Tumor Heterogeneity and the Immune Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Insights and Implications for Immunotherapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
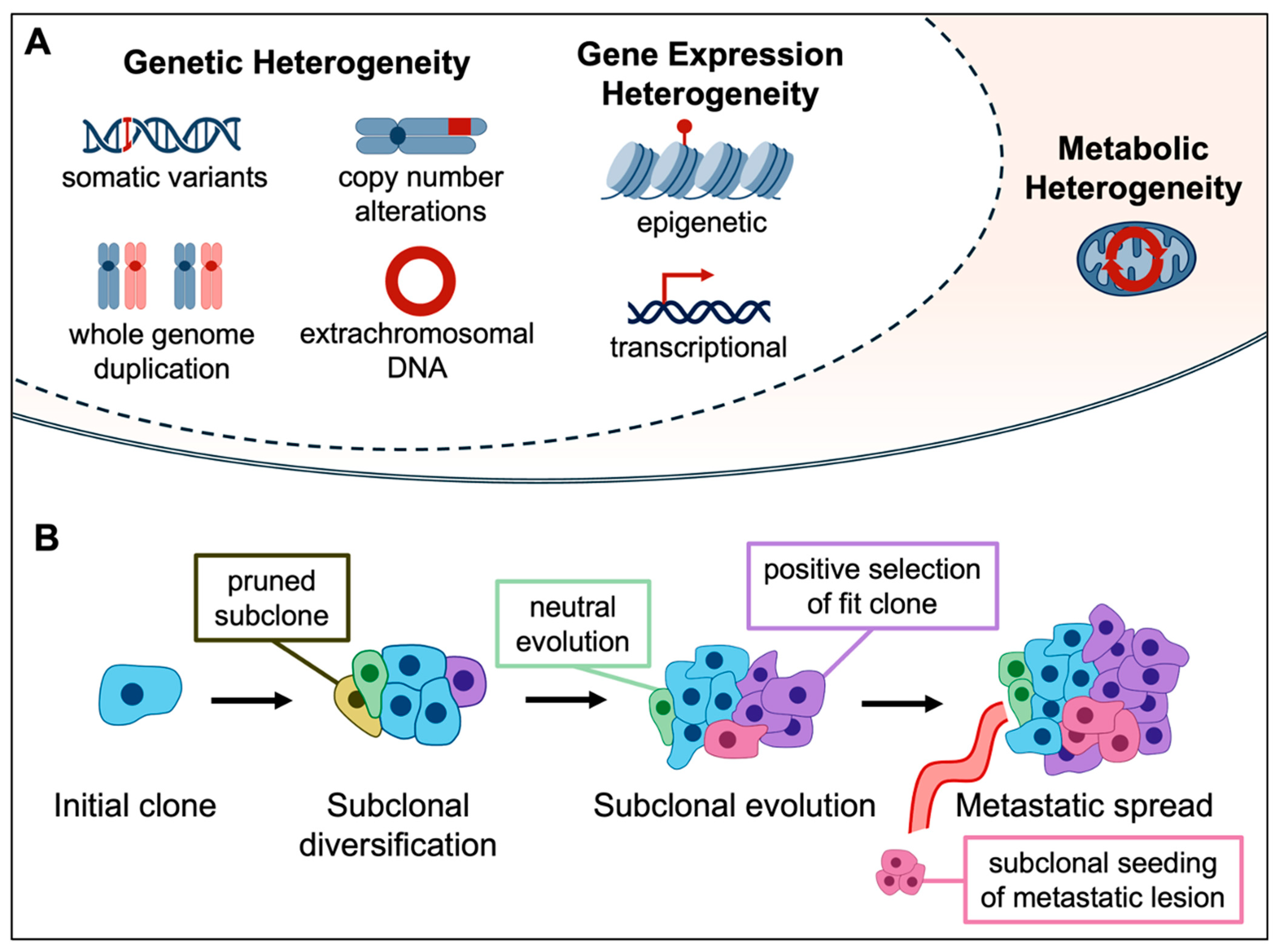
2. Genetic ITH and Clonal Evolution
3. Non-Genetic Sources of ITH
3.1. Gene Expression ITH
3.2. Metabolic ITH
4. ITH and the Immune Microenvironment
4.1. Heterogeneity of Immune Biomarkers in NSCLC
4.2. Determinants of Immune-Related ITH
4.3. Spatial Components of Immune-Related ITH
5. Clinical Impact of ITH
6. Current Techniques for Understanding ITH
6.1. Studying ITH with Improved Models
6.2. Assessing ITH in Clinical Samples
7. Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome ITH
7.1. Vaccination Strategies
7.2. Cytolytic Cellular Therapies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cairns, J. Mutation selection and the natural history of cancer. Nature 1975, 255, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.R.M.; McGranahan, N. Genetic and non-genetic clonal diversity in cancer evolution. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.A.; Sereno, M.; Das, M.; Baena Acevedo, J.D.; Sinnadurai, S.; Smith, C.; McSweeney, A.; Su, X.; Officer, L.; Jones, C.; et al. In situ growth in early lung adenocarcinoma may represent precursor growth or invasive clone outgrowth-a clinically relevant distinction. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Favero, F.; de Bruin, E.C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Szallasi, Z.; Swanton, C. Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 283ra254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.W.; Loeb, L.A.; Salk, J.J. The influence of subclonal resistance mutations on targeted cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal Heterogeneity and Tumor Evolution: Past, Present, and the Future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.; Makarov, V.; Merghoub, T.; Yuan, J.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Desrichard, A.; Walsh, L.A.; Postow, M.A.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennycuick, A.; Teixeira, V.H.; AbdulJabbar, K.; Raza, S.E.A.; Lund, T.; Akarca, A.U.; Rosenthal, R.; Kalinke, L.; Chandrasekharan, D.P.; Pipinikas, C.P.; et al. Immune Surveillance in Clinical Regression of Preinvasive Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaux, C.; Angelova, M.; Vasaturo, A.; Beane, J.; Hijazi, K.; Anthoine, G.; Buttard, B.; Rothe, F.; Willard-Gallo, K.; Haller, A.; et al. Immune evasion before tumour invasion in early lung squamous carcinogenesis. Nature 2019, 571, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, L.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Gadgeel, S.; Esteban, E.; Felip, E.; De Angelis, F.; Domine, M.; Clingan, P.; Hochmair, M.J.; Powell, S.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forde, P.M.; Spicer, J.; Lu, S.; Provencio, M.; Mitsudomi, T.; Awad, M.M.; Felip, E.; Broderick, S.R.; Brahmer, J.R.; Swanson, S.J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy in Resectable Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, H.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; La, K.; Chatila, W.; Jonsson, P.; Halpenny, D.; Plodkowski, A.; Long, N.; Sauter, J.L.; Rekhtman, N.; et al. Molecular Determinants of Response to Anti-Programmed Cell Death (PD)-1 and Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand (PD-L)-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Profiled with Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhunjhunwala, S.; Hammer, C.; Delamarre, L. Antigen presentation in cancer: Insights into tumour immunogenicity and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, K.; Reading, J.L.; Puttick, C.; Thakkar, K.; Abbosh, C.; Bentham, R.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Rosenthal, R.; Biswas, D.; Rowan, A.; et al. Meta-analysis of tumor- and T cell-intrinsic mechanisms of sensitization to checkpoint inhibition. Cell 2021, 184, 596–614.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, N.; Furness, A.J.; Rosenthal, R.; Ramskov, S.; Lyngaa, R.; Saini, S.K.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Hiley, C.T.; et al. Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade. Science 2016, 351, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, P.C.; Tran, L.M.; Bendris, N.; O’Byrne, S.; Tse, H.T.; Sharma, S.; Hoech, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Liclican, E.L.; Jing, Z.; et al. Identification of a Human Airway Epithelial Cell Subpopulation with Altered Biophysical, Molecular, and Metastatic Properties. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2017, 10, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, E.C.; McGranahan, N.; Mitter, R.; Salm, M.; Wedge, D.C.; Yates, L.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Shafi, S.; Murugaesu, N.; Rowan, A.J.; et al. Spatial and temporal diversity in genomic instability processes defines lung cancer evolution. Science 2014, 346, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navin, N.; Krasnitz, A.; Rodgers, L.; Cook, K.; Meth, J.; Kendall, J.; Riggs, M.; Eberling, Y.; Troge, J.; Grubor, V.; et al. Inferring tumor progression from genomic heterogeneity. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, N.; Gao, S.; Maity, T.K.; Banday, A.R.; Zhang, X.; Venugopalan, A.; Cultraro, C.M.; Patidar, R.; Sindiri, S.; Brown, A.L.; et al. APOBEC Mutagenesis and Copy-Number Alterations Are Drivers of Proteogenomic Tumor Evolution and Heterogeneity in Metastatic Thoracic Tumors. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2651–2666.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.; Pich, O.; Thol, K.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Luebeck, J.; Rowan, A.; Stavrou, G.; Weiser, N.E.; Dameracharla, B.; Bentham, R.; et al. Origins and impact of extrachromosomal DNA. Nature 2024, 635, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.L.; Jones, M.G.; Wong, I.T.; Curtis, E.J.; Lange, J.T.; He, B.J.; Luebeck, J.; Schmargon, R.; Scanu, E.; Bruckner, L.; et al. Coordinated inheritance of extrachromosomal DNAs in cancer cells. Nature 2024, 635, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Warrell, J.; Li, S.; McGillivray, P.D.; Meyerson, W.; Salichos, L.; Harmanci, A.; Martinez-Fundichely, A.; Chan, C.W.Y.; Nielsen, M.M.; et al. Passenger Mutations in More Than 2500 Cancer Genomes: Overall Molecular Functional Impact and Consequences. Cell 2020, 180, 915–927.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.J.; Werner, B.; Barnes, C.P.; Graham, T.A.; Sottoriva, A. Identification of neutral tumor evolution across cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleary, A.S.; Leonard, T.L.; Gestl, S.A.; Gunther, E.J. Tumour cell heterogeneity maintained by cooperating subclones in Wnt-driven mammary cancers. Nature 2014, 508, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, M.; Tabassum, D.P.; Castano, Z.; Cristea, S.; Yamamoto, K.N.; Kingston, N.L.; Murphy, K.C.; Shu, S.; Harper, N.W.; Del Alcazar, C.G.; et al. Subclonal cooperation drives metastasis by modulating local and systemic immune microenvironments. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbo, J.; van Montfort, E.; Proost, N.; van Drunen, E.; Beverloo, H.B.; Meuwissen, R.; Berns, A. A functional role for tumor cell heterogeneity in a mouse model of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.B.; Li, S.; Higgs, E.F.; Cabanov, A.