Abstract
Cost-effective procedures usually cannot achieve complete removal of priority contaminants present in water at very low concentrations (as pesticides or pharmaceuticals). Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) represent promising technologies for removing priority contaminants from water at trace concentrations, yet practical implementation remains limited due to technical and economic constraints. This study presents an innovative flow-through photodegradation device designed to overcome current limitations while achieving efficient contaminant removal at industrial scale. The device integrates a UVC 254 nm lamp-equipped flow chamber with automated dosing pumps for hydrogen peroxide and/or solid catalyst suspensions, coupled with a 30 nm porous membrane filtration system for catalyst recirculation. This configuration optimizes light–catalyst–pollutant contact while enabling combined catalytic processes. Performance evaluation using acesulfame (ACE) and iohexol (IHX) as model contaminants demonstrated rapid and effective removal. IHX degradation with UVC and 75 μM H2O2 achieved complete removal with t95% = 7.23 ± 1.21 min (pseudo-order 0.25, t1/2 = 3.27 ± 0.39 min), while ACE photolysis (with UVC only) required t95% = 14.88 ± 2.02 min (pseudo-order 1.27, t1/2 = 2.35 ± 0.84 min). The introduction of t95% as a performance metric provides practical insights for near-complete contaminant removal requirements. Real-world efficacy was confirmed using tertiary wastewater treatment plant effluents containing 14 μg/L IHX, achieving complete removal within 8 min. However, carbamazepine degradation proved slower (t95% > 74 h), highlighting the need for combined catalytic approaches for recalcitrant compounds. Spiking experiments (1000 μg/L) revealed concentration-dependent kinetics and synergistic effects between co-present contaminants. Analysis identified degradation byproducts consistent with previous studies, including tri-deiodinated iohexol (474.17 Da) intermediates. This scalable system, constructed from commercially available components, demonstrates potential for cost-effective industrial implementation. The modular design allows adaptation to various contaminants through adjustable AOP combinations (UV/H2O2, photocatalysts, ozone), representing a practical advancement toward addressing the gap between laboratory-scale photocatalytic research and full-scale water treatment applications.
1. Introduction
The terms “priority pollutants” or “contaminants of concern” (CECs) are defined broadly and vary by source. The 1976 EPA Clean Water Act focuses specifically on 13 metals (including arsenic, cadmium, mercury, etc.) and 114 organic compounds [1]. Other definitions extend to any potentially hazardous substance detected in the environment, such as personal care products and pharmaceuticals, that may pose significant risks to human health and ecosystems [2,3]. Consequently, a wide spectrum of such pollutants has been identified in surface and groundwater, including pesticides, pharmaceuticals (e.g., iodinated X-ray contrast agents), lifestyle and personal care compounds (such as caffeine and nicotine), industrial and water treatment by-products, food additives (e.g., parabens, artificial sweeteners), flame retardants, and emerging nanomaterials (e.g., quantum dots, dendrimers, nanocomposites) [4].
Over the past few years, several reviews have summarized methods for the efficient removal of these contaminants. Some compare a variety of techniques across different approaches [5,6,7,8], while others examine specific processes. These include biological treatments, such as membrane bioreactors [9], specialized hydrogels [10], adsorption on tailored sorbents [11,12,13,14], and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) [15,16,17]. For example, Rathi et al. [8] provide a detailed list of sorbents matched to specific trace pollutants and also discuss membrane separations and constructed wetlands. They conclude that hybrid strategies combining techniques such as ultrafiltration, activated carbon adsorption, and ultrasonic irradiation [18] can overcome the limitations of individual methods, noting that “emerging contaminants cannot be effectively treated by traditional wastewater treatment methods” and thus require supplementary treatments.
Advanced oxidation processes themselves are commonly classified in two ways: as chemical versus photochemical, depending on whether light is employed [17], and as homogeneous versus heterogeneous, based on whether the oxidant is dissolved or solid [19]. All AOPs share the principle of in situ generation of reactive oxygen species (ROSs) capable of degrading dissolved pollutants [20]. Typical ROSs include hydroxyl, hydroperoxyl, and superoxide radicals [21,22,23]. The ultimate goal is the complete mineralization of toxins, emerging contaminants, pesticides, and other priority pollutants [24].
It is nearly impossible to capture, in a single paper, the vast body of AOP research published to date. Since 2004, the number of AOP-focused publications has grown by over thirteen-fold [25,26,27,28]. Roughly 23% of these studies investigate heterogeneous photocatalysis—primarily TiO2-based systems—while about 12% explore direct photolysis or combined UV/H2O2 processes. Most laboratory studies employ batch-mode reactors or recirculating flow setups in which the effluent repeatedly passes through the catalyst or reactive membrane [29,30]. This arrangement simplifies operation, allows clear separation of treated and untreated streams for performance monitoring, and enables easy recovery of solid catalysts (e.g., by centrifugation). For practical, full-scale deployment, however, systems must operate in true continuous, flow-through mode, purifying contaminated water as it passes through rather than relying on repeated batch or recirculation cycles. Continuous flow-through designs are essential to meet real-world treatment demands.
Despite extensive research on AOP methods, an AI-based search conducted in August 2025 found only about 500 commercial installations worldwide, most of which employ ozone or UV disinfection systems [31]. Key challenges and limitations include high capital and operational costs, process complexity and selectivity, sludge and residue generation, and sensitivity to operational parameters such as pH, temperature, and reactant concentration [32]. Additional hurdles arise from reduced performance in complex natural water matrices, difficulties in recovering catalysts from slurry reactors, and mass-transfer limitations in immobilized photocatalyst membranes [33]. Consequently, although hundreds of laboratory-scale studies report successful photocatalytic water-treatment devices, only a few have been scaled up commercially [34]; examples include the Purifics Photo-Cat system [35] or TrojanUVPhox 72AL75 reactor [36].
