Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children with Malignancies or After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Polish Nationwide Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Analyzed
2.4. Definitions
2.5. Endpoints of Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Comparison of Study Group (PRES) vs. Control Group (Non-PRES)
3.3. Procedures Preceded PRES Within 7 Days
3.4. Clinical Symptoms of PRES
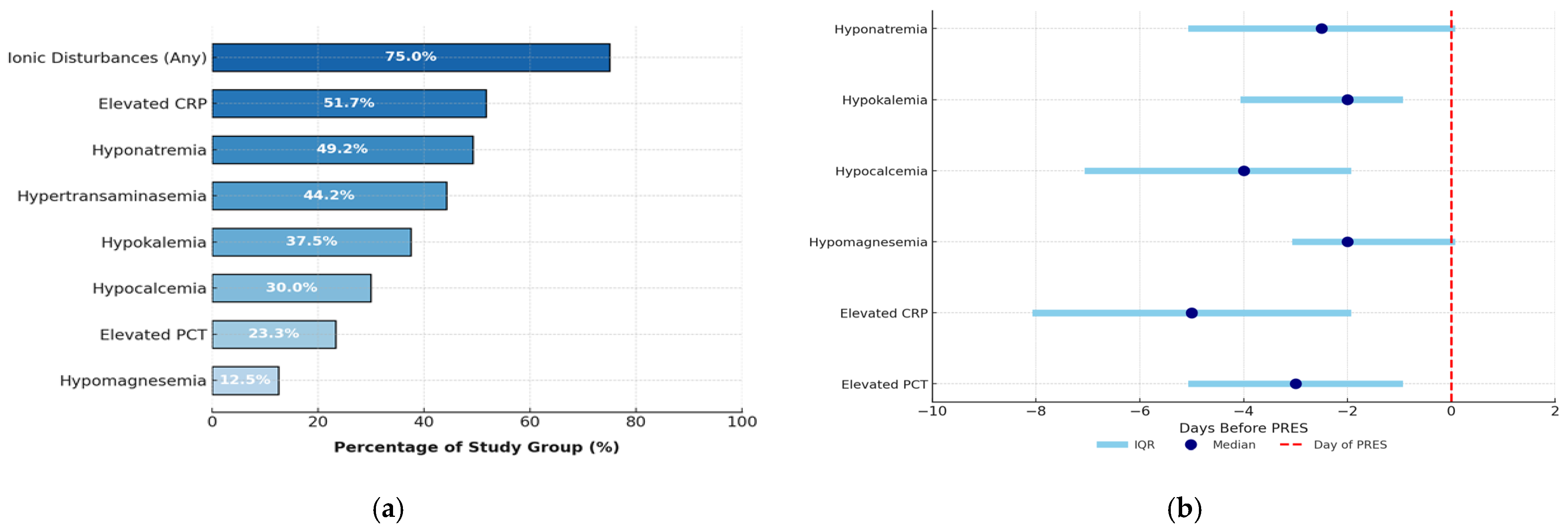
3.5. Laboratory Abnormalities in PRES
3.6. Treatment of PRES
3.7. PRES Complications
3.8. PRES in Children After HCT (N = 10)
3.9. Risk Factors Analysis of PRES Development
3.10. Determination of the Predictive Capacity of Selected Factors for PRES
3.11. PRES Predictive Index
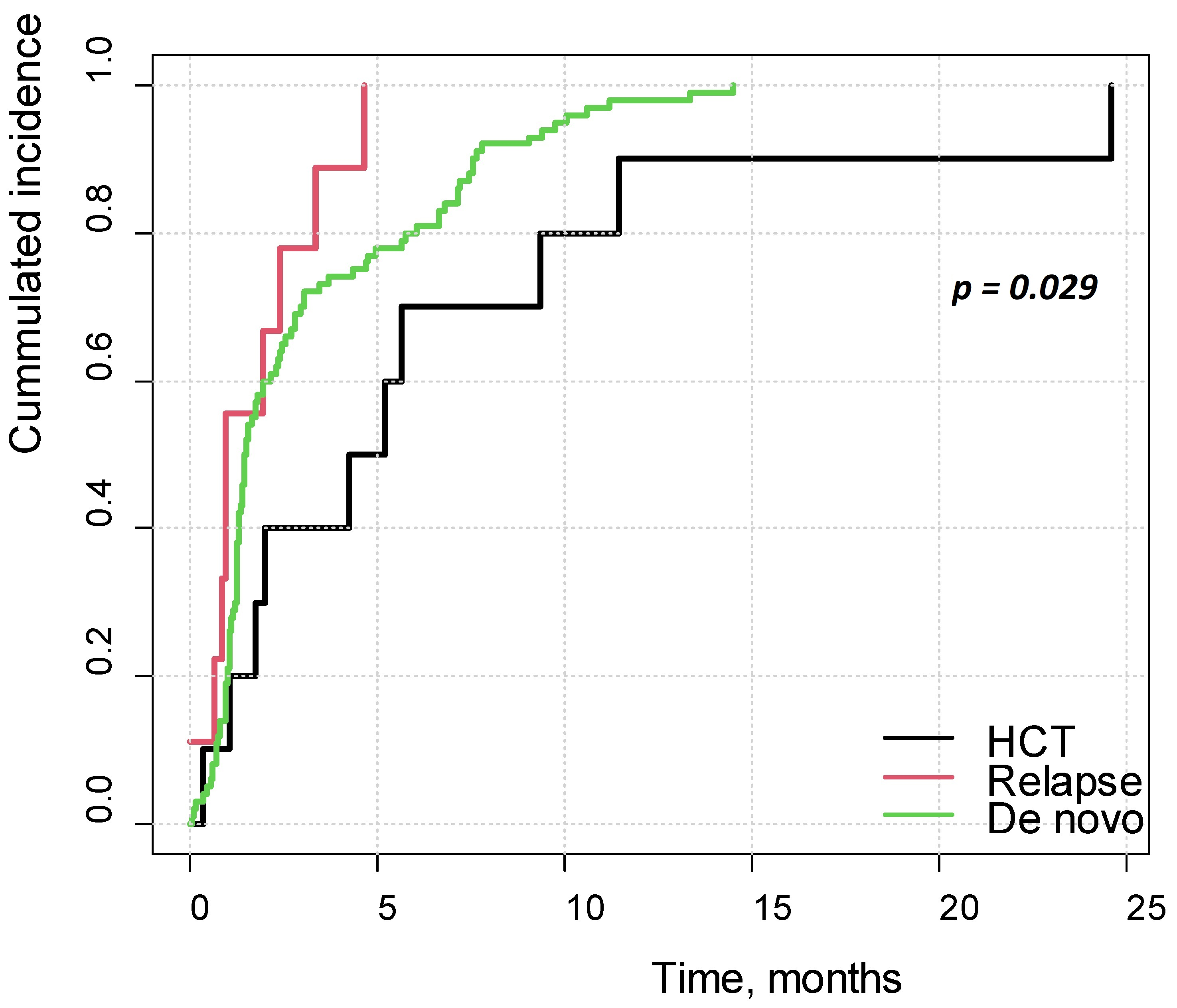
3.12. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Risk Factors
4.2. Clinical Symptoms and Laboratory Abnormalities
4.3. Early and Chronic Complications
4.4. Survival
4.5. Diagnostic Criteria and Predictive Index
4.6. Summary of Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABLC | Amphotericin B lipid complex |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| aGvHD | Acute graft versus host disease |
| cGvHD | Chronic graft versus host disease |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| HCT | Hematopoietic cell transplantation |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| L-AMB | Liposomal amphotericin B |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PHO | Pediatric hematology and oncology centers |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| PRES | Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome |
References
- Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Clinical and radiological manifestations, pathophysiology, and outstanding questions. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartynski, W.S. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 1: Fundamental imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, M.; Tian, J.; Xie, M.; She, Z.; Abdirahman, A.S.; Han, P.; Wan, W.; Wen, C. Analysis of Risk Factors Associated With Poor Outcome in Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome After Treatment in Children: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulou, S.; Eriksson, M.A.; Heyman, M.; Wang, C.; Niinimäki, R.; Mikkel, S.; Vaitkevičienė, G.E.; Johannsdottir, I.M.; Myrberg, I.H.; Jonsson, O.G.; et al. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Clinical characteristics, risk factors, course, and outcome of disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, J.S.; Heyman, M.; Palomäki, M.; Lähteenmäki, P.; Arola, M.; Riikonen, P.V.; Möttönen, M.I.; Lönnqvist, T.; Taskinen, M.H.; Harila-Saari, A.H. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Risk Factors and Impact on the Outcome in Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated With Nordic Protocols. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 40, e13–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaziev, J.; Marziali, S.; Paciaroni, K.; Isgrò, A.; Di Giuliano, F.; Rossi, G.; Marziali, M.; De Angelis, G.; Alfieri, C.; Ribersani, M.; et al. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Children with Hemoglobinopathies. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behfar, M.; Babaei, M.; Radmard, A.R.; Kooraki, S.; Farajifard, H.; Naji, P.; Taebi, S.; Hamidieh, A.A. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Pediatric Patients with Fanconi Anemia, a Prospective Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, e316–e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavamani, A.; Umapathi, K.K.; Puliyel, M.; Super, D.; Allareddy, V.; Ghori, A. Epidemiology, Comorbidities, and Outcomes of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children in the United States. Pediatr. Neurol. 2020, 103, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.M.; South, A.M. Association of kidney function with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children. Clin. Nephrol. 2022, 98, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara-Lemarroy, C.R.; Escobedo-Zúñiga, N.; Villarreal-Garza, E.; García-Valadez, E.; Góngora-Rivera, F.; Villarreal-Velázquez, H.J. Posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome (PRES) associated with severe eclampsia: Clinical and biochemical features. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2017, 7, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Miller, K.; McDermott, M. Preeclampsia, eclampsia, and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 172, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisowska-Adamiak, M.; Sakwińska, K.; Szymkuć-Bukowska, I.; Goclik, A.; Lunitz, I.; Mackiewicz-Milewska, M. A Case Report of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) in a Nonsevere Case of COVID-19. Brain Sci. 2022, 7, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhun, G.; Sencer, S.; Tüzün, E.; Bebek, N.; Özcan, P.E.; Barburoğlu, M.; Günver, M.G.; Esen, F. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy in Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy: Experience from a Single Center. Neurocrit. Care 2022, 36, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegal, D.; Keller, A.; Xu, W.; Bhuta, S.; Kim, D.H.; Kuruvilla, J.; Lipton, J.H.; Messner, H.; Gupta, V. Central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Incidence, manifestations, and clinical significance. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007, 13, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Cordelli, D.M.; Zama, D.; Vendemini, F.; Biagi, C.; Franzoni, E.; Pession, A. PRES in Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell or Solid Organ Transplantation. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajuria, B.; Khajuria, M.; Agrawal, Y. Mycophenolate-Induced Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome. Am. J. Ther. 2016, 23, e1072–e1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) attributed to mycophenolate mofetil during the management of SLE: A case report and review. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, W.; Hong, F. Post reversible encephalopathy syndrome attributed to mycophenolate mofetil used in the treatment of SLE: A case report and review of literature. J. Int. Med. Res. 2024, 52, 3000605231218620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manadan, A.; Kambhatla, S.; Gauto-Mariotti, E.; Okoli, C.; Block, J.A. Rheumatic Diseases Associated With Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, e391–e394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinchey, J.; Chaves, C.; Appignani, B.; Breen, J.; Pao, L.; Wang, A.; Pessin, M.S.; Lamy, C.; Mas, J.-L.; Caplan, L.R. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerac, A.; Bihan, K.; Psimaras, D.; Lebrun-Vignes, B.; Salem, J.-E.; Weiss, N. Drugs associated with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, a worldwide signal detection study. J. Neurol. 2023, 270, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugate, J.E.; Hawkes, M.A.; Rabinstein, A.A. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: Evolving insights in diagnosis, management, and outcomes. Lancet Neurol. 2025, 24, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.D.; Kunwor, R.; Sudanagunta, K. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after CD19 chimeric antigen receptor therapy for B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Case report. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1639892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gong, Y. Calcineurin inhibitors-related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in liver transplant recipients: Three case reports and review of literature. World J. Hepatol. 2024, 16, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Song, T.; Rao, Z.; Tan, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Calcineurin Inhibitors Associated Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Solid Organ Transplantation: Report of 2 Cases and Literature Review. Medicine 2016, 95, e3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cordelli, D.M.; Marra, C.; Ciampoli, L.; Barbon, D.; Toni, F.; Zama, D.; Giordano, L.; Milito, G.; Sartori, S.; Sainati, L.; et al. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in infants and young children. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 30, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommers, K.R.; Skiles, J.; Leland, B.; Rowan, C.M.M. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Incidence and Clinical Characteristics in Children With Cancer. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 44, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zama, D.; Gasperini, P.; Berger, M.; Petris, M.; De Pasquale, M.D.; Cesaro, S.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Mastrodicasa, E.; Savina, F.; Ziino, O.; et al. A survey on hematology-oncology pediatric AIEOP centres: The challenge of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 100, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Natsume, J.; Kidokoro, H.; Ishihara, N.; Suzuki, M.; Tsuji, T.; Kubota, T.; Yamada, A.; Ozeki, M.; Kato, Z.; et al. Clinical and neuroimaging findings in children with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, M.; Xie, M.; She, Z.; Abdirahman, A.S.; Li, C.; Wu, F.; Luo, S.; Han, P.; Phorn, R.; Wu, P.; et al. Management and Clinical Outcome of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Pediatric Oncologic/Hematologic Diseases: A PRES Subgroup Analysis With a Large Sample Size. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 678890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartynski, W.S. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 2: Controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donmez, F.Y.; Guleryuz, P.; Agildere, M. MRI Findings in Childhood PRES: What is Different than the Adults? Clin. Neuroradiol. 2016, 26, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triplett, J.D.; Kutlubaev, M.A.; Kermode, A.G.; Hardy, T. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): Diagnosis and management. Pract. Neurol. 