HPV Associated Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
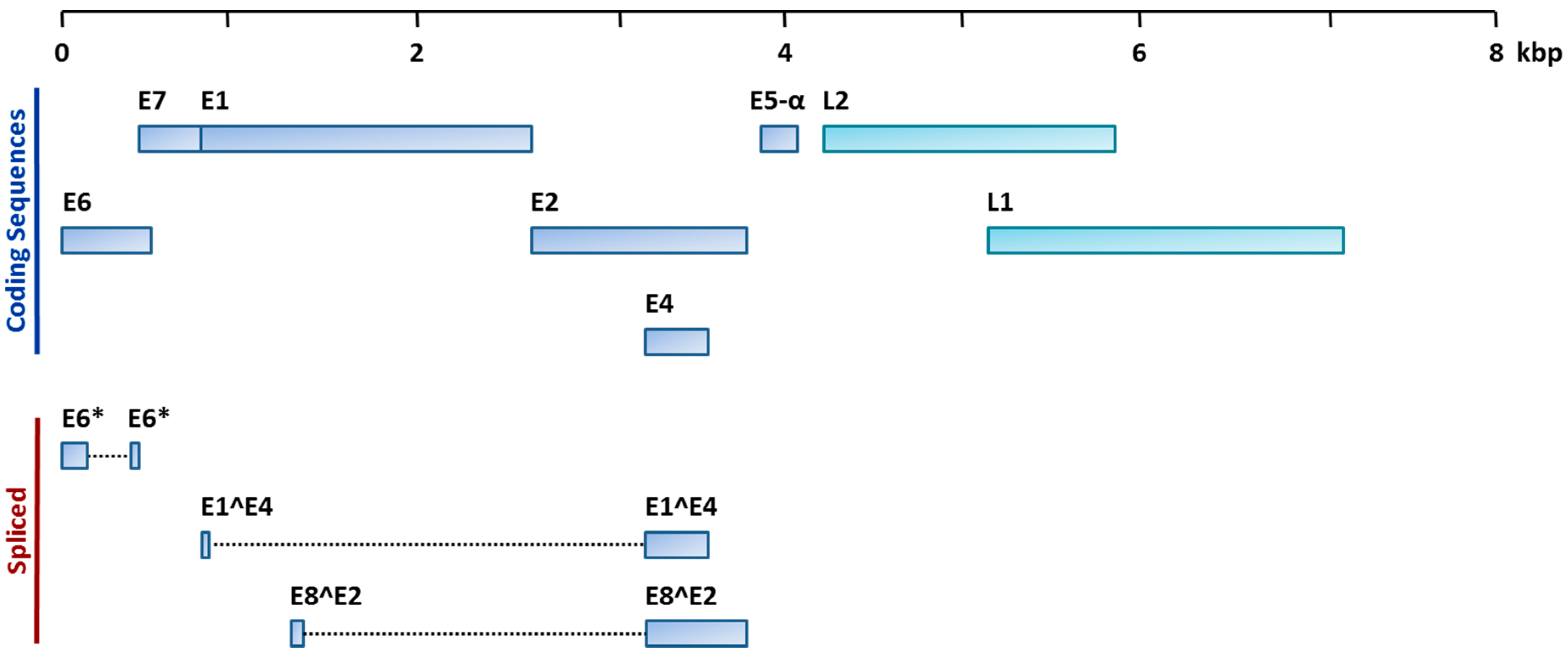
2. HPV and HNC
3. Clinical and Demographic Features of HPV+ HNC
4. Molecular Alterations in HPV+ vs. HPV− HNC
5. Determination of HPV Status and HPV as a Biomarker
5.1. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for HPV+ HNC
5.2. Circulating Biomarkers for HPV+ HNC
6. Therapeutic Perspectives: Treatment of HPV+ HNC as a Distinct Entity
HPV Subtype Specific Treatment Considerations
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC/UICC | American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control |
| CLC | circulating lymphocyte count |
| CMC | circulating monocyte count |
| CNC | circulating neutrophil count |
| CTC | circulating tumour cell |
| DFS | disease free survival |
| DM | distant metastases |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| HNC | head and neck cancer |
| HNSCC | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | human papillomavirus |
| HPV+ | human papillomavirus positive |
| HPV− | human papillomavirus negative |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| IMRT | intensity-modulated radiation therapy |
| ISH | in situ hybridization |
| LN | lymph node |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| NCIN | National Cancer Institute |
| OPC | oropharyngeal carcinoma |
| OS | overall survival |
| OSCC | oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| pCR | pathologic complete response |
| PFS | progression free survival |
| PY | pack years |
| pRb | retinoblastoma protein |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| RPA | recursive partitioning analysis |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamangar, F.; Dores, G.M.; Anderson, W.F. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashberg, A.; Boffetta, P.; Winkelman, R.; Garfinkel, L. Tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking, and cancer of the oral cavity and oropharynx among U.S. veterans. Cancer 1993, 72, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2008. Available online: http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2008/press.html (accessed on 20 May 2016).