In a previous study, we described a laboratory-scale, slurry-type continuous-flow device for the photocatalytic degradation of priority pollutants [37,38]. The reactor was loaded with either synthetic hectorite (SHCa-1) or catalytic-grade TiO2 nanoparticles and challenged with representative dyes, phenols, and pharmaceutical compounds. Under these controlled, synthetic-water conditions, the system achieved efficient degradation performance. However, all experiments to date were conducted in idealized matrices using relatively high pollutant concentrations (>1000 μg L−1). Real-world water sources, often bearing complex chemistries and ultralow contaminant levels, remain untested, leaving most studies’ practical applicability uncertain.
The device described in this study was evaluated for the degradation of two contaminants of emerging concern (CECs). Acesulfame potassium (potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate, ACE; Figure 1) is an artificial sweetener employed as a sewer tracer in aquatic environments, since it is only partially removed by conventional wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [39,40]. Iohexol (5-[N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodo-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)isophthalamide, IHX; Figure 1) is a non-biodegradable iodinated X-ray contrast agent detected at relatively high concentrations in water bodies worldwide [41,42,43]. Although both compounds’ degradation by advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) has been studied in batch experiments [39,41,44,45], there are no reports of their treatment in continuous-flow systems.
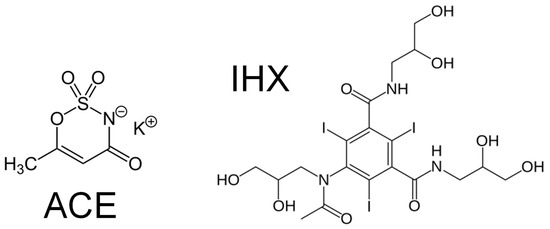
Figure 1.
Acesulfame (ACE) and iohexol (IHX) chemical structure.
In this work, we present an upscaled reactor that integrates multiple AOP modalities, including a slurry-phase nano-photocatalyst, ozone, and hydrogen peroxide, with UV irradiation. This study focuses on the UVC only, and UVC/H2O2 configuration and assesses its efficacy for the complete removal of low concentrations of acesulfame and iohexol in tertiary effluent from a large WWTP.
2. Results
2.1. Flow-Through Device for Photocatalytic Degradation
Figure 2 and Figure 3 present a schematic diagram and a photographic image of the photocatalytic degradation device developed for this project. A brief video (Video S1), demonstrating the device in operation, is available in the Supplementary Material. A detailed description of the individual modules is provided in Section 4.1.

Figure 2.
Schematic view of the photocatalytic degradation device. Solid and dashed lines and arrows indicate pipes and controlling cables, respectively (additional details in Section 4.1).
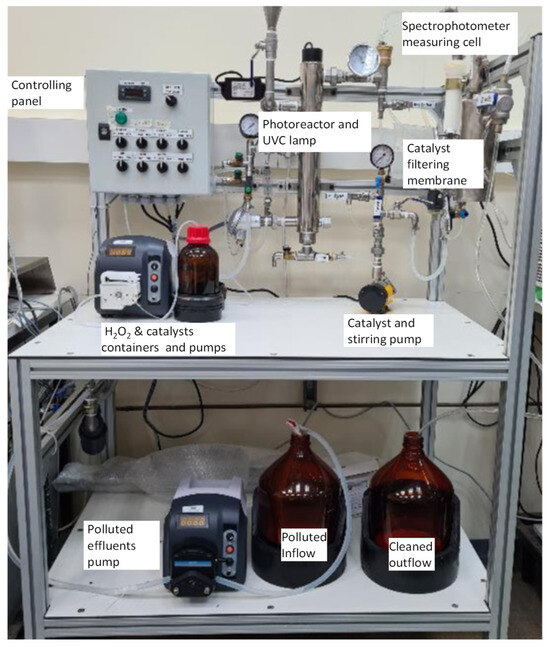

Figure 3.
Picture of the photocatalytic degradation device.
2.2. Preliminary Experiments
As outlined in Section 4.2.1, solutions containing 0.5 mg L−1 of ACE or IHX were allowed to flow at a rate of 2.7 L h−1 without activating the UVC system or introducing any additional reagents. This was done to verify that no significant loss of pollutants occurred due to adsorption onto pipes, filter membranes, or other components of the device. The results, presented in Figure S1 of the Supplementary Material, show that within the first minute, there was a sharp decline in the measured concentrations of both ACE and IHX (C/C0 values of 0.62 and 0.70, respectively). However, after 8 min, the concentrations increased substantially (C/C0 values of 0.76 and 0.92 for ACE and IHX, respectively), and by 20 min, the system had reached equilibrium with C/C0 values approaching 1.0.
2.3. Photodegradation Experiments in Synthetic Effluents
A detailed description of the procedure is provided in Section 4.2.2. A preliminary batch experiment was performed in a 100-mL UV-C-transparent quartz glass (refractive index n = 1.5048), 5.3 cm diameter beaker placed in a Rayonet RMR-600 mini photochemical chamber reactor (Southern New England Ultraviolet Company, Branford, Connecticut, USA) equipped with eight RMR 2537A lamps (254 nm wavelength), each lamp emitting an irradiance flux of 19 J m–2 s–1 at 254 nm, as measured in the center of the chamber using a Black Comet SR spectrometer with an F400 UV–VIS–SR calibrated fiber optic probe equipped with a CR2 cosine light receptor (StellarNet Inc., Tampa, Florida, USA), demonstrating that UVC light without any additional reagent yields photolysis of ACE, whereas degradation of IHX, requires addition H2O2. Similar results were reported in previous studies [46,47].
