Abstract
The continuous increase in solid waste poses a significant environmental challenge. Pyrolysis represents a crucial technology for the valorization of solid waste. As the primary product, biochar has found applications in numerous fields and garnered significant scientific interest. This study investigated the potential of NH4Cl and FeCl3 for modifying biochar. The resultant modified biochar achieved over 70% sulfamethoxazole (SMX) degradation within 30 min. The incorporation of NH4Cl and FeCl3 facilitated the formation of pyridinic nitrogen (N), graphitic nitrogen (N), and Fe(II) 1/2p, while the concomitant increase in persistent free radicals facilitated enhanced electron transfer rates. Notably, NH4Cl/FeCl3-modified biochar demonstrated superior efficacy compared with alternative activation techniques for real wastewater treatment. This study presents a novel material for persulfate (PDS)-based advanced oxidation processes, while also offering a cost-effective strategy for solid waste disposal.
1. Introduction
Currently, the continuous increase in solid wastes associated with agricultural and forestry development poses significant challenges [1]. As the world’s largest developing agricultural economy, China generates substantial volumes of farming and forestry wastes annually [2]. The inadequate valorization of these solid wastes presents formidable challenges due to their bulk properties and limited reusability, exacerbating environmental impacts [3].
Among prevalent disposal methods, combustion remains widely adopted in several regions despite causing substantial air pollution and energy loss [4]. Consequently, numerous countries have implemented environmental policies aimed at fostering solid waste recycling while mitigating the environmental impacts of combustion [5,6]. Thus, developing environmentally sustainable and economically viable waste valorization techniques is imperative.
Pyrolysis, as a promising waste-to-energy conversion technology, has garnered increasing attention [7,8]. This process significantly reduces solid waste volume while concurrently yielding valuable gaseous and liquid fuels, along with biochar [9]. The gaseous and liquid products derived from pyrolysis serve as energy sources, whereas the residual biochar finds applications in diverse fields, including catalysis, adsorption, and soil enhancement [10,11,12]. On the other hand, owing to its abundant active sites, biochar serves as an excellent catalyst in advanced oxidation processes.
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) represent a practical approach for environmental remediation [13], with persulfate (PDS)-based technologies garnering significant scientific interest due to their distinct advantages in aquatic system restoration [14,15,16]. Compared to conventional hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-based systems, PDS demonstrates superior aqueous solubility and stability [17]. The activated sulfate radicals (·SO4−) exhibit an extended half-life (30–40 μs) and higher redox potential (E0 = +2.6 V) [18,19]. PDS activation is a prerequisite for reactive oxygen species generation, with established methods including alkaline, radiation, thermal, transition metal, and UV activation [14,20,21]. Among these, heterogeneous catalysis has gained prominence owing to enhanced activation efficiency and structural stability.
Although metal-based catalysts demonstrate superior PDS activation efficacy, their practical implementation is constrained by heavy metal leaching risks [18,22]. Carbonaceous catalysts circumvent these limitations through environmental compatibility. Biochar, a carbon-rich pyrolysis product derived from solid waste, possesses a high specific surface area, exceptional adsorption capacity, abundant surface functionalities, and graphitic domains, positioning it as a promising remediation catalyst [23,24]. Recent studies implicate persistent free radicals (PFRs) on biochar surfaces as primary PDS activation sites, while structural defects facilitate the generation of ·OH and ·SO4− radicals [25].
Nevertheless, biochar exhibits comparatively lower oxidant activation and pollutant degradation kinetics relative to metal-based systems [18,26]. Consequently, modification strategies are increasingly employed to augment its catalytic performance [27,28,29]. Our prior research indicates chlorine incorporation promotes hierarchical pore formation and PFR generation, thereby modulating electron transfer kinetics and active site density [5]. Thus, synergistic modification of biochar with metallic species and chlorinated compounds presents a viable strategy for catalytic enhancement.
