Value Modeling for Ecosystem Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Value Modeling and Business Model Representations
2.2. Business, Innovation and Platform Ecosystems
2.3. Ecosystem Strategy and Ecosystem Risks
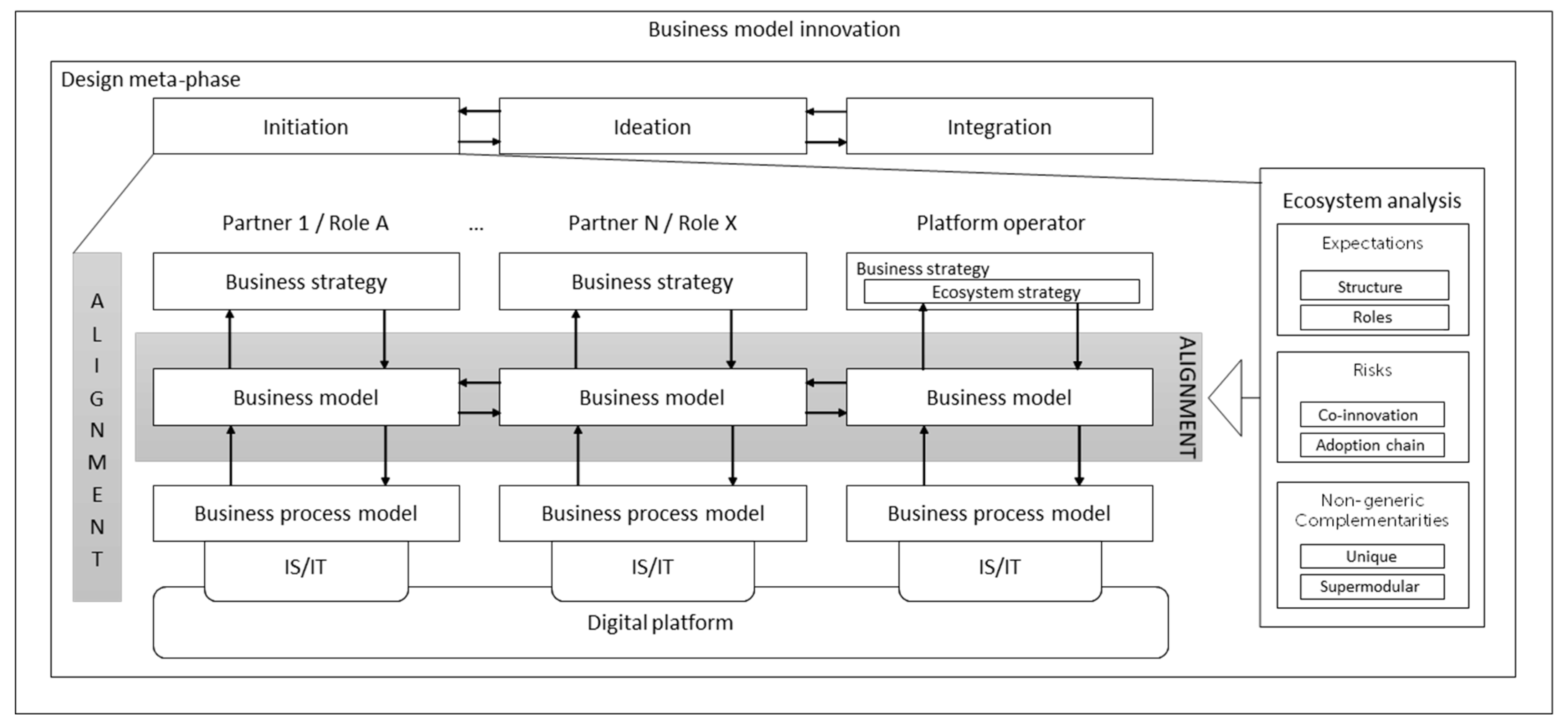
2.4. Towards an Integrative Theoretical Framework
3. Research Method
3.1. Literature Search Approach
3.2. Literature Synhtesis Approach
3.2.1. Alignment, Perspective, Notation and Tooling
3.2.2. Business Model Innovation and Cognitive Needs
3.2.3. Ecosystem Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Enabling Support for Ecosystem Analysis
5.2. Avenues of Future Research
5.3. Limitations
5.4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Business Model Representations Not Considered as Value Modeling Techniques | General Overview | Innovation Phase and Cognitive Need Fit | Ecosystem Analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Alignment Reach | Perspective | Notation | Tooling | Content | Graphic Form | Ecosystem Risks | Complementarities | |||||||||||||||||
| Strategy Layer | Business Model Layer | Process Layer | IT/IS Layer | Single | Multiple | Map-based | Network-based | Formalization | Design | Financial Evaluation | Other Evaluation | Elements | Transactions | Causality | Graphic Organizer | Brainstorming Web | Conceptual Map | Inter-firm Act. Conf. | Co-innovation Risks | Adoption Chain Risks | Unique | Supermodular | Non-generic | |
| Value net [72] | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Enterprise in business networks [73] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Semantic representation of exogenous and endogenous perspectives [74] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business model meta-model [75] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Components of a business model [76] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Key elements of a business model [77] | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business Engineering Metamodel [65] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Business model ontology [78] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||
| Business model design matrix [79] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business model framework [80] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| STOF Model [81] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unified business model framework [82] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business model framework [83] | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business models for e-government [84] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| V4 business model ontology [85] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Component business model [86] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Service value network structure [87] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Business Model Canvas [88] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Customer-integrated business model [89] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Strategic perspective of a business model [90] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Business model subcategory themes by level of analysis [91] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business model elements [92] | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business model framework [93] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Network efficiency business models [94] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| DYNAMOD [95] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Business model magic triangle [96] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Canvas business model mind map [97] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Value proposition canvas [98] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Network-based business model ontology [99] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Integrated business model concept [100] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| An Ontology for Open Government Data Business Model [101] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
References
- Gordijn, J.; Akkermans, H. E3-Value: Design and Evaluation of e-Business Models. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2001, 16, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, J.; Ionita, D.; Rubbens, B.; Wieringa, R. E3tools: Toolkit for Building and Analyzing Networked Business Models. 2016.