Figure 4 illustrates the photodegradation of ACE (without H2O2) and IHX (with H2O2 addition). Data points represent measured values (standard deviations from replicate experiments), and lines correspond to fits based on the pseudo-order kinetic model [48] briefly described in Section 4.2.2. Complete degradation of IHX was achieved after approximately 8 min, with a pseudo-order of 0.25 and a half-life (t1/2) of 3.27 ± 0.39 min. ACE reached near-complete degradation after approximately 15 min, with a pseudo-order of 1.27 and a half-life of 2.35 ± 0.84 min. Because regulatory focus on priority trace pollutants emphasizes near-total removal, we define the time to 95% degradation (t95%) as denoted in Eq. 4. For IHX, t95% is 7.23 ± 1.21 min, whereas for ACE, t95% is 14.88 ± 2.02 min. It should be noted that IHX degradation involved H2O2 injection, while ACE underwent direct photolysis without additional reagents or catalysts. The agreement between measured data and model predictions is excellent, with R2 = 0.989 for both ACE and IHX.

Figure 4.
Average photolysis of acesulfame (ACE, left panel) and photodegradation of iohexol (IHX, right panel) with injection of 75 μM (2.55 mg L−1) H2O2. Points indicate measured values with standard error. Lines indicate evaluated values based on the “pseudo-order method” [48]. Pollutant concentrations ranged between 0.1–0.5 mg L−1.
2.4. Photodegradation Experiments in Shafdan WWTP Effluents
2.4.1. Degradation of Pollutants on Tertiary Treatment Effluents
The first experiment was conducted on tertiary-treatment effluents from Israel’s largest wastewater treatment plant, prior to disinfection and chlorination, with the addition of 75 µM H2O2, as described in Section 4.2.3. The initial iohexol (IHX) concentration in the effluents was 14 µg L−1, whereas acesulfame (ACE) was below the LC-MS detection limit. A significant (22 µg L−1) trace concentration of carbamazepine (CBZ), an antiepileptic drug frequently detected in WWTP effluents [49], was also present. Although this study focused on ACE and IHX, we also monitored CBZ degradation in the real-world effluents. Figure 5 shows that IHX degradation is very rapid, reaching complete removal within 8 min, while CBZ degrades much more slowly. Previous UVC/H2O2 studies report efficient CBZ removal [49,50], but they employed H2O2 concentrations 50–100 times higher (5000–20,000 µM) than those used here.
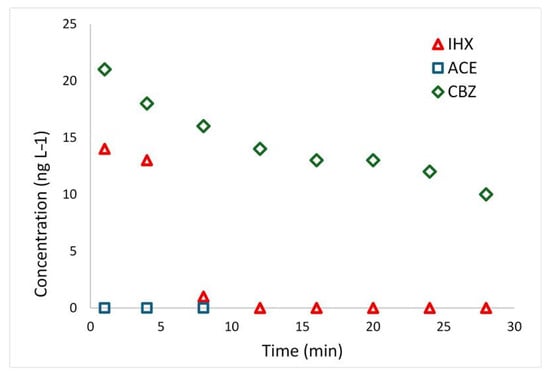
Figure 5.
Photodegradation of iohexol (IHX) and carbamazepine (CBZ) in Shafdan WWTP tertiary effluent, carried out with the addition of 75 µM (2.55 mg L−1) H2O2. Acesulfame (ACE) was not detected in the effluent.
Under our conditions, using the pseudo-order kinetic model yields a reaction order of 2.84 for CBZ, a half-life (t1/2) of 26.5 min, and t95% of 4484 min (>74 h). Given that most rapid AOPs for CBZ employ heterogeneous catalysts [51,52], such slow removal under low-H2O2 UVC photolysis is unsurprising. While exact kinetics depend on system parameters, including UVC intensity, previous work shows that combining low H2O2 doses with mineral catalysts (e.g., TiO2 or clay minerals) can reduce CBZ half-life to under 6 min [12].
2.4.2. Degradation on Tertiary Treatment Effluents with IHX and ACE Spiking
To evaluate the device’s performance under high pollutant loads representative of industrial discharges in real effluent, Shafdan WWTP tertiary effluent was spiked with 1000 µg L−1 of ACE and IHX, both individually and in combination. Figure 6 presents the results of these spiking experiments, as detailed in Section 4.2.3.

Figure 6.
Photodegradation of iohexol (IHX) and acesulfame (ACE) from Shafdan WWTP spiked with 1000 μg L−1 of pollutants, when added separately (ACE, IHX) or together (“combined” samples).
To enhance clarity in Figure 6, the Y-axis excludes the initial 1000 µg L−1 concentration for all samples, zooming in on the degradation dynamics. Iohexol (IHX) shows nearly identical decay profiles whether tested alone or with acesulfame (ACE), leveling off at about 130 µg L−1 even after 25 min, so complete removal is not achieved. ACE alone degrades at a comparable pace, but when combined with IHX it disappears entirely within 12 min. This suggests that pollutants’ interactions can accelerate the breakdown of the more labile compounds. The persistent IHX residue implies the process follows higher-order kinetics, which tend to be effective at high pollutant loads but less so at lower concentrations [48].
2.5. Suggested Photodegradation By-Products
The workflow for detecting and tracking photodegradation by-products is outlined in Section 4.3.2. Our LC-MS/MS method was optimized for quantifying the parent contaminants (ACE and IHX), so untargeted screening revealed only one plausible intermediate per compound, and those appeared within the first 4 min of irradiation.
2.5.1. ACE Screened Photodegradation By-Products
Compound Discoverer 3.1 (Thermo Xcalibur *.doc) flagged two intermediate species for ACE at 194 Da and 212 Da. Although UV-AOP studies, including direct solar [53] or LED-UVC photolysis at different wavelengths [44], UV/persulfate [45], and UV/hydrogen peroxide [44,54], have proposed by-products in the 148.9–222.2 Da range, our untargeted LC-MS/MS screen only confirmed the 194 Da and 212 Da species. Xue et al. [45] also identified these two; the 194 Da product forms after two successive oxidations (see Figure 7), and the 212 Da compound arises following an additional hydrolysis step.

