Abstract
The critical need to enhance the quality of indoor air leads to the improvement of catalyst activity for the removal of formaldehyde. Sepiolite can be utilized in catalytic reactions for its unique structure, composition and high surface area. The adhesion between sepiolite fibers and the blocked microporous channel (by impurities) demands the activation of natural sepiolite through acid treatment. This treatment successfully produces acid-modified sepiolite Pt-supported samples. The impacts of different acid concentrations, Pt loading content and calcination temperature on catalytic activity for formaldehyde (HCHO) oxidation are studied. The catalytic activity of HCHO is characterized and evaluated by techniques including specific surface area, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectrum, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The results show the maximum specific area of sepiolite at the optimized 0.06 M acid concentration. Among all the prepared samples, the 0.02Pt/Sep catalyst calcined at 500 °C exhibits the highest catalytic activity for the oxidation of HCHO.
1. Introduction
Formaldehyde (HCHO) is one of the main invisible pollutants in the indoor environment [1]. Reportedly, people spend more than 80% of their life in the indoor environment, and being in an environment containing HCHO for a long time will lead to allergic reactions or even poisoning [2]. Therefore, the development of cost-effective alternatives for the elimination of HCHO from indoor environments is crucial for human health [3,4,5]. The conventional procedures for HCHO exclusion include physical adsorption [6,7,8,9], photocatalytic degradation [10,11,12], plasma purification [13,14,15] and catalytic oxidation [16,17,18]. Among them, catalytic oxidation has been identified as the most efficient approach due to its non-toxic by-products and high activity under relatively mild conditions [19,20,21]. Heretofore, most studies about HCHO catalytic oxidation have focused on supported noble metal and metal oxide catalysts [22].
Supported noble metal catalysts are beneficial for their excellent stability, high activity, recyclability and no secondary pollutants. Meanwhile, their excellent catalytic performance at relatively low temperatures [23] makes them important. Chen et al. [16] optimized Pt/MnO2-BN with excellent catalytic activity for HCHO at room temperature. Wang et al. [2] found the advantages of nanosized Pt particles and strong metal support interaction between Pt and Fe2O3 for the catalytic degradation of HCHO at room temperature. Lei et al. [24] reported that the low-temperature HCHO decomposition of Pt/CTA is obtained via good Pt dispersion and the unique adsorption properties of cellulose triacetate (CTA). Substantially, platinum (noble metal) shows high dispersion and catalytic oxidation activity, which promote the effective decomposition of HCHO at room temperature.
The improvement in the mechanical properties of catalysts and the better surface area for ingredients’ activation is provided by supporting materials [25] such as silica (SiO2), alumina (Al2O3) and titania (TiO2) [26]. However, the activity still does not compensate for its activation cost. Therefore, the development of more active and sustainable supported catalysts is necessary. Sepiolite is a fibrous mineral with alternating blocks in the direction of the fibrous tunnels. The center of block structure is composed of MgO that is surrounded by two tetrahedral SiO2 components [27]. Sepiolite promises activity for various catalytic reactions due to its peculiar pore structure [28], special groups on the surface [29], abundant storage, non-toxicity, low cost and interior channels [30]. For example, Karaoglu et al. [31] reported an active basic catalyst obtained via KOH impregnation onto a sepiolite support for biodiesel production. Gao et al. [13] synthesized a NiO/sepiolite hybrid for application in dye removal in wastewater.
Acid treatment can increase the surface area of sepiolite [32], while keeping the original structure unchanged. We treated sepiolite with different concentrations of hydrochloric (HCl) acid and obtained optimized sepiolite, noted as Sep. The Pt nanoparticles were supported on Sep to obtain a Pt/Sep catalyst.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Textural Properties of Modified Sepiolite
The BET experiment confirmed the catalyst’s porous structure and determined the surface area and pore size distribution. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of sepiolite and modified sepiolite, shown in Figure 1a, belongs to type IV isotherms, with a type of H3 hysteresis loop, indicating porous materials [33]. The adsorption performance of sepiolite was significantly improved by acid treatment. The hysteresis loop closed at P0 = 0.4, indicating small mesopores in the sample. The pore size distribution of the sepiolite and modified sepiolite was approximately located at 3.8 nm, as indicated by the corresponding pore size distribution plots. Moreover, modified sepiolite demonstrated certain numbers of micropores and an increase in mesopores after acid modification.