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Gajewski, T.F. Tumor heterogeneity and clonal cooperation influence the immune selection of IFN-gamma-signaling mutant cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Rowan, A.J.; Horswell, S.; Math, M.; Larkin, J.; Endesfelder, D.; Gronroos, E.; Martinez, P.; Matthews, N.; Stewart, A.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multiregion sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentro, S.C.; Leshchiner, I.; Haase, K.; Tarabichi, M.; Wintersinger, J.; Deshwar, A.G.; Yu, K.; Rubanova, Y.; Macintyre, G.; Demeulemeester, J.; et al. Characterizing genetic intra-tumor heterogeneity across 2658 human cancer genomes. Cell 2021, 184, 2239–2254.e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.; Black, J.R.M.; Reading, J.L.; Litchfield, K.; Turajlic, S.; McGranahan, N.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Swanton, C. Tracking Cancer Evolution through the Disease Course. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankell, A.M.; Dietzen, M.; Al Bakir, M.; Lim, E.L.; Karasaki, T.; Ward, S.; Veeriah, S.; Colliver, E.; Huebner, A.; Bunkum, A.; et al. The evolution of lung cancer and impact of subclonal selection in TRACERx. Nature 2023, 616, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachida, S.; Jones, S.; Bozic, I.; Antal, T.; Leary, R.; Fu, B.; Kamiyama, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Eshleman, J.R.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bakir, M.; Huebner, A.; Martinez-Ruiz, C.; Grigoriadis, K.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Pich, O.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Ward, S.; Laycock, J.; et al. The evolution of non-small cell lung cancer metastases in TRACERx. Nature 2023, 616, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, M.; Mlecnik, B.; Vasaturo, A.; Bindea, G.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Buttard, B.; Morgand, E.; Bruni, D.; Jouret-Mourin, A.; et al. Evolution of Metastases in Space and Time under Immune Selection. Cell 2018, 175, 751–765.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.J.; Padmanaban, V.; Silvestri, V.; Schipper, K.; Cohen, J.D.; Fairchild, A.N.; Gorin, M.A.; Verdone, J.E.; Pienta, K.J.; Bader, J.S.; et al. Polyclonal breast cancer metastases arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor cell clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E854–E863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernari, D.; Battistello, E.; Dheilly, E.; Petruzzella, A.S.; Mina, M.; Sordet-Dessimoz, J.; Peters, S.; Krueger, T.; Gfeller, D.; Riggi, N.; et al. Nongenetic Evolution Drives Lung Adenocarcinoma Spatial Heterogeneity and Progression. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1490–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, I.; Izar, B.; Prakadan, S.M.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Treacy, D.; Trombetta, J.J.; Rotem, A.; Rodman, C.; Lian, C.; Murphy, G.; et al. Dissecting the multicellular ecosystem of metastatic melanoma by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 2016, 352, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Birkbak, N.J.; Rosenthal, R.; Hiley, C.T.; Lim, E.L.; Papp, K.; Boeing, S.; Krzystanek, M.; Djureinovic, D.; La Fleur, L.; et al. A clonal expression biomarker associates with lung cancer mortality. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Househam, J.; Heide, T.; Cresswell, G.D.; Spiteri, I.; Kimberley, C.; Zapata, L.; Lynn, C.; James, C.; Mossner, M.; Fernandez-Mateos, J.; et al. Phenotypic plasticity and genetic control in colorectal cancer evolution. Nature 2022, 611, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavish, A.; Tyler, M.; Greenwald, A.C.; Hoefflin, R.; Simkin, D.; Tschernichovsky, R.; Galili Darnell, N.; Somech, E.; Barbolin, C.; Antman, T.; et al. Hallmarks of transcriptional intratumour heterogeneity across a thousand tumours. Nature 2023, 618, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Merritt, E.; Hu, X.; Cruz, A.; Jiang, C.; Sarkodie, H.; Zhou, Z.; Malhotra, J.; Riedlinger, G.M.; De, S. Non-Genetic Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity Is a Major Predictor of Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Ongoing Evolutionary Dynamics in Lung Tumors. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2164–2174.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, N.D.; Hofree, M.; Chan, J.E.; Canner, D.; Wu, K.; Trakala, M.; Hartmann, G.G.; Smith, O.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Evans, K.V.; et al. Emergence of a High-Plasticity Cell State during Lung Cancer Evolution. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 229–246.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hong, W.; Wei, X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Koh, J.; Kim, S.; Song, S.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jeon, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Keam, B.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by tumor cell-intrinsic PD-L1 signaling predicts a poor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in PD-L1-high lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyes, S.; Bediaga, N.G.; Zippo, A. An Epigenetic Perspective on Intra-Tumour Heterogeneity: Novel Insights and New Challenges from Multiple Fields. Cancers 2021, 13, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Dadzadi, M.; Sahafnejad, Z.; Allahverdi, A. Epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. MedComm 2023, 4, e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, N.C.; Pierron, G.; Klughammer, J.; Datlinger, P.; Schonegger, A.; Schuster, M.; Hadler, J.; Surdez, D.; Guillemot, D.; Lapouble, E.; et al. DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, D.K.; Corleone, G.; Gyorffy, B.; Perone, Y.; Slaven, N.; Barozzi, I.; Erdos, E.; Saiakhova, A.; Goddard, K.; Vingiani, A.; et al. Enhancer mapping uncovers phenotypic heterogeneity and evolution in patients with luminal breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, O.G.; Li, X.; Saunders, T.; Tryggvadottir, R.; Mentch, S.J.; Warmoes, M.O.; Word, A.E.; Carrer, A.; Salz, T.H.; Natsume, S.; et al. Epigenomic reprogramming during pancreatic cancer progression links anabolic glucose metabolism to distant metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, V.H.; Pipinikas, C.P.; Pennycuick, A.; Lee-Six, H.; Chandrasekharan, D.; Beane, J.; Morris, T.J.; Karpathakis, A.; Feber, A.; Breeze, C.E.; et al. Deciphering the genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic landscapes of pre-invasive lung cancer lesions. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R.; Cadieux, E.L.; Salgado, R.; Bakir, M.A.; Moore, D.A.; Hiley, C.T.; Lund, T.; Tanic, M.; Reading, J.L.; Joshi, K.; et al. Neoantigen-directed immune escape in lung cancer evolution. Nature 2019, 567, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ruiz, C.; Black, J.R.M.; Puttick, C.; Hill, M.S.; Demeulemeester, J.; Larose Cadieux, E.; Thol, K.; Jones, T.P.; Veeriah, S.; Naceur-Lombardelli, C.; et al. Genomic-transcriptomic evolution in lung cancer and metastasis. Nature 2023, 616, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFave, L.M.; Kartha, V.K.; Ma, S.; Meli, K.; Del Priore, I.; Lareau, C.; Naranjo, S.; Westcott, P.M.K.; Duarte, F.M.; Sankar, V.; et al. Epigenomic State Transitions Characterize Tumor Progression in Mouse Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 212–228.