Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Architectures but Shared Vulnerabilities in Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Samples
2.2. Visium HD Spatial Transcriptomics
2.3. Data Processing, Clustering, and Analysis
3. Results
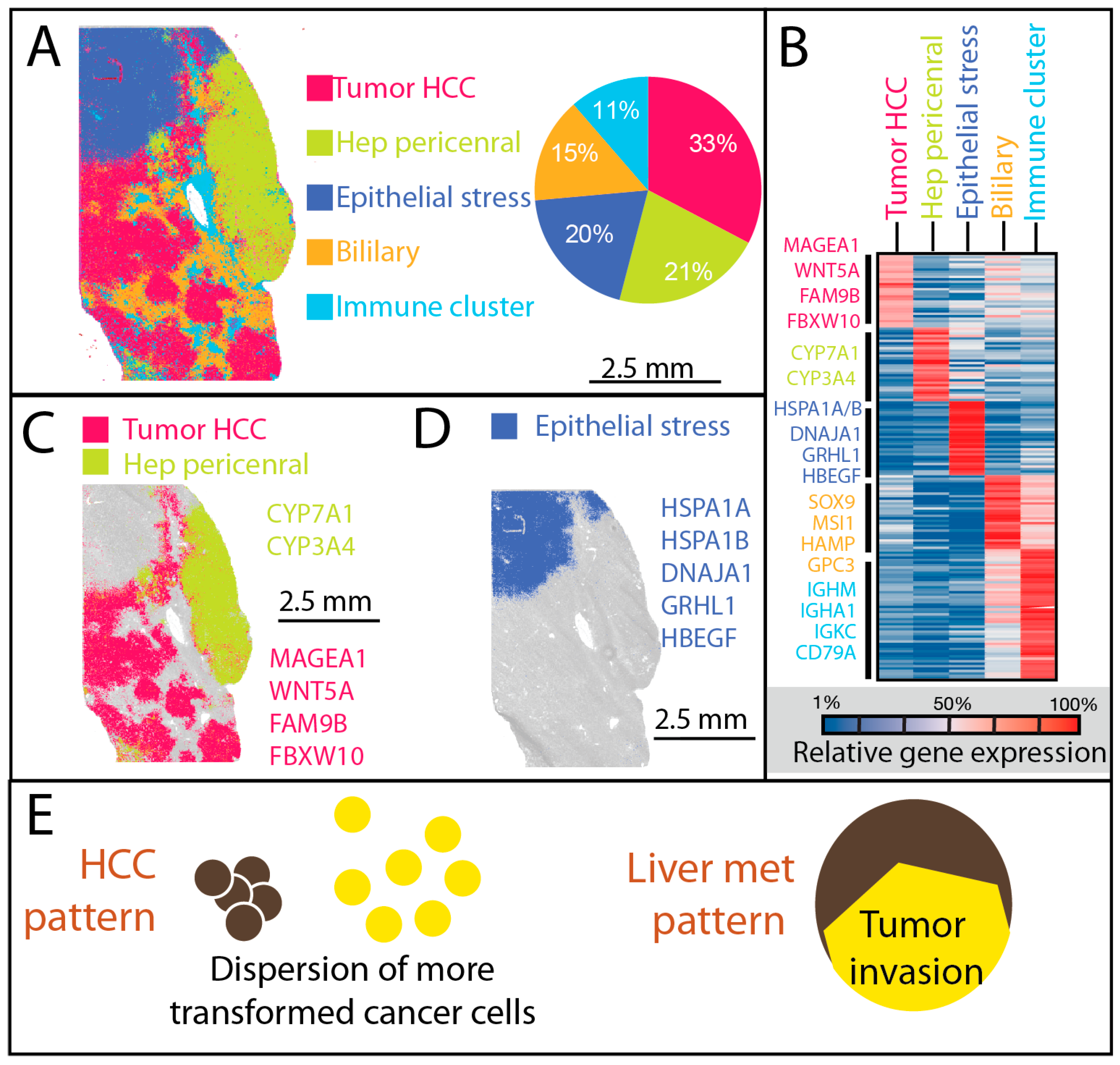
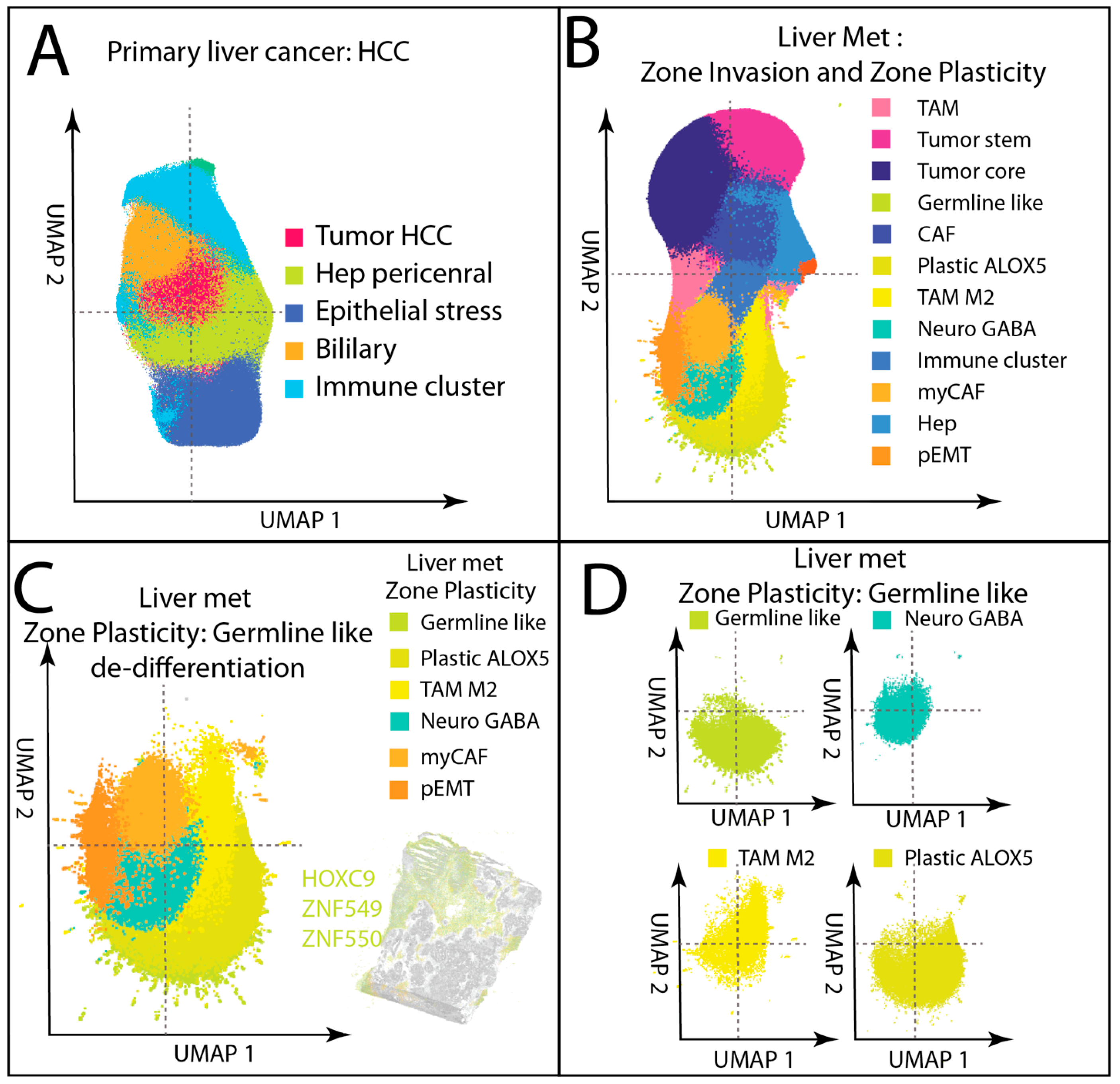
3.1. Dispersion Associated with Higher Transformation in Primary Liver Cancer
3.2. Spatial Complexity in Liver Metastasis
3.2.1. Zone Invasion—Invasive Front and Structured Tumor–Stroma Interface
3.2.2. Zone Plasticity—Dedifferentiation, Plasticity, and Immune Modulation
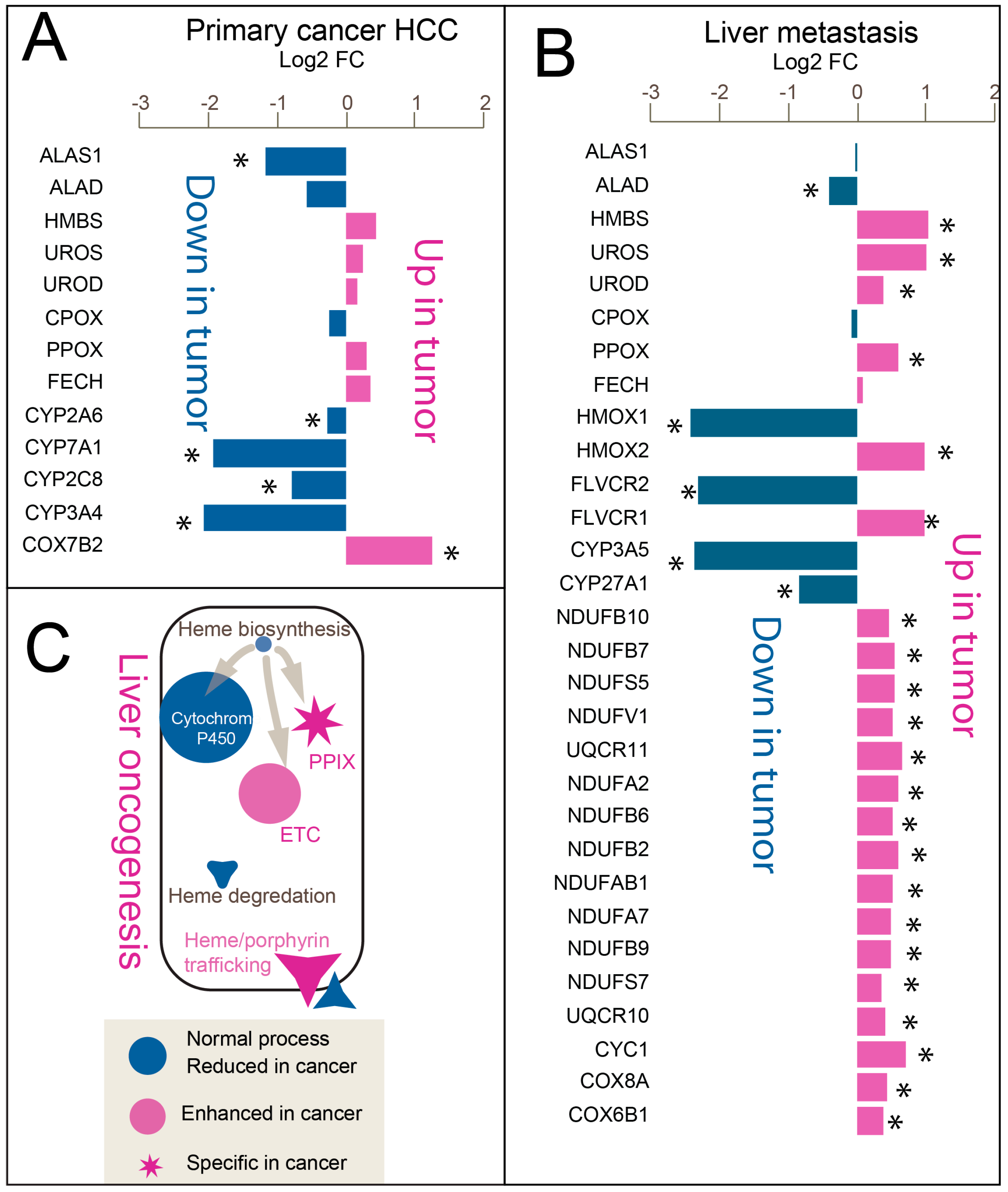
3.3. Imbalanced Linear Heme Biosynthesis Pathway Genes Reveal “Porphyrin Overdrive” in Both Tumors
3.4. Immune Cell Aggregates Diverge in Architecture Between HCC and Liver Metastases
3.5. Germline/Neural-like Plastic Tumor Dedifferentiation Hub in Liver Metastasis
3.6. Cross-Validation of Porphyrin- and Signaling Lipid-Related Protein Expression in Human Liver Tissues and Survival Data
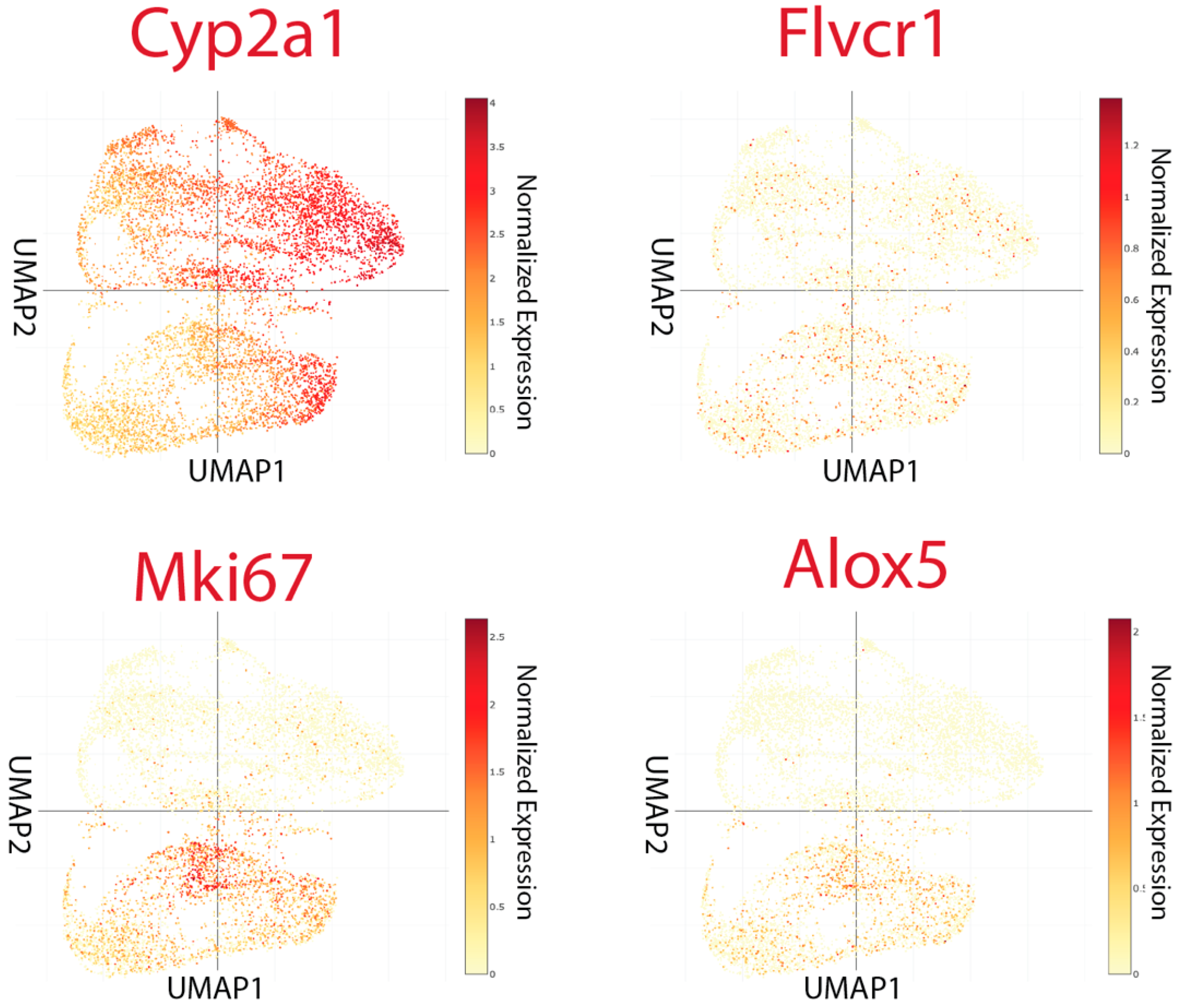
3.7. Distant Liver Metabolic Reprogramming Gene Expression Mirrors Tumor-Localized Processes in Murine Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, I.; Jakoby, W.; Popper, M.; Schachter, D. The Liver-Biology and Pathobiology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, A.; Quan, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, P.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the multicellular ecosystem of primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yan, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, F.; Zou, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, A.; Hou, L.; Zhong, Y.; Jing, Z.; et al. An invasive zone in human liver cancer identified by Stereo-seq promotes hepatocyte–tumor cell crosstalk, local immunosuppression and tumor progression. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 585–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.; Karalis, J.D.; Liu, C.; Murimwa, G.Z.; Voth Park, J.; Heid, C.A.; Reznik, S.I.; Huang, E.; Minna, J.D.; Brekken, R.A. The Colorectal Cancer Tumor Microenvironment and Its Impact on Liver and Lung Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Giraldo, N.A.; Kaplon, H.; Germain, C.; Fridman, W.H.; Sautès-Fridman, C. Tertiary lymphoid structures, drivers of the anti-tumor responses in human cancers. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 271, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Chao, G.; Zhang, S. Tertiary lymphoid structures in colorectal cancer. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2400314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-D.; Pang, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Dong, Y.; Hao, L.; Qin, J.