Figure 7.
Photodegradation-suggested path for screened byproducts of acesulfame (ACE).
2.5.2. IHX Screened Photodegradation By-Products
The degradation of iohexol (IHX) by various AOPs has been extensively investigated. Zilberman et al. [55] found ozonation to be inefficient, achieving only partial IHX removal; the resulting by-products exhibited persistence, stability, and toxicity profiles similar to the parent compound, with some even more toxic than IHX itself. Electro-enhanced activation promotes deiodination, amide hydrolysis, C–OH oxidation, hydroxyl addition, hydrogen abstraction, and elimination reactions, yet most by-products produced under these conditions showed low toxicity toward fish, daphnia, and algae [56]. Hu et al. [57] detailed the kinetics of UV-induced IHX oxidation but noted an increase in the toxic by-product iodoform (CHI3) during the process. A recent study that tested LED UV photodegradation at different wavelengths detected seven different transformation products and concluded that “overall toxicity increased after UV-LED photolysis, posing a considerable risk that requires careful attention” [58].
Under UV/H2O2 treatment analogous to the conditions in our device, Giannakis et al. [41] identified 13 IHX by-products (ranging from 444 to 712 Da) after 5 min of irradiation, whereas only three by products (514–653 Da) persisted after 15 min. Our LC-MS/MS analysis confirms the formation of a tri-deiodinated iohexol intermediate (C19H27N3O11, m/z 474.1726), in which the 2,4,6-triiodophenyl ring is converted to a hydroxylated benzene core while retaining the acetamido side chains (Figure 8). This structure corresponds to one of the by-products proposed by Giannakis et al. that is present after both 5 min and 15 min UV/H2O2 treatments. A detailed suggested degradation pathway that forms such a component, built with the help of Microsoft Copilot AI (Microsoft, 2025), is provided as Scheme S1 in the Supplementary Material.

Figure 8.
Photodegradation byproducts of iohexol (IHX).
3. Discussion
The flow-through device demonstrated rapid and near-complete photodegradation removal of low-concentration iohexol (IHX) and acesulfame (ACE) under UVC/H2O2 and UVC-only conditions, respectively. The UV/H2O2 configuration achieved complete IHX degradation within 8 min (t95% = 7.23 ± 1.21 min), confirming the device’s ability to generate sufficient reactive oxygen species for halogenated compounds. ACE photolysis required longer exposure (t95% = 14.88 ± 2.02 min) but proceeded efficiently without added reagents, highlighting UVC direct photolysis as a viable route for certain trace pollutants.
Spiking experiments at 1000 µg L−1 concentrations revealed concentration-dependent kinetics and pollutant interactions. Iohexol remained at ~130 μg L−1 after 25 min, whether alone or mixed with ACE, indicating higher-order kinetics that slow at lower residual levels. In contrast, ACE spiked alone followed similar decay to IHX alone, but its combined sample with IHX achieved full removal within 12 min, suggesting that co-contaminant interactions can accelerate degradation of the more labile species.
Real-world effluent trials underscored the system’s promise and its current limits. Using tertiary wastewater from Shafdan WWTP, IHX was eliminated within 8 min, mirroring synthetic results despite complex water matrices. Carbamazepine (CBZ), however, displayed sluggish kinetics (t95% > 74 h) under low H2O2 dosing, underscoring the need for heterogeneous catalysts or higher oxidant loads to tackle recalcitrant pharmaceuticals.
By-product screening confirmed known intermediates without revealing novel species. Acesulfame intermediates at 194 Da and 212 Da aligned with previous UV/AOP studies, while a tri-deiodinated iohexol (m/z 474.17) matched reported UV/H2O2 pathways. The absence of additional by-products in early irradiation stages suggests that extended treatment or catalytic enhancements may be required for full mineralization. More extensive detailed LC-MS/MS measurements are required to determine if toxic degradation byproducts remain after the process, as was reported in several prior studies. Additional experiments based on flow-through devices should be performed to test such persistent priority pollutants, at a relevant range of concentrations and conditions that fit real-world situations, by employing other AOP agents, such as TiO2 or similar solid catalysts, to exploit the combination of homo- and heterogeneous catalytic processes.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Description of the Device
The slurry-type continuous-flow device for photocatalytic degradation of priority pollutants (Figure 2) is an upscale of a previously reported laboratory-scale system [37,38]. Its core is the photoreactor module (denoted “photoreactor cell” or “photoreactor and UVC lamp” in Figure 2 and Figure 3), which integrates an AMD-UV-21 disinfection unit (Zalion Ltd., Bat Yam, Israel). This module houses a 21 W UVC lamp (254 nm) providing an irradiance of 15.2 μW cm−2 and supports a nominal flow rate up to 13.6 L h−1. Contaminated effluent is drawn from the feeding tank by a PP-X-575 peristaltic pump (MRC Laboratory Instruments, Holon, Israel) fitted with a YZ1515X head and S-18 tubing, delivering up to 35 L h−1 [59]. Hydrogen peroxide and heterogeneous catalyst suspensions are dosed directly into the photoreactor via two independent PP-X-576 peristaltic pumps (300–3000 mL h−1 each), which may operate separately or in tandem. An optional ozone generator can also be integrated. Downstream of the photoreactor, treated effluent passes through a 2 m2 polysulfone NUF® membrane (NUF Filtration, Caesarea, Israel) rated for 150 L h−1 and an absolute pore size of 30 nm (“catalyst filter,” Figure 2). Originally developed for hemodialysis [60], this membrane permits continuous recirculation of solid catalysts to the photoreactor (“catalyst recycling and stirring pump” in Figure 3) via an NH-1PX-Z magnetic-drive centrifugal pump (March May Ltd., Cambridgeshire, UK), and the transmembrane pressure (TMP) used was between 0.6–1.0 bar. Finally, the clarified effluent flows through a DP400 dip-probe cuvette connected to a Black Comet SR spectrophotometer (SpectraWiz software v.6.32; StellarNet Inc., Tampa, FL, USA), enabling real-time UV–Vis monitoring. All modules, including the main feed pump, H2O2 and catalyst dosing pumps, optional ozone generator, UVC photoreactor, membrane filtration and recycling system, and spectrophotometer monitoring cell, are controlled from a central panel to ensure full operational flexibility.
