HOXA5 as a Dual Modulator of Tumor Biology in Endometrial Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
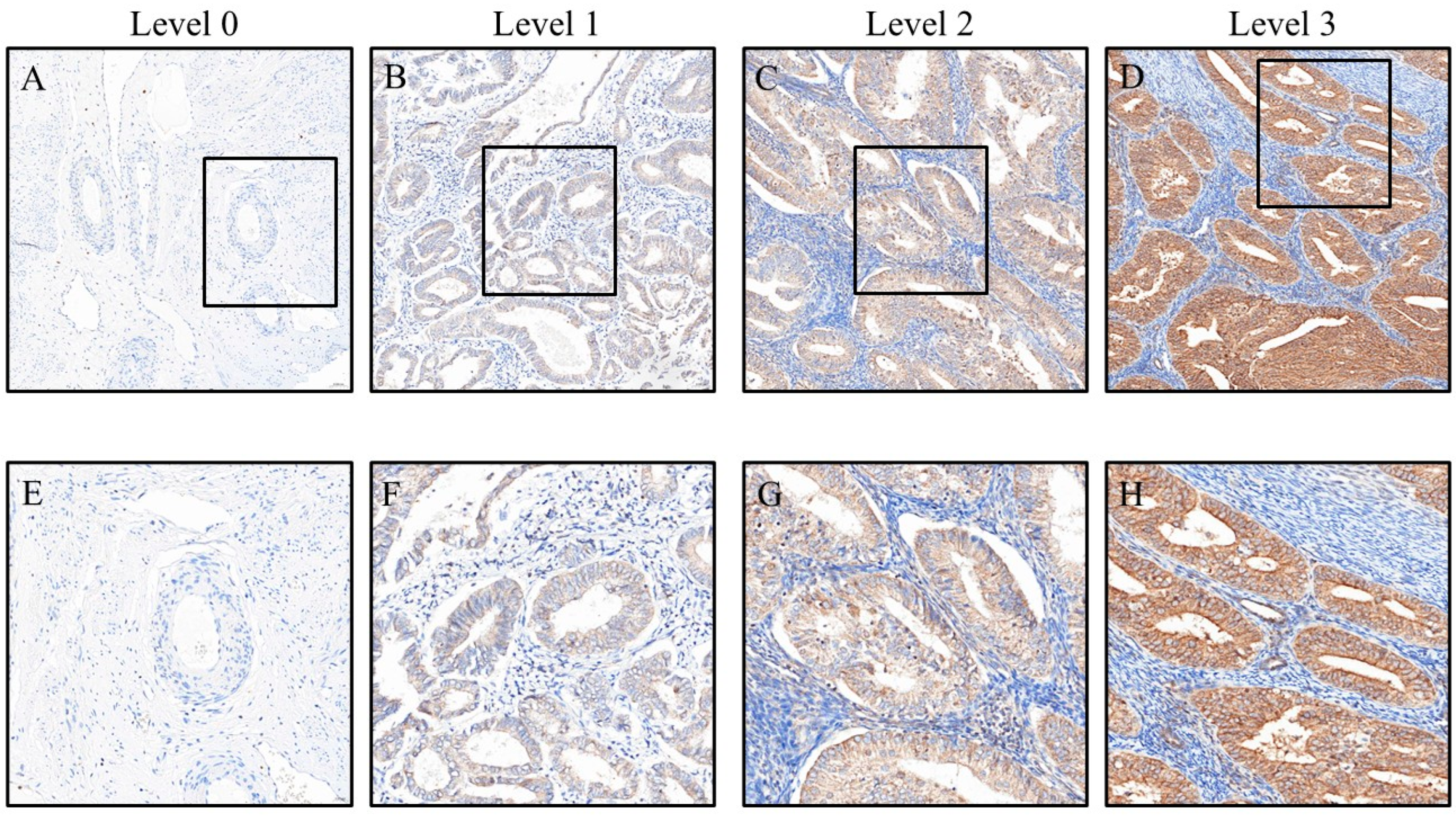
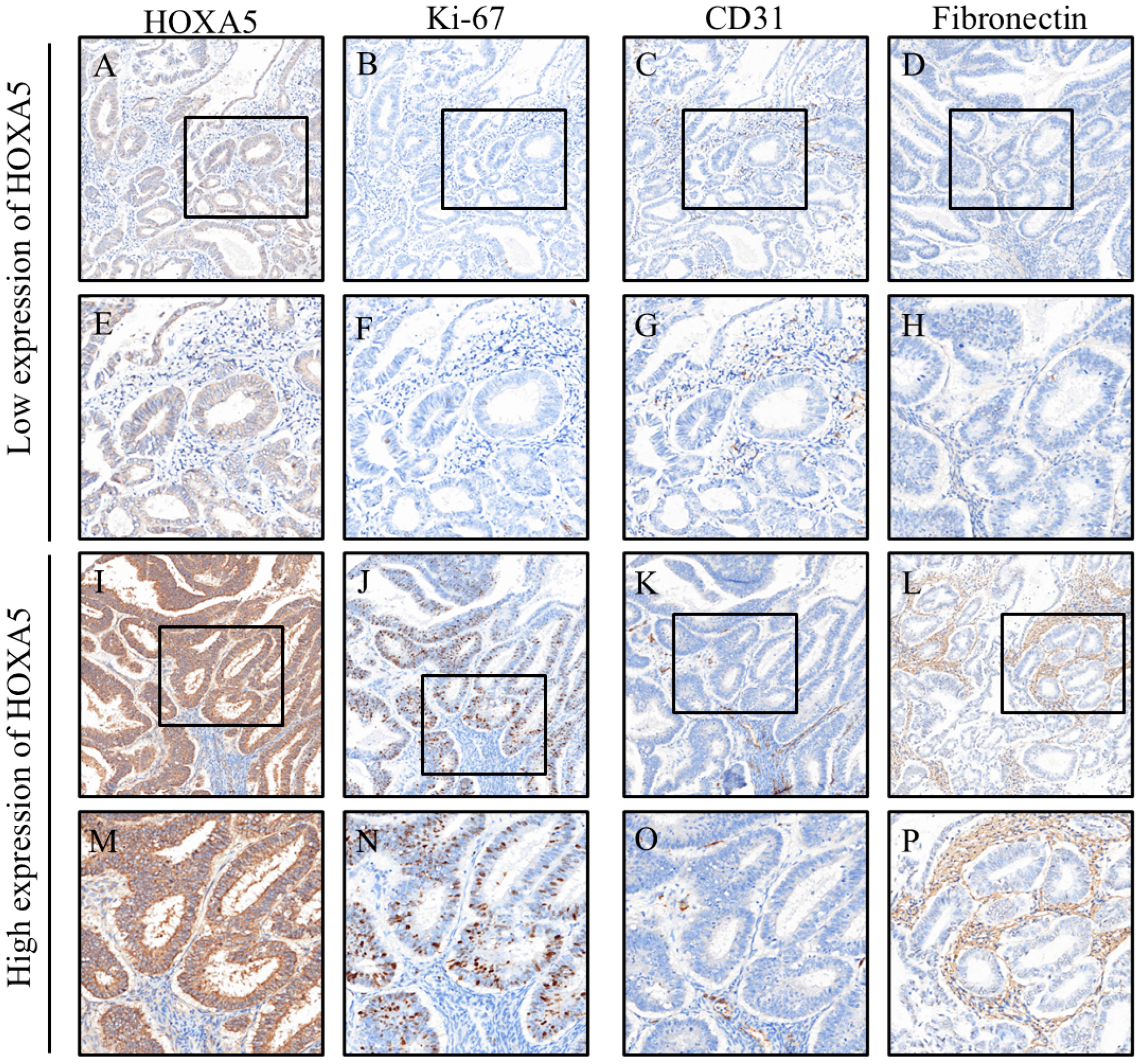
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Endometrial cancer |
| MVD | Microvessel density |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
References
- Crosbie, E.J.; Kitson, S.J.; McAlpine, J.N.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Powell, M.E.; Singh, N. Endometrial cancer. Lancet 2022, 399, 1412–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.H.; Broaddus, R.R. Endometrial Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raglan, O.; Kalliala, I.; Markozannes, G.; Cividini, S.; Gunter, M.J.; Nautiyal, J.; Gabra, H.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Tsilidis, K.K.; et al. Risk factors for endometrial cancer: An umbrella review of the literature. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadducci, A.; Multinu, F.; De Vitis, L.A.; Cosio, S.; Carinelli, S.; Aletti, G.D. Endometrial stromal tumors of the uterus: Epidemiology, pathological and biological features, treatment options and clinical outcomes. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 171, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cai, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Gao, L.; Jiang, L. The Expression of VEGF and CD31 in Endometrial Lesions and Its Associations with Blood Flow Parameters of Transvaginal 3D Power Doppler Ultrasonography: A Preliminary Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11211–11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, S.F.; Bao, W. Molecular subtypes of endometrial cancer: Implications for adjuvant treatment strategies. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2024, 164, 436–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, A.; Yoshida, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Yonemori, K. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 targeted therapy in endometrial cancer: Clinical and pathological perspectives. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lai, T.; Li, Z.; Mao, M.; Jin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R. Role of non-coding RNA intertwined with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in endometrial cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2023, 28, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, N.E.; Sebo, P.; Haller, D.M.; Maisonneuve, H. Primary care patients’ perspectives on the use of non-pharmacological home remedies in Geneva: A cross-sectional study. BMC Complement Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidle, U.H.; Birzele, F.; Kollmorgen, G.; Rueger, R. Mechanisms and Targets Involved in Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2016, 13, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraszczak, K.; Barczynski, B.; Tylus, B.; Bednarek, W. Expression