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, S.; Engelsen, A.S.T.; Buart, S.; Elsayed, W.S.; Venkatesh, G.H.; Chouaib, S. Hypoxia-driven intratumor heterogeneity and immune evasion. Cancer Lett. 2020, 492, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goveia, J.; Rohlenova, K.; Taverna, F.; Treps, L.; Conradi, L.C.; Pircher, A.; Geldhof, V.; de Rooij, L.; Kalucka, J.; Sokol, L.; et al. An Integrated Gene Expression Landscape Profiling Approach to Identify Lung Tumor Endothelial Cell Heterogeneity and Angiogenic Candidates. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 21–36.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, K.; Kim, J.; Murakami, I.; Rozeboom, L.; Shimoji, M.; Shimizu, S.; Rivard, C.J.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tan, A.C.; Hirsch, F.R. Innate Genetic Evolution of Lung Cancers and Spatial Heterogeneity: Analysis of Treatment-Naive Lesions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1496–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, Y.; Leake, J.; Odu, A.; Xi, Y.; Subramaniam, R.M. Tumor Heterogeneity on FDG PET/CT and Immunotherapy: An Imaging Biomarker for Predicting Treatment Response in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Song, S.; Hu, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, B. Heterogeneity derived from (18) F-FDG PET/CT predicts immunotherapy outcome for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, A.; Grizzi, F.; Toschi, L.; Rossi, S.; Rahal, D.; Marchesi, F.; Russo, C.; Finocchiaro, G.; Lopci, E. Tumor heterogeneity, hypoxia, and immune markers in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Ratcliffe, C.D.H.; Hooper, S.; Ellis, J.; MacRae, J.I.; Hennequart, M.; Dunsby, C.W.; Anderson, K.I.; Sahai, E. Single-cell resolved imaging reveals intra-tumor heterogeneity in glycolysis, transitions between metabolic states, and their regulatory mechanisms. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momcilovic, M.; Jones, A.; Bailey, S.T.; Waldmann, C.M.; Li, R.; Lee, J.T.; Abdelhady, G.; Gomez, A.; Holloway, T.; Schmid, E.; et al. In vivo imaging of mitochondrial membrane potential in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2019, 575, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Bushong, E.A.; Segawa, M.; Tiard, A.; Wong, A.; Brady, M.R.; Momcilovic, M.; Wolf, D.M.; Zhang, R.; Petcherski, A.; et al. Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer. Nature 2023, 615, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensley, C.T.; Faubert, B.; Yuan, Q.; Lev-Cohain, N.; Jin, E.; Kim, J.; Jiang, L.; Ko, B.; Skelton, R.; Loudat, L.; et al. Metabolic Heterogeneity in Human Lung Tumors. Cell 2016, 164, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdogan, A.; Faubert, B.; Ramesh, V.; Ubellacker, J.M.; Shen, B.; Solmonson, A.; Murphy, M.M.; Gu, Z.; Gu, W.; Martin, M.; et al. Metabolic heterogeneity confers differences in melanoma metastatic potential. Nature 2020, 577, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, J.; Neugent, M.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Choe, J.H.; Choi, H.; Jenkins, D.M.R.; Ruthenborg, R.J.; Robinson, M.W.; Jeong, J.Y.; Wake, M.; et al. The distinct metabolic phenotype of lung squamous cell carcinoma defines selective vulnerability to glycolytic inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafoglio, C.R.; Villegas, B.; Abdelhady, G.; Bailey, S.T.; Liu, J.; Shirali, A.S.; Wallace, W.D.; Magyar, C.E.; Grogan, T.R.; Elashoff, D.; et al. Sodium-glucose transporter 2 is a diagnostic and therapeutic target for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuneva, M.O.; Fan, T.W.; Allen, T.D.; Higashi, R.M.; Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T.; Mates, J.M.; Alonso, F.J.; Wang, C.; Seo, Y.; et al. The metabolic profile of tumors depends on both the responsible genetic lesion and tissue type. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.L.; Rak, J.W.; Carmeliet, P.; Nagy, A.; Kerbel, R.S.; Coomber, B.L. Heterogeneous vascular dependence of tumor cell populations. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson-Tessi, M.; Gillies, R.J.; Gatenby, R.A.; Anderson, A.R. Impact of metabolic heterogeneity on tumor growth, invasion, and treatment outcomes. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.V.; Carrer, A.; Shah, S.; Snyder, N.W.; Wei, S.; Venneti, S.; Worth, A.J.; Yuan, Z.F.; Lim, H.W.; Liu, S.; et al. Akt-dependent metabolic reprogramming regulates tumor cell histone acetylation. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Sato, Y.; Kogure, Y.; McClure, M.B.; Oshikawa-Kumade, Y.; Saito, Y.; Shingaki, S.; Ito, Y.; Yuasa, M.; Koya, J.; et al. Inter- and intra-tumor heterogeneity of genetic and immune profiles in inherited renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hu, H.; He, M.; Liu, L.; Liao, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; et al. Multiomic Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Tumor Heterogeneity and Distinct Immune Subtypes in Multifocal Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1896–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, J.M.; Young, G.D.; McMiller, T.L.; Chen, S.; Salas, J.T.; Pritchard, T.S.; Xu, H.; Meeker, A.K.; Fan, J.; Cheadle, C.; et al. Differential Expression of Immune-Regulatory Genes Associated with PD-L1 Display in Melanoma: Implications for PD-1 Pathway Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadevall, D.; Clave, S.; Taus, A.; Hardy-Werbin, M.; Rocha, P.; Lorenzo, M.; Menendez, S.; Salido, M.; Albanell, J.; Pijuan, L.; et al. Heterogeneity of Tumor and Immune Cell PD-L1 Expression and Lymphocyte Counts in Surgical NSCLC Samples. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 682–691.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, J.M.; Wages, N.A.; Hu, Y.; Deacon, D.H.; Slingluff, C.L., Jr. Heterogeneity of CD8(+) tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in non-small-cell lung cancer: Impact on patient prognostic assessments and comparison of quantification by different sampling strategies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.; Han, G.; Schalper, K.A.; Carvajal-Hausdorf, D.; Pelekanou, V.; Rehman, J.; Velcheti, V.; Herbst, R.; LoRusso, P.; Rimm, D.L. Quantitative Assessment of the Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haragan, A.; Field, J.K.; Davies, M.P.A.; Escriu, C.; Gruver, A.; Gosney, J.R. Heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: Implications for specimen sampling in predicting treatment response. Lung Cancer 2019, 134, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Horiuchi, S.; Morooka, H.; Ibi, T.; Takahashi, N.; Ikeya, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Hoshi, E. Inter-tumor heterogeneity of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4982–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Negrao, M.V.; Dibaj, S.S.; Chen, R.; Reuben, A.; Bohac, J.M.; Liu, X.; Skoulidis, F.; Gay, C.M.; Cascone, T.; et al. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Heterogeneity and Its Impact on Benefit From Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Rizvi, H.; Bandlamudi, C.; Sauter, J.L.; Travis, W.D.; Rekhtman, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Sawan, P.; Beras, A.; et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of PD-L1 expression in patients with lung adenocarcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Hou, L.; Wu, F.; Gao, G.; He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; et al. Heterogeneity of PD-L1 Expression Among the Different Histological Components and Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Patients With Resected Lung Adenosquamous Carcinoma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e421–e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.; Dong, D.; Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, X.; Sun, D.; Li, H.; et al. Immune microenvironment heterogeneity of concurrent adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in multiple primary lung cancers. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, A.; Gittelman, R.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yusko, E.C.; Wu, C.J.; Emerson, R.; Zhang, J.; Tipton, C.; Li, J.; et al. TCR Repertoire Intratumor Heterogeneity in Localized Lung Adenocarcinomas: An Association with Predicted Neoantigen Heterogeneity and Postsurgical Recurrence. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; de Massy, M.R.; Ismail, M.; Reading, J.L.; Uddin, I.; Woolston, A.; Hatipoglu, E.; Oakes, T.; Rosenthal, R.; Peacock, T.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity of the T cell receptor repertoire reflects the mutational landscape in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.; Xie, L.; Shu, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, P.; Su, X.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Personalized neoantigen pulsed dendritic cell vaccine for advanced lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Cui, H.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Kong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Multi-region sequencing unveils novel actionable targets and spatial heterogeneity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Alexander, P.B.; Sun, C.; Gong, Z.; Cheng, J.N.; Sun, H.; Guan, Y.; Xia, X.; et al. Local mutational diversity drives intratumoral immune heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.W.; McPherson, A.; Milne, K.; Kroeger, D.R.; Hamilton, P.T.; Miranda, A.; Funnell, T.; Little, N.; de Souza, C.P.E.; Laan, S.; et al. Interfaces of Malignant and Immunologic Clonal Dynamics in Ovarian Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 1755–1769.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marty, R.; Kaabinejadian, S.; Rossell, D.; Slifker, M.J.; van de Haar, J.; Engin, H.B.; de Prisco, N.; Ideker, T.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Font-Burgada, J.; et al. MHC-I Genotype Restricts the Oncogenic Mutational Landscape. Cell 2017, 171, 1272–1283.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, A.L.; Gukasyan, J.; Lu, H.Y.; Grogan, T.; Sunga, G.; Fares, C.M.; Hornstein, N.; Zaretsky, J.; Carroll, J.; Bachrach, B.; et al. Mutational landscape influences immunotherapy outcomes among patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with human leukocyte antigen supertype B44. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, N.; Rosenthal, R.; Hiley, C.T.; Rowan, A.J.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Veeriah, S.; Van Loo, P.; Herrero, J.; et al. Allele-Specific HLA Loss and Immune Escape in Lung Cancer Evolution. Cell 2017, 171, 1259–1271.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerden, M.; Castro, A.B.; Cui, Y.; Harake, N.; Kim, B.; Dye, J.; Maiorino, L.; White, F.M.; Irvine, D.J.; Litchfield, K.; et al. Neoantigen architectures define immunogenicity and drive immune evasion of tumors with heterogenous neoantigen expression. J. Immunother Cancer 2024, 12, e010249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, I.; Bedora-Faure, M.; Garcia, Z.; Thibaut, R.; Perie, L.; Shakhar, G.; Deriano, L.; Bousso, P. The immune system profoundly restricts intratumor genetic heterogeneity. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.D.; Ma, S.; Phua, C.Z.J.; Kaya, N.A.; Lai, H.L.H.; Lim, C.J.; Lim, J.Q.; Wasser, M.; Lai, L.; Tam, W.L.; et al. Intratumoural immune heterogeneity as a hallmark of tumour evolution and progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysan, K.; Tran, L.M.; Grimes, B.S.; Fishbein, G.A.; Seki, A.; Gardner, B.K.; Walser, T.C.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Yanagawa, J.; Lee, J.M.; et al. The Immune Contexture Associates with the Genomic Landscape in Lung Adenomatous Premalignancy. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5022–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fan, J.; He, Y.; Xiong, A.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, F.; Li, W.; et al. Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golkaram, M.; Kuo, F.; Gupta, S.; Carlo, M.I.; Salmans, M.L.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Tang, C.; Makarov, V.; Rappold, P.; Blum, K.A.; et al. Spatiotemporal evolution of the clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment links intra-tumoral heterogeneity to immune escape. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, A.; Cybulska, P.; Mager, K.L.; Koplev, S.; Cast, O.; Couturier, D.L.; Memon, D.; Selenica, P.; Nikolovski, I.; Mazaheri, Y.; et al. Unraveling tumor-immune heterogeneity in advanced ovarian cancer uncovers immunogenic effect of chemotherapy. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, A.; Hamilton, P.T.; Zhang, A.W.; Pattnaik, S.; Becht, E.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Bruun, J.; Micke, P.; de Reynies, A.; Nelson, B.H. Cancer stemness, intratumoral heterogeneity, and immune response across cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9020–9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, M.; Song, Q. The impact of tertiary lymphoid structures on tumor prognosis and the immune microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Koop, K.; Weigert, A. Heterogeneity of tertiary lymphoid structures in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1286850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Chong, L.C.; Takata, K.; Milne, K.; Hav, M.; Colombo, A.; Chavez, E.A.; Nissen, M.; Wang, X.; Miyata-Takata, T.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Disease-Defining T-cell Subsets in the Tumor Microenvironment of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launonen, I.M.; Niemiec, I.; Hincapie-Otero, M.; Erkan, E.P.; Junquera, A.; Afenteva, D.; Falco, M.M.; Liang, Z.; Salko, M.; Chamchougia, F.; et al. Chemotherapy induces myeloid-driven spatially confined T cell exhaustion in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 2045–2063.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.K.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Storrs, E.; Targino da Costa, A.L.N.; Houston, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Jayasinghe, R.G.; Iglesia, M.D.; Ma, C.; et al. Tumour evolution and microenvironment interactions in 2D and 3D space. Nature 2024, 634, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoschek, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Bocci, M.; Lovrot, J.; Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Lindgren, D.; Pekar, G.; Karlsson, G.; et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Sanchez, A.; Memon, D.; Pourpe, S.