan). Other reagents were all laboratory chemicals with high quality.
3.2. Protease Activity Assay
The assay for determining protease activity followed the previous report with some modification [12]. Briefly, a 50 µL sample was dropped into an Eppendorf containing 50 µL substrate (2% casein in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 7). Later on, the Eppendorf was gently vortexed and kept on an incubator at 37 °C for 30 min. The enzyme activity was eliminated by the addition of 300 µL trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution (5%). The solution was collected by centrifuging the Eppendorf at 11,000× g for 15 min, and then transferred to a mixture of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent and 20% Na2CO3 at a ratio of 8:2:15, respectively. After 20 min, the color of the solution was quantified based on 660 nm wavelength. Protease activity was described by the amount of required enzyme for liberating 1 µmol of tyrosine during 1 min of proteolytic reaction.
3.3. Screening of a Proteolytic Bacteria
The method of bacterial isolation was described in a previous report [8]. After isolation, the bacterial strains were cultivated in a liquid medium containing SPP (1%, w/v), MgSO4·7H2O (0.05%, w/v), and K2HPO4 (0.1%, w/v) at 37 °C (150 rpm) for 3 days. Later on, the culture supernatants were separated from bacterial cells and other sediments by centrifuging the medium (9000× g for 30 min). This supernatant was collected to measure protease activity, as described below. The screening step was done by selecting the strain which exhibited the highest protease productivity. The selected strain’s morphological and biochemical properties were characterized by light microscopy and API 50 CHB system (bioMérieux, Inc., Durham, NC, USA). The scientific name of the bacterial strain was identified by DNA sequencing method.
3.4. Screening C/N Source for Protease Production
Five fishery byproducts: deSSP, deCSP, SPP, SHP, and SSP, were supplemented to the basal medium containing MgSO4·7H2O (0.05%, w/v), and K2HPO4 (0.1%, w/v) at the same concentration (1%, w/v). Cultivation was started by injecting 1% of seed to the medium and maintained at 37 °C, 150 rpm for 3 days. The protease productivity of bacterial strain on different C/N sources were tested every 24 h.
3.5. Isolation of TKU047 Protease
Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 was cultivated as per the conditions described above. Two hundred milliliters of culture supernatant was concentrated with EtOH at a ratio of 1:4. The protein precipitate was obtained by centrifuging the miscellaneous solution of culture supernatant and EtOH for 30 min at 12,000× g, and then dissolved in sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM, pH 7). The first enzyme isolation step was carried out by a Macro-Prep High S column. The fractions, which exhibited protease activity, were pooled for the next isolation step via HPLC method (column, KW802.5; injection volume, 20 µL; mobile phase, 50 mM sodium phosphate buffer; detector, ultraviolet 280 nm; flowrate, 1 mL/min; temperature, 20 °C). The molecular mass determination of the isolated protease was done by SDS-PAGE method.
3.6. Effects of pH and Temperature
The optimal temperature of TKU047 protease was investigated by incubating the mixture of enzyme (50 µL) and substrate (50 µL) at different temperature points (20–100 °C) for 30 min. Thermal stability of TKU047 protease was determined by pre-incubating the enzyme solution in a range of temperature (up to 100 °C) for 30 min. After heat treatment, the enzyme solution was measured for activity under the protease activity assay as mentioned above. In order to investigate the optimum pH of TKU047 protease, several buffers (50 mM) were used to prepare enzyme solutions as well as substrate solutions, including sodium decarbonate–carbonate buffer (pH 9–11), sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6–8), sodium acetate buffer (pH 3.6–5), and glycine HCl buffer (pH 2–3.6). The pH stability of TKU047 protease was carried out by pre-incubating the enzyme at different pH points (pH 2–7) for 30 min. Later on, the pH of the enzyme solutions was adjusted to pH 7 by using sodium phosphate buffer (0.2 M). The treated enzyme solutions were measured for activity under protease activity assay as mentioned above.
