Predictors of Growth of Vestibular Schwannoma After Gamma Knife Treatment: A Systematic Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
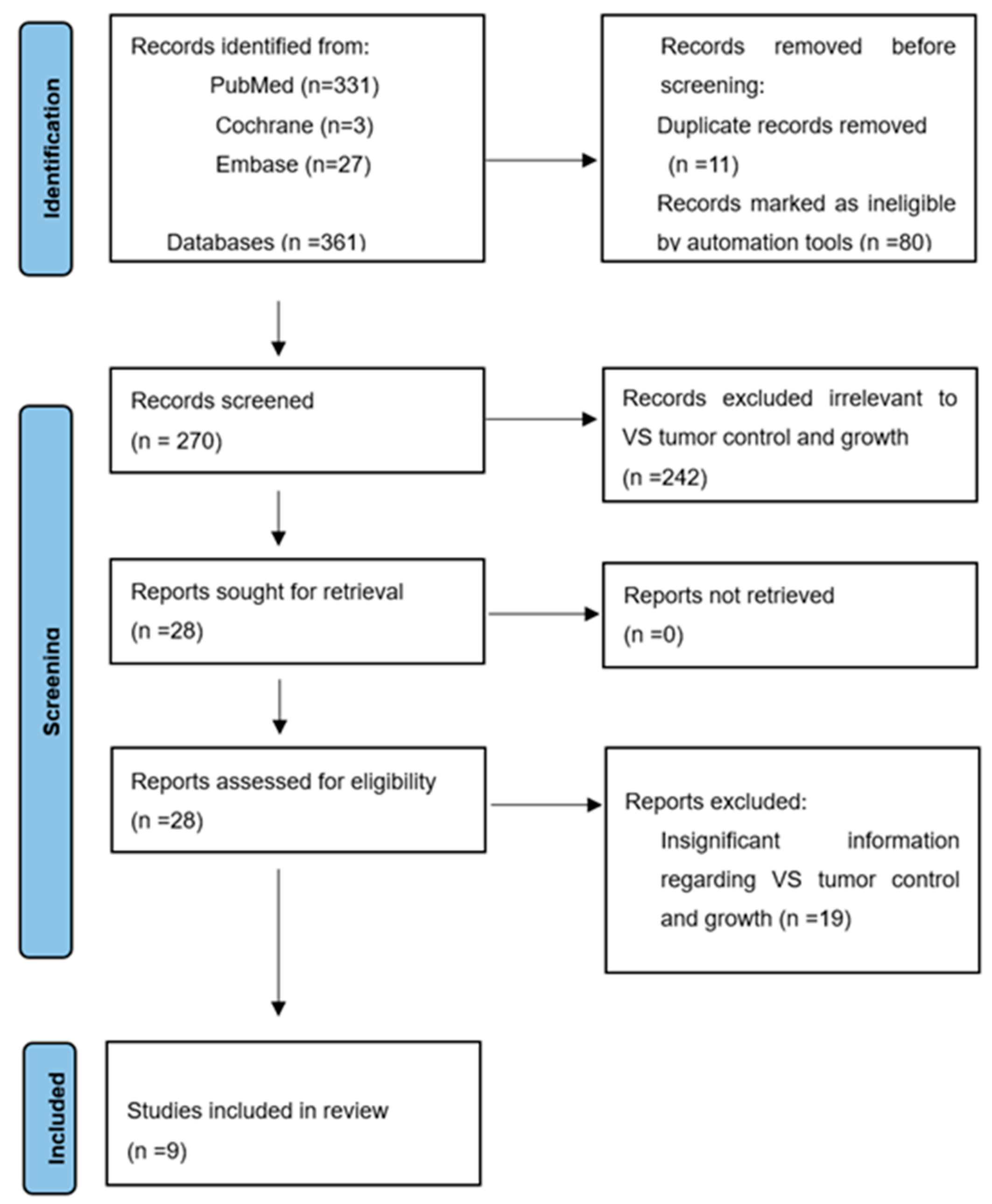
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Inclusion in the Study
3.2. Quality Assessment
3.3. Overall Findings
3.4. Patient Factors
3.5. Tumor Factors
3.6. Clinical Presentation
3.7. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC)
3.8. Correlation Between Clinical Parameters and Post-GKRS Growth Rates
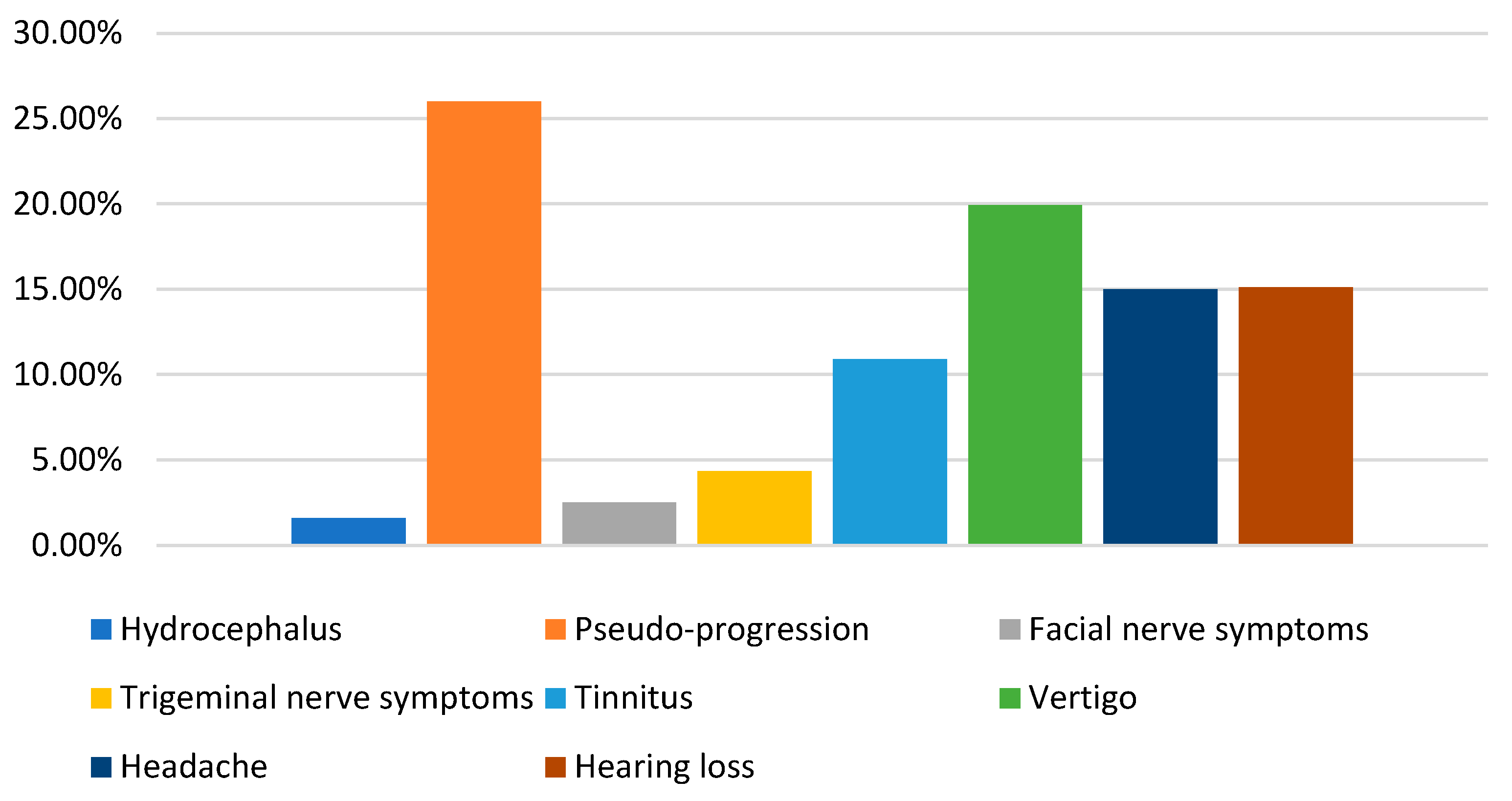
3.9. Complication and Sequelae
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldbrunner, R.; Weller, M.; Regis, J.; Lund-Johansen, M.; Stavrinou, P.; Reuss, D.; Evans, D.G.; Lefranc, F.; Sallabanda, K.; Falini, A.; et al. EANO guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of vestibular schwannoma. Neuro Oncol. 2020, 22, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.L.; Link, M.J. Vestibular Schwannomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1335–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, J.P.; Beeler, C.J.; Carlson, M.L.; Caye-Thomasen, P.; Spear, S.A.; Erbele, I.D. Global Incidence of Sporadic Vestibular Schwannoma: A Systematic Review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 167, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, E.X.; Wegner, R.; Conley, G.; Torok, J.; Heron, D.E.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Burton, S.; Ozhasoglu, C.; Quinn, A.; Hirsch, B.E. Treatment outcomes in patients treated with CyberKnife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Vasan, R.; van Loveren, H.; Downes, K.; Agazzi, S. The changing face of acoustic neuroma management in the USA: Analysis of the 1998 and 2008 patient surveys from the acoustic neuroma association. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 28, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Breshears, J.D.; Molinaro, A.M.; Sneed, P.K.; McDermott, M.W.; Theodosopoulos, P.V.; Tward, A.D. Impact of pretreatment growth on Tumor control for vestibular schwannomas following gamma knife. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2000. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm (accessed on 15 June 2012).