- Parker, G.; Van Alstyne, M.; Jiang, X. Platform Ecosystems: How Developers Invert the Firm. MIS Q. 2017, 41, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-debei, M.M.; Avison, D. Developing a Unified Framework of the Business Model Concept. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2010, 19, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola González, A.; Becker, K.; Cheng, C.-H.; Döricht, V.; Duchon, M.; Fehling, M.; von Grolman, H.; Hallensleben, S.; Hopf, S.; Ivandic, N.; et al. Digital Transformation: How Information and Communication Technology Is Fundamentally Changing Incumbent Industries; Fortiss GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veit, D.; Clemons, E.; Benlian, A.; Buxmann, P.; Hess, T.; Kundisch, D.; Leimeister, J.M.; Loos, P.; Spann, M. Business Models: An Information Systems Research Aagenda. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2014, 6, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adner, R. Ecosystem as Structure: An Actionable Construct for Strategy. J. Manag. 2017, 43, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobides, M.G.; Cennamo, C.; Gawer, A. Towards a Theory of Ecosystems. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 2255–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreola González, A.; Pfaff, M.; Krcmar, H. Business Model Representations and Ecosystem Analysis: An Overview. In Information Systems. EMCIS 2018. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing; Themistocleous, M., Rupino da Cunha, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 341, pp. 464–472. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, G.G.; Van Alstyne, M.W.; Choudary, S.P. Platform Revolution: How Networked Markets Are Transforming the Economy and How to Make Them Work for You; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 0393249131. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N. Digital Business Strategy: Toward a Next Generation of Insights. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessmann, A.; Legner, C. Designing Business Models for Cloud Platforms. Inf. Syst. J. 2016, 26, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Reuver, M.; Sørensen, C.; Basole, R.C. The Digital Platform: A Research Agenda. J. Inf. Technol. 2018, 33, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundisch, D.; John, T.; Honnacker, J.; Meier, C. Approaches for Business Model Representation: An Overview. In Multikonferenz Wirtschaftsinformatik; Mattfeld, D.C., Robra-Bissantz, S., Eds.; TU Braunschweig: Braunschweig, Germany, 2012; pp. 1839–1850. [Google Scholar]
- Täuscher, K.; Abdelkafi, N. Visual Tools for Business Model Innovation: Recommendations from a Cognitive Perspective. Creat. Innov. Manag. 2017, 26, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weill, P. The Relationship between Investment in Information Technology and Firm Performance: A Study of the Valve Manufacturing Sector. Inf. Syst. Res. 1992, 3, 307–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, A.; Lee, C.H.S.; Whinston, A.B. The Calculus of Reengineering. Inf. Syst. Res. 1996, 7, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, J.; Akkermans, J.M. Value-Based Requirements Eengineering: Exploring Innovative E-Commerce Ideas. Requir. Eng. 2003, 8, 114–134. [Google Scholar]
- Elhamdi, M. Modélisation et Simulation de Chaînes de Valeurs En Entreprise—Une Approche Dynamique Des Systèmes et Aide à La Décision; École Centrale Paris: SimulValor, Paris, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg, C.; Huemer, C.; Hofreiter, B.; Mayrhofer, D.; Braccini, A. The REA-DSL: A Domain Specific Modeling Language for Business Models. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, London, UK, 20–24 June 2011; pp. 252–266. [Google Scholar]
- Object Management Group. Value Delivery Metamodel; Object Management Group: Needham, MA, USA, 2015; p. 140. [Google Scholar]
- Cosenz, F. Supporting Start-up Business Model Design through System Dynamics Modelling. Manag. Decis. 2017, 55, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zott, C.; Amit, R.; Massa, L. The Business Model: Recent Developments and Future Research. J. Manag. 2011, 37, 1019–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, D.; Gordijn, J.; Yesuf, A.S.; Wieringa, R. Quantitative, Value-Driven Risk Analysis of e-Services. J. Inf. Syst. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, J. A Design Methodology for Modeling Trustworthy Value Webs. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2018, 9, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, J.; Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y. Comparing Two Business Model Ontologies for Designing E-Business Models and Value Constellations. In Proceedings of the 18th Bled eConference eIntegration in Action, Bled, Slovenia, 6–8 June 2005; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart, T.; Wolter, S.; Schief, M.; Krumeich, J.; Di Valentin, C.; Werth, D.; Loos, P.; Vanderhaeghen, D. A Comprehensive Approach towards the Structural Description of Business Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Management of Emergent Digital EcoSystems; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daaboul, J.; Castagna, P.; Da