Simple Summary
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States and worldwide. Advances in molecular profiling and targeted therapies have significantly transformed the treatment landscape for non-small cell lung cancer, especially among patients with oncogene-driven subtypes, leading to marked improvements in clinical outcomes. Despite these strides, disparities in access to molecular diagnostics and precision therapies persist, disproportionately impacting minority populations. These inequities result in lower rates of molecular testing, reduced access to specialized treatments, and underrepresentation in clinical trials, thereby limiting the generalizability of trial findings to diverse populations. In this review, we examine the current state of molecular diagnostics and precision medicine for minority patients with oncogene-driven lung cancer, emphasizing existing challenges, emerging opportunities, and future strategies to promote equity in precision oncology.
Abstract
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related death in the US and worldwide. Recent advances in molecular profiling and targeted therapies have revolutionized the management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), particularly in oncogene-driven subtypes. These therapies selectively target key molecular alterations in EGFR, ALK, KRAS, ROS1, MET, RET, ERBB2 (HER2), BRAF V600E, and NTRK, resulting in substantial improvements in survival rates and quality of life for lung cancer patients. However, disparities in molecular diagnostics and precision treatments persist, disproportionately affecting minority patients. These inequities include underrepresentation in clinical trials, disparities in molecular testing, and barriers to treatment access. The limited participation of racial and ethnic minorities in landmark clinical trials raises concerns about the generalizability of findings and their applicability to diverse populations. In this review, we examine the current landscape of molecular diagnosis and precision medicine in minority patients with oncogene-driven lung cancer, highlighting challenges, opportunities, and future directions for achieving equity in precision oncology. Additionally, we discuss differences in the prevalence of oncologic driver mutations across populations and emphasize the urgent need for greater diversity in clinical research. Addressing these gaps is critical to improving survival outcomes and ensuring equitable access to personalized lung cancer care for all patients.
1. Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the United States and globally [1], with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounting for the majority of cases. Over the past decade, the advent of molecular profiling and targeted therapies has transformed the management of NSCLC, particularly for patients with oncologic driver alterations, such as EGFR mutations, ALK rearrangement, RET rearrangement, ROS1 rearrangement, MET exon 14 skipping alterations, BRAF V600E, KRAS G12C, and ERRB2 (HER2) mutations, NTRK1/2/3 rearrangements, and NRG1 fusions. The development of targeted therapies for these molecular alterations has led to significant improvements in clinical outcomes, offering more effective and personalized treatment options for patients [2].
As impactful as these developments have been for patients with NSCLC, their generalizability to racial and ethnic minorities has been limited by the under-representation of minority patients in landmark clinical trials involving targeted therapies [3,4,5]. Recent studies have shown that Black and Hispanic/Latino patients have less than 5% enrollment in clinical trials, respectively, resulting in a gap in knowledge of clinical outcomes for these patients [6]. Additionally, evidence suggests that African American patients may have a distinct prevalence of driver alterations (Table 1 and Figure 1) and varying responses to treatment compared to White and Asian patients [7,8,9,10,11].
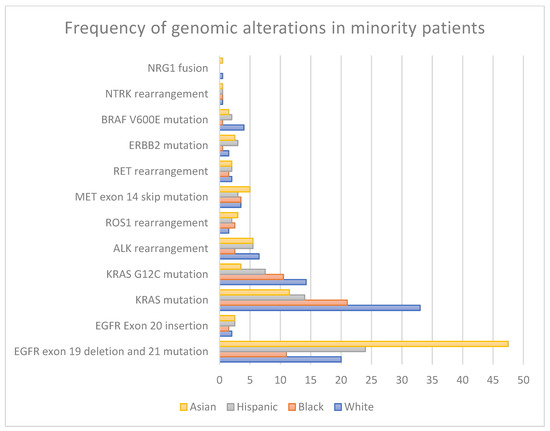
Figure 1.
Genomic alteration prevalence across racial groups.
Socioeconomic determinants such as income status and access to health insurance may also constitute potential barriers to care for these populations that ultimately impact their adherence to treatments and clinical outcomes. These socioeconomic disparities have become more salient as targeted therapies have become more widely employed in the frontline setting [8,12].
In this review, we examine the current landscape of molecular diagnosis and treatment for minority patients with oncogene-driven lung cancer. We will highlight the current challenges and barriers to accessing guideline-directed standard of care as well as the differences in the prevalence of oncogenic driver mutations across populations, emphasizing the need for greater diversity in clinical research to make results more applicable to minority populations. Addressing these gaps is critical to improving survival outcomes in minority populations and ensuring equitable access to personalized lung cancer care for all patients.

Table 1.
Frequency of genomic alterations in minority patients.
Table 1.
Frequency of genomic alterations in minority patients.
| Genomic Alteration | White or Caucasian | Black or African American | Hispanic or Latino | Asian |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR mutations: Exon 19 Deletion Exon 21 L858R | 10–20% [13,14,15,16] | 5–17% [13,14,15,16,17] | 22–26% [18,19] | 40–55% [13,14,15,20] |
| EGFR mutations: Exon 20 Insertion | 1–2% [21] | 1–2% [22] | 2–3% [21,22,23] | 1–4% [21,22,24] |
| KRAS mutations | 26–33% [25,26] | 15–27% [13,26] | 9–19% [18,23] | 11–12% [25,26] |
| KRAS G12C mutation | 13–15.5% [26,27] | 10–11% [26,28] | 7–8% [18] | 3–4% [26,27] |
| ALK rearrangement | 6–7% [25,29] | 1–4% [26,30,31] | 5–6% [12,18] | 5–6% [25,32] |
| ROS1 rearrangement | 1–2% [26,33,34] | 2–3% [26] | 2% [18] | 2–4% [35,36] |
| MET Exon 14 Skipping Alteration | 2–5% [26,37] | 3–4% [26,37] | 3% [18,26] | 1–9% [37,38] |
| RET rearrangement | 1–3% [26,39] | 1–2% [26] | 2% [18] | 1–3% [26,40] |
| ERBB2 mutation | 1–2% [25,26] | <1% [16,26] | 3% [18] | 2–3% [26] |
| BRAF V600E mutation | 3–5% [41,42] | <1% [16] | 2% [18] | 1–2% [43] |
| NTRK rearrangement | <1% [26] | <1% [26] | 1% [18,26] | <1% [26] |
| NRG1 fusion | 0–1% [44] | NR * | NR * | 0–1% [44] |
* Not Reported.
2. Molecular Diagnosis in Minority Patients: Access to Screening, NGS Testing, and Treatment
Lung cancer screening (LCS) is currently recommended by the United States Preventive Services Task Force for patients aged 50–80 years with a history of smoking 20-pack years or more and who are currently smoking or quit within the past 15 years [45,46]. This recommendation is based on the mortality benefit associated with early detection of lung cancer in 2 large, randomized trials: the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) and the NELSON trial [47,48]. A subgroup analysis of the NLST confirmed this mortality benefit in Black patients, though only 4.5% of enrolled patients were Black [49]. The guidelines were revised in 2021 to lower the age of screening from 55 to 50 years and decrease smoking exposure from 30 pack years to 20 pack years to accommodate minority patients, who have a lower pack year smoking history and a lower age at diagnosis than White patients [45,46,50]. This change has corresponded to an increase in LCS eligibility for minority patients, with a 109% increase seen for Black patients and an 86% increase seen for Hispanic patients [51].
Unfortunately, adherence to LCS in the real world is significantly lower than in randomized clinical trials. Lopez-Olivo et al. found a pooled LCS adherence rate of 55% in a systematic review and meta-analysis of 15 cohort studies with a total of 16, 863 individuals [52]. Current smokers and non-White patients have the lowest adherence rates [52,53]. This is reflected in the current disparity of early NSCLC diagnosis in minority patients, with Black patients 15% less likely to be diagnosed early than White patients, and Latino, Asian American, and Pacific Islander patients are 17% less likely to be diagnosed early compared to White patients [54].
Current standard practice after the confirmation of a new diagnosis of advanced NSCLC includes tissue- and/or liquid-based next-generation sequencing (NGS) to identify targetable genomic alterations and guide treatment decisions. More comprehensive molecular analysis with the identification of co-mutations, tumor mutational burden, and non-coding RNA can further optimize treatment selection [55]. Unfortunately, the prevalence of testing in the United States is only 50–60%, with a greater likelihood of testing in patients who have favorable socioeconomic strata, insurance access, a younger age, and access to hospitals and clinical trials [56]. Asians, Blacks, and Hispanics are less likely than Whites to receive the recommended molecular testing necessary for the receipt of targeted therapies [57]. This was demonstrated by Bruno et al., who illustrated that Black patients with NSCLC are less likely than White patients to undergo NGS testing before first line of therapy (36.6% versus 29.7%, p < 0.0001) or at any time point thereafter (54.7% versus 43.8%, p < 0.0001) [58].
Cost remains a significant barrier to accessing genomic and NGS testing, which is compounded by variability in insurance coverage [59]. Additionally, historical disparities in the healthcare system may have contributed to varying levels of patient trust, especially in the adoption of newer technologies [60]. Disparities in access to molecular testing can lead to suboptimal treatment outcomes and higher treatment-related mortality. This is particularly concerning for patients with certain targetable mutations (e.g., EGFR, ALK), who may face an increased risk of immune-related adverse events when treated with immunotherapy prior to starting targeted therapy due to delayed molecular testing [61].