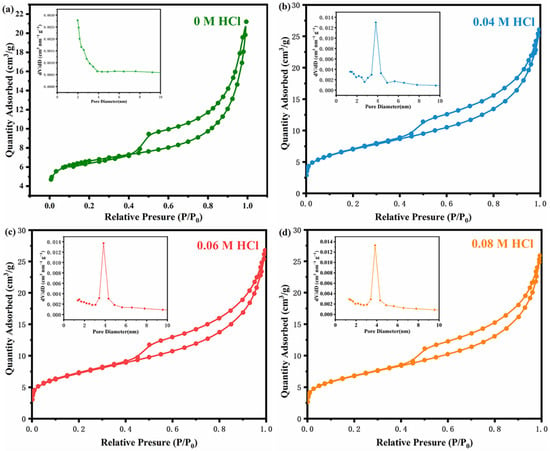
Figure 1.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of (a) sepiolite, (b) sepiolite modified by 0.04 M HCl, (c) sepiolite modified by 0.06 M HCl and (d) sepiolite modified by 0.08 M HCl. The insets are the corresponding pore size distribution plots.
The BET specific surface area and pore volume of the sepiolite after acid treatment with different concentrations are given in Table 1. Results showed an increase in the specific surface area of sepiolite with acid treatment, which then decreased with the acid concentration. The acid treatment converted the the Si-O-Mg-O-Si bond into a Si-OH- bond. Noticeably, the pore size and surface area increased with the internal framework destruction of sepiolite, opening internal channels and stripping fibers at different angles. The acid concentration of 0.06 M maximized the specific surface area, with 25.581 m2/g, and provided more active sites and interfaces for HCHO adsorption. Sometimes, HCl corrodes the sepiolite seriously and decreases the specific surface area. Sepiolite modified by 0.06 M HCl (noted as Sep) provided the largest specific surface area and was chosen for subsequent studies.

Table 1.
The BET specific surface area and pore volume of sepiolite after acid treatment with different concentrations.
2.2. The Influence of Calcination Temperature on Material Structure
The hybrid sample prepared with 0.02 M chloroplatinic acid-impregnated solution (noted as 0.02Pt/Sep) was selected for further heat treatment. The samples heat-treated at 400, 500, 600 and 700 °C are denoted as 0.02Pt/Sep-400, 0.02Pt/Sep-500, 0.02Pt/Sep-600 and 0.02Pt/Sep-700, respectively. The XRD patterns in Figure 2 show the exact phase composition, with mainly sepiolite, calcite and quartz for all samples. The XRF results showed that the major components of sepiolite are CaO, SiO2 and MgO, with a composition of 53.479%, 32.529% and 13.523%. However, the XRD patterns of 0.02Pt/Sep-700 showed the disappearance of the characteristic peaks of CaCO3 located at 2θ = 18.1°, 28.7° and 34.1°, corresponding to Ca(OH)2 [34]. This suggested the decomposition of CaCO3 to form CaO, according to the following chemical reaction:
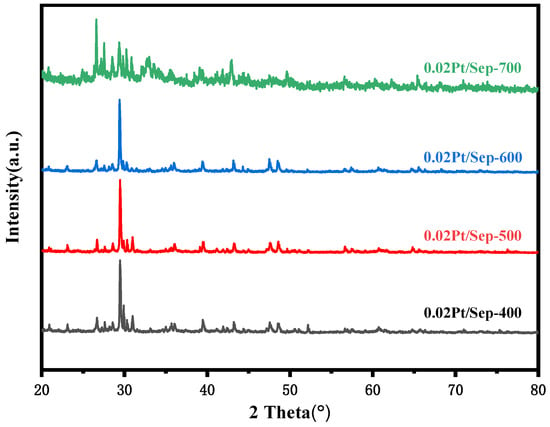
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of 0.02Pt/Sep treated at different treatment temperatures from 400 to 700 °C.