2022, 22, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasher, A.; Jhamb, R. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): Presentation, diagnosis and treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2020, 96, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, M.G.Z.; Davanzo, J.; Leo, M.; Rizk, E. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in pediatric patients: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Styczynski, J.; Balwierz, W.; Dembowska-Baginska, B.; Kazanowska, B.; Wachowiak, J.; Matysiak, M.; Klukowska, A.; Krawczuk-Rybak, M.; Adamkiewicz-Drożyńska, E.; Młynarski, W.; et al. Paediatric oncology and haematology in Poland: Position paper. Pediatr. Pol.-Pol. J. Paediatr. 2018, 93, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Fang, X.J.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Luo, L.L.; Li, H.L.; Cai, X.Y.; et al. Current concerns and future directions of large language model chatGPT in medicine: A machine-learning-driven global-scale bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2025; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | Study Group (PRES) | Control Group (Non-PRES) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients (%) | 120 (100.0) | 318 (100.0) | - |
| Female [n (%)] | 44 (36.7) | 137 (43.1) | 0.268 |
| Male [n (%)] | 76 (63.3) | 181 (56.9) | 0.268 |
| Week of gestation 37–42 * [n (%)] | 65 (90.3) | 186 (89.9) | >0.999 |
| Apgar < 8 pts. * [n (%)] | 1 (1.4) | 4 (2.0) | >0.999 |
| Epilepsy before malignancy [n (%)] | 6 (5.0) | 3 (0.9) | 0.015 |
| Hypertension before malignancy [n (%)] | 5 (4.2) | 3 (0.9) | 0.039 |
| Hypertension in the family [n (%)] | 5 (4.2) | 10 (3.1) | 0.567 |
| Developmental delay [n (%)] | 6 (5.0) | 18 (5.7) | 0.972 |
| Age at diagnosis, years, [M ± SD] | 7.99 ± 3.77 | 6.89 ± 4.54 | 0.019 |
| Treatment for relapse | 17 (14.2) | 24 (7.5) | 0.053 |
| Age at relapse, years, [M ± SD] | 10.11 ± 4.82 | 10.56 ± 4.55 | 0.808 |
| HCT [n (%)] | 10 (8.3) | 36 (11.3) | 0.462 |
| Age at HCT, years, [M ± SD] | 12.58 ± 4.68 | 10.66 ± 4.56 | 0.281 |
| Disease | 0.057 | ||
| Acute lymphoblastic leukemia [n (%)] | 92 (76.7) | 273 (85.8) | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | 4 (3.3) | 9 (2.8) | |
| Other malignancies [n (%)] | 24 (20.0) | 36 (11.3) | |
| CNS involvement [n (%)] | 23 (19.2) | 53 (16.7) | 0.635 |
| Hypertension during treatment [n (%)] | 89 (74.2) | 45 (14.2) | <0.001 |
| ICU admission [n (%)] | 60 (50.0) | 94 (29.6) | <0.001 |
| Seizures during treatment [n (%)] | 96 (80.0) | 21 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension during follow-up | 27 (22.5%) | 45 (14.2) | 0.035 |
| Epilepsy during follow-up | 25 (20.8%) | 0 ** | <0.001 |
| Remission at the end of follow-up [n (%)] | 92 (76.7) | 298 (93.7) | <0.001 |
| Death [n (%)] | 25 (20.8) | 21 (6.6) | <0.001 |
| Parameter | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 1 | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| Male | 1.31 | 0.85–2.03 | 0.225 | - | - | - |
| Age at diagnosis, years | 1.06 | 1.01–1.11 | 0.019 | - | - | ns |
| Relapse treatment | 2.02 | 1.03–3.89 | 0.037 | - | - | ns |
| Age at diagnosis of relapse, years | 0.98 | 0.82–1.16 | 0.799 | - | - | - |
| HCT | 0.71 | 0.33–1.43 | 0.365 | - | - | - |
| Disease | ||||||
