Abstract
The Internet’s expansion has changed how the services accessed and businesses operate. Blockchain is an innovative technology that emerged after the rise of the Internet. In addition, it maintains transactions on encrypted databases that are distributed among many computer networks, much like digital ledgers for online transactions. This technology has the potential to establish a decentralized marketplace for Internet retailers. Sensitive information, like customer data and financial statements, should be routinely transferred via e-commerce. As a result, the system becomes a prime target for cybercriminals seeking illegal access to data. As e-commerce increases, so does the frequency of hacker attacks that raise concerns about the safety of e-commerce platforms’ databases. Owing to the sensitivity of customer data, employee records, and customer records, organizations must ensure their protection. A data breach not only affects an enterprise’s financial performance but also erodes clients’ confidence in the platform. Currently, e-commerce businesses face numerous challenges, including the security of the e-commerce system, transparency and trust in its effectiveness. A solution to these issues is the application of blockchain technology in the e-commerce industry. Blockchain technology simplifies fraud detection and investigation by recording transactions and accompanying data. Blockchain technology enables transaction tracking by creating a detailed record of all the related data, which can assist in identifying and preventing fraud in the future. Using blockchain cryptocurrency will record the sender’s address, recipient’s address, amount transferred, and timestamp, which creates an immutable and transparent ledger of all transaction data.
1. Introduction
The most pressing concerns for individuals, corporations, and governments around the world are cyber security issues. The internet has not only made the world more interconnected, but also increased security risks, which are growing in scale and complexity. e-commerce has become a major factor in today’s digital business and economy [1]. Online businesses must prioritize security as a key aspect [2]. The need for a secure mode of communication between buyers and sellers is escalating as the e-commerce industry rapidly expands. As a result, cyberattacks have suddenly risen globally. As a result, network architecture security has been identified as the greatest threat to future e-commerce platforms [3]. Using blockchain technology in online transactions can greatly enhance user security and protection. Users can safely and publicly store their data without the assistance of outside parties. This technology can enhance the security of transactions and safeguard user data in e-commerce. For example to secure online payments, BitPay company has been used blockchain technology [4]. Allowing the business owners to accept cryptocurrency in order to obtain a secure payments. As a result the customers do not need to add their credit card information and complete their payments process using the Bitcoin. Encryption is an essential feature for BitPay systems to safeguard payment transactions [4]. By utilizing the blockchain, users’ identities can be verified. The user’s identity shall be verified in all transactions carried out over the Internet to prevent fraud. Every transaction conducted on the blockchain becomes viewable and traceable for all users. This can help improve the transparency of transactions, as well as prevent fraud associated with e-commerce. On the blockchain, user data like phone numbers, addresses, and credit card numbers can be safely saved. Only users with encryption keys will be able to access user data if it is kept on the blockchain. Users can easily track the products they purchase by using a decentralized tracking system that can be made using blockchain [5]. This measure has the potential to mitigate fraudulent activities and promote more secure transactions. The blockchain network’s unique architecture boosts database security, fortifying its defense against cyber threats. The blockchain employs a linked data structure to facilitate data verification and storage. Additionally, the blockchain relies on a distributed node system to enable data updating and generation. It is extremely unlikely that hackers will be able to crack all of the server’s nodes at once. Consequently, the application of blockchain technology can be a vital tool to guarantee the security of e-commerce transactions.
This study aims to explore the relationship between blockchain technology, e-commerce, security, and privacy. The primary focus is to analyze the current cybersecurity challenges in e-commerce, including issues like data breaches, phishing, payment fraud, and regulatory compliance. Furthermore, by improving data security, guaranteeing transaction transparency, protecting payment methods through smart contracts, and bolstering supply chain authenticity, the study intends to investigate the possibilities of blockchain technology as a viable solution to these problems. This exploration aims to demonstrate how blockchain can enhance e-commerce security and boost trust. Moreover, the study aims to highlight both the advantages and limitations of blockchain implementation in e-commerce, paving the way for future research and practical applications in this domain. In summary, the study’s goals are:
- Investigate the relationship between e-commerce, security, privacy, and blockchain.
- Analyze prevalent cybersecurity challenges in e-commerce, including data breaches, phishing attacks, and payment fraud.
- Explore the potential of blockchain in addressing e-commerce security concerns.
- Highlight the advantages of blockchain such as enhanced data security and transparency in transactions.
- Discuss the limitations and challenges of implementing blockchain in e-commerce.
- Review recent studies in the field, summarizing their key findings regarding e-commerce security and blockchain integration.
- Identify limitations highlighted in the reviewed studies and suggested mitigations with the best of our knowledge.
- Offer insights for future research and practical applications in leveraging blockchain for e-commerce security enhancement.
This study stands poised to offer substantial contributions to the domain of e-commerce, cybersecurity, and the integration of blockchain technology. By meticulously investigating the intricate interplay between these realms, the research endeavors to serve as a beacon of insight for the industry, academia, and policymakers alike. The comprehensive analysis of prevalent cybersecurity challenges within e-commerce elucidates the urgent need for heightened security measures in digital transactions, thereby accentuating the pivotal significance of this study. By exploring the potential of blockchain as a viable solution to fortify data security, ensure transparent transactions, and bolster trust within e-commerce environments, this research aims to introduce transformative possibilities that could reshape the landscape of online business. The study’s findings and nuanced understanding of blockchain’s advantages and limitations in e-commerce are poised to benefit practitioners and decision-makers seeking to fortify security protocols and streamline transactional processes. Moreover, this study is not merely an endpoint but serves as a springboard for future researchers by delineating uncharted territories and open challenges within this evolving field. By highlighting the avenues for future exploration, potential mitigations for limitations, and underscoring the importance of further research endeavors, this study aims to inspire and guide subsequent investigations. The significance of conducting such research lies in its potential to revolutionize the security paradigms of e-commerce, foster innovation, and pave the way for robust, secure, and trustworthy e-commerce platforms that safeguard user data and instill confidence among consumers and businesses alike. Therefore, this study is pivotal, not just for its immediate findings, but for the road map it provides to researchers interested in advancing the field of e-commerce security through the integration of blockchain technology.
The structure of this paper as shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 is as follows. Section 2 clarifies how we select and analyze the papers and studies that are relevant to our paper using the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram. Section 3 introduces the landscape of e-commerce and the pivotal role of security and privacy in this digital domain, highlighting the emerging significance of blockchain technology. Section 4 delves into the multifaceted aspects of security and privacy in e-commerce, elucidating encryption methods, payment security protocols, access control measures, website vulnerability management, data privacy compliance, customer education initiatives, and strategies for incident response and recovery. Section 5 this section significantly underscores how the integration of blockchain technology revolutionizes e-commerce, providing a robust, secure, and efficient platform for transactions and operations. Section 6 navigates through the realm of blockchain technology, encompassing its historical evolution, underlying technological components, diverse types, applications within e-commerce, intrinsic features, and the notable challenges impeding its widespread adoption. Section 7 undertakes a comprehensive discussion on the pressing cybersecurity challenges faced by e-commerce platforms, including data breaches, phishing attacks, ransomware, supply chain vulnerabilities, payment fraud, identity theft, IoT susceptibility, cybersecurity awareness deficits, and regulatory compliance hurdles. Additionally, Section 7 meticulously examines the role of blockchain in fortifying e-commerce security, emphasizing its advantages such as immutable ledgers, enhanced data security, fraud prevention, secure payments through smart contracts, supply chain transparency, and decentralized marketplace security. Section 9 explains a detailed comparison with other review papers. Section 10 presents an analysis of related studies, identifies existing limitations, and sheds light on prospective future directions in e-commerce security bolstered by blockchain technology. Finally, Section 13 draws the paper to a conclusion by synthesizing key findings, accentuating the significance of robust security in e-commerce, acknowledging the transformative potential of blockchain, and proposing avenues for further research and exploration in this dynamic field.
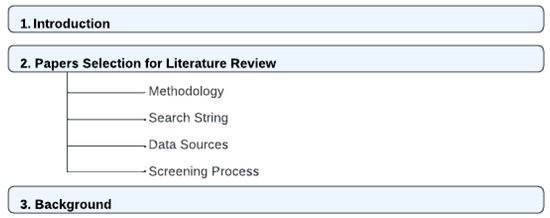
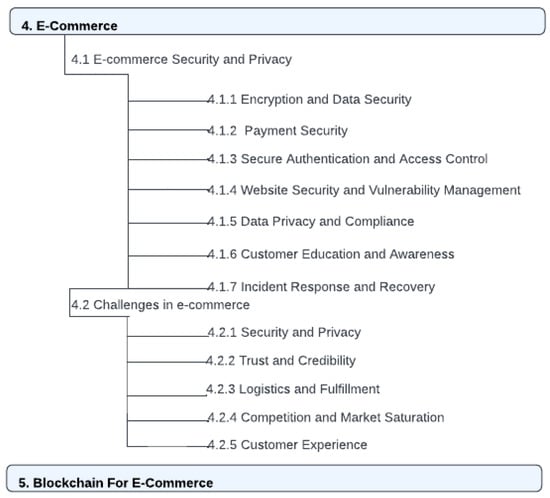
Figure 1.
Paper outline [6].
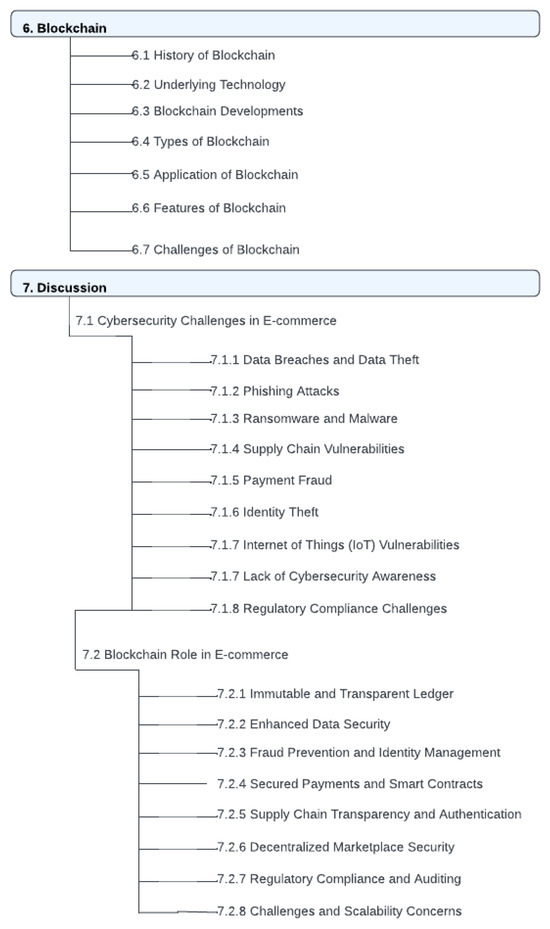
Figure 2.
Cont. paper outline [6].
2. Papers Selection for Literature Review
2.1. Methodology
The main objective of using a systematic literature review (SLR) is to gather and present all the important information from existing research in a specific field in a clear and organized way. In addition, our research paper aims to identify current research gaps and recognize future research paths. In this section, we used PRISMA methodology to conduct this SLR, which contains four stages (identifications, screening, eligibility, and included), identifying the list of papers that were published between 2019 and 2023 by using a search filter and then select the source type as academic journals or conference, determining the search string, identifying relevant sources of data, setting up criteria to determine which data are relevant (including both what should be included and excluded), and creating a plan for how the screening and selection process will be carried out.
2.2. Search String
The search was performed by determining the search string in several databases. It was implemented by using Boolean operators such as “ANDs” and “ORs” as follows: (“Blockchain” OR “Block chain”) AND (“E-commerce” OR “e commerce”) AND (“security” OR “network”).