Disparities in access to treatment also persist for minority patients. Studies suggest that Latino individuals are 30% less likely to receive treatment than White patients [54,62]. Black patients are less likely to receive surgical treatment than White patients for early-stage disease after adjustment for age, insurance status, TNM stage, income, and treatment at academic versus community hospitals [63]. These factors, combined with other barriers such as lack of awareness about clinical trials, restricted access to trial opportunities, socioeconomic constraints, competing responsibilities, provider biases, and clinical trial study design and enrollment criteria, also contribute to the underrepresentation of minority populations in clinical research. Addressing these challenges is essential to building a culturally competent healthcare structure and advancing equitable healthcare outcomes [64,65].
3. Treatment of Minority Patients with Oncogene Drivers: The Lack of Representation in Landmark Clinical Trials
Disparities in minority access to clinical trials have extended into the evaluation of targeted therapies for oncogene-driven NSCLC, which have played a pivotal role in reshaping the treatment paradigm of this disease. As a result, real-world population-based studies have increasingly been used as surrogates to clinical trials to help generalize findings to underrepresented populations. In the following sections, we review the common genomic oncogenic driver alterations with FDA-approved targeted therapies and assess the representation of minoritized populations in both landmark clinical trials and real-world settings. The mechanisms of action for currently approved targeted therapies are illustrated in Figure 2. Key clinical trials and real-world studies supporting these therapies are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.
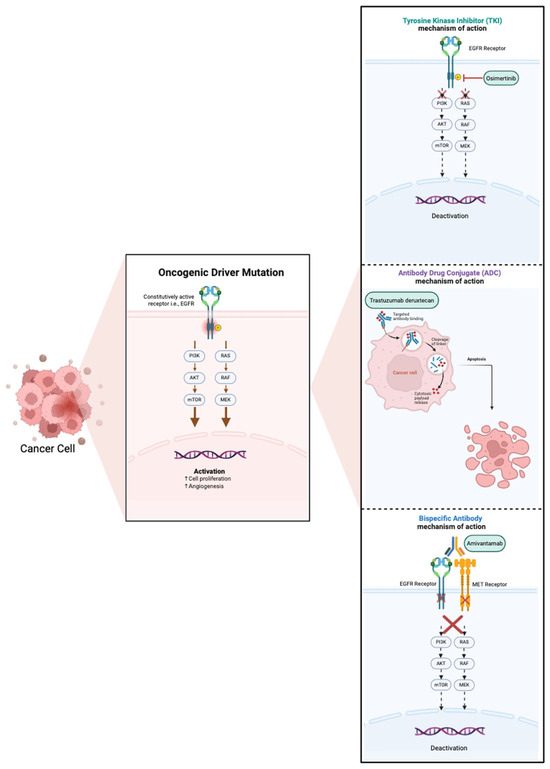
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of current FDA-approved targeted therapies.
3.1. EGFR Mutations
EGFR mutations are common targetable mutations in NSCLC, occurring in 10–20% of Caucasian patients and up to 40–50% of Asian patients [13,14,15,20]. These mutations are also common in Hispanic patients, occurring at a frequency of 22–26% [18,19]. In African American patients, these mutations are less common, occurring at a frequency of 5–17% [13,14,15,16,17,66]. 85–90% of all EGFR mutations in NSCLC consist of Exon 19 deletions and point mutations of L858R in Exon 21 [67].
Osimertinib, the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is the current standard first-line TKI for EGFR-mutated (exon 19 deletion or L858R) NSCLC. Osimertinib demonstrated superiority over earlier generations of EGFR TKIs (erlotinib and gefitinib) in the FLAURA trial with median progression-free survival (PFS) of 18.2 months as compared to 10.2 months with erlotinib and gefitinib (HR 0.46, CI 0.37–0.57) and a mean overall survival (OS) of 38.6 months as compared to 31.8 months with erlotinib and gefitinib (HR 0.8, 95% CI 0.64–1) [68,69]. More recently, an improved PFS has also been shown with the addition of chemotherapy to osimertinib in the FLAURA-2 study [3] and with the combination of amivantamab, an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, and lazertinib, another third-generation EGFR TKI, in the MARIPOSA study [70]. There is ongoing discussion on which patients benefit from first-line treatment intensification and how to incorporate these recent studies into the standard treatment paradigm for advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
There is, however, limited data from these pivotal trials on the outcomes for African American and Hispanic patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Most patients enrolled in these trials were White and Asian, with ≤1% of African American patients in the FLAURA and FLAURA 2 trials [3,69] and 5% of other patients (Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, multiple, unknown, and not reported) enrolled in the MARIPOSA trial [70]. The enrollment of Hispanic patients is not specified in any of the trials [3,69,70].
Real-world analysis on the outcomes of osimertinib in ethnic minorities has shown equivalent outcomes in Hispanic patients and worse outcomes in African American patients [19,23]. Inferior survival outcomes have been previously described in real-world analysis of African American patients on erlotinib and gefitinib for EGFR-mutated lung cancer [17]. In contrast, real-world analysis of Hispanic patients on EGFR TKI has shown similar outcomes to non-Hispanic patients with a median PFS of 14.4–15.9 months and OS of 32 months [19,23].
The use of osimertinib has also recently been expanded to earlier stages of NSCLC.

Table 2.
Treatment of minority patients with oncogene drivers: the lack of representation in landmark clinical trials.
Table 2.
Treatment of minority patients with oncogene drivers: the lack of representation in landmark clinical trials.
| Genomic Alteration | Treatment | Key Trials (Phase, n) | Racial/Ethnic Breakdown (%) | OS (%)/mOS | PFS (mo) | Other Endpoints | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | Hispanic | Asian | White | |||||||
| EGFR Exon 19 deletion and Exon 21 L858R | Osimertinib | FLAURA (III, 556) | - | - | 62 | 36 | 3 years OS 28 (Osi) vs. 9 (GE) | 18.9 (Osi) vs. 10.2 (GE) | ORR 80% (Osi) vs. 76% (GE) | [69] |
| Osi ± C | FLAURA2 (III, 557) | <1 | - | 64 | 28 | 2 years OS 79 (Osi + C) vs. 73 (Osi) | 25.5 (Osi + C) vs. 16.7 (Osi) | ORR 92% (Osi + C) vs. 83% (Osi) | [3] | |
| Osimertinib | ADAURA (III, 682) | - | - | 64 | - | 5 years OS 88 (Osi) vs. 78 (P) | NE | DFS 65.8 (Osi) vs. 28.1 (P) | [71,72,73] | |
| Osimertinib | LAURA (III, 216) | - | - | 81 | - | NR (interim) | 39.1 (Osi) vs. 5.6 (placebo) | ORR 57% (Osi) vs. 33% (P) DoR 36.9 mo (Osi) vs. 6.5 mo (P) | [74] | |
| Ami + Laz | MARIPOSA (III, 858) | <1 | - | 58 | 38 | 2 years OS 74 (Ami + Laz) vs. 69 (Osi) | 23.7 (Ami + Laz) vs. 16.6 (Osi) | ORR 86% (Ami + Laz) vs. 85% (Osi) | [70] | |
| Ami + C ± Laz | MARIPOSA-2 (III, 657) | - | - | 48 | 48 | NR (interim) | 6.3 (Ami + C) vs. 8.3 (Ami + Laz + C) vs. 4.2 (C) | ORR 64% (Ami + C) vs. 63% (Ami + Laz + C) vs. 36% (C) | [5] | |
| EGFR Exon 20 insertion | Amivantamab | CRYSALIS (I, 158) | <1 | - | 56 | 35 | 22.8 mo (Ami) | 8.3 (Ami) | ORR 40%, DOR 11.1 mo | [75] |
| PAPILLON (III, 308) | <0.01 | - | 60 | 35 | 2 years OS 72 (Ami + C) vs. 54 (C) | 11.4 mo (Ami + C) vs. 6.7 (C) | ORR 73% (Ami + C) vs. 47% (C) | [76] | ||
| KRAS G12C mutation | Sotorosib | CodeBreaK 100 (I/II, 126) | 2 | - | 15 | 82 | 12.5 mo | 6.3 | ORR 41% | [77] |
| CodeBreaK 200 (III, 345) | <0.01 | - | 12 | 83 | 10.6 mo (Soto) vs. 11.3 mo (Dt) | 5.6 (Soto) vs. 4.5 (Dt) | ORR 28.1% (Soto) vs. 13.2% (Dt) | [78] | ||
| Adagrasib | KRYSTAL-1 (I/II, 116) | 8 | - | 4 | 84 | 12.6 mo (interim) | 6.5 | ORR 42.9% | [79] | |
| ALK rearrangement | Alectinib | ALEX (III, 303) | - | - | 46 | - | NR (interim for both groups) | 34.8 (Alec) vs. 10.9 (Cri) | ORR 82.9% (Alec) vs. 75.5% (Cri) | [80] |
| ALINA (III, 257) | <0.01 | - | 56 | 42 | NR (interim) | DFS NR (Alec) vs. 41.3 mo (C) | 3y-DFS 88.7% (Alec) vs. 54% (C) | [4] | ||
| Brigatinib | ALTA-1L (III, 275) | - | - | 39 | - | 4 years OS 66 (Bri) vs. 60 (Cri) | 24 (Bri) vs. 11 (Cri) | ORR 71% (Bri) vs. 60% (Cri) | [81,82] | |
| Lorlatinib | CROWN (III, 296) | <0.01 | - | 44 | 49 | NR (second interim) | NR (Lor) vs. 9.1 (Cri) | ORR 81% (Lor) vs. 63% (Cri) | [83,84] | |
| ROS1 rearrangement | Entrectinib | ALKA-372-001 (I, 1) STARTRK-1 (I, 2) STARTRK-2 (II, 51) | - | - | 13 | 80 | 21 mo | 11.2 | ORR 57%, DOR 10.4 mo | [85] |
| Repotrectinib | TRIDENT-1 (I/II, 127) | - | - | 59 | 34 | NE (TN), 25.1 mo (PT) | 35.7 (TN), 9 (PT) | ORR 79% (TN), 38% (PT) DOR 34.1 mo (TN), 14.8 mo (PT) | [86] | |
| MET Exon 14 skipping mutation | Capmatinib | GEOMETRY mono-1 (II, 160) | - | - | 19 | 77 | NR (expansion cohort) | 12.4 (TN) 5.4 (PT) | ORR 68% (TN), 41% (PT) DOR 12.6 mo (TN), 9.7 mo (PT) | [87,88] |
| Tepotinib | VISION (II, 99) | - | - | 21 | 75 | NR (interim) | 8.5 | ORR 46%, DOR 11.1 mo | [89] | |
| RET rearrangement | Selperactinib | LIBRETTO -001 (I/II, 316) | <1 | - | 41 | 49 | 3 years OS 66 (TN), 57 (PT) | 22 (TN), 26.2 (PT) | ORR 82.6% (TN), 61.5% (PT) | [90,91] |
| Pralsetinib | ARROW (I/II, 233) * | - | - | 39 | 52 | NR (interim) | 10.9-NR (TN) vs. 12.8–16.5 (PT) | ORR 68–79% (TN), 59–73% (PT) | [92] | |
| BRAF V600E mutation | Dabrafenib/Trametinib | NCT01336634 (II, 93) | 3 | - | 8 | 85 | 5 years OS 22 (TN), 19 (PT) | 10.8 (TN), 10.2 (PT) | ORR 63.9% (TN), 68.4% (PT) | [93] |
| Encorafenib/Binimetinib | PHAROS (II, 98) | 3 | - | 7 | 88 | NE | NE (TN), 9.3 (PT) | ORR 75% (TN), 46% (PT) | [94] | |
| ERBB2 mutation | T-Dxd | DESTINY-Lung 01 (II, 91) | 1 | - | 34 | 44 | 17.8 mo | 8.2 | ORR 55%; DOR 9.3 mo | [95] |
Ada, adagrasib; Alec, alectinib; Ami, amivantamab; Bri, brigatinib; C, platinum-doublet chemotherapy; Cri, crizotinib; DFS, disease free survival; DOR, duration of response; Dt, docetaxel; GE, gefitinib or erlotinib; HR, hazard ratio; Laz, lazertinib; Lor, lorlatinib; Mo, months; NE, Not evaluated; NR, not reached; ORR, objective response rate; OS, overall survival; Osi, osimertinib; P, placebo; PFS, progression-free survival; PT, previously treated; Ref, references; Soto, sotorosib; T-Dxd, trastuzumab deruxtecan; TN, treatment naiive; VS, versus. * Eligibility changes.

