Abstract
Environmental contamination from industrial dyes, particularly Methylene Blue (MB), presents a growing challenge due to their toxicity and persistence in aquatic systems. This study explored the catalytic potential of cellulose acetate-stabilized nickel (CA/Ni) nanoparticles for the degradation of MB in aqueous solutions. CA/Ni was synthesized and characterized using FTIR and SEM, confirming its successful incorporation into the cellulose acetate matrix and uniform distribution across the membrane. UV-Vis spectrophotometry was employed to monitor the catalytic degradation of MB, revealing a significant decrease in absorbance at 665 nm over 28 min, indicating 68% degradation efficiency. Kinetic analysis showed that the degradation followed pseudo-first-order kinetics, with an apparent rate constant of 0.0348 min−1 and an R2 value of 0.9851, confirming excellent catalytic performance. The effects of temperature and pH on MB degradation were investigated, with the highest efficiency observed at 35 °C and a pH of 7. A room temperature (25 °C) and acidic conditions (pH 5) reduced the degradation rate to 52%. In comparison, a higher temperature (45 °C) and an alkaline pH (pH 9) resulted in a slight decline to 55%, likely due to changes in catalyst efficiency and MB solubility. These findings highlight the potential of Ni NP-stabilized membranes for wastewater treatment applications, providing a scalable and efficient approach to dye removal.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution, particularly from industrial wastewater, is a growing global concern, with synthetic dyes being significant contributors to this issue [1,2,3]. These dyes, commonly used in industries such as textiles, paper, and pharmaceuticals, pose serious ecological risks when discharged into aquatic ecosystems [4,5,6]. Among these, Methylene Blue (MB), a widely used synthetic dye, has diverse applications in various industries, including textiles, paper, pharmaceuticals, and chemistry [7]. Despite its utility, the environmental impact of MB is significant, especially when discharged into aquatic ecosystems as industrial wastewater. MB is classified as a hazardous pollutant due to its toxic effects on marine life and its resistance to natural degradation processes [8,9]. Once in the environment, MB can interfere with biological functions in aquatic organisms, posing long-term ecological risks [10,11]. Additionally, its intense color can block sunlight penetration, hindering photosynthesis in aquatic plants and disrupting the balance of ecosystems. As a result, the removal of MB from wastewater has become a pressing environmental issue, with various methods being explored to mitigate its harmful effects [8,11].
Traditional methods for removing dyes from wastewater include physical, chemical, and biological approaches such as adsorption, coagulation, flocculation, and microbial degradation. While these methods can be effective, they often come with significant drawbacks [12,13]. Physical methods, like adsorption using activated carbon, may be efficient in removing dyes, but are expensive and can generate secondary pollutants [14]. Chemical methods, such as oxidation, often require the use of strong reagents, which may lead to the formation of hazardous by-products [15,16,17,18]. Biological methods, although environmentally friendly, can be slow and inefficient for dyes [19]. Given these challenges, there is a growing interest in developing novel and more effective methods for dye degradation, particularly those involving nanotechnology.
One promising approach is using nano-catalysts to accelerate the degradation of organic pollutants like MB. Nanoparticles, due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio and unique catalytic properties, have emerged as efficient catalysts for a wide range of chemical reactions, including dye degradation [20,21]. Among these, metal nanoparticles have garnered significant attention for their ability to facilitate electron transfer and enhance the rate of redox reactions [19,22]. In particular, nickel nanoparticles (Ni NPs) have shown potential as effective catalysts due to their relatively low cost, high reactivity, and ability to participate in various catalytic processes [19]. Ni NPs have been employed in numerous applications, including hydrogenation, oxidation, and pollutant degradation, making them attractive candidates for environmental remediation [23,24,25,26,27].
However, one of the major challenges associated with the use of metal NPs in catalysis is their tendency to agglomerate. When nanoparticles cluster together, their effective surface area decreases, which can significantly reduce their catalytic efficiency. To overcome this limitation, stabilizing agents such as polymers are used to disperse nanoparticles and prevent agglomeration [28,29,30]. Cellulose acetate, a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer, is one such stabilizing agent that has been successfully employed to stabilize metal nanoparticles [6,22]. By embedding Ni NPs within a cellulose acetate matrix, it is possible to create a stable and effective catalytic system for dye degradation.
