Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional CT Imaging Features and Radiomics Signature in Differentiating Grade 1 Tumors from Higher-Grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CT Acquisition
2.3. Image Segmentation
2.4. Image Analysis
2.4.1. Conventional CT Imaging Features
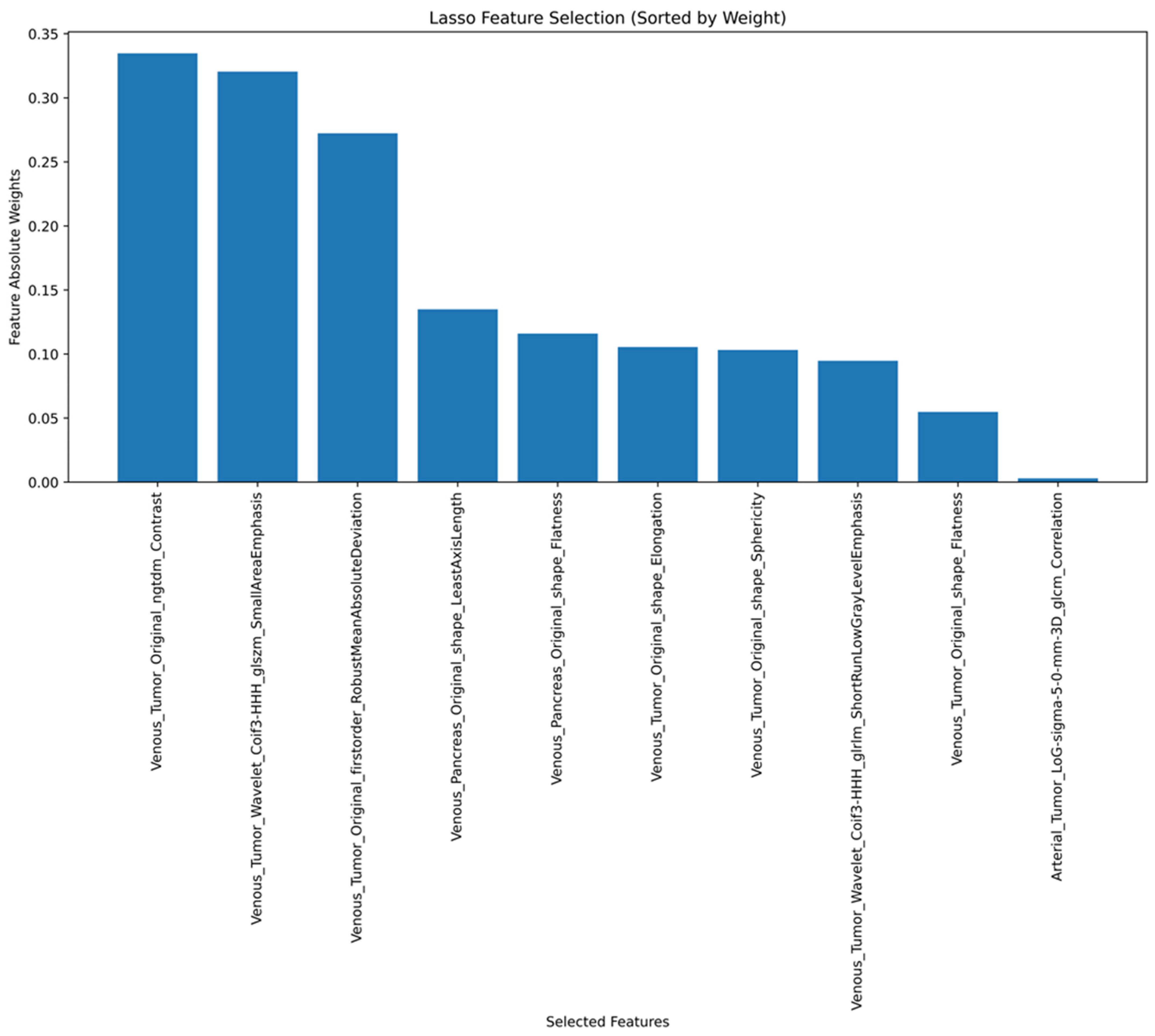
2.4.2. Radiomics Features
2.4.3. Clinical Features
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of PanNEN Patients
3.2. Surgery and Pathology Results
3.3. SVM Model Performance Using CT Features and Enhancement Patterns of PanNEN
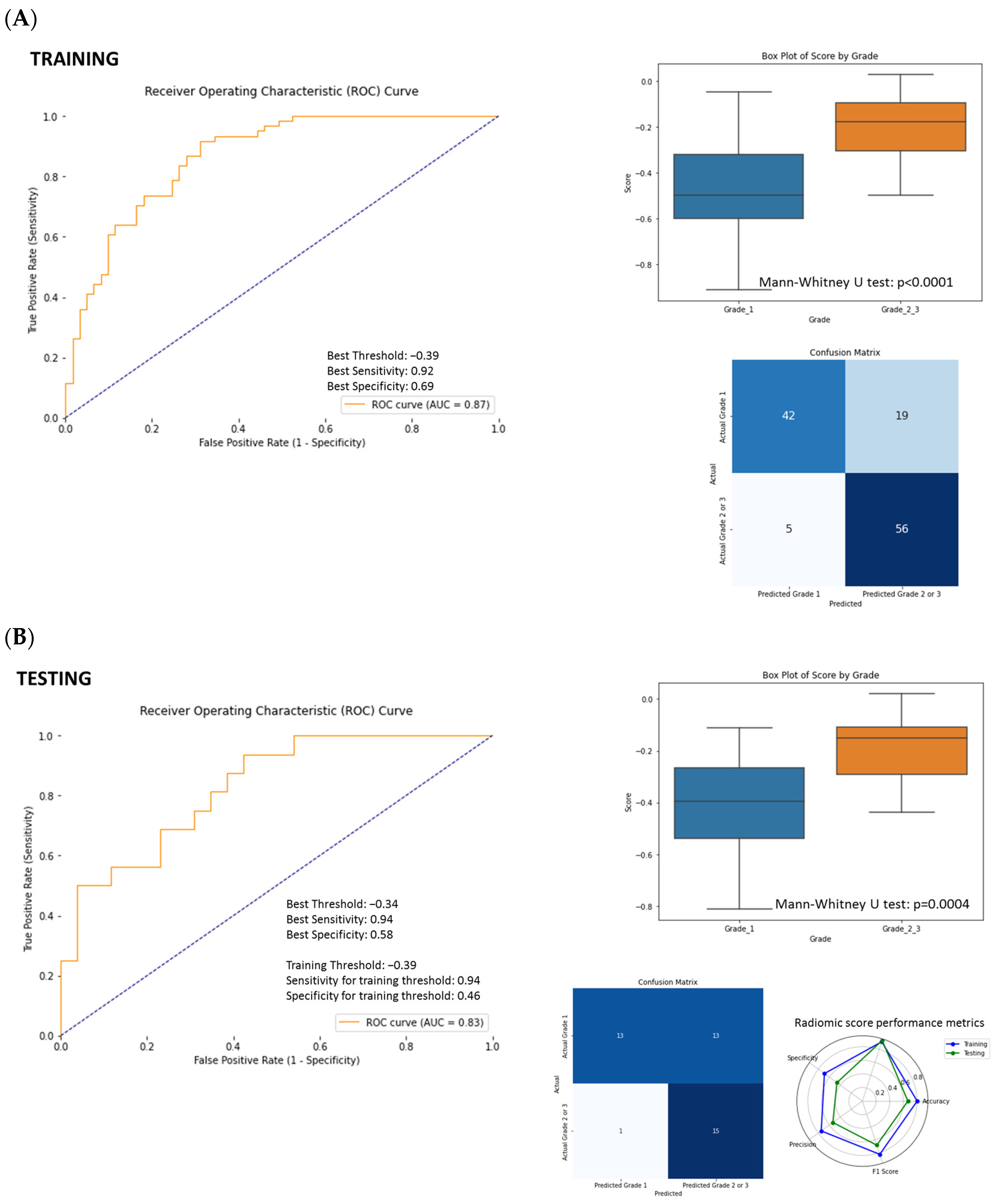
3.4. ROC Curve Analysis and SVM Model Performance Using Radiomics Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computed tomography |
| PanNET | Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor |
| PanNEN | Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm |
| PanNEC | Pancreatic neuroendocrine cancer |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| HPF | High power field |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| MPD | Main pancreatic duct |
| CBD | Common bile duct |
| HU | Hounsfield units |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| GLCM | Gray-level co-occurrence matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-level differences matrix |
| GLRLM | Gray-level run-length matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-level size-zone matrix |
| NGTDM | Gray-tone difference matrix |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
References
- Dasari, A.; Shen, C.; Halperin, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Y.; Shih, T.; Yao, J.C. Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Survival Outcomes in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors in the United States. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1335–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Dasari, A. Epidemiology, Incidence, and Prevalence of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Are There Global Differences? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimstra, D.S.; Gill, A.J.; Klöppel, G.; Rindi, G.; Asa, S.L. WHO Classification of Tumours. In Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Tumours; Osamura, R.Y., Washington, M.K., Mete, O., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jeune, F.; Taibi, A.; Gaujoux, S. Update on the Surgical Treatment of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Scand. J. Surg. 2020, 109, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; Oberg, K.; Falconi, M.; Krenning, E.P.; Sundin, A.; Perren, A.; Berruti, A.