- Syrjanen, K.J.; Pyrhonen, S.; Syrjanen, S.M.; Lamberg, M.A. Immunohistochemical demonstration of human papilloma virus (HPV) antigens in oral squamous cell lesions. Br. J. Oral Surg. 1983, 21, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Human Papillomaviruses. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1995, 64, 1–428. [Google Scholar]
- Pytynia, K.B.; Dahlstrom, K.R.; Sturgis, E.M. Epidemiology of HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Engels, E.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Xiao, W.; Kim, E.; Jiang, B.; Goodman, M.T.; Sibug-Saber, M.; Cozen, W.; et al. Human papillomavirus and rising oropharyngeal cancer incidence in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4294–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Kato, H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Pintilie, M.; Huang, S.; Hui, A.; O'Sullivan, B.; Waldron, J.; Cummings, B.; Kim, J.; et al. Comparative prognostic value of HPV16 E6 mRNA compared with in situ hybridization for human oropharyngeal squamous carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 6213–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, B.; Huang, S.H.; Siu, L.L.; Waldron, J.; Zhao, H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Kim, J.; Ringash, J.; Bayley, A.; et al. Deintensification candidate subgroups in human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal cancer according to minimal risk of distant metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- NIAID. Papillomavirus Episteme Kowledge Source: HPV16. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, National Institutes of Health. Available online: http://pave.niaid.nih.gov/ (accessed on 10 June 2016).
- Suzich, J.A.; Ghim, S.J.; Palmer-Hill, F.J.; White, W.I.; Tamura, J.K.; Bell, J.A.; Newsome, J.A.; Jenson, A.B.; Schlegel, R. Systemic immunization with papillomavirus L1 protein completely prevents the development of viral mucosal papillomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11553–11557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratman, S.V.; Bruce, J.P.; O’Sullivan, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Xu, W.; Yip, K.W.; Liu, F.F. Human papillomavirus genotype association with survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiaye, C.; Mena, M.; Alemany, L.; Arbyn, M.; Castellsague, X.; Laporte, L.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjose, S.; Trottier, H. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.A.; O’Rorke, M.A.; Wilson, R.; Jamison, J.; Gavin, A.T.; Northern Ireland HPV Working Group. HPV prevalence and type-distribution in cervical cancer and premalignant lesions of the cervix: A population-based study from Northern Ireland. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.T.; Saraiya, M.; Thompson, T.D.; Steinau, M.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Lynch, C.F.; Lyu, C.W.; Wilkinson, E.J.; Tucker, T.; Copeland, G.; et al. Human papillomavirus genotype and oropharynx cancer survival in the United States of America. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebner, C.M.; Laimins, L.A. Human papillomaviruses: Basic mechanisms of pathogenesis and oncogenicity. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, C.A.; Laimins, L.A. Human papillomavirus oncoproteins: Pathways to transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duensing, S.; Lee, L.Y.; Duensing, A.; Basile, J.; Piboonniyom, S.; Gonzalez, S.; Crum, C.P.; Munger, K. The human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperate to induce mitotic defects and genomic instability by uncoupling centrosome duplication from the cell division cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10002–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMaio, D.; Mattoon, D. Mechanisms of cell transformation by papillomavirus E5 proteins. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7866–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Werness, B.A.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990, 63, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, K.; Werness, B.A.; Dyson, N.; Phelps, W.C.; Harlow, E.; Howley, P.M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liem, A.; Miller, J.A.; Lambert, P.F. Human papillomavirus types 16 E6 and E7 contribute differently to carcinogenesis. Virology 2000, 267, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMaio, D.; Petti, L.M. The E5 proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goon, P.K.; Stanley, M.A.; Ebmeyer, J.; Steinstrasser, L.; Upile, T.; Jerjes, W.