Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events Display Distinct Clinical and Molecular Characteristics, Depending on Immune Checkpoints Targeted
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
2.4. Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
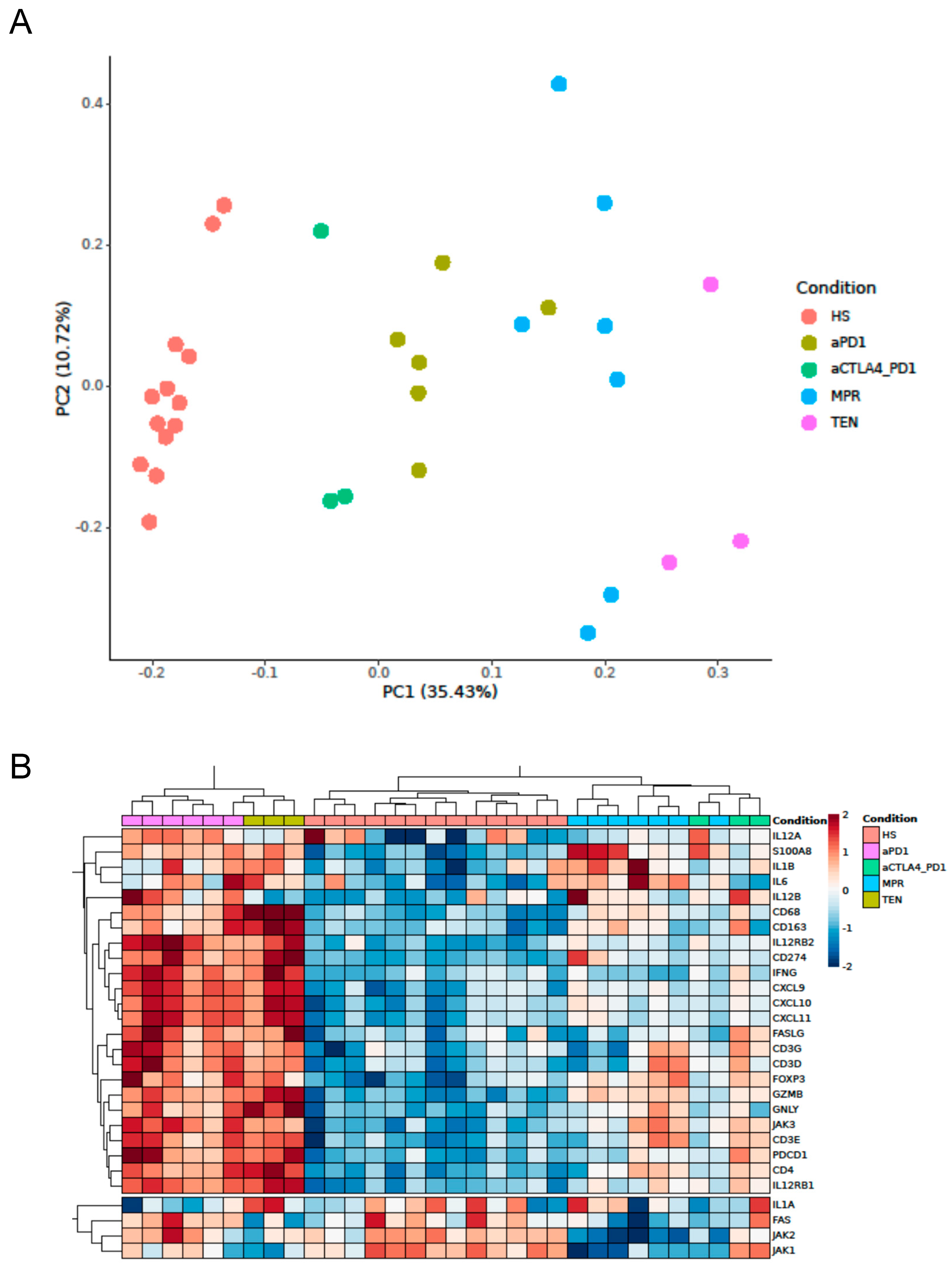
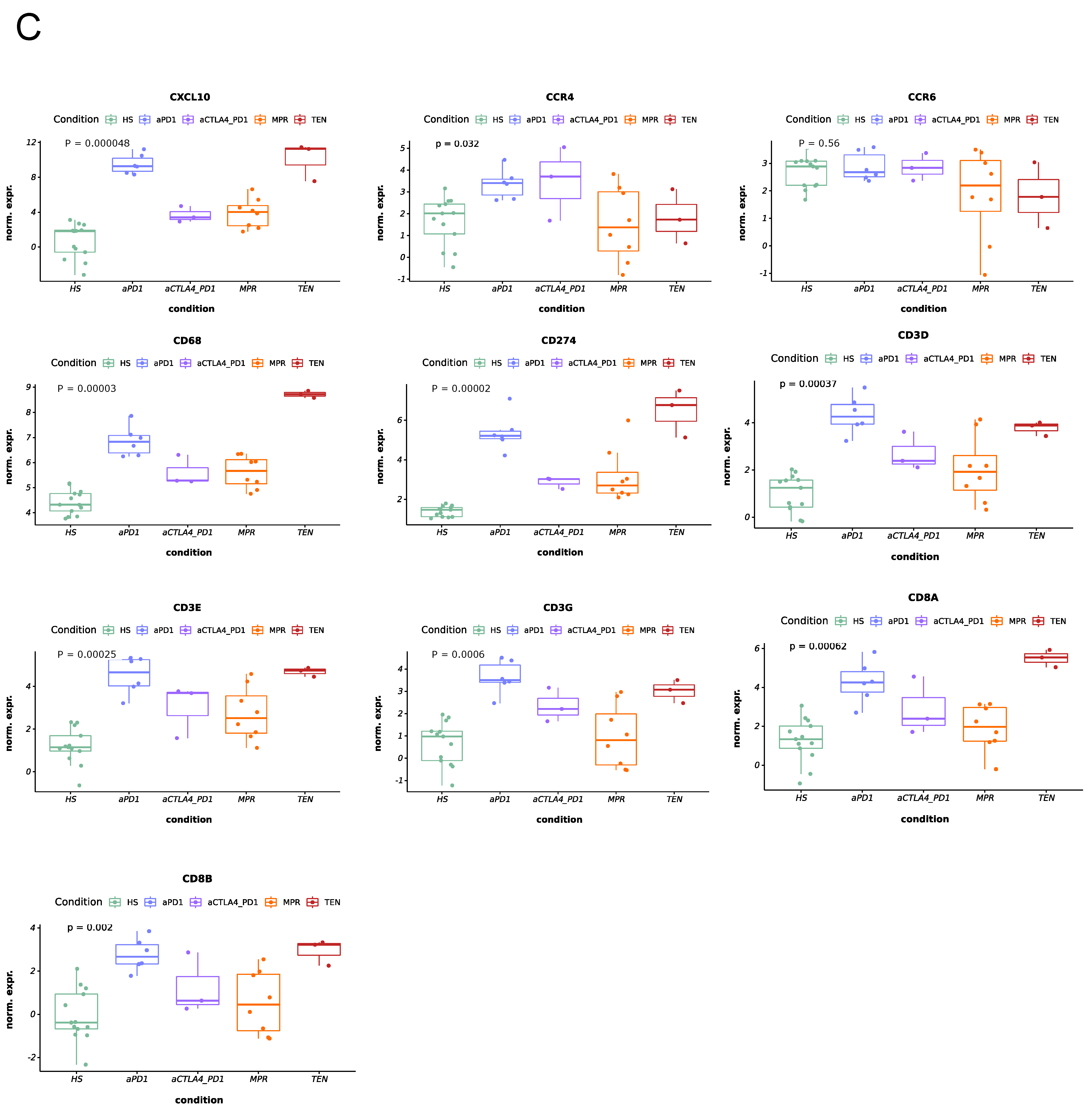
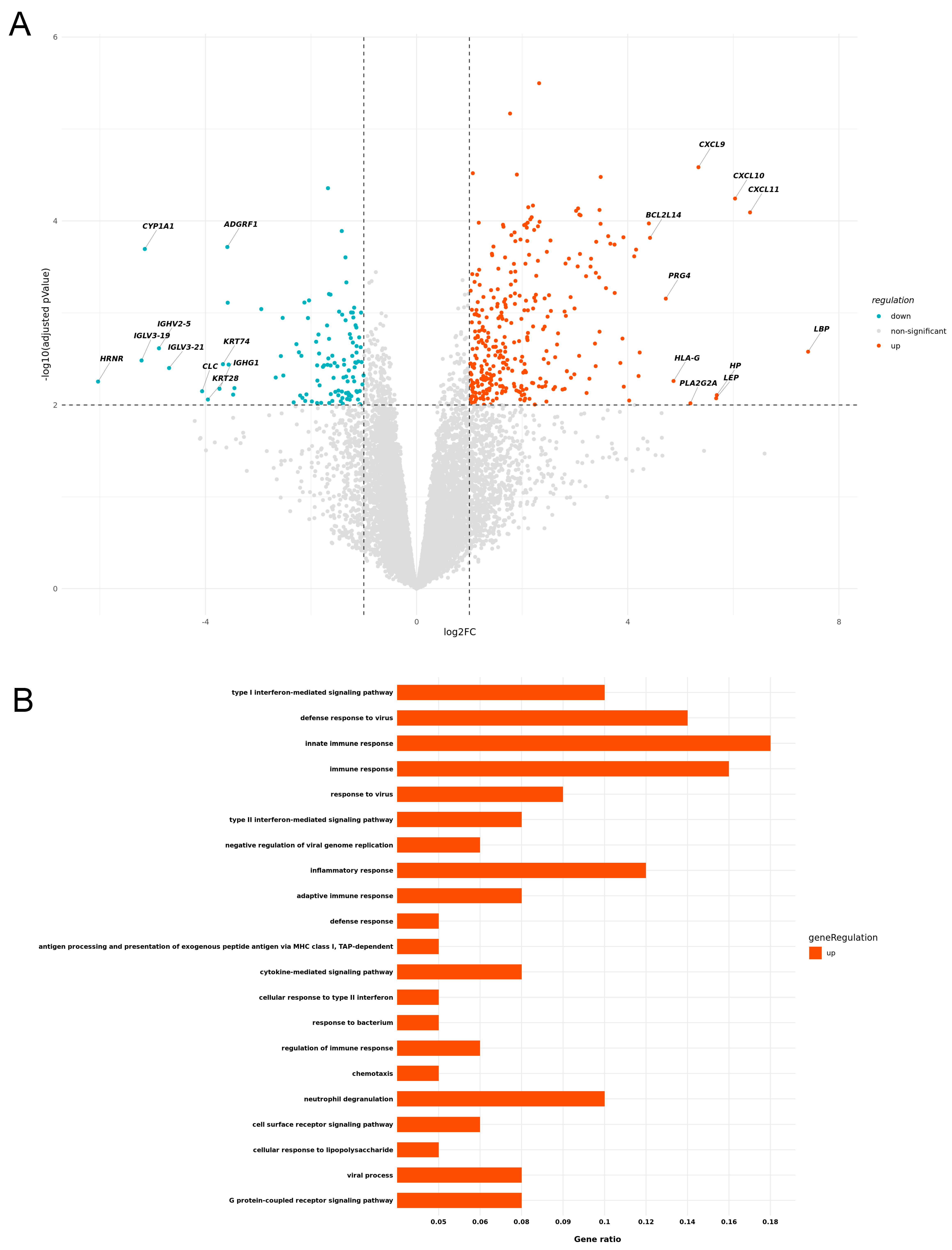
3.1. Expression of Cytotoxicity- and Inflammation-Related Genes in ircAEs Induced by aPD1 Monotherapy Mirrors TEN, Unlike P+C Therapy
3.2. IrcAEs Induced by aPD1 Monotherapy Exhibits Stronger Immune Activation Compared to P+C Therapy
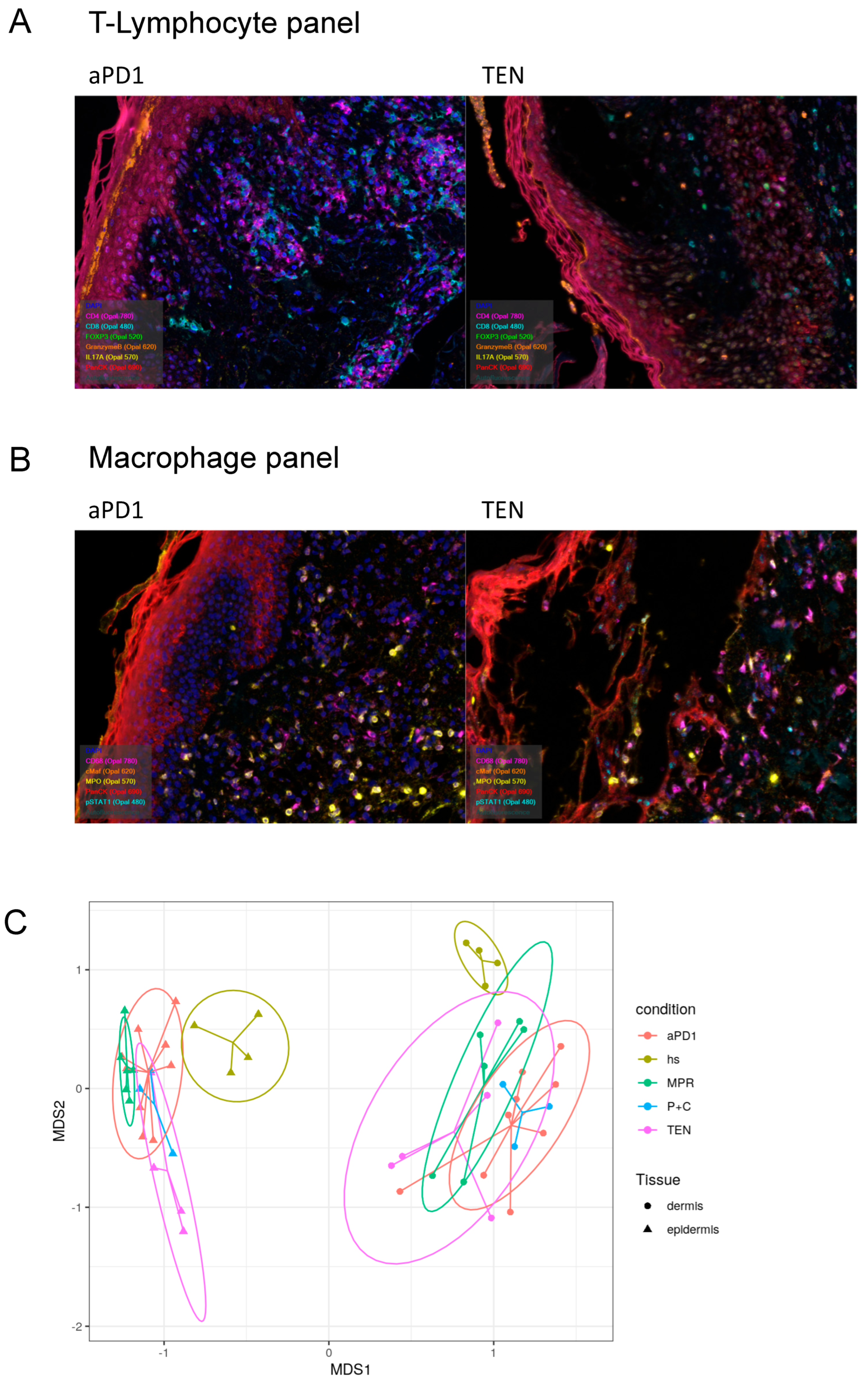
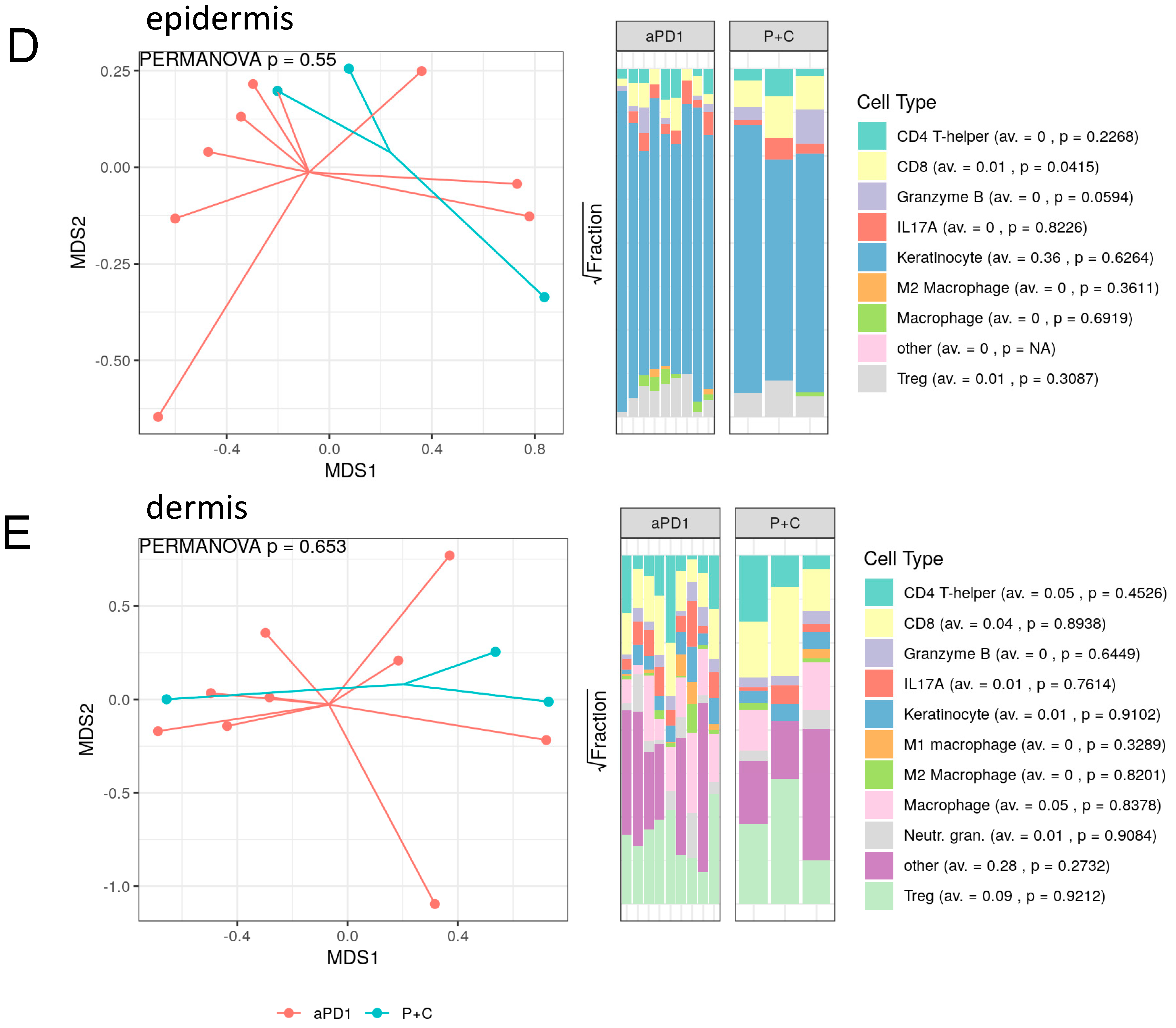
3.3. Spatial Assessment of Immune Infiltrates Reveals Distinct Cell Population Patterns in ircAEs and Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ircAEs | immune-related cutaneous adverse events |
| irAEs | immune-related adverse events |
| P+C | combined immunotherapy regimen |
| MPR | maculopapular rash |
| TEN | toxic epidermal necrolysis |
| PD1 | programmed cell death 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed cell death 1 ligand |
| CTLA4 | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| KEK | Cantonal Ethics Committee of the Canton of Zurich, Switzerland |
References
- Decker, W.K.; da Silva, R.F.; Sanabria, M.H.; Angelo, L.S.; Guimarães, F.; Burt, B.M.; Kheradmand, F.; Paust, S. Cancer Immunotherapy: Historical Perspective of a Clinical Revolution and Emerging Preclinical Animal Models. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Thomas, L.; Bondarenko, I.; O’Day, S.; Weber, J.; Garbe, C.; Lebbe, C.; Baurain, J.F.; Testori, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Kluger, H.; Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Segal, N.H.; Ariyan, C.E.; Gordon, R.A.; Reed, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, M.; Burotto, M.; Richardet, M.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Gonçalves, A.; Steeghs, N.; Schoffski, P.; Ascierto, P.A.; Maio, M.; Lugowska, I.; et al. Randomized, open-label, phase 2 study of nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab monotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors of high tumor mutational burden. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettinger, S.N.; Redman, M.W.; Bazhenova, L.; Hirsch, F.R.; Mack, P.C.; Schwartz, L.H.; Bradley, J.D.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Leighl, N.B.; Ramalingam, S.S.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab vs Nivolumab for Previously Treated Patients With Stage IV Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: The Lung-MAP S1400I Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Castillo Gutiérrez, E.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtari, A.N.; Friedman, C.F.; Navid-Azarbaijani, P.; Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Momtaz, P.; Panageas, K.S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chapman, P.B. Measuring Toxic Effects and Time to Treatment Failure for Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Melanoma. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibaud, V. Dermatologic Reactions to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Skin Toxicities and Immunotherapy. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, A.N.; Phillips, G.S.; Barrios, D.M.; Wu, J.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Moy, A.P.; Kern, J.A.; Lacouture, M.E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related dermatologic adverse events. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walocko, F.M.; Ly, B.C.; White, M.S.; Chen, S.C.; Yeung, H. Health-related quality of life measures and immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattersall, I.W.; Leventhal, J.S. Cutaneous Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: The Role of the Dermatologist. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2020, 93, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; Ketosugbo, K.; Kern, J.A.; Lacouture, M.E.; Leung, D.Y.M. Immune-related cutaneous adverse events due to checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, G.S.; Wu, J.; Hellmann, M.D.; Postow, M.A.; Rizvi, N.A.; Freites-Martinez, A.; Chan, D.; Dusza, S.; Motzer, R.J.; Rosenberg, J.E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes of Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.K.; Neulinger, M.M.; Stadler, P.-C.; Aoki, R.; French, L.E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced epidermal necrolysis: A narrative review evaluating demographics, clinical features, and culprit medications. J. Dermatol. 2024, 51, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, J.T.; Guillet, C.; Oschmann, A.; Maul, L.V.; Meier-Schiesser, B.; Stadler, P.C.; French, L.E.; Kerl, K. Cutaneous lichenoid drug eruptions: A narrative review evaluating demographics, clinical features and culprit medications. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibaud, V.; Meyer, N.; Lamant, L.; Vigarios, E.; Mazieres, J.; Delord, J.P. Dermatologic complications of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, A.; Jackson, C.; Harun, N.; Cooper, A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: Review of pathogenesis and management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergen, E.N.; Hughey, L.C. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrella-Alonso, A.; Aramburu, J.A.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, M.Y.; Cachafeiro, L.; Sanchez, M.S.; Lorente, J.A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: A paradigm of critical illness. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiv. 2017, 29, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoetzenecker, W.; Mehra, T.; Saulite, I.; Glatz, M.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Guenova, E.; Cozzio, A.; French, L.E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. F1000Research 2016, 5, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.; Bensussan, A.; Bachot, N.; Bagot, M.; Boumsell, L.; Roujeau, J.-C.; Dorothée, G.; Mami-Chouaib, F. Drug Specific Cytotoxic T-Cells in the Skin Lesions of a Patient with Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard, I.; Wehrli, P.; Bullani, R.; Schneider, P.; Holler, N.; Salomon, D.; Hunziker, T.; Saurat, J.-H.; Tschopp, J.; French, L.E. Inhibition of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis by Blockade of CD95 with Human Intravenous Immunoglobulin. Science 1998, 282, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.-H.; Hung, S.-I.; Yang, J.-Y.; Su, S.-C.; Huang, S.-P.; Wei, C.-Y.; Chin, S.-W.; Chiou, C.-C.; Chu, S.-C.; Ho, H.-C.; et al. Granulysin is a key mediator for disseminated keratinocyte death in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldinger, S.M.; Stieger, P.; Meier, B.; Micaletto, S.; Contassot, E.; French, L.E.; Dummer, R. Cytotoxic Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions during Anti-PD-1 Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4023–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Lun, A.T.L.; Baldoni, P.L.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR 4.0: Powerful differential analysis of sequencing data with expanded functionality and improved support for small counts and larger datasets. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hu, E.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; et al. Using clusterProfiler to characterize multiomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3292–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y. mixR: An R package for Finite Mixture Modeling for Both Raw and Binned Data. J. Open Source Softw. 2022, 7, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apalla, Z.; Nikolaou, V.; Fattore, D.; Fabbrocini, G.; Freites-Martinez, A.; Sollena, P.; Lacouture, M.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; Stratigos, A.; Peris, K.; et al. European recommendations for management of immune checkpoint inhibitors-derived dermatologic adverse events. The EADV task force ‘Dermatology for cancer patients’ position statement. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.M.; Gu, S.; Stoll, J.; Moy, A.P.; Dusza, S.W.; Gordon, A.; Haliasos, E.C.; Janjigian, Y.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; Quigley, E.A.; et al. Management of immune-related cutaneous adverse events with dupilumab. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.M.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; King, S.; Leung, D.Y.; Goleva, E.; Moy, A.P.; Lacouture, M.E.; Shah, N.J.; Faleck, D.M. Contribution of the Skin–Gut Axis to Immune-Related Adverse Events with Multi-System Involvement. Cancers 2022, 14, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, M.E.; Goleva, E.; Shah, N.; Rotemberg, V.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; Ketosugbo, K.F.; Merghoub, T.; Maier, T.; Bang, A.; Gu, S.; et al. Immunologic Profiling of Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events with Checkpoint Inhibitors Reveals Polarized Actionable Pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2822–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Schiesser, B.; Zecha, C.; Zierold, S.; Kolm, I.; Röckel, M.; Fröhlich, W.; Mittag, N.; Schmitt, C.; Kumbrink, J.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Checkpoint inhibitor–induced lichen planus differs from spontaneous lichen planus on the clinical, histological, and gene expression level. JAAD Int. 2024, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
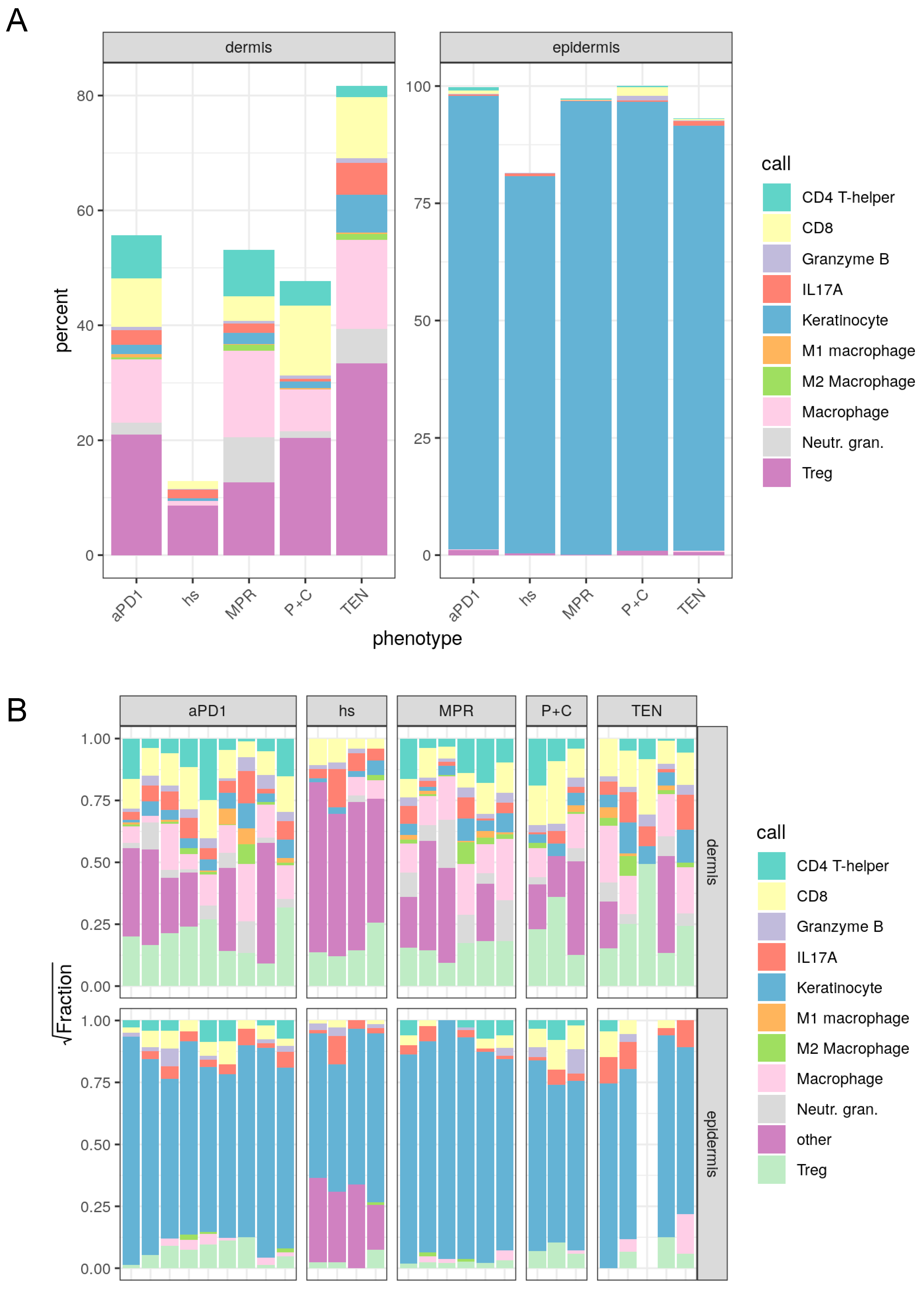
| hs | aPD1 | P+C | MPR | TEN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4 T-helper | 0.0000000 | 7.8935707 | 4.1027254 | 9.1723890 | 1.4977364 |