This study utilized sawdust-derived biochar modified with FeCl3 and NH4Cl to address four primary objectives: (1) characterize alterations in the physicochemical properties of biochar induced by FeCl3/NH4Cl modification; (2) evaluate the efficacy of modified biochar in PDS activation and pollutant degradation; (3) elucidate the mechanistic pathways governing PDS activation and SMX degradation; (4) assess the environmental remediation potential of FeCl3/NH4Cl-modified biochar. Collectively, this work aims to advance sustainable solid waste valorization strategies while contributing to the development of high-performance biochar materials for environmental applications.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Biochars
To elucidate the physicochemical properties of biochar, comprehensive characterization was performed via Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) and scanning electron microscope-energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS). BET results (Table S1) revealed that NH4Cl/FeCl3 co-modification increased biochar’s specific surface area from 506.0 to 819.0 m2/g. This enhancement might be attributed to HCl liberation during NH4Cl pyrolysis, which facilitates porous structure development [5]. Notably, NH4Cl-modified biochar (BCN) exhibited similarly elevated surface area (784.3 m2/g), corroborating the pore-forming role of HCl.
Conversely, FeCl3 modification (BCF) reduced surface area to 409.5 m2/g, indicating Fe-induced pore blockage that compromised PDS activation efficacy. Furthermore, co-modified biochar (BCNF) demonstrated significantly reduced electrical resistivity (Table S2), potentially enhancing electron transfer for PDS activation and SMX degradation. Figure S1 showed that the Fe existed in the pores of biochar. The results of EDS indicated that the modified biochar had more Fe content (Table S1), which stated that Fe had been successfully loaded on biochar. Meanwhile, the percentage of chlorine and nitrogen had increased significantly after the biochar was modified by NH4Cl and FeCl3, followed by lower carbon and oxygen content.
2.2. Degradation of SMX and Decomposition of PDS by Biochar
The catalytic performance of biochar variants in PDS activation was evaluated as shown in Figure 1. Unmodified biochar (BCS) achieved 20% SMX degradation within 30 min. The enhanced catalytic activity of BCF over BCS is likely due to the iron doping effect [30]. Conversely, BCN demonstrated reduced efficacy (<20% SMX degradation), underperforming relative to BCS.
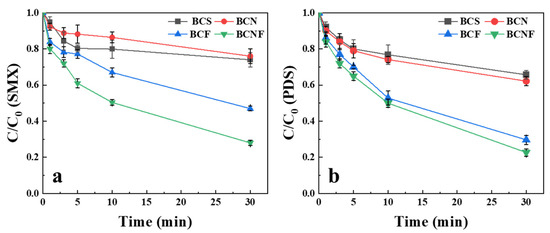
Figure 1.
The SMX degradation (a) and PDS activation (b) by biochars. [Biochar] = 1 g/L, [PDS] = 1 mM, [SMX] = 10 uM, pH = 7.
Notably, the BCNF exhibited exceptional performance with 75% SMX removal within 30 min. This catalytic superiority was consistent in PDS activation kinetics, indicating synergistic effects from FeCl3/NH4Cl incorporation that enhanced oxidant activation and subsequent pollutant degradation.
Comparatively, both BCS and BCN showed limited PDS activation (<30% within 30 min), resulting in lower SMX removal. These findings demonstrate that FeCl3/NH4Cl modification may significantly alter physicochemical properties of biochar, thereby enhancing catalytic functionality. Given its superior performance, BCNF was selected for subsequent mechanistic investigations.
2.3. Elucidation of Reactive Oxygen Species
To identify the reactive oxygen species in the BCNF/PDS system, electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy coupled with DMPO and TEMP as spin-trapping agents was performed. As depicted in Figure 2, distinguishable DMPO–·O2− signals were observed. Concurrently, the EPR spectrum employing TEMP displayed characteristic three-line signals of 1:1:1 intensity ratio (Figure 2, corresponding to the TEMP−1O2 adducts [5,25].
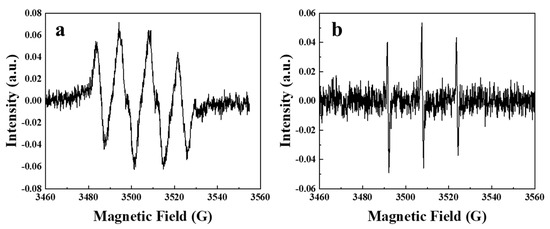
Figure 2.