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Gorner, M.; Sudhoff, H.H. HPV & head and neck cancer: A descriptive update. Head Neck Oncol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Engels, E.A.; Anderson, W.F.; Gillison, M.L. Incidence trends for human papillomavirus-related and -unrelated oral squamous cell carcinomas in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturgis, E.M.; Cinciripini, P.M. Trends in head and neck cancer incidence in relation to smoking prevalence: An emerging epidemic of human papillomavirus-associated cancers? Cancer 2007, 110, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rischin, D.; Young, R.J.; Fisher, R.; Fox, S.B.; Le, Q.T.; Peters, L.J.; Solomon, B.; Choi, J.; O’Sullivan, B.; Kenny, L.M.; et al. Prognostic significance of p16INK4A and human papillomavirus in patients with oropharyngeal cancer treated on TROG 02.02 phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4142–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillison, M.L.; Koch, W.M.; Capone, R.B.; Spafford, M.; Westra, W.H.; Wu, L.; Zahurak, M.L.; Daniel, R.W.; Viglione, M.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Evidence for a causal association between human papillomavirus and a subset of head and neck cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhry, C.; Westra, W.H.; Li, S.; Cmelak, A.; Ridge, J.A.; Pinto, H.; Forastiere, A.; Gillison, M.L. Improved survival of patients with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in a prospective clinical trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, M.R.; Lorch, J.H.; Goloubeva, O.; Tan, M.; Schumaker, L.M.; Sarlis, N.J.; Haddad, R.I.; Cullen, K.J. Survival and human papillomavirus in oropharynx cancer in TAX 324: A subset analysis from an international phase III trial. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rorke, M.A.; Ellison, M.V.; Murray, L.J.; Moran, M.; James, J.; Anderson, L.A. Human papillomavirus related head and neck cancer survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B.; Xu, W.; Zhao, H.; Chen, D.D.; Ringash, J.; Hope, A.; Razak, A.; Gilbert, R.; Irish, J.; et al. Temporal nodal regression and regional control after primary radiation therapy for N2–N3 head-and-neck cancer stratified by HPV status. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Xu, W.; Waldron, J.; Siu, L.; Shen, X.; Tong, L.; Ringash, J.; Bayley, A.; Kim, J.; Hope, A.; et al. Refining American Joint Committee on Cancer/Union for International Cancer Control TNM stage and prognostic groups for human papillomavirus-related oropharyngeal carcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.M.; Rubenstein, L.M.; Haugen, T.H.; Pawlita, M.; Turek, L.P. Complex etiology underlies risk and survival in head and neck cancer human papillomavirus, tobacco, and alcohol: A case for multifactor disease. J. Oncol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, B.; Huang, S.H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Massey, C.; Siu, L.L.; Weinreb, I.; Hope, A.; Kim, J.; Bayley, A.J.; Cummings, B.; et al. Outcomes of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer patients treated by radiotherapy alone using altered fractionation. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 103, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfenov, M.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Gehlenborg, N.; Freeman, S.S.; Danilova, L.; Bristow, C.A.; Lee, S.; Hadjipanayis, A.G.; Ivanova, E.V.; Wilkerson, M.D.; et al. Characterization of HPV and host genome interactions in primary head and neck cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15544–15549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepiashvili, L.; Bruce, J.P.; Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B.; Liu, F.F.; Kislinger, T. Novel insights into head and neck cancer using next-generation “omic” technologies. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, V.; Yin, X.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Cabanski, C.R.