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.R.; Merchant, N.B.; Conrad, C.; Keutgen, X.M.; Hallet, J.; Drebin, J.A.; Minter, R.M.; Lairmore, T.C.; Tseng, J.F.; Zeh, H.J.; et al. The North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society Consensus Paper on the Surgical Management of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas 2020, 49, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partelli, S.; Cirocchi, R.; Crippa, S.; Cardinali, L.; Fendrich, V.; Bartsch, D.K.; Falconi, M. Systematic review of active surveillance versus surgical management of asymptomatic small non-functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Gangi, A. The Evolving Landscape of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 32, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloyd, J.M.; Poultsides, G.A. The Landmark Series: Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.W.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, M.H.; Park, S.J.; Han, J.K. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: Prediction of the tumor grade using CT findings and computerized texture analysis. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi, K.; Fukukura, Y.; Higashi, M.; Ideue, J.; Umanodan, T.; Hakamada, H.; Kanetsuki, I.; Yoshiura, T. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Correlation between the contrast-enhanced computed tomography features and the pathological tumor grade. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, R.; Burk, K.S.; Parakh, A.; Sahani, D.V. Prediction of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Grade Based on CT Features and Texture Analysis. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.W.; Byun, J.H.; Song, K.B.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.M. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the pancreas at dynamic enhanced CT: Comparison between grade 3 neuroendocrine carcinoma and grade 1/2 neuroendocrine tumour. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Assignies, G.; Couvelard, A.; Bahrami, S.; Vullierme, M.P.; Hammel, P.; Hentic, O.; Sauvanet, A.; Bedossa, P.; Ruszniewski, P.; Vilgrain, V. Pancreatic endocrine tumors: Tumor blood flow assessed with perfusion CT reflects angiogenesis and correlates with prognostic factors. Radiology 2009, 250, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbís, M.; Godino, F.P.; Rodríguez-Comas, J.; Nava, E.; García-Figueiras, R.; Baleato-González, S.; Luna, A. Radiomics in CT and MR imaging of the liver and pancreas: Tools with potential for clinical application. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 322–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shur, J.D.; Doran, S.J.; Kumar, S.; Ap Dafydd, D.; Downey, K.; O’Connor, J.P.B.; Papanikolaou, N.; Messiou, C.; Koh, D.M.; Orton, M.R. Radiomics in Oncology: A Practical Guide. Radiographics 2021, 41, 1717–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Jin, G.; Lu, J. CT-Based Radiomics Score for Distinguishing Between Grade 1 and Grade 2 Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bian, Y.; Meng, Y.; Liu, F.; Cao, K.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Preoperative Prediction of G1 and G2/3 Grades in Patients with Nonfunctional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Using Multimodality Imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2022, 29, e49–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X. Application of Radiomics Analysis Based on CT Combined with Machine Learning in Diagnostic of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Patient’s Pathological Grades. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 521831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Cao, K.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Yue, X.; et al. CT-Radiomic Approach to Predict G1/2 Nonfunctional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, e272–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallieres, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whybra, P.; Zwanenburg, A.; Andrearczyk, V.; Schaer, R.; Apte, A.P.; Ayotte, A.; Baheti, B.; Bakas, S.; Bettinelli, A.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Convolutional Filters for Reproducible Radiomics and Enhanced Clinical Insights. Radiology 2024, 310, e231319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO Classification of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, J.R.; Cheema, A.; Weber, J.; Han, G.; Coppola, D.; Kvols, L.K. Prognostic validity of a novel American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Classification for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3044–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Martin, D.; Gemenetzis, G.; Parks, R. Surgical management of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Laparosc. Endosc. Robot. Surg. 2023, 6, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Gallotti, A.; Johnston, R.P.; Bonaffini, P.A.; Ingkakul, T.; Deshpande, V.