-X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.-S.; Han, C.-H. Tumor cell plasticity in targeted therapy-induced resistance: Mechanisms and new strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Bévant, K.; Blanpain, C. Cancer cell plasticity during tumor progression, metastasis and response to therapy. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.R.; Sethi, I.; Sadida, H.Q.; Rah, B.; Mir, R.; Algehainy, N.; Albalawi, I.A.; Masoodi, T.; Subbaraj, G.K.; Jamal, F.; et al. Cancer cell plasticity: From cellular, molecular, and genetic mechanisms to tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 197–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faubert, B.; Solmonson, A.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Metabolic reprogramming and cancer progression. Science 2020, 368, eaaw5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.D.; Clish, C.B.; Schmidt, B.; Gronert, K.; Serhan, C.N. Lipid mediator class switching during acute inflammation: Signals in resolution. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.R.; Hunter, G.A.; Amin, N.E.; Marinescu, C.; Borsky, A.; Sagatys, E.M.; Sebti, S.M.; Reuther, G.W.; Ferreira, G.C.; Jiang, R.H. Porphyrin overdrive rewires cancer cell metabolism. Life Sci. Alliance 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.R.; Meshram, P.; Sami, A.; Jiang, R.H.Y. Harnessing Porphyrin Accumulation in Liver Cancer: Combining Genomic Data and Drug Targeting. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.C. Heme Synthesis. In The Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry; Lennarz WaL, M.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 539–542. [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich, F.P. Cytochrome P450s and other enzymes in drug metabolism and toxicity. AAPS J. 2006, 8, E101–E111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Montellano, P.R.O. Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Batlle, A.M. Porphyrins, porphyrias, cancer and photodynamic therapy—A model for carcinogenesis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1993, 20, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L. Heme Biology: The Secret Life of Heme in Regulating Diverse Biological Processes; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sohoni, S.; Ghosh, P.; Wang, T.; Kalainayakan, S.P.; Vidal, C.; Dey, S.; Konduri, P.C.; Zhang, L. Elevated heme synthesis and uptake underpin intensified oxidative metabolism and tumorigenic functions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2511–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adapa, S.R.; Sami, A.; Meshram, P.; Ferreira, G.C.; Jiang, R.H.Y. Uncovering porphyrin accumulation in the tumor microenvironment. Genes 2024, 15, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halade, G.V.; Kain, V.; Hossain, S.; Parcha, V.; Limdi, N.A.; Arora, P. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is essential for biosynthesis of specialized pro-resolving mediators and cardiac repair in heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 323, H721–H737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, E.R.; Huang, S.; Serhan, C.N.; Panigrahy, D. Regulation of inflammation in cancer by eicosanoids. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 96, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Maurin, M.M.; Rodriguez-Silva, J.; Upadhyay, G.; Alden, A.J.; Gowda, S.G.B.; Schell, M.J.; Yang, M.; Levine, N.J.; Gowda, D.; et al. Integration of lipidomics with targeted, single cell, and spatial transcriptomics defines an unresolved pro-inflammatory state in colon cancer. Gut 2025, 74, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Duan, P.; Long, J.; Zhu, H. ALOX5-5-HETE promotes gastric cancer growth and alleviates chemotherapy toxicity via MEK/ERK activation. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5246–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, G.; Rao, D.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Immune Landscape of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis at Single-Cell Level. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Lin, D.-C. Moving closer towards a comprehensive view of tumor biology and microarchitecture using spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilento, M.A.; Sweeney, C.J.; Butler, L.M. Spatial transcriptomics in cancer research and potential clinical impact: A narrative review. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelka, K.; Hofree, M.; Chen, J.H.; Sarkizova, S.; Pirl, J.D.; Jorgji, V.; Bejnood, A.; Dionne, D.; Ge, W.H.; Xu, K.H.; et al. Spatially organized multicellular immune hubs in human colorectal cancer. Cell 2021, 184, 4734–4752.e4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.K.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Storrs, E.; Targino da Costa, A.L.N.; Houston, A.; Wendl, M.C.; Jayasinghe, R.G.; Iglesia, M.D.; Ma, C.; et al. Tumour evolution and microenvironment interactions in 2D and 3D space. Nature 2024, 634, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbon, A.; Mizuno, R.; Konishi, R.; Onishi, M.; Masuda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kawamoto, H.; Suzuki, A.; He, C.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Murine breast cancers disorganize the liver transcriptome in a zonated manner. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dries, R.