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Ang, M.K.; Hayward, M.C.; Salazar, A.H.; Hoadley, K.A.; et al. Molecular subtypes in head and neck cancer exhibit distinct patterns of chromosomal gain and loss of canonical cancer genes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.; Frampton, G.M.; Fenton, T.; Feber, A.; Palmer, G.; Jay, A.; Pillay, N.; Forster, M.; Cronin, M.T.; Lipson, D.; et al. Targeted next-generation sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma identifies novel genetic alterations in HPV+ and HPV− tumors. Genome Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, N.; Egloff, A.M.; Tward, A.D.; Kostic, A.D.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lawrence, M.S.; Sougnez, C.; McKenna, A.; et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 2011, 333, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korzeniewski, N.; Spardy, N.; Duensing, A.; Duensing, S. Genomic instability and cancer: Lessons learned from human papillomaviruses. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seethala, R.R.; Weinreb, I.; Carlson, D.L.; McHugh, J.B.; Harrison, L.B.; Richardson, M.S.; Sahah, J.; Ferris, R.L.; Wenig, B.M.; Thompson, L.D.R. Protocol for the examination of specimens from patients with carcinomas of the larynx. College of American Pathologists. Available online: http://www.cap.org/ShowProperty?nodePath=/UCMCon/Contribution%20Folders/WebContent/pdf/larynx-13protocol-3300.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2016).
- Westra, W.H. Detection of human papillomavirus (HPV) in clinical samples: Evolving methods and strategies for the accurate determination of HPV status of head and neck carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2014, 50, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosel, S.; Burggraf, S.; Engelhardt, W.; Olgemoller, B. Increased levels of HPV16 E6*I transcripts in high-grade cervical cytology and histology (CIN II+) detected by rapid real-time RT-PCR amplification. Cytopathology 2007, 18, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, L.; Coletti, A.; Syrjanen, K.; Favalli, C.; Ciotti, M. Comparison of DNA sequencing and Roche Linear array in human papillomavirus (HPV) genotyping. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3939–3941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.Q.; Qin, H.D.; Ruan, H.L.; Shugart, Y.Y.; Jia, W.H. Quantitative association of tobacco smoking with the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A comprehensive meta-analysis of studies conducted between 1979 and 2011. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 178, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, G.; Cava, C.; Castiglioni, I. MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1122–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lin, J.; Kong, D.; Huang, M.; Xu, C.; Kim, T.K.; Etheridge, A.; Luo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, K. Current state of circulating microRNAs as cancer biomarkers. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, A.B.; Lin, A.; Xu, W.; Waldron, L.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Shi, W.; Bruce, J.; Huang, S.H.; O’Sullivan, B.; et al. Potentially prognostic miRNAs in HPV-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2154–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, G.; Fazzari, M.; Kung, G.; Kawachi, N.; Brandwein-Gensler, M.; McLemore, M.; Chen, Q.; Burk, R.D.; Smith, R.V.; Prystowsky, M.B.; et al. Low-level expression of microRNAs let-7d and miR-205 are prognostic markers of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, H.E.; Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Patiar, S.; Winter, S.C.; Betts, G.; Homer, J.; Corbridge, R.; Cox, G.; West, C.M.; et al. hsa-mir-210 is a marker of tumor hypoxia and a prognostic factor in head and neck cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, T.; Bruce, J.; Yip, K.W.; Liu, F.F. MicroRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinhofer, I.; Konschak, R.; Stromberger, C.; Raguse, J.D.; Dreyer, J.H.; Johrens, K.; Keilholz, U.; Budach, V. Detection of circulating tumor cells for prediction of recurrence after adjuvant chemoradiation in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Hope, A.; Massey, C.; Waldron, J.N.; Kim, J.; Bayley, A.J.; Cummings, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Natural course of distant metastases following radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy in HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Waldron, J.N.; Milosevic, M.; Shen, X.; Ringash, J.; Su, J.; Tong, L.