The EPR results of the BCNF/PDS system.
To elucidate reactive oxygen species (ROS) contributions to SMX degradation, radical quenching experiments were systematically conducted using specific scavengers. As presented in Figure 3, introduction of 0.1 M L-H significantly suppressed SMX degradation from 75% to 10% within 30 min (Δ65% inhibition), indicating singlet oxygen serves as a primary oxidative species in the BCNF/PDS system [30]. Benzoquinone quenching further revealed substantial ·O2− involvement in SMX degradation (Figure 3). Previous studies had reported that ·O2− cannot degrade SMX, but ·O2− was a key intermediate medium in the generation of 1O2 [25]. In order to make sure the role of ·O2−, the BCNF/PDS system coupled with benzoquinone was used to detect the signal of 1O2. Figure S2 found that no signal was observed. It indicated that ·O2− was a key intermediate product, which was consistent with our previous research. Conversely, negligible degradation inhibition occurred with TBA and EtOH addition, demonstrating minimal contributions from ·OH and ·SO4−. Collectively, these results establish 1O2 as the dominant SMX-degrading species in the BCNF/PDS system, with ·O2− functioning as the critical intermediate for 1O2 formation [25].
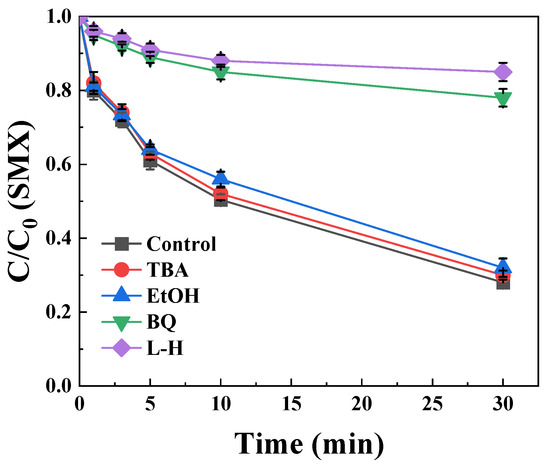
Figure 3.
The effect of quenching agents in SMX degradation. [BCNF] = 1 g/L, [PDS] = 1 mM, [SMX] = 10 μM, [TBA] = 0.17 M, [EtOH] = 0.1 M, [BQ] = 1 mM, [L-H] = 0.1 M, pH = 9.
2.4. Possible Mechanism of PDS Activated by Biochar
Previous studies had established the doping of nitrogen as a critical modulator of material performance in oxidation activation [31]. Thus, to understand the activation mechanism of PDS by biochar, XPS analysis was performed in this study, and the corresponding results are depicted in Figure 4. The N 1s spectrum revealed that the proportion of pyridinic N and graphite N was initially as high as 16.8% and 47.3% before reacting with PDS, indicating a high surface graphitization degree and homogeneous nitrogen distribution structural features conducive to catalytic persulfate activation. After interacting with PDS for specific durations of time, the pyridinic N and graphite N content decreased to 12.96% and 44.73% after 30 min of reaction. This reduction in pyridinic N and graphite N content is an indication that these functional groups act as activators for PDS and are consumed during the reaction, resulting in an increase in the concentration of 1O2. Concurrently, the content of Fe(II) 1/2p reduced from 43.53% at 0 min to 39.35% at 30 min, indicating a decline in its abundance during the reaction. And the content of Fe(III) 3/2p increased from 30.1% to 32.33% after reacting with PDS. These redox transitions confirm iron’s pivotal role in electron transfer processes during PDS activation.
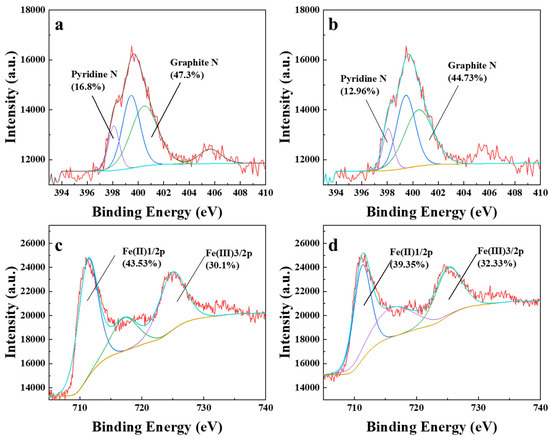
Figure 4.