of E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin in the Endocervix as a Predictive Factor in Patients with Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Asanoma, K.; Yagi, H.; Onoyama, I.; Hori, E.; Matsumura, Y.; Okugawa, K.; Yahata, H.; Kato, K. Fibronectin mediates activation of stromal fibroblasts by SPARC in endometrial cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, S.N.; Hajiyeva, S.; Baghirzada, L.; Ashina, S.; Alekberli, T.; Healthcare Professionals for, P. The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict and the politicisation of science. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e253–e254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, A.L.; Rivera, G.; Lucas, E.; John, G.; Cuevas, I.; Castrillon, D.H. PI3K Pathway Effectors pAKT and FOXO1 as Novel Markers of Endometrioid Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2019, 38, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscardini, E.H.; Hill, R.M.; Dodd, C.G.; Do, C.; Kaplow, J.B.; Tucker, R.P. Suicide Safety Planning: Clinician Training, Comfort, and Safety Plan Utilization. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Kim, K.B.; Lee, G.S.; Shin, S.; Kim, B. Is HOXA5 a Novel Prognostic Biomarker for Uterine Corpus Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Mo, H.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qu, C.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. HOXA5: A crucial transcriptional factor in cancer and a potential therapeutic target. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhong, F.; Huang, X.; Zhang, N.; Du, J.; Long, Z.; Zheng, B.; Lin, W.; Liu, W.; Ma, W. High expression of HOXA5 is associated with poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2021, 45, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaiche, H.; Tounsi-Kettiti, H.; Ben Jemii, N.; Jaballah Gabteni, A.; Mezghanni, N.; Ardhaoui, M.; Fehri, E.; Maaloul, A.; Abdelhak, S.; Boubaker, S. New insights in the clinical implication of HOXA5 as prognostic biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 30, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zha, L.; Chen, A.; Wang, Z. HOXA5 is a tumor suppressor gene that is decreased in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, S.; Zhang, M. TRAF7-targeted HOXA5 acts as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer progression and stemness via transcriptionally activating SPRY2 and regulating MEK/ERK signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Tamori, A.; Vali, M.; Zeller, K.; Korz, D.; Sukumar, S. HOXA5 regulates expression of the progesterone receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26551–26555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tan, L.; Ruan, J.; Wei, X.P.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, L.X.; Jiang, W.Q.; Fang, W.J. Aberrant Expression of HOXA5 and HOXA9 in AML. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3941–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeannotte, L.; Gotti, F.; Landry-Truchon, K. Hoxa5: A Key Player in Development and Disease. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Human Protein, A. Expression of HOXA5 in endometrial cancer—The Human Protein Atlas. In The Human Protein Atlas Database; 2025; Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000106004-HOXA5/cancer/endometrial+cancer (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Galant, N.; Krawczyk, P.; Monist, M.; Obara, A.; Gajek, L.; Grenda, A.; Nicos, M.; Kalinka, E.; Milanowski, J. Molecular Classification of Endometrial Cancer and Its Impact on Therapy Selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpel, H.; Slomovitz, B.; Coleman, R.L.; Pothuri, B. Biomarker-driven therapy in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouzi, R.; Barr, C.E.; Crosbie, E.J. HE4 as a Biomarker for Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Minimally invasive approaches for the early detection of endometrial cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronconi, F.; Nero, C.; Giudice, E.; Salutari, V.; Musacchio, L.; Ricci, C.; Carbone, M.V.; Ghizzoni, V.; Perri, M.T.; Camarda, F.; et al. Advanced and recurrent endometrial cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 180, 103851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Hsieh, C.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, J.J.W.; Wang, C.C. HOXA5 and p53 cooperate to suppress lung cancer cell invasion and serve as good prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, D. HOXA5 counteracts the function of pathological scar-derived fibroblasts by partially activating p53 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.M.; Cui, N.; Zheng, P.S. HOXA5 inhibits the proliferation and neoplasia of cervical cancer cells via downregulating the activity of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and transactivating TP53. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Martensen, S.A.; Reisman, D.; Evron, E.; Odenwald, W.F.; Jaffee, E.; Marks, J.; Sukumar, S. Compromised HOXA5 function can limit p53 expression in human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 405, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.S.; van Diest, P.J.; Burger, H.; Russo, J.; Raman, V. Expression pattern of a homeotic gene, HOXA5, in normal breast and in breast tumors. Cell. Oncol. 