2.3. The Influence of Pt Loading on Structure and Morphology
The XRD analysis examined the crystal structure of samples. Figure 3a displays the characteristic peaks of Sep localized at 2θ = 26.6°, 29.3°, 42.5° and 44.5°. The XRD patterns of the 0.02Pt/Sep samples indicated the unchanged structure and lack of diffraction peak of Sep after Pt loading, reflecting the evenly dispersed Pt nanoparticles. The XRD patterns of samples loaded with different concentrations of platinum are shown in Figure 3b. The absence of diffraction peaks of platinum in all samples is mainly due to the low content and even dispersion of Pt nanoparticles.
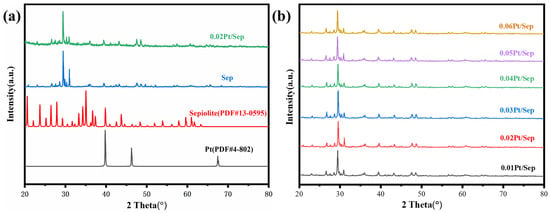
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of (a) 0.02Pt/Sep, Sep, Sepiolite and Pt; (b) 0.01Pt/Sep, 0.02Pt/Sep, 0.03Pt/Sep, 0.04Pt/Sep, 0.05Pt/Sep and 0.06Pt/Sep.
The functional groups present on the surfaces of sepiolite, Sep, 0.02Pt/Sep-fresh and 0.02Pt/Sep-used were determined by FTIR spectroscopy (Figure 4). The peaks after acid treatment were found at 1661 and 3442 cm−1, which were ascribed to δ (H2O) and the stretching vibration absorption peak of the OH group, respectively. There is a hydrogen bond between HCHO and the hydroxyl group [35], which can facilitate the adsorption of HCHO. Thus, the oxidation procession was accelerated. The similar characteristic peaks for Sep and 0.02Pt/Sep show the unaffected structure after Pt nanoparticle loading. The peaks attributed to H2O and OH− disappeared after HCHO exposure, which shows their involvement in the reaction (oxidation process), and the formation of a new peak at 2967 cm−1 is ascribed to the formate (CHO2−) species [27] on the sample surface as an intermediate.
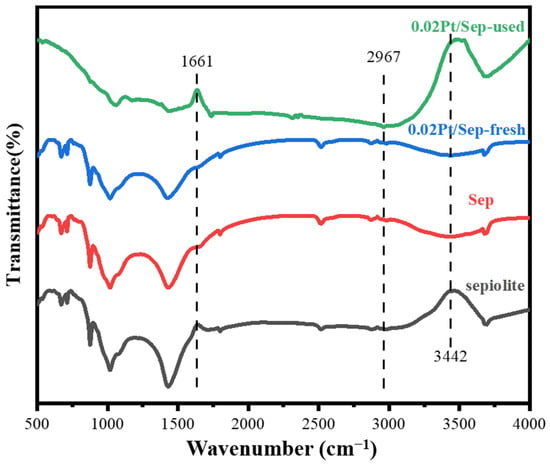
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra of sepiolite, Sep, 0.02Pt/Sep-used and 0.02Pt/Sep-fresh.
High-resolution XPS spectra of Pt 4f of the 0.02Pt/Sep sample are shown in Figure 5. The spectrum of Pt 4f can be fitted to Pt 4f7/2 (71.04 and 74.51 eV) and Pt 4f5/2 (72.54 and 75.74 eV) [36], because of their spin orbit interaction, matching with Pt0 and Pt ions (Pt2+ and Pt4+), separately.