| ALL | 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| AML | 1.32 | 0.35–4.15 | 0.652 | - | - | - |
| Other neoplasms | 1.98 | 1.11–3.48 | 0.019 | - | - | ns |
| CNS involvement | 1.19 | 0.68–2.02 | 0.538 | - | - | - |
| Hypertension during therapy * | 17.42 | 10.52–29.59 | <0.001 | 23.60 | 10.36–61.86 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension before malignancy | 4.57 | 1.10–22.54 | 0.040 | - | - | ns |
| Hypertension in the family | 1.34 | 0.41–3.85 | 0.601 | - | - | - |
| Seizures during therapy * | 56.57 | 30.84–108.91 | <0.001 | 86.58 | 36.81–237.86 | <0.001 |
| Epilepsy before cancer | 5.53 | 1.43–26.53 | 0.017 | - | - | ns |
| Seizure before cancer | 2.34 | 0.74–7.18 | 0.134 | - | - | - |
| Week of gestation 37–42 | 1.05 | 0.44–2.76 | 0.918 | - | - | - |
| Apgar < 8 points | 0.71 | 0.04–4.93 | 0.765 | - | - | - |
| Developmental delay | 0.88 | 0.31–2.15 | 0.787 | - | - | - |
| Criteria | Points |
|---|---|
| Hypertension with sudden onset | 4 |
| Specific electrolyte disturbances * | 3 |
| Apathy/fatigue | 2 |
| Abdominal pain | 1 |
| Headache | 1 |
| Visual disturbances | 1 |
| Clinical Criteria (at Least One) | Radiological Criterium (Mandatory) |
|---|---|
| 1. Seizures or impaired consciousness | Characteristic findings in MRI: vasogenic edema of the subcortical white matter ± gray matter of the cerebral cortex |
| 2. Hypertension | |
| 3. Apathy/fatigue | |
| 4. Headache | |
| 5. Abdominal pain | |
| 6. Visual disturbances |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brzeski, T.; Badowska, W.; Mycko, K.; Tyszka, P.; Korzeniewicz, M.; Kolodrubiec, J.; Mlynarski, W.; Gawle-Krawczyk, K.; Koch, K.; Laguna, P.; et al. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children with Malignancies or After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Polish Nationwide Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 3789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233789
Brzeski T, Badowska W, Mycko K, Tyszka P, Korzeniewicz M, Kolodrubiec J, Mlynarski W, Gawle-Krawczyk K, Koch K, Laguna P, et al. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children with Malignancies or After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Polish Nationwide Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(23):3789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233789
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrzeski, Tomasz, Wanda Badowska, Katarzyna Mycko, Patrycja Tyszka, Martyna Korzeniewicz, Julia Kolodrubiec, Wojciech Mlynarski, Karolina Gawle-Krawczyk, Katarzyna Koch, Pawel Laguna, and et al. 2025. "Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children with Malignancies or After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Polish Nationwide Study" Cancers 17, no. 23: 3789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233789
APA StyleBrzeski, T., Badowska, W., Mycko, K., Tyszka, P., Korzeniewicz, M., Kolodrubiec, J., Mlynarski, W., Gawle-Krawczyk, K., Koch, K., Laguna, P., Kiermasz, A., Mizia-Malarz, A., Malczewska, M., Drabko, K., Malecka, A., Irga-Jaworska, N., Marciniak-Stepak, P., Derwich, K., Wachowiak, J., ... Styczynski, J. (2025). Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in Children with Malignancies or After Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Polish Nationwide Study. Cancers, 17(23), 3789. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233789