2006, 28, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizen, B.; Claus, M.; Jeannotte, L.; Rijli, F.M.; Gofflot, F. Perinatal induction of Cre recombination with tamoxifen. Transgenic Res. 2015, 24, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.N.; McDermid, R.L.; Weinberg, A.L.; Greco, T.L.; Xu, X.; Murdoch, F.E.; Fritsch, M.K. Differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells induces progesterone receptor gene expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 311, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, M.C.; Gong, T.; Lu, Y.; Lee, J.; Zhong, Y.; Lacunza, E.; Butti, M.; Takata, Y.; Gaddis, S.; Shen, J.; et al. A Molecular Portrait of High-Grade Ductal Carcinoma In Situ. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3980–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; He, F.; Wang, E. Identification and validation of DNA methylation markers to predict axillary lymph node metastasis of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, P.; Wang, G.; Teo, W.W.; Raez-Rodriguez, D.; Gabrielson, K.L.; Gyorffy, B.; Downs, B.M.; Aggarwal, A.; Sukumar, S. HOXA5-Mediated Stabilization of IkappaBalpha Inhibits the NF-kappaB Pathway and Suppresses Malignant Transformation of Breast Epithelial Cells. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3802–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti-Valls, M.; Megino-Luque, C.; Macia, A.; Gatius, S.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Eritja, N. Metabolomic-Based Approaches for Endometrial Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Review. Cancers 2023, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizner, T.L.; Romano, A. The discovery of biomarkers for endometrial cancer: Update over the last years. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2025, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, I.S.; Mihaila, M.; Roman, V.; Radu, N.; Neagu, M.T.; Bostan, M.; Mehedintu, C. Landscape of Endometrial Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Target Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, Y.; Devins, K.M.; Milane, L.; Manning, W.B.; Mazina, V.; Yeku, O.O.; Rueda, B.R. High-Grade Endometrial Cancer: Molecular Subtypes, Current Challenges, and Treatment Options. Reprod. Sci. 2024, 31, 2541–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addante, F.; d’Amati, A.; Santoro, A.; Angelico, G.; Inzani, F.; Arciuolo, D.; Travaglino, A.; Raffone, A.; D’Alessandris, N.; Scaglione, G.; et al. Mismatch Repair Deficiency as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Endometrial Cancer: A Review on Immunohistochemistry Staining Patterns and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, A.; D’Oria, O.; Corrado, G.; Bruno, V.; Sperduti, I.; Bogani, G.; Lagana, A.S.; Chiantera, V.; Caserta, D.; Vizza, E. The role of L1CAM as predictor of poor prognosis in stage I endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 309, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Jia, M.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lai, L.; Ding, S.; Hu, Z. Prognostic Value of Ki67 in Patients with Stage 1–2 Endometrial Cancer: Validation of the Cut-off Value of Ki67 as a Predictive Factor. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 10841–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Kong, W.; Tu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, R. Comprehensive Assessment of ERalpha, PR, Ki67, P53 to Predict the Risk of Lymph Node Metastasis in Low-Risk Endometrial Cancer. J. Investig. Surg. 2023, 36, 2152508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrandina, G.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Gallotta, V.; Martinelli, E.; Zannoni, G.F.; Gessi, M.; Scambia, G. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), receptors for estrogen (ER), and progesterone (PR), p53, ki67, and neu protein in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 98, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atak, Z.; Turhan, E.I.; Rahimli Ocakoglu, S.; Uyaniklar, O.O. Symptom-related Ki-67 expression in endometrial polyps. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 272, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, W.; Liu, K.; Gao, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, J.; Kamal, M.A.; Yuan, C. Endometrial Cancer: Genetic, Metabolic Characteristics, Therapeutic Strategies and Nanomedicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 8755–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitev, D.; Slavov, S.; Dimitrov, G.; Shikova, I.; Hristova, J.; Kostov, S.; Yordanov, A. Serum fibronectin levels in malignant and benign endometrial diseases. Prz. Menopauzalny 2024, 23, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padeznik, T.; Oleksy, A.; Cokan, A.; Takac, I.; Sobocan, M. Changes in the Extracellular Matrix in Endometrial and Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Manufacturer | Country | City | Catalog Number | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOXA5 | Abcam | UK | Cambridge | ab82645 | 1:50 |
| Caspase-3 | Cell Signaling | USA | Danvers, MA | 9664 | 1:100 |
| Ki67 | BioLegend | USA | San Diego, CA | 350503 | 1:100 |
| CD31 | Abbiotec | USA | San Diego, CA | 250590 | 1:500 |
| E-cadherin | Abcam | UK | Cambridge | ab40772 | 1:100 |
| N-cadherin | Abcam | UK | Cambridge | ab76011 | 1:100 |
| Fibronectin | Santa Cruz | USA | Dallas, TX | SC-8422 | 1:50 |
| pAkt | GeneTex | USA | Irvine, CA | GTX11901 | 1:50 |
| pErk | R&D | USA | Minneapolis, MN | AF1018 | 1:200 |
| pStat3 | Abcam | UK | Cambridge | ab76315 | 1:50 |
| pAMPK | Cell Signaling | USA | Danvers, MA | 2535 | 1:100 |
| Low Expression of HOXA5 (N = 30) | High Expression of HOXA5 (N = 45) | Total (N = 75) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 56.5 (50.5, 64.0) | 56.0 (50.0, 59.5) | 56.0 (50, 60) | 0.482 |
| Grading | 0.631 | |||
| Well | 6 (20.0%) | 12 (26.7%) | 18 (24.0%) | |
| Moderate | 17 (56.7%) | 26 (57.8%) | 43 (57.3%) | |
| Low | 7 (23.3%) | 7 (15.6%) | 14 (18.7%) | |
| Size | 3.8 (1.4, 6.6) | 2.8 (1.6, 5.0) | 3.0 (1.5, 5.0) | 0.661 |
