Temporal Dynamics and Clinical Predictors of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Two-Decade Cohort Analysis Toward Tailored CNS Screening
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
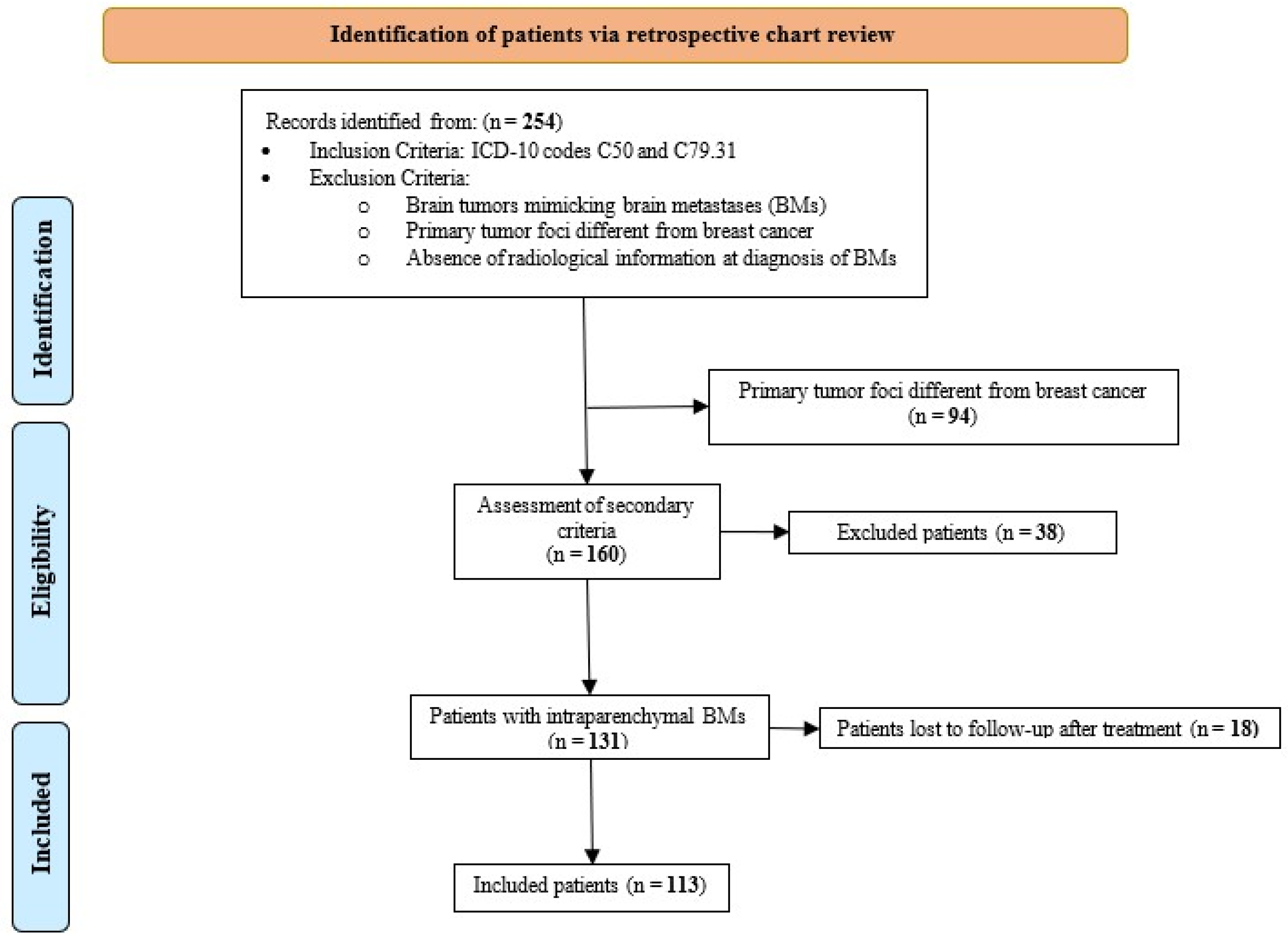
2.1. Study Cohort and Patient Selection
2.2. Clinical, Tumor, and Treatment Characteristics
2.3. Survival Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Survival Analysis
3.3. Univariate Analysis
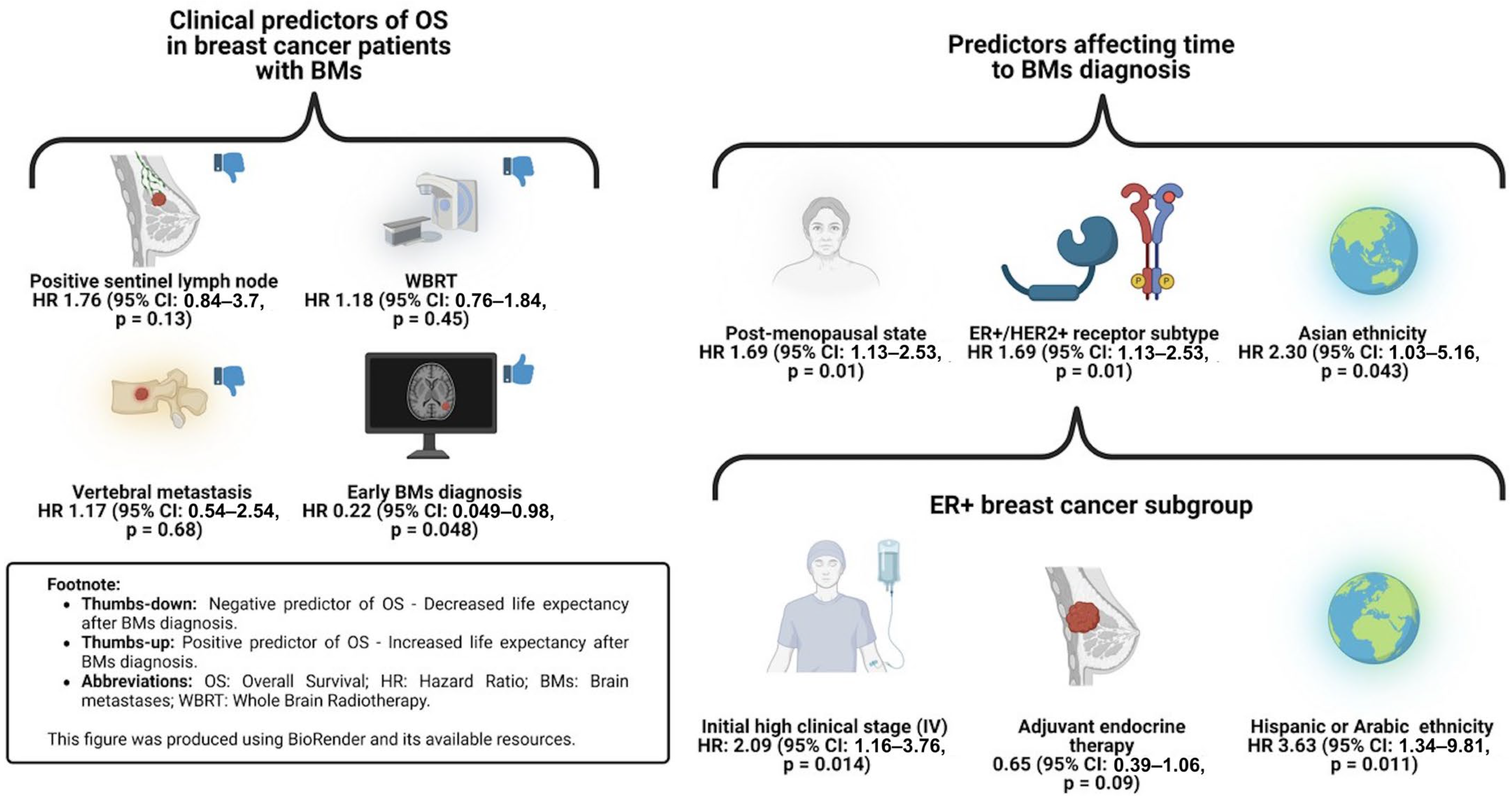
3.4. Cox Regression Model for Overall Survival
3.5. Cox Regression Model for Time to BM Diagnosis
3.6. Cox Regression Model for ER+ Subgroup
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Predictors of Time to Overall Survival
4.2. Clinical Predictors of Time to BM Diagnosis
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestrino, R.; Rudà, R.; Soffietti, R. Brain Metastasis from Unknown Primary Tumour: Moving from Old Retrospective Studies to Clinical Trials on Targeted Agents. Cancers 2020, 12, 3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darlix, A.; Louvel, G.; Fraisse, J.; Jacot, W.; Brain, E.; Debled, M.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Goncalves, A.; Dalenc, F.; Delaloge, S.; et al. Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.U.; Gaspar, L.E.; Soffietti, R. Breast Cancer in the Central Nervous System: Multidisciplinary Considerations and Management. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2017, 37, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.D.; Weathers, T.; Haney, L.G.; Timmerman, R.; Dickler, M.; Shen, J.; Sledge, G.W. Occult central nervous system involvement in patients with metastatic breast cancer: Prevalence, predictive factors and impact on overall survival. Ann. Oncol. 2003, 14, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwińska, A.; Tacikowska, M.; Pieńkowski, T. Occult brain metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer patients: Frequency and response to radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2007, 46, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Winer, E.P. Brain metastases: The HER2 paradigm. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestalozzi, B.C. Brain metastases and subtypes of breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Weller, M.; Brandsma, D.; Van den Bent, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Henriksson, R.; Boulanger, T.; Peters, S.; Watts, C.; Wick, W.; et al. EANO-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. S4), iv84–iv99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, B.D.; Cheung, V.J.; Patel, A.J.; Suki, D.; Rao, G. Epidemiology of metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 22, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Chao, S.T.