2.3. Data Sources
The digital search procedure involved Saudi Digital Library and executing the search query in Google scholar database.
2.4. Screening Process
During the initial screening phase, we chose papers by looking at their titles and evaluating whether they were related to the research field or not. If we encountered a difficult-to-evaluate paper, we introduced an additional screening phase. In this phase, we examine the abstract of every paper that was chosen in the previous step. Figure 3 explains the details of the PRISMA methodology.
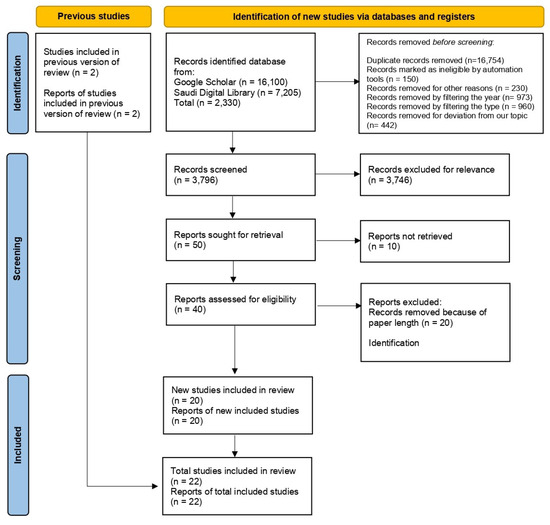
Figure 3.
Papers selection for literature review using PRISMA.
3. Background
The beginning of blockchain technology can be traced back to 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin. Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the concept of a decentralized system called blockchain, designed to keep track of Bitcoin transactions. People initially thought blockchain and Bitcoin were the same thing, but around 2014, folks realized that blockchain could do more than just handle digital money. This understanding led to investments in exploring its uses beyond cryptocurrencies. While blockchain indeed found success in digital currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, it expanded its reach to different areas, thanks to its secure and decentralized structure [7]. Sectors like data sharing, supply chain management, healthcare, and finance started using blockchain because it ensures the reliability and truthfulness of information. So, from being associated mainly with Bitcoin, blockchain has become a versatile technology influencing various aspects of our digital world.
Blockchain technology has found a valuable use in e-commerce transactions, particularly in managing supply chains effectively. It allows companies to track and trace products from origin to the end consumer, creating an immutable and transparent audit trail. This allows individuals involved to confirm the genuineness and origin of products, ensuring that fraudulent items do not enter the supply chain. Additionally, blockchain can help streamline processes such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and payment reconciliation, reducing inefficiencies and improving overall supply chain visibility. Blockchain can also revolutionize payments and financial transactions in e-commerce. Traditional systems often involve intermediaries, leading to delays, fees, and security risks. Blockchain-based payment systems enable direct peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating intermediaries [8]. Smart contracts automate payment settlements based on predefined conditions, reducing fraud and enabling faster and cost-effective processing. Furthermore, blockchain enhances data security and privacy in e-commerce. Personal and and transactional information can be protected and saved in a secure way using encryption, protecting it from unauthorized access. Users are empowered with greater control over their data and have the ability to grant specific permissions, effectively addressing privacy concerns associated with centralized platforms.
The purpose of using blockchain technology with e-commerce is to provide a greater level of security while performing transactions. This approach involves incorporating a decentralized and tamper-resistant system, providing a more robust framework for securing sensitive transaction data. By utilizing advanced cryptographic techniques, information integrity will be ensured by using blockchain, making it challenging for unauthorized parties to tamper with or access critical data. The transparency feature inherent in blockchain contributes to a trustworthy environment by allowing all transaction participants real-time access to the same information. Furthermore, the implementation of smart contracts automates and secures the execution of predefined terms in agreements [9], reducing the likelihood of disputes and enhancing the overall reliability of e-commerce transactions. In summary, the integration of blockchain in e-commerce is a strategic move to fortify the security measures surrounding online transactions, ensuring the security and reliability of digital marketplace.
4. E-Commerce
The online buying and selling of goods and services, known as e-commerce, has brought about a revolutionary change in how transactions are conducted over the internet. It has had a significant impact on the business world, transforming transactions and changing the global marketplace. e-commerce includes various activities like online retail, auctions, digital downloads, electronic payments, and ticketing. The convenience and accessibility of e-commerce allow consumers to shop from anywhere at any time using internet-connected devices [10]. This has eliminated geographical barriers and time constraints, giving consumers access to a huge amount of products and services from around the world. E-commerce has leveled the playing field for businesses, empowering small enterprises and individual entrepreneurs to reach a global customer base without the traditional resources of physical stores. It has also expanded consumer choices through price comparisons, product reviews, and research.
The consumer can access detailed product information, including descriptions, images, and customer reviews, to make informed buying decisions. The checkout process involves providing shipping details, payment information, and applying any available discounts. Credit cards, digital wallets or any of secure electronic payment methods are used to complete transactions, with data encryption ensuring security [11]. Once the payment is successful, sellers are notified, and orders are processed for fulfillment. This includes packaging, shipping, and providing tracking information to buyers. In the case of digital products or services, delivery is often instantaneous, allowing immediate access or downloads. E-commerce benefits both buyers and sellers. Buyers enjoy convenience, access to a wide range of products, price comparisons, and personalized recommendations. Sellers can expand their reach globally, operate 24/7, reduce costs associated with physical stores, optimize inventory management, and gather valuable customer data for marketing and improving customer experiences.
E-commerce has been really helpful during the COVID-19 pandemic [12]. It has provided a safe and easy way for people to buy essential things from home, so they do not have to go out and risk getting sick. It has also provided that important items like food, medicine, and protective gear are available to those who need them. E-commerce has helped small businesses and entrepreneurs by letting them sell their products to more customers online, even when there are lockdowns and restrictions. This has not only helped the economy but also encouraged new ideas and businesses. E-commerce has generated employment opportunities in fields such as delivery services, online advertising, and customer support, which is important when many people have lost their jobs. Overall, the pandemic has shown how valuable and reliable e-commerce is. It gives us convenience, safety, and stability during tough times.
However, security remains a challenge, with fraud and data breaches being significant concerns. Building consumer trust and implementing robust cybersecurity measures are crucial for the continued growth of e-commerce. E-commerce has fundamentally changed the way businesses and consumers engage. Its convenience, accessibility, and global impact have reshaped the modern business landscape. As technology advances and consumer behaviors evolve, e-commerce is expected to continue its rapid growth, offering both opportunities and challenges for businesses in the digital age.
4.1. E-Commerce Security and Privacy
Protecting the security and privacy of data in e-commerce is very important. The following measures contribute significantly to ensure their protection:
4.1.1. Encryption and Data Security
Encryption ensures the confidentiality of sensitive information by transforming it into an unreadable format for unauthorized individuals. In the context of e-commerce, when users provide payment details or personal data on a website, encryption protocols such as Secure Socket Layer or Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) are employed to encrypt the data before it is transmitted over the Internet [13]. This means that if someone were to intercept the data during transit, they would only see a series of encrypted characters that are virtually impossible to decipher without the encryption key. Encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), provide robust protection against unauthorized access, thus reducing the risk of data breaches and identity theft. Also, SSL/TLS certificates serve as visual indicators to users that a website is secure. Users typically see padlock icons or green address bars in their browsers, indicating that the connection is encrypted [13]. This visible demonstration of encryption protocols enhances customer trust and confidence in the practices of security for e-commerce websites. As a result, customers are more likely to have a positive user experience and complete transactions, leading to increased sales and stronger customer loyalty. Moreover, SSL/TLS encryption provides protection against data interception in insecure network environments such as open Wi-Fi networks or public hotspots. Data transmitted without encryption in these settings is vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. Data transmitted without encryption in these settings is vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. Even if data are intercepted, SSL/TLS emphasize that it remains unreadable and unusable to unauthorized parties. This level of protection is particularly crucial for e-commerce transactions conducted by customers on public networks, as their sensitive information is effectively safeguarded against potential attackers [13].
4.1.2. Payment Security
To ensure secure payment processing and prevent fraud in e-commerce, certain essential components come into play. These include utilizing secure payment methods, adhering to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), implementing tokenization, and employing two-factor authentication (2FA) [14]. Secure payment methods, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and bank transfers, employ encryption protocols to ensure the secure transmission of data. PCI DSS compliance involves implementing various security measures to protect cardholder data [14]. Tokenization is a method that replaces sensitive card data with unique tokens, minimizing the risk of exposure in the event of a security breach. Two-factor authentication provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two forms of identification before accessing their accounts. By combining these measures, e-commerce businesses can enhance payment security, build trust with customers, and mitigate the risks associated with fraud.
4.1.3. Secure Authentication and Access Control
Robust authentication methods play a crucial role in preventing unauthorized access to customer accounts and sensitive information in e-commerce. In this study, we determine some key authentication methods that enhance security. Firstly, biometrics employ unique physical or behavioral traits like fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, or voice recognition to verify identity, providing highly secure authentication [15]. E-commerce platforms can integrate biometric authentication to verify the identity of individuals and restrict access to customer accounts and confidential data exclusively to authorized users. Secondly, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) combines multiple independent factors [15], such as something the user knows, something the user possesses, or something the user is, to verify identity, introducing an additional layer of security that makes unauthorized access significantly more difficult. Thirdly, strong passwords are essential, and e-commerce platforms should enforce password policies requiring complex, lengthy, and unique passwords that combine uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Regularly updating passwords and avoiding reusing them across multiple accounts further enhance security [15]. Lastly, access control measures, including role-based access control (RBAC) and the use of secure protocols like virtual private networks (VPNs) and secure remote desktop protocols, restrict access to authorized individuals and protect against unauthorized access to internal systems.
4.1.4. Website Security and Vulnerability Management
Regularly conducting security audits, managing patches, and performing vulnerability assessments is important for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses in e-commerce websites and applications. Security audits enable a comprehensive review of security measures, policies, and practices, helping identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. By proactively assessing their security posture, e-commerce businesses can implement necessary measures to prevent security incidents and strengthen overall security [16]. Patch management involves promptly applying software updates to address known vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploitation by attackers. Keeping software up to date is vital in closing security gaps and protecting against emerging threats. Vulnerability assessments systematically scan and test e-commerce platforms to identify security flaws that could be exploited. Regular assessments allow businesses to proactively remediate vulnerabilities and prevent potential exploitation.
4.1.5. Data Privacy and Compliance
Adhering to data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is extremely important for businesses that handle customer data. These regulations aim to protect individuals’ privacy rights, enhance data security, and establish guidelines governing the collection, processing, and storage of personal data [17]. Compliance with these regulations is significant because it helps businesses avoid severe penalties and reputational harm that can result from non-compliance, it prioritizes the privacy rights of customers by requiring explicit consent for data collection and processing, providing options for opting out, and granting individuals the right to access, rectify, and erase their data. Also, it emphasizes the importance of implementing robust data security measures like encryption and access controls to safeguard personal data. They also mandate the prompt reporting of any data breaches that may occur. Moreover, businesses must be transparent about their data handling practices, clearly communicating the types of data collected, processing purposes, retention periods, and data sharing details. They are also encouraged to minimize data collection and processing to only what is necessary and regularly review their practices to ensure compliance. Additionally, businesses must carefully manage third-party vendors with access to customer data, ensuring they comply with regulations through data processing agreements, and employ appropriate safeguards when transferring data internationally [17]. To handle and protect customer data in compliance with data protection regulations, businesses should conduct privacy assessments, implement strong data security measures, obtain explicit consent, provide clear privacy notices, establish procedures for data subject requests, train employees on data protection practices, and regularly update policies and procedures to align with evolving regulations and best practices. By adhering to these regulations, businesses can protect customer privacy, reduce legal risks, and build trust with their customers, thus demonstrating a commitment to privacy and data security [17].