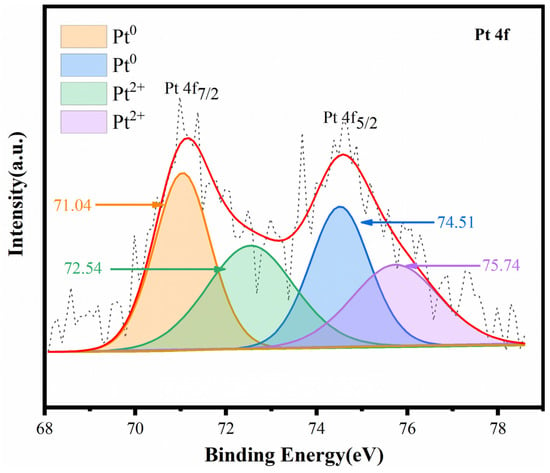
Figure 5.
High-resolution XPS spectra of Pt 4f for 0.02Pt/Sep.
Figure 6 shows the O-1s XPS spectra of Sep and 0.02Pt/Sep. The presence of O in [SiO4] tetrahedra and [Mg(Al)O6] octahedra (532.1 eV) [37] is confirmed by the peaks in Figure 6a. The binding energy of O-1s in the 0.02Pt/Sep sample is shifted lower relative (531.86 eV) to Sep (Figure 6b). It indicates the electron density around the O atom due to Pt nanoparticle loading and proves the chemical bond between Sep and Pt, rather than the physical adsorption. The peak at 532.8 eV was attributed to water adsorption.
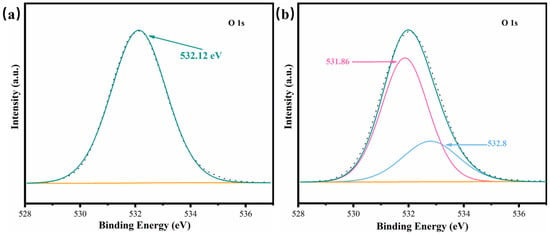
Figure 6.
(a) O-1s high-resolution XPS scans (dark line) and (b) corresponding fittings of Sep and 0.02Pt/Sep (colored lines).
Figure 7 shows the Pt concentration’s effect on the morphology of Sep. The micrographs in Figure 7a,e,i prove the Pt nanoparticles’ distribution over Sep and show the fibrous structure of Sep. Meanwhile, for Pt nanoparticles attached to the fibers, the fibrous morphology was still retained. The nanoparticles’ size distribution on the fibers was very narrow, with a size of approximately 2.77 nm in diameter for the 0.01Pt/Sep sample. The 0.02Pt/Sep sample showed Pt nanoparticles with a 3.16 nm size distribution. Moreover, agglomeration is observed with the increase in Pt loading, as in the case of the 0.05Pt/Sep sample. The crystalline Pt nanoparticles on the above-mentioned three samples are depicted in Figure 7b,f,j. The measured lattice spacing associated with the (111) plane is 0.2285, 0.2253 and 0.2315 nm, respectively. Furthermore, the EDS maps corresponding to 0.01Pt/Sep, 0.02Pt/Sep and 0.05Pt/Sep are shown in Figure 7d,h,l, in which Mg and Si are associated with Sep, indicating the successful loading of platinum nanoparticles on the Sep surface.
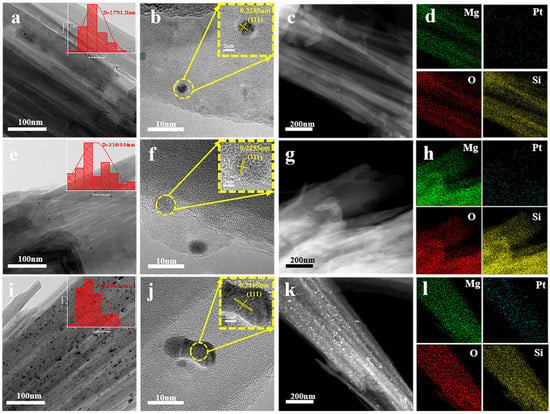
Figure 7.
Structural and morphological characterization of 0.01Pt/Sep, 0.02Pt/Sep and 0.05Pt/Sep samples: (a,e,i) TEM images, (b,f,j) HRTEM images, (c,g,k) STEM-HAADF images, (d,h,l) EDS elemental mapping.
