Abstract
Water, the source of life, is undeniably essential to all living beings in nature. However, the process of industrialization has led to the pollution of water resources. Photocatalytic water treatment technology can convert solar energy into environmentally friendly and renewable chemical energy, effectively degrading organic pollutants in water. This offers a promising solution for the purification of water environments. The development of high-performance photocatalysts is crucial for photocatalytic reactions. Polyoxometalates (POMs) are anionic metal oxide clusters that come in various sizes and shapes. Their unique electronic properties, tunable structures, and photocatalytic activity make them highly promising materials for the efficient degradation of organic pollutants in water. This review summarizes the recent advances in emerging POM-based photocatalytic materials for water treatment, elaborating on their mechanisms of action. Finally, the current development prospects and the future challenges of POM-based photocatalytic materials are envisioned.
1. Introduction
In the context of rapid modern societal development, water pollution has become a global challenge with lasting and far-reaching negative impacts on all living beings on Earth. The process of industrialization continues to accelerate, resulting in the discharge of large quantities of industrial waste into the natural environment—either directly or indirectly—posing a serious threat to global water resources. These pollutants are diverse, consisting of toxic metal ions, dyes, antibiotics, and other hazardous chemicals [1,2,3,4]. They not only directly contaminate water bodies, leading to a decline in water quality, but also impact the health of the entire food chain through complex chemical reactions and bioaccumulation, resulting in cascading damage to ecosystems. Additionally, water pollution poses a direct threat to human health, contributing to various diseases and health problems, including heavy metal poisoning and endocrine disruption [5,6,7,8]. Moreover, water pollution has inflicted significant harm on biodiversity, putting many species at risk of extinction due to their inability to adapt to polluted water environments. Therefore, implementing effective measures to combat water pollution and protect water resources is an urgent global priority.
Photocatalytic technology has demonstrated significant potential for application in water pollution treatment due to its numerous advantages, including high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and a broad range of applications [9,10]. This technology primarily harnesses solar energy as an energy source, avoiding the need for additional chemical reagents or significant energy consumption, which makes it a green and sustainable water treatment solution [11]. Photocatalytic technology is effective in degrading various recalcitrant organic pollutants, such as dyes, pesticides, and antibiotics. In this process, photocatalysts can effectively generate highly reactive oxidative free radicals, which facilitate the complete mineralization of organic pollutants into harmless carbon dioxide and water.
The fundamental mechanism of photocatalytic technology is based on the absorption of photon energy by photocatalysts. This absorption triggers electrons to jump from the valence band (VB) to the conduction band (CB), forming photogenerated holes (h+) in the valence band [12,13]. This process is influenced by the energy band structure of the photocatalyst, where the energy difference between the valence band and the conduction band is referred to as the band gap. When the photon energy is equal to or greater than the band gap, electron excitation can occur, leading to the generation of photogenerated electrons and holes, which possess significant redox capabilities [14,15]. Specifically, the holes in the valence band are highly oxidative and can directly oxidize water molecules or organic pollutants adsorbed onto the catalyst’s surface, leading to the formation of hydroxyl radicals (·OH). Concurrently, the photogenerated electrons in the conduction band can reduce dissolved oxygen in water to form superoxide radicals (·O2−). Both of these radicals are potent oxidants with very high reactivity [16]. These ·OH and ·O2− can swiftly react with organic pollutants. Among these, hydroxyl radicals have elevated reactivity. They can non-selectively attack carbon–hydrogen (C-H) and carbon–carbon (C-C) bonds within organic molecules, initiating a series of oxidative reactions, including hydroxylation, addition, and cleavage [17,18]. These reactions progressively decompose complex organic pollutants into smaller molecular fragments. As the reaction proceeds, these smaller molecular fragments undergo further oxidation. Ultimately, this process leads to their mineralization into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), thereby achieving the complete degradation of organic pollutants. Consequently, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biological oxygen demand (BOD) of the water body are significantly reduced, enhancing overall water quality [19]. The remarkable degradation capability of photocatalytic technology highlights its broad potential applications in the realm of water pollution treatment.
The limited light absorption range of conventional photocatalysts, such as TiO2, hinders their practical applications in water purification. Additionally, these photocatalysts have a high rate of photogenerated carrier recombination and low photocatalytic efficiency [20,21]. As a result, developing efficient materials with superior properties for pollutant treatment in aqueous environments remains a significant challenge. Recently, polyoxometalates (POMs), a cluster of metal oxide anions, have emerged as promising photocatalysts due to their unique physicochemical properties and exceptional catalytic performance [22,23]. Composed of counterbalancing cations and early transition metals in high oxidation states (e.g., V5+, Nb5+, Ta5+, Mo6+, and W6+), these metal–oxygen anion clusters form unique inorganic complexes [24]. Their distinctive atomic-level structure, tunable acid-base properties, and inherent thermal, hydrolytic, and oxidative stability have attracted increasing interest from researchers [25]. Moreover, akin to semiconductor materials, POMs can absorb light energy via oxygen-to-metal charge transfer (i.e., transitions from the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), generating photogenerated electrons and holes [26,27]. This capability holds promise for photocatalysis. The effective separation and transfer of photogenerated charges are critical steps in photocatalytic reactions, and the structural characteristics of POMs facilitate this process [28]. By rationally designing the composition and structure of POMs, we can optimize their light absorption properties and the utilization efficiency of photogenerated charges, thereby enhancing the overall performance of photocatalytic reactions. Notably, POMs possess a low LUMO energy level, which enables them to function as efficient electron acceptors when coupled with other photocatalysts exhibiting compatible energy levels [29]. In this coupling system, POMs can act as “electron reservoirs”, efficiently receiving electrons from donors, thereby promoting the separation and transfer of photogenerated carriers, reducing reaction activation energy [30,31,32,33]. This energy-matched coupling strategy not only facilitates the transfer of multiple electrons but also effectively mitigates the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes, enhancing the overall performance of the photocatalytic system. Consequently, POMs hold substantial potential for constructing efficient photocatalytic composite systems, offering new opportunities for realizing complex photocatalytic reactions.
With the growth of research focused on POM-based photocatalysts for the degradation of pollutants in water, their potential in photocatalysis has been comprehensively established. However, existing reviews in this field fail to incorporate recent developments, highlighting the necessity for a systematic summary and discussion of pertinent studies. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the preparation methods, structural characteristics, and recent advancements related to POM-based photocatalysts in water purification. We specifically address gaps in the current literature that overlook the latest research findings. Moreover, our review explores the structural features of POM-based photocatalysts and the impact of carrier selection on their photocatalytic performance. It highlights the significance of POMs’ unique physicochemical properties and the potential for enhancing photocatalytic efficiency through careful tuning of these properties. Finally, on the basis of summarizing the existing research results, this paper offers an in-depth outlook on future directions and challenges facing POM-based photocatalysts. We are confident that this review will serve as a valuable resource for researchers in related fields, thereby enriching and advancing the prospects of POMs in photocatalysis.
2. POMs and Their Composites
In the field of photocatalysis, POMs and their composites have garnered significant attention due to their unique physicochemical properties. Common POM-based photocatalysts primarily include pure POMs, POM-based organic–inorganic hybrid photocatalysts, POM/oxide composites, and POM-based frameworks, among others (Table 1). These materials demonstrate broad application potential in catalytic reactions due to their respective advantages and characteristics. This chapter will provide a detailed overview of the preparation methods, structures, and catalytic mechanisms of these common POM-based photocatalysts, offering readers a comprehensive perspective.

Table 1.
Summary of important data on POM-based photocatalysts.
2.1. Pure POM Photocatalysts
Wang et al. [34] synthesized pure POM nanorods, designated as AgxH3−xPMo12O40, via concentration-induced self-assembly in aqueous solution at room temperature, utilizing PMo12O403− anions and silver ions (Ag+) as precursors (Figure 1). The controllable concentrations of cationic and anionic components in the aqueous solution were identified as crucial factors for the successful synthesis. This adjustable concentration not only facilitated the smooth progression of the reaction but also provided the necessary driving force for the formation of the nanorods. Furthermore, the long-axis orientation of the AgHPMo12 nanorods effectively guides the migration of photogenerated electrons and reduces the likelihood of electron–hole recombination. Their optoelectronic performance was found to be superior to that of AgHPMo12 particles, indicating that the one-dimensional morphology offers a direct electrical pathway for photogenerated electron transport. Li et al. [35] developed three POM photocatalysts with ruthenium-induced structural interconversion through a straightforward hydrothermal synthesis strategy. This interconversion can be achieved by varying the number of active sites within the compounds. Their findings revealed that the catalytic performance is strongly influenced by the elemental composition of these active sites, with compound 1 demonstrating particularly efficient photocatalytic activity. Consequently, the catalytic efficiency and stability of POM-based photocatalysts can be optimized by carefully designing and controlling their structural properties. In another report, Huang et al. [36] utilized thermal treatment strategies to modify POMs, successfully preparing carbon-doped POMs with various morphologies. By controlling the calcination temperature, they expanded the absorption spectrum of the POM photocatalyst into the visible light region. The carbon-doped POM photocatalysts exhibited strong absorption capabilities in the visible light range, achieving a photocatalytic degradation efficiency of 76.30% for imidacloprid and a rate constant of 0.34 h−1. Their study paves the way for the advancement of doped polyoxometalate photocatalysts.