Table 3.
Treatment of minority patients with oncogene drivers: clinical outcomes in real-world studies.
Table 3.
Treatment of minority patients with oncogene drivers: clinical outcomes in real-world studies.
| Mutation | Treatment | Racial/Ethnic Background | ORR | OS (95% CI) | PFS (95% CI) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR Exon 19 Deletion and Exon 21 L858R | erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib | Black 36% Non-Black 64% | Blacks 63.6% Non-Black 76.0% | 2-year survival rates: Black 33.3% Non-Black 61.3% | NA | [17] |
| EGFR TKIs | Hispanic 100% | 60.5% (52.10–69.09) | 32 mo (12.4–20.6 mo) | 15.9 mo (12.4–20.6 mo) | [23] | |
| Osimertinib | Hispanic 100% | NA | NA | 14.4 mo (95% CI 12.4–18.2 mo) | [19] | |
| EGFR Exon 20 Insertion | C 54% IO 15% EGFR Targeted Therapy 12% Surgery 24% | White 63% Asian 3.1% Black 9% Hispanic 2% | NA | 23.8 mo in the entire group 17 mo in Stage IV patients | NA | [22] |
| C 52.7% C + Bev 11.8% C+ Pem 4.3% 1G TKIs 21.5% Osi 3.2% Afatinib 3.2% Exon20 inh 5.2% | Hispanic 100% | NA | C + Bev 18 vs. 14.5 mo (HR = 0.57, 0.36–0.90) 1 G TKIs 16.36 vs. C 14.5 mo (HR = 0.49, 0.25–0.98) Osi 19.4 vs. C 14.5 mo (HR = 0.13; 0.02–0.82) Exon20 inhibitors 25.6 vs. C 15 mo (HR = 0.26, 0.06–1.07) | C + Bev 5.35 vs. C 4.8 mo (HR = 0.47; 0.24–0.89) TKIs 6.6 vs. C 4.8 mo (HR = 0.36, 0.21–0.61) C + Pem 5.53 vs. C 4.8 mo (HR = 0.25, 0.06–1.01) | [96] | |
| KRAS G12C mutation | sotorasib v docetaxel | White 71% Black 11% | NA | ≥2L Setting sotorasib 10.2 mo (8–14.6 mo) docetaxel 7.2 mo (5.1–10.6 mo) | NA | [97] |
| sotorasib | White 77% Black 19% Hispanic 2% | 34% | 12 mo (10.2–16.5) | 6 mo (4.3–8.1) | [98] | |
| sotorasib | White 81% Asian 4% Black 6% Hispanic 3% | 28% | 12.6 months (8.3 mo—NA) | 5.3 months (3.6–6.6 mo) | [99] | |
| ALK Rearrangements | alectinib 59.8% crizotinib 40.2% | White 45.3% Asian 30.8% Black 2.6% | NA | alectinib 54.1 mo crizotinib 45.8 mo | alectinib 29.3 mo crizotinib 10.4 mo | [100] |
| alectinib 30.4% crizotinib 69.6% | alectinib White 60.3% Asian 14.9% Black 4.3% Hispanic 3.5% crizotinib White 65.9% Asian 5.4% Black 6.3% Hispanic 5.8% | alectinib 78.7% (71–85.2) crizotinib 48.9% (42.4–55.6) | alectinib NR (29.2-NR) crizotinib 23 mo (17–33.5) | alectinib 24.5 mo (15.8-NR) crizotinib 12 mo (9.3–14.4) | [101] | |
| ROS1 Rearrangements | entrectinib, crizotinib | entrectinib White 49% Asian 44% Black 4% Hispanic 1% crizotinib White 54% Asian 9% Black 12% Hispanic 17% | NA | entrectinib NR crizotinib 18.5 mo (15.1–47.2 mo) | entrectinib 16.8 mo (12–26.3 mo) crizotinib 8.2 mo (6.5–9.9 mo) | [102] |
| MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation | capmatinib 50.9% IO 14.3% C 14.6% C + IO 15% | White 49.1% Black 26.8% Hispanic 9.4% | capmatinib 73.4% IO 68.6% C 52% C + Io 54.8% | capmatinib NE IO NE (14.3 mo-NE) C 17.6 mo (10.9 mo-NE) C + IO 29.9 months (20.2–32.1 mo) | capmatinib NE IO 12.6 mo (11.1 mo-NE) C 10.1 mo (5.9 mo-NE) C + IO 12 months (9–12.6 mo) | [103] |
| capmatinib | White 79.4% Asian 7.4% Black 13.2% Hispanic 19.1% | (1 + 2L) 85.3% (74.6–92.7) 1L 90.9% (80.1–97.0) 2L 61.5% (31.6–86.1) | 1L 14.1 mo (13.9 mo-NE) | Any line 14.5 mo (14.1 mo-NE) 1L 14.1 mo (10.1 mo-NE) | [104] | |
| RET Rearrangements | selpercatinib | Asian 10% Non-Asian 90% | Any line 68% 1L 69% ≥2L 68% | NA | Any line 15.6 mo (8.8–22.4 mo) 1L 15.6 mo ≥ 2L 12.2 mo | [105] |
1G, first generation; 1L, first line; 2L, second line; Bev, Bevacizumab; C, chemotherapy; Exon20 inh anti-EFGR Exon20 inhibitor agents (Amivantamab, Mobocertinib); HR, Hazard Ratio; IO, immunotherapy; Mo, months; NA, Not available; NE, not evaluable NR, not reached; ORR, objective response rate; OS, overall survival; Osi, osimertinib; PFS, progression-free survival; Ref: References; Pem, pembrolizumab; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
The ADAURA trial showed an 80% reduction in the risk of disease recurrence or death with three years of adjuvant osimertinib (HR 0.27, 0.21–0.34) [71,72]. Benefit of adjuvant osimertinib after chemoradiation has also been shown for patients with stage III NSCLC in the LAURA trial, which showed a median PFS of 39.1 months with osimertinib versus 5.6 months with placebo (HR 0.16, 0.10–0.24) [74]. Similarly to the trials for advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC, most patients enrolled in the ADAURA and LAURA trials were also Asian [71,74].
EGFR Exon 20 insertion mutations are the third most common EGFR mutations, accounting for 9% of all EGFR mutations [21]. They are similarly more common in Asian patients (1–4%), with a lower prevalence reported in Hispanic (2–3%) and African American patients (1–2%) [21,22,23,24,106]. Amivantamab was approved as a second-line treatment after progression on platinum doublet chemotherapy (PDC) based on the phase 1 CHRYSALIS trial, with an objective response rate (ORR) of 40% with median PFS of 8.3 months, and a median OS of 22.8 months [75]. More recently, the combination of amivantamab and PDC has been approved as a first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions: The PAPILLON trial reported a median PFS of 11.4 months with the combination of amivantamab-PDC versus 6.7 months with PDC alone (HR 0.40, CI 0.3–0.53) [76].
