Design of Bimetallic Active Sites via Transition Metal Doping JANUS In2S2X for Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
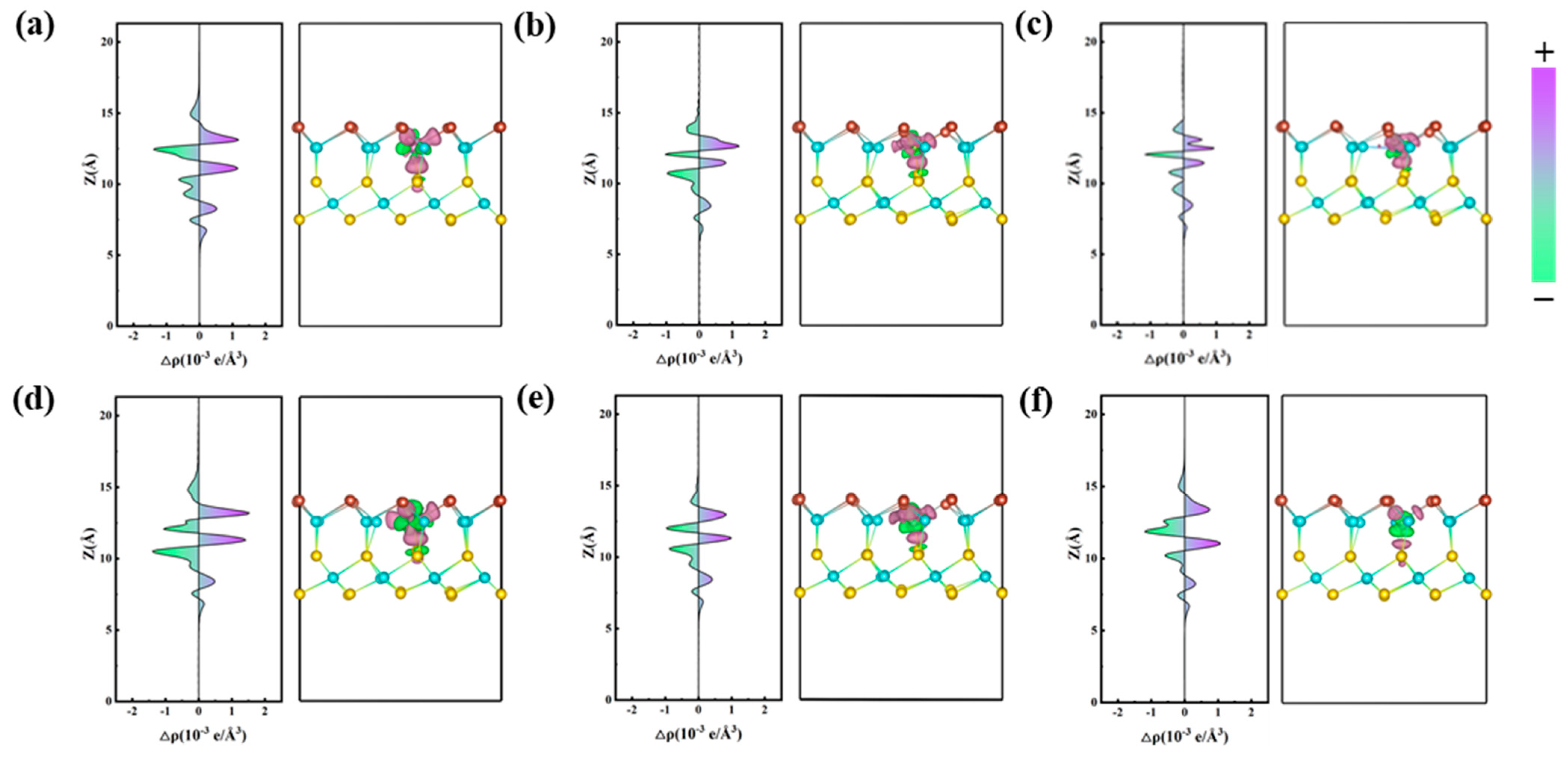
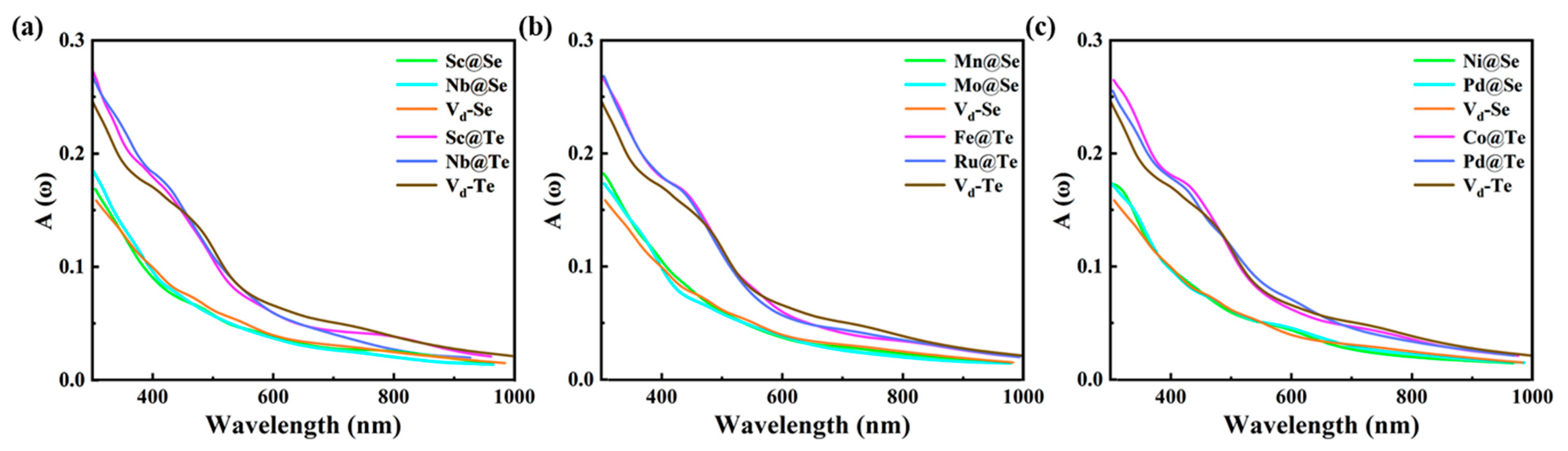
2.1. Electronic Structures and Optical Properties of M@ In2S2X (X = Se, Te)
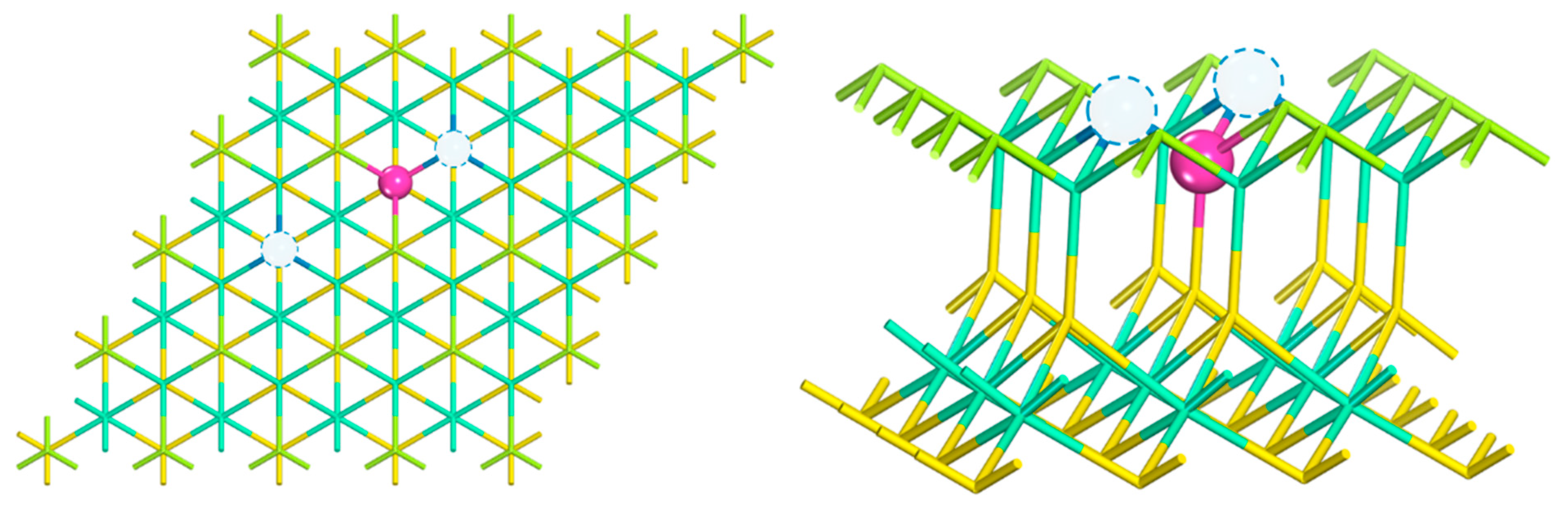
2.1.1. Crystal Structure
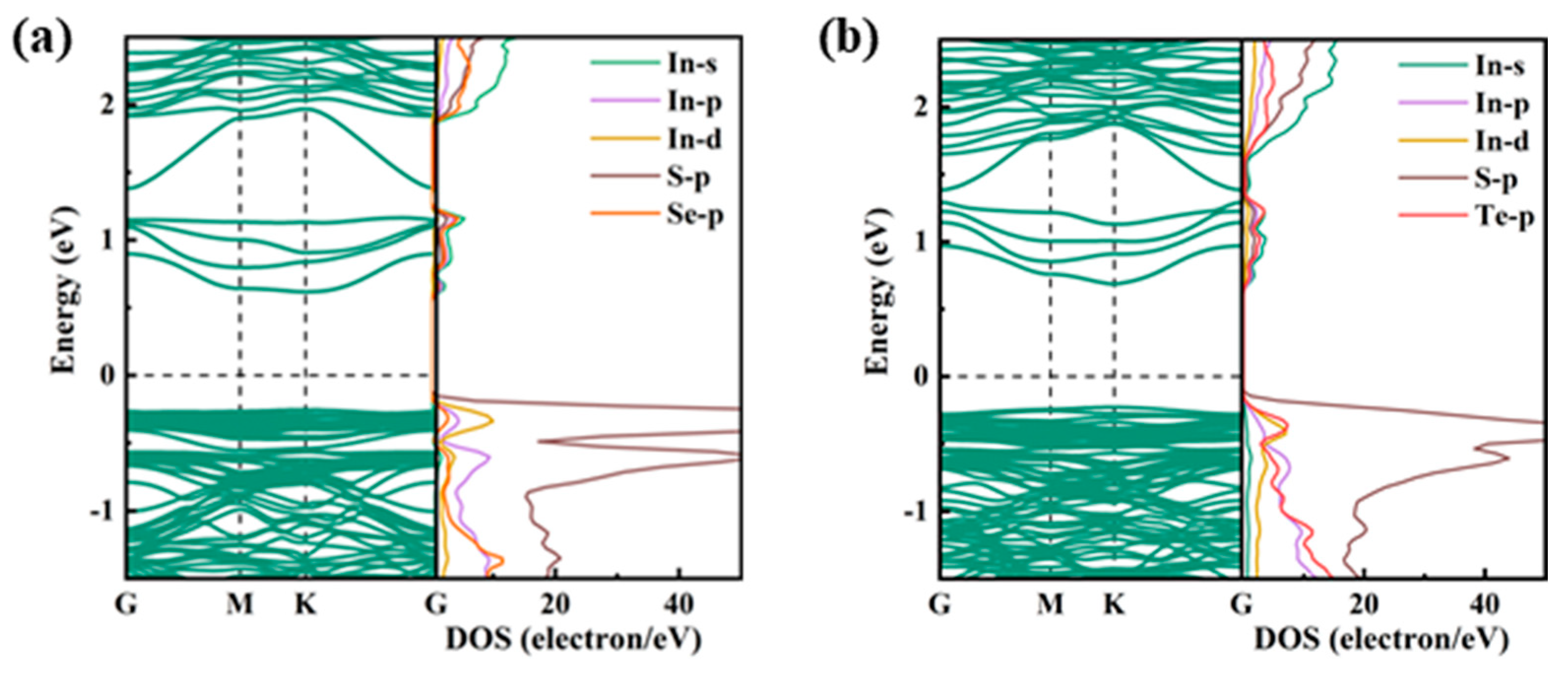
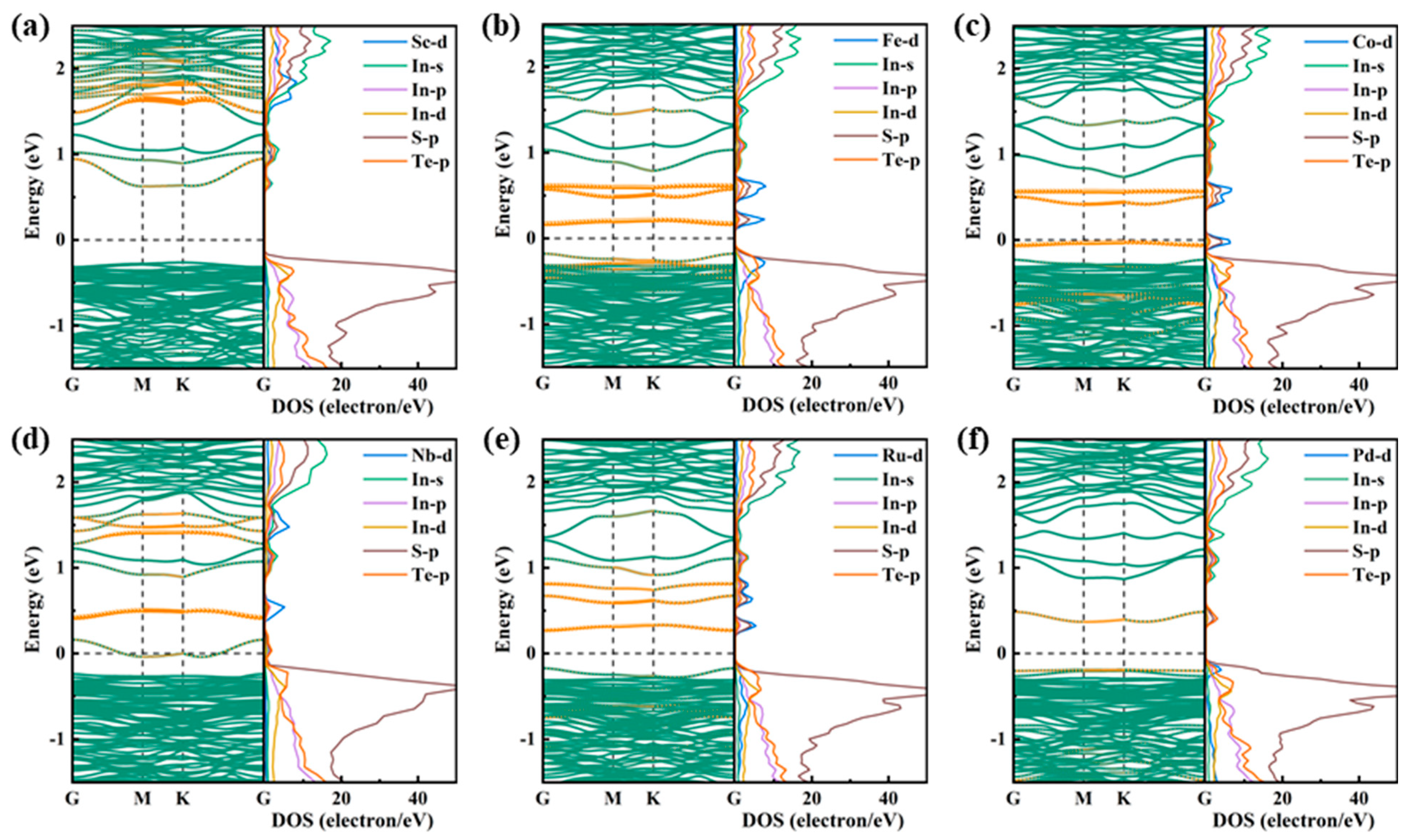
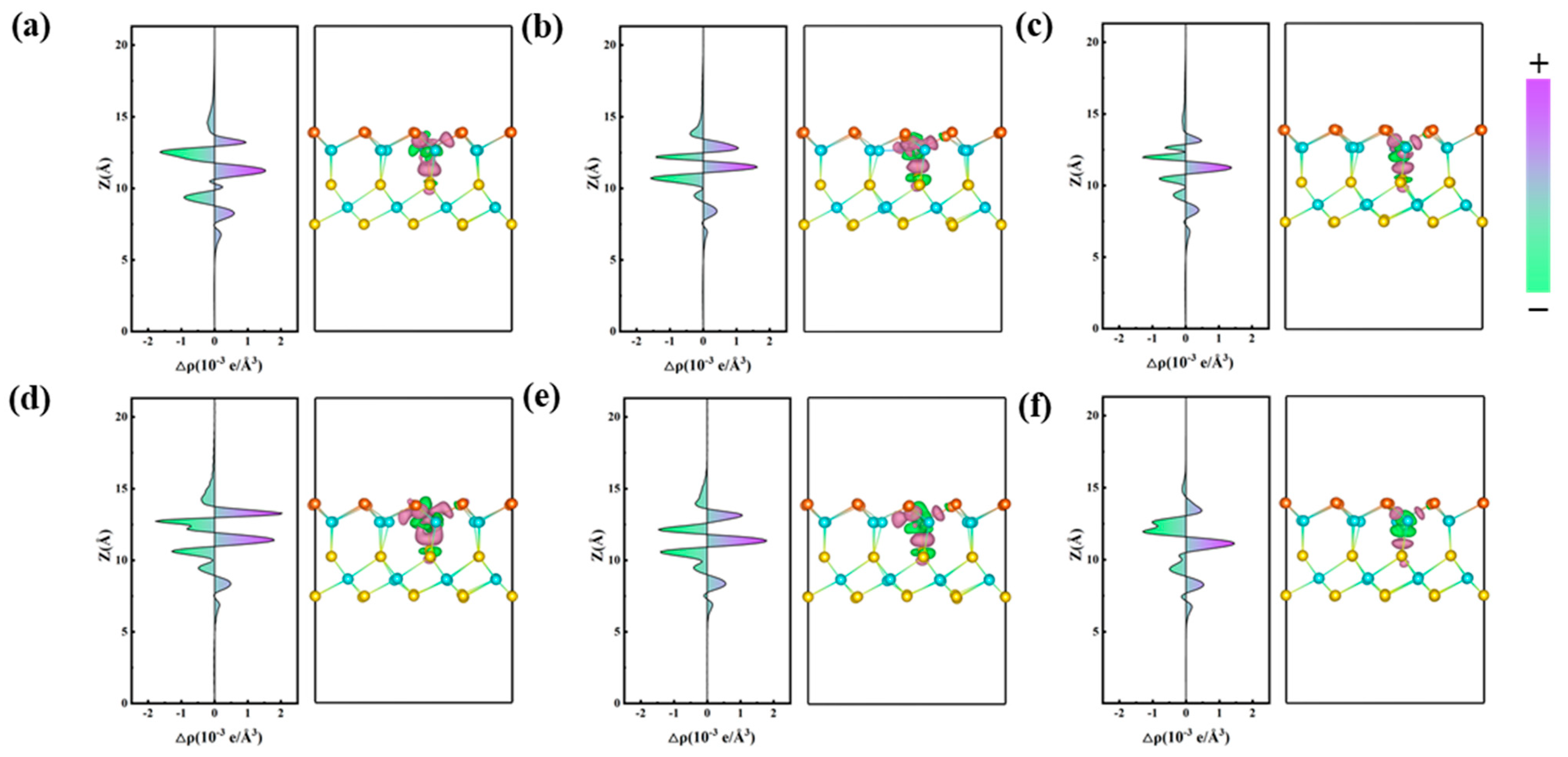
2.1.2. Electronic Properties
2.1.3. Optical Properties
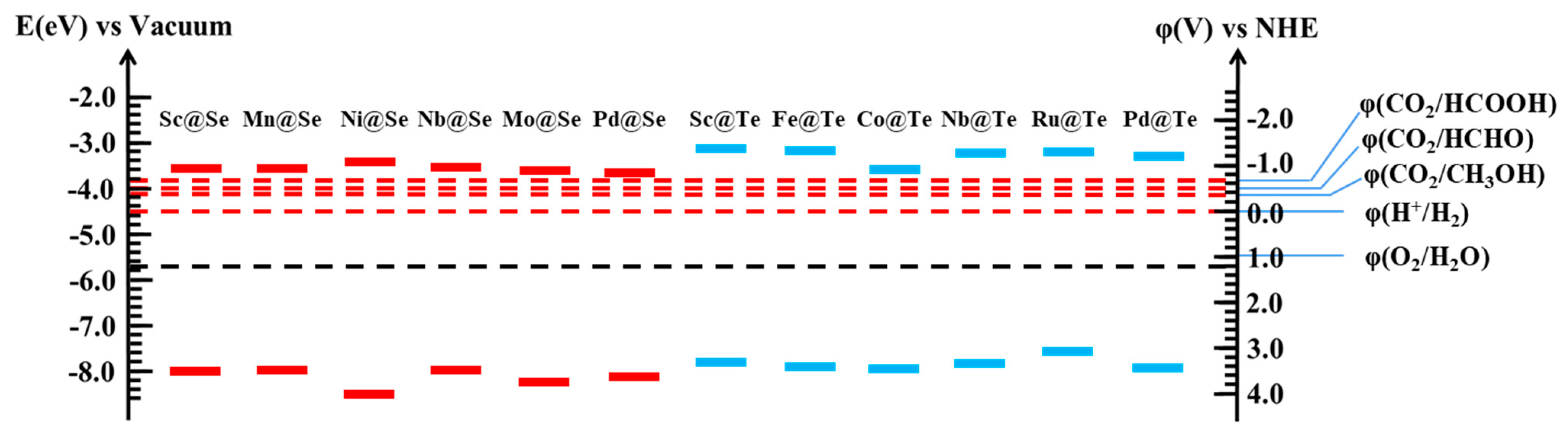
2.2. Photocatalytic Performance of M@X
2.2.1. Edge Potential
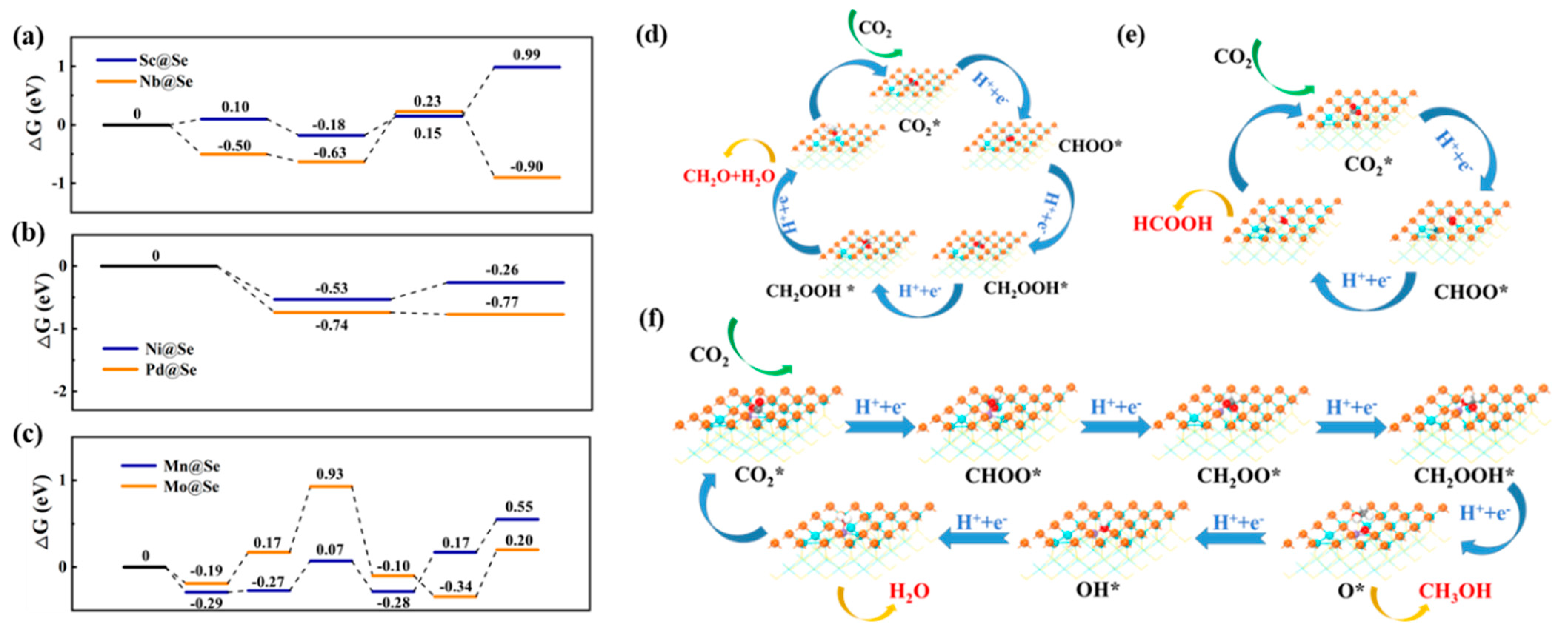
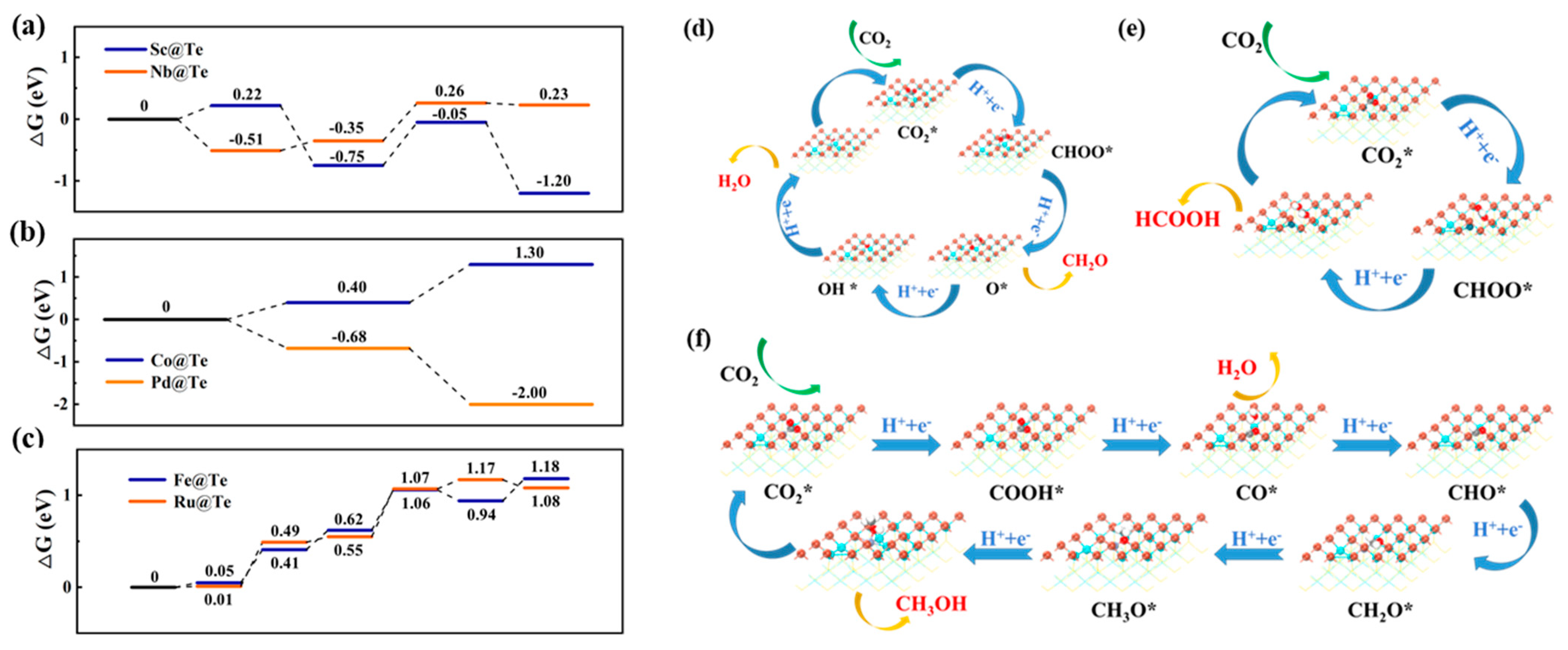
2.2.2. Photocatalytic Performance of M@X for CO2 Reduction
- I
- Photocatalytic performance of M@Se
- II
- Photocatalytic performance of M@Te
3. Computational Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Xue, W.; Sun, K.; Song, X.; Wu, C.; Nie, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y.; et al. Author Correction: Self-adaptive dual-metal-site pairs in metal-organic frameworks for selective CO2 photoreduction to CH4. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Ma, F.; Jin, T.; He, P.; Luo, Z.M.; Kupfer, S.; Karnahl, M.; Zhao, F.; Xue, Z.; Jin, T. Homoleptic Al (III) Photosensitizers for Durable CO2 Photoreduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, E.; Ali, S.; Hiragond, C.B.; Kim, H.S.; Powar, N.S.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; In, S. Solar fuels: Research and development strategies to accelerate photocatalytic CO2 conversion into hydrocarbon fuels. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 880–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, B.