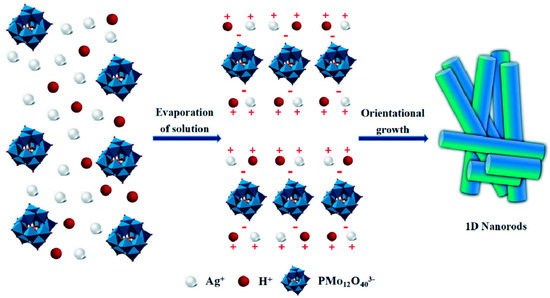
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the formation process of AgHPMo12 nanorods. Reprinted with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry [34].
2.2. POM-Based Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Photocatalysts
POM-based organic–inorganic hybrids are increasingly capturing the attention of researchers due to their distinctive chemical structures and electronic properties. The electronic structure of POM clusters can be finely tuned by the incorporation of metal–organic species, which modifies the band gap between the HOMO and the LUMO. This modulation of the band gap not only enhances the light absorption capacity of the material and improves the electron transfer pathways but also significantly boosts its photocatalytic activity [37,38]. Li et al. [39] demonstrated that the photocatalytic activity of the Dawson-type POM anion, P2W18O626− (P2W18), can be enhanced when co-crystallized with the protonated cation 2-(pyridin-4-yl)-1H-benzotriazole (PHB), resulting in the successful synthesis of a novel POM-based inorganic–organic hybrid compound (P-PW). In this hybrid compound, the P2W18 anion and the PHB cation are closely associated through noncovalent interactions. This interaction not only imparts exceptional stability to the compound but also leads to significant improvements in the electronic structure and photocatalytic properties of the materials.
In another report, Li et al. [40] synthesized an organic–inorganic hybrid material based on POM using the hydrothermal method: [Ni6(trz)2(Htrz)13][H4P4Mo11O50]·7H2O. In this compound, each [H4P4Mo11O50] cluster serves as a four-membered node bridging four [Ni6(trz)2(Htrz)13] SBUs. Photocatalytic results indicate that the composite exhibits excellent stability and a broad response range under visible light. The photocatalytic mechanism was confirmed through Mott–Schottky, photocurrent, and fluorescence quenching experiments, providing new insights for the development of efficient POM-based catalysts. To optimize electron transfer efficiency, Yamaguchi et al. [41] developed and reported a novel porphyrin–polyoxotungstate molecular hybrid photocatalyst. The structure of this hybrid, referred to as hybrid I, consists of face-to-face stacked dimers of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-pyridyl)porphyrin (H2TPyP), anchored by four double-deficient polyoxotungstates ([SiW10O36]8−) with bridging units (Figure 2a). This innovative structural design enables efficient electronic coupling between the porphyrin and polyoxotungstate, significantly enhancing electron transfer during the photocatalytic process (Figure 2b). The porphyrin–polyoxotungstate hybrids exhibit exceptional photocatalytic activity, primarily owing to the heavy-atom effect associated with POMs. This effect greatly facilitates the intersystem crossing from photoexcited singlet to triplet states, leading to improved light energy utilization and enhanced catalytic activity. Furthermore, by fine-tuning the energy level of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of the polyoxotungstates, the electron transfer process can be precisely regulated, further optimizing photocatalytic efficiency. Importantly, the heavy-atom effect of polyoxotungstates is crucial in promoting the generation of singlet oxygen (1O2).
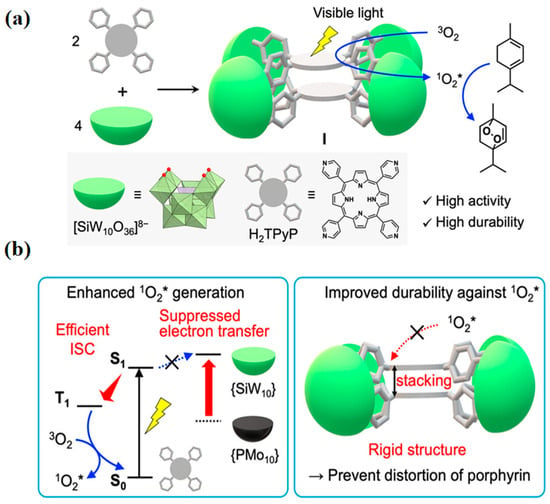
Figure 2.
(a) Illustration depicting the progression of a molecular porphyrin–polyoxotungstate hybrid photocatalyst. (b) Proposed photocatalytic enhancement mechanism. Reprinted with permission from American Chemical Society [41].
2.3. POMs/Oxide Composites
Grafting of co-catalysts on semiconductor oxides has been reported to help charge separation. Notably, the LUMO energy level of Keggin-type POMs is lower than the conduction band energy level of TiO2, thereby positioning Keggin-type POMs as effective electron acceptors when coupled with TiO2 [42]. Sun et al. [32] prepared a series of novel POMs/TiO2 photocatalysts through simple impregnation of Keggin-type POMs (including H3PW12O40, H3PMo12O40, H4SiW12O40, and H4SiMo12O40) dispersed on a titanium dioxide support (TiO2, P25). The synergistic effect between the POMs and TiO2 resulted in enhanced performance of these catalysts under solar irradiation. BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) surface area analysis indicated that the surface area decreased with increasing HSiMo content, suggesting that HSiMo molecules occupied active sites on the surface of the TiO2 particles. Energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) elemental mapping revealed a uniform distribution of titanium, oxygen, silicon, and molybdenum, further indicating the effective dispersion of HSiMo on the P25 TiO2 nanoparticles.
Considering that TiO2 possesses a large specific surface area and excellent redox stability, Nandan et al. [43] effectively utilized APTES as a linking agent to securely immobilize Keggin-type POMs on the TiO2 surface. When compared to TiO2 alone, this composite demonstrated superior photocatalytic performance, particularly in light-driven hydrolysis oxidation reactions. In this context, TiO2 serves a dual role as both a solid support for POM anchoring and an efficient light absorber. This unique configuration significantly enhances the long-term activity of the heterogenized POM clusters. Further investigations suggested that the remarkable performance of the composites in water oxidation catalysis (WOC) is primarily attributed to the efficient extraction of photogenerated holes by the POM clusters. This mechanism not only facilitates effective charge separation but also enables water to participate in more efficient oxidation reactions at the POM sites through direct hole attack. This innovative approach represents a significant breakthrough in the field of photocatalytic water decomposition and provides new perspectives and directions for the development of more efficient and stable photocatalysts. In another study, Jiang et al. [44] incorporated phosphotungstic acid (PW12) into SnO2/TiO2 composites through coaxial electrospinning followed by calcination, resulting in the creation of one-dimensional SnO2@PW22@Rutile/TiO2 core–shell coaxial nanofibers. These nanofibers exhibited outstanding photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline (TC). Their research demonstrated that the integration of the PW12 interlayer facilitated the formation of a double Z-type heterointerface with TiO2 and SnO2, effectively inhibiting the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes. This enhancement in charge carrier separation significantly improved the utilization of photogenerated carriers, thereby boosting the photocatalytic activity.
ZnO also serves as a highly effective photocatalytic support material. In a study, Xing et al. [45] successfully grafted Cu-POMs onto the surface of ZnO using a polydopamine (PDA) layer through an innovative post-grafting method, resulting in the development of a novel photocatalytic material, ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs (Figure 3a). This synthesis strategy not only harnesses the complementary advantages of both materials but also significantly enhances photocatalytic performance. The researchers employed ZnO nanosheets as nanosubstrates in their synthesis process. They initiated an in situ self-polymerization reaction of dopamine monomers, leading to the spontaneous formation of a uniform PDA coating on the surface of ZnO. This PDA layer not only provided active sites for subsequent grafting but also acted as an effective interfacial buffer, enhancing the stability of the composite material. Subsequently, Cu-POMs particles were irreversibly embedded within the PDA layer on the ZnO surface under ultrasonic conditions, successfully constructing the ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs heterostructure. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images clearly reveal the core–shell structure of the composite, where ZnO@PDA functions as the core and Cu-POMs particles are tightly adhered to its surface, providing direct evidence for the successful immobilization of Cu-POMs on the modified ZnO nanosheets. In examining the photocatalytic mechanism, they discovered that the synergistic effects of the PDA layer and Cu-POMs significantly enhance the separation and migration of photogenerated carriers. Specifically, e− in the CB of ZnO@PDA tend to combine with h+ in the VB of Cu-POMs, leaving highly oxidizing h+ in the VB of ZnO@PDA and e− in the CB of Cu-POMs. Effective separation of photogenerated charges in ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs is thus achieved (Figure 3b). Furthermore, they investigated the detailed degradation pathway of the composite concerning TC and assessed the toxicity of its degradation products (Figure 3c). This study not only offers a novel approach for designing ZnO-based photocatalytic materials but also provides essential theoretical foundations and experimental support for the development of efficient and stable photocatalytic systems.
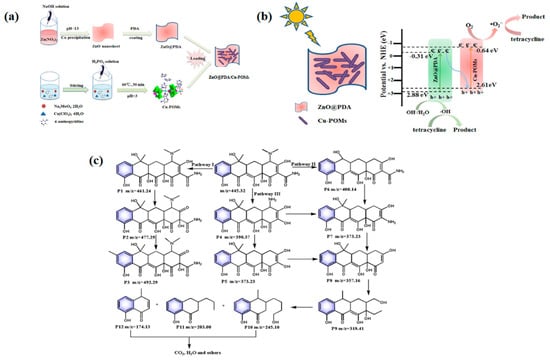
Figure 3.
(a) Process diagram for the preparation of ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs. (b) The proposed photocatalytic mechanism for degrading TC. (c) The proposed degradation pathways. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [45].