Real-world studies predating the use of amivantamab have shown a limited median OS of 14–16 months in stage IV patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations [22,96]. Interestingly, a review of the ASCO CancerLinQ Discovery data set did show significantly lower risk of death in African American patients as compared to White patients (HR 0.62, 0.42–0.91), but the stage and treatment for these patients were not specified [22]. A more recent real-world analysis of a cohort of Hispanic patients with NSCLC included 6 patients who received amivantamab and mobocertinib had a median OS of 25.6 months versus 15 months with chemotherapy (HR 0.26, 0.06–1.07), showing efficacy of EGFR Exon 20 insertion inhibiting agents in this population [96].
3.2. KRAS Mutations
KRAS mutations are among the most prevalent driver oncogenes in patients with NSCLC, occurring in 25–30% of non-squamous NSCLC [107]. Unlike EGFR mutations, KRAS mutations are generally associated with smoking and are more commonly found in Caucasians (26–33%) and African Americans (15–27%) than Asians (11–12%) [13,25,26]. Among KRAS mutations, G12C is the most common mutation and is similarly more common in Caucasians (13–15.5%) than African Americans (10–11%) and Asians (3–4%) [26,27]. The frequency of KRAS mutations in Hispanic patients is 9–19%, with G12C similarly being the most frequent mutation, with a 7–8% prevalence [18,23].
Unlike EGFR-mutated or ALK-positive cases, NSCLC patients with KRAS mutations have shown favorable responses to combination chemoimmunotherapy in the first-line setting [108]. Unfortunately, patients who progress beyond the first line of treatment have a poor prognosis with second-line docetaxel with or without antiangiogenic therapy or single-agent pemetrexed [109,110,111]. Sotorasib and adagrasib are the two KRAS G12C inhibitors that were approved for clinical use in the second-line setting and beyond based on their efficacy, safety, and tolerability demonstrated in the phase 2 CodeBreaK 100 and KRYSTAL-1 trials, respectively [77,79,112]. Phase 3 trials comparing the use of sotorasib and adagrasib to docetaxel have confirmed meaningful improvements in median PFS (5.6 months sotorasib versus 4.5 months docetaxel; HR 0.66 in CodeBreaK 200 and 5.49 months adagrasib versus 3.84 months docetaxel; HR 0.58 in KRYSTAL-12), but have not detected a significant difference in OS (median OS of 10.6 months with sotorasib versus 11.3 months with docetaxel; HR 0.96) [78,113]. Most patients enrolled in CodeBreaK 200 for sotorasib were Caucasian; 1.2% of enrolled patients were African Americans [77,79,112]. A greater proportion of African Americans (7.8%) were enrolled in KRYSTAL-1 [78,79,112,113].
Real-world studies (which have included 6–19% African Americans) have confirmed the effectiveness of sotorasib, seen in clinical trials, with a median PFS of 5–6 months and median OS of 10–12 months [97,98,99]. No difference has been seen in response and survival rates according to race. Even though sotorasib was not seen to provide an OS benefit in clinical trials, it remains an option for patients who are unable to tolerate chemotherapy. OS with docetaxel in clinical trials and real-world studies has also been discordant, with docetaxel demonstrating a longer overall survival benefit in clinical trials than in the real-world setting [97].
3.3. ALK Rearrangements
Rearrangements of the ALK gene are present in 3–5% of NSCLC [4,114]. Patients with ALK rearrangements are typically younger, non-smokers, and have a higher likelihood of developing brain metastasis [80]. The frequency of African American patients with ALK rearrangements is lower (1–4%) than that seen in White, Asian, and Hispanic patients [26,31].
Alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib are three next-generation ALK inhibitors that are currently FDA-approved for the treatment of ALK-positive advanced NSCLC. Alectinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor, was evaluated against crizotinib in the ALEX study and showed a median PFS of 35 months (versus 11 months with crizotinib; HR 0.43), lower time to central nervous system (CNS) progression (12% with alectinib versus 45% with crizotinib; HR 0.16) and lower frequency of grade 3–5 adverse events [80,114]. Brigatinib is another second-generation ALK inhibitor that showed comparable efficacy to alectinib against crizotinib in the ALTA 1L trial, though it has been associated with more toxicities, including increased creatinine kinase level and interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis [81,82]. Lorlatinib, a third-generation ALK inhibitor, was evaluated against crizotinib in the CROWN trial with an ORR of 76% (versus 58% with crizotinib) and an impressive 5-year PFS of 60% (versus 8% with crizotinib). Unfortunately, the increased efficacy observed with lorlatinib does come at the cost of more side effects, including hyperlipidemia, edema, and neurocognitive events [83,84,115].
A majority of Caucasian and Asian patients were recruited in the ALEX, ALTA 1L, and CROWN trials [80,82,83]. Real-world studies (including 2–4% African American patients and 3–5% Hispanic patients) have confirmed the effectiveness of alectinib against crizotinib, with a median PFS of 25–29 months (versus 10–12 months with crizotinib) [100,101]. Limited real-world studies are available for brigatinib and lorlatinib use in minority patients.
The use of ALK inhibitors, like EGFR inhibitors, has also been expanded to earlier stages of NSCLC with the ALINA trial that showed a 2-year disease-free survival of 93.8% for patients with stage II or IIIA ALK-positive NSCLC with adjuvant alectinib (versus 63% with PDC; HR 0.24) [4]. Adjuvant alectinib was also associated with an improvement in CNS disease-free survival (HR 0.22, CI 0.08–0.58). Unlike the ADAURA trial in early-stage EGFR-mutated NSCLC, patients did not receive adjuvant PDC in addition to alectinib in the ALINA trial. African American patients were also under-represented in the trial (<1% of patients), limiting its generalizability [4].
3.4. Other Targetable Mutations
ROS1 rearrangements, MET Exon 14 skipping mutations, RET rearrangements, ERBB2 mutations, BRAFV600E mutations, NTRK rearrangements, and NRG1 fusions are all rare driver mutations in NSCLC. It is therefore more difficult to determine the characteristics and outcomes of populations with these mutations, to recruit sufficient patients for large phase 3 trials to evaluate the effectiveness of targeted treatments, and to analyze the use of targeted medications in broader populations in real-world studies.
ROS1 rearrangements occur in 2% of patients with NSCLC and are commonly associated with brain metastasis [85,86,102,116]. Entrectinib, a ROS1, TRK, and ALK TKI, has become a key treatment option for patients with ROS1-rearranged NSCLC. Its approval was supported by three phase 1/2 studies (ALKA-372-001, STARTRK-1, and STARTRK-2), which demonstrated deep and durable responses across a broad range of solid tumors with ROS1 rearrangements [85]. In ROS1 fusion-positive NSCLC, entrectinib demonstrated an ORR of 68%, a median PFS of 15.7 months, and a median OS of 47.8 months [85,102,116]. Entrectinib also has better CNS penetration than its predecessor, crizotinib, with an intracranial ORR of 80%, although response is more limited in patients with prior crizotinib exposure.
Repotrectinib, a ROS1 and TRK TKI, was recently approved after the phase 1/2 TRIDENT-1 study showed an ORR of 79%, 89% intracranial response rate, and median PFS of 35.7 months in patients with no prior exposure to TKIs [86]. Patients who had prior exposure to TKIs (crizotinib 82%, entrectinib 16%) had an ORR of 21% with a median PFS of 9 months and median OS of 25.1 months. Limited real-world analysis is present to confirm the efficacy of entrectinib and repotrectinib.
MET Exon 14 skipping mutations occur in 3–4% of patients with NSCLC, with equivalent distribution among race and geographic region [18,26,37]. Capmatinib and tepotinib are two selective MET inhibitors that were approved for use in newly diagnosed and relapsed patients based on their efficacy and tolerability in the phase 2 GEOMETRY mono-1 and VISION studies, respectively [87,88,89,104]. In the first-line setting, response rates are 57.3% with tepotinib, with a median PFS of 12.6 months and median OS of 21.3 months. In the second line setting, response rates are 45% with tepotinib, with a median PFS of 11 months and median OS of 19.3 months [89,104]. Similar efficacy data are observed with capmatinib.
Both phase 2 trials evaluating selective MET inhibitors enrolled mostly Caucasian (~75%) and Asian patients (~20%). Real-world analyses have confirmed the efficacy of first-line capmatinib in a more diverse population (Black 26.8% and Hispanic 9.4%) with a response rate of 73.4% (versus 52% with chemotherapy alone and 54.8% with chemotherapy and immunotherapy) [103].
RET rearrangements are oncogenic drivers of 1–2% of NSCLC [90]. Similarly to EGFR and ALK alterations, patients with RET rearrangements are less responsive to chemoimmunotherapy in the first-line setting for advanced and metastatic disease [117]. Selpercatinib, a highly selective RET inhibitor, was compared to PDC with or without pembrolizumab in the phase 3 LIBRETTO-431 trial and demonstrated an ORR of 84% (versus 65% with chemoimmunotherapy), intracranial response rate of 82% (versus 58% with chemoimmunotherapy) and median PFS of 24.8 months (versus 11.2 months with chemoimmunotherapy; HR 0.46) [90,118]. Pralsetinib is another selective RET inhibitor that has been approved for use in patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC based on an ORR of 72% seen in the phase 1/2 ARROW trial. Real-world analysis has corroborated the benefit of RET inhibitors with an ORR of 70% and median PFS of 15–16 months, but the populations evaluated in both clinical trials and real-world studies have been mostly Asian and Caucasian [105].
ERBB2 (HER2) mutations occur in ~1–3% of NSCLC [95]. Historically, HER2-targeted therapy has had a limited response in NSCLC, and patients have been treated with standard first-line chemoimmunotherapy, with limited options on progression [119,120]. Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-Dxd) is an antibody-drug conjugate that consists of a humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody linked to a topoisomerase I inhibitor payload that has received tumor-agnostic approval for HER2-positive solid tumors on immunohistochemistry. The use of T-Dxd in the second or greater line of treatment for patients with HER2-mutated NSCLC was evaluated in the DESTINY-Lung01 phase 2 study and showed an ORR of 55% with a median PFS of 8.2 months and median OS of 17.8 months [95].