- Turek, G.; Dzierzęcki, S.; Obierzyński, P.; Rogala, A.; Ząbek, Z.; Milewski, R.; Kiprian, D.; Zielińska-Turek, J.; Ząbek, M. Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in the Treatment of Intracanalicular Vestibular Schwannomas Using Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiation. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, F.C.; Mulder, J.J.; Hanssens, P.E.; van Overbeeke, J.J.; Donders, R.T.; Cremers, C.W.; Graamans, K. Gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: Identification of predictors for continued tumor growth and the influence of documented tumor growth preceding radiation treatment. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1834–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, A.P.; Jacob, J.T.; Carlson, M.L.; Pollock, B.E.; Driscoll, C.L.W.; Link, M.J. Pretreatment growth rate as a predictor of tumor control following Gamma Knife radiosurgery for sporadic vestibular schwannoma. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangerid, T.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Svensson, M.; Förander, P. Long-term quality of life and tumour control following gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Kano, H.; Faramand, A.; Pease, M.; Nakamura, A.; Hassib, M.; Spencer, D.; Sisterson, N.; Faraji, A.H.; Arai, Y.; et al. Long term results of primary radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Langenberg, R.; Hanssens, P.E.; Verheul, J.B.; van Overbeeke, J.J.; Nelemans, P.J.; Dohmen, A.J.; de Bondt, B.J.; Stokroos, R.J. Management of large vestibular schwannoma. Part II. Primary Gamma Knife surgery: Radiological and clinical aspects. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Guo, W.Y.; Chung, W.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Lin, C.J.; Lee, C.C.; Liu, K.D.; Yang, H.C. Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics and the prediction of outcome of vestibular schwannomas following Gamma Knife radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larjani, S.; Monsalves, E.; Pebdani, H.; Krischek, B.; Gentili, F.; Cusimano, M.; Laperriere, N.; Hayhurst, C.; Zadeh, G. Identifying predictors of early growth response and adverse radiation effects of vestibular schwannomas to radiosurgery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klijn, S.; Verheul, J.B.; Beute, G.N.; Leenstra, S.; Mulder, J.J.; Kunst, H.P.; Hanssens, P.E. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: Evaluation of tumor control and its predictors in a large patient cohort in The Netherlands. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, H.; Benedict, N.T.; Tringali, S.; Gurusinghe, N.T.; Roberts, G.; Fieux, M.; Alalade, A.F. Identifying Factors Associated with the Growth of Vestibular Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2021, 149, e766–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egiz, A.; Nautiyal, H.; Alalade, A.F.; Gurusinghe, N.; Roberts, G. Evaluating growth trends of residual sporadic vestibular schwannomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2022, 159, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Alvarado, D.; Ravindran, P.K.; Keizer, M.E.; Hovinga, K.; Broen, M.P.G.; Kunst, H.; Temel, Y. Untreated Vestibular Schwannoma: Analysis of the Determinants of Growth. Cancers 2024, 16, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, S.; Litofsky, N.S. Daily Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Quality of Life and Survival in Glioblastoma: A Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeberg, S.; Bernhardt, D.; Foerster, R.; Bostel, T.; Koerber, S.A.; Mohr, A.; Koelsche, C.; Rieken, S.; Debus, J. The influence of hyperglycemia during radiotherapy on survival in patients with primary glioblastoma. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezey, G.; Cahill, J.; Rowe, J.G.; Yianni, J.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Walton, L.; Rodgers, J.; Radatz, M.W.R. A Retrospective Analysis of the Role of Single-Session Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Sporadic Vestibular Schwannomas with Tumor Volumes Greater Than 10 cm3: Is It Worth Stretching the Boundaries? Ster. Funct. Neurosurg. 