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Ji, M.X.; Ren, H.; Chi, Y.H. Research on Adjusting Electronic Transport with MoSi2N4/ZrS2(HfS2) II-Type Heterojunction for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Acta Chim. Sinica 2025, 83, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Song, J.Q.; Pan, M.; Su, C.Y.A. 2D layered cobalt-based metal–organic framework for photoreduction of CO2 to syngas with a controllable wide ratio range. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, D.D.; Yin, H.Y.; Chen, Z.N.; Zhao, W.; Chi, Y.H. Density Functional Theory Study of Janus In2S3X Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 under “Double Carbon” Target. Acta Chim. Sinica 2023, 81, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Song, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, D. Photo-and Electro-Catalytic Processes: Water Splitting, N2 Fixing, CO2 Reduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-3-527-83007-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xie, H. Electrochemically Regenerated Amine for CO2 Capture Driven by a Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 13578–13588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Q.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, D.; Jiang, D. Regulating photocatalytic CO2 reduction selectivity via steering cascade multi-step charge transfer pathways in 1T/2H-WS2/TiO2 heterojuncitons. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 447, 137485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Liu, C.; Kang, Y.; Wu, L. Cu+–Ti3+ interface interaction mediated CO2 coordination model for controlling the selectivity of photocatalytic reduction CO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 301, 120803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, B.; Guo, Q.; Guo, S.; Peng, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Van der Waals heterojunction for selective visible-light-driven photocatalytic CO2 reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 284, 119733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.J.; Putri, L.K.; Mohamed, A.R. Rational design of carbon-based 2D nanostructures for enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction: A dimensionality perspective. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9710–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khdary, N.H.; Alayyar, A.S.; Alsarhan, L.M.; Alshihri, S.; Mokhtar, M. Metal oxides as catalyst/supporter for CO2 capture and conversion, review. Catalysts 2022, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.M.M.; Li, Y.; Halawani, W.; Narasimharao, K.; Salam, M.A.; Alshehri, A.A.; Khdary, N.H.; Al-Faifi, S.; Gu, L.; Chowdhury, A.D. Evaluating the efficacy of nanosized CuZnAl and CuZnZr mixed oxides for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Dalton Trans. 2023, 52, 5155–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.Z.; Chen, S.; Duan, M.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, C.; Long, R.; Hao, W.; Chi, Z. Isolated single atom cobalt in Bi3O4Br atomic layers to trigger efficient CO2 photoreduction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, R.; Yin, W.; Zhao, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Zhang, T. Selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction over Zn-based layered double hydroxides containing tri or tetravalent metals. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Song, Q.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, D. Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into CH4 over Ru-doped TiO2: Synergy of Ru and oxygen vacancies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2809–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, P.K.; Malik, A.; Nandal, N.; Pandita, S.; Singh, R.; Bhandari, S.; Saran, S.; Jain, S.L. Morphology