2.4. POM-Based Frameworks
In recent years, the encapsulation of POMs within the cage-like structures of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) has led to the development of POMs-based MOF crystalline materials (POMs@MOFs), providing a valuable new avenue for understanding electron transfer mechanisms in photocatalytic reactions [22,46]. In the POM@MOF composite system, the MOF serves as a matrix that exhibits a remarkable long-range ordered spatial structure, endowing the material with a highly regular pore network [47]. These pores not only create an ideal microenvironment for hosting POMs but also facilitate their homogeneous dispersion at the molecular level, maximizing the catalytic activity of the POMs [30]. Importantly, this innovative structural design optimizes the separation and transport efficiency of photogenerated carriers, significantly enhancing the overall performance of photocatalytic reactions [31,48,49]. For instance, Guo et al. [25] employed an in situ assembly strategy to thermally process mixtures of ZrCl4, H2L2/H2L1/H2L3, and Ni-Sb9/Co-Sb9/Ni4P2 (in varying molar ratios) to synthesize novel Ni-Sb9@UiO-Ir-C6 composites. This method achieves dual regulation of the sensitization and catalytic centers in Ni4P2@UiO-Ir (Figure 4). Experimental studies indicated that this dual modulation strategy enhances the exposure of active sites within the POM@MOF composites, improves visible light absorption, and facilitates efficient charge transfer between components, thereby significantly boosting catalytic activity. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) characterization results revealed that Ni-Sb9@UiO-Ir-C6 possesses a porous surface with a regular octahedral morphology. The elements C, N, O, S, Zr, Ir, Ni, and W are uniformly distributed throughout the MOF’s framework, further confirming the successful incorporation of Ni-Sb9 and Ir-C6 (Figure 5). This homogeneous distribution not only optimizes the structural properties of the materials but also provides additional active sites for the photocatalytic reaction, significantly enhancing their catalytic efficiency. As shown in Figure 6, the light absorption process mainly involves transitions from the ground state (So) to the singlet excited state (1IL). The long-lived triplet excited state (3IL) is obtained through intersystem crossing (ISC). Subsequently, electrons efficiently transfer from the 3IL state to the Ni−Sb9 site of [NiO3(H2O)3], thereby achieving a photocatalytic enhancement mechanism characterized by strong visible light absorption, long excited state lifetime, and efficient electron transfer.
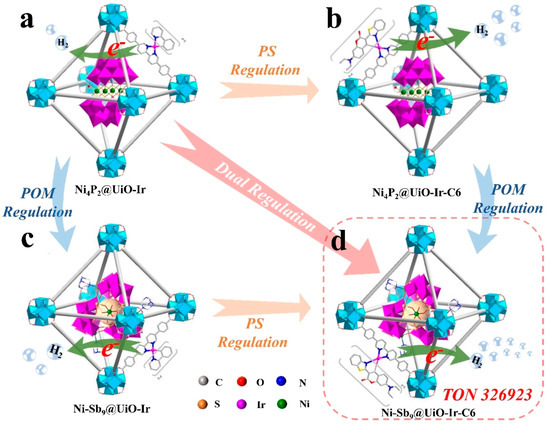
Figure 4.
The dual regulation of POMs and PSs in POM@MOF for PHE with (a) Ni4P2@UiO−Ir, (b) Ni4P2@UiO−Ir−C6, (c) Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir, and (d) Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir−C6 as structural models. Reprinted with permission from Wiley [25].
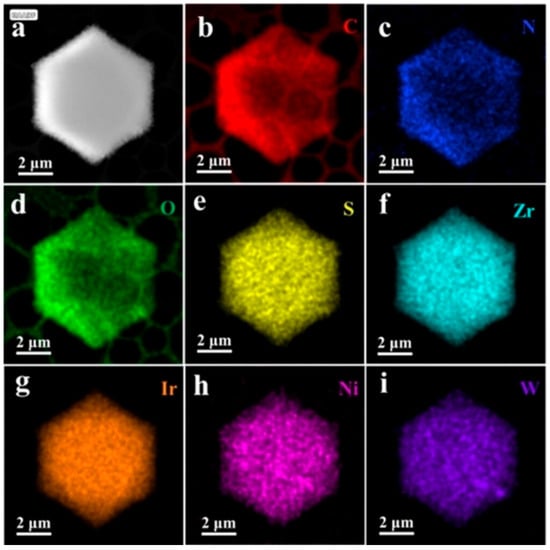
Figure 5.
HAADF-STEM corresponding elemental mapping images for Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir−C6. (a) HAADF-STEM. (b–i) elemental mapping images for Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir−C6. Reprinted with permission from Wiley [25].
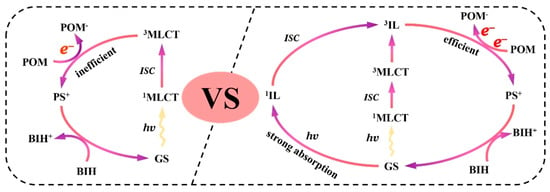
Figure 6.
Possible photocatalytic mechanisms of photocatalytic H2 evolution on Ni4P2@UiO−Ir and Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir−C6. Reprinted with permission from Wiley [25].
Du et al. [27] successfully developed a series of novel Keggin-type polyoxometalate-encapsulated cadmium cluster organic framework crystalline materials (POM@CdMOF) through a one-pot hydrothermal synthesis involving CdCl2·5/2H2O, DTAB, and Keggin-type polyoxometalates (Figure 7). Single-crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD) analysis revealed that the POM@CdMOF crystals possess an iso-network structure, with different POM guests encapsulated within the same CdMOF cationic host framework. The varying POM guests exhibited distinct electron transfer pathways and charge separation behaviors within the photoactive CdMOF host, leading to different photocatalytic activities. DFT calculations highlighted the crucial regulatory roles of the different POM units in interfacial electron transfer and the adsorption behaviors of key intermediates.
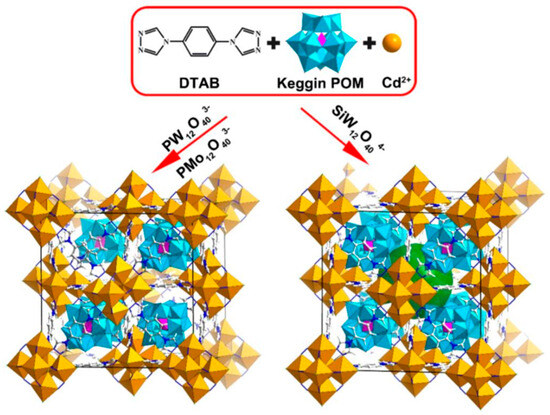
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of the synthesis of POM@CdMOF. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [27].
Su et al. [50] synthesized a series of composites, including SiW9M3@MIL-101(Cr) (where M = Fe, Co, V, Mo) and D-SiW9Mo3@MIL-101(Cr) (D for Disordered), through a simple one-step solvothermal method to load POMs onto MIL-101(Cr). UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy revealed that doping with transition metals significantly broadens the light absorption range of the POMs. Additionally, the decomposition temperature of the composites was shifted to higher temperatures due to the formation of hydrogen bonding between the POM and MIL-101(Cr). The uniform distribution of elements (Cr, W, Mo, and Si) observed in the high-angle annular dark field (HAADF) images confirmed the successful preparation of uniformly loaded guest molecules SiW9Mo3@MIL-101(Cr). Notably, the researchers found that the electron cloud density of the active element W in POMs could be modified by adjusting the composition and arrangement of transition metals within the POMs, resulting in significantly enhanced photocatalytic performance. Dai et al. [51] prepared defect-rich CsPW@UNH (Hf-Zr) photocatalytic materials, where Hf3+ and Zr3+ coexisted in a defect-laden POM-encapsulated MOF (POM@MOF). In this process, Keggin-type CsPW was incorporated as a guest within the UNH(Hf-Zr) framework (Figure 8a). Under visible light irradiation, electrons in the CB of CsPW transfer through the heterojunction interface and recombine with holes in the VB of UNH (0.65), thereby enhancing the separation efficiency of photogenerated carriers. Meanwhile, the amine-based chromophores in the defect states of UNH(0.65Hf) can absorb photons and transition to the excited state, subsequently transferring the photogenerated electrons to the Hf-Zr bimetallic cluster, further promoting the effective separation and transfer of charges. The strong interactions between the CsPW and UNH(0.65Hf) components facilitated charge transfer capabilities, leading to improved photocatalytic activity (Figure 8b).
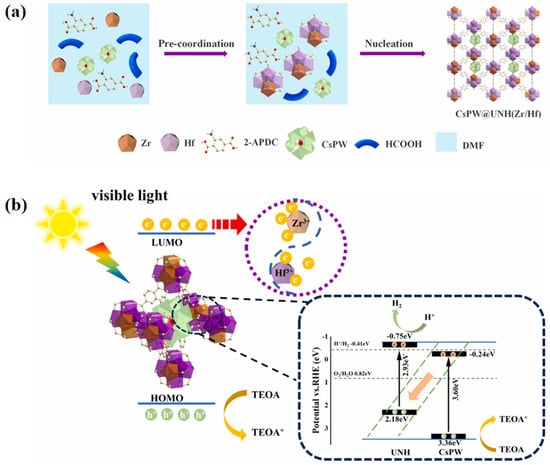
Figure 8.
(a) Illustration of the synthesis of CsPW@UNH (Hf-Zr) samples. (b) The photocatalytic mechanism for CsPW@UNH(0.65Hf) composite. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [51].