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, R.; Eng, C.L.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Sarkar, A.; Bao, F.; et al. Giotto: A toolbox for integrative analysis and visualization of spatial expression data. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S.M.; Farris, J.C.; Pifer, P.M. Roles of Grainyhead-like transcription factors in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6067–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriarca, C.; Macchi, R.M.; Marschner, A.K.; Mellstedt, H. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326) in cancer: A short review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J. Carcinoembryonic antigen as a marker for colorectal cancer: Is it clinically useful? Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.; Nosho, K.; Shima, K.; Freed, E.; Irahara, N.; Philips, J.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Hornick, J.L.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Fuchs, C.S.; et al. Relationship of CDX2 Loss with Molecular Features and Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4665–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.W.; Wong, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Bicknell, D.; Turley, H.; Hollins, L.; Miller, C.J.; Wilding, J.L.; Bodmer, W.F. Gastrointestinal differentiation marker Cytokeratin 20 is regulated by homeobox gene CDX1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lin, M.; Ruan, W.J.; Dong, L.L.; Chen, E.G.; Wu, X.H.; Ying, K.J. Nkx2-1: A novel tumor biomarker of lung cancer. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2012, 13, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, S.; Rashid, A.; Wang, H.; Katz, M.H.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H. SOX9: A useful marker for pancreatic ductal lineage of pancreatic neoplasms. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Takeuchi, K.K.; Ruggeri, J.M.; Bailey, P.; Chang, D.; Li, J.; Leonhardt, L.; Puri, S.; Hoffman, M.T.; Gao, S.; et al. PDX1 dynamically regulates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma initiation and maintenance. Genes. Dev. 2016, 30, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.J.; Jain, R.K.; Leung, S.; Choo, J.; Nielsen, T.; Huntsman, D.; Nakshatri, H.; Badve, S. FOXA1 is an independent prognostic marker for ER-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 131, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braxton, D.R.; Cohen, C.; Siddiqui, M.T. Utility of GATA3 immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic breast carcinoma in cytology specimens. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, S.; Parra-Herran, C. Immunohistochemical characterization of appendiceal mucinous neoplasms and the value of special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 in their distinction from primary ovarian mucinous tumours. Histopathology 2016, 68, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Pozadzides, J.; Kopetz, S.; Wen, S.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Wolff, R.A.; Wang, H. Immunophenotype and molecular characterisation of adenocarcinoma of the small intestine. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, G.A.; Ferreira, G.C. Molecular enzymology of 5-Aminolevulinate synthase, the gatekeeper of heme biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1814, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnad, P.; Schwarz, P.; Rasenack, M.C.; Kucukoglu, O.; Habib, R.I.; Heuberger, D.; Ehehalt, R.; Müller, M.W.; Stiehl, A.; Adler, G.; et al. Hepcidin is an antibacterial, stress-inducible peptide of the biliary system. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimata, K.; Yoshii, D.; Yokouchi, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Inomata, Y.; Hibi, T. Effect of SOX9 on Ductular Reaction and Fibrogenesis. Transplantation 2018, 102, S729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, R.; Pietras, K. Heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblasts: Opportunities for precision medicine. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ge, G. Lysyl oxidase, extracellular matrix remodeling and cancer metastasis. Cancer Microenviron. 2012, 5, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Cheng, D.; Wang, J.; Gu, J.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Qin, L.; Mao, F.; Cao, Y.; Cai, K. MYL9 expressed in cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate the immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor progression in an autocrine manner. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Recent advancements in understanding of biological role of homeobox C9 in human cancers. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 15, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, D.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H.; Di, X. The role of zinc finger proteins in malignant tumors. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Wei, C.; Ning, N.; Li, J. GABAergic signaling facilitates breast cancer metastasis by promoting ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation. Cancer Lett. 2014, 348, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomer, H.; Dame, H.B.; Parker, S.R.; Oudin, M.J. Neuronal mimicry in tumors: Lessons from neuroscience to tackle cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025, 44, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, B.P.; Apolónio, J.D.; Binnie, A.; Castelo-Branco, P. Roadmap of DNA methylation in breast cancer identifies novel prognostic biomarkers. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.Y.; Houwing, S.; Kaaij, L.J.T.; Meppelink, A.; Redl, S.; Gauci, S.; Vos, H.; Draper, B.W.; Moens, C.B.; Burgering, B.M.; et al. Tdrd1 acts as a molecular scaffold for Piwi proteins and piRNA targets in zebrafish. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3298–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.S.; Guruvayoorappan, C.; Sakthivel, K.M.; Rasmi, R.R. Ki-67 protein as a tumour proliferation marker. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 491, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Long, J.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.X.; Da, T.T.; Wang, X.Q.; Huang, C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Yao, X.Q.; Ma, H.Q.; et al. Single-cell and spatial transcriptome analysis reveals the cellular heterogeneity of liver metastatic colorectal cancer. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemin, J.-P.; Bassaganyas, L.; Pourquier, D.; Boissière, F.; Cabello-Aguilar, S.; Crapez, E.; Tanos, R.; Cornillot, E.; Turtoi, A.; Colinge, J. Inferring ligand-receptor cellular networks from bulk and spatial transcriptomic datasets with BulkSignalR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 4726–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, B.; Ming, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, D. SpaTopic: A statistical learning framework for exploring tumor spatial architecture from spatially resolved transcriptomic data. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.-Y.; Zhou, C.; Gan, W.; Tang, Z.; Sun, B.-Y.; Huang, J.-L.; Liu, G.; Liu, W.-R.; Tian, M.-X.; Jiang, X.-F.; et al. Single-cell and spatial architecture of primary liver cancer. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Liao, Z.; Gao, X.; Lu, C.; Lu, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, H.; et al. Single cell-spatial transcriptomics and bulk multi-omics analysis of heterogeneity and ecosystems in hepatocellular carcinoma. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ouyang, L.; Tang, J.; Qian, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Ming, J.; Xi, R. Spatial transcriptomics: A new frontier in cancer research. Clin. Cancer Bull. 2024, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shi, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S. Significance of Liver Zonation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 806408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalha, H.; Bahar Halpern, K.; Abu-Gazala, S.; Jana, T.; Massasa, E.E.; Moor, A.E.; Buchauer, L.; Rozenberg, M.; Pikarsky, E.; Amit, I.; et al. A single cell atlas of the human liver tumor microenvironment. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Long, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Cheng, B.; Pan, W. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals dynamic changes in the liver microenvironment during colorectal cancer metastatic progression. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, S.; Metic, N.; Leylek, O.; Smith, E.A.; Berner, A.M.; Baker, A.M.; Uddin, I.; Buzzetti, M.; Gerlinger, M.; Graham, T.; et al. Phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity in colorectal cancer metastasis. Cell Genom. 2025, 5, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorman, A.; Benitez, E.K.; Cambulli, F.; Jiang, Q.; Mahmoud, A.; Lumish, M.; Hartner, S.; Balkaran, S.; Bermeo, J.; Asawa, S.; et al. Progressive plasticity during colorectal cancer metastasis. Nature 2025, 637, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, S.; Ba, Y.; Zuo, A.; Luo, P.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, H.; Han, X. Multi-stage mechanisms of tumor metastasis and therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Bado, I.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Rosen, J.M.; Zhang, X.H. Metastasis Organotropism: Redefining the Congenial Soil. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Hoffmann, A.D.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Organotropism: New insights into molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Rao, D.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Q. Metabolic reprogramming in the tumor microenvironment of liver cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.D. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: Advances in eicosanoid biology. Science 2001, 294, 1871–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruys, E.; Toussaint, M.J.; Niewold, T.A.; Koopmans, S.J. Acute phase reaction and acute phase proteins. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Oyang, L.; Lin, J.; Tan, S.; Han, Y.; Wu, N.; Yi, P.; Tang, L.; Pan, Q.; Rao, S.; et al. The cancer metabolic reprogramming and immune response. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Cazares, D.; Chavez-Dominguez, R.; Marroquin-Muciño, M.; Perez-Medina, M.; Benito-Lopez, J.J.; Camarena, A.; Rumbo-Nava, U.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.S. The systemic-level repercussions of cancer-associated inflammation mediators produced in the tumor microenvironment. Front. Endocrinol 2022, 13, 929572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, V.; Nikoloudakis, E.; Ladomenou, K.; Charalambidis, G.; Coutsolelos, A.G. Porphyrins—Valuable pigments of life. Front. Chem. Biol. 2024, 2, 1346465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, L.; Rund, K.M.; Ostermann, A.I.; Hartung, N.M.; Galano, J.