In this study, we explored the catalytic degradation of MB using cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni nanoparticles. The catalytic process was facilitated by the addition of sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a reducing agent, which, in combination with the Ni NPs, accelerated the breakdown of MB. Sodium borohydride is a well-known reducing agent that provides electrons for the reduction of dye molecules, thus aiding in their decolorization and eventual degradation. The role of Ni NPs in this system is to mediate the transfer of electrons from NaBH4 to the dye molecules, thereby enhancing the overall degradation rate. This article not only demonstrates the effectiveness of Ni NPs in catalysis, but also highlights the importance of using a stabilizing agent like cellulose acetate to improve nanoparticle dispersion and prevent agglomeration.
Furthermore, the kinetic behavior of the degradation process was investigated using pseudo-first-order kinetics to validate the results. The high degradation efficiency observed in this study suggests that CA/Ni could be a promising solution for the treatment of dye-contaminated wastewater. The application of such nanocatalytic systems offers an environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and efficient method for removing hazardous dyes like MB from industrial effluents, contributing to cleaner water systems and improved environmental sustainability.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Cellulose Acetate-Stabilized Nickel Nanoparticles
FTIR spectroscopy was used to identify the functional groups in the cellulose acetate membrane and to assess any changes upon the incorporation of Ni nanoparticles. In both spectra, characteristic absorption bands of cellulose acetate were observed. A peak at around 1730 cm−1 was attributed to the C=O stretching of ester groups, peaks at 1360 cm−1 and 1235 cm−1 corresponded to C–H bending and C–O stretching, respectively, and a broad band near 3400 cm−1 was assigned to O–H stretching vibrations. After functionalization with Ni nanoparticles, no significant shifts in the major functional group peaks were observed, suggesting that the primary structure of cellulose acetate remained intact and that no strong interaction occurred between the polymer and the nanoparticles. The increased intensity in the O–H band at 3400 cm−1 in the CA/Ni membrane may indicate a higher density of surface-exposed hydroxyl groups, possibly due to changes in surface morphology or nanoparticle interaction via weak forces such as hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions. FTIR spectra are provided in Figure 1.
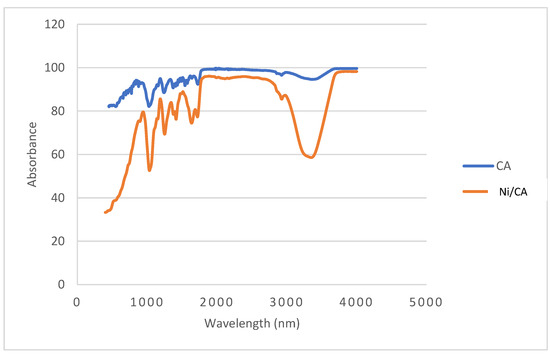
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of the cellulose acetate membrane and Ni/CA.
The surface morphology and structural characteristics of the prepared membrane were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). SEM provided high-resolution images that revealed the distribution and dispersion of Ni nanoparticles within the cellulose acetate matrix. The micrographs showed a uniform distribution of Ni NPs throughout the membrane, with irregular shapes. The images also demonstrated that the nanoparticles were well embedded in the polymer, which helped prevent agglomeration, a common issue in nanoparticle synthesis. The surface of the membrane appeared smooth with a few dispersed aggregates of Ni NPs, confirming the success of the stabilization process. This even dispersion was crucial for maximizing the surface area available for catalysis, ensuring efficient interaction between the nanoparticles and Methylene Blue during the degradation reaction. The SEM analysis thus confirmed the structural integrity and uniformity of the Ni NP-stabilized membrane, which was essential for maintaining consistent catalytic activity. The SEM result is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
FESEM image of cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni NPs.
The progress of the degradation reaction was tracked using UV-Vis spectrophotometry, which is a widely used method for monitoring changes in absorbance related to chemical reactions. As MB absorbs strongly at 665 nm, this wavelength was used to track the degradation process over time. Initially, the UV-Vis spectrum of the MB solution showed a prominent absorption peak at 665 nm, corresponding to the dye’s chromophoric structure. Upon adding NaBH4 as the reducing agent, a slight decrease in absorbance was observed, indicating a partial reduction of MB. However, it was the addition of the Ni NP-stabilized membrane that significantly accelerated the degradation process. Spectra recorded at regular 2 min intervals showed a progressive decrease in the intensity of the peak at 665 nm, confirming the catalytic role of Ni NPs in facilitating the breakdown of MB molecules. By the end of the reaction, the absorption peak had nearly disappeared, indicating complete degradation of the dye. UV-Vis spectrophotometric analysis not only confirmed the efficacy of the catalyst, but also provided quantitative data to calculate the degradation efficiency and reaction kinetics.