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Li, Y.; Vargas, H.A.; Gill, M.B.; Park, K.J.; Zivanovic, O.; Konner, J.; et al. Heterogeneous Tumor-Immune Microenvironments among Differentially Growing Metastases in an Ovarian Cancer Patient. Cell 2017, 170, 927–938.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Cai, Y.X.; He, Y.Z.; Xu, J.; Tian, S.F.; Li, Z.Q. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of tumor immune microenvironment between primary tumor and brain metastases in NSCLC. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuben, A.; Spencer, C.N.; Prieto, P.A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Reddy, S.M.; Miller, J.P.; Mao, X.; De Macedo, M.P.; Chen, J.; Song, X.; et al. Genomic and immune heterogeneity are associated with differential responses to therapy in melanoma. NPJ Genom. Med. 2017, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altorki, N.K.; Markowitz, G.J.; Gao, D.; Port, J.L.; Saxena, A.; Stiles, B.; McGraw, T.; Mittal, V. The lung microenvironment: An important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Verduzco, D.; Gatenby, R.A. Evolutionary dynamics of carcinogenesis and why targeted therapy does not work. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, N.; Brown, A.L.; Wei, J.S.; Pack, S.; Trindade, C.; Kim, C.; Restifo, O.; Gao, S.; Sindiri, S.; Mehrabadi, F.; et al. Clonal Evolution and Heterogeneity of Osimertinib Acquired Resistance Mechanisms in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, Y.; Busch, G.T.; Pillai, M.; Li, J.; Boe, R.H.; Grody, E.I.; Chelvanambi, M.; Dardani, I.P.; Emert, B.; Bodkin, N.; et al. Diverse clonal fates emerge upon drug treatment of homogeneous cancer cells. Nature 2023, 620, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gejman, R.S.; Chang, A.Y.; Jones, H.F.; DiKun, K.; Hakimi, A.A.; Schietinger, A.; Scheinberg, D.A. Rejection of immunogenic tumor clones is limited by clonal fraction. Elife 2018, 7, e41090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andor, N.; Graham, T.A.; Jansen, M.; Xia, L.C.; Aktipis, C.A.; Petritsch, C.; Ji, H.P.; Maley, C.C. Pan-cancer analysis of the extent and consequences of intratumor heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, K.A.; Kawaguchi, T.; Qi, Q.; Peng, X.; Asaoka, M.; Young, J.; Opyrchal, M.; Yan, L.; Patnaik, S.; Otsuji, E.; et al. Tumor Heterogeneity Correlates with Less Immune Response and Worse Survival in Breast Cancer Patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, R.F.; Ng, C.K.; Cooke, S.L.; Newman, S.; Temple, J.; Piskorz, A.M.; Gale, D.; Sayal, K.; Murtaza, M.; Baldwin, P.J.; et al. Spatial and temporal heterogeneity in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: A phylogenetic analysis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losic, B.; Craig, A.J.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; Martins-Filho, S.N.; Akers, N.; Chen, X.; Ahsen, M.E.; von Felden, J.; Labgaa, I.; D’Avola, D.; et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity and clonal evolution in liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Meng, X.; Wen, J.; Corral, J.M.; Andreev, D.; Kachler, K.; Schett, G.; Chen, X.; Bozec, A. Intratumor Heterogeneity Correlates With Reduced Immune Activity and Worse Survival in Melanoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 596493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fujimoto, J.; Zhang, J.; Wedge, D.C.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Seth, S.; Chow, C.W.; Cao, Y.; Gumbs, C.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity in localized lung adenocarcinomas delineated by multiregion sequencing. Science 2014, 346, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; McGranahan, N.; Birkbak, N.J.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Veeriah, S.; Shafi, S.; Johnson, D.H.; Mitter, R.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Tracking the Evolution of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Zhao, W.; Pesatori, A.C.; Consonni, D.; Caporaso, N.E.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B.; Wang, M.; Jones, K.; Hicks, B.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic intratumor heterogeneity impacts prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Temko, D.; Maliga, Z.; Moreira, A.L.; Sei, E.; Minussi, D.C.; Dean, J.; Lee, C.; Xu, Q.; Hochart, G.; et al. Spatial intra-tumor heterogeneity is associated with survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Pluzanski, A.; Lee, J.S.; Otterson, G.A.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Minenza, E.; Linardou, H.; Burgers, S.; Salman, P.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Lung Cancer with a High Tumor Mutational Burden. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; et al. Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab: Prospective biomarker analysis of the multicohort, open-label, phase 2 KEYNOTE-158 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Jin, H.; Zhou, H.; Hong, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity as a predictive biomarker in anti-PD-(L)1 therapies for non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, F.; Mina, M.; Tavernari, D.; Ciriello, G. Pan-cancer inference of intra-tumor heterogeneity reveals associations with different forms of genomic instability. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, N.; Havel, J.J.; Makarov, V.; Desrichard, A.; Urba, W.J.; Sims, J.S.; Hodi, F.S.; Martin-Algarra, S.; Mandal, R.; Sharfman, W.H.; et al. Tumor and Microenvironment Evolution during Immunotherapy with Nivolumab. Cell 2017, 171, 934–949.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, B.; Hutchinson, A.; Pesatori, A.C.; Consonni, D.; Caporaso, N.E.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Shi, J.; Landi, M.T. Clinical Implications of Inter- and Intratumor Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Markers in Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de Rodas, M.; Nagineni, V.; Ravi, A.; Datar, I.J.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Corredor, G.; Barrera, C.; Behlman, L.; Rimm, D.L.; Herbst, R.S.; et al. Role of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and spatial immune heterogeneity in sensitivity to PD-1 axis blockers in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magen, A.; Hamon, P.; Fiaschi, N.; Soong, B.Y.; Park, M.D.; Mattiuz, R.; Humblin, E.; Troncoso, L.; D’Souza, D.; Dawson, T.; et al. Intratumoral dendritic cell-CD4(+) T helper cell niches enable CD8(+) T cell differentiation following PD-1 blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, D.G.; Politi, K.; Bhutkar, A.; Chen, F.K.; Song, X.; Pirun, M.; Santiago, P.M.; Kim-Kiselak, C.; Platt, J.T.; Lee, E.; et al. Mutational landscape of EGFR-, MYC-, and Kras-driven genetically engineered mouse models of lung adenocarcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6409–E6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.; Bartok, O.; Patkar, S.; Eli, G.B.; Cohen, S.; Litchfield, K.; Levy, R.; Jimenez-Sanchez, A.; Trabish, S.; Lee, J.S.; et al. UVB-Induced Tumor Heterogeneity Diminishes Immune Response in Melanoma. Cell 2019, 179, 219–235.