Akbari et al. [52] developed a ZIF-8 catalyst (AgNPs@PW@ZIF-8) with a tungsten phosphate (PW) bridge layer to fix silver nanoparticles for the efficient removal of congo red (CR). Under light irradiation, electrons in the conduction band of ZIF-8 can be transferred to the vacant orbitals of PW, thereby oxidizing PW to PW*. PW then transfers electrons to an oxidizing agent (such as oxygen molecules) and is reduced again. In this process, the photoactive PW bridging layer provides additional driving force, enabling strong electron transfer capability between ZIF-8 and silver nanoparticles.
Frameworks based on POMs can also be constructed through covalent bonds between POMs and organic building units (covalent organic frameworks), i.e., POMs@COFs. For instance, Wang et al. [53] successfully synthesized a hierarchical covalent organic framework (POM@COF) using electrostatic interactions to encapsulate pre-synthesized polyoxometalate (POM, [PV2W10O40]5−, PV2W10) clusters. This material features a large specific surface area, a porous structure, and an abundance of Lewis acid-base sites, which facilitate charge transfer between PV2W10 and EB-TFP.
2.5. POMs on Other Carriers
In the study of polyoxometalate-based photocatalytic new materials, the selection and design of carriers are crucial for optimizing catalyst performance. Besides conventional oxides (e.g., titanium dioxide, zinc oxide) and metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), recent years have seen the exploration of a diverse range of novel materials as carriers for POMs. These include carbon-based materials (e.g., graphene, carbon nanotubes) and certain two-dimensional materials with unique structures (e.g., transition metal sulfides). Such innovative carriers open new avenues for enhancing the performance of POM-based photocatalysts and broaden both the applicability and the research landscape of polyacid-based photocatalytic materials.
For example, Xing et al. [54] successfully developed a Z-type photocatalyst (HPM/ZIS) featuring heteropolyoxometallate (HPM) clusters embedded in ZnIn2S4 (ZIS) nanosheets using a one-step solvothermal method under aqueous conditions (Figure 9a). The synergistic interactions between the POM and ZnIn2S4 facilitated interfacial contacts at the molecular level, promoting the formation of the Z-type heterojunction structure and enabling faster charge transfer at the interface, which consequently enhanced the redox capacity of the photocatalytic system. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples revealed that when the mass ratio of HPM to ZIS exceeded 1%, the diffraction peak at 21.26°, associated with the (006) crystalline plane in the POM, shifted to a lower angle, while the peak corresponding to the (004) crystalline plane at 14.19° disappeared (Figure 9b). This suggests that the embedding of HPM clusters may have induced a slight lattice change. Elemental mapping further confirms the presence and uniform distribution of Zn, In, S, Mo, and P, validating the complete incorporation of the HPM clusters (Figure 9c).
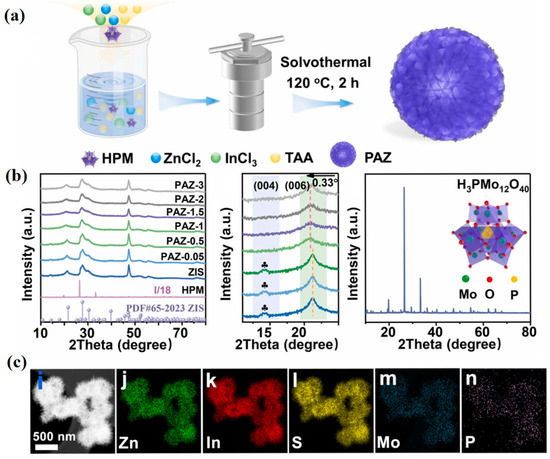
Figure 9.
(a) Schematic synthesis process of HPM-incorporated ZIS nanohybrids (PAZ). (b) XRD patterns and enlarged part of HPM, ZIS, and PAZ-x samples. (c) HAADF-STEM image of PAZ-1 and corresponding elemental mappings. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [54].
In another report, Ren et al. [55] successfully deposited a series of POMs, including H3PW12O40, H3PMo12O40, and [TBA(MnMo6)], onto the surface of CdS nanorods (CdS-NRs) to create a binary composite material using a straightforward deposition strategy. The CdS-NRs served as an effective support for the POMs, which extended the visible light absorption range, reduced the rate of electron–hole recombination, and enhanced the photogenerated charge transfer, ultimately leading to remarkable photocatalytic performance. TEM results confirmed the successful immobilization of POM crystals on the CdS-NRs, demonstrating the formation of a binary system (Figure 10A–C). The difference in transparency between the two phases indicated a strong interaction between the POM crystals and the CdS-NRs. Notably, the lattice fringe with a spacing of 0.316 nm corresponds to the CdS-NRs within the composite, while the lattice fringe associated with the POM crystals supported on the surface of the CdS-NRs is measured at 0.86 nm. Additionally, elemental mapping further demonstrated that the POMs are uniformly dispersed on the surface of the carriers (Figure 10D–H). The possible photocatalytic mechanism is shown in Figure 11. Under light irradiation, POMs cause oxygen–tungsten charge transfer and generate excited species (POM*). Within the POM cage, an O2p → W5d orbital transition occurs, with charge transfer from O2− to the W6+ in the W-O-W group of POM, resulting in the formation of a pair of holes and a trapped electron center (W5+), which oxidizes and decomposes organic dyes. Their research has opened up a new viable path for the design of novel heterostructure photocatalysts using POMs and sulfides to eliminate pollutants in water. Tang et al. [56] presented a novel photocatalytic material that combines nickel (Ni)-doped polyoxometalate K6Na4[Ni4(H2O)2(PW9O34)2]·32H2O (Ni4POM) with a CdxZn1−xS solid solution. The unique integration of multivalent Ni centers and an S-scheme charge transfer pathway in this material significantly enhances the separation and transfer efficiency of photogenerated charges. Specifically, the Ni centers introduce additional energy levels within the band structure, facilitating the trapping and transfer of photogenerated electrons. Meanwhile, the S-scheme charge transfer mechanism ensures the efficient separation and transport of electrons and holes to the material’s surface, thereby minimizing recombination losses. This synergistic effect not only improves overall charge dynamics but also broadens the visible-light absorption range, allowing the material to capture and utilize a wider spectrum of solar energy for photocatalytic reactions.
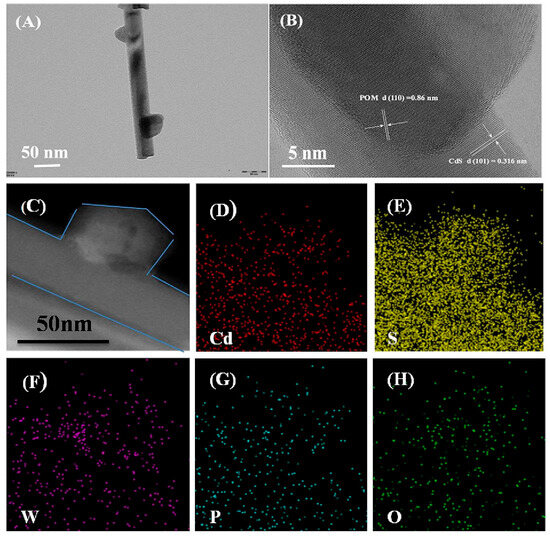
Figure 10.
(A) presents the TEM image of CdS-NRs@PW12O40 (C), while (B) displays the HRTEM image of the same material. Additionally, (D–H) illustrate the elemental mapping of CdS-NRs@PW12O40 (C). Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [55].
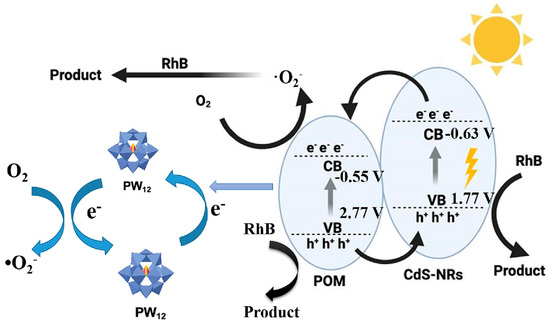
Figure 11.
The proposed photocatalytic mechanism for the degradation of RhB. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [55].
Polyimide (PI), known for its excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties, also serves as an effective photocatalytic carrier material. Meng et al. [57] reported the synthesis of silver phosphotungstate/polyimide (MAPI) materials exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic properties through self-assembly and in situ solid-phase thermopolymerization, utilizing a Z-type charge-transfer mechanism. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results confirmed the successful synthesis of the composites, which featured AgPW nanoparticles primarily sized between 2 nm and 5 nm, exhibiting close contact with the polyimide matrix. The ligand interactions between the Keggin anion and the organic ligand improved electron delocalization, enabling the Keggin units released during heat treatment to function as a shuttling redox mediator within the Z-type heterojunction photocatalysts, thereby facilitating electron transfer in the MAPI photocatalysts.
In addition, g-C3N4, with its unique π-conjugated structure and excellent light-absorbing properties, acts as an efficient carrier material to enhance the separation and transfer of photogenerated charges. Huang et al. [58] utilized g-C3N4 as a carrier to self-assemble with KPW through in situ solid-phase transformation, yielding a series of photocatalysts designated as CNPI/KPW. KPW bound tightly to CNPI, thereby enhancing the POM-π interactions. The polyacid structure of POM acted as an electron acceptor, forming an effective charge transfer channel with the π-conjugated system of g-C3N4. This arrangement enabled the rapid migration of photogenerated electrons to the surface of POM, resulting in lower electron–hole recombination rates and thereby generating more active species to participate in subsequent photocatalytic reactions.