4.1.6. Customer Education and Awareness
Empowering customers to protect themselves from cyber threats through education on online security best practices is important. Businesses play a significant role in promoting awareness and providing guidance to help customers avoid phishing scams, use secure connections, and be cautious when sharing personal information [18]. Educating customers in these areas involves emphasizing the following key points: being cautious of unsolicited requests for personal or financial information, verifying website legitimacy, avoiding suspicious links and attachments, and enabling anti-phishing features. Additionally, it is advisable to promote secure connections and discourage customers from utilizing public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive activities. Also, customers should be encouraged to regularly update their devices and software for optimal security. Furthermore, customers need to understand the importance of safeguarding personal information, limiting its sharing on public platforms, reviewing privacy settings, and using strong, unique passwords. Businesses can educate customers through various channels, including website content, email communication, social media engagement, and knowledge bases [18].
4.1.7. Incident Response and Recovery
The presence of an incident response plan is essential in the e-commerce industry for promptly addressing security breaches, minimizing damages, and rebuilding customer trust following an incident. This plan will help to safe sensitive customer data, ensure business continuity, mitigate financial and reputational losses, comply with data protection regulations, restor customer trust, and foster continuous improvement. By having an incident response plan in place, e-commerce organizations can effectively respond to security incidents, protect customer data, and maintain a secure and trusted environment for their customers.
4.2. Challenges in E-Commerce
Some common challenges related to e-commerce are presented in this section:
4.2.1. Security and Privacy
Security poses a major challenge to e-commerce, as sensitive data, such as customer card data and personal information, is transmitted over the Internet. Therefore, this type of data must be protected from unauthorized access, modification, or tampering. In addition, compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) must be taken into consideration.
4.2.2. Trust and Credibility
It can be difficult for startups to build trust with customers over the internet. Customers may hesitate to provide their sensitive information, such as payment data or personal information. Therefore, secure payment methods and transparent policies must be provided to gain customer trust in e-commerce.
4.2.3. Logistics and Fulfillment
Managing inventory levels, coordinating with shipping companies, and ensuring timely delivery of shipments are among the most prominent challenges that e-commerce may face. Therefore, effective implementation is essential for the success of e-commerce.
4.2.4. Competition and Market Saturation
Being the best among competitors and attracting customers may be difficult and a major challenge in the field of e-commerce. Where companies can differentiate themselves through unique offers, competitive prices, and effective marketing strategies.
4.2.5. Customer Experience
Companies should direct most of their attention to designing easy-to-use websites, responding quickly to customer questions and inquiries, and diverse and simplified payment processes, in order to provide a smooth and satisfactory experience for customers.
5. Blockchain for E-Commerce
By leveraging blockchain technology, e-commerce platforms experience enhanced security, simplicity, and speed in transactions. Users can participate in safer transactions and securely store their digital assets. Unlike traditional online transactions that require validation from third parties like credit cards or banks, blockchain provides a protective layer [19]. User data breaches are a potential risk for traditional e-commerce platforms. Thus, integrating blockchain technology is essential to improving the security of e-commerce platforms. Blockchain’s distributed ledger removes the possibility of tampering by guaranteeing transaction integrity and authenticity. Integrating blockchain-based applications offers a range of advantages, such as streamlining corporate operations, reducing operational costs, reducing security risks and enhancing overall efficiency (See Figure 4).
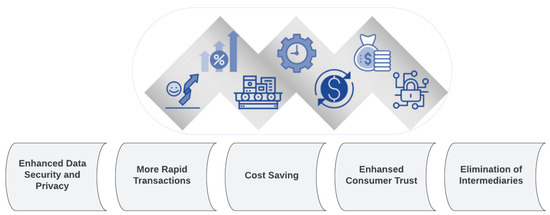
Figure 4.
The advantages of using blockchain technology for e-commerce.
6. Blockchain
Blockchain is a technology that operates in a decentralized and distributed manner to securely and transparently store and transfer digital information. It operates through a consensus mechanism where transactions are validated and added to a digital ledger known as a blockchain. The blockchain consists of linked blocks that form an immutable record of transactions, protected by cryptographic hashes. The decentralized nature of blockchain eliminates the necessity for a central authority and ensures transparency and security [19]. Through consensus among network participants, transactions are validated, added to the blockchain, and propagated across the network. This technology has found applications in various industries beyond cryptocurrencies, providing trust, security, and accountability.
6.1. History of Blockchain
The concept of a decentralized digital currency, known as blockchain, was first proposed by Nakamoto [20], who also described the underlying technology. Nakamoto created cryptocurrency and started the blockchain revolution in January 2009 when he was able to mine the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, also known as the “genesis block”. Initially closely tied to Bitcoin, blockchain technology expanded beyond cryptocurrencies as developers recognized its potential in various industries. Ethereum’s introduction of smart contracts in 2015 enabled the creation of decentralized applications and decentralized finance. Several consensus mechanisms, including Proof of Stake, have emerged to solve the problems of scalability and energy consumption. Blockchain gained attention globally, with industries exploring its potential in supply chain management, identity verification, healthcare, and more. Alliances facilitated collaboration and standardization, and major technology companies offered blockchain-as-a-service solutions. Efforts to address scalability and interoperability continue. Blockchain’s evolution is ongoing, with expected growth and impact on industries and society.
6.2. Blockchain Developments
Blockchain technology was created with Bitcoin in 2008. It was used as a public ledger to store all the transactions happening in cryptocurrencies [21]. However, with time, it has become a technology that is having a great impact on modern society due to its transparency, decentralization, and security characteristics. Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the way we live, interact, and perform business. Nowadays, academics, industrialists, and researchers are aggressively investigating different aspects of blockchain as an emerging technology. This technology has been used to authorize, authenticate, and audit data that has been generated by the Internet of Things (IoT) devices [21]. It can also provide a secure means of exchanging various services, goods, and transactions. With vast and rapid applications development, it is obvious that blockchain will do for trusted transactions what the Internet did for communications [21].
In recent studies, the development of blockchain technology has witnessed advancements across various domains. It has been recognized as the underlying technology for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. Blockchain has expanded into diverse industries. The focus of it was to enhance scalability, security, and interoperability [22]. Researchers have explored different consensus mechanisms, Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and other consensus algorithms to improve transaction speed and energy efficiency. Moreover, advancements in smart contracts which gives the automation of complex agreements and operations within decentralized applications (dApps). Interoperability solutions, aimed to facilitate communication between distinct blockchain networks, and influencing greater connectivity among different platforms [22]. Additionally, developments in privacy protocols and the integration of blockchain with other technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) have expanded the potential applications of blockchain beyond finance, encompassing supply chain management, healthcare, governance [22]. Overall, recent studies emphasize not only refining the technical aspects of blockchain but also exploring its diverse real-world applications. As result, we can tell that blockchain technology is now a technology that as its significant implications in various industries [22].
6.3. Underlying Technology
Here, we will discuss the technical aspects of blockchain, including cryptographic hashing, consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake and Proof of Work, smart contracts, and the role of nodes in the network [7].
1. Hash Functions: Hashing is an essential part of blockchain technology. It uses cryptographic algorithms to transform data into a specific-sized code referred to as a hash. Each input generates a unique hash, meaning that even a small modification in the input will produce a completely different hash. This feature guarantees that the data stored on the blockchain remains unaltered and cannot be modified, providing assurance of its integrity and immutability.
Blockchain technology also contains public key encryption and digital signatures, which authenticate and protect transactions. Public key cryptography is used to enable public and private functions. Each participant in the blockchain has a pair of keys (public and private). The public key is used to create a digital signature for a transaction while the private key is used to verify that signature. If the signature is valid, this guarantees that the transaction was actually initiated by the owner of this key and was not modified during transmission. This confirms that transactions are encrypted and cannot be tampered with by unauthorized parties.
2. Consensus Mechanisms:
- a.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Proof of Work, or PoW, is the consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin. Miners solve challenging mathematical puzzles with the use of computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block to the blockchain and gets a reward for their work. PoW is secure but requires a significant amount of computational resources and energy.
- b.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Block validators in Proof of Stake (PoS) are selected according to the quantity of cryptocurrency tokens they own and “stake” in the network. Validators are selected to generate new blocks using a deterministic algorithm, where their likelihood of being chosen is directly proportional to the amount of stake they hold. PoS is known for its energy efficiency but has its own security considerations.
- c.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): It is an extension of (PoS), where a specific number of delegates are chosen by participants to validate transactions and create blocks. Compared to PoS and PoW, DPoS offers scalability and faster block confirmation times, but it depends on a few number of trusted delegates.
- d.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): It is often used in enterprise applications. A specific group of validators who take turns proposing blocks and collectively agreeing on the validity of transactions. It can tolerate errors and provides fast response times.
3. Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are code-written agreements, characterized by predefined rules and conditions, and have the capacity to execute themselves automatically. They enforce the terms of an agreement automatically once the specified conditions are satisfied. Smart contracts facilitate the execution of decentralized applications on blockchain such as Ethereum. They offer transparency, immutability, and eliminate the need for intermediaries in contract enforcement.
4. Nodes in the Network: In the blockchain network, nodes refer to individual computers or devices that actively participate. Every node has a major part in distributing and validating transactions in addition to keeping a full copy of the blockchain in storage. Nodes come in various varieties:
- a.
- Full Nodes: Full nodes actively participate in the consensus process by validating and spreading transactions. They also maintain a complete copy of the blockchain. They verify the rules of the blockchain protocol independently, ensuring the integrity of the network.
- b.
- Mining Nodes: Mining nodes are specialized nodes that participate in the PoW consensus mechanism. They compete to add new blocks to the blockchain and solve cryptographic puzzles. It takes a significant amount of computational power and energy resources for mining nodes to carry out their tasks efficiently.
- c.
- Light Nodes: Light nodes, also known as lightweight or thin clients, do not save the complete blockchain. For relevant data about transactions and blocks, they depend on full nodes. Light nodes are more lightweight and consume fewer resources, making them suitable for devices with limited storage or processing capabilities.
Nodes play a vital role in maintaining the decentralized nature of the blockchain network. They contribute to consensus, validate transactions, propagate blocks, and ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain. These technical components form the foundation of blockchain technology, enabling secure and transparent decentralized systems with applications in various industries (See Figure 5).
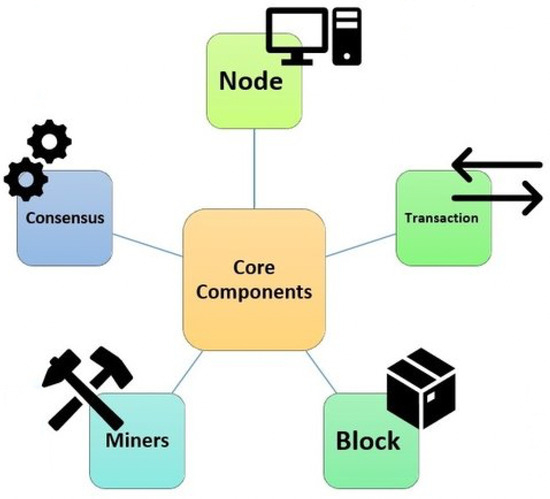
Figure 5.
Technical components of Blockchain.
6.4. Types of Blockchain
There are three different types of blockchains: consortium (also called federated) blockchains, private blockchains, and public blockchains [23]. The choice of blockchain type depends on the specific requirements of the use case. Public blockchains prioritize transparency and openness, while private and consortium blockchains prioritize privacy, control, and scalability within a restricted network. Table 1 explores each type and their characteristics:

Table 1.
Blockchain types.