XPS (N 1s) spectra of BCNF before (a) and after (b) reacting with PDS; XPS (Fe 2p) spectra of BCNF before (c) and after (d) reacting with PDS.
Our previous study demonstrated that chlorine incorporation promotes PFRs formation. The PFRs had been verified to be reactive species that can directly transfer electrons and potentially contribute to the activation of PDS [5,31]. In order to measure its effect in the BCNF/PDS system, EPR spectroscopy was used to determine the presence of PFRs in BCNF. Based on the EPR results, the g factor of BCNF was 2.004, which indicated that PFRs of BCNF were mainly composed of carbon-centered radicals with an adjacent oxygen atom. EPR analysis revealed that the spin density of BCNF was 3.6×1016 spins/g. According to our previous studies, the PFRs with sufficient concentration could play a vital role in electron transfer. Thus, potassium iodide (KI) was used to quench the PFRs. After treatment with KI, the spin densities of the PFRs decreased to 1.1×1016 spins/g, and the electrical resistivity of BCNF increased from 2.578 Ω to 3.89 Ω, accompanied by a decrease in PDS activation and SMX degradation of BCNF (Figure 5). This triad of evidence established PFRs as critical electron transfer agents governing system reactivity.
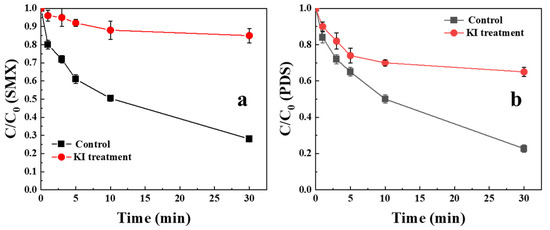
Figure 5.
(a)The SMX degradation and (b) PDS activation after treatment with KI. [BCNF] = 1 g/L, [PDS] = 1 mM, [SMX] = 10 μM, pH = 7.
Concurrently, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-2Na) was introduced to isolate the contribution of structural defects to PDS activation [32]. As shown in Figure S3, EDTA-2Na treatment exhibited a negligible impact on BCNF-mediated SMX degradation and PDS activation efficiency, effectively excluding defect-mediated mechanisms.
While prior studies implicate carbonyl (C=O) and carboxyl (-COOH) groups in carbonaceous materials as potential PDS activation sites, our Fourier Transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) analysis revealed minimal alterations in biochar’s functional group composition post-reaction (Figure S4). To explicitly probe these groups’ roles, selective deactivation experiments were performed: Phenylhydrazine (PH) targeted ketonic C=O groups, while 2-bromo-1-phenylethanone (BrPE) specifically quenched carboxyl functionalities without perturbing other structural elements [33,34]. Figure S5 demonstrates that neither C=O nor -COOH deactivation significantly impaired PDS activation or SMX degradation.
Collectively, these findings establish that NH4Cl/FeCl3 modification modulates pyridinic N, graphitic N, iron species, and PFRs − the principal components governing PDS activation and contaminant degradation efficacy. It should be noted that the individual contributions of nitrogen, chlorine, and iron species were not decoupled in this study. The proposed synergistic effect, while supported by the enhanced performance and characterization, remains a mechanistic speculation and warrants further validation through more controlled experiments in future work.
2.5. Application in Wastewater Remediation
To evaluate the practical applicability of the BCNF/PDS system, comparative degradation experiments were conducted in pharmaceutical wastewater and chemical plant effluent matrices (Figure 6). Relative to ultrapure water performance (Figure 1), SMX degradation efficiency declined from 75% to approximately 30% within 30 min in these complex matrices, as depicted in Figure 6. This attenuation primarily stems from two mechanistic interferences: (i) competitive consumption of superoxide radicals (·O2−) by background anions and natural organic matter (NOM), suppressing singlet oxygen generation; (ii) active-site masking through anion complexation, diminishing reactive species production [25].