controlled Fe and Ni-doped CeO2 nanorods as an excellent heterojunction photocatalyst for CO2 reduction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 588, 152912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.N.; Chi, Y.H.; Ma, H.; Yuan, S.; Hao, C.; Ren, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, H.Y.; Guo, W. Effect of vacancy concentration on the production selectivity of Janus In2S2X (X = Se, Te) monolayer heterojunction photocatalytic reduction of CO2. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2023, 146, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Ren, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, Q. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by Ca doped β-In2S3 with varying Ca concentration. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2022, 48, 1813–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, B.Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, S.P.; Zhen, L. Ca (II) doped β-In2S3 hierarchical structures for photocatalytic hydrogen generation and organic dye degradation under visible light irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 491, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yang, Z.; He, S.; Niu, X.; Zhang, T.; Ding, A.; Liang, H.; Feng, X. Photocatalytic reduction of Uranium (VI) under visible light with Sn-doped In2S3 microspheres. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia, C.; Berglund, S.P.; Friedrich, D.; Dittrich, T.; Bogdanoff, P.; Liu, Y.; Levcenko, S.; Unold, T.; Conesa, J.C.; Lacey, A.L.D. Synthesis and characterization of V-doped β-In2S3 thin films on FTO substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 28753–28761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, L.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Y. Zr-doped β-In2S3 ultrathin nanoflakes as photoanodes: Enhanced visible-light-driven photoelectrochemical water splitting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2606–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Yu, J.L.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lu, P.M. Influence of Ag and Sn incorporation in In2S3 thin films. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 078103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.L.; Hennig, R.G. Single-layer group-III monochalcogenide photocatalysts for water splitting. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio Molecular Dynamics for Liquid Metals. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.A.; Bird, D.M. Implementation of gradient-corrected exchange-correlation potentials in Car-Parrinello total-energy calculations. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 4954–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernzerhof, M.; Scuseria, G.E. Assessment of the Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof exchange-correlation functional. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 5029–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, K.; Sundararaman, R.; Letchworth-Weaver, K.; Arias, T.A.; Hennig, R.G. Implicit solvation model for density-functional study of nanocrystal surfaces and reaction pathways. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 084106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, K.; Kolluru, V.S.C.; Mula, S.; Steinmann, S.N.; Hennig, R.G. Implicit self-consistent electrolyte model in plane-wave density-functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 234101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneval, F.; Vast, N.; Reining, L.; Izquierdo, M.; Sirotti, F.; Barrett, N. Exchange and correlation effects in electronic excitations of Cu2O. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 267601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trani, F.; Vidal, J.; Botti, S.; Marques, M.A.L. Band structures of delafossite transparent conductive oxides from a self-consistent GW approach. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 085115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Reining, L.; Del Sole, R.; Onida, G. Ab initio calculation of excitonic effects in the optical spectra of semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 4510–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onida, G.; Reining, L.; Rubio, A. Electronic excitations: Density-functional versus many-body Green’s-function approaches. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 601–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruning, M.; Marini, A.; Gonze, X. Exciton-plasmon states in nanoscale materials: Breakdown of the Tamm−Dancoff approximation. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2820–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdoš, M.; Hummer, K.; Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J.; Bechstedt, F. Linear optical properties in the projector-augmented wave methodology. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 045112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zou, X.; Najmaei, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Kong, J.; Lou, J.; Ajayan, P.M.; Yakobson, B.I.; Idrobo, J.C. Intrinsic structural defects in monolayer molybdenum disulfide. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Teixeira, I.F.; Naik, A.; Heske, J.; Cruz, D.; Antonietti, M.; Savateev, A.; Kuhne, T.D. Photocatalytic water splitting reaction catalyzed by ion-exchanged salts of potassium poly (heptazine imide) 2D materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 13749–13758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toroker, M.C.; Kanan, D.K.; Alidoust, N.; Isseroff, L.Y.; Liao, P.; Carter, E.A. First