Cunha, C.; Bernard, A. Value Network Modelling and Simulation for Strategic Analysis: A Discrete Event Simulation Approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 5002–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.F. The Death of Competition: Leadership and Strategy in the Age of Business Ecosystems; HarperCollins: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, A.; Tang, X. Information Technology-Enabled Business Models: A Conceptual Framework and a Coevolution Perspective for Future Research. Inf. Syst. Res. 2014, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwana, A. Platform Ecosystems: Aligning Architecture, Governance, and Strategy; Morgan Kaufmann: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazawneh, A.; Henfridsson, O. Balancing Platform Control and External Contribution in Third-Party Development: The Boundary Resources Model. Inf. Syst. J. 2013, 23, 173–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, K.; Weiblen, T. The 4l-Framework of Business Model Innovation: A Structured View on Process Phases and Challenges. Int. J. Prod. Dev. 2013, 18, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R.T. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Q. 2002, 5, xii. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, H.; Penker, M. Business Modeling with UML; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Weigand, H.; Johannesson, P.; Andersson, B.; Bergholtz, M.; Edirisuriya, A.; Ilayperuma, T. Strategic Analysis Using Value Modeling-The C3-Value Approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2007; p. 175c. [Google Scholar]
- Hotie, F.; Gordijn, J. Value-Based Process Model Design. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2019, 61, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, S. Beschreibung von Geschäftsmodellen Internetbasierter Unternehmen—Konzeption, Umsetzung, Anwendung. Ph.D. Thesis, University St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, N.; Weisbecker, A. A Business Model Framework for the Design and Evaluation of Business Models in the Internet of Services. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual SRII Global Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 29 March–2 April 2011; pp. 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. What Is Strategy? Har. Bus. Rev. 1996, 74, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allee, V. Reconfiguring the Value Network. J. Bus. Strategy 2000, 21, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapscott, D.; Ticoll, D.; Lowy, A. Digital Capital; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, J.; Cantrell, S. Changing Business Models: Surveying the Landscape; Accenture Institute for Strategic Change Conducts: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, M.; Weill, P. Place to Space: Migrating to Ebusiness Models; Harvard Business Review Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Casadesus-Masanell, R.; Ricart, J.E. Competing Through Business Models (No. D/713); IESE Business School: Madrid, Spain, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Horsti, A. Essays on Electronic Business Models and Their Evaluation; Helsinki School of Economics: Helsinki, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Poel, M.; Renda, A.; Ballon, P. Business Model Analysis as a New Tool for Policy Evaluation: Policies for Digital Content Platforms. info 2007, 9, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelos, C.; Mair, J. Profitable Business Models and Market Creation in the Context of Deep Poverty: A Strategic View. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2007, 21, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pynnonen, M.; Hallikas, J.; Savolainen, P. Mapping Business: Value Stream-Based Analysis of Business Models and Resources in Information and Communications Technology Service Business. Int. J. Bus. Syst. Res. 2008, 2, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasl, O. Business Model Analysis—Method and Case Studies; University of St. Gallen: St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani, B.; Gholamian, M.R.; Hamzehei, A.; Hosseini, S.H. Using Causal Loop Diagram to Achieve a Better Understanding of E-Business Models. Int. J. Electron. Bus. Manag. 2009, 7, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Casadesus-Masanell, R.; Ricart, J.E. From Strategy to Business Models and onto Tactics. Long Range Plan. 2010, 43, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerch, C.; Selinka, G. Dynamics of Business Models: Long-Ranging Impact Assessment of Business Models in the Capital Goods Industry. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference of the System Dynamics Society, Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2010; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Casadesus-Masanell, R.; Ricart, J.E. How to Design a Winning Business Model. Harvard Bus. Rev. 2011, 89, 100–107. [Google Scholar]