3.7. Effect of Metal ions, Protease Inhibitors, and Surfactants
TKU047 protease was prepared in various chemical solutions, including: Ba2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Cu2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, EDTA, PMSF, Triton X-100, tween 40, 2-ME, and SDS. The final concentration of metal ions, and protease inhibitors in the solutions were 5 mM, whereas those of surfactants was 10%. The mixtures were kept in an incubator at 37 °C for 30 min. Residual protease activity was then measured, using the methods described above.
3.8. Substrate Specificity
TKU047 protease was prepared in sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM) with numerous substrates. These included casein, fibrinogen, keratin, albumin, gelatin, elastin, and collagen. Later on, the mixtures were kept in an incubator under the following conditions of protease assay as mentioned above.
3.9. Detergent Compatibility
TKU047 protease was prepared in a sodium phosphate buffer (50 mM) with four kinds of commercial detergents at 30 °C for 60 min. These included: EKOS from Maobao Co. (Hsinchu, Taiwan), Yigan Sanjing from Maobao Co. (Hsinchu, Taiwan), AMAH concentrated lavender laundry detergent from Magic Amah household Co. (New Taipei, Taiwan), and YEUHYANG eco-friendly laundry powder from YEUHYANG Manufacture Technology (Hsinchu, Taiwan).
4. Conclusions
Paenibacillus has several strains with the potential to convert fishery processing by-products into various bioactive compounds [11,12,13,30,43,48,49,50,51]. This study continued to reveal more abilities of Paenibacillus, which could contribute to the biotechnological field. In the current study, protease was produced by Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 using shrimp heads, a marine byproduct, as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen. Purified Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 protease had a mass of 32 kDa. Characterization revealed that the TKU047 enzyme was a thermotolerant, detergent-stable, alkaline protease. The excellent characteristics of Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 suggest that it may be applied as a detergent additive.
Author Contributions
S.-L.W. and C.T.D. conceptualized and designed the study; C.T.D., T.N.T., and I.H.W. performed the experiment; C.T.D., T.N.T., I.H.W., V.B.N., and A.D.N. compiled and analyzed the data; S.-L.W. and C.T.D. wrote the paper; S.-L.W. acquired funding and supervised the project.
Funding
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 106-2320-B-032-001-MY3).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Halim, N.R.A.; Yusof, H.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Functional and bioactive properties of fish protein hydolysates and peptides: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.M.; Lee, G.C.; Liang, W.S.; Yang, J.I. Process optimization for production of antioxidant gelatin hydrolysates from tilapia skin. J. Fish Soc. Taiwan 2009, 36, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Lv, S.; Li, B. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory and antihypertensive properties of squid skin gelatin hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2013, 131, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Doan, C.T.; Nguyen, A.D.; Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L. Reclamation of Fishery Processing Waste: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Liang, T. Microbial reclamation of squid pens and shrimp shells. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 3445–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Yu, H.T.; Tsai, M.H.; Doan, C.T.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D. Conversion of squid pens to chitosanases and dye adsorbents via Bacillus cereus. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4903–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.N.; Doan, C.T.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. The isolation of chitinase from Streptomyces thermocarboxydus and its application in the preparation of chitin oligomers. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Vo, T.P.K.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Chitin extraction from shrimp waste by liquid fermentation using an alkaline protease-producing strain, Brevibacillus parabrevis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Chio, S.H. Deproteination of shrimp and crab shell with the protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa K-187. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1998, 22, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.K.; Shih, I.L.; Tzeng, Y.M.; Wang, S.L. Production and purification of protease from a Bacillus subtilis that can deproteinize crustacean wastes. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Production of a thermostable chitosanase from shrimp heads via Paenibacillus mucilaginosus TKU032 conversion and its application in the preparation of bioactive chitosan oligosaccharides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Reclamation of marine chitinous materials for chitosanase production via microbial conversion by Paenibacillus macerans. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Conversion of squid pens to chitosanases and proteases via Paenibacillus sp. TKU042. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, M.T.