2.2. Degradation of Methylene Blue
The catalytic degradation of MB in the presence of cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni nanoparticles (Ni NPs) was thoroughly investigated using UV-Vis spectrophotometry. This technique enabled real-time monitoring of the reduction in MB concentration by measuring the absorbance at its characteristic wavelength, 665 nm, over the course of the reaction. As MB possesses a distinct absorption peak at 665 nm due to its chromophoric structure, any decrease in the absorbance at this wavelength directly corresponds to the breakdown of dye molecules. As shown in Figure 3a, UV-Vis spectra were recorded at 2 min intervals to track the degradation process. Initially, the MB solution exhibited a strong absorption peak at 665 nm, which was used as the baseline measurement for the unreacted dye concentration. Upon the introduction of cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni NPs, a noticeable and steady decrease in the intensity of this peak was observed over time, indicating the catalytic action of Ni nanoparticles in facilitating the degradation of MB. The degradation process was significantly accelerated by the presence of Ni NPs, demonstrating their effective catalytic role in the reaction. Nanoparticles embedded in the cellulose acetate membrane enhanced electron transfer from sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to MB molecules, promoting the rapid reduction and subsequent breakdown of the dye. Over the 28 min reaction period, the absorbance of MB at 665 nm gradually decreased, and by the end of the reaction, the characteristic peak had completely disappeared, signifying the near-total degradation of MB. Quantitatively, a 68% (Figure 3b) degradation of MB was achieved after 30 min of reaction time. The steady decline in absorbance, coupled with the eventual disappearance of the peak at 665 nm, indicates the high catalytic efficiency of the Ni NP-stabilized membrane in breaking down MB molecules. These results from the UV-Vis analysis are consistent with the expected behavior of pseudo-first-order kinetics, where the rate of reaction is proportional to the concentration of MB. The kinetic data, derived from plotting the natural logarithm of absorbance versus time, revealed a linear relationship, confirming the applicability of first-order kinetics to the degradation process. The rate constant was determined from the slope of the linear plot, further reinforcing the rapid catalytic activity of CA/Ni. This efficient degradation can be attributed to the unique properties of cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni NPs, which provided a high surface area for interaction with MB molecules. Control experiments were also considered based on the prior literature. In previous studies and similar reports, NaBH4 alone showed negligible degradation of MB under identical conditions. Although direct control runs were not included in this specific study, its findings are aligned with well-established reports where NaBH4 alone or CA membrane without Ni NPs failed to significantly degrade MB [6]. The polymer matrix not only stabilized the Ni nanoparticles, but also prevented their agglomeration, ensuring that the active sites remained available for catalysis. The uniform dispersion of nanoparticles within the cellulose acetate membrane, as confirmed by SEM analysis, played a critical role in enhancing catalytic performance. Additionally, the color of the MB solution progressively lightened throughout the reaction, ultimately becoming transparent at the end of 28 min, providing a visual confirmation of the degradation. The complete disappearance of the blue coloration of MB coincided with the UV-Vis spectroscopic data, reinforcing observations regarding the efficiency of the catalytic process. In conclusion, cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni nanoparticles exhibited excellent catalytic activity in the degradation of MB, achieving 68% degradation within a short reaction time. The UV-Vis spectrophotometric analysis provided a clear indication of the catalyst’s effectiveness, while the application of first-order kinetics further validated the reaction mechanism. These findings highlight the potential of Ni NP-based catalysts for the remediation of dye-contaminated wastewater, offering a promising solution for environmental clean-up applications.
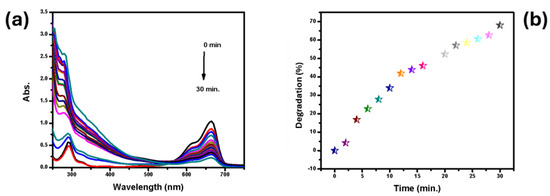
Figure 3.
Degradation of MB (a) and percentage removal of MB using CA/Ni (b).