- Velu, C.; Stiles, P. Managing Decision-Making and Cannibalization for Parallel Business Models. Long Range Plan. 2013, 46, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Täuscher, K.; Abdelkafi, N. Business Model Robustness: A System Dynamics Approach. In Proceedings of the 15th EURAM Conference, Warsaw, Poland, 17–20 June 2015; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Groesser, S.N.; Jovy, N. Business Model Analysis Using Computational Modeling: A Strategy Tool for Exploration and Decision-Making. J. Manag. Control 2016, 27, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, E.; Ballon, P.; Bouwman, H.; Haaker, T.; Rietkerk, O.; Steen, M. Designing Business Models for Mobile ICT Services. In Proceedings of the 16th Bled Electronic Commerce Conference eTransformation, Bled, Slovenia, 9–11 June 2003; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, B.; Bergholtz, M.; Edirisuriya, A.; Ilayperuma, T.; Johannesson, P.; Grégoire, B.; Schmitt, M.; Dubois, E.; Abels, S.; Hahn, A.; et al. Towards a Common Ontology for Business Models. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2006, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavi, R.; Yu, E.; Topaloglou, T. Strategic Reasoning about Business Models: A Conceptual Modeling Approach. Inf. Syst. E-Bus. Manag. 2008, 7, 171–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallmo, D.; Brecht, L. Business Model Innovation in Business-to-Business Markets—Procedure and Examples. In Proceedings of the 3rd ISPIM Innovation Symposium: “Managing the Art of Innovation: Turning Concepts into Reality”, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 12–15 December 2010; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kundisch, D.; John, T. Business Model Representation Incorporating Real Options: An Extension of E3-Value. In Proceedings of the 2012 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2012; pp. 4456–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, J.; Akkermans, H. Value Webs: Understanding e-Business Innovation, 1st ed.; The Value Engineers B.V.: Soest, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ionita, D.; Wieringa, R.J.; Gordijn, J. Automated Identification and Prioritization of Business Risks in E-Service Networks. Lect. Notes Bus. Inf. Process. 2016, 247, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österle, H.; Blessing, D. Business Engineering Modell. In Business Engineering; Österle, H., Winter, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, R.; Gordijn, J.; Ionita, D. Tool Support for Value Modeling and Risk Analysis of E-Services. In Proceedings of the 24th Joint International Conference on Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality Workshops, Doctoral Symposium, REFSQ-JP 2018, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 19 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kartseva, V. Designing Controls for Network Organization: A Value-Based Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kartseva, V.; Gordijn, J.; Tan, Y. Toward a Modeling Tool for Designing Control Mechanisms for Network Organizations. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2005, 10, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uschold, M.; Jasper, R.; Benjamins, V.R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Gomez-Perez, A.; Guarino, N. A Framework for Understanding and Classifying Ontology Applications. In Proceedings of the IJCAI-99 Workshop on Ontologies and Problem-Solving Methods (KRR5), Stockholm, Sweden, 2 August 1999; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Brews, P.J.; Tucci, C.L. Internetworking: Building Internet-Generation Companies. Acad. Manag. Exec. 2003, 17, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, V.N.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.; Bharadwaj, A. Theorizing Digital Business Innovation: Platforms and Capabilities in Ecosystems. Fox School Bus. Res. Pap. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, C. The Value Net: A Tool for Competitive Strategy, 1st ed.; Wiley: Milan, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Österle, H.; Fleisch, E.; Alt, R. Business Networking: Shaping Enterprise Relationships on the Internet, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, B. Das Geschäftsmodell Als Instrument Zur Positionierung Des Unternehmens. In Retail Banking im Informationszeitalter–Integrierte Gestaltung der Geschäfts-, Prozess- und Applikationsebene; Leist, S., Winter, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 53–72. [Google Scholar]