2.4. HCHO Catalytic Oxidation
2.4.1. Effect of Pt Loading
The catalytic oxidation of HCHO by the Pt/Sep catalysts with different Pt loadings at ambient temperature is shown in Figure 8 (the values of 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 and 60 correspond to concentrations of 0.01 M to 0.06 M of chloroplatinic acid solution). The 0.02Pt/Sep catalyst exhibited the highest HCHO oxidation efficiency (around 52%), whereas the 0.01Pt/Sep catalyst could partly oxidize the HCHO, by 47%. However, the adsorbed HCHO was hardly oxidized to CO2 due to the shortage of Pt nanoparticles. Moreover, the 0.03Pt/Sep, 0.04Pt/Sep, 0.05Pt/Sep and 0.06Pt/Sep catalysts possess certain catalytic ability for the oxidation of HCHO to CO2, but it is still lower than the efficiency of 0.02Pt/Sep. This is because excessive loading can cause the agglomeration of Pt nanoparticles [38], by which the reactive sites and active surface were reduced and the Sep nanofibers’ pores and tunnels were also blocked. This confirms the optimized Sep acid treatment with 0.02 M solution.
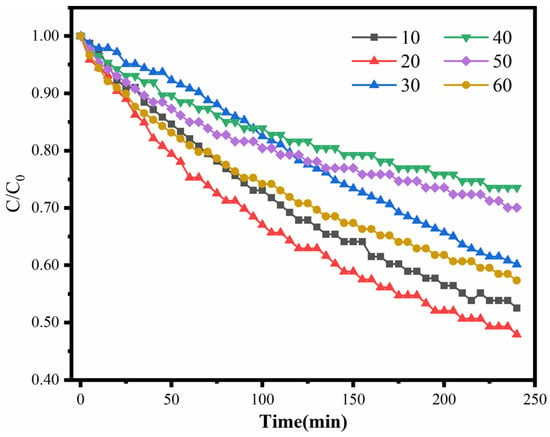
Figure 8.
The catalytic oxidation of HCHO by Pt/Sep catalysts with varied Pt loading.
2.4.2. Effect of Calcination Temperature
Figure 9 shows the catalytic oxidation of HCHO with the 0.02Pt/Sep catalyst obtained at different calcination temperatures. Among the catalysts calcined at 400, 500, 600 and 700 degrees, the catalyst calcined at 500 degrees had the best performance, and the formaldehyde degradation rate was 52%. A suitable temperature is beneficial to the reduction of the platinum precursor and the improvement of the catalytic performance of the catalyst, whereas higher temperatures (600 and 700 °C) destroy the basic structure of Sep nanofibers. Furthermore, a higher temperature leads to grain growth [39], which reduces the catalytic active sites, resulting in lower HCHO reduction. Therefore, 500 °C is regarded as the optimal calcination temperature for the 0.02Pt/Sep sample.
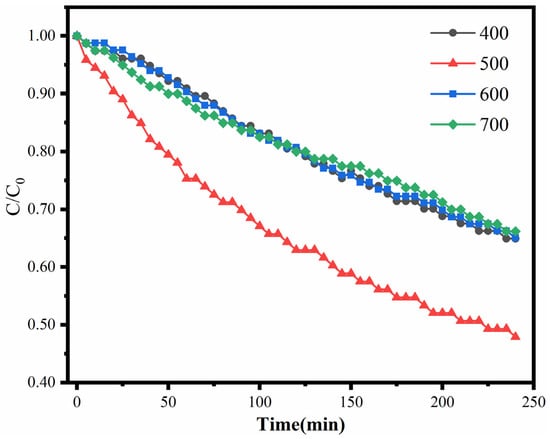
Figure 9.
The catalytic oxidation of HCHO with 0.02Pt/Sep catalyst obtained at different calcination temperatures.