Activating mutations in BRAF occur in 3–5% of patients with NSCLC [41,42,43,121,122]. The majority of BRAF mutations (≥50%) occur on codon 600 (V600E). BRAF V600E mutated NSCLC has been associated with varying responses to first-line chemoimmunotherapy [42,121,123,124]. Given the efficacy and tolerability of the combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors (dabrafenib and trametinib, encorafenib and binimetinib) in BRAF V600E-mutated melanoma, the combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors was evaluated in BRAF V600E-mutated NSCLC in the phase 2 NCT01336634 and PHAROS studies [125,126,127,128]. The ORR in treatment-naive patients was 65–75% with a median PFS of 30.2 months seen with the combination of encorafenib and binimetinib. In previously treated patients, response rates were 45–63% with a median PFS of 9 months and OS of 17–22 months [93,125,126,127]. Real-world studies have confirmed an ORR of 74.1%, PFS of 19.9 months, and OS of 29.9 months in treatment-naive patients, though in a predominantly Caucasian population [129].
NTRK 1/2/3 rearrangements are extremely rare oncogenic drivers in NSCLC, occurring in ~0.2% of cases [85,116]. Larotrectinib and entrectinib both have tumor-agnostic approval in the treatment of TRK fusion-positive cancers and have demonstrated an ORR of 60–65% in NSCLC with durable responses (median PFS of 22 months and median OS of 39.3 months with larotrectinib) [85,86,116,130].
NRG1 fusions are similarly rare oncogenic drivers of NSCLC, occurring in ~0.2–0.5% of cases [131]. Their presence is enriched in invasive mucinous adenocarcinomas, where incidence has been documented to be as high as 30% in Asian and Caucasian patients [131]. Zenocutuzumab, an IgG1 bispecific antibody directed against HER2 and HER3, was recently approved for patients with advanced NRG1 fusion-positive NSCLC and pancreatic cancer after it demonstrated an ORR of 29% and a median duration of response of 12.7 months in NSCLC in the eNRGy trial [132].
4. Impact of Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities on NSCLC Outcomes
Advances in lung cancer screening, molecular diagnostic techniques, and the advent of targeted treatment have improved mortality for patients with NSCLC. However, non-Hispanic Black men continue to be disproportionately affected with the highest incidence and mortality from lung cancer compared to other racial and ethnic groups [133,134]. Black patients are more likely to be diagnosed with lung cancer at a younger age and to have more advanced-stage disease at diagnosis compared to their White counterparts [64,134]. As highlighted by this review, evidence suggests that Black patients also have a distinct prevalence of driver alterations and worse outcomes on certain targeted therapies. Understanding the biological and socioeconomic factors driving disparities in treatment outcomes is critical in optimizing clinical responses.
Distinctions in risk factors for NSCLC, such as smoking and smoking-related comorbidities, contribute to the disparity in lung cancer incidence and outcomes in racial and ethnic minorities [64,133,135]. Risk of lung cancer correlates more with smoking duration than intensity and hence is higher in Black patients, who tend to smoke fewer packs per day but for a greater number of years [64,136,137]. Differential rates of tobacco cessation after diagnosis can also be seen with increased nicotine dependence from the use of mentholated cigarettes and weaker social supports [64,133,135]. Smoking additionally drives neoantigen richness and somatic mutations, causing heterogeneity across the tumor microenvironment, and may explain the differences in oncogenic driver mutation prevalence and limited responses seen with targeted therapies in minoritized populations.
Racial and ethnic disparities in social determinants of health (i.e., insurance status, transportation, access to primary care) can further exacerbate adverse outcomes [64,133,135]. Geographic and economic disparities in minoritized communities can reduce access to high-quality healthcare, including lung cancer screening, molecular diagnostic testing, and targeted treatments, and have been linked to a higher prevalence of comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease and HIV [138]. Limited job prospects and housing availability for economically compromised populations can lead to significantly increased exposure to workplace carcinogens (i.e., asbestos, silica, radon, arsenic), increasing the risk for developing NSCLC [64,136,139]. Redlining has additionally been associated with later-stage cancer diagnosis, decreased likelihood of receiving guideline-concordant treatment, and increased cancer mortality [140].
5. Future Directions
The next step in ensuring equitable advancements in NSCLC treatment is to improve minority representation in clinical trials. We have so far discussed many improvements and advancements in targeted treatment for patients with NSCLC with actionable gene alterations. However, representation of minorities—particularly Black and Hispanic populations—has remained low, limiting the generalizability of available data. While real-world data provides important insights into the effectiveness and safety of targeted therapies across diverse racial and ethnic populations, prospective clinical trials remain essential for confirming these outcomes and guiding treatments.
Enhanced recruitment strategies tailored to underrepresented populations are needed to address barriers to participation [141,142]. These efforts include engaging community physicians, patient advocacy organizations, and culturally competent study coordinators to raise awareness of trial opportunities. Inclusive trial designs should be developed with input from diverse patient populations to reflect broader clinical needs, such as addressing comorbidities and socioeconomic factors. Regulatory agencies and sponsors can play a vital role by incentivizing inclusive enrollment through targeted funding, public–private partnerships, and diversity reporting requirements.
To overcome barriers to recruiting and retaining underrepresented populations, logistical challenges such as transportation, financial toxicities, as well as cultural competencies and education must be addressed [143]. Additionally, implementing telehealth solutions and decentralized trial models can increase access for patients in remote or underserved areas [144]. Offering financial support, such as travel reimbursement and modest compensation, can also alleviate the economic burdens that disproportionately affect minority populations. Sustained funding from public and private sources is crucial to support these efforts. Equally important is culturally competent outreach and education, which includes providing multilingual materials and partnering with community leaders and organizations to foster trust and dispel misconceptions about clinical research [145].
Finally, translational research is needed to explore whether intrinsic genomic differences or external access-to-care issues contribute to observed disparities in the outcomes of minority patients. Large-scale databases and real-world registries that include robust demographic details can help identify trends, refine therapeutic strategies, and guide clinical decision-making. Multidisciplinary collaborations involving oncologists, community outreach, as well as research coordinators can develop comprehensive approaches to address these disparities. Together, these efforts will ensure that the benefits of precision oncology are equitably extended to all populations.
6. Conclusions
Molecularly targeted therapies have revolutionized the treatment landscape for NSCLC by offering personalized, mutation-driven approaches. However, the underrepresentation of Black and Hispanic patients in clinical trials remains a critical limitation that hinders our understanding of outcomes and management in these populations. Real-world evidence suggests that while Hispanic patients often achieve comparable results to non-Hispanic patients, Black patients may experience worse outcomes on certain targeted therapies, underlining the urgent need for more robust prospective data. Overcoming socioeconomic and logistical barriers to trial participation, ensuring inclusive study designs, and dedicating sufficient financial resources are essential next steps.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing, and editing—A.B., N.Y., M.L., H.J. and H.C.; Supervision—H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The Figure 2 were created using BioRender.com (accessed on 10 May 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| ALK | anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| BRAF V600E | b-raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (V600E mutation) |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERBB2 (HER2) | erbb2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| ILD | interstitial lung disease |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog |
| LCS | lung cancer screening |
| MEK | mitogen activate protein kinase enzymes |
| MET | Mesenchymal–Epithelial transition factor |
| NGS | next generation sequencing |
| NLST | national lung screening trial |
| NRG1 | neuregulin-1 |
| NTRK | neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| ORR | objective response rate |
| OS | overall survival |
| PDC | platinum doublet chemotherapy |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| ROS1 | c-ros oncogene 1 |
| T-Dxd | traztuzumab deruxtecan |
| TKI | tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| TNM | tumor, node, metastasis |
| TRK | tyrosine receptor kinase |
References
- Bandi, P.; Travis, W.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Freedman, N.D.; Jemal, A.; Smith, R.A.; Kratzer, T.B. Lung cancer statistics, 2023. Cancer 2024, 130, 1330–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, K.E.; Pao, W. Chipping away at the lung cancer genome. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Kobayashi, K.; Fan, Y.; Ahmed, S.; Planchard, D.; Kim, S.-W.; Yanagitani, N.; Sugawara, S.; Andrasina, I.; Laktionov, K.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Ahn, J.S.; Barlesi, F.; Nishio, M.; Lee, D.H.; Solomon, B.J. Alectinib in Resected ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Cobo, M.; Sun, T.; Owen, S.; Salinas, J.; Tan, J.-L.; Girard, N.; MacKean, M.; Tomasini, P.; Azuma, K.; et al. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy with and without lazertinib in EGFR-mutant advanced NSCLC after disease progression on osimertinib: Primary results from the phase III MARIPOSA-2 study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 35, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Rackauskas, M.; Yoon, H.-S.; Mehta, H.J.; Karanth, S.; Wheeler, M.; Divaker, J.; Braithwaite, D.; Ratcliffe, M.; Blair, M. Participation in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Clinical Trials in the United States by Race/Ethnicity. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 26, 52–57.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.G.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Wozniak, A.J.; Malysa, A.; Sukari, A.; Cote, M.L.; Murphy, V.; Bepler, G. Frequency of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) positive tumors among African American non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Judd, J.; Chin, S.; Ragin, C. Disparities in Lung Cancer Treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, A.C.; Sheehan, D.F.; Palazzo, L.L.; Kong, C.Y. Disparities and Trends in Genetic Testing and Erlotinib Treatment among Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, A.; Segal, J.; Cursio, J.; Choudhury, N.J.; Ritterhouse, L.; Patel, J.D.; Eghtesad, M.; Kadri, S. Fewer actionable mutations but higher tumor mutational burden characterizes NSCLC in black patients at an urban academic medical center. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 5817–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, G.; Lonardo, F.; Gadgeel, S.; Craig, D.; Lusk, C.M.; Purrington, K.; Watza, D.; Ratliff, V.; Bepler, G.; Wenzlaff, A.S.; et al. Profiling the Mutational Landscape in Known Driver Genes and Novel Genes in African American Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4300–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avorn, J.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Roberts, T.J. Variation in Use of Lung Cancer Targeted Therapies Across State Medicaid Programs, 2020–2021. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2252562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, P.A.; Johnson, B.E.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, S.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Garon, E.B.; Behera, M.; Berry, L.; Rossi, M.; Steuer, C.E.; et al. Role of race in oncogenic driver prevalence and outcomes in lung adenocarcinoma: Results from the Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium. Cancer 2015, 122, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-Y.; Tang, J.-L.; Fu, X.-H.; Yuan, J.-Q.; Wang, K.-F.; Threapleton, D.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Han, X.-R.; Mao, C. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78985–78993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.; Chao, C.; Abu Rous, F.; Jaeger, E.; Teslow, E.; Stoppler, M.C.; Potguari, B.; Gutta, R. Racial Diversity and Co-Mutational Analysis of Biologically Relevant Alterations in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Lung Cancer 2025, 26, 307–313.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.G.; Zhang, J.; Natarajan, T.G.; Coombes, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Eisenberg, R.; Timmers, C.; Liu, T.; Lammers, P.E.; Carbone, D.P.; et al. Somatic Mutation Spectrum of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer in African Americans: A Pooled Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, H.D.; Halmos, B.; Perez-Soler, R.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Ye, K.; Deng, L.; Su, C.; Sharma, J. Survival Disparities in Black Patients With EGFR-mutated Non–small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, L.; Vargas, M.P.; Castañeda-González, J.P.; Parra-Medina, R.; Gómez-Gómez, M.P.; Cabezas, D.C. Prevalence of oncogenic driver mutations in Hispanics/Latin patients with lung cancer. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2023, 185, 107378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Vargas, C.; Raez, L.; Rolfo, C.; Malapelle, U.; Zatarain-Barrón, Z.L.; Rosell, R.; Cuello, M.; Otero, J.; Burotto, M.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to First-Line Osimertinib in Hispanic Patients With EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (FRESTON-CLICaP). Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Bunn, P.; Hirsch, F.R. EGFR testing in lung cancer is ready for prime time. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belani, C.P.; Wynes, M.W.; Switchenko, J.; Behera, M.; Jiang, R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Bunn, B.; Huang, Z. Natural History and Real-World Treatment Outcomes for Patients With NSCLC Having EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation: An International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer–American Society of Clinical Oncology CancerLinQ Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 5, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.; Bramuglia, G.; Cuello, M.; Otero, J.; Powazniak, Y.; Sánchez-Reyes, R.; Trigo, M.; Carranza, H.; Cardona, A.F.; Amieva-Rivera, E.; et al. Updated Frequency of EGFR and KRAS Mutations in NonSmall-Cell Lung Cancer in Latin America: The Latin-American Consortium for the Investigation of Lung Cancer (CLICaP). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Emich, H.; Mahadevia, P.; Stapleton, N.; Burnett, H.; Carroll, C. Epidemiological and clinical burden of EGFR Exon 20 insertion in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic literature review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, S.; Blowers, D.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.-L. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Chen, R.; Manochakian, R.; Seegobin, K.; Zhou, K.; Lou, Y.; Heng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, H. Genomic landscape of lung adenocarcinomas in different races. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 946625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.H.; Adib, E.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Distribution of KRAS (G12C) Somatic Mutations across Race, Sex, and Cancer Type. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, H.; Settleman, J.; Clark, J.W.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A.; Lynch, T.J.; Bang, Y.-J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibition in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, M.A.; Huberman, M.S.; Kent, M.S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Canepa, H.M.; Kocher, O.N.; Boucher, D.H.; Majid, A.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Smoking status and self-reported race affect the frequency of clinically relevant oncogenic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancers at a United States-based academic medical practice. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lopes, G.; Rodriguez, E.; Pinheiro, P.S.; Liu, Q.; Medina, H.; Cranford, H.M.; Herna, S.J. Disparities in the prevalence of EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements by racial-ethnic group in South Florida with a focus on Hispanic patients, 2011–2019. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, e20528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.; Tamariz, L.; Paul, Y.; Iyer, S.; Saul, E.E.; da Silva, L.L.; Costa, P.A. Prevalence of Targetable Mutations in Black Patients With Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2021, 17, e629–e636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-C.; Yang, J.-J.; Chen, Z.-H.; Guo, W.-B.; Tian, H.-X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.-L. Clinical characteristics and sequence complexity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene fusions in Chinese lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2017, 114, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustugun, O.T.; Lund-Iversen, M.; Suhrke, P.; Moe, J.O.; Eide, I.J.Z.; Dyrbekk, A.P.H.; Warsame, A.A.; Ludahl, M.O. Evaluation of ROS1 expression and rearrangements in a large cohort of early-stage lung cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Jasielski, P.; Krawczyk, P.; Jankowski, T.; Wójcik-Superczyńska, M.; Reszka, K.; Milanowski, J. Ocena rearanżacji genu ROS1 przy pomocy fluorescencyjnej hybrydyzacji in situ w niedrobnokomórkowym raku płuca. Oncol. Clin. Pract. 2020, 16, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Manegold, C.; Su, C.; Schmid-Bindert, G.; Zhou, C.; Zheng, L.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Fei, K. ROS1 fusions in Chinese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, J.; Qiu, X.; Fu, S.; Mu, D.; Wu, C.; Ma, L.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Prevalence of ROS1 fusion in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 10, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortot, A.B.; Chen, Z.; Heeg, B.; Campden, R.I.; Pfeiffer, B.M.; Vioix, H.; Mazieres, J. MET Exon 14 Skipping in NSCLC: A Systematic Literature Review of Epidemiology, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, Q.; Lizaso, A.; Xiang, J.; Mao, X.; Han-Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Lin, L.; et al. Characterization of MET exon 14 alteration and association with clinical outcomes of crizotinib in Chinese lung cancers. Lung Cancer 2020, 148, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenius, G.; Johansson, M.; Bergman, B.; Botling, J.; Lewensohn, R.; Hussein, A.; Staaf, J.; Monsef, N.; Lamberg, K.; Planck, M.; et al. FP16.04 A Nationwide Population-Based Mapping of Mutations and Gene Fusions in Lung Cancer Among Never-Smokers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Luo, X.; Pan, Y.; Ye, T.; Sun, Y.; Garfield, D.; Lu, Y.; Pao, W.; et al. RET Fusions Define a Unique Molecular and Clinicopathologic Subtype of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4352–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.; Lim, G.H.T.; Poskitt, B.; Balbi, K.J.; Moore, D.A. Prevalence and breakdown of non-small cell lung cancer BRAF driver mutations in a large UK cohort. Lung Cancer 2022, 173, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felicioni, L.; Buttitta, F.; Sciarrotta, M.G.; Malatesta, S.; Guetti, L.; Mucilli, F.; Chella, A.; Marchetti, A.; Pullara, C.; Viola, P. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3574–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Jia, B.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhuo, M.; Yan, J.; et al. Prevalence, genetic variations and clinical outcomes of BRAF-V600 mutated advanced NSCLC in China: A retrospective real-world multi-centre study. EBioMedicine 2025, 114, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Liu, S.V.; Oliveira, J.; Lopes, A.R.; Adamo, V.; Scilla, K.; Russo, A.; Rolfo, C. NTRK and NRG1 gene fusions in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Precis. Cancer Med. 2020, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juon, H.-S.; Kane, G.C.; Evans, N.R.; Barta, J.A.; Shusted, C.S. Analysis of Lung Cancer Screening by Race After USPSTF Expansion of Screening Eligibility in 2021. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2217578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, T.R.; Meza, R.; Levy, D.T. Comparison of Smoking History Patterns Among African American and White Cohorts in the United States Born 1890 to 1990. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2016, 18, S16–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, H.J.; van Der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Oudkerk, M. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egede, L.E.; Silvestri, G.A.; Payne, E.; Halbert, C.H.; Gebregziabher, M.; Tanner, N.T. Racial Differences in Outcomes within the National Lung Screening Trial. Implications for Widespread Implementation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.T.; Winn, R.A.; Smith, R.; Wisnivesky, J.P.; Wiener, R.S.; Henderson, L.M.; Crothers, K.; Sakoda, L.C.; Aldrich, M.C.; Rivera, M.P.; et al. Addressing Disparities in Lung Cancer Screening Eligibility and Healthcare Access. An Official American Thoracic Society Statement. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, e95–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lund, J.L.; Reuland, D.S.; Rivera, M.P.; Su, I.-H.; Henderson, L.M.; Pak, J. Prevalence of Lung Cancer Screening in the US, 2022. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e243190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Olivo, M.A.; Maki, K.G.; Choi, N.J.; Hoffman, R.M.; Shih, Y.C.T.; Lowenstein, L.M.; Volk, R.J. Patient Adherence to Screening for Lung Cancer in the US: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 2020, 3, e2025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, J.; Lam, S.; Darling, G.; Stewart, E.L.; Cheung, S.; Xu, W.; Aggarwal, R.; Lam, A.C.; Liu, G. Predictors of participant nonadherence in lung cancer screening programs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racial and Ethnic Disparities: American Lung Association. Available online: https://www.lung.org/research/state-of-lung-cancer/racial-and-ethnic-disparities (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Bhaskar, L.; Verma, H.K.; Suri, C.; Swarnkar, S. Non-Coding RNA as a Biomarker in Lung Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiopoulos, S.; Fleury, M.E.; Lofgren, K.T.; Meyer, C.S.; Flores, C.; Sheinson, D.M.; Adams, D.V.; Wong, W.B. Trends in Use of Next-Generation Sequencing in Patients With Solid Tumors by Race and Ethnicity After Implementation of the Medicare National Coverage Determination. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2138219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulos, P.R.; Gross, C.P.; Longtine, J.A.; Agarwala, V.; Chiang, A.C.; Herbst, R.S.; Sorg, R.A.; Adelson, K.B.; Abernethy, A.P.; Tang, D.; et al. Association of Broad-Based Genomic Sequencing With Survival Among Patients With Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Community Oncology Setting. JAMA 2018, 320, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, E.W.; Patel, M.; Bruno, D.S.; Li, X.; Hess, L.M. Disparities in Biomarker Testing and Clinical Trial Enrollment Among Patients With Lung, Breast, or Colorectal Cancers in the United States. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.W.; Phillips, K.A.; Ragavan, M.V.; Blakely, C.M.; Kumar, A.; Douglas, M.P.; Chen, C. Private Payer and Medicare Coverage Policies for Use of Circulating Tumor DNA Tests in Cancer Diagnostics and Treatment. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 609–616.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanois, R.; Alme, E.B.; Leiman, L.C.; Carter, G.C.; Martin, N.; Febbo, P.G.; Kiernan, E.; Allo, M.; Essig, A.; Kubler, C.B.; et al. Recommendations for the Equitable and Widespread Implementation of Liquid Biopsy for Cancer Care. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, e2300382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.W.; Fong, W.; Cho, W.C.S. Immunotherapy in Treating EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: Current Challenges and New Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 635007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezer, N.; Mhango, G.; Bagiella, E.; Goodman, E.; Flores, R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Racial Disparities in Resection of Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Variability Among Surgeons. Med Care 2020, 58, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneuertz, P.J.; Abdel-Rasoul, M.; Merritt, R.E.; D’SOuza, D.M. Racial Disparities in Overall Survival and Surgical Treatment for Early Stage Lung Cancer by Facility Type. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e691–e698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Facts & Figures for African American/Black People 2022–2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/cancer-facts-and-figures-for-african-americans/2022-2024-cff-aa.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Policy and Global Affairs. Committee on Improving the Representation of Women and Underrepresented Minorities in Clinical Trials and Research. In Improving Representation in Clinical Trials and Research; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cancer Statistics: Esophageal Cancer, 2025. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/esophagus-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- MacLennan, G.T.; Cramer, H.M.; E Alexander, R.; Cummings, O.W.; Davidson, D.D.; Zhang, S.; Montironi, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cheng, L. Molecular pathology of lung cancer: Key to personalized medicine. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 347–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Besse, B.; Sethi, S.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Prabhash, K.; Girard, N.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Lee, K.-H.; Felip, E.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Tsuboi, M.; He, J.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Herbst, R.S. Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohe, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Majem, M.; Huang, X.; Mukhametshina, G.; John, T.; Bolanos, A.; Stachowiak, M.; de Marinis, F.; et al. Adjuvant Osimertinib for Resected EGFR-Mutated Stage IB-IIIA Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the Phase III Randomized ADAURA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Poole, L.; Herbst, R.S.; Su, W.-C.; Shepherd, F.A.; Majem, M.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Lee, K.H.; Grohé, C.; Kato, T.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Cobo, M.; Sriuranpong, V.; Wang, C.-L.; Inoue, T.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Huang, X.; Kato, T.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Soparattanapaisarn, N.; et al. Osimertinib after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haura, E.B.; Girard, N.; Thayu, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, T.-Y.; Viteri, S.; Haddish-Berhane, N.; Xie, J.; Roshak, A.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Popat, S.; Park, K.; Girard, N.; Paz-Ares, L.; Felip, E.; Zhou, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Shreeve, S.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Amivantamab plus Chemotherapy in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, W.; Sacher, A.G.; Hindoyan, A.; Skoulidis, F.; Dooms, C.; Tomasini, P.; Velcheti, V.; Jones, S.; Hong, D.S.; Addeo, A.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Molecular Correlates of Sotorasib Efficacy in Patients With Pretreated KRAS G12C-Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: 2-Year Analysis of CodeBreaK 100. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3311–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Langen, A.J.; Johnson, M.L.; Mazieres, J.; Dingemans, A.M.C.; Mountzios, G.; Pless, M.; Paz-Ares, L. Sotorasib versus docetaxel for previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer with KRAS(G12C) mutation: A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Riely, G.J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Heist, R.S.; Ou, S.H.I.; Pacheco, J.M.; Spira, A.I. Adagrasib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring a KRAS(G12C) Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kim, H.R.; Ahn, M.J.; Yang, J.C.H.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Popat, S. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Felip, E.; Delmonte, A.; Gettinger, S.N.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.R.; Spira, A.; Califano, R.; Zhang, P.; et al. Brigatinib Versus Crizotinib in Advanced ALK Inhibitor–Naive ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Second Interim Analysis of the Phase III ALTA-1L Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3592–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Goto, Y.; Mok, T.; Felip, E.; Mazieres, J.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Polli, A.; Thurm, H.; Bauer, T.M.; et al. First-Line Lorlatinib or Crizotinib in Advanced ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, R.; Polli, A.; Paolini, J.; Thomaidou, D.; de Marinis, F.; Felip, E.; Mazieres, J.; Liu, G.; Soo, R.A.; Wu, Y.-L.; et al. Lorlatinib Versus Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: 5-Year Outcomes From the Phase III CROWN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3400–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.; Paz-Ares, L.; Siena, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Farago, A.F.; Blakely, C.M.; Seto, T.; Cho, B.C.; Tosi, D.; et al. Entrectinib in patients with advanced or metastatic NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Camidge, D.R.; Lin, J.J.; Kim, S.W.; Solomon, B.J.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Cho, B.C. Repotrectinib in ROS1 Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.F.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Yovine, A.; Reguart, N.; Groen, H.J.M.; Akerley, W.; Seto, T.; Souquet, P.-J.; Heist, R.S.; Han, J.-Y.; et al. Capmatinib in MET exon 14-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: Final results from the open-label, phase 2 GEOMETRY mono-1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.; Heist, R.S. Capmatinib in MET Exon 14-Mutated or MET-Amplified Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Han, H.; Park, K.; Zhou, C.; Solomon, B.; Wolf, J.; Novello, S.; Arriola, E.; Soldatenkova, V.; Payakachat, N.; et al. First-Line Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab in RET Fusion–Positive NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Park, K.; Solomon, B.J.; Tomasini, P.; Loong, H.H.; De Braud, F.; Drilon, A. Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Final Safety and Efficacy, Including Overall Survival, From the LIBRETTO-001 Phase I/II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, JCO2402076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curigliano, G.; Besse, B.; Cassier, P.A.; Cho, B.C.; Lopes, G.; Thomas, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Garralda, E.; Liu, S.V.; Turner, C.D.; et al. Pralsetinib for RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARROW): A multi-cohort, open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.; Tan, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Santarpia, L.; Mazieres, J.; Planchard, D.; Quoix, E.; Souquet, P.-J.; Kelly, R.J.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With BRAF V600E-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC: Updated 5-Year Survival Rates and Genomic Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Smit, E.F.; Ahn, M.J.; Felip, E.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Tsao, A.; Johnson, B.E. Phase II, Open-Label Study of Encorafenib Plus Binimetinib in Patients With BRAF(V600)-Mutant Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Jänne, P.A. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, L.; Corrales, L.; Freitas, H.; Arrieta, O.; Aliaga, C.; Cruz, G.; Carracedo, C.; Motta, R.; Bacon, L.; Raez, L.; et al. EP12.01-61 Clinical Features, Outcomes, and Biology of EGFR exon 20 Insertions in a Cohort of Hispanic Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, S.T.; Balasubramanian, A.; Spira, A.; Brookhart, M.A.; Younan, D.; Johnson, M.; Mesa-Frias, M. Real-world comparative effectiveness of sotorasib versus docetaxel in second line and beyond among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 2024, 197, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, N.; Dowell, J.E.; Tseng, C.-L.; Kelley, M.J.; Lin, C.; Zhou, K.I. Brief Report: Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Sotorasib in U.S. Veterans with KRAS G12C-Mutated NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2024, 5, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Santini, F.C.; Li, B.T.; Arbour, K.C.; Lito, P.; Riely, G.J.; Ladanyi, M.; Yang, S.-R.; Sabari, J.K.; Shen, R.; et al. Clinical and Genomic Features of Response and Toxicity to Sotorasib in a Real-World Cohort of Patients With Advanced KRAS G12C-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, e2300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Datta, D.; Lin, C.-W.; Bazhenova, L.; Ogale, S.; Sussell, J.; Butte, A.J.; Slatter, S.; Rudrapatna, V.A. ALK Inhibitor Treatment Patterns and Outcomes in Real-World Patients with ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Target. Oncol. 2023, 18, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Archer, V.; Trinh, H.; Hilton, M.; Pal, N.; Lin, J.J.; Smoljanović, V.; Zhang, Q.; Kurtsikidze, N.; Krebs, M.G. Real-World Comparative Effectiveness of First-Line Alectinib Versus Crizotinib in Patients With Advanced ALK-Positive NSCLC With or Without Baseline Central Nervous System Metastases. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.; Martina, R.; Martinec, M.; Crane, G.; Perez, L.; Riehl, T.; Krebs, M.G.; Doebele, R.C.; Meropol, N.J.; Wong, W.B. Comparative effectiveness analysis between entrectinib clinical trial and crizotinib real-world data in ROS1+ NSCLC. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2021, 10, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, T.; Caro, N.; Davis, K.L.; Furqan, M.; Rombi, J.; Cai, B.; Karanth, S.; Goyal, R.K. Effectiveness of standard treatments in non-small-cell lung cancer with METexon14 skipping mutation: A real-world study. Futur. Oncol. 2024, 20, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Price, M.; Caro, N.; Davis, K.L.; Cai, B.; Ansquer, V.D.; Goyal, R.K.; Paik, P.K.; Saliba, T.R. Real-world outcomes in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with MET Exon 14 skipping mutation and brain metastases treated with capmatinib. Futur. Oncol. 2023, 19, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, M.; Wermke, M.; Schumacher, M.; Addeo, A.; Banerji, S.; Clarke, S.; Duruisseaux, M.; Absenger, G.; Wöll, E.; Pall, G.; et al. Selpercatinib in RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (SIREN): A retrospective analysis of patients treated through an access program. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211019675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.E.; Jackman, D.M.; Nishino, M.; Lo, P.C.; Oxnard, G.R.; Lindeman, N.I.; Jänne, P.A.; Butaney, M.; Dahlberg, S.E. Natural History and Molecular Characteristics of Lung Cancers Harboring EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsongalis, G.J.; Amos, C.I.; Tafe, L.J.; Biernacka, A.; Gutmann, E.J.; Black, C.C.; Peterson, J.D.; Tsongalis, P.D.; Liu, X.; de Abreu, F.B. The potential utility of re-mining results of somatic mutation testing: KRAS status in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genet. 2016, 209, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Beaver, J.A.; Nakajima, E.C.; Akinboro, O.; Pazdur, R.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Vallejo, J.J.; Larkins, E.A.; Drezner, N.L.; Singh, H.; et al. Outcomes of first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors with or without chemotherapy according to KRAS mutational status and PD-L1 expression in patients with advanced NSCLC: FDA pooled analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, L.; Bunn, P.A.; De Marinis, F.; Gervais, R.; Shepherd, F.A.; Pless, M.; Manegold, C.; Gatzemeier, U.; Paoletti, P.; Szondy, K.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Pemetrexed Versus Docetaxel in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhash, K.; Park, K.; Dakhil, S.; Thomas, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Gorbunova, V.; Yurasov, S.; Bidoli, P.; Syrigos, K.N.; Goksel, T.; et al. Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dancey, J.; Vincent, M.; Levitan, N.; Burkes, R.; Berille, J.; Gralla, R.; Mattson, K.; Coughlin, S.; Gressot, L.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Prospective Randomized Trial of Docetaxel Versus Best Supportive Care in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated With Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Govindan, R. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Felip, E.; Gregorc, V.; Russo, G.L.; Linardou, H.; Duruisseaux, M.; Yao, W.; Barlesi, F.; Mok, T.S.K.; Jotte, R.M.; et al. KRYSTAL-12: Phase 3 study of adagrasib versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring a KRASG12C mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, LBA8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, T.; Rosell, R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Ahn, J.; Hilton, M.; Gadgeel, S.; Camidge, D.; Pérol, M.; et al. Updated overall survival and final progression-free survival data for patients with treatment-naive advanced ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in the ALEX study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jassem, J.; Polli, A.; Thurm, H.; Penkov, K.; Peltz, G.; Calella, A.M.; Mok, T.; Wu, Y.-L.; Arrieta, O.; et al. Post Hoc Analysis of Lorlatinib Intracranial Efficacy and Safety in Patients With ALK-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer From the Phase III CROWN Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, C.E.; Cho, B.C.; Goto, K.; Chiu, C.-H.; Garrido, P.; Massarelli, E.; Heinzmann, S.; Osborne, S.; Bordogna, W.; John, T.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety of entrectinib in patients (pts) with locally advanced/metastatic NTRK fusion-positive (fp) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-C.; Bai, J.; Lu, C.; Chen, H.-J.; Chen, X.-F.; Dong, X.-R.; Wang, Y.-N.; An, G.-L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Shan, J.-L.; et al. Association of genetic and immuno-characteristics with clinical outcomes in patients with RET-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective multicenter study. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.; Loong, H.H.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; Subbiah, V. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westeel, V.; Rosell, R.; Besse, B.; Barlesi, F.; Dansin, E.; Fournel, P.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Gautschi, O.; Früh, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: Results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisier, F.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Viñas, F.; Doubre, H.; Ricordel, C.; Ropert, S.; Bylicki, O. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Patients With Advanced NSCLC With BRAF, HER2, or MET Mutations or RET Translocation: GFPC 01-2018. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.; Chmielewska, I.; Milanowski, J.; Grenda, A.; Kieszko, R.; Gil, M.; Stencel, K.; Wójcik-Superczyńska, M.; Jankowski, T. Exploring immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer patients with BRAF mutations: A case series and literature review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combination of Toripalimab and Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04006041 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Spina, M.; De Carlo, E.; Bearz, A.; Stanzione, B.; Del Conte, A.; Bertoli, E.; Bortolot, M.; Torresan, S. Navigating Therapeutic Challenges in BRAF-Mutated NSCLC: Non-V600 Mutations, Immunotherapy, and Overcoming Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, N.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Xu, L. Efficacy of chemo-immunotherapy in metastatic BRAF-mutated lung cancer: A single-center retrospective data. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1353491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Johnson, B.; Usari, T.; Alcasid, A.; Felip, E.; Ahn, M.-J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Wilner, K.D.; Smit, E.F.; Tsao, A.S.; Wissel, P.S.; et al. Encorafenib Plus Binimetinib in Patients with BRAF V600-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Phase II PHAROS Study Design. Futur. Oncol. 2021, 18, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Souquet, P.-J.; Quoix, E.; Baik, C.S.; Barlesi, F.; Kim, T.M.; Mazieres, J.; Novello, S.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously treated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.M., Jr.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.; Grob, J.J.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Karaszewska, B.; Hauschild, A.; Levchenko, E.; Chiarion Sileni, V.; Schachter, J.; Garbe, C.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardini, L.; Chella, A.; Cappelli, S.; Carrozzi, L.; Massa, V.; Petrini, I.; Sbrana, A. Dabrafenib-trametinib in BRAF V600-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: A single center real world experience. Futur. Oncol. 2024, 20, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyvraz, S.; Kummar, S.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Dubashi, B.; Kp, H.; Drilon, A.E.; Shen, L.; Mussi, C.E.; Lin, J.J.; Moreno, V.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of larotrectinib in patients with TRK fusion lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadranel, J.; Jones, M.; Cheema, P.; Solca, F.; Liu, S.; Duruisseaux, M.; Heining, C.; Cseh, A.; Schlenk, R.; Tolba, K.; et al. NRG1 fusion-driven tumors: Biology, detection, and the therapeutic role of afatinib and other ErbB-targeting agents. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, A.M.; Goto, K.; Kim, D.W.; Macarulla, T.; Hollebecque, A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Drilon, A. Efficacy of Zenocutuzumab in NRG1 Fusion-Positive Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.C.; Mercaldo, S.F.; Blume, J.D.; Wenzlaff, A.S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Chen, H.; Deppen, S.A.; Bush, W.; Crawford, D.; Chanock, S.J.; et al. Racial Disparities in Lung Cancer Survival: The Contribution of Stage, Treatment, and Ancestry. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Alduais, Y.; Fan, F. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicine 2023, 102, e32899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea-Ilies, G.; Flenaugh, E.L.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Mir, H.; Brock, B.A. Social and Biological Determinants in Lung Cancer Disparity. Cancers 2024, 16, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, B.M. Lung cancer health disparities. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malcoe, L.H.; Laurent, S.E.; Richardson, J.; Lynch, E.E.; Meier, H.C.; Mitchell, B.C. The legacy of structural racism: Associations between historic redlining, current mortgage lending, and health. SSM Popul. Heal. 2021, 14, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntire, R.; Juon, H.-S.; Barta, J.A.; Rojulpote, M.; Hong, A.; Pimpinelli, M. Racial disparities in occupational risks and lung cancer incidence: Analysis of the National Lung Screening Trial. Prev. Med. 2021, 143, 106355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, N.; Chen, J.T.; Waterman, P.D.; Arcaya, M.; Wright, E.; Huntley, E.R. Cancer Stage at Diagnosis, Historical Redlining, and Current Neighborhood Characteristics: Breast, Cervical, Lung, and Colorectal Cancers, Massachusetts, 2001–2015. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.; Rangachari, P.; Yousafi, S. Barriers to Recruitment and Retention Among Underrepresented Populations in Cancer Clinical Trials: A Qualitative Study of the Perspectives of Clinical Trial Research Coordinating Staff at a Cancer Center. J. Health Leadersh. 2024, 16, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ison, M.G.; Jedraszko, A.M.; Herzog, K.A.; Golbeck, E.; McColley, S.A.; Barrera, L.; Guzman, Z.R.; Hays, P.T.; Heffernan, M.E.; D’aQuila, R.T. Barriers and facilitators to recruitment of underrepresented research participants: Perspectives of clinical research coordinators. J. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 7, e193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolen, S.; Ford, J.G.; Gibbons, M.C.; Wilson, R.F.; Tanpitukpongse, T.P.; Howerton, M.W.; Lai, G.Y.; Baffi, C.; Powe, N.R.; Tilburt, J.; et al. Barriers to recruiting underrepresented populations to cancer clinical trials: A systematic review. Cancer 2007, 112, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conducting Clinical-Trials Decentralized Elements. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/conducting-clinical-trials-decentralized-elements (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Hong, K.; Nipp, R.D.; Paskett, E.D. Overcoming Barriers to Clinical Trial Enrollment. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).