principles scheme to evaluate band edge positions in potential transition metal oxide photocatalysts and photoelectrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 16644–16654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, J.; Neumann, R.; Antonietti, M.; Saalfrank, P. Adsorption and Photocatalytic Splitting of Water on Graphitic Carbon Nitride: A Combined First Principles and Semiempirical Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15917–15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørskov, J.K.; Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Lindqvist, L.; Kitchin, J.R.; Bligaard, T.; Jonsson, H. Origin of the overpotential for oxygen reduction at a fuel-cell cathode. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Ju, H.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y. Selective visible-light-driven photocatalytic CO2 reduction to CH4 mediated by atomically thin CuIn5S8 layers. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmeisl, J.; Chan, K.; Skulason, E.; Bjorketun, M.E.; Tripkovic, V. On the pH dependence of electrochemical proton transfer barriers. Catal. Today 2016, 262, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, C.; Karmakar, S.; Datta, A. Monolayer group IV–VImonochalcogenides: Low-dimensional materials for photocatalytic water splitting. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 7615–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Slab | Reduction Products | Control Step | Catalyst Screening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sc@Se, Ti@Se, V@Se, Y@Se, Zr@Se, Nb@Se | CH2O | The fourth hydrogenation reaction | Interactions between intermediates and photocatalyst surfaces |
| Cr@Se, Mn@Se, Fe@Se, Mo@Se, Ru@Se | CH3OH | The second hydrogenation reaction | Interactions between intermediates and photocatalyst surfaces |