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Sahani, D.V. Incidental neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas: MDCT findings and features of malignancy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumoto, S.; Kodama, Y.; Sakurai, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Katanuma, A.; Maguchi, H. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm: Correlation between computed tomography enhancement patterns and prognostic factors of surgical and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy specimens. Abdom. Imaging 2013, 38, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, F.; Yasrab, M.; Tixier, F.; Kawamoto, S.; Fishman, E.K.; Chu, L.C. The Role of AI in the Evaluation of Neuroendocrine Tumors: Current State of the Art. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, H.; Han, M.; Wu, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hou, B. Predicting histologic grades for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by radiologic image-based artificial intelligence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1332387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Ciaravino, V.; Cardobi, N.; De Robertis, R.; Cingarlini, S.; Landoni, L.; Capelli, P.; Bassi, C.; Scarpa, A. CT Enhancement and 3D Texture Analysis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Hu, Y.; Ding, H.; Wei, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Zeng, M.; Tian, J. CT radiomics may predict the grade of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A multicenter study. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6880–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, H.J.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Ooi, C.; Adler, A.S.; Gollub, J.; Chen, X.; Chan, B.K.; Matcuk, G.R.; Barry, C.T.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Decoding global gene expression programs in liver cancer by noninvasive imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, F.; Cheze-le-Rest, C.; Schick, U.; Simon, B.; Dufour, X.; Key, S.; Pradier, O.; Aubry, M.; Hatt, M.; Corcos, L.; et al. Transcriptomics in cancer revealed by Positron Emission Tomography radiomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