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Anti-α-glucosidase activity by a protease from Bacillus licheniformis. Molecules 2019, 24, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Tseng, W.N.; Liang, T.W. Biodegradation of shellfish wastes and production of chitosanases by a squid pen-assimilating bacterium, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus TKU024. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.D.; Huang, C.C.; Liang, T.W.; Nguyen, V.B.; Pan, P.S.; Wang, S.L. Production and purification of a fungal chitosanase and chitooligomers from Penicillium janthinellum D4 and discovery of the enzyme activators. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L. Microbial reclamation of squid pen. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, H.; Velayutham, K.; Ravichandran, R. Chitin and chitosan preparation from shrimp shells Penaeus monodon and its human ovarian cancer cell line, PA-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, I.; Özogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M. Industrial applications of crustacean by-products (chitin, chitosan, and chitooligosaccharides): A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, D.; George, N.; Sharma, P.; Gupta, N. A process for complete biodegradation of shrimp waste by a novel marine isolate Paenibacillus sp. AD with simultaneous production of chitinase and chitin oligosaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, M.M.; Górak, A. New ionic liquids for modification of chitin particles. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4841–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiranpattanakul, P.; Jongjitpissamai, T.; Aungwerojanawit, S.; Tachaboonyakiat, W. Fabrication of a chitin/chitosan hydrocolloid wound dressing and evaluation of its bioactive properties. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4913–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.S.; Chin, H.Y.; Tsai, M.L. Preparation of chitin with puffing pretreatment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4939–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of chitin or chitosan/nano ceramic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Ramos, P.; Mirón, J.; Valcarcel, J.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Production of chitin from Penaeus vannamei by-products to pilot plant scale using a combination of enzymatic and chemical processes and subsequent optimization of the chemical production of chitosan by response surface methodology. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.; Antelo, L.T.; Franco-Uría, A.; Alonso, A.A.; Pérez-Martín, R. Chitin production from crustacean biomass: Sustainability assessment of chemical and enzymatic processes. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 172, 4140–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Su, Y.C.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D. Reclamation of shrimp heads for the production of α-glucosidase inhibitors by Staphylococcus sp. TKU043. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L. Reclamation of marine chitinous materials for the production of α-glucosidase inhibitors via microbial conversion. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.H.; Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Conversion of shrimp heads to α-glucosidase inhibitors via co-culture of Bacillus mycoides TKU040 and Rhizobium sp. TKU041. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 4597–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, T.H.; Doan, C.T.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, A.D.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wang, S.L. Production and bioactivity-guided isolation of antioxidants with α-glucosidase inhibitory and anti-NO properties from marine chitinous materials. Molecules 2018, 23, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Nguyen, A.D.; Wang, S.L. Utilization of fishery processing byproduct squid pens for Paenibacillus sp. fermentation on producing potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parjikolaei, B.R.; El-Houri, R.B.; Fretté, X.C.; Christensen, K.V. Influence of green solvent extraction on carotenoid yield from shrimp (Pandalus borealis) processing waste. J. Food Eng. 2015, 155, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahúa, T.B.; Santos, S.D.; Mendes, A.; Córdula, C.R.; Chavante, S.F.; Carvalho, L.B., Jr.; Nader, H.B.; Bezerra, R.S. Recovery of protein, chitin, carotenoids and glycosaminoglycans from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) processing waste. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Fish protein hydrolysates: Application in deep-fried food and food safety analysis. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, E108–E115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Medina, R.; Pérez-Gálvez, R.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M. Multiobjective optimization of the antioxidant activities of horse mackerel hydrolysates produced with protease mixtures. Process Biochem. 2017, 52, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slizyte, R.; Rommi, K.; Mozuraityte, R.; Eck, P.; Five, K.; Rustad, T. Bioactivities of fish protein hydrolysates from defatted salmon backbones. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 11, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Blanco, M.; Massa, A.E.; Amado, I.R.; Pérez-Martín, R.I. Production of fish protein hydrolysates from Scyliorhinus canicula discards with antihypertensive and antioxidant activities by enzymatic hydrolysis and mathematical optimization using response surface methodology. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Fraguas, J.; Sotelo, C.G.; Pérez-Martín, R.I.; Vázquez, J.A. Production of chondroitin sulphate from head, skeleton and fins of Scyliorhinus canicula by-products by combination of enzymatic, chemical precipitation and ultrafiltration methodologies. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3287–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šližytė, R.; Rustad, T.; Storrø, I. Enzymatic hydrolysis of cod (Gadus morhua) by-products: Optimization of yield and properties of lipid and protein fractions. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 3680–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.F.X.; Ribeiro, K.; Silva, J.F.; Cahú, T.B.; Bezerra, R.S. Utilization of tilapia processing waste for the production of fish protein hydrolysate. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 196, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.W.; Wang, S.L. Recent advances in exopolysaccharides from Paenibacillus spp.: Production, isolation, structure, and bioactivities. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1847–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.W.; Wu, C.C.; Cheng, W.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, I.L.; Wang, S.L. Exopolysaccharides and antimicrobial biosurfactants produced by Paenibacillus macerans TKU029. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.W.; Tseng, S.C.; Wang, S.L. Production and characterization of antioxidant properties of exopolysaccharides from Paenibacillus mucilaginosus TKU032. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.H.; Nguyen, A.D.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, S.L. Tyrosinase inhibitors and insecticidal materials produced by Burkholderia cepacian using squid pen as the sole carbon and nitrogen source. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.M.; Kumar, R.; Panwar, S.; Kumar, A. Microbial alkaline proteases: Optimization of production parameters and their properties. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contesini, F.J.; Melo, R.R.; Sato, H.H. An overview of Bacillus proteases: From production to application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, M.H. Microbial proteases. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 1988, 38, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Grady, E.N.; MacDonald, J.; Liu, L.; Richman, A.; Yuan, Z.C. Current knowledge and perspectives of Paenibacillus: A review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.L. New novel α-glucosidase inhibitors produced by microbial conversion. Process Biochem. 2018, 65, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Li, H.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Lin, Z.H.; Kuo, Y.H. Conversion of squid pen to homogentisic acid via Paenibacillus sp. TKU036 and the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of homogentisic acid. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.W.; Chen, W.T.; Lin, Z.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Nguyen, A.D.; Pan, P.S.; Wang, S.L. An amphiprotic novel chitosanase from Bacillus mycoides and its application in the production of chitooligomers with their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K.; Roy, J.K.; Mukherjee, A.K. Characterisation of a detergent-stable alkaline protease from a novel thermophilic strain Paenibacillus tezpurensis sp. nov. AS-S24-II. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antúnez, K.; Arredondo, D.; Anido, M.; Zunino, P. Metalloprotease production by Paenibacillus larvae during the infection of honeybee larvae. Microbiology 2011, 157, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; She, Q.; Chen, L. A novel carboxyl-terminal protease derived from Paenibacillus lautus CHN26 exhibiting high activities at multiple sites of substrates. BMC Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Saxena, J.; Yadav, B.; Alam, A.; Prakash, A. Optimization of protease production from bacteria isolated from soil. Appl. Res. J. 2015, 1, 388–394. [Google Scholar]
- Dodia, M.S.; Joshi, R.H.; Patel, R.K.; Singh, S.P. Characterization and stability of extracellular alkaline proteases from halophilic and alkaliphilic bacteria isolated from saline habitat of coastal Gujarat, India. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafee, N.; Aris, S.N.; Rahman, R.N.Z.A.; Basri, M.; Salleh, A.B. Optimization of environmental and nutritional conditions for the production of alkaline protease by a newly isolated bacterium Bacillus cereus strain 146. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2005, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, K.S.B.; Devi, K.L. Optimization of thermostable alkaline protease production from species of Bacillus using rice bran. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 724–726. [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar, A.; Sivakumar, N.; Gujarathi, A.M.; Victor, R. Production of thermotolerant, detergent stable alkaline protease using the gut waste of Sardinella longiceps as the substrate: Optimization and characterization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami-Kamoun, A.; Haddar, A.; Ali, N.E.H.; Ghorbel-Frikha, B.; Kanoun, S.; Nasri, M. Stability of thermostable alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis RP1 in commercial solid laundry detergent formulations. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Batra, N.; Sobti, R.C. Serine alkaline protease from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. SSR1. Process Biochem. 2011, 36, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).