| Co@Se, Ni@Se, Rh@Se, Pd@Se | HCOOH | The second hydrogenation reaction | D-band centers of dopant atoms |
| Slab | Reduction Products | Control Step | Catalyst Screening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sc@Te, Ti@Te, V@Te, Y@Te, Zr@Te, Nb@Te | CH2O | The fourth hydrogenation reaction | Interactions between intermediates and photocatalyst surfaces |
| Cr@Te, Mn@Te, Fe@Te, Mo@Te, Ru@Te | CH3OH | The third hydrogenation reaction | Interactions between intermediates and photocatalyst surfaces |
| Co@Te, Ni@Te, Rh@Te, Pd@Te | HCOOH | The second hydrogenation reaction | D-band centers of dopant atoms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, M.; Cai, W.; Ren, H.; Zhao, W.; Guo, W. Design of Bimetallic Active Sites via Transition Metal Doping JANUS In2S2X for Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Catalysts 2025, 15, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060567
Chi Y, Chen Z, Ji M, Cai W, Ren H, Zhao W, Guo W. Design of Bimetallic Active Sites via Transition Metal Doping JANUS In2S2X for Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Catalysts. 2025; 15(6):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060567
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Yuhua, Zhengnan Chen, Mengxin Ji, Wei Cai, Hao Ren, Wen Zhao, and Wenyue Guo. 2025. "Design of Bimetallic Active Sites via Transition Metal Doping JANUS In2S2X for Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction" Catalysts 15, no. 6: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060567
APA StyleChi, Y., Chen, Z., Ji, M., Cai, W., Ren, H., Zhao, W., & Guo, W. (2025). Design of Bimetallic Active Sites via Transition Metal Doping JANUS In2S2X for Highly Selective Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Catalysts, 15(6), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060567