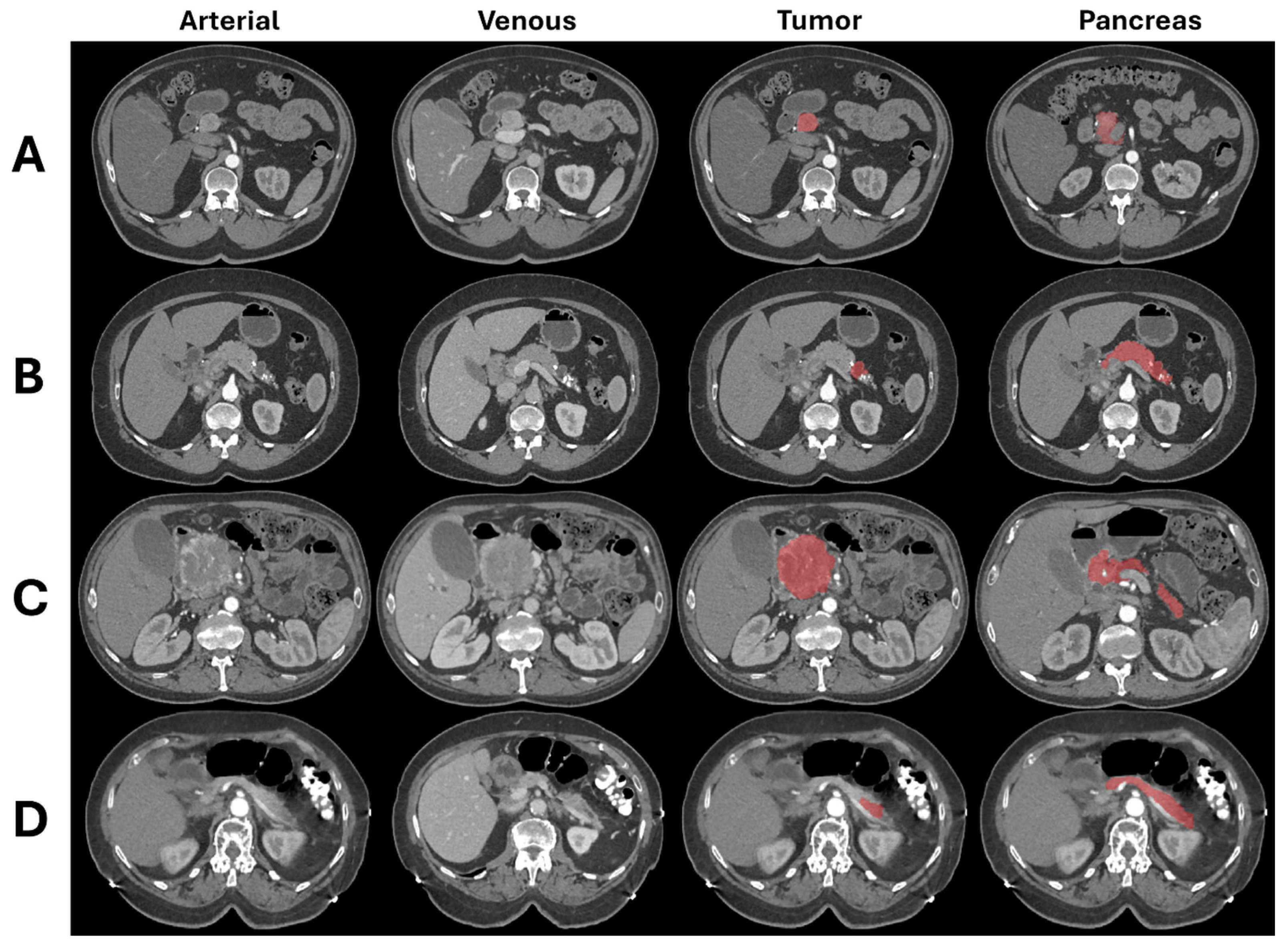
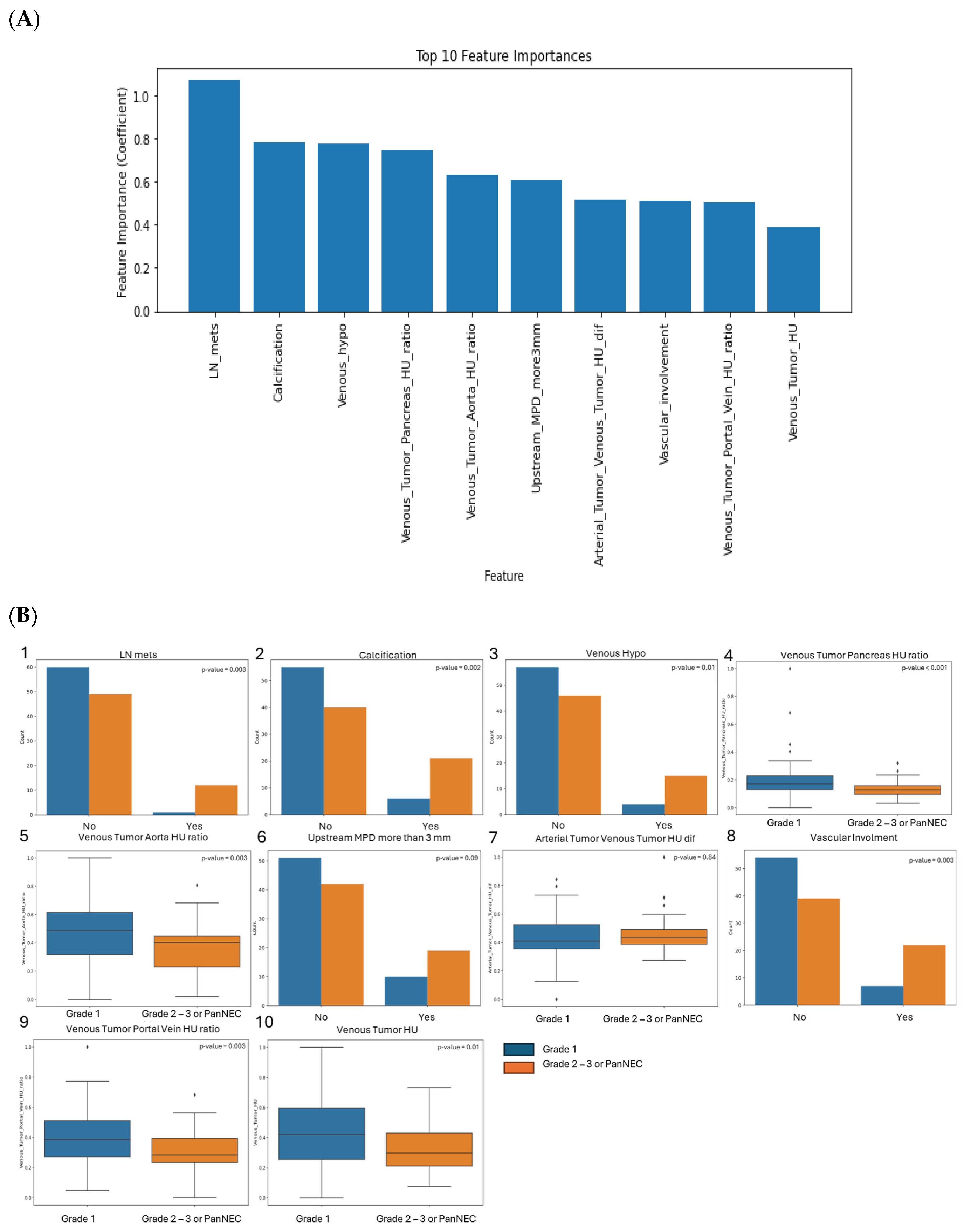


| Features Name | Description | Categorical |
|---|---|---|
| Arterial hypo | Hypoattenuating tumor relative to normal pancreas in arterial phase | Yes |
| Venous hypo | Hypoattenuating tumor relative to normal pancreas in venous phase | Yes |
| Margin ill defined | Ill-defined tumor margin | Yes |
| Upstream MPD more than 3 mm | Main pancreatic duct more than 3 mm upstream to tumor | Yes |
| CBD more than 1 cm mass or stent | Common bile duct more than 1 cm by tumor or presence of CBD stent | Yes |
| Upstream atrophy | Subjective pancreatic atrophy upstream to tumor | Yes |
| Exophytic more than 50% volume | ≥50% of tumor volume protruding from expected pancreatic contour | Yes |
| Liver mets | Presence of liver mass(es) suspicious for metastasis | Yes |
| LN mets | Presence of abnormal abdominal lymph node(s) suspicious for metastasis | Yes |
| Vascular involvement | Presence of involvement of major peripancreatic vessels | Yes |
| Calcification | Presence of calcification within the tumor | Yes |
| Cystic | Well-defined area(s) of homogeneous fluid attenuation within tumor | Yes |
| Necrotic | Ill-defined nonenhancing area(s) of low attenuation within tumor | Yes |
| Arterial Tumor HU | Attenuation of solid component of tumor in arterial phase | No |
| Arterial Pancreas HU | Attenuation of normal pancreas in arterial phase | No |
| Arterial Aorta HU | Attenuation of abdominal aorta in arterial phase | No |
| Venous Tumor HU | Attenuation of solid component of tumor in venous phase | No |
| Venous Pancreas HU | Attenuation of normal pancreas in venous phase | No |
| Venous Aorta HU | Attenuation of abdominal aorta in venous phase | No |
| Venous Portal Vein HU | Attenuation of main portal vein in venous phase | No |
| Arterial Tumor Aorta HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU)/aortic attenuation (HU) in arterial phase | No |
| Venous Tumor Aorta HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU)/aortic attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Arterial Tumor Pancreas HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU)/pancreas attenuation (HU) in arterial phase | No |