- Markus, B. Zur Herleitung von Geschäftsmodellen Für Finanzdienstleistungsunternehmen. Methode Und Fallbeispiele. Ph.D. Thesis, University St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hedman, J.; Kalling, T. The Business Model Concept: Theoretical Underpinnings and Empirical Illustrations. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2003, 12, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelpel, S.C.; Leibold, M.; Tekie, E.B. The Wheel of Business Model Reinvention: How to Reshape Your Business Model to Leapfrog Competitors; 03–10; Hitotsubashi University Institute of Innovation Research: Tokyo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Osterwalder, A. The Business Model Ontology a Proposition in a Design Science Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballon, P. Business Modelling as the Configuration of Control and Value. In Proceedings of the 20th Bled eConference eMergence: Merging and Emerging Technologies, Processes, and Institutions, Bled, Slovenia, 3–6 June 2007; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, F. Rethinking the Business Model with RFID. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2008, 22, 635–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, H.; Faber, E.; Haaker, T.; Kijl, B.; De Reuver, M. Mobile Service Innovation and Business Models; Bouwman, H., de Vos, H., Haaker, T., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 31–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, F. The Unified Business Model Framework; Lille Economie Management: Lille, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Manning, T. Understanding Business Models and Business Model Risks. J. Priv. Equity 2009, 12, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinel, G.; Jarke, M.; Rose, T. Business Models for EGovernment Services. Electron. Gov. Int. J. 2010, 7, 380–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Debei, M.M.; Fitzgerald, G. The Design and Engineering of Mobile Data Services: Developing an Ontology Based on Business Model Thinking. In IFIP Working Conference on Human Benefit through the Diffusion of Information Systems Design Science Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, H. Business Model Innovation: Opportunities and Barriers. Long Range Plan. 2010, 43, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijl, B.; Nieuwenhuis, B. Deploying a Telerehabilitation Service Innovation: An Early Stage Business Model Engineering Approach. In Proceedings of the 43rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y. Business Model Generation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Plé, L.; Lecocq, X.; Angot, J. Customer-Integrated Business Models: A Theoretical Framework. Management 2010, 13, 226–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, N.; Renner, T.; Kett, H. Geschäftsmodelle Im Internet Der Dienste; Fraunhofer-Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2010; Volume 64. [Google Scholar]
- George, G.; Bock, A.J. The Business Model in Practice and Its Implications for Entrepreneurship Research. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2011, 35, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, K.; Spring, M. The Sites and Practices of Business Models. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2011, 40, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkafi, N.; Makhotin, S.; Posselt, T. Business Model Innovations for Electric Mobility—What Can Be Learned from Existing Business Model Patterns? Int. J. Innov. Manag. 2013, 17, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S. Simple Rules for Designing Business Models. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2013, 55, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zutshi, A.; Grilo, A.; Jardim-Goncalves, R. DYNAMOD: A Modelling Framework for Digital Businesses Based on Agent Based Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, Bangkok, Thailand, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 1372–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann, O.; Frankenberger, K.; Csik, M. The St. Gallen Business Model Navigator. Int. J. Prod. Dev. 2013, 18, 249–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilova, T.; Alsufyev, A.; Yanson, A.-S. Transforming Canvas Model: Map Versus Table. Int. J. Knowl. Innov. Entrep. Vol. 2014, 2, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y.; Bernarda, G.; Smith, A. Value Proposition Design, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nekoo, A.R.H.; Ashourizadeh, S.; Zarei, B. Designing Network-Based Business Model Ontology. Int. J. Netw. Virtual Organ. 2015, 15, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, B.W.; Pistoia, A.; Ullrich, S.; Göttel, V. Business Models: Origin, Development and Future Research Perspectives. Long Range Plan. 2015, 49, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleti, F.A.; Ojo, A. An Ontology for Open Government Data Business Model. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Theory and Practice of Electronic Governance, New Delhi, India, 7–9 March 2017; pp. 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Business Model Representations Considered Also Value Modeling Techniques | General Overview | Innovation Phase and Cognitive Need Fit | Ecosystem Analysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Alignment Reach | Perspective | Notation | Tooling | Content | Graphic Form | Ecosystem Risks | Complementarities | ||||||||||||||||||