4.2. ACE and IHX Photodegradation Experiments
Analytical ACE, IHX, and a 30% (9.79 M) concentrated H2O2 solution were obtained from Merck/Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Stock solutions of 1 mg L−1 of both pollutants were prepared and kept in dark large bottles at room temperature (23 ± 1 °C). Experiments were performed by pumping pollutants at concentrations ranging between 0.15–0.5 mg L−1 at 25 RPM (equivalent to a rate flow of 2.27 L h−1).
4.2.1. Preliminary Evaluation and Maintenance of the System
To avoid biases caused by potential adsorption of pollutants onto the pipes and membranes, a preliminary assessment of the system’s performance was conducted by running a 0.5 mg L−1 solution of each pollutant through the setup without activating the UVC lamp or adding any reagents. The results are presented in Section 2.2.
Since previously used pollutants in the system may leave residues that could affect subsequent measurements, the system was cleaned after each run with 1 L of 5% ethanol in distilled water, followed by 2 L of distilled water. At the end of the process, the effluent was tested using the spectrophotometer monitoring device described in Section 4.1, and the first sample in the subsequent LC-MS/MS analysis confirmed that no residues of the previous pollutants remained.
4.2.2. Photodegradation Experiments in Synthetic Effluents
Based on preliminary experiments and literature indicating that ACE undergoes photolysis under UVC radiation without the need for additional reagents [44], experiments involving ACE did not include the addition of H2O2. In contrast, experiments with IHX involved the injection of H2O2 to achieve an inflow concentration of 75 µM (2.55 mg L−1). Concentrations of pollutants in the outflow were measured using HPLC, and samples were additionally analyzed by LC-MS/MS to suggest and monitor potential degradation by-products. The measured concentrations of remaining pollutants were evaluated as relative residual concentrations (C/C0), and the average was calculated across three independent experiments. To assess process efficiency, half-life times (t1/2) and the time required to achieve 95% degradation (t95%) were determined using the “pseudo-order method” extensively described by Rytwo and Zelkind [48]. Briefly, pseudo-order kinetic models are based on the integration of the simplified rate law [61,62]:
where is the reaction rate, ka is the apparent rate coefficient, and na is the apparent or “pseudo” reaction order. Simple integration of Equation (1) (as long as na ≠ 1) yields:
To relatively objectively compare efficiency of processes, “half-life time” (t1/2) can be calculated by solving Equation (2) for the case where the concentration is half of its initial value, thus [A](t) = 0.5, yielding:
Considering that in priority trace pollutants the goal is almost complete removal, it is worth defining the evaluated time until 95% of the pollutant is removed (t95%), as follows:
Specific adaptation to Equations (2) and (3) for pseudo-first-order (na = 1) [63] yields:
Estimates of the best-fit pseudo-order (n), and the rate constant (ka) are made by minimizing the overall root mean square error (RMSE) [48]. The procedure can be easily performed using the “Solver” add-on in Excel® software (Microsoft 365 for Enterprise, Version 2507). Following that, t1/2 and t95% can be evaluated based on na and ka. These calculations enable comparison between different processes without requiring an a priori assumption about the reaction’s kinetic order, thus providing a relatively objective evaluation of the process’s efficiency by identifying the pseudo-order and corresponding degradation times [64,65].
4.2.3. Photodegradation Experiments on Shadan WWTP Tertiary Effluents
To evaluate the effectiveness of ACE and IHX degradation in real effluents, water from Shafdan WWTP [66] after tertiary treatment but before chlorination were brought to the laboratory. A full description of the WTTP and the methods adopted in the establishment can be found in previous reports [67]. The pH was 7.55 and turbidity < 4 NTU. Such values are similar to those reported for Shafdan effluent in the literature [68]. Preliminary LC-MS screening measurements for priority pollutants indicated that the effluents contained 14 μg L−1 IHX and 22 μg L−1 carbamazepine (CBZ), but no ACE. Three different experiments were performed, all of them with injection of 75 μM (2.55 mg L−1) of H2O2: (a) Shafdan original effluents, (b) Shafdan original effluents spiked with 1000 μg L−1 of ACE or IHX in separate experiments, and (c) Shafdan original effluents spiked with 1000 μg L−1 of both ACE and IHX.
4.3. Chromatography Measurements
4.3.1. HPLC Measurements
Part of the measurements were performed by injecting 5 μL of the extracted solutions into a UHPLC connected to a photodiode array detector (Dionex Ultimate 3000) with a reverse-phase column (ZORBAX Eclipse plus C18, 3.0 × 100 mm, 1.8 μm). The mobile phase consisted of (A) DDW with 0.1% formic acid and (B) acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid. The gradient started with 2% B and was kept isocratic for 2 min, then increased to 75% B in 16 min, then increased to 95% in 1 min and kept isocratic at 95% B for 4 min. Phase B returned to 5% in 2 min and the column was allowed to equilibrate at 5% B for 3 min before the next injection. The flow rate was 0.4 mL/min. Column temperature was set to 35 °C.