2.3. Kinetic Study
The kinetic study of MB degradation using CA/Ni as a catalyst demonstrated significant findings. The results obtained from UV-Vis spectrophotometric analysis revealed a marked decline in absorbance at the characteristic wavelength of MB (665 nm) over time, indicating effective degradation of the dye. The calculated apparent rate constant for the pseudo-first-order reaction was 0.0348 min−1, with a corresponding R-squared value of 0.9851, as shown in Figure 4. This high R2 value indicates an excellent fit with the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, confirming that the degradation of MB by CA/Ni predominantly followed these kinetics, which is characteristic of many catalytic processes in which the reactant concentration is much higher than that of the catalyst.
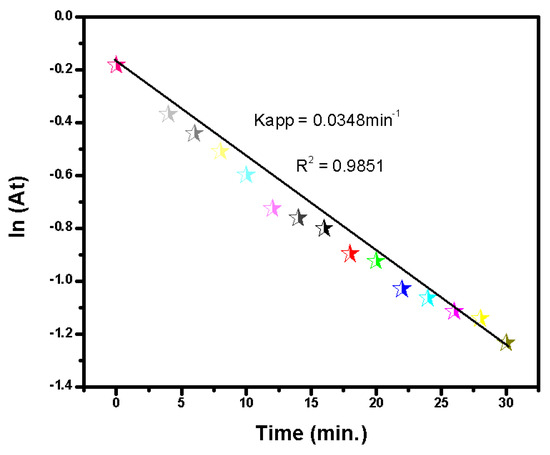
Figure 4.
Pseudo-first-order kinetics of the degradation of MB using CA/Ni.
Efficient degradation can be attributed to several factors. First, the high catalytic activity of Ni NPs was crucial; the nanoparticles embedded within the cellulose acetate matrix provided a large surface area for interactions with MB molecules, allowing for effective electron transfer from the NaBH4 reducing agent to MB. This facilitated the reduction and subsequent degradation of the dye. The observation that the reaction followed pseudo-first-order kinetics suggests that the degradation rate was primarily dependent on the MB concentration rather than on the catalyst. The moderate rate constant of 0.0348 min−1 indicates favorable reaction kinetics for practical applications in wastewater treatment. Visual confirmation of degradation was achieved through the gradual decline in absorbance at 665 nm and the color change of the MB solution from blue to nearly transparent. The complete disappearance of the characteristic peak at 665 nm after 30 min reinforces the catalyst’s effectiveness in breaking down dye molecules. The kinetic study demonstrated that CA/Ni is a highly effective catalyst for the degradation of MB through a pseudo-first-order kinetic mechanism. These findings not only underscore the potential of utilizing Ni NPs in environmental applications, but also offer valuable insights into the design of effective catalytic systems for dye degradation and wastewater treatment. These promising results indicate that this approach could be scaled for practical applications, contributing significantly to the remediation of dye-contaminated effluents.
2.4. Optimizations
2.4.1. Effect of Catalyst Concentration
The results indicated that varying the concentration of nickel nanoparticles significantly affected the degradation of MB. At 20 mg of Ni NPs, the degradation efficiency reached a peak of 68%. However, increasing the concentration to 40 mg resulted in a slight decrease in degradation efficiency to 60% (Figure 5). This decrease might be attributed to particle aggregation or a potential saturation effect, because nano composite catalyst particles in high concentration aggregate in solution [31]. The optimal concentration allows for sufficient active sites for reaction while maximizing interactions with MB molecules [25].

Figure 5.
The effect of the catalyst dose on the degradation of MB.
2.4.2. Temperature and pH Effects
Experiments conducted at different temperatures and pH levels revealed important insights into the environmental factors influencing the catalytic process. The highest degradation (68%) occurred at 35 °C and a neutral pH (7). At a lower temperature (25 °C) and in acidic conditions (pH 5), the degradation rate was significantly lower (52%), suggesting that temperature enhances the kinetic energy of molecules, promoting more frequent and effective collisions between the catalyst and substrate. The decrease in efficiency at a higher temperature (45 °C) and an alkaline pH (pH 9) may indicate a reduction in catalyst effectiveness, possibly due to changes in the solubility of MB or the charge of the catalyst and dye, which can hinder adsorption and reaction rates (Figure 6) [32].