| Stage | 0.796 | |||
| I | 24 (80.0%) | 37 (82.2%) | 61 (81.3%) | |
| II | 2 (6.7%) | 4 (8.9%) | 6 (8.0%) | |
| III | 4 (13.3%) | 4 (8.9%) | 8 (10.7%) |
| Low Expression of HOXA5 | High Expression of HOXA5 | Total | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caspase-3 | 6.3 (4.5, 9.3) | 8.6 (5.4, 13.7) | 7.1 (5.2, 12.8) | 0.062 |
| Ki67 | 2.3 (0.3, 7.1) | 9.0 (1.7, 24.4) | 5.2 (1.3, 16.1) | 0.001 ** |
| CD31 | 8.2 (6.4, 14.8) | 6.4 (4.8, 8.4) | 6.9(5.1, 96) | 0.007 ** |
| E-cad | 108.5 (101.6, 115.6) | 110 (105.8, 118.5) | 109.4 (103.5, 116.1) | 0.216 |
| N-cad | 8.9 (3.5, 19.9) | 7.3 (2.5, 40.6) | 7.6 (2.5, 34.1) | 0.665 |
| Fibronectin | 16.6 (6.3, 51.5) | 2.9 (1.1, 23.4) | 8.9 (2.1, 31.9) | 0.001 ** |
| pAkt | 2.5 (1.2, 3.6) | 4.1 (1.9, 6.8) | 3.0 (1.6, 6.5) | 0.031 * |
| pErk | 0.2 (0.0, 2.8) | 0.7 (0.2, 5.3) | 0.4 (0.1, 4.6) | 0.069 |
| pStat3 | 0.2 (0.1, 0.4) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.3) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.4) | 0.414 |
| pAMPK | 16.1 (13.2, 25.4) | 13.6 (10.0, 21.9) | 14.8 (12.0, 22.6) | 0.218 |
| Univariable | p-Value | Multivariable | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.98 (0.93–1.03) | 0.329 | ||
| Grading | ||||
| Well | Reference | |||
| Moderate | 0.77 (0.24–2.43) | 0.649 | ||
| Low | 0.50 (0.12–2.10) | 0.344 | ||
| Size | 0.94 (0.80–1.11) | 0.450 | ||
| Stage | ||||
| I | Reference | |||
| II | 1.30 (0.22–7.64) | 0.774 | ||
| III | 0.65 (0.15–2.84) | 0.566 | ||
| Marker | ||||
| Caspase-3 | 1.07 (0.99–1.16) | 0.088 | ||
| Ki67 | 1.08 (1.02–1.14) | 0.008 ** | 1.12 (1.03–1.19) | 0.004 ** |
| CD31 | 0.91 (0.83–0.98) | 0.018 * | 0.89 (0.78–1.01) | 0.063 |
| E-cad | 1.04 (0.98–1.11) | 0.189 | ||
| N-cad | 1.01 (0.99–1.03) | 0.241 | ||
| Fibronectin | 0.98 (0.97–1.00) | 0.021 * | 0.98 (0.96–1.00) | 0.057 |
| pAkt | 1.02 (0.95–1.09) | 0.597 | ||
| pErk | 1.01 (0.97–1.05) | 0.628 | ||
| pStat3 | 0.75 (0.50–1.13) | 0.163 | ||
| pAMPK | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | 0.257 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.-K.; Shih, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Ho, H.; Chen, Y.-L. HOXA5 as a Dual Modulator of Tumor Biology in Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152473
Fu Y-K, Shih C-Y, Cheng C-Y, Ho H, Chen Y-L. HOXA5 as a Dual Modulator of Tumor Biology in Endometrial Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152473
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yi-Kai, Ching-Yu Shih, Chiao-Yin Cheng, Hua Ho, and Yen-Lin Chen. 2025. "HOXA5 as a Dual Modulator of Tumor Biology in Endometrial Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152473
APA StyleFu, Y.-K., Shih, C.-Y., Cheng, C.-Y., Ho, H., & Chen, Y.-L. (2025). HOXA5 as a Dual Modulator of Tumor Biology in Endometrial Cancer. Cancers, 17(15), 2473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152473