Zeolites also serve as effective carriers for POMs, benefiting from their favorable pore structure and chemical stability, which create an optimal environment for POM loading. A report by Sivakumar et al. [59] described the synthesis of POM-embedded zeolite loaded with AgNTiO2 nano-chains (AgNTiO2@POM-zeolite) using an in situ method. This configuration facilitated proton-assisted Z-type electron transfer between the AgNTiO2 nano-chains and POM, leading to efficient cationic catalyzed reduction of CO2 to CH3OH and water decomposition.
Graphene oxide (GO), recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity and specific surface area, also serves as a promising carrier material that effectively promotes the separation and transfer of photogenerated charges. Gao et al. [60] synthesized a series of ternary AgBr/polymetallic oxalate/graphene oxide (AgBr/POM/GO) composites via an ionic liquid-assisted hydrothermal method. In this study, Bpy+ ions in the ionic liquid acted as bridging cations, interacting with the POM polyacid anion to facilitate its deposition on the graphene surface. The findings indicated that the types of POMs could be modulated to enhance the photochemical properties of the ternary nanocomposites.
3. Applications for the Removal of Pollutants from Water
3.1. Dyes
With the acceleration of industrialization, a substantial number of organic dyes are widely utilized in the textile, printing and dyeing, paper, and plastics industries. Unfortunately, these dyes are often released into the environment without adequate treatment after use. Common dyes, such as methylene blue (MB) and rhodamine B (RhB), are particularly challenging to degrade in the environment and can pose significant threats to human health when they accumulate in the food chain. To address this environmental issue, Bani-Atta et al. [61] successfully designed and developed a calcium polyanion H60N6Na2Ca2W12O60 (Ca-POM) photocatalyst. Their findings demonstrated that Ca-POM possesses a polycrystalline structure and exhibits excellent photocatalytic degradation capability, achieving a high degradation efficiency of 81.21% for MB. The molecular structure of POM can be fine-tuned by modifying organic ligands to optimize electron transfer pathways and enhance charge transfer kinetics.
Man et al. [62] designed and synthesized a series of five Mn–Schiff base complexes with varying substituents for the modification of SiW12O40, resulting in the novel compounds 1–5. The modified SiW12O40 demonstrated a reduction in the band gap, accompanied by a significant enhancement in visible light absorption. The best-performing sample achieved a removal rate of RhB of up to 94% within 70 min under light conditions. At the same time, compound 2 exhibits excellent stability. After four cycles, the degradation activity loss under visible light was only 12%. DFT calculations indicate that electron-withdrawing substituents enable the excited state electrons of POMs in the HOMO to transfer more efficiently to the organic coordination units in the LUMO, thereby reducing the resistance to electron migration. Active species capture experiments revealed that superoxide radicals were the main active species in the system.
Qin et al. [63] integrated a MnMo6O18 cluster featuring two rare triple-coordinated copper sites and attached them via the organic ligand (OCH2)3CN=CH-4-Py (where Py = pyridine) on both sides of the MnMo6O18, resulting in the synthesis of an organo-inorganic hybridized Anderson-type polyoxometallate (POM 1). This material exhibited excellent photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye, as evidenced by the decrease in the intensity of the ultraviolet–visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectrum of MB in aqueous solution from 1.26 to 0.09, coupled with a color change from blue to transparent after 8 h of light exposure. Importantly, the degradation properties of POM 1 remained stable, demonstrating no significant loss in effectiveness after four cyclic experiments.
Zhang et al. [64] coupled P2Mo18 with Fe2O3 nanosheets to prepare hybridized Fe2O3/P2Mo18 composites. The incorporation of P2Mo18 not only enhanced the specific surface area and the number of active sites of the catalysts but also accelerated the migration of photogenerated carriers through the heterojunction interfaces formed, significantly boosting photocatalytic activity. The degradation rate of MB by the optimal sample, Fe2O3/P2Mo18-5%, reached an impressive 96.86% under illuminated conditions. Furthermore, the catalyst exhibited excellent cycling stability, with the degradation rate decreasing by only about 5% after four cycling experiments. When excited by visible light, the photogenerated electrons in P2Mo18 transition from the HOMO to the LUMO. The photo-excited electrons in P2Mo18 immediately recombine with the valence band holes in Fe2O3, maintaining the photogenerated holes on the HOMO of P2Mo18, where they collaborate with electrons in the conduction band of Fe2O3 to participate in photocatalytic activity. This work provides new insights for designing efficient photocatalysts for removing heavy metals.
Yu et al. [65] reported a novel heterojunction photocatalyst, Co4PW9/CeO2, with a magnetic field-assisted enhancement effect, addressing the issue of recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes in traditional photocatalytic systems. Under visible light irradiation, the photogenerated electrons and holes are subjected to opposing Lorentz forces, effectively hindering carrier recombination. Specifically, electrons in the CB of CeO2 combine with holes in the VB of Co4PW9, due to the strong electrostatic attraction between electrons in the conduction band of CeO2 and holes in Co4PW9. This results in electrons accumulating in the more negative conduction band of Co4PW9 and holes accumulating in the more positive valence band of CeO2. The photodegradation rate of Co4PW9/CeO2–IV for methyl orange (MO) reaches 91.83% in 120 min, which is 10 and 11 times higher than that of pure Co4PW9 and CeO2, respectively. It is worth noting that this catalyst has high reusability. After four cycles of experimentation, it still maintains high photocatalytic activity. This study provides new insights into utilizing material structure design to achieve magnetic field-enhanced electron spin polarization for enhancing photocatalytic efficiency. Table 2 provides a detailed summary of recent research advancements regarding POM-based photocatalysts in the degradation of dyes in water.

Table 2.
The performance of some POM-based materials in the photocatalytic removal of dyes from wastewater.
3.2. Antibiotics
In recent years, the escalating misuse of antibiotics has emerged as a significant global public health concern. The consumption of antibiotics continues to rise across various countries and regions, particularly in agriculture, animal husbandry, and healthcare settings. Antibiotic residues are not only challenging to degrade but are also prevalent in water bodies and soil, leading to serious water pollution issues. This pollution disrupts the balance of aquatic ecosystems and may pose potential threats to human health, ultimately affecting the safety and sustainable use of water resources. To effectively mitigate antibiotic residues in aquatic environments, Shi et al. [78] developed a novel Ag/PW12/TiO2 photocatalyst utilizing electrospinning/photoreduction technology. The incorporation of PW12 and the modification of TiO2 with Ag nanoparticles significantly broadened the visible light absorption spectrum and enhanced the effective separation of photogenerated carriers, resulting in a remarkable improvement in photocatalytic performance. Under light conditions, the degradation efficiencies of the Ag/PW12/TiO2 photocatalyst for TC, enrofloxacin (ENR), and methyl orange (MO) reached 78.19%, 93.65%, and 99.29%, respectively. In another study, Shi et al. [69] synthesized a novel Cs3PMo12O40/g-C3N4 photocatalyst via a dissolution–precipitation method. The formation of a Z-type heterojunction accelerated the separation efficiency of photogenerated carriers, leading to a significant enhancement in photocatalytic activity. The optimal sample demonstrated photodegradation efficiencies of up to 83.11% (k = 0.01255 min−1), 65.43% (k = 0.00591 min−1), and 100% (k = 0.64822 min−1) for tetracycline hydrochloride (TCH), ciprofloxacin (CIP), and RhB, respectively, under visible light irradiation. The ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs photocatalyst developed by Xing et al. [45] also showcased superior photocatalytic degradation activity for TC. This material can remove up to 90.75% of TC under light conditions. Importantly, ZnO@PDA/Cu-POMs showed good stability. After three cycles, the performance did not decline significantly and the structure remained stable. The enhancement of its photocatalytic activity is primarily attributed to the successful construction of a Z-type heterostructure and the synergistic interactions between ZnO@PDA and Cu-POMs, which facilitate rapid electron transfer and reduce the recombination of photogenerated carriers. They used the ecological toxicity assessment software tool (T.E.S.T) for QSAR to further determine the ecological toxicity of TC and its intermediates. They found that TC had the lowest zebrafish LC50 value, indicating that the toxicity of all intermediates was lower than that of tetracycline TC. The study highlights the potential of POMs assembled on specific carriers to form novel heterostructures with enormous water purification potential. In a report by He et al. [79], three POMs (PMA, PTA, and STA) were loaded onto nitrogen-deficient g-C3N4. The establishment of stable chemical bonds between C+ in g-C3N4 and the bridging oxygen in the POMs exhibited a 97.4% degradation rate of CIP within a mere 5 min of light exposure (Figure 12a). Furthermore, the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of this sample remained stable after five degradation cycles, demonstrating excellent cycling performance (Figure 12b). Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis was used to identify intermediates and products during the degradation process. Ciprofloxacin has a high electron density and is easily attacked by hydroxyl radicals (·OH). In these processes, after being attacked by active free radicals, the ciprofloxacin molecule undergoes a series of decarboxylation, defluorination, and deprotonation reactions to form the final product. Among these, the direct detachment of the piperazine ring during decarboxylation and defluorination results in the most efficient degradation of CIP into small molecules. Table 3 offers a summary of recent research advancements regarding POM-based photocatalysts in the degradation of antibiotics in water.
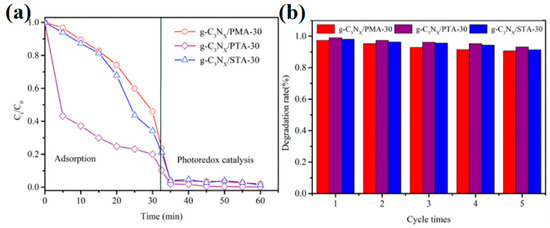
Figure 12.