| CD8 | 1.4211965 | 8.7100173 | 11.6251376 | 4.6560604 | 12.3676716 |
| Granzyme B | 0.0971758 | 0.6571705 | 0.5572157 | 0.5788885 | 0.4311665 |
| IL17A | 1.5851807 | 2.6123781 | 0.3999371 | 1.9213111 | 5.3736966 |
| Keratinocyte | 0.3826298 | 1.6830588 | 1.0515200 | 2.2456883 | 5.1785370 |
| Ml macrophage | 0.0000000 | 0.8402752 | 0.7010133 | 0.1317470 | 0.4311665 |
| M2 macrophage | 0.1457637 | 0.4612456 | 0.0943672 | 1.2426142 | 1.7473591 |
| Macrophage | 1.5669602 | 10.6953243 | 10.4410542 | 17.5712632 | 19.2549896 |
| Neutr. gran. | 0.1457637 | 2.1646494 | 1.5233559 | 9.4169195 | 1.9459226 |
| Treg | 8.5089584 | 22.1494046 | 19.5564743 | 14.6718301 | 37.8110356 |
| Other | 86.1463711 | 42.1329056 | 49.9471993 | 38.3912887 | 13.9607185 |
| Call | hs | aPD1 | P+C | MPR | TEN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD4 T-helper | 0.0000000 | 1.0734042 | 0.2959414 | 0.4121304 | 0.0795281 |
| CD8 | 0.0795042 | 0.7045840 | 1.7051860 | 0.1803070 | 0.7157532 |
| Granzyme B | 0.1734637 | 0.3293258 | 1.6065389 | 0.0901535 | 0.6362251 |
| IL17A | 0.6017021 | 0.3091041 | 0.2113867 | 0.1442456 | 1.9285572 |
| Keratinocyte | 80.1618994 | 95.9794184 | 95.1803833 | 98.9585122 | 93.7239048 |
| M2 macrophage | 0.0216830 | 0.0259994 | 0.0000000 | 0.0257581 | 0.0000000 |
| Macrophage | 0.0000000 | 0.2729938 | 0.0422773 | 0.1030326 | 1.5905627 |
| Treg | 0.5637569 | 1.3051703 | 0.9582864 | 0.0858605 | 1.3254689 |
