Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Cu-Rich Layered Double Hydroxides and Improved Catalytic Performances for Water–Gas Shift Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
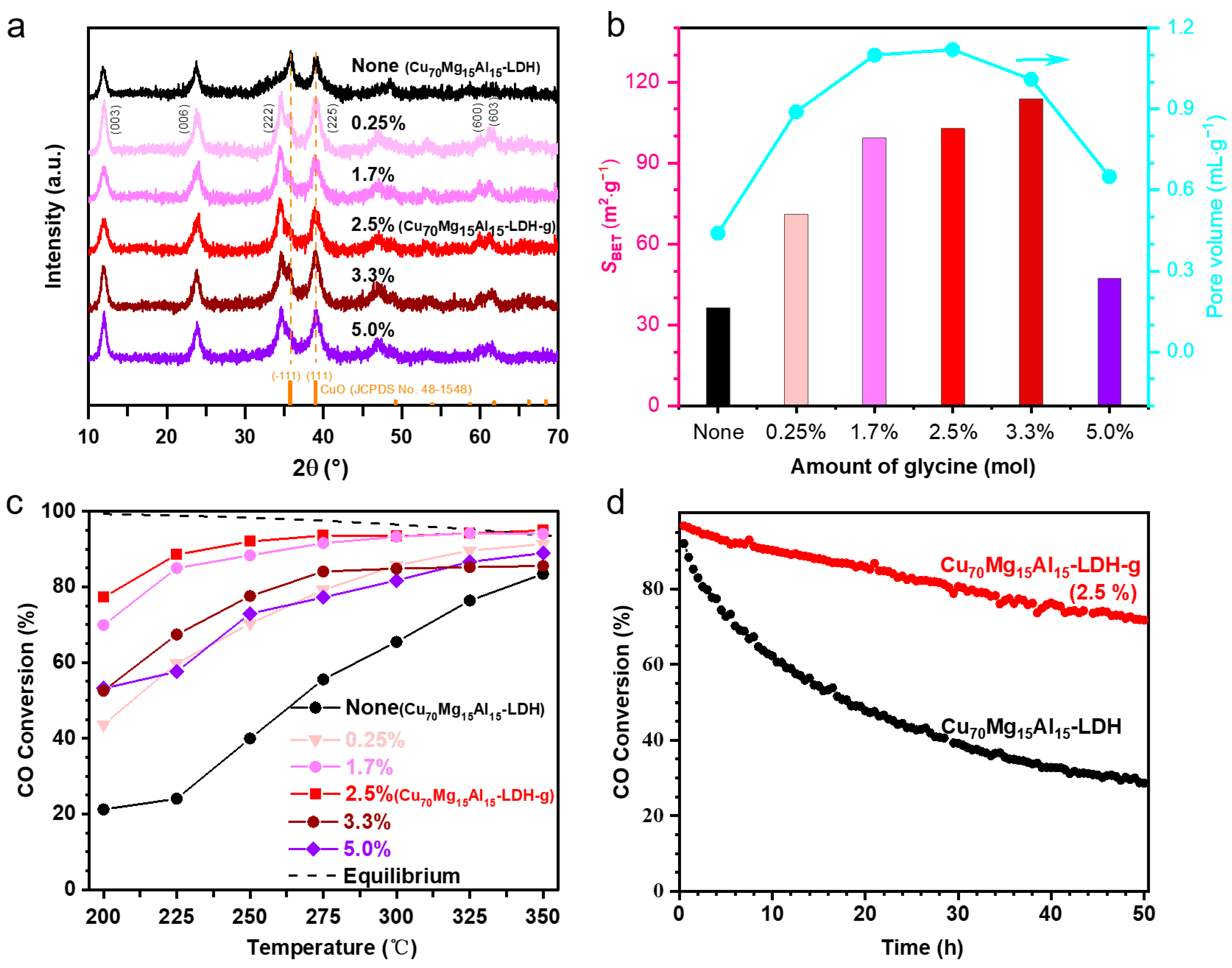
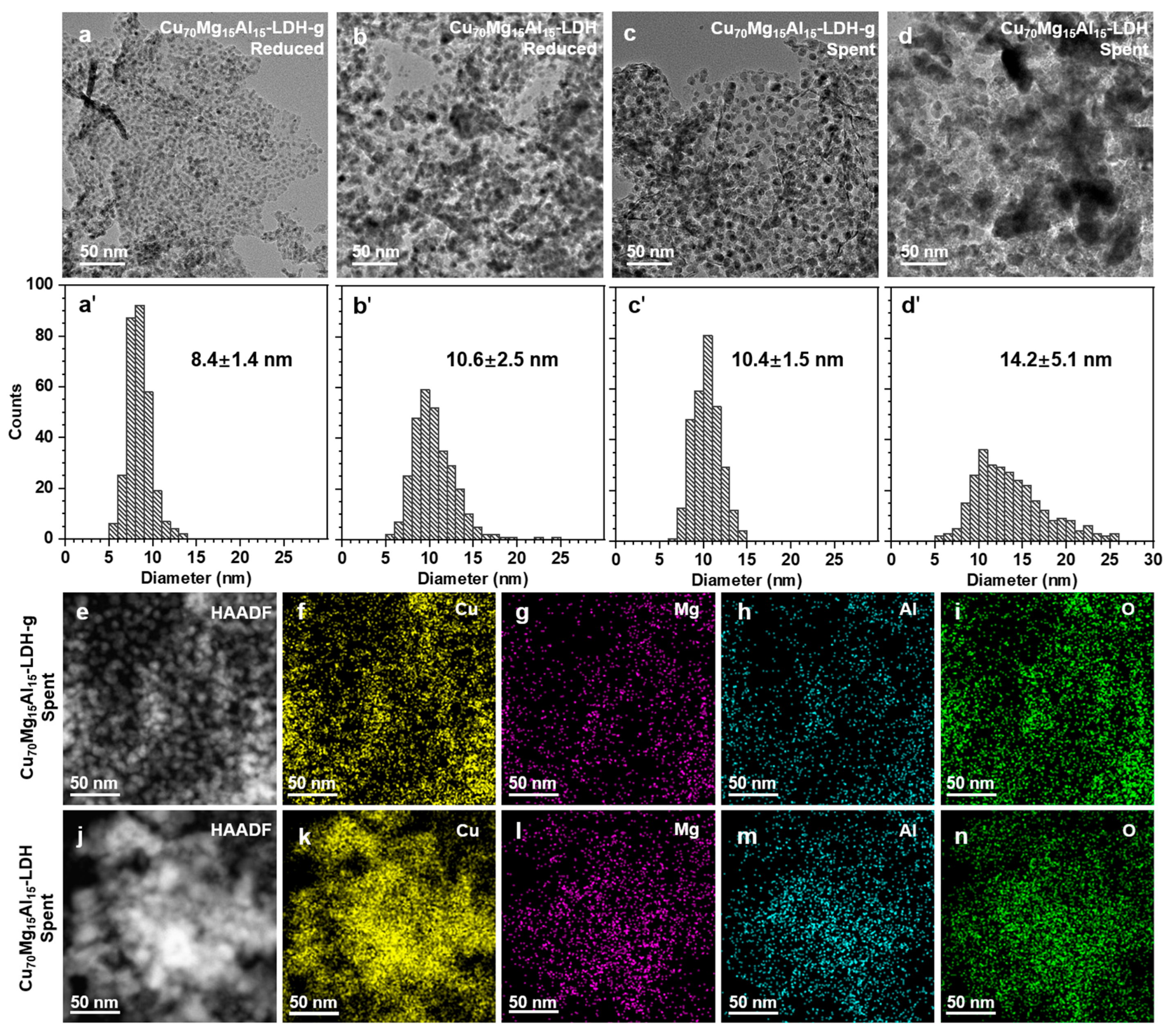
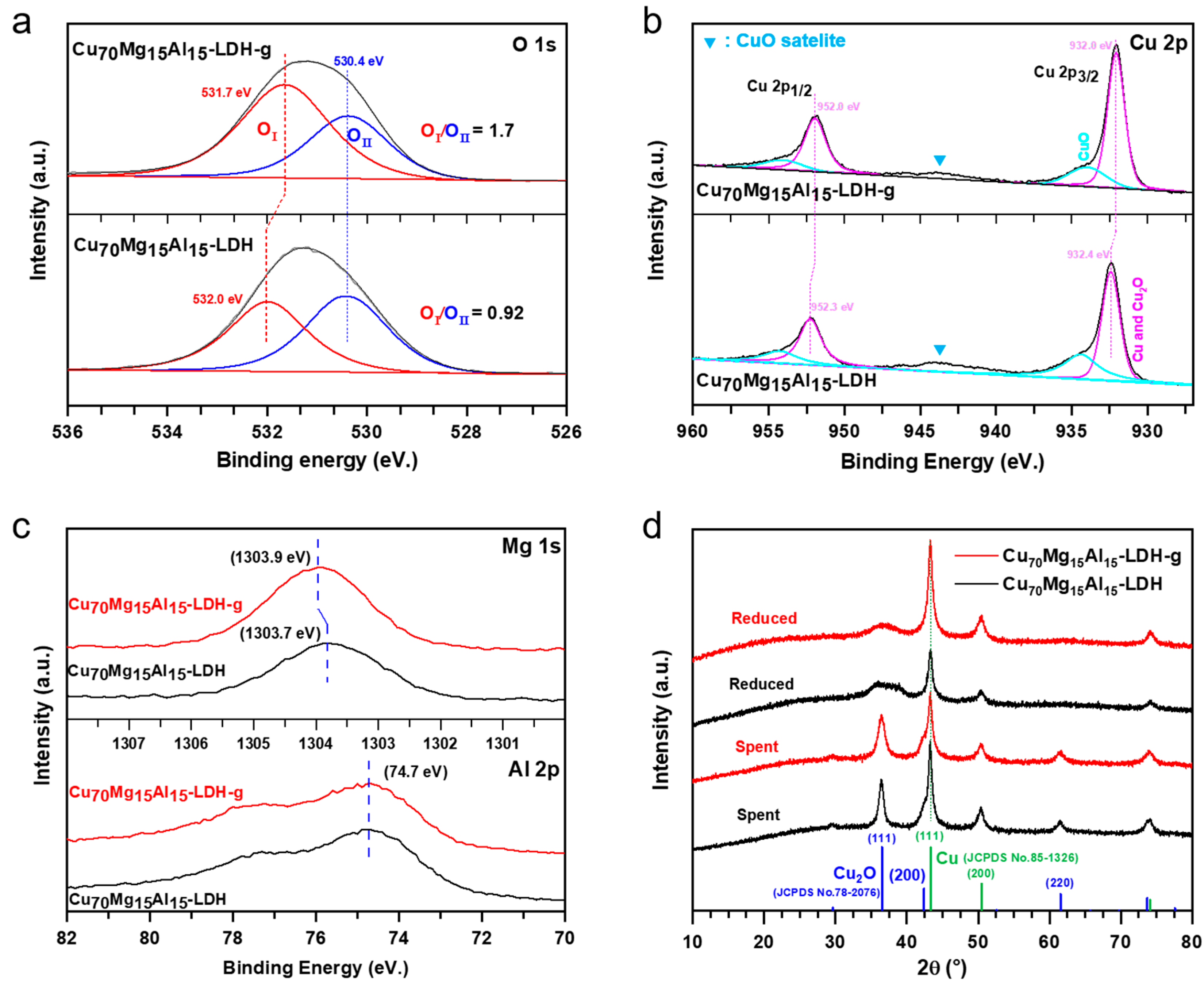
2. Results and Discussion

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Samples
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, M.; Wei, M. Layered double hydroxide-based catalysts: Recent advances in preparation, structure, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, D. Supported catalysts based on layered double hydroxides for catalytic oxidation and hydrogenation: General functionality and promising application prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5291–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, J.; Niu, H.; Li, R.; Liang, C. Structure evolution of Ni-Cu bimetallic catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides for selective hydrogenation of furfural to tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 12953–12965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, G.; Zheng, L.; Li, F. Synergistic surface-interface catalysis in potassium-loaded Cu/CoOx catalysts to boost ethanol production from CO2 hydrogenation. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2025, 17, 13747–13761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, S.; Guan, R.; Jin, Z.; Xiao, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, P. Modulating the surface concentration and lifetime of active hydrogen in Cu-based layered double hydroxides for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 12042–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; El-Sharkawy, R.M.; Allam, E.A.; Nabil, G.M.; Louka, F.R.; Salam, M.A.; Elsayed, S.M. Recent progress in water decontamination from dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other miscellaneous nonmetallic pollutants by layered double hydroxide materials. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 57, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelalak, R.; Hassani, A.; Heidari, Z.; Zhou, M. State-of-the-art recent applications of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) material in Fenton-based oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Yang, B.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Wen, X.-D.; et al. Plasmonic Cu nanoparticles for the low-temperature photo-driven water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202219299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Shen, R.; Liu, T.; Gao, J.; Sun, K.; Li, B.; et al. For more and purer hydrogen-the progress and challenges in water gas shift reaction. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 83, 363–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehimi, L.; Alioui, O.; Benguerba, Y.; Yadav, K.K.; Bhutto, J.K.; Fallatah, A.M.; Shukla, T.; Alreshidi, M.A.; Balsamo, M.; Badawi, M.; et al. Hydrogen production by the water-gas shift reaction: A comprehensive review on catalysts, kinetics, and reaction mechanism. Fuel Process. Technol. 2025, 267, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhan, Y.; Jiang, L. Characterization and catalytic performance of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 water-gas shift catalysts derived from Cu-Zn-Al layered double hydroxides. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 3175–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; Reina, T.R.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Gold promoted Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts prepared from hydrotalcite precursors: Advanced materials for the wgs reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 201, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Fang, L.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Ni, Z. Water-gas shift reaction catalyzed by layered double hydroxides supported Au-Ni/Cu/Pt bimetallic alloys. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 272, 118949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Kasatkin, I.; Kühl, S.; Weinberg, G. Phase-Pure Cu,Zn,Al Hydrotalcite-like materials as precursors for copper rich Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarelli, C.; Molinari, C.; Faure, R.; Fornasari, G.; Gary, D.; Schiaroli, N.; Vaccari, A. Novel Cu-Zn-Al catalysts obtained from hydrotalcite-type precursors for middle-temperature water-gas shift applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 155, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Geng, J.; Lei, H.; Zhuo, O. Interfaces and oxygen vacancies-enriched catalysts derived from Cu-Mn-Al hydrotalcite towards high-efficient water-gas shift reaction. Molecules 2023, 28, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginés, M.J.L.; Amadeo, N.; Laborde, M.; Apesteguía, C.R. Activity and structure-sensitivity of the water-gas shift reaction over Cu-Zn-Al mixed oxide catalysts. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 1995, 131, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.M.V.M.; Ferreira, K.A.; Neto, O.R.d.M.; Ribeiro, N.F.P.; Schmal, M. Copper-based catalysts prepared from hydrotalcite precursors for shift reaction at low temperatures. Catal. Today 2008, 133–135, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, N.; Wang, N.; Zhou, B.; Yu, J.; Song, B.; Yin, P.; Yang, Y. Metal-support interaction induced ZnO overlayer in Cu@ ZnO/Al2O3 catalysts toward low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 5509–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cai, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, M.; Jiang, L. Layered double hydroxides as precursors of Cu catalysts for hydrogen production by water-gas shift reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 10016–10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.; Yoon, H.J.; Yoon, C.W.; Lee, K.B. Water gas shift and sorption-enhanced water gas shift reactions using hydrothermally synthesized novel Cu-Mg-Al hydrotalcite-based catalysts for hydrogen production. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2021, 145, 111064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Qin, X.; Yang, Y.; Lv, M.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Ren, Z.; Song, B.; Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; et al. Highly stable Pt/CeO2 catalyst with embedding structure toward water-gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, K.; Porter, W.N.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Chen, J.G. Role of H2O in catalytic conversion of C1 molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2857–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, K. Low-temperature water-gas shift reaction enhanced by oxygen vacancies in Pt-loaded porous single-crystalline oxide monoliths. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, B.J.; Shim, J.O.; Jang, W.J.; Roh, H.S. Unravelling the active sites and structure-activity relationship on Cu-ZnO-Al2O3 based catalysts for water-gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2023, 325, 122320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.; An, K.; Cho, S. Versatile layered hydroxide precursors for generic synthesis of Cu-based materials. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Rives, V.; Knözinger, H. High-temperature transformations of Cu-rich hydrotalcites. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yin, P.; Wang, W.; Shao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, M. Synergetic effect of Cu0-Cu+ derived from layered double hydroxides toward catalytic transfer hydrogenation reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2022, 314, 121515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Tran, T.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, G. Synthesis, characterization and activity evaluation of Cu-based catalysts derived from layered double hydroxides (LDHs) for DeNOx reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, M.; Patzschke, C.F.; Zheng, L.; Zeng, D.; Gavalda Diaz, O.; Ding, N.; Chien, K.H.H.; Zhang, Z.; Wilson, G.E.; Berenov, A.V.; et al. Precursor engineering of hydrotalcite-derived redox sorbents for reversible and stable thermochemical oxygen storage. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Stenger, H.G. Water gas shift reaction kinetics and reactor modeling for fuel cell grade hydrogen. J. Power Sources 2003, 124, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.S.; Song, R.; Cao, T.; Luo, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, W.X.; Huang, W. The most active Cu facet for low-temperature water gas shift reaction. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.L.; Li, S.Q.; Ma, C.; Fu, X.P.; Xu, Y.S.; Wang, W.W.; Dong, H.; Jia, C.J.; Wang, F.R.; Yan, C.H. Promoting molecular exchange on rare-earth oxycarbonate surfaces to catalyze the water-gas shift reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Yang, C.; Shao, W.P.; Cai, L.H.; Wang, W.W.; Jin, Z.; Jia, C.J. Construction of stabilized bulk-nano interfaces for highly promoted inverse CeO2/Cu catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Silva, T.; Assaf, J.M.; Lucrédio, A.F.; Reis, C.G.M.; Almeida, K.A. Influence of La2O3 addition on CuO/CeO2 Catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Langmuir 2025, 41, 3108–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.C.; Li, X.C.; Xie, Z.W.; Yuan, C.Y.; Wang, D.J.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, H.C.; Zhang, Y.W. Strong metal-support interactions between highly dispersed Cu+ species and ceria via mix-MOF pyrolysis toward promoted water-gas shift reaction. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 91, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Zhuge, K.; Ma, X.; Mou, X.; Ren, M.; Chang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, L.; Lin, R.; Ding, Y. Interfacial effects of Cu/Fe3O4 in water-gas shift reaction: Role of Fe3O4 crystallite sizes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 78, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza Fuentes, E.; Rodríguez Ruiz, J.; Massin, L.; Cadete Santos Aires, F.J.; Da Costa Faro, A.; Assaf, J.M.; Rangel, M.d.C. Characterization and performance within the wgs reaction of Cu catalysts obtained from hydrotalcites. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 32455–32470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, A.E.; Smith, R.M. Critical Stability Constants: Second Supplement; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 6, pp. 2, 301, 428, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, J.; López-Durán, D.; Liu, Z.; Duchoň, T.; Evans, J.; Senanayake, S.D.; Crumlin, E.J.; Matolín, V.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Ganduglia-Pirovano, M.V. In Situ and theoretical studies for the dissociation of water on an active Ni/CeO2 catalyst: Importance of strong metal-support interactions for the cleavage of O-H bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3917–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Peng, M.; Tang, H.; Zhou, W.; Qiao, B.; Ma, D. Renaissance of strong metal-support interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2290–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Soldemo, M.; Degerman, D.; Lömker, P.; Schlueter, C.; Nilsson, A.; Amann, P. Direct evidence of subsurface oxygen formation in oxide-derived Cu by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202111021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesinger, M.C. Advanced analysis of copper X-ray photoelectron spectra. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinós, J.P.; Morales, J.; Barranco, A.; Caballero, A.; Holgado, J.P.; González-Elipe, A.R. Interface effects for Cu, CuO, and Cu2O deposited on SiO2 and ZrO2. XPS determination of the valence state of copper in Cu/SiO2 and Cu/ZrO2 catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 6921–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhi, G.; Chen, C.; Luo, Y.; Lin, X.; Jiang, L. Copper phyllosilicate-derived Cu catalyst for the water-gas shift reaction: Insight into the role of Cu+-Cu0 and reaction mechanism. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 5546–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Wang, G.C. Water-gas shift reaction over CuxO/Cu(111) (x < 2) from a DFT-MKM-kMC study. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 4239–4250. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Kang, J.; Yu, Z.; Tian, J.; Gong, Z.; Jia, A.; You, R.; Qian, K.; He, S.; et al. The active sites of Cu–ZnO catalysts for water gas shift and CO hydrogenation reactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagypál, I.; Debreczeni, F. NMR relaxation studies in solution of transition metal complexes. XI. Dynamics of equilibria in aqueous solutions of the copper(II)-ammonia system. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1984, 81, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, X.; Cui, H.; Li, F.; Lei, H.; Zhuo, O. Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Cu-Rich Layered Double Hydroxides and Improved Catalytic Performances for Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts 2025, 15, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060546
Liu S, Hu Y, Zhang Q, Tan X, Cui H, Li F, Lei H, Zhuo O. Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Cu-Rich Layered Double Hydroxides and Improved Catalytic Performances for Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts. 2025; 15(6):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060546
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shicheng, Yinjie Hu, Qian Zhang, Xia Tan, Haonan Cui, Fei Li, Huibin Lei, and Ou Zhuo. 2025. "Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Cu-Rich Layered Double Hydroxides and Improved Catalytic Performances for Water–Gas Shift Reaction" Catalysts 15, no. 6: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060546
APA StyleLiu, S., Hu, Y., Zhang, Q., Tan, X., Cui, H., Li, F., Lei, H., & Zhuo, O. (2025). Synthesis of Well-Crystallized Cu-Rich Layered Double Hydroxides and Improved Catalytic Performances for Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts, 15(6), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060546