| Nature of Analysis | Strategy Layer | Business Model Layer | Process Layer | IT/IS Layer | Single | Multiple | Map-based | Network-based | Formalization | Design | Financial Evaluation | Other Evaluation | Elements | Transactions | Causality | Graphic Organizer | Brainstorming Web | Conceptual Map | Inter-firm Act. Conf. | Co-rnnovation Risks | Adoption Chain Risks | Unique | Supermodular | Non-generic | |
| Conceptual | Activity system map [40] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| E3-value [1,18] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Eriksson-Penker business extensions [35] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Value map [41,42] | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating business model [43] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| E-business model schematics [44] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| C3-value [36] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Main virtuous circle [45] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| E-business model and factors [46] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business model for digital content platforms [47] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Conceptual | Business model of alliances [48] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Value stream map [49] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business model system dynamics modules [50] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Causal loop diagram of e-Business model ontology [51] | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Causal loop diagram [52] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dynamic structure of business models [53] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Depiction of a business model [54] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| [moby]business model ontology [39] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Trading business model [55] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business model causal loop diagram [56] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Business model extract in the system dynamics notation [57] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Dynamic business model canvas [22] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Value-based process model design [37] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||
| Heuristic | E3tool [24] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Mathematical | Value model of reengineering [17] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| SimulValor [19] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Modified SimulValor [28] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||
| Ontological | B4U design framework [58] | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Description model for internet-based business models [38] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
| Reference ontology for business models [59] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Ontological | Reference ontology for business models [59] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Strategic business model ontology [60] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Relationships of business model elements [61] | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||||
| Resource-event-agent [20] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||||
| Multi-level business model ontology [27] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||||
| Value delivery metamodel [21] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||||||||
| Stochastic | E3-value + real options [62] | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arreola González, A.; Pfaff, M.; Krcmar, H. Value Modeling for Ecosystem Analysis. Computers 2019, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers8030068
Arreola González A, Pfaff M, Krcmar H. Value Modeling for Ecosystem Analysis. Computers. 2019; 8(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers8030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleArreola González, Alejandro, Matthias Pfaff, and Helmut Krcmar. 2019. "Value Modeling for Ecosystem Analysis" Computers 8, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers8030068
APA StyleArreola González, A., Pfaff, M., & Krcmar, H. (2019). Value Modeling for Ecosystem Analysis. Computers, 8(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers8030068