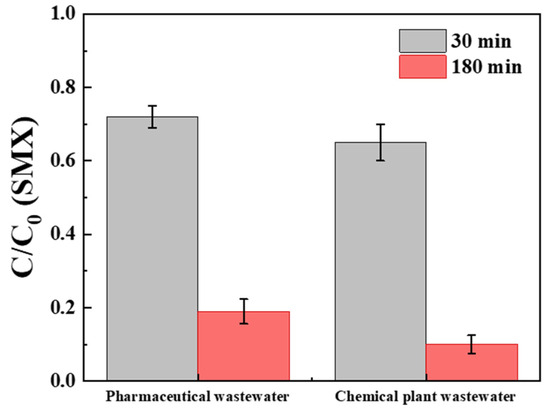
Figure 6.
The SMX degradation by the BCNF/PDS system in real wastewater. [BCNF] = 1 g/L, [PDS] = 1 mM, [SMX] = 10 μM, pH = 7.
Despite these inhibitory effects, the system achieved 80% SMX removal within 180 min, demonstrating notable resilience. This sustained efficacy is attributed to the inherent interference resistance of non-radical pathways (predominantly 1O2-mediated oxidation) [6], wherein overall catalytic performance remains uncompromised. These findings established BCNF/PDS as an effective advanced oxidation platform for wastewater remediation.
2.6. Comparison with Other Materials
Zero-valent iron (ZVI) and activated carbon (AC)—a benchmark carbonaceous catalyst—were comparatively evaluated against BCNF for SMX degradation via PDS activation.
As illustrated in Figure 7, ZVI exhibited moderate PDS activation and SMX degradation capacity, but its efficiency was lower than that of BCNF. Previous research indicated that the activation of PDS by ZVI could produce ·OH and ·SO42− [35]. However, ·OH and ·SO42− can be suppressed in the presence of interfering ions in the wastewater matrix, and ferric ions may become deactivated through hydroxide precipitate formation at high pH levels, ultimately hindering SMX degradation. Although AC demonstrated detectable PDS activation, its efficacy remained substantially lower than theoretical predictions. This might be attributed to the fact that the reactive oxygen species produced in the AC/PDS system were ·OH and ·SO42−, which can be quenched by the interfering ions and dissolved organic matter [36]. The superior performance of the BCNF/PDS system (75% SMX degradation within 30 min) established its catalytic advantage over conventional activation materials under identical reaction conditions.
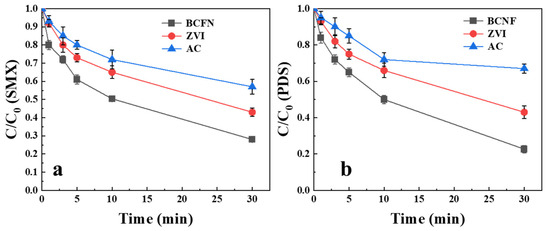
Figure 7.
Comparison of different materials in (a) SMX degradation and (b) PDS activation. [BCNF] = 1 g/L, [PDS] = 1 mM, [SMX] = 10 μM, pH = 7.
2.7. Toxicity of Biochar
Due to the application of FeCl3 in biochar modification, the potential risk of metal leaching should be considered. Analysis of reaction solutions (Table S2) detected no measurable iron content, precluding significant environmental hazards to soil or groundwater systems.
To comprehensively assess environmental impacts, bacterial bioluminescence assays were used to evaluate the toxicity of BCNF. Figure S6 demonstrated that biochar leachates enhanced luminescence by approximately 50% versus controls. Notably, despite iron and chlorine incorporation during synthesis, no luminescence inhibition occurred. Previous research demonstrated that the incorporation of chlorine-containing components during pyrolysis does not result in the formation of harmful substances, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and dioxins [5,37]. This stimulatory effect suggests biochar releases growth-promoting constituents that support bacterial metabolic activity [37].
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
Waste biomass was collected from the campus of Tianjin University in Tianjin, China. Sulfamethoxazole (SMX; purity: 99%), potassium persulfate, NaOH, and HCl were obtained from HEOWNS Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Ultrapure water was acquired from a Merck Milli-Q Reference system (Darmstadt, Germany). Ferric chloride (FeCl3) was obtained from Heowns Corporation (AR, 99.8%, Tianjin, China). Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) was purchased from Kermel Industrial Corporation (AR, 99%, Tianjin, China).