| Other | 18.3979907 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kraehenbuehl, L.; Winkelbeiner, N.; Turko, P.; Staeger, R.; Ghosh, A.; Kaiser, V.; Stadler, P.-C.; Nordmann, T.M.; Brüggen, M.-C.; Levesque, M.P.; et al. Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events Display Distinct Clinical and Molecular Characteristics, Depending on Immune Checkpoints Targeted. Cancers 2025, 17, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121992
Kraehenbuehl L, Winkelbeiner N, Turko P, Staeger R, Ghosh A, Kaiser V, Stadler P-C, Nordmann TM, Brüggen M-C, Levesque MP, et al. Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events Display Distinct Clinical and Molecular Characteristics, Depending on Immune Checkpoints Targeted. Cancers. 2025; 17(12):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121992
Chicago/Turabian StyleKraehenbuehl, Lukas, Nicola Winkelbeiner, Patrick Turko, Ramon Staeger, Adhideb Ghosh, Vivienn Kaiser, Pia-Charlotte Stadler, Thierry M. Nordmann, Marie-Charlotte Brüggen, Mitchell P. Levesque, and et al. 2025. "Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events Display Distinct Clinical and Molecular Characteristics, Depending on Immune Checkpoints Targeted" Cancers 17, no. 12: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121992
APA StyleKraehenbuehl, L., Winkelbeiner, N., Turko, P., Staeger, R., Ghosh, A., Kaiser, V., Stadler, P.-C., Nordmann, T. M., Brüggen, M.-C., Levesque, M. P., Contassot, E., French, L. E., Dummer, R., & Meier-Schiesser, B. (2025). Immune-Related Cutaneous Adverse Events Display Distinct Clinical and Molecular Characteristics, Depending on Immune Checkpoints Targeted. Cancers, 17(12), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121992