(a) The photocatalytic activities of samples. (b) Cyclic experiment. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier [79].

Table 3.
The performance of some POM-based materials in the photocatalytic removal of antibiotics from wastewater.
3.3. Other Contaminants
Nitrate is a prevalent pollutant in aquatic environments, primarily resulting from the application of nitrogenous fertilizers in agriculture, the discharge of domestic sewage, industrial wastewater, and atmospheric deposition. Elevated levels of nitrate can have numerous detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems. Wang et al. [82] developed an innovative material, SiW11/TiO2/Cu, demonstrating superior photocatalytic performance achieved by loading SiW11 and Cu2+ onto TiO2 using the sol–gel method. The incorporation of SiW11 and Cu2+ not only inhibited the recombination of conduction band electrons and valence band holes in TiO2 but also enhanced the material’s responsiveness to visible light. With a catalyst dosage of 1.2 g/L and formic acid employed as a hole scavenger, the removal rate of nitrate nitrogen reached an impressive 96%. The improved photocatalytic activity of SiW11/TiO2/Cu can be attributed to several critical factors. Firstly, the introduction of SiW11 and Cu2+ created additional active sites on the TiO2 surface, facilitating the separation and transfer of photogenerated charge carriers. The unique electronic structure of the SiW11 units efficiently captured electrons from the conduction band of TiO2, while Cu2+ ions served as electron acceptors, further reducing the recombination rate of electron–hole pairs. This synergistic effect significantly extended the lifetime of the photogenerated charges, thereby enhancing their participation in redox reactions.
Radioactive elements, including uranium, thorium, and radium, are chemical elements that exhibit radioactivity. Their presence in aquatic environments poses significant threats to both ecosystems and human health. To tackle this issue, Dong et al. [83] developed a novel material, POM@Cu-MOFs. The abundant oxygen-containing functional groups within the POMs provide effective adsorption sites for radioactive ions, while the electron-attracting properties of the Cu atoms significantly enhance the charge carrier dynamics. These synergistic effects impart POM@Cu-MOFs with remarkable photocatalytic degradation capabilities. Under light irradiation, this material can remove up to 99.4% of U(vi), exhibiting an impressive adsorption capacity of 1987.4 mg g−1. After five reaction cycles, the photocatalytic reduction efficiency of U(vi) remained at 90%, indicating that POM@Cu-MOFs possess excellent structural stability and good cycle reusability. The exceptional performance of POM@Cu-MOFs can be attributed to several critical factors. Firstly, the oxygen-containing functional groups in the POMs, such as hydroxyl and carboxyl groups, create multiple active sites that can selectively capture and immobilize radioactive ions like UO22+. This selective adsorption is essential for the efficient removal of radioactive contaminants from water.
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a widely used compound in industrial production and a well-known environmental endocrine disruptor, posing various potential hazards to human health and ecosystems. In recent years, increasing attention has been directed toward the problem of BPA pollution, prompting researchers to develop efficient photocatalytic degradation materials for its rapid removal from the environment. For instance, Qiu et al. [84] successfully constructed a double Z-type heterojunction material by depositing Fe-POMs (Fe-based polyoxometalates) and AgVO3 onto the surface of hollow cubic Cu2−xS (Cu2−xS/Fe-POMs/AgVO3). This material exhibited excellent photocatalytic degradation performance. The Fe-POMs acted as linkers, establishing an effective electron transfer channel between Cu2−xS and AgVO3 while providing abundant active sites, which significantly improved the separation efficiency of photogenerated charge carriers. Experimental results indicated that the photocatalytic Fenton degradation rate of BPA by this material reached as high as 98.6% within 150 min. Notably, after five cycles, the degradation rate of Cu2−xS/Fe-POMs/AgVO3 showed only a slight decrease that was negligible, demonstrating its excellent stability and reusability. Their work provides new insights into the preparation of superstructure photocatalysts with high performance and broad spectral response.
Thiamethoxam (TMX) is a commonly used second-generation nicotinic insecticide. While it is highly effective in controlling insect populations, its potential environmental and ecological impacts have garnered significant concern. To address this pitfall, Lu et al. [85] incorporated Ni4P2 into the pores of NU-1000 through hydrogen bonding. The resulting hydrogen bonds not only effectively prevented the leakage of Ni4P2 from the NU-1000 pores but also enhanced electron transfer. The degradation rate of the optimal photocatalyst, 0.3-Ni4P2@NU-1000, was 7.80 times greater than that of pure NU-1000, achieving a remarkable TMX degradation rate of 75.1% within 120 min. The 0.3-Ni4P2@NU-1000 photocatalyst also exhibited excellent reusability. After 10 cycles, it still maintained excellent degradation activity within 120 min. Additionally, XRD, FTIR, and SEM analyses were conducted before and after the photocatalytic reaction. After 10 cycles, the catalyst still maintained good morphology and peak intensity. Chia seed growth experiments and toxicity assessment software analysis showed that the aquatic toxicity of TMX intermediates and final products was lower than that of undegraded TMX. Their work has opened up new application prospects for the photodegradation of TMX pollutants in wastewater using POM-based MOFs.
In another study, Xiao et al. [86] developed a photocatalyst based on g-C3N4 (graphite-phase carbon nitride) and POMs using an impregnation activation method. The unique Keggin structure of the POMs played a dual role in the photocatalytic reaction, serving as both an electron acceptor and a mediator, forming a strong interaction with g-C3N4. This interaction significantly enhanced the absorption of visible light and the separation efficiency of photogenerated charge carriers in the material. Experimental results showed that the degradation rate of g-C3N4/KPW-0.2 on thiamethoxam (TMX) was as high as 91.72% after 3 h of visible light irradiation. Furthermore, the material exhibited excellent stability and maintained high photocatalytic activity even after five cycles of use, offering a significant advantage for practical applications. Mechanistic studies revealed that photogenerated holes and superoxide radicals are the key active species in the photocatalytic degradation process. Through electron spin resonance measurements and free radical burst experiments, the researchers confirmed the dominant role of these active species in the degradation reaction. These findings not only provide important insights into the photocatalytic degradation mechanism but also offer theoretical support for the design and optimization of novel photocatalytic materials. Table 4 offers a detailed summary of recent research advancements regarding POM-based photocatalysts in the degradation of other contaminants in water.

Table 4.
The performance of some POM-based materials in the photocatalytic removal of other contaminants from wastewater.
4. Conclusions and Outlook
POMs-based photocatalytic new materials have demonstrated considerable potential for photocatalytic water purification applications due to their superior photocatalytic performance, the advantages of composites, and their environmentally friendly and cost-effective solutions. As a result, they have emerged as a significant focus in the advancement of water treatment technologies. Nevertheless, this field continues to encounter critical challenges that necessitate further research and breakthroughs to enable the broader implementation of these materials in practical water treatment scenarios.
- 1.
- Low utilization rate of visible light
The light absorption efficiency of POMs still needs to be further improved. Classical POM clusters, such as those based on Keggin, Dawson, and Anderson structures, display limited visible light utilization, which significantly constrains their photocatalytic applications. Therefore, future research should delve deeper into the photocatalytic mechanism, combining theoretical calculations with experimental studies to elucidate the relationship between electronic structure and photocatalytic performance. Additionally, strategies to enhance visible light absorption must be introduced, such as doping with transition metal ions (e.g., Ni, Cu) or incorporating organic ligands to modify the energy band structures of POMs and broaden their visible light absorption range.
- 2.
- Small specific surface area and poor stability
POMs typically possess a low specific surface area, which restricts their interactions with pollutants and adversely impacts photocatalytic efficiency. Furthermore, POMs are prone to leaching in aqueous solutions, which severely hinders their practical applications. Future research should focus on developing innovative synthesis strategies that facilitate robust binding of POMs to support through covalent bonding, ion exchange, or in situ growth methods to improve adhesion. Additionally, optimizing the composite structures by employing core–shell and heterojunction architectures, along with enhancing mechanical stability through cross-linking agents or the construction of three-dimensional network structures, is vital to reduce material loss in aqueous environments.
- 3.
- pH sensitivity
The catalytic activity of POMs is highly sensitive to pH, which limits their effectiveness across varying water conditions. Future studies could explore the incorporation of buffering agents within the systems to stabilize the pH of the reaction medium, thereby improving their adaptability to diverse water quality conditions. Moreover, designing pH-responsive structures through chemical modification or structural modulation is crucial. Such modifications can create POMs that exhibit resilience and maintain high photocatalytic performance across different pH environments.
- 4.
- High synthesis costs
The substantial costs associated with synthesizing POMs and their composites present a significant obstacle to large-scale production and practical implementation. Future efforts should concentrate on simplifying synthesis steps, optimizing processes, and minimizing the use of expensive reagents to drive down overall synthesis costs. Improving material recyclability through effective recycling techniques will help minimize resource waste and reduce operational costs. Furthermore, optimizing production processes and equipment is essential to facilitate large-scale production of POMs and their composites, thereby lowering unit costs.