2.5. Catalyst Oxidation Mechanism
Figure 10 demonstrates a possible mechanism for the catalytic oxidation of HCHO with the 0.02Pt/Sep sample. Firstly, HCHO, H2O and O2 are adsorbed onto 0.02Pt/Sep. Moreover, O2 is excited by the Pt nanoparticles to oxygen radicals. Later, the oxygen radicals oxidize HCHO and H2O to dioxymethylene (DOM) and OH− ions, respectively. DOM reacts with -OH to create formate species, which further react with OH− to form CO2 and H2O. The OH− ions on the sepiolite surface are conductive to the adsorption of HCHO throughout the mechanism. The catalyst’s wettability plays a critical role in the desorption and transfer of water [40], by the current water forming reaction:
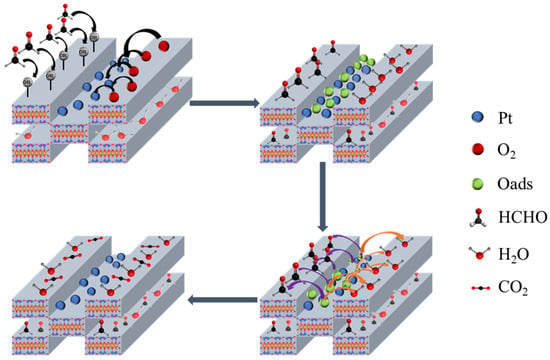
Figure 10.
Mechanism for catalyst oxidation of HCHO.
Therefore, the physical and chemical properties of the sepiolite support enhance the catalytic oxidation of HCHO.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation
3.1.1. Sepiolite Acid Treatment
Sepiolite powder (Mg8 (H2O)4 [Si6O16]2 (OH)4·8H2O, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) (1 g) was added to 20 mL HCl (37%, Aladdin, Shanghai, China) with different concentrations (0.04 M, 0.06 M and 0.08 M) at 25 °C for 3 h. Later, the samples were separated, washed and dried in an oven at 75 °C for 12 h. The resulting acid-treated sepiolite samples were named sepiolite-0.04, sepiolite-0.06 and sepiolite-0.08, according to their corresponding 0.04, 0.06 and 0.08 M acid concentration treatments, respectively.
3.1.2. Catalyst Preparation
The acid-modified sepiolite samples were stirred at room temperature for 1 h in chloroplatinic acid solution for the purpose of vacuum impregnation. Then, the samples were filtered, rinsed three times with deionized water and dried at 60 °C for 12 h. Finally, the samples were calcined under N2/H2 flow at 500 °C for 2 h to obtain the Pt/Sep catalyst.
3.2. Characterization
The X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy instrument from RIGAKU ZSX Priums (Tokyo, Japan) was employed to evaluate the composition of sepiolite samples. The surface area, pore volume and pore size distributions of the catalysts were measured with an ASAP 2020 micromeritics instrument (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). The XRD patterns of powdered samples were obtained with a PANalytical X’ Pert PRO, Almelo, Holland. FTIR spectra analysis was carried out on Spectrum One (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA), and XPS spectra of the samples were obtained, where XPS results were recorded on a PHI 5000 VersaProbe III electron spectroscope (ULVAC-PHI, Chigasaki, Japan). Morphological analysis of samples was carried out via transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Model FEI Tecnai G2 F30, Portland, OR, USA) and chemical analysis was performed using ICP-OES (Agilent725-Es, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
3.3. Catalytic Activity Tests
A box with a legitimate opening and closing mechanism with a connecting metal rod was filled with 1 g of Pt/Sep catalyst and enclosed in an airtight chamber. Then, 10 mL HCHO was rapidly volatilized when added to the heated aluminum foil. The constant signals on the attached detector (PN-2000-CH2O; range: 0–500 ppm; accuracy: 0.1 ppm) showed the complete and even dispersion of HCHO in the airtight chamber, and the connecting rods of the lid helped to evenly expose the Pt/Sep in HCHO gas. Finally, the variation in HCHO concentration was recorded by the attached detector.
4. Conclusions
We prepared Pt/Sep catalysts through the impregnation route, where Pt nanoparticles were formed by calcination and combined with the Sep, having a higher specific area after acid treatment for the oxidation of HCHO at very low loading (0.16 wt.%). The acid-treatment with 0.6 M HCl solution maximized the surface area to 25.581 m2/g. The sites for HCHO oxidation were increased by acid treatment, as illustrated by the characteristic band of the hydroxyl group in the FTIR results. The oxidation results with different Pt loading content and calcination temperatures were discussed. The results showed the enhanced and optimal catalytic properties for sepiolite impregnated with 0.02 M solution and at a 500 °C calcination temperature, demonstrating 52% efficiency.