2020, 98, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, L.; Mom, T.; Guillemin, F.; Puechmaille, M.; Khalil, T.; Biau, J. The Recent Management of Vestibular Schwannoma Radiotherapy: A Narrative Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicella, G.; Paolini, M.; Deantonio, L.; Masini, L.; Krengli, M. Radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma: Review of recent literature results. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2016, 21, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chvetsov, A.V.; Hanin, L.G.; Stewart, R.D.; Zeng, J.; Rengan, R.; Lo, S.S. Tumor control probability in hypofractionated radiotherapy as a function of total and hypoxic tumor volumes. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, S.; Samanci, Y.; Ozdemir, I.E.; Kunst, H.P.M.; Eekers, D.B.P.; Temel, Y. Long-term results of upfront, single-session Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large cystic vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 46, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.; Cavaleri, J.; Monaco, E., III; Niranjan, A.; Flickinger, J.; Lunsford, L.D. Cystic Vestibular Schwannomas Respond Best to Radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaad, E.; Hamidi, N.; Goetz, J.; Padmanaban, V.; Mau, C.; Tsang, D.; de Moraes, F.Y.; Chung, C.; Zacharia, B.E.; Mansouri, A. Equivalent Efficacy and Safety of Radiosurgery for Cystic and Solid Vestibular Schwannomas: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2021, 146, 322–331.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George-Jones, N.A.; Chkheidze, R.; Moore, S.; Wang, J.; Hunter, J.B. MRI Texture Features are Associated with Vestibular Schwannoma Histology. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2000–E2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Brouchet, A.; Delisle, M.B.; Cognard, C.; Bonafe, A.; Charlet, J.P.; Deguine, O.; Fraysse, B. Vestibular schwannomas: Correlations between magnetic resonance imaging and histopathologic appearance. Otol. Neurotol. 2001, 22, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George-Jones, N.A.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Hunter, J.B. Prediction of Vestibular Schwannoma Enlargement After Radiosurgery Using Tumor Shape and MRI Texture Features. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, e348–e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenhuizen, P.; Zinger, S.; Leenstra, S.; Kunst, H.P.M.; Mulder, J.J.S.; Hanssens, P.E.J.; de With, P.H.N.; Verheul, J.B. Radiomics-Based Prediction of Long-Term Treatment Response of Vestibular Schwannomas Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e1321–e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speckter, H.; Santana, J.; Bido, J.; Hernandez, G.; Rivera, D.; Suazo, L.; Valenzuela, S.; Oviedo, J.; Gonzalez, C.F.; Stoeter, P. Texture Analysis of Standard Magnetic Resonance Images to Predict Response to Gamma Knife Radiosurgery in Vestibular Schwannomas. World Neurosurg. 2019, 132, e228–e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, O.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Shalom, N.B.; Wangerid, T.; Jakola, A.S.; Förander, P. Stereotactic radiosurgery vs. fractionated radiotherapy for tumor control in vestibular schwannoma patients: A systematic review. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, P.; Green, S.; Germano, I. Communicating hydrocephalus after radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: Does technique matter? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Shin, M.; Takahashi, W.; Shinya, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Kashio, A.; Nakatomi, H.; Saito, N. Long-term Outcomes of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Treating Vestibular Schwannoma with a Lower Prescription Dose of 12 Gy Compared with Higher Dose Treatment. Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e1314–e1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, R.M.; Przybylowski, C.J.; Sugoto, M.; Fezeu, F.; Awad, A.J.; Ding, D.; Nguyen, J.H.; Sheehan, J.P. Gamma Knife radiosurgery of large skull base meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 122, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Number | Author, Year | Type | Number of Patients | Age (Year) | Tumor Control | Length of Follow-Up (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Grzegorz Turek [9], 2023 | Gamma Knife | 94 | 55 | 87.2% | 41 (6–69) |