With ongoing research and exploration of POM-based photocatalytic materials, their application in water purification technology will continue to expand and deepen. By optimizing material composition, structure, and performance while fostering collaboration with advanced technologies, POM-based photocatalytic materials have the potential to tackle increasingly complex water pollution challenges. Such advancements will play a pivotal role in achieving efficient and environmentally friendly water purification, contributing significantly to the sustainable use of water resources and ecological conservation.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, X.Q.; writing—review and editing, X.Q., R.W.; supervision, R.W.; project administration, R.W.; funding acquisition, R.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Scientific Research Program of Shandong Province (2017GSF217006).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, J.; Yi, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, H. Coupled piezo-pyro-photocatalysis of oxygen vacancies and Bi quantum dots co-modified BaTiO3 for highly efficient removal of ciprofloxacin. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Q. Progress on mechanism and efficacy of heterogeneous photocatalysis coupled oxidant activation as an advanced oxidation process for water decontamination. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Shah, S.S.; Sharma, C.; Gupta, V.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Arya, S. An approach towards different techniques for detection of heavy metal ions and their removal from waste water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, Q. Highly sensitive passive sampling of new pollutants in urban reclaimed water using hydrophilic-lipophilic balance sorbent-embedded cellulose acetate membrane. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Fei, H.; Feng, Z.; Shao, Q.; Zhao, T.; Guo, W.; Li, F. Tri-phase interface to enhance the performance of piezoelectric photocatalysis and recyclability of hydrophobic BiOI/BaTiO3 heterojunction. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 440, 140886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zheng, H.; Liu, F.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ding, A. Heavy metal contamination assessment and source attribution in the Vicinity of an iron slag pile in Hechi, China: Integrating multi-medium analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, J.; Lou, G.; Shan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Man, Y.B.; Li, Y. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in Chinese surface water: Temporal trends and geographical distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 170127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Khu, S.-T.; Zhang, Y. Which organic contaminants should be paid more attention: Based on an improved health risk assessment framework. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Cui, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Q.; Yuan, W. Advancements in iron-based photocatalytic degradation for antibiotics and dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 374, 123991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, M.; Aima-tul-ayesha; Yang, B.; Jia, X.; Zafar, M.N. Progress on synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic applications of bismuth oxyhalide based nanomaterials in cleaner environment and energy—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 494, 144868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D.; Zong, S.; Wang, J. Synthesis of InP quantum dot decorated Bi2WO6 microspheres for the efficient photocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide in water. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1011, 178253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Gong, Y.Q.; Chen, X.; Li, R.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, M.J.; Tang, X.R. Investigation into the Feasibility of a Synergistic Photocatalytic Degradation Process for Fracturing Flowback Fluid Streams Utilizing O3 and Ti/Ni Composite Materials. Molecules 2025, 30, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Pandey, A.; Chen, W.H.; Ahmed, S.F.; Nizetic, S.; Ng, K.H.; Said, Z.; Duong, X.Q.; Agbulut, U.; Hadiyanto, H.; et al. Hydrogen Production by Water Splitting with Support of Metal and Carbon-Based Photocatalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 1221–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lin, S.; Li, J.; Guo, L. One-Step Coprecipitation Synthesis of BiOClxBr1–x Photocatalysts Decorated with CQDs at Room Temperature with Enhanced Visible-Light Response. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 10999–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Varbanov, P.S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Yin, C. Nanocatalysts in photocatalytic water splitting for green hydrogen generation: Challenges and opportunities. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruziwa, D.T.; Oluwalana, A.E.; Mupa, M.; Meili, L.; Selvasembian, R.; Nindi, M.M.; Sillanpaa, M.; Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N. Pharmaceuticals in wastewater and their photocatalytic degradation using nano-enabled photocatalysts. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 54, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yue, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Hou, R.; Xiao, J.; Huang, X.; Ishag, A.; Sun, Y. Recent advances on energy and environmental application of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, N.; Jamalzadeh, M.; Askari, A.; Liu, N.; Samali, B.; Sillanpaa, M.; Sheppard, L.; Li, H.; Dewil, R. Unveiling the photocatalytic marvels: Recent advances in solar heterojunctions for environmental remediation and energy harvesting. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 148, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Puspa, M.B.; Kumoro, A.C.; Hanif, M.I.; Othman, M.H.D.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Utomo, D.P. Superior photocatalytic and self-cleaning performance of PVDF-TiO2@NH2-MIL-125(Ti)/PVA membranes for efficient produced water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 72, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Yue, D.; Wu, J.; Song, H. Constructing NH2-MIL-125(Ti) derived evaporator for simultaneous photocatalytic decontamination and water evaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qiu, J.; Li, Z.; Fu, A.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Lu, B. A bifunctional polyacrylamide-alginate-TiO2 hydrogel solar evaporator for integrated high-efficiency desalination and photocatalytic degradation. Desalination 2025, 611, 118920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.F.; Wu, H.Z.; Shi, X.J.; Wu, L.X. Polyoxometalate-based frameworks for photocatalysis and photothermal catalysis. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 9242–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, G.; Panigrahi, T.H.; Saha, S. Recent advances in the development of polyoxometalates and their composites for the degradation of toxic chemical dyes. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2024, 76, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashtian, K.; Shahsavarifar, S.; Usman, M.; Joseph, Y.; Ganjali, M.R.; Yin, Z.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. A comprehensive review on advances in polyoxometalate based materials for electrochemical water splitting. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 504, 215644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Pan, C.W.; Hou, M.; Hou, Y.T.; Yao, S.; Lu, T.B.; Zhang, Z.M. Dual Regulation of Sensitizers and Cluster Catalysts in Metal-Organic Frameworks to Boost H2 Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202420398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Chen, W.; Shan, G.G.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.L.; Su, Z. The roles of polyoxometalates in photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 21, 100760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Cui, W.-J.; Zhang, S.-M.; Han, Z.-G.; Li, R.-H.; Han, X.-Q.; Guan, W.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-Q.; et al. Unraveling photocatalytic electron transfer mechanism in polyoxometalate-encapsulated metal-organic frameworks for high-efficient CO2 reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 318, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.Y.; Wang, G.N.; Chen, T.T.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J.H.; Pang, H.J. Polyoxometalate-Derived Photocatalysts Enabling Progress in Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, 9, 2400752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-J.; Zhu, B.; Su, Z.-M.; Guan, W. Theoretical insights and predictions: Photocatalytic functionalization of C(sp3)−H bonds in methane using [W10O32]4−. J. Catal. 2025, 447, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, M.Z.; Wang, H.N.; Zhang, D.P.; Zhou, Z. Polyoxometalate-Based Frameworks: Construction Strategies and Photocatalytic Applications. Chemcatchem 2024, 16, e202400006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, K.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Ma, P.; Niu, J.; Wang, J. Enhanced Carrier Separation in Visible-Light-Responsive Polyoxometalate-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Highly Efficient Oxidative Coupling of Amines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 27882–27890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.W.; Wang, C.L.; Hu, Y.H. Highly selective photocatalytic conversion of methane to liquid oxygenates over silicomolybdicacid/TiO2 under mild conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; Ma, H.; Ma, R.; Xia, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.; Xie, G.; Chen, S. Heterointerface Connection with Multiple Hydrogen-Bonding in Z-Scheme Heterojunction SiW9Co3@UiO-67-NH2 Deciding High Stability and Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction Performance. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 20401–20411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Song, Y.T.; Li, F.Y.; Xu, W.J.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, L. A “concentration-induced self-assembly” strategy for AgxH3−xPMo12O40 nanorods: Synthesis, photoelectric properties and photocatalytic applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Chen, W.J.; Yuan, Z.L.; Jin, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.J.; Ma, P.T.; Niu, J.Y.; Wang, J.P. Controlled Assembly of Ru-Containing Polyoxometalates for Photocatalytic Activity of the Primary Amine Coupling Reaction. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 9935–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X. Morphology control of highly efficient visible-light driven carbon-doped POM photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recepoglu, Y.K.; Goren, A.Y.; Orooji, Y.; Vatanpour, V.; Kudaibergenov, N.; Khataee, A. Polyoxometalate-based hybrid composites in multi-functional wastewater treatment applications. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-Q.; Han, Q.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Li, Z.-B.; Zhu, L.-T.; Wu, Q.-X.; Ren, Z.-M.; Du, J.; Han, Z.-G. Polyoxometalate-based nickel-phosphine oxide compounds based on ligand in situ oxidation and rearrangement. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1330, 141578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.A.; Chen, R.; Tang, L.X.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.X.; Liao, J.S.; Wang, W. Constructing a P2W18O626− Containing Hybrid Photocatalyst via Noncovalent Interactions for Enhanced H2 Production. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 18556–18565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fu, Y.; You, S.; Yang, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhao, L.; Su, Z. Hexanuclear nickel-based [P4Mo11O50] with photocatalytic reduction of CO2 activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 134, 109009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Shioya, K.; Li, C.; Yonesato, K.; Murata, K.; Ishii, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Suzuki, K. Porphyrin–Polyoxotungstate Molecular Hybrid as a Highly Efficient, Durable, Visible-Light-Responsive Photocatalyst for Aerobic Oxidation Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, Y. Control over energy level match in Keggin polyoxometallate-TiO2 microspheres for multielectron photocatalytic reactions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 234, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, S.P.; Gumerova, N.I.; Schubert, J.S.; Saito, H.; Rompel, A.; Cherevan, A.; Eder, D. Immobilization of a [CoIII CoII (H2O)W11O39]7− Polyoxoanion for the Photocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Mater. Au 2022, 2, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, T.; Li, F.