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Suh, J.; Weil, R.J.; Jensen, A.W.; et al. The effect of tumor subtype on the time from primary diagnosis to development of brain metastases and survival in patients with breast cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 112, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Effect of tumor subtype on survival and the graded prognostic assessment for patients with breast cancer and brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watase, C.; Shiino, S.; Shimoi, T.; Noguchi, E.; Kaneda, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yonemori, K.; Takayama, S.; Suto, A. Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis—Overview of Disease State, Treatment Options and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachis, A.; Carlqvist, P.; Ma, Y.; Szilcz, M.; Freilich, J.; Vertuani, S.; Holm, B.; Lindman, H. Overall survival of patients with metastatic breast cancer in Sweden: A nationwide study. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.U.; Bellon, J.R.; Winer, E.P. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, K.; Shikama, N.; Okazaki, S.; Koyama, T.; Takahashi, T.; Kato, S. Predicting prognosis of short survival time after palliative whole-brain radiotherapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsbergen, A.F.C.; Lamba, N.; Claes, A.; Kavouridis, V.K.; Lin, N.U.; Smith, T.R.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; Broekman, M.L.D. Prognostic Value of Brain Metastasis-Free Interval in Patients with Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2019, 128, e157–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STROBE. Available online: https://www.strobe-statement.org/ (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, S.Y.; Lin, L.; Alghamdi, A.G.; Daehne, S.; Roma, A.A.; Hasteh, F.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Fadare, O. Breast cancers with a HER2/CEP17 ratio of 2.0 or greater and an average HER2 copy number of less than 4.0 per cell: Frequency, immunohistochemical correlation, and clinicopathological features. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 83, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, G.; Ejikeme, T.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Blackwell, K.L.; Clarke, J.M.; Lad, S.P.; Fecci, P.E. Leptomeningeal disease: Current diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73312–73328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jatoi, I.; Kunkler, I.H. Omission of sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer: Historical context and future perspectives on a modern controversy. Cancer 2021, 127, 4376–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabourel, G.; Terrier, L.-M.; Dubory, A.; Cristini, J.; Nail, L.-R.L.; Cook, A.-R.; Buffenoir, K.; Pascal-Moussellard, H.; Carpentier, A.; Mathon, B.; et al. Are spine metastasis survival scoring systems outdated and do they underestimate life expectancy? Caution in surgical recommendation guidance. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2021, 35, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Linden, Y.M.; Dijkstra, S.P.D.S.; Vonk, E.J.A.; Marijnen, C.A.M.; Leer, J.W.H. Dutch Bone Metastasis Study Group Prediction of survival in patients with metastases in the spinal column: Results based on a randomized trial of radiotherapy. Cancer 2005, 103, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viani, G.A.; Castilho, M.S.; Salvajoli, J.V.; Pellizzon, A.C.A.; Novaes, P.E.; Guimarães, F.S.; Conte, M.A.; Fogaroli, R.C. Whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases from breast cancer: Estimation of survival using two stratification systems. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mix, M.; Elmarzouky, R.; O’Connor, T.; Plunkett, R.; Prasad, D. Clinical outcomes in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer treated with single-session radiosurgery or whole brain radiotherapy. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125 (Suppl. S1), 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankey, E.W.; Tsvankin, V.; Grabowski, M.M.; Nayar, G.; Batich, K.A.; Risman, A.; Champion, C.D.; Salama, A.K.S.; Goodwin, C.R.; Fecci, P.E. Operative and peri-operative considerations in the management of brain metastasis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6809–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelbaum, M.A.; Brown, P.D.; Messersmith, H.; Brastianos, P.K.; Burri, S.; Cahill, D.; Dunn, I.F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gatson, N.T.N.; Gondi, V.; et al. Treatment for Brain Metastases: ASCO-SNO-ASTRO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 492–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, J.P.; Lee, A.V.; Brufsky, A.M. Prognostic factors and survival of patients with brain metastasis from breast cancer who underwent craniotomy. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiricuta, I.C.; Kölbl, O.; Willner, J.; Bohndorf, W. Central nervous system metastases in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1992, 118, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Rothman, M.S. Postmenopausal Hyperandrogenism: Evaluation and Treatment Strategies. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Androgen and AR contribute to breast cancer development and metastasis: An insight of mechanisms. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2775–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Sakhuja, S.; Waterbor, J.; Pisu, M.; Altekruse, S.F. Racial/ethnic disparities in de novo metastases sites and survival outcomes for patients with primary breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.A.; Friend, S.; Lomo, L.; Wiggins, C.; Barry, M.; Prossnitz, E.; Royce, M. Breast Cancer Survival, Survival Disparities, and Guideline-Based Treatment. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, C.; Lawrenson, R.; Edwards, M.; Campbell, I. Treatment and survival of Asian women diagnosed with breast cancer in New Zealand. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 177, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Díaz, B.; Tripathy, D.; Arrieta, V.A.; Escamilla-Ramirez, A.; Alvarado-Miranda, A.; Rodríguez-Mayoral, O. Real-World Experience in Hispanic Patients with Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases Using Different Prognostic Tools. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 120, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Li, X.; Yang, A.; Chen, B.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, G.; Deng, W.; Liao, N. Analysis of Prognostic Factors Affecting the Brain Metastases Free Survival and Survival After Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Unni, N.; Peng, Y. The Changing Paradigm for the Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, J.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Z. Incidence, pattern and prognosis of brain metastases in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackshaw, M.D.; Danysh, H.E.; Henderson, M.; Wang, E.; Tu, N.; Islam, Z.; Ladner, A.; Ritchey, M.E.; Salas, M. Prognostic factors of brain metastasis and survival among HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients: A systematic literature review. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; Grubb, C.S.; Hwang, M.E.; Tai, C.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Jani, A.; Lapa, M.E.; Andrews, J.I.S.; Vanderkelen, S.; Isaacson, S.R.; et al. Breast cancer subtype and stage are prognostic of time from breast cancer diagnosis to brain metastasis development. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 134, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdie, C.A.; Baker, L.; Ashfield, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Jordan, L.B.; Quinlan, P.; Adamson, D.J.A.; Dewar, J.A.; Thompson, A.M. Increased mortality in HER2 positive, oestrogen receptor positive invasive breast cancer: A population-based study. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosonaga, M.; Saya, H.; Arima, Y. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying brain metastasis of breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.K.; Khan, P.; Rehman, A.U.; Kanchan, R.K.; Perumal, N.; Mahapatra, S.; Chand, H.S.; Santamaria-Barria, J.A.; Batra, S.K.; Nasser, M.W. Rethinking the Chemokine Cascade in Brain Metastasis: Preventive and Therapeutic Implications. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 86 Pt 3, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensee, I.; Chuang, H.-N.; Grottke, A.; Werner, S.; Schulte, A.; Horn, S.; Lamszus, K.; Bartkowiak, K.; Witzel, I.; Westphal, M.; et al. PTEN mediates the cross talk between breast and glial cells in brain metastases leading to rapid disease progression. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, B.; Deal, A.M.; Burrows, E.; Geradts, J.; Hamilton, E.; Blackwell, K.L.; Livasy, C.; Fritchie, K.; Prat, A.; Harrell, J.C.; et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway activation in breast cancer brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, J.; Leone, J.; Vallejo, C.T.; Lin, N.U.; Leone, J.P. Survival analysis of patients with brain metastases at initial breast cancer diagnosis over the last decade. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 205, 579–587. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10549-024-07290-1 (accessed on 27 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Prowell, T.; Stearns, V. Chemoprevention of breast cancer: Tamoxifen, raloxifene, and beyond. Am. J. Ther. 2006, 13, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.; Costantino, J.P.; Wickerham, D.L.; Redmond, C.K.; Kavanah, M.; Cronin, W.M.; Vogel, V.; Robidoux, A.; Dimitrov, N.; Atkins, J.; et al. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: Report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, U.; Maisonneuve, P.; Costa, A.; Sacchini, V.; Maltoni, C.; Robertson, C.; Rotmensz, N.; Boyle, P. Prevention of breast cancer with tamoxifen: Preliminary findings from the Italian randomised trial among hysterectomised women. Italian Tamoxifen Prevention Study. Lancet 1998, 352, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Carneiro, B.A.; Wainwright, D.A.; Santa-Maria, C.A.; Kumthekar, P.; Chae, Y.K.; Gradishar, W.J.; Cristofanilli, M.; Giles, F.J. Developmental therapeutics for patients with breast cancer and central nervous system metastasis: Current landscape and future perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Xu, F.; Qin, T.; Zheng, Q.; Shi, D.; Xia, W.; Tian, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; et al. Palbociclib inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in breast cancer via c-Jun/COX-2 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41794–41808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, K.; Solomon, D.A.; Oermann, E.; Kim, J.-S.; Zhong, W.-Z.; Prados, M.D.; Ozawa, T.; James, C.D.; Waldman, T. Pharmacologic inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 arrests the growth of glioblastoma multiforme intracranial xenografts. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3228–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groheux, D.; Hindie, E. Breast cancer: Initial workup and staging with FDG PET/CT. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2021, 9, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Choi, J.Y. Impact of 18F-FDG PET, PET/CT, and PET/MRI on Staging and Management as an Initial Staging Modality in Breast Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Placido, S.; De Angelis, C.; Giuliano, M.; Pizzi, C.; Ruocco, R.; Perrone, V.; Bruzzese, D.; Tommasielli, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Cammarota, S.; et al. Imaging tests in staging and surveillance of non-metastatic breast cancer: Changes in routine clinical practice and cost implications. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines Detail. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1419 (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Ramakrishna, N.; Temin, S.; Chandarlapaty, S.; Crews, J.R.; Davidson, N.E.; Esteva, F.J.; Giordano, S.H.; Kirshner, J.J.; Krop, I.E.; Levinson, J.; et al. Recommendations on Disease Management for Patients With Advanced Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2804–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditsch, N.; Untch, M.; Kolberg-Liedtke, C.; Jackisch, C.; Krug, D.; Friedrich, M.; Janni, W.; Müller, V.; Albert, U.