3.2. Pyrolysis Experiments
Pyrolysis was performed under oxygen-limited conditions using a muffle furnace (ZHX-G03183, Tianjin Zhonghuan Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China). The collected raw material was processed through a crusher to produce sawdust of uniform particle size. Sawdust feedstock was milled to particulate form, sequentially treated with aqueous FeCl3 (biomass–Fe mass ratio = 10:1) for 24 h, and dry-mixed with NH4Cl (biomass–NH4Cl ratio = 10:1). All samples were prepared following an identical procedure. The mixture was transferred to a covered crucible without inert gas purging, heated to 700 °C at 10 °C min−1, and maintained for 2 h. The resulting biochar was ground and stored under anhydrous conditions. Specimens were designated as: BCS (sawdust biochar), BCF (FeCl3-modified), BCN (NH4Cl-modified), and BCNF (co-modified with FeCl3/NH4Cl).
3.3. Characterization of Biochar
Surface functional group evolution was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR; HORIBA EMAX, Kyoto, Japan). Specific surface area analysis employed N2 physisorption at 77 K (ASAP2020M, Micromeritics, Norcross, America). Raman spectra (Renishaw inVia plus, Gloucestershire, UK) were acquired at 532 nm excitation wavelength. Electrical conductivity measurements utilized a four-point probe system. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS; Escalab 250Xi, Waltham, America) determined surface chemical compositions. Morphological features were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM; FEI Apreo S, Waltham, America). Charge transfer resistance was quantified via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS; CorrTestTM CS310H, Wuhan, China). Elemental composition (C, H, O, N, Cl, Fe) was analyzed by energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS; FEI Apreo S, Waltham, America). Electron spin resonance (ESR; Bruker EMXPLUS 10/12, Karlsruhe, Germany) monitored radical species under ambient conditions with the following parameters: 9.84 GHz resonance frequency, 20.00 mW microwave power, 100.00 kHz modulation frequency, 2.00 G modulation amplitude.
3.4. Experimental Procedures
In all batch experiments, a 100 mL screw-sealed bottle containing 50 mL of solution was placed on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature. To evaluate the catalytic performance of the prepared biochar in advanced oxidation processes, the solution pH was adjusted to 7.0 using NaOH (0.1 M) and HCl (0.1 M). Biochar and SMX were sequentially added to the bottles, followed by the introduction of a PDS solution to initiate the reaction. To terminate the reaction, 10 μL of ascorbic acid was immediately added, and the vial was used for quantifying the remaining concentrations of SMX and PDS. To eliminate the impact of adsorption, desorption experiments with 95% recovery were performed by utilizing methanol and 1 M NaHCO3 in a 10:1 (v/v) ratio to desorb SMX from the biochar surface. Quenching experiments were conducted using tert-butanol (TBA; 0.17 M), ethanol (EtOH; 0.1 M), benzoquinone (BQ; 1 mM), and L-histidine (L-H; 0.1 M) to verify the presence of hydroxyl radicals (·OH), sulfate radical (·SO4−), superoxide radical (·O2−), and singlet oxygen (1O2).
3.5. Analytical Methods
PDS concentration was quantified by UV–Vis spectrophotometry using the potassium iodide chromogenic method [29]. SMX analysis employed high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC; Shimadzu 2030C, Kyoto, Japan) with a Zorbax SB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm) maintained at 30 °C, coupled to a diode array detector. The mobile phase comprised methanol and 0.1% (w/w) phosphoric acid with the following gradient program: 10% methanol (0–1 min), linear increase to 50% (1–6 min), linear decrease to 10% (6–10 min), and isocratic elution at 10% (10–15 min). SMX quantification was performed at 254 nm based on peak area [30]. The post-reaction solution was filtered and analyzed for iron content using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES; Thermo iCAP Q, Waltham, America).