6.5. Application of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has expanded its uses beyond cryptocurrencies and has made significant progress in various industries [24]. For example, in supply chain management, it improves transparency, traceability, and efficiency, benefiting sectors like food, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. In healthcare, blockchain securely manages medical records, enhances data sharing, and supports clinical trials. In finance and banking, it simplifies transactions, reduces costs, and enables e-finance applications. Additionally, blockchain assists in establishing and managing intellectual property rights, simplifies real estate transactions and ownership, and offers opportunities for automation and trust. These examples demonstrate how blockchain technology has the potential to transform industries by revolutionizing asset management, data integrity, and transaction processes as it continues to evolve.
6.6. Features of Blockchain
Blockchain technology possesses several features that differentiate it from traditional centralized systems [8]. The following are blockchain’s primary features:
1. Decentralization: Blockchain operates on a network of computers (nodes) spread across multiple locations, eliminating the need for a central authority. Consensus mechanisms ensure agreement among participants.
2. Distributed Ledger: Blockchain consists of a distributed ledger that maintains an unchangeable and chronological history of transactions or data. Resilience is increased because every node keeps a copy of the ledger.
3. Transparency and Immutability: All participants can see and understand the transparency of transactions that are recorded on the blockchain. An auditable and unchangeable record is created once a transaction is added, making it very difficult to change or remove.
4. Security: Blockchain employs cryptographic techniques to secure transactions. Public key cryptography ensures secure authentication, digital signatures, and data encryption. Consensus mechanisms protect against malicious activities.
5. Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are programmable contracts that are frequently supported by blockchain platforms. These self-executing contracts carry out transactions and obligations automatically by enforcing predetermined guidelines and conditions.
6. Trust and Consensus: Blockchain relies on consensus algorithms to establish agreement on transaction validity. Using techniques such as Proof of Stake or Proof of Work, participants reach a consensus, maintaining trust and preventing fraud.
7. Privacy: While blockchain is transparent, privacy measures can be implemented to protect sensitive information. Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs or private transactions allow for selective data disclosure, preserving privacy while maintaining blockchain integrity.
6.7. Challenges of Blockchain
Blockchain technology, despite its promise, encounters several challenges that must be tackled for widespread adoption. These challenges include scalability limitations, energy consumption concerns, regulatory complexities, interoperability issues and security risks. Scalability problems arise as transaction volumes increase, leading to congestion and slower processing times. Energy efficiency becomes crucial to ensure the sustainability of blockchain networks. Regulatory compliance across jurisdictions poses a challenge, necessitating a delicate balance between innovation and adherence to regulations. Interoperability gaps hinder seamless data and asset exchange between different blockchain platforms. Security vulnerabilities, such as smart contract bugs and hacking attacks, need constant research and robust security practices. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative research and continuous improvements in protocols, infrastructure, and ecosystem. The evolution of the technology will bring forth innovative solutions and best practices to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology.
7. Discussion
Protecting electronic business assets from unauthorized access, modification, or harm constitutes e-commerce security. Customers worry about the possible compromise of their financial details, whereas online businesses are anxious about the financial consequences resulting from security breaches. Principal social and organizational concerns linked to security encompass creating robust risk management procedures, formulating security protocols, enforcing division of responsibilities, guaranteeing security validation, and overseeing access control. A notable obstacle arises from the reality that the most vulnerable aspect in security often rests with the employees or users rather than the technology itself. Additionally, software engineering management plays a crucial role in overseeing the deployment of security technology. An enduring challenge involves users possessing diverse and inaccurate understandings of security, resulting in their hesitation or inability to comply with fundamental security protocols. For instance, users might store passwords in unsecured files on susceptible devices, while employees could disclose their passwords to external entities.
Unauthorized access pertains to illicit entry into information, systems, or applications for malicious purposes. Passive unauthorized access involves hackers eavesdropping on communication channels to acquire sensitive information for harmful objectives. On the other hand, active unauthorized access occurs when hackers manipulate or modify systems or information with malicious intent. Denial of Service (DoS) attacks can occur through spamming and viruses. Spamming denotes the excessive bombardment of emails by a hacker directed at a computer or network. In contrast, Distributed Denial of Service Attacks (DDoS) entail hackers deploying software agents on third-party systems to concurrently send requests to a specific target. Viruses, which are self-replicating computer programs with undesirable actions, can result in theft and fraud. As a result, the system becomes a prime target for cybercriminals seeking illegal access to data. Stolen software refers to illegal copying from organizational servers, while hackers might breach insecure merchant web servers to access credit card numbers and personal data collected during online transactions. Concerns about data theft extend to the merchant back-end and databases, particularly involving third-party fulfillment centers and other processing agents.
7.1. Cybersecurity Challenges in E-Commerce
7.1.1. Data Breaches and Data Theft
Data breaches represent a significant and ongoing danger in e-commerce, posing a constant threat to sensitive customer information [25]. Cyber attackers focus on acquiring valuable data such as credit card details, personal information, and login credentials that are stored by online businesses. These breaches have a profound impact, causing serious repercussions for both businesses and customers [25]. Organizations experiencing data breaches may encounter financial setbacks, reputational harm, legal repercussions, and a decline in customer trust. Customers, on the other hand, face the risk of identity theft, financial fraud, and privacy violations when their sensitive information falls into the wrong hands. The aftermath of these breaches often involves financial distress, stress, and a loss of confidence in online services, affecting customers’ willingness to engage in e-commerce transactions [13]. Preventing and mitigating these breaches are essential to maintaining trust and safeguarding the security of e-commerce transactions for businesses and customers alike.
7.1.2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are sneaky tricks used by cybercriminals to fool both customers and employees into revealing sensitive information [13]. They do this by sending deceptive emails or creating fake websites that look real, aiming to trick people into sharing their personal details like passwords, credit card numbers, or login information. These attacks often appear urgent or convincing, urging individuals to act quickly. To tackle these threats, educating people about the signs of phishing and how to spot suspicious emails or websites is crucial. Encouraging practices like verifying sender identities, avoiding clicking on unknown links, and reporting suspicious messages can help in reducing the risks of falling for phishing attempts. Additionally, regularly updating security software, implementing multi-factor authentication, and conducting cybersecurity training sessions can strengthen defenses against these deceptive attacks [13].
7.1.3. Ransomware and Malware
Ransomware and malware are two kinds of cyber threats causing trouble in the online world. Ransomware attacks can lock up important data or computer systems, making them unusable until a ransom, or payment is given to the attackers. These attacks can seriously disrupt business operations, making it difficult or impossible to access crucial information [13]. On the other hand, malware, which stands for malicious software, can harm e-commerce by sneaking into systems and causing various problems. It can steal or compromise sensitive customer data, leading to privacy issues and financial losses. Moreover, malware can disrupt e-commerce operations by slowing down systems, causing crashes, or spreading across networks. Protecting against these threats involves using robust cybersecurity measures like installing reliable antivirus software, regularly updating systems, and creating backups of important data to prevent significant disruptions or losses [13].
7.1.4. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Supply chain vulnerabilities and common vulnerabilities in e-commerce refer to risks linked with outside vendors, software connections, and partners involved in the business process [26]. These vulnerabilities become problematic because they can open doors to potential cyber threats. When e-commerce companies rely on third-party vendors or integrate various software systems, any weaknesses in these interconnected parts can become entry points for cyber attackers [26]. For instance, if a supplier’s systems are not properly secured, hackers might gain access to sensitive information or disrupt operations. Similarly, when e-commerce businesses use multiple software applications, any vulnerability in one of these programs can expose the entire system to risks [26]. Therefore, it is essential for companies to thoroughly vet their partners, ensure they have strong cybersecurity measures in place, and regularly monitor and update systems to minimize vulnerabilities and safeguard against potential threats.
7.1.5. Payment Fraud
Payment fraud in e-commerce comes in different forms, posing serious risks to businesses and customers alike. A prevalent form of fraud is card-not-present fraud, where perpetrators utilize stolen card information to conduct online purchases without physically presenting the card during the transaction [13]. Another type is account takeover, where hackers gain unauthorized access to a user’s account to make fraudulent transactions or steal personal information. Additionally, there is friendly fraud, where a customer falsely claims a transaction as unauthorized or seeks refunds after receiving the purchased item [13]. Fraudsters exploit vulnerabilities in payment processes, such as weak authentication methods or gaps in transaction monitoring, to carry out these fraudulent activities [26]. To prevent such fraud, e-commerce businesses can implement robust security measures like using advanced fraud detection tools, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly monitoring transactions for suspicious activities. Educating customers about safe online practices and promptly addressing any fraudulent incidents can also help in preventing payment fraud in e-commerce.
7.1.6. Identity Theft
Identity theft in e-commerce poses serious risks as cybercriminals target personal information to conduct unauthorized transactions or create fake accounts, causing financial and reputational harm to individuals [27]. These criminals steal sensitive details like names, addresses, social security numbers, or financial data to impersonate someone else. To prevent identity theft, e-commerce businesses employ measures to verify customer identities, such as using multi-factor authentication, biometric identification, or identity verification services. Robust encryption methods and secure storage of customer data are also crucial to safeguard against data breaches that could lead to identity theft [27]. Educating customers about the importance of strong passwords, avoiding sharing personal information on suspicious websites, and regularly monitoring financial statements for any unusual activity are additional steps to protect against identity theft in e-commerce.
7.1.7. Internet of Things (IoT) Vulnerabilities
IoT vulnerabilities in e-commerce relate to the potential risks posed by interconnected devices like smart home assistants or connected payment systems [18]. These devices, while offering convenience, can also become targets for cyber attacks due to their interconnected nature. Vulnerabilities in IoT devices arise from security gaps such as weak authentication, outdated software, or inadequate encryption [18]. Hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access, manipulate data, or launch cyber attacks. For instance, a compromised smart home assistant might be used to access sensitive information or control connected devices [18]. Similarly, vulnerabilities in connected payment systems could allow hackers to intercept transactions or steal financial data. To address these risks, it is crucial to regularly update device software, use strong passwords, employ encryption methods, and implement robust security measures to protect against potential IoT vulnerabilities in e-commerce.
7.1.8. Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness
The lack of cybersecurity awareness among employees, customers, and stakeholders is a significant concern in the realm of online safety. Understanding the importance of cybersecurity is crucial for everyone involved in e-commerce. Employees need to be aware of potential threats like phishing emails or malware attacks to prevent security breaches within the company [13]. Customers must recognize the risks associated with sharing personal information online and adopt safe practices while making online transactions [18]. Similarly, stakeholders play a vital role in maintaining a secure environment by staying informed about cybersecurity measures and supporting initiatives to bolster online safety. Providing regular training sessions, workshops, and updates on security best practices is essential to enhance awareness and minimize potential risks [18]. These efforts help individuals recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively, fostering a safer e-commerce ecosystem for everyone involved.
7.1.9. Regulatory Compliance Challenges
Businesses encounter significant challenges in meeting the requirements set by data protection regulations such as CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) [7]. These regulations impose strict rules on how companies handle and protect sensitive data, including customer information [7]. One major challenge is the complexity of these regulations, as they often have specific and intricate guidelines that businesses must follow. Ensuring compliance while maintaining efficient e-commerce operations can be tricky, as it requires substantial resources, time, and expertise to implement the necessary changes in processes, systems, and policies [7]. Balancing the demands of compliance without hampering the smooth functioning of e-commerce operations poses a significant hurdle. Companies need to invest in robust data protection measures, employee training, secure technology infrastructure, and regular audits to adhere to these regulations while ensuring uninterrupted e-commerce activities.