4.3.2. MS/MS Analysis
Measurements for analysis of degradation byproducts were made with mass spectrometry (MS) analysis performed with a heated electrospray ionization (HESI-II) source connected to a Q Exactive™ Plus Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific ™, Waltham, MA, USA). ESI capillary voltage was set to 3900 V in positive mode and 3500 V in negative mode, capillary temperature to 350 °C, gas temperature to 350 °C. Sheath gas flow was set to 35 mL/min, aux gas flow to 10 mL/min, and sweep gas flow to 1 mL/min. The mass spectra in positive-ion mode (m/z 67–900) and in negative mode (m/z 50–300) was acquired with high resolution (FWHM = 70,000 at m/z = 200. For MS2 analysis, collision energy was set to 20, 30, and 50 EV.
Data preprocessing for MS targeted analysis was conducted using Thermo Scientifc™ Xcalibur™ instrument control software (version 4.7.69.37). Extracted ion chromatograms for figure production were generated in Xcalibur 4.0.27.19 software using a mass window of (+/−) 5 ppm. Exact m/z values used for figure creation and peak integration corresponded to theoretical [M + H]+ ion m/z values and were as follows: iohexol 821.8876 m/z, [M − H] Acesulfame 161.9866 m/z. Peak integration was performed using QuanBrowser Thermo Xcalibur 4.7.69.37 software. After determining LOD, LOQ, and linearity for each analyte, data preprocessing for MSMS untargeted analysis and peak determination and peak area integration for IHX and ACE decomposition products was performed with Compound Discoverer 3.1 (Thermo Xcalibur, Version 3.3.0.305) using metabolism workflow. Auto-integration was manually inspected and corrected if necessary. For some of the compounds, identification was performed based on the MzCloud database using MS2 data and the ChemSpider database using MS2 data and HRMS.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15080778/s1, Figure S1: Concentrations of ACE or IHX without turning on the UVC system or adding any additional reagent.; Video S1: Short video of the device in action; Scheme S1: Copilot (AI)-generated detailed breakdown of hydrolysis and deiodination pathways of iohexol.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.R.; methodology, R.S., S.K., L.L. and G.R.; software, R.S. and S.K.; validation, R.S., S.K., L.L. and G.R.; formal analysis, R.S. and G.R.; investigation, R.S., S.K., L.L. and G.R.; resources, G.R. and S.K.; data curation, R.S., L.L. and G.R.; writing—original draft preparation, G.R.; writing—review and editing, R.S., S.K., L.L. and G.R.; visualization, R.S., L.L. and G.R.; supervision, G.R. and S.K.; project administration, G.R.; funding acquisition, G.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Israel Innovation Authority Grant #75367, in cooperation with Mekorot Water Company Ltd. (Tel Aviv, Israel), Israel’s national water company. Additional financial support (Lior Levy scholarship) was received from CSO-MOH (Israel) in the frame of the collaborative international consortium (REWA) financed under the GA Nº 869178. Joint call of the Aquatic Pollutants ERA-NET Co-fund (GA Nº 869178).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Eng. Ilan Katz and Gonen Eshel for their full technical support, including the detailed descriptions, planning, and construction of the device. We also want to thank Mordi Tubul, Chen Barak, Ilil Levakov, and other students and technicians at the Environmental Physical Chemistry Laboratory at MIGAL Research Institute. Of course, none of those results would be achieved without the logistical support of all the staff at MIGAL Research Institute and at Tel Hai College. Special thanks to Ori Ben Herzl for encouraging us along the way in such a difficult period in our region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ACE | Potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate-acesulfame |
| AOP | Advanced oxidation process |
| C/C0 | Ration between measured concentration and initial concentration |
| CBZ | Carbamazepine |
| EPA | US Environmental Protection Agency |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| IHX | 5-[N-(2,3-Dihydroxypropyl)acetamido]-2,4,6-triiodo-N,N′-bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)isophthalamide, iohexol |
| min | Minutes |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species I |
| t1/2 | Half-life time |
| t95% | Evaluated time for the degradation of 95% of a pollutant |
| TiO2 | Catalytic grade titanium dioxide |
| TMP | Trans-membrane pressure |
| UV | Ultraviolet light |
| UVC | Ultraviolet light in the range 190–280 nm |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plant |
References
- EPA Toxic and Priority Pollutants Under the Clean Water Act|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/toxic-and-priority-pollutants-under-clean-water-act (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Sauvé, S.; Desrosiers, M. A Review of What Is an Emerging Contaminant. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Malule, H.; Quiñones-Murillo, D.H.; Manotas-Duque, D. Emerging Contaminants as Global Environmental Hazards. A Bibliometric Analysis. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Arias Espana, V.A.; Liu, Y.; Jit, J. Emerging Contaminants in the Environment: Risk-Based Analysis for Better Management. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathi, S.; El Din Mahmoud, A. Trends in Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater: A Comprehensive Review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Fourmentin, M.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Mapelli, F.; Fenyvesi, É.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; et al. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Using Advanced Treatments. A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1333–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Momin, S.; Ali, R.; Naeem, A.; Khan, A.; Mahmood, T.; Momin, S.; Ali, R.; Naeem, A.; Khan, A. Technologies for Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater. Wastewater Treat. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Show, P.L. A Review on Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Aquatic Systems: Current Trends and Scope for Further Research. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Jebur, M.; Kamaz, M.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater Streams Using Membrane Bioreactors: A Review. Membranes 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Choudhary, P.; Majeed, A.; Guleria, S.; Kumar, M.; Rana, A.K.; Rajauria, G. Cellulose Based Membranes, Hydrogels and Aerogels for Water Treatment Application. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, M.; Kaykioglu, G.; Belgiorno, V.; Lofrano, G. Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater by Adsorption Process; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9789400739161. [Google Scholar]