-S.; Banys-Paluchowski, M.; et al. AGO Recommendations for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Locally Advanced and Metastatic Breast Cancer: Update 2020. Breast Care 2020, 15, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Cortés, J.; de Azambuja, E.; DeMichele, A.; Dent, R.; Fenlon, D.; Gligorov, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; et al. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 113) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age in years, mean ± SD | 53.5 ± 11.27 | |
| Age ≥ 50 years, n (%) | 66 (58.4) | |
| Smoking history, n (%) | 31 (27.4) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | White | 76 (70) |
| African American | 24 (18.5) | |
| Asian | 8 (7.1) | |
| Other (i.e., Hispanic, Arabic) | 5 (4.4) | |
| Histological type, n (%) | Ductal Carcinoma | 82 (72.6) |
| Lobular Carcinoma | 17 (15) | |
| Other | 4 (3.5) | |
| Not available | 10 (8.9) | |
| Receptor type, n (%) * | ER+ | 82 (73.2) * |
| HER2+ | 35 (31.3) * | |
| Receptor subtype, n (%) * | ER+/HER2− | 58 (51.8) * |
| ER−/HER2+ | 13 (11.6) * | |
| ER+/HER2+ | 20 (17.9) * | |
| ER−/HER2− | 21 (18.8) * | |
| Initial tumor grade, n (%) | T1–T2 | 33 (29.2) |
| T3–T4 | 59 (52.2) | |
| Not available | 21 (18.6) | |
| Positive sentinel lymph node, n (%) | Yes | 20 (17.7) |
| No | 75 (66.4) | |
| Not available | 18 (15.9) | |
| Initial clinical stage, n (%) | I–III | 80 (70.8) |
| IV | 24 (21.2) | |
| Not available | 9 (8) | |
| Distal lymph node metastasis, n (%) | 33 (29.2) | |
| Osseus metastasis, n (%) | 28 (24.8) | |
| Vertebral metastasis, n (%) | 25 (22.1) | |
| Visceral metastasis, n (%) | 44 (38.9) | |
| Low KPS at initial BM diagnosis, n (%) | 68 (60.2) | |
| BM therapeutic approach, n (%) | Open surgery | 31 (27.4) |
| SRS | 29 (25.7) | |
| WBRT | 53 (46.9) | |
| Clinical Predictors | Unadjusted Cox Regression | Adjusted Cox Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 50 years old at breast cancer diagnosis | 1.54 (95% CI: 0.75–3.16, p = 0.24) | - | ||
| Age ≥ 55 years old at BM diagnosis | 2.02 (95% CI: 0.91–4.44, p = 0.083) | - | ||
| Post-menopausal state | 1.77 (95% CI: 0.89–3.5, p = 0.1) | - | ||
| Smoking history | 1.54 (95% CI: 0.78–3.01, p = 0.21) | - | ||
| Ethnicity | White | 1 | - | |
| African American | 0.88 (95% CI: 0.33–2.33, p = 0.79) | - | ||
| Asian | 1.49 (95% CI: 0.44–5.05, p = 0.52) | - | ||
| Other (i.e., Hispanic or Arabic) | 0.89 (95% CI: 0.14–3.86, p = 0.89) | - | ||
| Histological type | Invasive ductal carcinoma | 1 | - | |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 1.72 (95% CI: 0.79–3.72, p = 0.17) | - | ||
| Other | 0.25 (95% CI: 0.033–1.85, p = 0.18) | - | ||
| Receptor type | ER+ | 1.66 (95% CI: 0.72–3.83, p = 0.23) | - | |
| HER2+ | 1.01 (95% CI: 0.49–2.04, p = 0.89) | - | ||
| Receptor subtype | ER+/HER2− | 1 | - | |
| ER−/HER2+ | 0.69 (95% CI: 0.24–2.01, p = 0.49) | - | ||
| ER+/HER2+ | 1.58 (95% CI: 0.69–3.57, p = 0.27) | - | ||
| ER−/HER2− | 1.17 (95% CI: 0.41–3.29, p = 0.76) | - | ||