4. Conclusions
This study establishes that NH4Cl/FeCl3 co-modification significantly enhances biochar’s physicochemical properties, enabling exceptional catalytic performance in PDS activation and SMX degradation. The introduced modifiers synergistically promote the following: (i) pyridinic N formation, (ii) graphitic N content, (iii) Fe(II) 1/2p species abundance, and (iv) persistent free radical generation, collectively augmenting electron transfer kinetics. These transformations render BCNF an efficient PDS-activating material for rapid SMX degradation.
Dominated by non-radical singlet oxygen with superoxide radicals as key precursors, the BCNF/PDS system demonstrated remarkable wastewater remediation potential. Crucially, negligible iron leaching and absence of ecotoxic compounds (as confirmed by bioluminescence assays) ensure minimal environmental hazards. These findings established waste-derived biochar as a sustainable, environmentally benign catalyst for persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes, while facilitating an integrated solid waste upcycling strategy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15090880/s1, Text S1. Materials and Methods. Surface functional groups elimination experiments; Text S2. The elimination of PFRs and defects; Table S1. The physical and chemical properties of CRs; Table S2. The change in components of CRs; Figure S1. The SEM results of BCNF; Figure S2. The EPR results of the BCNF/PDS system with BQ; Figure S3. The SMX degradation and PDS activation of BCNF after being treated with EDTA-2Na; Figure S4. The FTIR results of BCNF; Figure S5. The effects of surface groups elimination on (a) SMX degradation and (b) PDS activation; Figure S6. The bacterial luminescence results in BCNF solution.
Author Contributions
Z.L.: writing—review and editing, writing—original draft, methodology, investigation, funding acquisition. H.Z.: writing—review and editing, supervision. W.G.: writing—review and editing. T.M.: writing—review & editing. H.C.: writing—review and editing, methodology. C.M.: writing—review and editing, supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the project from Shengli Oilfield Company of Sinopec (NO. YKB 2510, YKD 2506, and YKD 2407), and Project SDCX-ZG-202503149, funded by the Postdoctoral Innovation Program of Shandong Province.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Zhipeng Li, Wanjiang Guo and Hongru Cui were employed by the company Shengli Oilfield Company, Sinopec. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Song, Q.; Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Yang, L.; Lv, W.; Bao, J.; Shu, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, P. Pyrolysis of municipal solid waste with iron-based additives: A study on the kinetic, product distribution and catalytic mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, K.; Shrivastava, A.; Vimal, V.; Gupta, A.K.; Bhujbal, S.K.; Biswas, J.K.; Singh, L.; Ghosh, P.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, P.; et al. Biochar application for greenhouse gas mitigation, contaminants immobilization and soil fertility enhancement: A state-of-the-art review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Du, Z.; Zhang, A.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Tian, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Long-term biochar addition alters the characteristics but not the chlorine reactivity of soil-derived dissolved organic matter. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, A.; Veksha, A.; Yin, K.; Weerachanchai, P.; Giannis, A.; Lisak, G. Environmental impact assessment of converting flexible packaging plastic waste to pyrolysis oil and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Y.; Yao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Sun, P. Carbon Residue from Copyrolysis of Cartons and Plastics As an Efficient H2O2 Activator. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Bolan, N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Conversion of biological solid waste to graphene-containing biochar for water remediation: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Batalha, N.; Mahmudul, H.M.; Perkins, G.; Konarova, M. A review on advanced catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass and hydrogen-rich feedstock: Insights into synergistic effect, catalyst development and reaction mechanism. Bio Resour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Y. Facile preparation of activated carbon foam via pyrolysis of waste bread under CO2 atmosphere. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2019, 9, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Razzak, S.A. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and different plastic waste to reduce hazardous waste and subsequent production of energy products: A review on advancement, synergies, and future prospects. Renew. Energy 2024, 224, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayiania, M.; Terrell, E.; Dunsmoor, A.; Carbajal-Gamarra, F.M.; Garcia-Perez, M. Characterization of solid and vapor products from thermochemical conversion of municipal solid waste woody fractions. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. Thermal behaviour and kinetic study of co-pyrolysis of micro-algae with different plastics. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Bashir, S.; Younas, A.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Chhajro, M.A.; Kubar, K.A.; Ali, U.; Rana, M.S.; Mehmood, M.A.; et al. A concise review of biochar application to agricultural soils to improve soil conditions and fight pollution. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Das, U.; Dalai, A.K. In-situ chemical oxidation: Principle and applications of peroxide and persulfate treatments in wastewater systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-L.; Chang, J.