| Venous Tumor Pancreas HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU)/pancreas attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Venous Tumor Portal Vein HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU)/portal vein attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Arterial Tumor Venous Portal Vein HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU) in arterial phase/portal vein attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Arterial Tumor Venous Tumor HU Ratio | Tumor attenuation (HU) in arterial phase/tumor attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Arterial Tumor Venous Tumor HU Dif | Tumor attenuation (HU) in arterial phase/tumor attenuation (HU) in venous phase | No |
| Training | Testing | All | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 93 * | 42 * | 133 * | |
| Tumors | 96 | 42 | 138 | |
| Grade | ||||
| PanNET | ||||
| Grade 1 | 62 (64%) | 26 (62%) | 88 (63%) | |
| Grade 2 | 30 (33%) | 15 (36%) | 45 (33%) | |
| Grade 3 | 1 (1%) | 1 (1%) | ||
| PanNEC | 3 (3%) | 1 (2%) | 4 (3%) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 48 (52%) | 24 (57%) | 70 (54%) | |
| Male | 47 (48%) | 18 (43%) | 63 (46%) | |
| Surgery | ||||
| No (biopsy only) | 2 (2%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (1%) | |
| Yes | 91 (98%) | 42 (100%) | 136 (99%) | |
| Location | ||||
| Head | 27 (28%) | 13 (31%) | 40 (29%) | |
| Body | 21 (22%) | 4 (10%) | 25 (18%) | |
| Tail | 43 (45%) | 23 (55%) | 66 (48%) | |
| Neck | 1 (1%) | 1 (2%) | 2 (1%) | |
| Uncinate | 3 (3%) | 1 (2%) | 4 (3%) | |
| Diffuse | 1 (1%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1%) | |
| Patient with incidental cyst | ||||
| No | 91 (95%) | 40 (95%) | 131 (95%) | |
| Yes | 5 (5%) | 2 (5%) | 7 (5%) | |
| Age | ||||
| Median [range] | 60.3 [23.2–82.2] | 61.6 [21.5–83.4] | 60.6 [21.5–83.4] | |
| Functional Type | ||||
| Nonfunctional | 20 (21%) | 10 (24%) | 30 (22%) | |
| Serotonin | 2 (2%) | 2 (5%) | 4 (3%) | |
| Insulinoma | 6 (6%) | 2 (5%) | 8 (6%) | |
| Unknown | 68 (70%) | 28 (67%) | 95 (69%) | |
| Tumor Focality | ||||
| Unifocal | 85 (89%) | 41 (98%) | 126 (91%) | |
| Multifocal | 11 (11%) | 1 (2%) | 12 (9%) | |
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM Radiologist | 0.79 (0.67–0.90) | 0.75 (0.53–0.94) | 0.81 (0.64–0.95) | 0.71 (0.50–0.92) | 0.73 (0.55–0.87) |
| SVM Radiologist + clinical | 0.76 (0.64–0.88) | 0.69 (0.45–0.92) | 0.81 (0.63–0.94) | 0.69 (0.45–0.91) | 0.69 (0.47–0.85) |