7.2. Blockchain Role in E-Commerce
7.2.1. Immutable and Transparent Ledger
The immutable and transparent nature of the blockchain makes it a powerful tool for strengthening safety in e-commerce, by creating an unchangeable record of transactions. This ledger is like an uneditable logbook, where once information is added, it cannot be altered or deleted [28]. This feature helps prevent data manipulation or unauthorized changes because every transaction is linked to the previous one, forming a chain that is extremely hard to tamper with [28]. Moreover, its transparency enables every participant within the blockchain network to access the complete history of transactions, fostering openness and trust among users. This transparency, coupled with immutability, guarantees the integrity and genuineness of transactional data, creating a high level of resistance against fraudulent activities or tampering attempts. As a result, blockchain technology brings a high level of security and trust to e-commerce by providing a tamper-proof and transparent ledger that maintains the accuracy and reliability of transaction records [28].
7.2.2. Enhanced Data Security
Blockchain technology significantly enhances data security in e-commerce by using advanced cryptographic methods and a decentralized structure [28]. Through encryption, sensitive information is encoded and can only be accessed by authorized individuals, keeping it safe from unauthorized eyes. Hashing further secures data by converting it into unique strings of characters, making it incredibly challenging for hackers to manipulate or decipher the original information [28]. Moreover, blockchain’s consensus mechanisms ensure that data stored on the network is agreed upon by multiple participants, making it difficult for any single entity to alter the information without consensus. This decentralized structure means data are not stored in a single location, reducing the risk of a central point of failure and making it extremely challenging for cyber attackers to breach the system. Through the utilization of cryptographic techniques and a decentralized structure, blockchain technology plays a pivotal role in protecting customer information, consequently reducing the chances of data breaches in e-commerce transactions [28].
7.2.3. Fraud Prevention and Identity Management
Blockchain technology offers decentralized identity management systems that significantly aid in fraud prevention and bolstering identity verification in e-commerce [29]. Such systems facilitate a more secure and dependable method of managing and verifying identities through the utilization of digital identities stored on the blockchain [29]. Through blockchain-based digital identities, individuals gain greater control over their personal information. This empowerment enables them to selectively disclose only essential details for transactions while safeguarding sensitive data from exposure. Self-sovereign identity solutions, a part of this system, empower individuals to manage their identities independently without reliance on centralized authorities [29]. This advancement boosts trust and security in e-commerce interactions by securely verifying identities without relying on intermediaries, thereby lessening the risk of identity theft or fraudulent activities. Leveraging blockchain’s decentralized identity management, e-commerce can establish a safer and more reliable environment for transactions, safeguarding user identities and thwarting fraudulent attempts [30].
7.2.4. Secured Payments and Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based payment systems play a crucial role in bolstering security by offering secure and transparent transactions without relying on intermediaries like banks or payment processors [28]. These systems use the blockchain’s decentralized ledger to record and verify transactions securely, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities or unauthorized alterations [28]. Additionally, smart contracts, a key feature of blockchain technology, automate and enforce predefined conditions in transactions without the need for intermediaries [9]. These contracts are like digital agreements that execute automatically when specific conditions are met, ensuring that both parties fulfill their obligations transparently and securely [9]. Automating processes through encoding and executing contract terms as programmed helps minimize the risk of disputes or fraudulent activities. This reduction in reliance on a central authority for trust is due to the encoded execution of contract terms. Through blockchain-powered payment systems and smart contracts, e-commerce transactions become more secure, efficient, and resistant to disputes or fraudulent actions, enhancing trust between parties involved in transactions.
7.2.5. Supply Chain Transparency and Authentication
Blockchain technology is instrumental in improving supply chain transparency by establishing an immutable record of critical information. This includes details regarding the origin of products, their trajectory within the supply chain, and the verification of their authenticity [31]. This immutable record ensures that every step in the supply chain is securely and transparently documented, making it difficult to alter or tamper with the information [28]. This transparency helps in preventing counterfeit products as it becomes easier to trace the origin and movement of goods [31]. By providing a reliable way to verify the authenticity of products, blockchain helps in ensuring that customers receive genuine items when making purchases in e-commerce. In essence, the contribution of blockchain to supply chain transparency and authentication instills greater trust and confidence among consumers. This ensures the receipt of authentic and high-quality products while acting as a deterrent to counterfeit activities within the e-commerce sphere [31].
7.2.6. Decentralized Marketplace Security
Decentralized marketplaces employing blockchain technology show potential in transforming e-commerce by eliminating the necessity for a central authority. This facilitates secure transactions directly between peers [28]. These marketplaces operate without a single controlling entity, relying instead on the decentralized nature of blockchain [32]. As a result, they provide a more secure environment for transactions, as data are not stored in a central location vulnerable to attacks [28]. Blockchain’s decentralized structure spreads transaction data across the network, making it extremely challenging for hackers to breach the system or manipulate information. By eliminating the reliance on a central authority, decentralized marketplaces reduce the risk of data breaches and hacking attacks, enhancing security and trust among participants engaging in peer-to-peer transactions in e-commerce.
7.2.7. Regulatory Compliance and Auditing
Blockchain technology offers e-commerce businesses a transparent and easily auditable system that greatly aids in meeting regulatory compliance requirements [7]. Moreover, the decentralized characteristic of blockchain ensures that no single entity possesses control over the data, thereby bolstering trust and diminishing the risk of manipulation. By utilizing blockchain’s transparent and immutable records, e-commerce businesses can streamline audits, demonstrate compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA, and maintain the integrity of their transactional data, fostering trust among stakeholders and regulatory bodies [7].
7.2.8. Limitations of Implementing Blockchain in E-Commerce
Blockchain encounters significant challenges regarding scalability and integration within existing e-commerce systems [33]. As blockchain networks grow larger, the technology faces issues in handling a high number of transactions quickly and efficiently. Integrating blockchain into current e-commerce infrastructures also poses challenges due to compatibility issues and the need for substantial changes to established systems [33]. To overcome these hurdles, ongoing efforts focus on improving blockchain scalability by developing solutions like sharding, off-chain transactions, or layer-two protocols [33]. These aim to enhance the capacity of blockchain networks to process more transactions without compromising security. Additionally, efforts are directed towards interoperability standards that enable different blockchains to communicate and work together seamlessly. Addressing these scalability concerns while ensuring smooth integration into existing e-commerce infrastructures remains a key focus, as it enables businesses to leverage blockchain’s security benefits without compromising on performance or usability.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends are poised to significantly impact the security of e-commerce transactions. One such trend is the development and adoption of Layer-two solutions, designed to improve the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks. Layer-two solutions, including sidechains and off-chain protocols like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and similar options for other cryptocurrencies, aim to relieve congestion on the main blockchain, thereby enhancing transaction speed and reducing costs without compromising security [33]. Another crucial trend is the focus on interoperability, enabling different blockchain networks to communicate and share information seamlessly. Initiatives like cross-chain communication protocols and interoperability-focused projects facilitate the exchange of assets and data across disparate blockchains, fostering a more connected and versatile ecosystem for e-commerce. Moreover, advancements in consensus mechanisms, such as the exploration of newer, more energy-efficient protocols beyond Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), are underway. Innovations like Proof of Authority (PoA) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) offer enhanced security, scalability, and energy efficiency, potentially transforming the landscape of e-commerce transactions by providing faster and more secure validation processes [33]. These trends and innovations collectively signify a promising future for blockchain technology in securing e-commerce transactions, promising improved scalability, interoperability, and robust security measures.
Moreover, since countries have different laws and regulations, this make it quite difficult to implement blockchain in e-commerce. Collaboration between governments is important, and developing standard regulations between countries. To make the Blockchian implementation possible [7].
Every transaction and data entry in blockchain is recorded and stored in a sequential manner. The blockchain size increases when more transaction occurs. Each participant in the network will have a complete copy of the blockchain which makes storage a serious challenge to the participants. To overcome this load issue, the blockchain data could be divided into smaller segments and distributed through multiple nodes. Without affecting data integrity, irrelevant data will be removed. Furthermore, off-chain can be optimum solution to handle less sensitive data [33]. By using cloud services scalability will be increased and storage responsibilities will be reduced [33]. Table 2 shows the different challenges in implementing blockchain along with their mitigations.

Table 2.
Challenges in implementing blockchain in e-commerce.
8. Blockchain in Action: Real-World Implementations
- Data Breaches and Security Threats:E-commerce platforms store massive amounts of sensitive data. This will make them a target for attackers. Blockchain offers decentralization and immutable ledger which can overcome this risk by distributing data across a network of nodes. Each transaction will be cryptography linked which make it difficult for attackers to interrupt or alter the data. By implementing blockchain, Walmart has been able to enhance the security in several ways, which are as follows:
- Blockchain technology enables Walmart to maintain immutable records of all transactions and activities in its supply chain. This means that once data are recorded on the blockchain, they cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring the integrity and security of the data.
- Blockchain technology enables Walmart to capture real-time data at every stage of the supply chain. This real-time data access allows Walmart to monitor the supply chain processes, identify any issues, and take corrective action in a timely manner.
- Blockchain technology facilitates secure and transparent information sharing across the supply chain. By storing data on a public blockchain, all parties in the supply chain can access the same information, increasing trust and transparency. This also reduces the risk of fraud, as data cannot be tampered with.
- By recording data on the blockchain, Walmart has reduced the need for manual data management. This has improved the accuracy and security of data in the supply chain.
- Payment Fraud and Identity Theft:Unauthorized transactions and identity theft are considered as a major concerns in e-commerce. Blockchain can offer a secured payment system and peer-to-peer transactions without needing intermediaries. Cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum will enable users to make a secure transactions. BitPay implemented the Bitcoin for e-commerce to reduce the risks of fraud [34]. BitPay, has a main role in the Bitcoin ecosystem, implemented the blockchain in its operations as part of its seller services. The blockchain is the public ledger that records all Bitcoin transactions. BitPay utilized the blockchain to verify and record Bitcoin transactions made by customers of the seller using its services. This allowed for secure and transparent verification of transactions without the need for a central authority, aligning with the decentralized nature of Bitcoin.
- Centralized Points of Failure:Traditional e-commerce are facing a single point of failure by having a centralized approach. This will make them targets and vulnerable to attacks. Decentralization nature of the blockchain technology will elimantes this single point of failure and enhancing the overall security situation. OpenBazaar is an example of a decentralized e-commerce platform built on blockchain, allowing users to buy and sell goods without relying on a central authority [35].
- Smart Contracts for Trustworthy Transactions:Blockchain’s smart contracts enables a secure agreements between parties. This will enhance different e-commerce processes such as refunds, delivery confirmations, and escrow services, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing trust. IBM has been working on blockchain-based supply chain solutions that utilize smart contracts to automate and enforce agreements between multiple parties [36]. IBM has implemented blockchain technology to enhance security through its Hyperledger Fabric framework. The Hyperledger framework provides a blockchain infrastructure, offering a high level of security and privacy for enterprise solutions. By leveraging Hyperledger framework, IBM aims to address existing technology limitations related to privacy, confidentiality, auditability, performance, and scalability. The use of a distributed ledger and an unchangeable transaction log accessible to all network participants ensures the security and integrity of the data [36].
9. Comparison with Other Review Papers
Our study main aim is to explore the relationship between blockchain technology, e-commerce, security, and privacy. The primary focus is to analyze the current cybersecurity challenges in e-commerce, including issues like data breaches, phishing, payment fraud, and regulatory compliance. While the other studies did not explore similar issues regarding cybersecurity. Furthermore, by improving data security, guaranteeing transaction transparency, protecting payment methods through smart contracts, and bolstering supply chain authenticity, the study intends to investigate the possibilities of blockchain technology as a viable solution to these problems. This exploration aims to demonstrate how blockchain can enhance e-commerce security and boost trust. Moreover, the study aims to highlight both the advantages and limitations of blockchain implementation in e-commerce, paving the way for future research and practical applications in this domain. On the other hand, other studies did not clarify limitations of implementing blockchain technology. Moreover, this study presents an analysis of related studies, identifies existing limitations, and sheds light on prospective future directions in e-commerce security bolstered by blockchain technology. In our paper, we investigated the different blockchain platforms with a detailed comparison with highlighting the current applications of these platforms along with the possibilities suggestions. Furthermore, they presented various protocols of blockchain technology in general aspects while we elaborated more in investigating these protocols. We have defined blockchain technology in detail, which gives the reader the ability to understand this technology, how it works, and what its various types are.