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written with the contributions of all authors. X.M. and B.Y. conceived the project and oversaw all the research phases. Y.Z. (Yidi Zhou) designed the project and collected and analyzed the data. X.H. built the activity testing equipment and performed corresponding tests. L.W., Y.L., M.F. and Z.H. discussed the results. Y.Z. (Yajing Zhao), X.W. and D.Z. wrote and revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Mineral Processing (BGRIMM-KJSKL-2021-11), the Engineering Research Center of Non-Metallic Minerals of Zhejiang Province (No. ZD2020K04) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 5217042069).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dong, B.; Lan, S. Experimental research of pulsed discharge plasma and TiO2/Zeolite coupling technology for formaldehyde removal. J. Phys. Conf. 2013, 418, 012121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Han, K.; Yu, H. Efficient elimination of formaldehyde over Pt/Fe3O4 catalyst at room temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yu, Y.; Fan, J.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. Room-temperature formaldehyde catalytic decomposition. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 3655–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Sharma, V.K. Active Site Directed Tandem Catalysis on Single Platinum Nanoparticles for Efficient and Stable Oxidation of Formaldehyde at Room Temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3610–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Xia, Q. Complete catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature on MnxCo3−xO4 catalysts derived from metal-organic frameworks. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 611, 117975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Miao, H.; Rui, Z.; Ji, H. Enhanced Formaldehyde Removal from Air Using Fully Biodegradable Chitosan Grafted β-Cyclodextrin Adsorbent with Weak Chemical Interaction. Polymers 2019, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liew, K.M.; Pan, C. Influence of hydroxyl groups on the adsorption of HCHO on TiO2-B(100) surface by first-principles study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. Pccp 2013, 15, 3866–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Luo, C. First Principles Study of HCHO Adsorption on Hydroxylated TiO2-B(100) Surfaces. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 36, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Kan, W.; Miao, J.; Cheng, M.; Jing, Z. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Amino-PVC/DE Composite and Its Adsorption Performance for Formaldehyde. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 12934–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, R.; Fan, Y.; Huang, J.; Niu, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and simultaneous formaldehyde degradation over Z-scheme ZnIn2S4-NiO/BiVO4 hierarchical heterojunction under visible light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Li, K.; Lin, F.; Hou, L.A. Insoluble matrix proteins from shell waste for synthesis of visible-light response photocatalyst to mineralize indoor gaseous formaldehyde. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Lv, S.; Jin, T.; Xu, P.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y. Degradation of gaseous HCHO in a rotating photocatalytic fuel cell system with an absorption efficiency of up to 94%. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asilevi, P.J.; Boakye, P.; Oduro-Kwarteng, S.; Fei-Baffoe, B.; Sokama-Neuyam, Y.A. Indoor air quality improvement and purification by atmospheric pressure Non-Thermal Plasma (NTP). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, C. Study on Effects of Nano-Photocatalysis and Non-Thermal Plasma on the Removal of Indoor HCHO. In Proceedings of the Asme Second International Conference on Micro/nanoscale Heat & Mass Transfer, Shanghai, China, 18–21 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C. Synergistic Effect of Nanophotocatalysis and Nonthermal Plasma on the Removal of Indoor HCHO. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 354032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Pt/MnO2 Nanoflowers Anchored to Boron Nitride Aerogels for Highly Efficient Enrichment and Catalytic Oxidation of Formaldehyde at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. 2020, 60, 6377–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Yu, H. CoMn2O4 supported on carbon nanotubes for effective low-temperature HCHO removal. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 859, 157808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Deng, L.; Zeng, T.; Huang, H. Preparation of Porous MnO2/CeO2 Composite for the Effective Removal of Formaldehyde from Air. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 150, 111751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Hui, J.; Tan, N. Research progress on catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde over supported platinum catalysts. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2017, 36, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; He, H. A Nonoxide Catalyst System Study: Alkali Metal-Promoted Pt/AC Catalyst for Formaldehyde Oxidation at Ambient Temperature. ACS Catal. 2020, 11, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; He, H.; Xiao, F.-S. Complete oxidation of formaldehyde at room temperature over an Al-rich Beta zeolite supported platinum catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 219, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huang, B.; Dong, X.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Miao, D.; Pan, Y.; Jiao, F.; Xiao, J.; et al. Bifunctional zeolites-silver catalyst enabled tandem oxidation of formaldehyde at low temperatures. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lin, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, P. Review on noble metal-based catalysts for formaldehyde oxidation at room temperature—ScienceDirect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Wei, T.; Xiao, H. Excellent Low-Temperature Formaldehyde Decomposition Performance over Pt Nanoparticles Directly Loaded on Cellulose Triacetate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 21720–21728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvitepe, N.; Balbay, A.; Saka, C. Optimisation of sepiolite clay with phosphoric acid treatment as support material for CoB catalyst and application to produce hydrogen from the NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16387–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Li, J.; Hao, J. Progress in research on catalysts for catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Ye, Q.; Chen, M.; Cheng, S.; Dai, H. Catalytic Oxidation of HCHO over the Sodium-Treated Sepiolite-Supported Rare Earth (La, Eu, Dy, and Tm) Oxide Catalysts. Catalysts 2020, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, S.; Aka, N.; Karaoglu, M.H. NaOH impregnated sepiolite based heterogeneous catalyst and its utilization for the production of biodiesel from canola oil. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 41, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meşe, E.; Figen, A.K.; Filiz, B.C.; Pişkin, S. Cobalt-boron loaded thermal activated Turkish sepiolite composites (Co-B@tSe) as a catalyst for hydrogen delivery. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L.; Hu, F. Activation and β-FeOOH modification of sepiolite in one-step hydrothermal reaction and its simulated solar light catalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaolu, M.H.; Zholobenko, V.; Aslan, S.; Karaolu, M.H.; Zholobenko, V.; Aslan, S. Preparation and application of KOH impregnated sepiolite as a solid base catalyst for biodiesel production using microwave irradiation. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2021, 66, 5320–5323. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Yang, B.B.; Duan, E.H.; Guo, B. Adsorption of Styrene on Hydrochloric Acid-Modified Sepiolite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 518, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.B.; Mahabadi, H.A.; Jafari, A.J. Catalytic Removal of Toluene from Air Streams by Cobalt Oxide Supported on Sepiolite. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncea, M.; Deak, G.; Ana-Maria, P.; Baraitaru, A.; Dumitru, F.D. Handy and sustainable method of nano-Ca(OH)2 synthesis used in conservation and consolidation works. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 11, 531–538. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, L.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, B.; Liu, G.; Jaroniec, M. Enhanced performance of NaOH-modified Pt/TiO2 toward room temperature selective oxidation of formaldehyde. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2777–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanchenko, A.; Likhatski, M.; Mikhlin, Y. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Study of the Products Formed on Sulfide Minerals Upon the Interaction with Aqueous Platinum (IV) Chloride Complexes. Minerals 2018, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. Influence of the interaction between surfactants and sepiolite on the rheological properties and thermal stability of organo-sepiolite in oil-based drilling fluids. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 272, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wei, D.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, W.; Shen, H.; Qu, Y.; Wen, S.; Kwon, Y.U.; Zhao, Y. Facile synthesis of Nafion-supported Pt nanoparticles with ultra-low loading as a high-performance electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Du, F.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Chu, J.; Wang, X.; Xiong, S. Effects of annealing temperature of PtCu/MWCNT catalysts on their electrocatalytic performance of electrooxidation of methanol. Ionics 2021, 28, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, B.-B.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, S.; Pan, S.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; et al. Exceptional activity for formaldehyde combustion using siliceous Beta zeolite as a catalyst support. Catal. Today 2020, 339, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).