| Radiomics Score | 0.69 (0.54–0.83) | 0.94 (0.80 – 1.0) | 0.46 (0.34–0.74) | 0.56 (0.38–0.74) | 0.70 (0.50–0.84) |
| SVM Radiomics | 0.69 (0.55–0.81) | 0.88 (0.69–1.0) | 0.58 (0.38–0.77) | 0.56 (0.36–0.76) | 0.68 (0.50–0.84) |
| SVM Radiomics + Clinical | 0.74 (0.62–0.86) | 0.94 (0.79–1.0) | 0.62 (0.42–0.79) | 0.60 (0.41–0.81) | 0.73 (0.57–0.87) |
| SVM Radiomics + Radiologist | 0.71 (0.57–0.86) | 0.94 (0.80–1.0) | 0.58 (0.39–0.76) | 0.58 (0.38–0.77) | 0.71 (0.53–0.85) |
| SVM Radiomics + Radiologist + Clinical | 0.79 (0.64–0.90) | 0.94 (0.78–1.0) | 0.69 (0.52–0.87) | 0.65 (0.45–0.84) | 0.77 (0.60–0.91) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tixier, F.; Lopez-Ramirez, F.; Blanco, A.; Javed, A.A.; Chu, L.C.; Hruban, R.H.; Yasrab, M.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Ghandili, S.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional CT Imaging Features and Radiomics Signature in Differentiating Grade 1 Tumors from Higher-Grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Cancers 2025, 17, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061047
Tixier F, Lopez-Ramirez F, Blanco A, Javed AA, Chu LC, Hruban RH, Yasrab M, Fouladi DF, Shayesteh S, Ghandili S, et al. Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional CT Imaging Features and Radiomics Signature in Differentiating Grade 1 Tumors from Higher-Grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061047
Chicago/Turabian StyleTixier, Florent, Felipe Lopez-Ramirez, Alejandra Blanco, Ammar A. Javed, Linda C. Chu, Ralph H. Hruban, Mohammad Yasrab, Daniel Fadaei Fouladi, Shahab Shayesteh, Saeed Ghandili, and et al. 2025. "Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional CT Imaging Features and Radiomics Signature in Differentiating Grade 1 Tumors from Higher-Grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms" Cancers 17, no. 6: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061047
APA StyleTixier, F., Lopez-Ramirez, F., Blanco, A., Javed, A. A., Chu, L. C., Hruban, R. H., Yasrab, M., Fouladi, D. F., Shayesteh, S., Ghandili, S., Fishman, E. K., & Kawamoto, S. (2025). Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional CT Imaging Features and Radiomics Signature in Differentiating Grade 1 Tumors from Higher-Grade Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Cancers, 17(6), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061047