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Rad, R.; Li, R.; Tran, L.M.; Lim, R.J.; Abascal, J.; Momcilovic, M.; Park, S.J.; Ong, S.L.; Shabihkhani, M.; Huang, Z.L.; et al. Novel Kras-mutant murine models of non-small cell lung cancer possessing co-occurring oncogenic mutations and increased tumor mutational burden. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Kim, J.; Deng, Q.; Ricciuti, B.; Alessi, J.V.; Eglenen-Polat, B.; Bender, M.E.; Huang, H.C.; Kowash, R.R.; Cuevas, I.; et al. Loss of p53 and mutational heterogeneity drives immune resistance in an autochthonous mouse lung cancer model with high tumor mutational burden. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1731–1748.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pham, N.A.; Tong, J.; Sakashita, S.; Allo, G.; Kim, L.; Yanagawa, N.; Raghavan, V.; Wei, Y.; To, C.; et al. Molecular heterogeneity of non-small cell lung carcinoma patient-derived xenografts closely reflect their primary tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cheng, J.; Zhuang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Qian, H.; Lu, Y.; Han, F.; et al. Pharmacogenomic profiling of intra-tumor heterogeneity using a large organoid biobank of liver cancer. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 535–551.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Byrne, K.T.; Yan, F.; Yamazoe, T.; Chen, Z.; Baslan, T.; Richman, L.P.; Lin, J.H.; Sun, Y.H.; Rech, A.J.; et al. Tumor Cell-Intrinsic Factors Underlie Heterogeneity of Immune Cell Infiltration and Response to Immunotherapy. Immunity 2018, 49, 178–193.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Jones, M.G.; Naranjo, S.; Rideout, W.M., 3rd; Min, K.H.J.; Ho, R.; Wu, W.; Replogle, J.M.; Page, J.L.; Quinn, J.J.; et al. Lineage tracing reveals the phylodynamics, plasticity, and paths of tumor evolution. Cell 2022, 185, 1905–1923.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowman, R.L.; Dunbar, A.J.; Mishra, T.; Xiao, W.; Waarts, M.R.; Maestre, I.F.; Eisman, S.E.; Cai, L.; Mowla, S.; Shah, N.; et al. In vivo models of subclonal oncogenesis and dependency in hematopoietic malignancy. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 1955–1969.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusyk, A.; Tabassum, D.P.; Altrock, P.M.; Almendro, V.; Michor, F.; Polyak, K. Non-cell-autonomous driving of tumour growth supports sub-clonal heterogeneity. Nature 2014, 514, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driessens, G.; Beck, B.; Caauwe, A.; Simons, B.D.; Blanpain, C. Defining the mode of tumour growth by clonal analysis. Nature 2012, 488, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snippert, H.J.; van der Flier, L.G.; Sato, T.; van Es, J.H.; van den Born, M.; Kroon-Veenboer, C.; Barker, N.; Klein, A.M.; van Rheenen, J.; Simons, B.D.; et al. Intestinal crypt homeostasis results from neutral competition between symmetrically dividing Lgr5 stem cells. Cell 2010, 143, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadien, I.D.; Adler, S.; Mehmed, S.; Bailey, S.; Sawle, A.; Couturier, D.L.; Eldridge, M.; Adams, D.J.; Kemp, R.; Lourenco, F.C.; et al. Polyclonality overcomes fitness barriers in Apc-driven tumorigenesis. Nature 2024, 634, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddipati, R.; Stanger, B.Z. Pancreatic Cancer Metastases Harbor Evidence of Polyclonality. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, A.G.; Snippert, H.J.; Stange, D.E.; van den Born, M.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Clevers, H. Lineage tracing reveals Lgr5+ stem cell activity in mouse intestinal adenomas. Science 2012, 337, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabichi, M.; Salcedo, A.; Deshwar, A.G.; Ni Leathlobhair, M.; Wintersinger, J.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Morris, Q.D.; Boutros, P.C. A practical guide to cancer subclonal reconstruction from DNA sequencing. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambotto, A.; Dworacki, G.; Cicinnati, V.; Kenniston, T.; Steitz, J.; Tuting, T.; Robbins, P.D.; DeLeo, A.B. Immunogenicity of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) in BALB/c mice: Identification of an H2-Kd-restricted CTL epitope. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 2036–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, F.J.; Krishna, S.; Yossef, R.; Parikh, N.B.; Chatani, P.D.; Zacharakis, N.; Parkhurst, M.R.; Levin, N.; Sindiri, S.; Sachs, A.; et al. Molecular signatures of antitumor neoantigen-reactive T cells from metastatic human cancers. Science 2022, 375, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simarro, J.; Perez-Simo, G.; Mancheno, N.; Ansotegui, E.; Munoz-Nunez, C.F.; Gomez-Codina, J.; Juan, O.; Palanca, S. Impact of Molecular Testing Using Next-Generation Sequencing in the Clinical Management of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in a Public Healthcare Hospital. Cancers 2023, 15, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, M.; Rezanejad, M.; Karimi, E.; Fiset, B.; Desharnais, L.; Perus, L.J.M.; Milette, S.; Yu, M.W.; Maritan, S.M.; Dore, S.; et al. Single-cell spatial landscapes of the lung tumour immune microenvironment. Nature 2023, 614, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.G.; Lee, H.J.; Asatsuma, T.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Haque, A. An introduction to spatial transcriptomics for biomedical research. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrajan, R.; Sailem, H.; Mardakheh, F.K.; Arias Garcia, M.; Tape, C.J.; Dowsett, M.; Bakal, C.; Yuan, Y. Microenvironmental Heterogeneity Parallels Breast Cancer Progression: A Histology-Genomic Integration Analysis. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, A.; Liu, Y.; Chen, O.; Liu, Z.; Cai, H.; Wang, L.; Qi, L. Editorial: Multi-omics approaches for decoding heterogeneity in cancer immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1324212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdulJabbar, K.; Raza, S.E.A.; Rosenthal, R.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Veeriah, S.; Akarca, A.; Lund, T.; Moore, D.A.; Salgado, R.; Al Bakir, M.; et al. Geospatial immune variability illuminates differential evolution of lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, F.; Schmidt, K.; Choti, M.A.; Romans, K.; Goodman, S.; Li, M.; Thornton, K.; Agrawal, N.; Sokoll, L.; Szabo, S.A.; et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cescon, D.W.; Bratman, S.V.; Chan, S.M.; Siu, L.L. Circulating tumor DNA and liquid biopsy in oncology. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabon, J.J.; Simmons, A.D.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Esfahani, M.S.; Newman, A.M.; Haringsma, H.J.; Kurtz, D.M.; Stehr, H.; Scherer, F.; Karlovich, C.A.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA profiling reveals heterogeneity of EGFR inhibitor resistance mechanisms in lung cancer patients. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.C.; Sivapalan, L.; Hummelink, K.; Balan, A.; White, J.R.; Niknafs, N.; Rhymee, L.; Pereira, G.; Rao, N.; Weksler, B.; et al. Elucidating the Heterogeneity of Immunotherapy Response and Immune-Related Toxicities by Longitudinal ctDNA and Immune Cell Compartment Tracking in Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridland, S.; Choi, J.; Nam, M.; Schellenberg, S.J.; Kim, E.; Lee, G.; Yoon, N.; Chae, Y.K. Assessing tumor heterogeneity: Integrating tissue and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis in the era of immuno-oncology—Blood TMB is not the same as tissue TMB. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chang, L.; Yang, Y.; Fang, W.; Guan, Y.; Wu, A.; Hong, S.; Zhou, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity comparison among different subtypes of non-small-cell lung cancer through multi-region tissue and matched ctDNA sequencing. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiter, S.; Vormehr, M.; van de Roemer, N.; Diken, M.; Lower, M.; Diekmann, J.; Boegel, S.; Schrors, B.; Vascotto, F.; Castle, J.C.; et al. Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer. Nature 2015, 520, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.; von Witzleben, A.; Thomas, J.; Wang, C.; Wood, O.; Singh, D.; Boukas, K.; Bendjama, K.; Silvestre, N.; Nielsen, F.C.; et al. Targeting the tumor mutanome for personalized vaccination in a TMB low non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tang, S.; Guo, Y.; Tang, R.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Chen, G.; Qiu, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Personalized neoantigen vaccine enhances the therapeutic efficacy of bevacizumab and anti-PD-1 antibody in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2024, 73, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Govindan, R.; Balogh, K.N.; Spigel, D.R.; Garon, E.B.; Bushway, M.E.; Poran, A.; Sheen, J.H.; Kohler, V.; Esaulova, E.; et al. Personalized neoantigen vaccine NEO-PV-01 with chemotherapy and anti-PD-1 as first-line treatment for non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1010–1026.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Deng, L.; Jackson, K.R.; Talukder, A.H.; Katailiha, A.S.; Bradley, S.D.; Zou, Q.; Chen, C.; Huo, C.; Chiu, Y.; et al. Neoantigen vaccination induces clinical and immunologic responses in non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring EGFR mutations. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.S.; Carlino, M.S.; Khattak, A.; Meniawy, T.; Ansstas, G.; Taylor, M.H.; Kim, K.B.; McKean, M.; Long, G.V.; Sullivan, R.J.; et al. Individualised neoantigen therapy mRNA-4157 (V940) plus pembrolizumab versus pembrolizumab monotherapy in resected melanoma (KEYNOTE-942): A randomised, phase 2b study. Lancet 2024, 403, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Xie, C.; Xia, X. Recent progress in mRNA cancer vaccines. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2307187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bakir, M.; Reading, J.L.; Gamble, S.; Rosenthal, R.; Uddin, I.; Rowan, A.; Przewrocka, J.; Rogers, A.; Wong, Y.N.S.; Bentzen, A.K.; et al. Clonal driver neoantigen loss under EGFR TKI and immune selection pressures. Nature 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.L.; Murphy, K.M. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, J.; Oh, M.S.; Liclican, E.L.; Dubinett, S.M.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Liu, B. Dendritic Cell Vaccination in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Remodeling the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Cells 2023, 12, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingels, J.; De Cock, L.; Stevens, D.; Mayer, R.L.; Thery, F.; Sanchez, G.S.; Vermijlen, D.; Weening, K.; De Smet, S.; Lootens, N.; et al. Neoantigen-targeted dendritic cell vaccination in lung cancer patients induces long-lived T cells exhibiting the full differentiation spectrum. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantoff, P.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.D.; Berger, E.R.; Small, E.J.; Penson, D.F.; Redfern, C.H.; Ferrari, A.C.; Dreicer, R.; Sims, R.B.; et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, M.H.; Garon, E.; Goldman, J.W.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Baratelli, F.E.; Schaue, D.; Wang, G.; Rosen, F.; Yanagawa, J.; et al. Phase I Trial of Intratumoral Injection of CCL21 Gene-Modified Dendritic Cells in Lung Cancer Elicits Tumor-Specific Immune Responses and CD8(+) T-cell Infiltration. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4556–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratelli, F.; Takedatsu, H.; Hazra, S.; Peebles, K.; Luo, J.; Kurimoto, P.S.; Zeng, G.; Batra, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Dubinett, S.M.; et al. Pre-clinical characterization of GMP grade CCL21-gene modified dendritic cells for application in a phase I trial in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2008, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi-Rad, R.; Lim, R.J.; Du, Y.; Tran, L.M.; Li, R.; Ong, S.L.; Ling Huang, Z.; Dumitras, C.; Zhang, T.; Park, S.J.; et al. CCL21-DC in situ vaccination in murine NSCLC overcomes resistance to immunotherapy and generates systemic tumor-specific immunity. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, R.J.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Tran, L.M.; Oh, M.S.; Dumitras, C.; Crosson, W.P.; Li, R.; Patel, T.S.; Man, S.; Yean, C.E.; et al. CXCL9/10-engineered dendritic cells promote T cell activation and enhance immune checkpoint blockade for lung cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Robinson, M.; Han, Z.Q.; Branston, R.H.; English, C.; Reay, P.; McGrath, Y.; Thomas, S.K.; Thornton, M.; Bullock, P.; et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating, and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andtbacka, R.H.; Kaufman, H.L.; Collichio, F.; Amatruda, T.; Senzer, N.; Chesney, J.; Delman, K.A.; Spitler, L.E.; Puzanov, I.; Agarwala, S.S.; et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Inoue, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yamada, M.; Sakamoto, C.; Urata, Y.; Okazaki, T.; Marumoto, T.; Takahashi, A.; Takayama, K.; et al. Coxsackievirus B3 is an oncolytic virus with immunostimulatory properties that is active against lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2609–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Zhang, T.H.; Crosson, W.P.; Abascal, J.; Chen, D.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, H.; Tseng, Y.W.; Ma, X.; et al. Hyper-Interferon Sensitive influenza induces adaptive immune responses and overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 in murine non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2024, 12, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermke, M.; Chesney, J.A.; Whitman, E.; Kluger, H.; Thomas, S.; Sarnaik, A.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Larkin, J.; Weber, J.S.; Hamid, O.; et al. Long-term efficacy and patterns of response of lifileucel tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cell therapy in patients with advanced melanoma: A 4-year analysis of the C-144-01 study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 100589. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Lee, S.M.; Doger de Speville, B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Hafliger, S.; Sukari, A.; Papa, S.; Rodriguez-Moreno, J.F.; Graf Finckenstein, F.; Fiaz, R.; et al. Lifileucel, an Autologous Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Monotherapy, in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistant to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poschke, I.C.; Hassel, J.C.; Rodriguez-Ehrenfried, A.; Lindner, K.A.M.; Heras-Murillo, I.; Appel, L.M.; Lehmann, J.; Lovgren, T.; Wickstrom, S.L.; Lauenstein, C.; et al. The Outcome of Ex Vivo TIL Expansion Is Highly Influenced by Spatial Heterogeneity of the Tumor T-Cell Repertoire and Differences in Intrinsic In Vitro Growth Capacity between T-Cell Clones. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4289–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albelda, S.M. CAR T cell therapy for patients with solid tumours: Key lessons to learn and unlearn. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Araujo, D.M.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; Agulnik, M.; Attia, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Carrasco Garcia, I.; Charlson, J.A.; Choy, E.; Demetri, G.D.; et al. Afamitresgene autoleucel for advanced synovial sarcoma and myxoid round cell liposarcoma (SPEARHEAD-1): An international, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 1460–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, P.; Chu, W.; Jin, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Lou, J.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger-Ruckstuhl, C.A.; Specht, J.M.; Voutsinas, J.M.; MacMillan, H.R.; Wu, Q.V.; Muhunthan, V.; Berger, C.; Pullarkat, S.; Wright, J.H.; Yeung, C.C.S.; et al. Phase 1 Study of ROR1 Specific CAR T Cells in Advanced Hematopoietic and Epithelial Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 31, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzner, R.G.; Mackall, C.L. Tumor Antigen Escape from CAR T-cell Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, H.G.; Hurton, L.V.; Najjar, A.; Rushworth, D.; Ang, S.; Olivares, S.; Mi, T.; Switzer, K.; Singh, H.; Huls, H.; et al. Tuning Sensitivity of CAR to EGFR Density Limits Recognition of Normal Tissue While Maintaining Potent Antitumor Activity. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3505–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, S.; Fang, C.; Yang, S.; Olalere, D.; Pequignot, E.C.; Cogdill, A.P.; Li, N.; Ramones, M.; Granda, B.; et al. Affinity-Tuned ErbB2 or EGFR Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Exhibit an Increased Therapeutic Index against Tumors in Mice. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3596–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Sun, Q.; Xia, J.; Gu, W.; Qian, J.; Zhuang, W.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, F.; et al. Anti-BCMA/GPRC5D bispecific CAR T cells in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: A single-arm, single-centre, phase 1 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e751–e760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Johnson, B.D.; Schneider, D.; Zhu, F.; Szabo, A.; Keever-Taylor, C.A.; Krueger, W.; Worden, A.A.; Kadan, M.J.; Yim, S.; et al. Bispecific anti-CD20, anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed B cell malignancies: A phase 1 dose escalation and expansion trial. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.A.; Cheung, N.V. Overcoming tumor heterogeneity by ex vivo arming of T cells using multiple bispecific antibodies. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaretsky, J.M.; Garcia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Hugo, W.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Sandoval, S.; Barthly, L.; et al. Mutations Associated with Acquired Resistance to PD-1 Blockade in Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Luo, H.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, A.; Niu, L.; Jiang, Y. Pembrolizumab plus allogeneic NK cells in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multhoff, G.; Seier, S.; Stangl, S.; Sievert, W.; Shevtsov, M.; Werner, C.; Pockley, A.G.; Blankenstein, C.; Hildebrandt, M.; Offner, R.; et al. Targeted Natural Killer Cell-Based Adoptive Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Patients with NSCLC after Radiochemotherapy: A Randomized Phase II Clinical Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5368–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusyk, A.; Janiszewska, M.; Polyak, K. Intratumor Heterogeneity: The Rosetta Stone of Therapy Resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisier, F.; Cousse, S.; Jeanvoine, M.; Thiberville, L.; Salaun, M. A rationale for surgical debulking to improve anti-PD1 therapy outcome in non small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson-Arvelund, J.; Cuadrado-Castano, S.; Pantsulaia, G.; Kim, K.; Aleynick, M.; Hammerich, L.; Upadhyay, R.; Yellin, M.; Marsh, H.; Oreper, D.; et al. Expanding cross-presenting dendritic cells enhances oncolytic virotherapy and is critical for long-term anti-tumor immunity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dichwalkar, T.; Chang, J.Y.H.; Cossette, B.; Garafola, D.; Zhang, A.Q.; Fichter, M.; Wang, C.; Liang, S.; Silva, M.; et al. Enhanced CAR-T cell activity against solid tumors by vaccine boosting through the chimeric receptor. Science 2019, 365, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.; Zhou, L.; Huang, R.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, X.; Li, Y. Dendritic cell vaccines extend CAR T-cell persistence and improve the efficacy of CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in refractory or relapsed adult B-ALL patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Vercher, E.; Soria-Castellano, M.; Suarez-Olmos, J.; Mancheno, U.; Elizalde, E.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Glez-Vaz, J.; Casares, N.; Rodriguez-Garcia, E.; et al. Epitope spreading driven by the joint action of CART cells and pharmacological STING stimulation counteracts tumor escape via antigen-loss variants. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.G.; Son, G.W.; Choi, M.Y.; Jung, J.S.; Rho, J.K.; Ji, W.; Yoon, B.G.; Jo, J.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Ko, D.H.; et al. Safety and efficacy of SNK01 (autologous natural killer cells) in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or cetuximab after failure of prior tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer: Non-clinical mouse model and phase I/IIa clinical study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, M.S.; Abascal, J.; Rennels, A.K.; Salehi-Rad, R.; Dubinett, S.M.; Liu, B. Tumor Heterogeneity and the Immune Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Insights and Implications for Immunotherapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061027
Oh MS, Abascal J, Rennels AK, Salehi-Rad R, Dubinett SM, Liu B. Tumor Heterogeneity and the Immune Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Insights and Implications for Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061027
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Michael S., Jensen Abascal, Austin K. Rennels, Ramin Salehi-Rad, Steven M. Dubinett, and Bin Liu. 2025. "Tumor Heterogeneity and the Immune Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Insights and Implications for Immunotherapy" Cancers 17, no. 6: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061027
APA StyleOh, M. S., Abascal, J., Rennels, A. K., Salehi-Rad, R., Dubinett, S. M., & Liu, B. (2025). Tumor Heterogeneity and the Immune Response in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Emerging Insights and Implications for Immunotherapy. Cancers, 17(6), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17061027