- Levakov, I.; Shahar, Y.; Rytwo, G. Carbamazepine Removal by Clay-Based Materials Using Adsorption and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Rahman, R.O.A.; Imai, T.; Hung, Y.-T.; Almeida-Naranjo, C.E.; Guerrero, V.H.; Alejandra Villamar-Ayala, C. Emerging Contaminants and Their Removal from Aqueous Media Using Conventional/Non-Conventional Adsorbents: A Glance at the Relationship between Materials, Processes, and Technologies. Water 2023, 15, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.F.; Khoruzhenko, O.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Q.L.; Jiao, D.; Du, M.; Breu, J.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Magneto-Orientation of Magnetic Double Stacks for Patterned Anisotropic Hydrogels with Multiple Responses and Modulable Motions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Recent Advances in the Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water by Novel Molecularly Imprinted Materials in Advanced Oxidation Processes—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriou Dionysiou, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Emerging Contaminant Removal; MDPI Books: Basel, Switzerland, 2023; 298p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypart-Pawul, A.; Neczaj, E.; Grobelak, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Removal of Organic Micropollutants from Wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 305, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secondes, M.F.N.; Naddeo, V.; Belgiorno, V.; Ballesteros, F. Removal of Emerging Contaminants by Simultaneous Application of Membrane Ultrafiltration, Activated Carbon Adsorption, and Ultrasound Irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, J.M.; Muñio, M.M.; Almecija, M.C.; Torres, J.C.; Hontoria, E.; Osorio, F. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: State of the Art. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 205, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazille, F.; Spuhler, D. Advanced Oxidation Processes. Available online: https://sswm.info/sswm-university-course/module-6-disaster-situations-planning-and-preparedness/further-resources-0/advanced-oxidation-processes (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Ghime, D.; Ghosh, P.; Ghime, D.; Ghosh, P. Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Powerful Treatment Option for the Removal of Recalcitrant Organic Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comninellis, C.; Kapalka, A.; Malato, S.; Parsons, S.A.; Poulios, I.; Mantzavinos, D. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment: Advances and Trends for R&D. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, U.; Spahr, S.; Lutze, H.; Wieland, A.; Rüting, S.; Gernjak, W.; Wenk, J. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment-Guidance for Systematic Future Research. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water Treatment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 2112–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude AI Advanced Oxidation Processes Publications Trends (2004–2024)|Claude|Claude. Available online: https://claude.ai/public/artifacts/68bf09bc-f715-44d0-ae01-efeaf6784d7f (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Macías-Quiroga, I.F.; Henao-Aguirre, P.A.; Marín-Flórez, A.; Arredondo-López, S.M.; Sanabria-González, N.R. Bibliometric Analysis of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment: Global and Ibero-American Research Trends. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23791–23811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Cardenas, J.A.; Esteban-García, B.; Agüera, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Wastewater Treatment by Advanced Oxidation Process and Their Worldwide Research Trends. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clímaco Cunha, I.L.; Machado, P.G.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, C.; Kulay, L. Bibliometric Analysis of Advanced Oxidation Processes Studies with a Focus on Life Cycle Assessment and Costs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 22319–22338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida da Silva, T.C.; Marchiori, L.; Oliveira Mattos, B.; Ullah, S.; Barud, H. da S.; Romano Domeneguetti, R.; Rojas-Mantilla, H.D.; Boldrin Zanoni, M.V.; Rodrigues-Filho, U.P.; Ferreira-Neto, E.P.; et al. Designing Highly Photoactive Hybrid Aerogels for In-Flow Photocatalytic Contaminant Removal Using Silica-Coated Bacterial Nanocellulose Supports. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 23146–23159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, M.; Barrocas, B.T.; Serôdio, R.M.N.; Oliveira, M.C.; Lopes, J.M.; Marques, A.C. Robust Photocatalytic MICROSCAFS® with Interconnected Macropores for Sustainable Solar-Driven Water Purification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veolia Disinfection & Oxidation Water Treatment: Ozone & UV Systems|Veolia. Available online: https://www.watertechnologies.com/products/disinfection-oxidation (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Waterandwastewater.com Advanced Oxidation Processes in Wastewater Treatment: Efficiency and Innovation-Water & Wastewater. Available online: https://www.waterandwastewater.com/advanced-oxidation-processes-in-wastewater-treatment-efficiency-and-innovation/ (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- Hodges, B.C.; Cates, E.L.; Kim, J.-H. Challenges and Prospects of Advanced Oxidation Water Treatment Processes Using Catalytic Nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cates, E.L. Photocatalytic Water Treatment: So Where Are We Going with This? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benotti, M.J.; Stanford, B.D.; Wert, E.C.; Snyder, S.A. Evaluation of a Photocatalytic Reactor Membrane Pilot System for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds from Water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojan UV Resources Environmental Contaminant Treatment Product Brochure. Available online: https://www.trojanuv.com/resources//Products/TrojanUVPhox/TrojanUV_ECT_Products_Brochure.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Rytwo, G.; Klein, T.; Margalit, S.; Mor, O.; Naftaly, A.; Daskal, G. A Continuous-Flow Device for Photocatalytic Degradation and Full Mineralization of Priority Pollutants in Water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 16424–16434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytwo, G.; Daskal, G. A System for Treatment of Polluted Effluents. PCT/IL2015/050944, WO2016042558 A1. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20170297933A1/en (accessed on 24 March 2016).