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Dong, X. Polyoxometalate as pivotal interface in SnO2@PW12@TiO2 coaxial nanofibers: From heterojunction design to photocatalytic and gas sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 390, 133928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Ma, M.; Chang, J.; Ji, Z.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.; Li, S.; Li, M. Polyoxometalate anchored zinc oxide nanocomposite as a highly effective photocatalyst and bactericide for wastewater decontamination. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Hong, Y.; Ma, P.; Wang, J.; Niu, J. [Ru(bpy)3]2+ Derivatives-Incorporated POM@MOFs with Good Photocatalytic Activity for Visible-Light-Driven Oxidative Coupling of Amines to Imines. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 64, 7832–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.Y.; Xue, Y.N.; Liu, X.M.; Li, N.F.; Wang, J.L.; Mei, H.; Xu, Y. An unprecedented polyoxometalate-encapsulated organo-metallophosphate framework as a highly efficient cocatalyst for CO2 photoreduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 3469–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, C.; Cheng, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, S.; Lei, L.; Chen, Y.; Yi, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, L. Polyoxometalate@Metal–Organic Framework Composites as Effective Photocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13374–13396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.A.; Yuan, Z.L.; Li, L.N.; Ma, P.T.; Wang, J.P.; Niu, J.Y. Visible-Light-Responsive Polyoxometalate@Metal-Organic Frameworks Involving Ir Metalloligands for Highly Selective Photocatalytic Oxidation of Sulfides to Sulfoxide. Chem. A Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202303401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Ding, W.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, Q.; Luo, M. Microchemical environmental regulation of POMs@MIL-101(Cr) promote photocatalytic nitrogen to ammonia. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 646, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Yan, L.; Yang, W.; Li, R.; Dong, Y.; Shen, Y. Integration of polyoxometalate into defective UiO-66-NH2(Zr/Hf) for visible-light-driven hydrogen photogeneration. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 362, 124715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, F.A.; Ostad, M.I.; Shahrak, M.N.; Ayati, A. Unveiling the remarkable simultaneous adsorption-photocatalytic potential of Ag nanoparticles-anchored phosphotungestic acid loaded ZIF-8 for Congo red removal. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wang, W.; Niu, J.F.; Lu, Z.Y.; He, P.L. Polyoxometalates coupled covalent organic frameworks as highly active photothermal nanoreactor for CO2 cycloaddition. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 5975–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Zeng, R.; Cheng, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, C. POM-incorporated ZnIn2S4 Z-scheme dual-functional photocatalysts for cooperative benzyl alcohol oxidation and H2 evolution in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 306, 121087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Li, W.; Ma, X.; Dong, M.; Liu, X.; Ren, C. Novel binary photocatalysts containing polyoxometalate immobilized on CdS nanorods surface for enhance photocatalytic performance. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 443, 114854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, H.; Sun, L.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Su, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q. Incorporating Ni-Polyoxometalate into the S-Scheme Heterojunction to Accelerate Charge Separation and Resist Photocorrosion for Promoting Photocatalytic Activity and Stability. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 11778–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, G.; Liu, W.; Liang, S.; Yang, R.; Sun, C. In-situ construction of Z-scheme silver phosphotungstate/polyimide photocatalysts and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic degradation of aflatoxin B1 in vegetable oil. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 483, 149153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X. The synergistic effect of POM-π interaction and solid phase amidation on the visible light photocatalytic of g–C3N4–based photocatalyst. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 178, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Park, K.; Thomas, J.; Yoon, S.M.; Yoon, M. Solar catalytic CO2 reduction over POM-entrapped zeolites decorated with TiO2 nanocomposites in water: Highly efficient and selective production of CH3OH via Z-scheme charge separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, Q.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Gao, Y. AgBr/Polyoxometalate/Graphene Oxide Ternary Composites for Visible Light-Driven Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani-Atta, S.A.; Darwish, A.A.A.; Shwashreh, L.; Alotaibi, F.A.; Al-Tweher, J.N.; Al-Aoh, H.A.; El-Zaidia, E.F.M. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Using Calcium-Polyoxometalate Under Ultraviolet Irradiation. Processes 2024, 12, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, C.; Xu, C.P.; Wang, J.F.; Li, X.L.; Li, T.; Ma, Y.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Qiao, Y.F.; Wu, Q. Mechanistic study on the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B via Mn-Schiff-base-modified Keggin-type polyoxometalate composite materials. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 12364–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ren, R.; Huang, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, H.; Huai, R.; Song, N.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; et al. Photocatalytic activity of an Anderson-type polyoxometalate with mixed copper(I)/copper(II) ions for visible-light enhancing heterogeneous catalysis. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 310, 123052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Zhao, M.Y.; Huang, J.B.; Zhao, N.; Yu, H.H. Controllable Synthesis, Photocatalytic Property, and Mechanism of a Novel POM-Based Direct Z-Scheme Nano-Heterojunction α-Fe2O3/P2Mo18. Molecules 2023, 28, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Kong, L. Magnetic field-assisted enhancement of photocatalytic activity: Modified Co-POMs direct Z-scheme heterojunction Co4PW9/CeO2 for efficient carrier separation and transport. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1316, 139015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, T.; Lin, Y. Visible light assisted heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine B based on the Co-POM/N-TiO2 composites: Catalyst properties, photogenerated carrier transfer and degradation mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Kong, L.Y.; Fei, B.L. Highly efficient catalytic reduction of organic dyes, Cr (VI) and 4-nitrophenol, and photocatalytic degradation of MB by an inorganic-organic hybrid polyoxometalate. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-H.; Li, X.; Chi, J.-Q.; Su, Z.-M. Two functional hybrids based on polyoxometalate coordination polymers: Synthesis, electrochemical and photocatalytic properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Jin, T.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Jiang, W.; Qu, X.; Chen, Z. Construction of Z-scheme Cs3PMo12O40/g-C3N4 composite photocatalyst with highly efficient photocatalytic performance under visible light irradiation. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 311, 123069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.H.; Kang, N.; Wang, C.M.; Yu, K.; Lv, J.H.; Wang, C.X.; Zhou, B.B. An inorganic-organic hybrid nanomaterial with a core-shell structure constructed by using Mn-BTC and Ag5[BW12O40] for supercapacitors and photocatalytic dye degradation. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, M.; Xue, C.; Huang, J.; Zhao, N.; Kong, L. All-solid-state Z-scheme nanojunction PW12/Ag/ZnO photocatalyst: Effective carriers transfer promotion and enhanced visible light driven. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1300, 137272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, B.C.; Lim, H.K.; Tay, C.Y.; Lim, T.T.; Dong, Z.L. Polyoxometalates for bifunctional applications: Catalytic dye degradation and anticancer activity. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Uribe, C.; Duran, F.; Vallejo, W.; Puello, E.; Zarate, X.; Schott, E. Photocatalytic study of TiO2 thin films modified with Anderson-type polyoxometalates (Cr, Co and Ni): Experimental and DFT study. Polyhedron 2023, 231, 116253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Yang, L.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Su, K.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.X.; Yang, L. A Carboxylic-Functionalized Anderson-Type Polyoxoanion for Efficient Selective Cationic Dye Adsorption. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 35, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Fan, Z.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ma, P.T.; Niu, J.Y.; Wang, J.P. Synthesis and Structure of a Copper-Based Functional Network for Efficient Organic Dye Adsorption. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 19764–19772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, H.; Bedi, P.; Pradeep, C.P. Transformation of a Polyoxometalate Precursor into Carbon Doped Bismuth Molybdate Nanosheets for the Visible Light Photocatalytic Degradation of Aqueous Pollutants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 17596–17610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samajdar, S.; Murmu, G.; Biswas, M.; Manna, S.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, S. Polyoxometalate-loaded reduced graphene oxide-modified metal vanadate catalysts for photoredox reactions through an indirect Z-scheme mechanism. Energy Adv. 2025, 4, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.F.; Wang, H.S.; Zhang, E.J.; Qu, X.S.; Li, J.P.; Zhao, S.S.; Gao, H.J.; Chen, Z. Boosted Photocatalytic Performance for Antibiotics Removal with Ag/PW12/TiO2 Composite: Degradation Pathways and Toxicity Assessment. Molecules 2023, 28, 6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Xue, K.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Peng, Y.; Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W. Nitrogen-deficient g-C3Nx/POMs porous nanosheets with P–N heterojunctions capable of the efficient photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, X.; Li, F.; Shi, W.; Han, Q. Incorporating [Mo4O13]2− into a Fe-based metal-organic framework for efficiently photocatalysis degradation of tetracycline through synergistic effect. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1326, 141059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Pal, T.; Pal, A. Efficient catalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin in synthetic and real wastewater under aerobic condition using microporous ammonium phosphomolybdate. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Fu, W.Z.; Sun, S.J.; Liu, H.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zhong, W.Z.; Ma, B. Preparation, characterization, and removal of nitrate from water using vacant polyoxometalate/TiO2 composites. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.M.; Zeng, D.L.; Li, Z.F.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cao, X.H.; Yang, G.P.; Zhang, Z.B.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, F. Polyoxometalate-encapsulated metal-organic frameworks for photocatalytic uranium isolation. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 19126–19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Xing, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhou, W. Hollow cubic Cu2−xS/Fe-POMs/AgVO3 dual Z-scheme heterojunctions with wide-spectrum response and enhanced photothermal and photocatalytic-fenton performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 298, 120628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.-B.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Lu, J.-C.; Chen, Z.-L.; Wang, R.; Kong, X.-C.; Yu, J.-H.; Fu, Y.; Ye, F. Incorporating nickel-substituted polyoxometalate into a photoactive metal–organic framework for efficient photodegradation of thiamethoxam insecticide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 691, 137457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Huang, X.; Tang, H.; Liu, X. Modified carbon nitride incorporating Keggin-type potassium phosphotungstate enhances photocatalytic degradation of imidacloprid under visible light. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2024, 171, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, D.; Tian, A. Two Anderson-based complexes with adjustable structures for efficient and selective photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI). J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1337, 142237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).