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Weinreb, I.; Bayley, A.J.; et al. Prognostic value of pretreatment circulating neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes in oropharyngeal cancer stratified by human papillomavirus status. Cancer 2015, 121, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wansom, D.; Light, E.; Worden, F.; Prince, M.; Urba, S.; Chepeha, D.B.; Cordell, K.; Eisbruch, A.; Taylor, J.; D'Silva, N.; et al. Correlation of cellular immunity with human papillomavirus 16 status and outcome in patients with advanced oropharyngeal cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Banh, A.; Kwok, S.; Shi, X.; Wu, S.; Krakow, T.; Khong, B.; Bavan, B.; Bala, R.; Pinsky, B.A.; et al. Quantitation of human papillomavirus DNA in plasma of oropharyngeal carcinoma patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, e351–e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimple, R.J.; Smith, M.A.; Blitzer, G.C.; Torres, A.D.; Martin, J.A.; Yang, R.Z.; Peet, C.R.; Lorenz, L.D.; Nickel, K.P.; Klingelhutz, A.J.; et al. Enhanced radiation sensitivity in HPV-positive head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4791–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dok, R.; Kalev, P.; van Limbergen, E.J.; Asbagh, L.A.; Vazquez, I.; Hauben, E.; Sablina, A.; Nuyts, S. p16INK4a impairs homologous recombination-mediated DNA repair in human papillomavirus-positive head and neck tumors. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, J.; Eriksen, J.G.; Nordsmark, M.; Alsner, J.; Horsman, M.R.; the Danish Head and Neck Cancer Study Group. Plasma osteopontin, hypoxia, and response to the hypoxia sensitiser nimorazole in radiotherapy of head and neck cancer: Results from the DAHANCA 5 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2005, 6, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, L.S.; Johansen, J.; Kallehauge, J.; Primdahl, H.; Busk, M.; Lassen, P.; Alsner, J.; Sorensen, B.S.; Toustrup, K.; Jakobsen, S.; et al. FAZA PET/CT hypoxia imaging in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with radiotherapy: Results from the DAHANCA 24 trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 105, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Busk, M.; Olthof, N.; Speel, E.J.; Horsman, M.R.; Alsner, J.; Overgaard, J. Radiosensitivity and effect of hypoxia in HPV positive head and neck cancer cells. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; D’Souza, G.; Westra, W.H.; Forastiere, A.A. HPV-associated head and neck cancer: A virus-related cancer epidemic. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusinkveld, M.; Goedemans, R.; Briet, R.J.; Gelderblom, H.; Nortier, J.W.; Gorter, A.; Smit, V.T.; Langeveld, A.P.; Jansen, J.C.; van der Burg, S.H. Systemic and local human papillomavirus 16-specific T-cell immunity in patients with head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E74–E85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, M.J.; Thirdborough, S.M.; Mellows, T.; Riley, C.; Harris, S.; Suchak, K.; Webb, A.; Hampton, C.; Patel, N.N.; Randall, C.J.; et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes predict for outcome in HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.K.; Arsov, C.; Schirlau, K.; Bas, M.; Friebe-Hoffmann, U.; Klussmann, J.P.; Scheckenbach, K.; Balz, V.; Bier, H.; Whiteside, T.L. T cells specific for HPV16 E7 epitopes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, A.; Abe, K.; Hunt, J.; Wang, J.; Lopez-Albaitero, A.; Schaefer, C.; Gooding, W.; Whiteside, T.L.; Ferrone, S.; DeLeo, A.; et al. Antitumor activity of human papillomavirus type 16 E7-specific T cells against virally infected squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11146–11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deboni, A.L.; Giordani, A.J.; Lopes, N.N.; Dias, R.S.; Segreto, R.A.; Jensen, S.B.; Segreto, H.R. Long-term oral effects in patients treated with radiochemotherapy for head and neck cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corry, J.; Peters, L.J.; Rischin, D. Optimising the therapeutic ratio in head and neck cancer. Lancet. Oncol. 