- Ishii, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Agusa, T.; Hosono, T.; Nakata, H. Acesulfame as a Suitable Sewer Tracer on Groundwater Pollution: A Case Study before and after the 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ren, Y.; Fu, Y.; Gao, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, G.; Ren, H.; Geng, J. Fate of Artificial Sweeteners through Wastewater Treatment Plants and Water Treatment Processes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Jovic, M.; Gasilova, N.; Pastor Gelabert, M.; Schindelholz, S.; Furbringer, J.-M.; Girault, H.; Pulgarin, C. Iohexol Degradation in Wastewater and Urine by UV-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs): Process Modeling and by-Products Identification. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chèvre, N. Pharmaceuticals in Surface Waters: Sources, Behavior, Ecological Risk, and Possible Solutions. Case Study of Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2014, 1, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrkal, Z.; Adomat, Y.; Rozman, D.; Grischek, T. Efficiency of Micropollutant Removal through Artificial Recharge and Riverbank Filtration: Case Studies of Káraný, Czech Republic and Dresden-Hosterwitz, Germany. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Nguyen Song Thuy Thuy, G.; Srivastava, V.; Ambat, I.; Sillanpää, M. Photocatalytic Degradation of an Artificial Sweetener (Acesulfame-K) from Synthetic Wastewater under UV-LED Controlled Illumination. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 123, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B. Performance of Ultraviolet/Persulfate Process in Degrading Artificial Sweetener Acesulfame. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Park, J.; An, S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Choe, J.K. Formation Dynamics of Inorganic Iodine Species during UV-Based Advanced Oxidation of Iopamidol and Iohexol and Their Correlation with Iodinated Disinfection by-Product Yields. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkola, N.; Vaalgamaa, S.; Jernberg, J.; Vähätalo, A.V. Degradation of Artificial Sweeteners via Direct and Indirect Photochemical Reactions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13288–13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rytwo, G.; Zelkind, A.L. Evaluation of Kinetic Pseudo-Order in the Photocatalytic Degradation of Ofloxacin. Catalysts 2022, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogna, D.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M.; d’Ischia, M. Kinetic and Chemical Assessment of the UV/H2O2 Treatment of Antiepileptic Drug Carbamazepine. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lu, G.; Zhu, X.; Pu, C.; Guo, J.; Liang, X. Insight into the Generation of Toxic By-Products during UV/H2O2 Degradation of Carbamazepine: Mechanisms, N-Transformation and Toxicity. Chemosphere 2024, 358, 142175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroune, L.; Salaun, M.; Ménard, A.; Legault, C.Y.; Bellenger, J.P. Photocatalytic Degradation of Carbamazepine and Three Derivatives Using TiO2 and ZnO: Effect of PH, Ionic Strength, and Natural Organic Matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 475, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Laera, G.; Saint, C.P. Evaluating the Photodegradation of Carbamazepine in a Sequential Batch Photoreactor System: Impacts of Effluent Organic Matter and Inorganic Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.; Chowdhury, P.; Ray, A.K. Study of Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of Acesulfame K to Limit the Outpouring of Artificial Sweeteners. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Geng, J.; Wu, G.; Gao, X.; Fu, Y.; Ren, H. Removal of Artificial Sweeteners and Their Effects on Microbial Communities in Sequencing Batch Reactors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberman, A.; Gozlan, I.; Avisar, D. Pharmaceutical Transformation Products Formed by Ozonation—Does Degradation Occur? Molecules 2023, 28, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, C.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Shi, K.; Xu, Z.; Yang, S.; et al. Improved Degradation of Iohexol Using Electro-Enhanced Activation of Persulfate by a CuxO-Loaded Carbon Felt with Carbon Nanotubes as an Interlayer. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 312, 123336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Hou, Y.Z.; Lin, Y.L.; Deng, Y.G.; Hua, S.J.; Du, Y.F.; Chen, C.W.; Wu, C.H. Kinetics and Model Development of Iohexol Degradation during UV/H2O2 and UV/S2O82−Oxidation. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Zeng, C.; Lin, Y.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, H.X.; Luo, Z.N.; Zheng, Z.X.; Cao, T.C.; Hu, C.Y.; et al. Wavelength Dependency and Photosensitizer Effects in UV-LED Photodegradation of Iohexol. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MRC PP-X-575PP-X-575, Basic Speed–Variable Peristaltic Pump. Available online: https://www.mrclab.co.il/Media/Doc/PP-X-575-V2_SPEC.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- NUF Technology Overview. Available online: https://www.nufiltration.com/technology (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- White, D. PPT—Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics PowerPoint Presentation, free download—ID:4450074 [WWW Document]. Prentice Hall. 2003. Available online: https://www.slideserve.com/manny/chapter-12-chemical-kinetics-powerpoint-ppt-presentation (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology: Gold Book; IUPAC: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2014; p. 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, Y.; Rytwo, G. Elementary Steps in Steady State Kinetic Model Approximation for the Homo-Heterogeneous Photocatalysis of Carbamazepine. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.D.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Do, P.T.; Tran, U.N.P. Kinetics of Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Compounds: A Mini-Review and New Approach. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 16915–16925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, N.O.; Ukpe, R.A.; Ameh, P.; Ogbodo, R.; Garg, R.; Garg, R. Theoretical and Experimental Studies on Photocatalytic Removal of Methylene Blue (MetB) from Aqueous Solution Using Oyster Shell Synthesized CaO Nanoparticles (CaONP-O). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 81417–81432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekorot Shafdan Wastewater Treatment Plant. Available online: https://www.mekorot-int.com/blog/project/shepdan/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Elkayam, R.; Lev, O.; Negev, I.; Sued, O.; Shtrasler, L.; Vaizel-Ohayon, D.; Katz, Y. Soil Aquifer Treatment System Performance: Israel’s Shafdan Reclamation System as an Ultimate Case Study; Springer Nature Link: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkayam, R.; Sopliniak, A.; Gasser, G.; Pankratov, I.; Lev, O.; Pankratov, I.; Zone, V. Oxidizer Demand in the Unsaturated Zone of a Surface-Spreading Soil Aquifer Treatment System. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).