The study [28] explored how the blockchain technology can enhance the security of e-commerce platforms. They found that once data are recorded on a blockchain, they cannot be messed with. That means attackers cannot access the data or make any alterations, which helps in ensuring the data’s integrity and authenticity. In addition, they also found that digital signature and encryption security features in blockchain can make sure the transactions are safe and private. The decentralization of the blockchain technology can also give a further enhancement of the validation of e-commerce transactions, which distributes it through various nodes. The smart contract is also beneficial to make the execution faster and secure. The study did not provide a comprehensive analysis of the potential challenges and limitations of implementing blockchain technology in e-commerce security. They did not consider the scalability issues and performance limitations of blockchain technology in the context of e-commerce transactions. Moreover, they did not explore the potential regulatory and compliance challenges associated with the adoption of blockchain technology in e-commerce security.
In [37], the authors focused on exploring the different applications of blockchain in e-commerce industry. Defining, in a short view, what e-commerce is, what blockchain technology is, and what the benefits of implementing this technology are. They discussed how blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the efficiency of e-commerce by addressing challenges related to online transaction processing, data security, order and payment processing, and transparency. They highlighted several companies that are already implemented blockchain in e-commerce. Additionally, they addressed that the implementation of blockchain technology in e-commerce platforms may face challenges related to scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance. The weakness of this paper is that it did not focus on the various violations that e-commerce may be exposed to. The authors suggested that further research is needed to address these limitations. The forthcoming Table 3 shows a comparison between our study and other relevant studies.

Table 3.
Comparison with other review papers: (✓: the criteria was mentioned and discussed).
10. Related Study
This section reviews recent studies in the field and summarizes their key findings regarding e-commerce security and blockchain integration, along with what the possible mitigations are according to the best of our knowledge presented in Table 4.
Dahal et al. [28]. This study aims to examine the effectiveness of blockchain technology in securing e-commerce transactions and preventing fraudulent activities. It explores the application of blockchain across various e-commerce platforms, evaluating its capability to enhance transaction security and reduce the risks associated with fraud. The research highlights several benefits of blockchain in securing e-commerce transactions. A primary discovery underscores the immutability of blockchain records, ensuring the inability to tamper with transaction data once they are recorded. This attribute substantially impedes fraudulent manipulation, thereby upholding the authenticity and integrity of the data. Furthermore, cryptographic security stands out as a crucial element that enhances the safety of e-commerce transactions within blockchain technology. Methods like digital signatures, hash functions, and encryption algorithms reinforce secure and confidential transactions, preventing unauthorized access to transaction data. Another crucial finding revolves around decentralized consensus: validating and confirming transactions through a network of nodes instead of a central authority. This decentralized validation deters fraudsters from manipulating or altering transactions, as compromising numerous nodes becomes exceedingly challenging. Furthermore, the investigation highlights that the utilization of smart contracts automates e-commerce transactions, executing them based on predetermined rules and conditions. This approach diminishes the necessity for intermediaries and consequently minimizes the risks associated with fraud. Moreover, the traceability of transactions and associated data enabled by blockchain simplifies the identification and investigation of fraudulent activities. This technology permits the thorough tracking of transactions, providing comprehensive records that aid in detecting and preventing fraudulent actions in subsequent occurrences.
Deshmukh et al. [32]. This study conducts a systematic review to outline the fundamental characteristics and architecture of the blockchain in the context of e-commerce. Additionally, the researchers propose an application based on blockchain technology as part of their investigation.
Treiblmaier et al. [7]. This study’s objective is to systematically formulate research questions exploring the impact of blockchain on e-commerce. This involves correlating the essential aspects of e-commerce with the potentially disruptive characteristics of blockchain technology. This paper provides a brief discussion focusing on the pertinent characteristics of both e-commerce and blockchain technology. In conclusion, a comprehensive research framework is compiled for each of the questions. The paper discusses the implications for academia and industry while also highlighting several limitations. Furthermore, it offers brief insights into potential directions for the next generation of research.
Jiang et al. [38]. The researchers of this study aim to elucidate privacy concerns related to the disclosure of sensitive information, including identities, addresses, and telephone numbers, within the sphere of e-commerce. They design a model to protect privacy in e-commerce systems that use blockchain technology. In order to secure users’ identities and validate ownership, the researchers employ a cryptographic method called zero-knowledge succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge (zk-SNARKs).
The study conducted by E.Cristina [39], “Blockchain in e-commerce”, presents an overview of blockchain, offering a concise definition and emphasizing its significance. It delineates the fundamental elements within blockchain architecture such as blocks, hashes, transactions, chains, and nodes. Furthermore, the study details the operational mechanism of blockchain technology and explores its advantages in the realm of e-commerce, particularly in terms of security, cost-effectiveness, speed, tracking capabilities, reliability, and transparency.
Xuan, T., Alrashdan, T., and Al-Maatouk, Q. (2020) [40]. These authors underscore the significance of integrating blockchain technology into e-commerce. Their research highlights the crucial role of blockchain in safeguarding sensitive organizational information, mitigating potential data breaches, and thwarting unauthorized access to databases. Explore and identify effective methods of minimizing data breach issues in e-commerce platforms by applying blockchain technology, highlighting the two primary types of blockchain, namely public and private, and provide insights into their respective applications.
A study carried out by Bulsara, H. and Vaghela, P. [37], highlights the multiple challenges that conventional e-commerce encounters, encompassing transaction processing, data security, order and payment procedures, and transparency issues. Their study delves into the potential solutions offered by integrating blockchain technology into e-commerce, elucidating how such integration effectively tackles these challenges. Additionally, their research explores the wide-ranging applications of blockchain in various domains, including payment systems, security enhancement, supply chain management, and promoting ethical practices to ensure transparency within e-commerce operations. Finally, the conclusion highlights that the utilization of blockchain will foster an environment of transparency and trust, empowering customers with an anti-fraud system within e-commerce platforms.
In the research conducted by Guntara, R., Nurfirmansyah, M., and Ferdiansyah [4], The characteristics of integrating blockchain technology with e-commerce are highlighted, underscoring its advantages in terms of ensuring secure transactions and protecting user information. Multiple approaches to implementing blockchain in online e-commerce transactions are examined, payments using cryptocurrencies for faster and safer payments, digital identity verification to prevent fraud, item tracking to track purchased products easily, and application development to enhance transaction security. For instance, an application can notify users of any modifications to their transactions, further enhancing security measures.
Jiang, Ji et al. [23]. Here, a thorough examination is conducted, emphasizing the integration of blockchain technology into e-commerce platforms, with a particular focus on Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). As a result, this research establishes a conceptual framework that outlines the structure of e-commerce platforms empowered by blockchain technology specifically tailored for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Furthermore, they put forward three primary applications to illustrate how this platform aids SMEs in effectively managing security and privacy concerns. The researchers regard blockchain technology as a fitting solution for the challenges faced by SMEs since it guarantees the authenticity and transparency of data. They utilized blockchain to record and track all information, effectively addressing the problem of product counterfeiting. For SMEs, the blockchain’s chain structure assures the authenticity and transparency of data. Its encryption algorithm resolves the conflict between safeguarding data privacy and fulfilling information sharing requisites. Moreover, its smart contract functionality guarantees the automatic execution of transactions based on predefined conditions. Although the integration of blockchain technology with e-commerce platforms can effectively address specific privacy and security concerns encountered by SMEs, there still exist unresolved issues. An ongoing challenge lies in ensuring the authenticity of data before its entry onto the blockchain, thereby potentially exposing all nodes to the risk of fraudulent or misleading source data.
The study presented in [30] conducts an extensive investigation into PRODCHAIN, a blockchain-based solution designed to integrate product/value chains and supply chains. The development of this solution aims to prevent data manipulation by offering a transparent view of the data across the entire lifecycle of products, spanning from their creation to consumption. The primary contributions highlighted in the paper involve the consolidation of value chains and supply chains within a unified, transparent blockchain-based solution. Additionally, it emphasizes the integration of blockchain technology across e-commerce stages, encompassing product development to customer acquisition. Furthermore, the paper underscores the integration of lattice-based cryptography in the blockchain sign-cryption process. Consequently, organizations have consistently acknowledged the significance of establishing a transparent and decentralized value-chaining process. Hence, blockchain technology has been embraced within the value chain and supply chain sectors to prevent unauthorized access and fraudulent activities. Its adoption ensures data integrity, prevents tampering, and facilitates trust, transparency, and comprehensive traceability of stored transaction records. The researchers provide detailed insights into their proposed approach, presenting a blockchain-based solution that seamlessly integrates both the value chain and supply chain through the utilization of blockchain lattice. The foundational elements of blockchain concepts integrated into the proposed operational model comprise a distributed network, a shared ledger, consensus algorithms, and cryptographic digital transactions. As a result, the PRODCHAIN network facilitates a fully transparent process, allowing all stakeholders access to product information at any given time.
In [19], the authors carry out a study investigating blockchain-based e-commerce, emphasizing its suitability and the challenges it presents. They deliberated on the issues linked with conventional e-commerce and explored how blockchain technology can effectively resolve these challenges. In certain instances, traditional e-commerce faces vulnerabilities such as data leaks, underscoring the importance of employing blockchain to fortify the security of e-commerce platforms. Through the utilization of a distributed ledger within blockchain, transactions can uphold their integrity and authenticity while mitigating the risk of tampering. Blockchain enhances the security, simplicity, and speed of transactions within e-commerce platforms. Blockchain offers protection, allowing users to conduct transactions more securely and store their digital assets in a secure manner. Blockchain technology possesses the potential to address challenges such as fraud, cyberattacks, and data breaches, consequently bolstering customer trust and confidence in online transactions. The authors elaborate on blockchain’s capability to encrypt all transactions, thereby facilitating highly secure services without necessitating intermediaries. In the final sections of the study, the authors delve into the challenges associated with implementing blockchain in e-commerce. Among the challenges highlighted are considerations for future use, particularly the incorporation of an alliance chain connecting subsidiary chains and main chains within supply chain transaction systems. This is prompted by the constraints associated with the limited storage efficiency and capacity of a single blockchain. Furthermore, contracts on the blockchain are either immutable or exceedingly challenging to modify, raising concerns regarding potential loopholes in contracts. As a result, emphasis on information security should pivot toward refining smart contracts.
The paper by Ismanto, L. et al. [8] explores the utilization of blockchain, cryptocurrency, and smart contracts in the context of e-commerce in Indonesia, with the objective of augmenting transaction security and efficiency. The findings seek to advocate for the adoption of blockchain technology as the foundational architecture for e-commerce systems in Indonesia. While e-commerce has gained traction among numerous companies in Indonesia, it is not without flaws and room for improvement. Incorporating blockchain technology possesses the potential to effectively tackle and resolve current issues prevalent in e-commerce. By utilizing cryptocurrency, blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating commission fees and limitations in buyer–seller interactions. Smart contracts play a crucial role in ensuring fairness and security by enforcing predefined conditions. Additionally, transparent and decentralized ledgers foster an environment conducive to trust. However, despite its promise, blockchain remains a relatively new and evolving technology that lacks full maturity. Regulatory frameworks in countries like Indonesia remain unclear due to associated risks with blockchain and cryptocurrency, such as money laundering and the emergence of black markets. The objective of this paper is to make a contribution to future research efforts within the domain of blockchain technology, recognizing both its promise and the present challenges it entails.