-H.; Lyu, S.-Y.; Hung, C.-M. Degradation of 4-nonylphenol in marine sediments by persulfate over magnetically modified biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, H. Persulfate activation with sawdust biochar in aqueous solution by enhanced electron donor-transfer effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Oh, S. Biochar-mediated oxidation of phenol by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3932–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Ifthikar, J.; Shi, L.; Du, Y.-A.; Zhu, J.; Xi, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. Treatment of refractory contaminants by sludge-derived biochar/persulfate system via both adsorption and advanced oxidation process. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-Z.; Huang, D.-L.; Liu, Y.-G.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, X.-M.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Recent advances in biochar-based catalysts: Properties, applications and mechanisms for pollution remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 380–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, T.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yin, D. Efficient removal of several estrogens in water by Fe-hydrochar composite and related interactive effect mechanism of H2O2 and iron with persistent free radicals from hydrochar of pin-ewood. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, X.; Geng, M.; Chen, D.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Catalytic oxidation of clofibric acid by peroxydisulfate activated with wood-based biochar: Effect of biochar pyrolysis temperature, performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-F.; Ling, L.-L.; Chen, W.-J.; Liu, W.-J.; Li, D.-C.; Jiang, H. High efficient removal of bisphenol A in a peroxymonosul-fate/iron functionalized biochar system: Mechanistic elucidation and quantification of the contributors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Zeng, G.; Feng, H.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, C.; Zhu, X.; Ouyang, X.; et al. Hierarchical porous biochar from shrimp shell for persulfate activation: A two-electron transfer path and key impact factors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Li, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Fu, S. In situ loading metal oxide particles on bio-chars: Reusable materials for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, F.A.; Alakhras, A.I.; Heikal, M.; Ibrahim, S.M. Stabilization of lead bearing sludge by utilization in fly ash-slag based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Sun, P. Persulfate Activation by Municipal Solid Waste-Derived Carbon Residue: Mechanism and Application. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 4004–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, B.; Liu, L. Insights into biochar and hydrochar production and applications: A review. Energy 2019, 171, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Huang, F.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Yi, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Fabrication of novel magnetic MnFe2O4/biochar composite and heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline in near neutral pH. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Chong, C.C.; Liew, R.K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Park, Y.-K.; Liu, Z.; Wong, C.S.; Peng, W. Engineering pyrolysis biochar via single-step microwave steam activation for hazardous landfill leachate treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tong, Y.; Sun, P. Biochar-activated peroxydisulfate as an effective process to eliminate pharma-ceutical and metabolite in hydrolyzed urine. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wei, K.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X. Enhanced H2O2 activation and sulfamethoxazole degradation by Fe-impregnated biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 385, 123921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Show, P.; Mahlknecht, L.; Wang, C. Degradation of tetracycline by nitrogen-doped biochar as a perox-ydisulfate activator: Nitrogen doping pattern and non-radical mechanism. Sustain. Horizons 2024, 10, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, Q.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; et al. New notion of biochar: A review on the mechanism of biochar applications in advannced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, B.; Gu, X.; Guo, X.; Su, D. Oxidative Dehydrogenation on Nanocarbon: Identification and Quantification of Active Sites by Chemical Titration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 14224–14228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, A.; Gao, N.; Li, K.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Deciphering a Nanocarbon-Based Artificial Peroxidase: Chemical Identification of the Catalytically Active and Substrate-Binding Sites on Graphene Quantum Dots. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7176–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Wu, Z.; Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, S. Investigation on the improvement of activated sludge dewaterability using different iron forms (ZVI vs. Fe (II))/peroxydisulfate combined vertical electro-dewatering processes. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.-F.; An, L.; Wu, D.-D. The use of carbon materials in persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes: A review. New Carbon Materials 2020, 35, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Huang, J.; Yu, D.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Sun, P. Carbon residue from co-pyrolysis of cartons and plastics: Characteristics, environmental behaviors and applications. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).