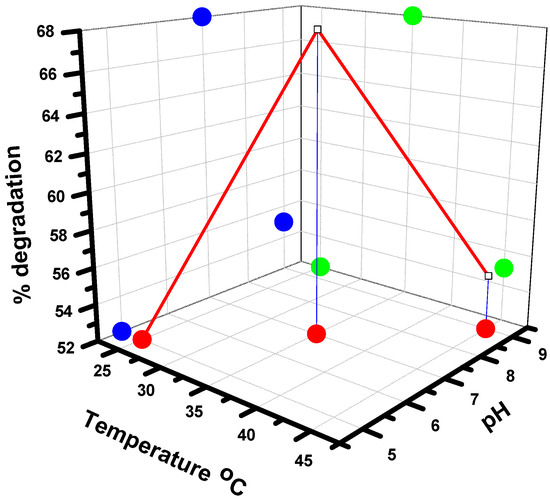
Figure 6.
The effect of pH and temperature on the degradation of MB (red—pH; blue—Temperature; green—Degradation).
3. Mechanism of Degradation
The degradation of MB in the presence of Ni NPs and NaBH4 is a reduction-driven process. The reaction mechanism involves the adsorption of MB molecules onto the surface of Ni nanoparticles, followed by electron transfer from NaBH4 to MB via the Ni NP surface. NaBH4 serves as the reducing agent, providing electrons that reduce MB into its colorless leuco form, breaking down the chromophoric groups responsible for its blue color. The role of Ni NPs is crucial, as they facilitate electron transfer, significantly accelerating the degradation process [33,34].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Cellulose acetate (MW = 30,000 g/mol) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA) and used as received. Nickel chloride (NiCl2, 98%), sodium borohydride (NaBH4, 99%), and Methylene Blue (MB, dye content 82%) were procured from Merck (Boston, MA, USA). Acetone (purity ≥ 99.5%) was purchased from Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Deionized water was used throughout the experiments.
4.2. Preparation of Cellulose Acetate Membrane
A total of 4 g of cellulose acetate granules was dissolved in 80 mL of a water–acetone mixture (60 mL deionized water and 40 mL acetone) under constant stirring at room temperature. The solution was stirred until a homogeneous, clear paste formed, indicating the complete dissolution of cellulose acetate. The paste was cast onto a glass petri dish and dried in an oven at 50 °C for 24 h to evaporate the solvent and form a thin, flexible membrane. The membrane was peeled off the dish and stored in a desiccator for future use.
4.3. Nickel Ions Uptake and Reduction
The prepared cellulose acetate membrane was immersed in a 0.1 M NiCl2 solution for 24 h at room temperature to facilitate metal ion uptake. After 24 h, the membrane was removed and rinsed thoroughly with deionized water to eliminate any loosely bound or residual chloride ions. To reduce Ni2+ ions to metallic nickel (Ni0), the membrane was then treated with a freshly prepared 0.01 M NaBH4 solution for 2 h. During this process, the membrane’s color changed from light brown to black, indicating the successful reduction of Ni2+ ions to Ni0 nanoparticles.
4.4. Instrumental Characterizations
The functional groups present in the CA/Ni membrane were identified using FTIR model FTIR-990 China (Fourier transform infrared, Tianjin Labor Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China) spectroscopy. The spectrum was recorded in the range of 4000–400 cm1 to confirm the presence of characteristic bands of cellulose acetate and assess any changes following nanoparticle formation. The morphology and surface characteristics of the prepared membrane were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). This technique provided high-resolution images to visualize the distribution and size of Ni NPs within the cellulose acetate matrix. UV-Vis spectrophotometry (UV2601 China, Beijing Beifen-Ruili Analytical Instrument Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) was used to monitor the degradation of MB. The absorption spectrum was recorded over time at regular intervals to track the progress of the reaction, particularly the decrease in absorbance at 665 nm, which corresponded to the concentration of MB in the solution.
4.5. Degradation Reaction
To investigate the catalytic activity of CA/Ni membranes, the degradation of MB was monitored using UV-Vis spectrophotometry. First, 2.5 mL of 0.05 mM MB solution was transferred to a quartz cuvette, and the baseline absorbance was measured at 665 nm. Next, 0.5 mL of freshly prepared NaBH4 solution was added, followed by the addition of 20 mg of the CA/Ni membrane. The mixture was monitored by recording absorbance at 2 min intervals over 28 min.
The extent of degradation was quantitatively assessed by calculating the percentage of MB degradation over time. This was calculated using the following formula:
where A0 is the initial absorbance of MB at time t = 0 and At is the absorbance at a specific time t. Using this formula, the degradation of MB was calculated at each time point, showing a steady increase in the percentage of degradation as time progressed. By the end of the experiment, 88% of the MB had been degraded after 28 min of reaction time.