-M.; Balas, L.; Durand, T.; Balzer, M.S.; David, S.; Schebb, N.H. Development of an Optimized LC-MS Method for the Detection of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Biological Samples. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, V.; Allocco, A.L.; Petrillo, S.; Gazzano, E.; Torretta, S.; Marchi, S.; Destefanis, F.; Pacelli, C.; Audrito, V.; Provero, P.; et al. The heme synthesis-export system regulates the tricarboxylic acid cycle flux and oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiabrando, D.; Marro, S.; Mercurio, S.; Giorgi, C.; Petrillo, S.; Vinchi, F.; Fiorito, V.; Fagoonee, S.; Camporeale, A.; Turco, E.; et al. The mitochondrial heme exporter FLVCR1b mediates erythroid differentiation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 4569–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S. Zileuton inhibits arachidonate-5-lipoxygenase to exert antitumor effects in preclinical cervical cancer models. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.M.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhu, K.F.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Z.C.; Chang, J. The ALOX5 inhibitor Zileuton regulates tumor-associated macrophage M2 polarization by JAK/STAT and inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 121, 110505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adapa, S.R.; Porshe, S.; Talada, D.P.; Nywening, T.M.; Anderson, M.L.; Shaw, T.I.; Jiang, R.H.Y. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Architectures but Shared Vulnerabilities in Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors. Cancers 2025, 17, 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193210
Adapa SR, Porshe S, Talada DP, Nywening TM, Anderson ML, Shaw TI, Jiang RHY. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Architectures but Shared Vulnerabilities in Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193210
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdapa, Swamy R., Sahanama Porshe, Divya Priyanka Talada, Timothy M. Nywening, Mattew L. Anderson, Timothy I. Shaw, and Rays H. Y. Jiang. 2025. "Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Architectures but Shared Vulnerabilities in Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193210
APA StyleAdapa, S. R., Porshe, S., Talada, D. P., Nywening, T. M., Anderson, M. L., Shaw, T. I., & Jiang, R. H. Y. (2025). Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Distinct Architectures but Shared Vulnerabilities in Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors. Cancers, 17(19), 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193210