Fuli Zhou et al. [41]. This research systematically examines the influence of blockchain on cross-border e-commerce supply chain management through bibliometric analysis. The study covers the period from 2013 to 2021 and sources pertinent publications from the Web of Science database. Utilizing VosViewer for network and co-word analyses, this research visually represents collaborative relationships within the chosen literature. The findings highlight the substantial applications of blockchain in cross-border e-commerce supply chains, particularly in the realms of e-commerce platforms, supply chain operations, and data governance. The study recommends that embracing blockchain technology can stimulate innovative practices in cross-border e-commerce supply chain management, benefiting both academic researchers and industry leaders alike. Moreover, the study endeavors to provide guidance for forthcoming research and engineering endeavors aimed at harnessing blockchain technology to improve cross-border e-commerce supply chain management. The analysis indicates that research on blockchain has diversified across multiple fields, encompassing areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT), supply chain, intelligent communities, cloud computing, the chemical industry, and aviation. Underlining blockchain’s significance in cross-border e-commerce, supply chain management, information management, and data governance, the study underscores its potential contributions to innovative management practices. Significantly, the paper discusses blockchain’s capability to tackle challenges in cross-border e-commerce, encompassing aspects such as customer information security, logistical efficiency, product authenticity, and traceability. Furthermore, it explores blockchain’s distinct roles in procurement, manufacturing, and distribution chains within the cross-border e-commerce supply chain, highlighting opportunities for innovation. Moreover, the study provides theoretical insights and practical implications. It proposes that blockchain technology enables flexible management and efficient resource allocation within cross-border e-commerce supply chains through the implementation of innovative practices.
The research study [42] discusses a technology called “layer 2” and its potential impact on making e-commerce safer. It outlines the challenges faced by online stores and how using layer 2 technology, based on secure blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, can help solve these issues. It explores various ways this technology can be applied in e-commerce while considering factors like costs and the amount of money needed for larger transactions. From a security standpoint, layer 2 technology holds promise in making online payments more secure, faster, and cheaper compared to using credit cards. It is especially beneficial for online stores handling numerous transactions and diverse products, offering enhanced security and faster processing without high transaction fees. New participants joining this technology can engage in transactions securely and efficiently without requiring significant upfront investments. This technology appears well-suited for large-scale e-commerce scenarios due to its adaptability and reduced financial requirements. Considering the time and cost factors, integrating this technology seems advantageous for ensuring a more secure e-commerce experience.
This study [20] suggests using blockchain technology in cross-border e-commerce to share records across different areas and track them. It looks at the good and bad sides of this new idea in terms of protecting data, how fast you can get to it, how safe it is, how easy it is to set up, and more. They explained blockchain and how it works in their study and came up with different methods that make their idea work better. The test results show that our plan is pretty good at storing information well, being quick with transactions, tracking things, and using less power. However, there might be some security issues, like someone getting hold of secret keys when they are being shared. In the future, they plan to use special codes like attribute encryption and others, together with blockchain, to keep users’ private information safe. They made special contracts that use unchangeable blockchain tech and tricky codes to store files and keep users’ private details safe in e-commerce across different areas. Also, they designed another contract to check and make sure both sides sharing data are who they say they are and to do it quickly without needing a third party. Their experiments show that the conducting plan in this research is better at stopping data theft, checking if everyone involved is who they should be, and using fewer system resources compared to regular ways of storing information in the cloud. This could be a helpful way to make sharing data safer using blockchain’s way of not being in one place and being easy to check.
This paper [25] aims to improve trust in e-commerce by providing guidance on enhancing security measures. It investigates how people view security in both business-to-customer (B2C) and customer-to-customer (C2C) e-commerce websites, considering both customer and authoritative perspectives. With e-commerce growing rapidly, concerns about security are becoming more prominent. Security during transactions is a significant issue in e-commerce development. This paper addresses security concerns in e-commerce activities by suggesting strategies related to technology and system improvements. The goal is to create a safer environment for e-commerce growth and foster further development in this field. E-commerce security involves safeguarding e-commerce assets from unauthorized access, use, or damage. Customers express concerns about the safety of their financial information, while e-commerce platforms are apprehensive about potential financial losses resulting from security breaches. Several crucial social and organizational issues are associated with security concerns. Firstly, it is vital to establish robust organizational procedures encompassing risk management, security policies, and stringent access controls. Secondly, security vulnerabilities often stem from human factors, such as employees or users, rather than inherent flaws in the technology itself. Thirdly, the effective implementation and management of security technology are paramount. A persistent challenge is the misunderstanding or neglect of basic security protocols by users. For example, storing passwords in unprotected files or sharing passwords with unauthorized individuals pose significant risks.
Sumit Badotra et al. [13] conduct a systematic literature review that aims to explore security measures and challenges by surveying publications from the past decade. It details prominent attacks in e-commerce, providing insights for researchers and academics in this field to understand current trends. The primary goal is to analyze the security status of e-commerce systems. Through a comprehensive review of literature spanning the last decade, this paper offers a year-by-year overview of attacks on e-commerce sites. Additionally, it includes discussions concerning security measures and challenges within this context. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers focusing on e-commerce system security.
A study conducted in [43] introduces a model that leverages blockchain technology to improve e-commerce, focusing particularly on the consumer-to-consumer (C2C) aspect. This model aims to streamline business processes and eliminate the role of large corporations, allowing consumers to directly exchange products and services with each other. By leveraging an online markets like eBay, this model creates a trustworthy and reliable environment for consumers, fostering decentralized markets. The C2C market is expected to grow due to its cost-effectiveness, as blockchain reduces transaction costs by eliminating the need for third-party fees typically imposed by large companies. The research proposes that adopting this model enhances the credibility of business processes by harnessing the benefits of blockchain technology. It emphasizes advantages like data distribution among all participants and the monitoring of consumer behavior. Blockchain is regarded as an effective alternative for ensuring transaction credibility and preventing manipulation, enabling individuals to engage in trade without dependence on third-party intermediaries. Consumers value transparency, trust, and ethics, and many base their purchasing decisions on information stored in the blockchain. However, the study acknowledges the challenge of practically implementing this model across various areas of e-commerce operations, transitioning from traditional to practical practices. Future work will involve thoroughly examining technical aspects and conducting real-world testing with experts.
The study conducted in [44] provides an outline of blockchain technologies, highlighting their advantages and challenges specifically within the realm of online shopping. Consequently, the authors propose the utilization of blockchain’s features, such as traceability and trustlessness, in two e-commerce applications: social shopping and loyalty programs. These applications aim to enhance customer engagement within the e-commerce sphere. These applications harness the complete potential of blockchain to elevate the customer experience by offering heightened security and necessitating minimal investment in technological infrastructure. The study contributes significantly to the continuous advancement of both e-commerce and blockchain technologies.

Table 4.
Existing work in this field.
Table 4.
Existing work in this field.
| Reference | Key Findings | Limitations/Research Gaps | Suggested Mitigation |
|---|---|---|---|
| [7] |
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
|
| [40] |
|
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
|
Jebamikyous, H. et al. [45]. This study conducted an extensive review focusing on the benefits derived from integrating blockchain technology with machine learning techniques. The distinctive characteristics of blockchain, such as decentralization, persistence, and transparency, are merged with the intelligent processes and decision making facilitated by machine learning algorithms. The review elucidates the core concepts and attributes of both blockchain and machine learning technologies. Furthermore, it delves into their cutting-edge applications in various domains, including but not limited to e-commerce and the burgeoning IoT. These chosen domains share common traits, such as engaging with multiple partners and handling extensive volumes of data. The review elaborates on the substantial advantages derived from the integration of machine learning and blockchain within each application area. Simultaneously, it addresses the limitations associated with this integration. Through harnessing machine learning’s ability to manage vast amounts of data and blockchain’s dependable data storage capabilities, the fusion of these technologies facilitates enhanced security in classification and prediction decisions. This is achieved by offering secure and private access to data. The authors underscore the challenges linked to merging blockchain and machine learning, encompassing concerns about the accuracy, sustainability, and scalability of machine learning models. Additionally, they highlight aspects related to the security, suitability, memory, and infrastructure within blockchain technology. They emphasize the critical importance of accuracy, sustainability, and scalability in the adopted machine learning models, particularly due to the abundance of big data across various domains, crucial for effective decision making. Hence, it is crucial to meticulously choose suitable machine learning methods and assess their vulnerability and scalability levels. This scrutiny ensures the sustainability and efficiency of intelligent decision-making systems.
11. Open Challenges and Limitations
Given the compelling exploration of blockchain’s potential in fortifying e-commerce security, several challenges and limitations within this domain warrant attention. A key challenge revolves around the scalability limitations inherent in blockchain technology. As transaction volumes increase, blockchain networks might encounter constraints in processing speed and throughput. This issue could potentially impede seamless and swift transaction processing. Another significant challenge relates to the substantial energy consumption linked with blockchain operations, notably in proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, prevalent in many blockchain implementations. The substantial computational power required for mining and validating transactions raises concerns about the environmental impact and sustainability of such systems. Additionally, while blockchain offers an immutable ledger, ensuring data integrity, the technology confronts challenges in reconciling the right to erasure or modification of personal data in compliance with evolving data protection regulations like the GDPR. Moreover, the reliance on smart contracts in blockchain-based e-commerce introduces challenges in ensuring the accuracy of contract terms and executing complex conditions accurately, potentially leading to legal ambiguities or disputes. Furthermore, the complexity of implementing blockchain into existing e-commerce infrastructures poses a considerable hurdle, requiring significant resources, expertise, and compatibility considerations. Lastly, user adoption and trust in blockchain-based e-commerce platforms remain a challenge, as the technology’s intricacies and its association with cryptocurrency may create barriers for widespread acceptance among consumers and businesses. Addressing these challenges necessitates concerted efforts in research, innovation, and collaborative endeavors to refine blockchain technology’s application in e-commerce, striving for a balance between security, efficiency, sustainability, and regulatory compliance.
12. Future Directions
In the future, the integration of blockchain technology into the realm of e-commerce opens up promising avenues for exploration and development. As the digital realm continues to evolve, future research should delve into optimizing and fine-tuning blockchain applications to enhance the security of online transactions. Given the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats, obtaining a thorough comprehension of the interaction between blockchain technology and emerging security challenges becomes imperative. Investigating novel methods to integrate blockchain with other advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning holds the potential to strengthen the e-commerce sector against evolving cyber threats.
Moreover, future research efforts should concentrate on devising standardized protocols and frameworks to facilitate the smooth integration of blockchain across various e-commerce platforms. Addressing issues related to scalability, interoperability, and user adoption will be crucial for the widespread and effective deployment of blockchain solutions. The collaboration between academia, industry experts, and regulatory bodies will play a pivotal role in creating a favorable environment for the adoption of blockchain in e-commerce. This collaboration will aid in fostering a secure and robust digital marketplace.
Furthermore, research initiatives should delve into the socio-economic implications stemming from the adoption of blockchain in e-commerce. This investigation should encompass aspects such as user trust, regulatory compliance, and the broader economic impact on businesses. Comprehending the enduring impacts of blockchain integration on consumer behavior and market dynamics will offer valuable insights crucial for shaping future policies and strategies.
Table 5 provide a comparison between different blockchain protocols (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum, Hyperledger) based on factors such as consensus mechanisms, scalability, transaction speed, security features, and suitability for e-commerce transactions.

Table 5.
Different blockchain protocols to enhance e-commerce transactions.