4.6. Kinetic Analysis
The degradation kinetics of MB were studied using pseudo-first-order kinetics described by the equation:
where Ct is the final and Co is the initial concentration of the pollutant, and kapp is the apparent rate constant. The linearity of the plot versus time confirmed the pseudo-first-order behavior of the reaction. These methods were employed to validate the degradation data and assess the significance of the results obtained during the catalytic degradation process. The high correlation coefficient values obtained confirmed the consistency of the experimental procedure and the efficiency of the catalyst.
4.7. Effect of Catalyst Dose
To evaluate the effect of the CA/Ni concentration on the degradation of MB, several catalyst loads (20 mg, 30 mg, and 40 mg) were prepared. For each concentration, a 2.5 mL solution of 0.05 mM MB was placed in a quartz cuvette, and its initial absorbance was measured at 665 nm using UV-Vis spectrophotometry. The NaBH4 solution was added (0.5 mL), and the reaction was initiated. The absorbance was monitored at 2 min intervals for 30 min.
4.8. Temperature and pH Optimazation
To assess the influence of pH and temperature on the catalytic degradation of Methylene Blue (MB), a series of experiments was conducted under strictly controlled conditions. For each set, all parameters except the one under investigation were kept constant: the MB concentration was fixed at 0.05 mM, the catalyst dosage was 20 mg (CA/Ni composite), the NaBH4 concentration was held constant, and the reaction volume remained the same.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the effectiveness of cellulose acetate-stabilized nickel nanoparticles (Ni NPs) as a catalyst for the degradation of Methylene Blue (MB) in aqueous solutions. Characterization through FTIR and SEM confirmed the successful incorporation and uniform dispersion of Ni NPs within the cellulose acetate matrix, which are essential for maintaining catalytic activity. UV-Vis spectrophotometric analysis revealed that the Ni NP-stabilized membrane achieved a 68% degradation of MB in 28 min, with the degradation process following pseudo-first-order kinetics, as indicated by a rate constant of 0.0348 min1 and an R2 value of 0.9851. Environmental factors such as temperature and pH were shown to significantly impact degradation efficiency. The highest performance was observed at 35 °C and a neutral pH (7), with efficiency decreasing under acidic (pH 5) and alkaline (pH 9) conditions, and at both lower (25 °C) and higher (45 °C) temperatures. This suggests that temperature and pH play crucial roles in optimizing the catalytic activity of Ni NPs. Overall, the cellulose acetate-stabilized Ni NPs present a promising, efficient, and scalable solution for dye degradation and wastewater treatment, with the potential for practical environmental remediation applications.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data associated with this work are presented in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The author greatly acknowledges the Department of Pharmaceutical Science, College of Pharmacy, Umm Al-Qura University, Makkah, for providing experimental facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Uddin, F. Environmental hazard in textile dyeing wastewater from local textile industry. Cellulose 2021, 28, 10715–10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkaczyk, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Repon, M.R.; Islam, T.; Sarwar, Z.; Rahman, M.M. Impact of textile dyes on health and ecosystem: A review of structure, causes, and potential solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 9207–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Roy, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, A.; Nanda, S.; Rajak, P. Contamination of textile dyes in aquatic environment: Adverse impacts on aquatic ecosystem and human health, and its management using bioremediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohny, B.O.; Ahmad, Z.; Shah, S.A.; Anwar, Y.; Khan, S.A. Cellulose acetate composite films fabricated with zero-valent iron nanoparticles and its use in the degradation of persistent organic pollutants. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A. Review on methylene blue: Its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoye, P.O.; Ajiboye, T.O.; Omotola, E.O.; Oyewola, O.J. Methylene blue dye: Toxicity and potential elimination technology from wastewater. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Aguilar, D.-M.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.-A.; Murillo-Tovar, M.-A.; Vergara-Sánchez, J.; Ramírez-Aparicio, J.; Magallón-Cacho, L.; García-Betancourt, M.-L. Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in carbon nanotubes: A review with bibliometric analysis. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila-Leal, L.D.; Poutou-Piñales, R.A.; Pedroza-Rodríguez, A.M.; Quevedo-Hidalgo, B.E. A brief history of colour, the environmental impact of synthetic dyes and removal by using laccases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.; Weng, Y.; Lam, W.H.; Lai, S.Y. Environmental Footprint Assessment of Methylene Blue Photodegradation using Graphene-based Titanium Dioxide. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2023, 18, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.K.; Maity, K.; Islam, S.S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a glucan of an edible mushroom and study of catalytic activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soomro, R.A.; Sherazi, S.H.; Memon, N.; Shah, M.; Kalwar, N.; Hallam, K.R.; Shah, A. Synthesis of air stable copper nanoparticles and their use in catalysis. Adv. Mater. Lett 2014, 5, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raninga, M.; Mudgal, A.; Patel, V.K.; Patel, J.; Sinha, M.K. Modification of activated carbon-based adsorbent for removal of industrial dyes and heavy metals: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Stark, W.J.; Grass, R.N. Rapid production of a porous cellulose acetate membrane for water filtration using readily available chemicals. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saleh, T.A.; Siddiqui, M.; Agarwal, S. Chromium removal from water by activated carbon developed from waste rubber tires. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, C.; Ali, I.; Chandra, S.; Agarwal, S. Removal of lindane and malathion from wastewater using bagasse fly ash—A sugar industry waste. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pal, D.B.; Mohammad, A.; Alhazmi, A.; Haque, S.; Yoon, T.; Srivastava, N.; Gupta, V.K. Biological remediation technologies for dyes and heavy metals in wastewater treatment: New insight. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, J. Carbon Aerogels Loaded with Noble Metal Nanocrystal Electrocatalysts for Efficient Full Water Splitting. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 12150–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, B.; Fang, X.; Ma, T.; Yu, D.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z. A facile approach to fabricate sustainable and large-scale photothermal polydopamine-coated cotton fabrics for efficient interfacial solar steam generation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 18109–18120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Khan, S.B.; Kamal, T.; Alamry, K.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Sobahi, T.R. Synthesis and characterization of metal nanoparticles templated chitosan-SiO2 catalyst for the reduction of nitrophenols and dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Sato, M.; Sato, Y.; Ando, N.; Takayama, T.; Fujita, M.; Ishihara, M. Synthesis and application of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for the prevention of infection in healthcare workers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Kaur, H.; Singh, J.; Matharu, A.S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Bechelany, M. Recent advances in green synthesis of Ag NPs for extenuating antimicrobial resistance. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Khan, N.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, M.; Hemeg, H.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Enhanced catalytic reduction/degradation of organic pollutants and antimicrobial activity with metallic nanoparticles immobilized on copolymer modified with NaY zeolite films. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Khan, S.A.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, N.; ur Rehman, M.; Jabli, M.; Khan, S.B. Biomass impregnated zero-valent Ag and Cu supported-catalyst: Evaluation in the reduction of nitrophenol and discoloration of dyes in aqueous medium. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 938, 121756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.B. A template of cellulose acetate polymer-ZnAl/C layered double hydroxide composite fabricated with Ni NPs: Applications in the hydrogenation of nitrophenols and dyes degradation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, N.; Irum, U.; Farooq, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Cellulose acetate-Ce/Zr@ Cu0 catalyst for the degradation of organic pollutant. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; Farooq, A.; Asiri, A.M. A facile synthesis of CuAg nanoparticles on highly porous ZnO/carbon black-cellulose acetate sheets for nitroarene and azo dyes reduction/degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Wang, X.; Tam, K.C. Gold nanoparticles stabilized by poly (4-vinylpyridine) grafted cellulose nanocrystals as efficient and recyclable catalysts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 182, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Devi, A.; Bhattacharyya, K.G. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue in aqueous solution with silver-kaolinite-titania nanocomposite under visible light irradiation. J. Nanostructures 2022, 12, 426–445. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, N.; Shahida, B.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Saeeduddin; Sheikh, Z.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Alraddadi, H.M.; Fagieh, T.M.; Khan, S.B. Anchoring zero-valent Cu and Ni nanoparticles on carboxymethyl cellulose-polystyrene–block polyisoprene–block polystyrene composite films for nitrophenol reduction and dyes degradation. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Yan, X.; Hu, X.; Feng, R.; Zhou, M. Synthesis of silver decorated silica nanoparticles with rough surfaces as adsorbent and catalyst for methylene blue removal. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 89, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Koduru, J.R.; Yang, J.-K. Potential degradation of methylene blue (MB) by nano-metallic particles: A kinetic study and possible mechanism of MB degradation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).