| High tumor grade (III–IV) | 1 (95% CI: 0.48–2.07, p = 0.99) | - | ||
| Positive sentinel lymph node | 2.1 (95% CI: 1.01–4.3, p = 0.041) | 1.76 (95% CI: 0.84–3.7, p = 0.13) | ||
| Initial high clinical stage (IV) | 1.7 (95% CI: 0.9–3.5, p = 0.13) | - | ||
| Distal lymph node metastasis | 1.57 (95% CI: 0.78–3.17, p = 0.21) | - | ||
| Osseus metastasis | 1.43 (95% CI: 0.72–2.84, p = 0.3) | - | ||
| Vertebral metastasis | 2.01 (95% CI: 1.01–4.28, p = 0.046) | 1.17 (95% CI: 0.54–2.54, p = 0.68) | ||
| Visceral metastasis | 0.94 (95% CI: 0.47–1.87, p = 0.86) | - | ||
| Low KPS at initial BM diagnosis | 1.64 (95% CI: 0.73–3.7, p = 0.23) | - | ||
| Early BM diagnosis (<2 years) | 0.24 (95% CI: 0.074–0.83, p = 0.025) | 0.22 (95% CI: 0.049–0.98, p = 0.048) | ||
| BM therapeutic approach | Open surgery | 1 | - | |
| SRS | 1.7 (95% CI: 0.63–4.6, p = 0.29) | - | ||
| WBRT | 2.7 (95% CI: 1.11–6.5, p = 0.03) | 1.18 (95% CI: 0.76–1.84, p = 0.45) | ||
| Clinical Predictors | Unadjusted Cox Regression | Adjusted Cox Regression | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 50 years old at breast cancer diagnosis | 1.45 (95% CI: 0.98–2.15, p = 0.06) | - | |
| Post-menopausal state | 1.49 (95% CI: 1.02–2.21, p = 0.04) | 1.69 (95% CI: 1.13–2.53, p = 0.01) | |
| Smoking history | 1.05 (95% CI: 0.69–1.59, p = 0.81) | - | |
| Ethnicity | White | 1 | - |
| African American | 1.16 (95% CI: 0.73–1.84, p = 0.54) | 1.21 (95% CI: 0.75–1.96, p = 0.43) | |
| Asian | 1.73 (95% CI: 0.79–3.79, p = 0.17) | 2.30 (95% CI: 1.03–5.16, p = 0.043) | |
| Other (i.e., Hispanic or Arabic) | 2.40 (95% CI: 1.02–5.63, p = 0.04) | 2.45 (95% CI: 0.98–6.07, p = 0.053) | |
| Histological type | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma | 1 | - |
| Invasive Lobular Carcinoma | 0.81 (95% CI: 0.49–1.34, p = 0.41) | - | |
| Other | 0.93 (95% CI: 0.43–2.03, p = 0.18) | - | |
| Receptor type | ER+ | 0.76 (95% CI: 0.49–1.16, p = 0.21) | - |
| HER2+ | 2.19 (95% CI: 1.26–3.82, p = 0.01) | 1.27 (95% CI: 0.37–4.27, p = 0.71) | |
| Receptor subtype | ER+/HER2− | 1 | - |
| ER−/HER2+ | 2.21 (95% CI: 1.22–4.01, p = 0.01) | 2.39 (95% CI: 0.65–8.85, p = 0.19) | |
| ER+/HER2+ | 2.14 (95% CI: 1.25–3.65, p = 0.01) | 2.06 (95% CI: 1.14–3.71, p = 0.016) | |
| ER−/HER2− | 0.89 (95% CI: 0.53–1.49, p = 0.66) | 0.99 (95% CI: 0.59–1.65, p = 0.97) | |
| High tumor grade (III–IV) | 0.91 (95% CI: 0.59–1.41, p = 0.69) | - | |
| Positive sentinel lymph node | 1.26 (95% CI: 0.76–2.1, p = 0.36) | - | |
| Initial high clinical stage (IV) | 1.41 (95% CI: 0.89–2.23, p = 0.15) | - | |
| Distal lymph node metastasis | 0.90 (95% CI: 0.59–1.37, p = 0.63) | - | |
| Osseus metastasis | 0.89 (95% CI: 0.58–1.38, p = 0.62) | - | |
| Vertebral metastasis | 0.81 (95% CI: 0.52–1.26, p = 0.35) | - | |
| Visceral metastasis | 0.77 (95% CI: 0.53–1.13, p = 0.19) | - | |
| Clinical Predictors | Unadjusted Cox Regression | Adjusted Cox Regression | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 50 years old at breast cancer diagnosis | 1.42 (95% CI: 0.90–2.22, p = 0.13) | - | |