| 2 | Ferdinand C. A. Timmer [10], 2011 | Gamma Knife | 100 | 57 (25–85) | 92% | 26 (24–48) |
| 3 | Alexander P. Marston [11], 2017 | Gamma Knife | 68 | 67 (23–88) | 86.8% | 43.5 (14–147) |
| 4 | Theresa Wangerid [12], 2014 | Gamma Knife | 128 | 64 (23–89) | 92% | 86 (5–170) |
| 5 | Stephen Johnson [13], 2019 | Gamma Knife | 871 | 57 (18–95) | 97% | 62.4 (96–240) |
| 6 | Rick van de Langenberg [14], 2011 | Gamma Knife | 33 | 54.8 (30–83) | 88% | 30 (12–72) |
| 7 | Chih-Chun Wu [15], 2017 | Gamma Knife | 187 | 52.2 (20.4–82.3) | 90.9% | 60.8 (24–128.9) |
| 8 | Soroush Larjani [16], 2014 | Gamma Knife | 63 | 64 (26–83) | 88.9% | 32 (12–72) |
| 9 | Stijn Klijn [17], 2016 | Gamma Knife | 420 | 57.6 ± 12.7 | 89.3% | 61.2 (48.0–84.0) |
| Author, Year | Growth Rate Definition | Gender | Age | Radiation Dose | Initial Tumor Size | Tumor Growth Rate Before GKRS | Location | Cystic Exist | Clinical Presentation | MRI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theresa Wangerid [12], 2014 | Linear > 2 mm | / | × | / | / | × | × | / | / | / |
| Stijn Klijn [17], 2016 | Linear > 2 mm | / | × | × | √ | / | / | × | / | / |
| F.C.A. Timmer [10], 2011 | Linear > 2 mm | × | × | × | × | / | × | / | × | / |
| Alexander P. Marston [11], 2017 | Linear > 2 mm | / | / | / | × | √ | √ | / | / | / |
| Grzegorz Turek [9], 2023 | Volume > 10% | × | × | × | / | / | × | × | / | / |
| Stephen Johnson [13], 2019 | Volume > 15% | / | × | × | √ | / | × | / | / | / |
| Chih-Chun Wu [15], 2017 | Volume > 10% | × | × | × | × | / | / | √ | / | √ |
| Soroush Larjani [16], 2014 | Volume > 20% | × | × | / | × | × | / | / | / | / |
| Rick van de Langenberg [14], 2011 | No need for further treatment | × | × | / | × | / | × | × | / | / |
| New or Increase Complication/Sequelae | No. of Patients |
|---|---|
| Hydrocephalus (HCP) | 12/768 (1.6%) |
| Pseudo-progression | 133/510 (26%) |
| Facial nerve symptoms | 43/1709 (2.52%) |
| Trigeminal nerve symptoms | 67/1546 (4.33%) |
| Tinnitus | 169/1548 (10.9%) |
| Vertigo | 135/677 (19.94%) |
| Headache | 15/100 (15%) |
| Hearing loss | 5/33 (15.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Alvarado, D.; Ravindran, P.K.; Keizer, M.E.; Hovinga, K.; Broen, M.P.G.; Eekers, D.; Compter, I.; Kunst, H.P.M.; Temel, Y. Predictors of Growth of Vestibular Schwannoma After Gamma Knife Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121993
Yang C, Alvarado D, Ravindran PK, Keizer ME, Hovinga K, Broen MPG, Eekers D, Compter I, Kunst HPM, Temel Y. Predictors of Growth of Vestibular Schwannoma After Gamma Knife Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cancers. 2025; 17(12):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121993
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Cheng, Daniel Alvarado, Pawan Kishore Ravindran, Max E. Keizer, Koos Hovinga, Martinus P. G. Broen, Danielle Eekers, Inge Compter, Henricus P. M. Kunst, and Yasin Temel. 2025. "Predictors of Growth of Vestibular Schwannoma After Gamma Knife Treatment: A Systematic Review" Cancers 17, no. 12: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121993
APA StyleYang, C., Alvarado, D., Ravindran, P. K., Keizer, M. E., Hovinga, K., Broen, M. P. G., Eekers, D., Compter, I., Kunst, H. P. M., & Temel, Y. (2025). Predictors of Growth of Vestibular Schwannoma After Gamma Knife Treatment: A Systematic Review. Cancers, 17(12), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121993