Table 6 determines some security features that are afforded by blockchain to enhance security of e-commerce transactions.

Table 6.
Security features offered by blockchain to protect e-commerce transactions.
In addition, Table 7 illustrates various use cases of blockchain implementation in e-commerce from a security perspective, outlining the specific challenges faced, the solutions applied to address these challenges, and the outcomes achieved in terms of enhancing security within each use case scenario.

Table 7.
Use case examples of blockchain implementation in e-commerce.
Table 8 compares smart contract capabilities in different blockchain networks concerning e-commerce transactions, particularly focusing on security-related aspects. It provides a summarized view of security features, formal verification practices, available auditing tools, and the emphasis placed on security within each blockchain network’s smart contract ecosystem, tailored for future research directions.

Table 8.
Smart contract capabilities in various blockchain networks.
In Table 9, we provide a summarized comparison of privacy-enhancing mechanisms in different blockchain platforms for securing e-commerce transactions, along with potential future research directions aimed at improving these mechanisms for enhanced privacy and wider adoption.

Table 9.
Privacy-enhancing mechanisms in different blockchain platforms.
In summary, the future direction of research in blockchain technology and its application in e-commerce should encompass a multidisciplinary approach. By addressing technological challenges, regulatory considerations, and the broader socio-economic landscape, researchers can contribute to the continued evolution of secure and transparent digital transactions, thereby shaping the future of e-commerce in an era of heightened connectivity and digital interdependence.
13. Conclusions
In conclusion, the rapid evolution of the Internet has transformed the way services are delivered and businesses operate. Blockchain technology, emerging as a significant development subsequent to the inception of the Internet, holds tremendous promise in reshaping online transactions. By utilizing digital ledgers distributed across computer networks, blockchains offer a secure basis for decentralized buying and selling platforms within the domain of e-commerce. The growing reliance on e-commerce for transmitting sensitive information, alongside the rising occurrence of cyber attacks, emphasizes the crucial necessity for robust security measures. As demonstrated in this study, blockchain technology emerges as a viable solution to the multitude of security challenges encountered by e-commerce businesses.
The introduction highlights the escalating importance of cybersecurity in the interconnected world of the internet, with e-commerce becoming a pivotal element of the digital business landscape. The growing demand for secure communication between consumers and sellers has led to a surge in cyber attacks, identifying network architecture security as a major threat to future e-commerce platforms. Blockchain technology, introduced as a means to enhance the security and protection of user information in online transactions, offers a decentralized and tamper-resistant system. This technology not only verifies user identities and ensures transparent transactions but also safeguards sensitive user data through encryption. The distinctive architecture of the blockchain network, with its linked data structure and distributed node system, contributes to heightened security in database systems, offering a potent defense against cyber threats.
Exploring its origins, the paper traces the genesis of blockchain technology to the inception of Bitcoin in 2008, highlighting its evolution beyond its initial association solely with cryptocurrency applications. Initially synonymous with Bitcoin, the versatile applications of blockchain have expanded across various sectors, including but not limited to data sharing, supply chain management, healthcare, and finance. Within the realm of e-commerce, the integration of blockchain seeks to enhance the security of online transactions by establishing a decentralized and tamper-resistant framework. This approach ensures data integrity through advanced cryptographic techniques, real-time transparency, and the automation of transactions through smart contracts.
The discussion underscores the multifaceted challenges faced by e-commerce security, ranging from unauthorized access and denial of service attacks to the vulnerabilities posed by users and employees. The importance of effective risk management processes, security policies, and access control is emphasized, with the understanding that the weakest link often lies in human factors rather than technological shortcomings. In addressing these challenges, blockchain technology emerges as a strategic tool, offering not only heightened security but also transparency and fraud detection capabilities. As the paper traverses the intricacies of e-commerce security concerns, the overarching theme converges on the efficacy of blockchain technology as a comprehensive solution to fortify the security measures surrounding online transactions, ensuring a safer and more reliable digital marketplace.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A. and S.A.; methodology, L.A., S.A. and M.M.H.R.; software, L.A. and S.A.; validation, L.A., S.A. and M.M.H.R.; formal analysis, L.A., S.A. and M.M.H.R.; investigation, L.A. and S.A.; resources, L.A. and S.A.; writing original draft preparation, L.A. and S.A.; writing review and editing, L.A., S.A. and M.M.H.R.; supervision, M.M.H.R.; project administration, M.M.H.R.; funding acquisition, M.M.H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia under the [GRANT 5,510].
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, Vice Presidency for Graduate Studies and Scientific Research, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia [GRANT 5,510]. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful scholastic comments and suggestions, which improved the quality and clarity of the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Taher, G. E-commerce: Advantages and limitations. Int. J. Acad. Res. Account. Financ. Manag. Sci. 2021, 11, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrubei, S.M.; Ball, E.; Rigelsford, J.M. A secure blockchain platform for supporting AI-enabled IoT applications at the edge layer. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 18583–18595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apau, R.; Koranteng, F.N.; Gyamfi, S.A. Cyber-crime and its effects on E-commerce technologies. J. Inf. 2019, 5, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntara, R.G.; Nurfirmansyah, M.N. Blockchain Implementation in E-Commerce to Improve The Security Online Transactions. J. Sci. Res. Educ. Technol. (JSRET) 2023, 2, 328–338. [Google Scholar]
- Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.; Hamid, B.; Ahmed, G. Emerging smart logistics and transportation using IoT and blockchain. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2020, 3, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; You, X.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Haas, H.; et al. On the road to 6G: Visions, requirements, key technologies and testbeds. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 905–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiblmaier, H.; Sillaber, C. The impact of blockchain on e-commerce: A framework for salient research topics. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2021, 48, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismanto, L.; Ar, H.S.; Fajar, A.; Bachtiar, S. Blockchain as E-commerce platform in Indonesia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1179, 12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; RoJa, N.T.; Almalki, F.A.; Aljohani, M. Revolutionizing E-Commerce Using Blockchain Technology and Implementing Smart Contract. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 2213336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Malviya, B.; Arya, S. An overview of electronic commerce (e-Commerce). J. Contemp. Issues Bus. Gov. 2021, 27, 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.A.; Shukur, Z.; Hasan, M.K. An efficient secure electronic payment system for e-commerce. Computers 2020, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.; Akram, H.; Basit, H.M.; Khan, A.U.; Raza, S.M.; Naqvi, M.B. E-commerce trends during COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Future Gener. Commun. Netw. 2020, 13, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Badotra, S.; Sundas, A. A systematic review on security of E-commerce systems. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M. Prevention of E-Commerce Fraud in Bangladesh: A Critical Study on Legal and Institutional Framework. SSRN 2023, 4477507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anakath, A.; Rajakumar, S.; Ambika, S. Privacy preserving multi factor authentication using trust management. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 10817–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osita, G.C.; Chisom, C.D.; Okoronkwo, M.C.; Esther, U.N.; Vanessa, N.C. Application of Emerging Technologies in Mitigation of e-Commerce Security Challenges. CCU J. Sci. 2022, 2, 2734–3766. [Google Scholar]
- Sarda, S.; Sharma, S.; Pal, R. Consumer Protection Regulation in Light of E-Commerce and Product Liability. Issue 2 Indian JL Leg. Rsch. 2022, 4, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, R.; Fernando, M.; Akter, S. Privacy concerns in E-commerce: A taxonomy and a future research agenda. Electron. Mark. 2020, 30, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. Blockchain-Based E-Commerce: A Review on Applications and Challenges. Electronics 2023, 12, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongmei, Z. A cross-border e-commerce approach based on blockchain technology. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 2006082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, M.N.M.; Khwaja, A.A.; Nadeem, A.; Ahmad, H.F.; Khan, M.K.; Hanif, M.A.; Song, H.; Alshamari, M.; Cao, Y. A survey on blockchain technology: Evolution, architecture and security. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 61048–61073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaroodi, J.; Mohamed, N. Blockchain in industries: A survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36500–36515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, J. Framework of blockchain-supported e-commerce platform for small and medium enterprises. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Choi, T.M.; Somani, S.; Butala, R. Blockchain technology in supply chain operations: Applications, challenges and research opportunities. Transp. Res. Part Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 142, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, D.S.W. Cyber security issues and challenges in E-commerce. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Digital Strategies for Organizational Success, Gwalior, India, 5–7 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruwitaarachchi, N.; Abeygunawardena, P.; Rupasingha, L.; Udara, S. A systematic review of security in electronic commerce-threats and frameworks. Glob. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2019, 19, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A.C.; Benjamin, A.C. A Survey of E-Commerce; Its Security Issues and Way-Out. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. (IJERT) 2014, 3, 495–502. [Google Scholar]
- Dahal, S.B. Enhancing E-commerce Security: The Effectiveness of Blockchain Technology in Protecting Against Fraudulent Transactions. Int. J. Inf. Cybersecur. 2023, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaan, R.K.; Abumatar, G.; Hussein, A.M.A.; Al-Lozi, M. Management information system using blockchain technology in an e-commerce enterprise: A systematic review. J. Bus. Manag. (COES&RJ-JBM) 2019, 7, 216–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.; Saha, R.; Buchanan, W.J.; Geetha, G.; Thomas, R.; Rai, M.K.; Kim, T.H.; Alazab, M. Decentralized accessibility of e-commerce products through blockchain technology. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z. A blockchain-based framework of cross-border e-commerce supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Chaudhary, S.; Kulkarni, Y.; Bhole, G.; Jadhav, S.; Suryawanshi, T.; Kasar, M. Blockart: The Blockchain Solution to E-Commerce. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2023, 12, 5505–5513. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, D.; Jung, L.T.; Hashmani, M.A. Systematic literature review of challenges in blockchain scalability. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreessen, M.; Paul, R. Bitcoin: The Future of Digital Payments? Harvard College: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Earle, P.C.; Gulker, M.; Stringham, E.P. Decentralized Marketplaces with Privately Enforced Contracts: A Case Study of OpenBazaar. J. Priv. Enterp. 2022, 37, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvana, R.; Aithal, P. Blockchain based service: A case study on IBM blockchain services & hyperledger fabric. Int. J. Case Stud. Bus. Educ. (IJCSBE) 2020, 4, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bulsara, H.P.; Vaghela, P.S. Blockchain technology for e-commerce industry. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 3793–3798. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L. A privacy-preserving e-commerce system based on the blockchain technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Blockchain Oriented Software Engineering (IWBOSE), Hangzhou, China, 24 February 2019; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Cristina, E.M. Blockchain in Ecommerce. Risk Contemp. Econ. 2021, 1, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, T.M.; Alrashdan, M.T.; Al-Maatouk, Q.; Alrashdan, M.T. Blockchain technology in E-commerce platform. Int. J. Manag. 2020, 11, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, Y. Blockchain-enabled cross-border e-commerce supply chain management: A bibliometric systematic review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; O’Mahony, D. Applying blockchain layer2 technology to mass e-commerce. Cryptol. Eprint Arch. 2020. Available online: https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/502 (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Shorman, S.M.; Allaymounq, M.; Hamid, O. Developing the E-commerce model a consumer to consumer using blockchain network technique. Int. J. Manag. Inf. Technol. (IJMIT) 2019, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.H.; Hashim, H.; Poo, N.; Poo, D.C.C.; Nguyen, H.D. Blockchain technologies in e-commerce: Social shopping and loyalty program applications. In Social Computing and Social Media. Communication and Social Communities: 11th International Conference, SCSM 2019, Held as Part of the 21st HCI International Conference, HCII 2019, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–31 July 2019; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jebamikyous, H.; Li, M.; Suhas, Y.; Kashef, R. Leveraging machine learning and blockchain in E-commerce and beyond: Benefits, models, and application. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).