| Post-menopausal state | 1.39 (95% CI: 0.89–2.17, p = 0.14) | - | |
| Smoking history | 1.08 (95% CI: 0.67–1.76, p = 0.75) | - | |
| Ethnicity | White | 1 | - |
| African American | 1.23 (95% CI: 0.72–2.10, p = 0.46) | 1.48 (95% CI: 0.81–2.71, p = 0.2) | |
| Asian | 1.24 (95% CI: 0.44–3.44, p = 0.69) | 2.39 (95% CI: 0.68–1.41, p = 0.17) | |
| Other (i.e., Hispanic or Arabic) | 2.89 (95% CI: 1.21–6.92, p = 0.017) | 3.63 (95% CI: 1.34–9.81, p = 0.011) | |
| Histological type | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma | 1 | - |
| Invasive Lobular Carcinoma | 0.79 (95% CI: 0.47–1.33, p = 0.38) | - | |
| Other | 0.78 (95% CI: 0.28–2.18, p = 0.78) | - | |
| Receptor subtype | ER+/HER2+ | 1.81 (95% CI: 1.09–2.96, p = 0.02) | 3.1 (95% CI: 0.93–10.41, p = 0.066) |
| High tumor grade (III–IV) | 0.67 (95% CI: 0.39–1.12, p = 0.13) | - | |
| Positive sentinel lymph node | 1.22 (95% CI: 0.70–2.1, p = 0.48) | - | |
| Initial high clinical stage (IV) | 1.83 (95% CI: 1.1–3.18, p = 0.03) | 2.09 (95% CI: 1.16–3.76, p = 0.014) | |
| Distal lymph node metastasis | 1.03 (95% CI: 0.63–1.66, p = 0.92) | - | |
| Osseus metastasis | 0.78 (95% CI: 0.5–1.2, p = 0.26) | - | |
| Vertebral metastasis | 0.84 (95% CI: 0.52–1.38, p = 0.49) | - | |
| Visceral metastasis | 0.75 (95% CI: 0.48–1.18, p = 0.22) | - | |
| Adjuvant endocrine therapy | 0.61 (95% CI: 0.39–0.95, p = 0.03) | 0.65 (95% CI: 0.39–1.06, p = 0.09) | |
| Palbociclib | 0.51 (95% CI: 0.28–0.96, p = 0.04) | 0.57 (95% CI: 0.29–1.10, p = 0.09) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terry, F.; Orrego-Gonzalez, E.; Enríquez-Marulanda, A.; Pacheco-Barrios, N.; Merenzon, M.; Komotar, R.J.; Vega, R.A. Temporal Dynamics and Clinical Predictors of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Two-Decade Cohort Analysis Toward Tailored CNS Screening. Cancers 2025, 17, 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060946
Terry F, Orrego-Gonzalez E, Enríquez-Marulanda A, Pacheco-Barrios N, Merenzon M, Komotar RJ, Vega RA. Temporal Dynamics and Clinical Predictors of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Two-Decade Cohort Analysis Toward Tailored CNS Screening. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060946
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerry, Fernando, Eduardo Orrego-Gonzalez, Alejandro Enríquez-Marulanda, Niels Pacheco-Barrios, Martin Merenzon, Ricardo J. Komotar, and Rafael A. Vega. 2025. "Temporal Dynamics and Clinical Predictors of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Two-Decade Cohort Analysis Toward Tailored CNS Screening" Cancers 17, no. 6: 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060946
APA StyleTerry, F., Orrego-Gonzalez, E., Enríquez-Marulanda, A., Pacheco-Barrios, N., Merenzon, M., Komotar, R. J., & Vega, R. A. (2025). Temporal Dynamics and Clinical Predictors of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer: A Two-Decade Cohort Analysis Toward Tailored CNS Screening. Cancers, 17(6), 946. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060946