2010, 11, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chera, B.S.; Amdur, R.J.; Tepper, J.; Qaqish, B.; Green, R.; Aumer, S.L.; Hayes, N.; Weiss, J.; Grilley-Olson, J.; Zanation, A.; et al. Phase 2 Trial of de-intensified chemoradiation therapy for favorable-risk human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marur, S.; Li, S.; Cmelak, A.; Gillison, M.; Ferris, R.L.; Bauman, J.; Zhao, W.; W., W.; Chung, C.H.; Wagner, L.; et al. E 1308: A phase II trial of induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by cetuximab with low dose versus standard dose IMRT in patients with human papilloma virus (HPV)-associated resectable squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx (OPSCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31. abstr 6005. [Google Scholar]
| Method | Principle | Advantage | Disadvantage | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPV16 E1 PCR | HPV16, the most common HPV subtype implicated in HNC, is quantified by qRT-PCR in DNA extracted from bulk tumour tissue | Highly sensitive | False positives may occur; technically more difficult to perform than IHC/ISH; detects only HPV16 | [10] |
| p16 IHC | p16 is upregulated indirectly via repression of pRb by E7; loss of p16 is common in HPV- HNC | Technically easy to perform and clinically feasible; comparatively low cost | Indirect method of HPV detection; does not distinguish between HPV subtypes | [10] |
| HPV16 ISH | HPV16, the most common HPV subtype implicated in HNC, is quantified and directly visualized in tumour cells | Technically easier to perform and clinically feasible; comparatively low cost; allows direct visualization of HPV in tumour nuclei | Detects only HPV16 | [10] |
| RNA-Seq | Specific HPV viral transcripts can be detected by sequencing RNA transcripts | Accurate method for detecting HPV positivity and HPV subtype | High cost; technically difficult, requiring specialized resources; limited clinical feasibility at present | [14] |
| DNA Sequencing | HPV can be detected by DNA sequencing | Accurate method for detecting HPV positivity and HPV subtype | High cost; technically difficult, requiring specialized resources; limited clinical feasibility at present | [48] |
| Roche Linear Array | Detection of HPV by PCR amplification of DNA using HPV subtype specific primers | Accurate method for detecting HPV positivity and HPV subtype; most accurate method for resolving the presence of multiple HPV subtypes in one sample | Requires specialized resources; limited clinical feasibility at present | [48] |
| MicroRNAs | HNC Subtype | Expression in HNC ¥ | Role as Biomarkers | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-20b, miR-9, miR-9* | OPC | miR-9, miR-9* (up) | Associated with HPV/p16-status | [53] |
| miR-20b (down) | ||||
| miR-107, miR-151, miR-492 | OPC | miR-107, miR-151(up) | Correlated with overall survival | [53] |
| miR-492 (down) | ||||
| miR-20b, miR-107, miR-151, miR-182, miR-361 | OPC | miR-107, miR-151, miR-182, miR-361 (up) | Correlated with disease free survival | [53] |
| miR-20b (down) | ||||
| miR-151, miR-152, miR-324-5p, miR-361, miR-492 | OPC | miR-151, miR-324-5p, miR-361 (up) | Correlated with distant metastases | [53] |
| miR-152, miR-492 (down) | ||||
| let-7d, miR-205 | HNSCC | down | Associated with disease free and overall survival | [54] |
| miR-210 | HNC overall | down | Associated with hypoxia; correlate with reduced overall and disease free survival | [55] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spence, T.; Bruce, J.; Yip, K.W.; Liu, F.-F. HPV Associated Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8080075
Spence T, Bruce J, Yip KW, Liu F-F. HPV Associated Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2016; 8(8):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8080075
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpence, Tara, Jeff Bruce, Kenneth W. Yip, and Fei-Fei Liu. 2016. "HPV Associated Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 8, no. 8: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8080075
APA StyleSpence, T., Bruce, J., Yip, K. W., & Liu, F.-F. (2016). HPV Associated Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 8(8), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers8080075





