Breath Insights: Advancing Lung Cancer Early-Stage Detection Through AI Algorithms in Non-Invasive VOC Profiling Trials
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Volunteer Recruitment and Characterization
2.2. Exhaled Breath Sampling
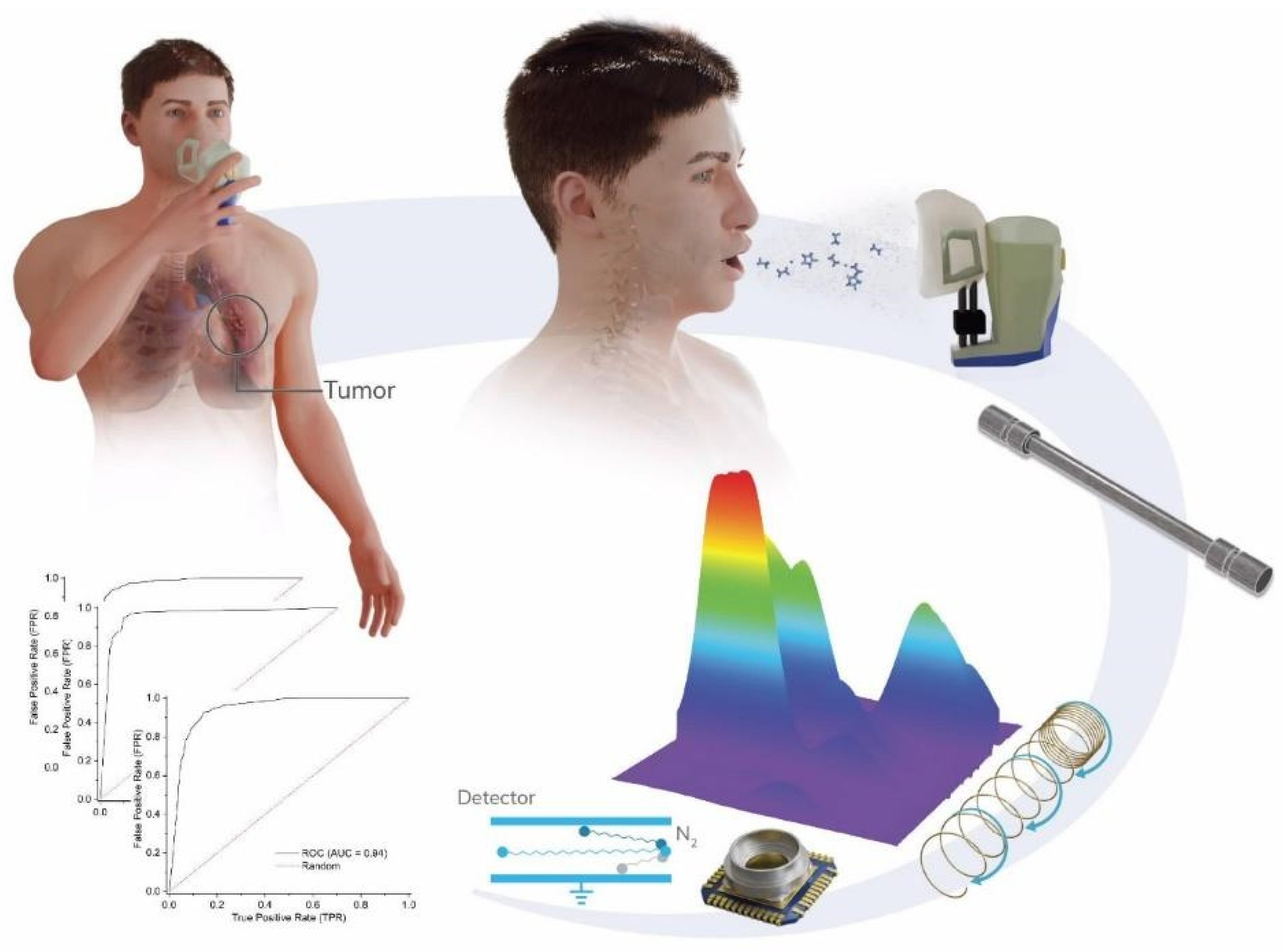
2.3. GC-IMS Analysis
2.4. Classification Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characterization
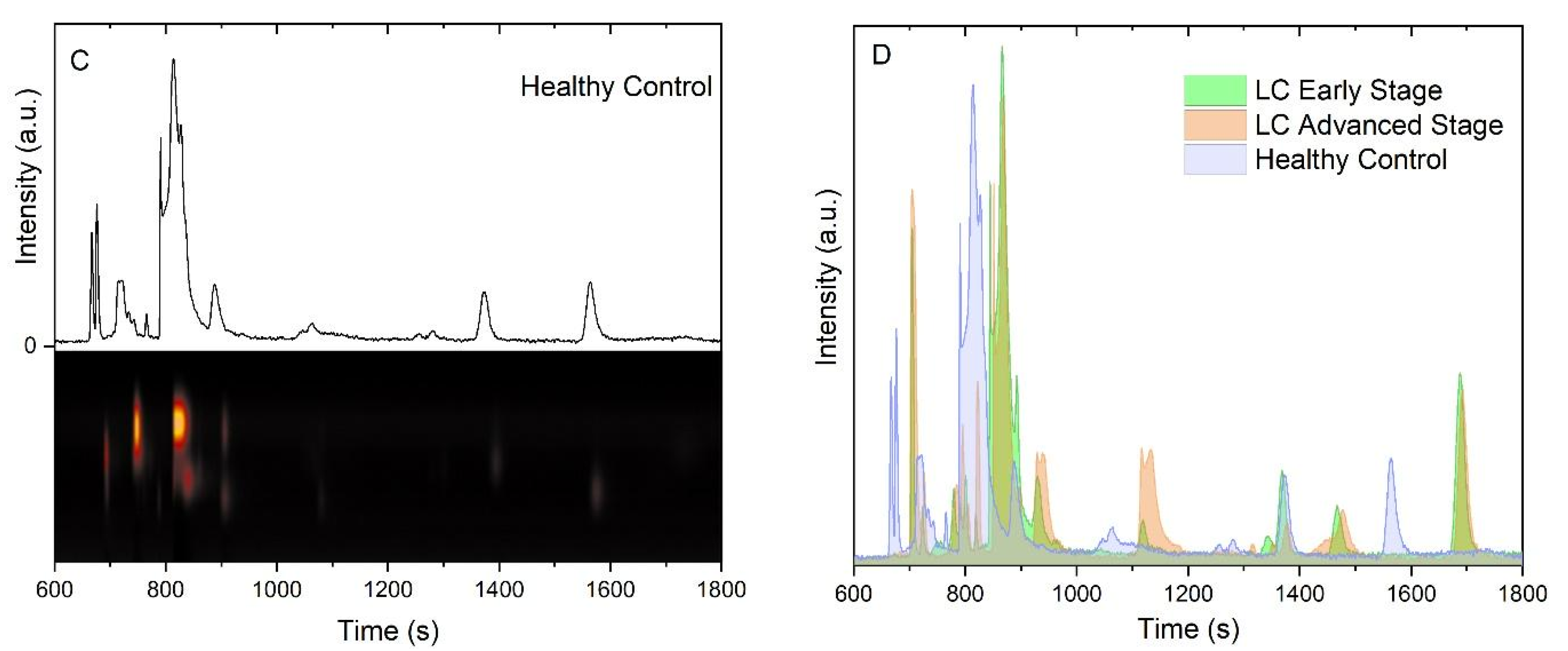
3.2. Chemical Analysis of Exhaled Breath Samples
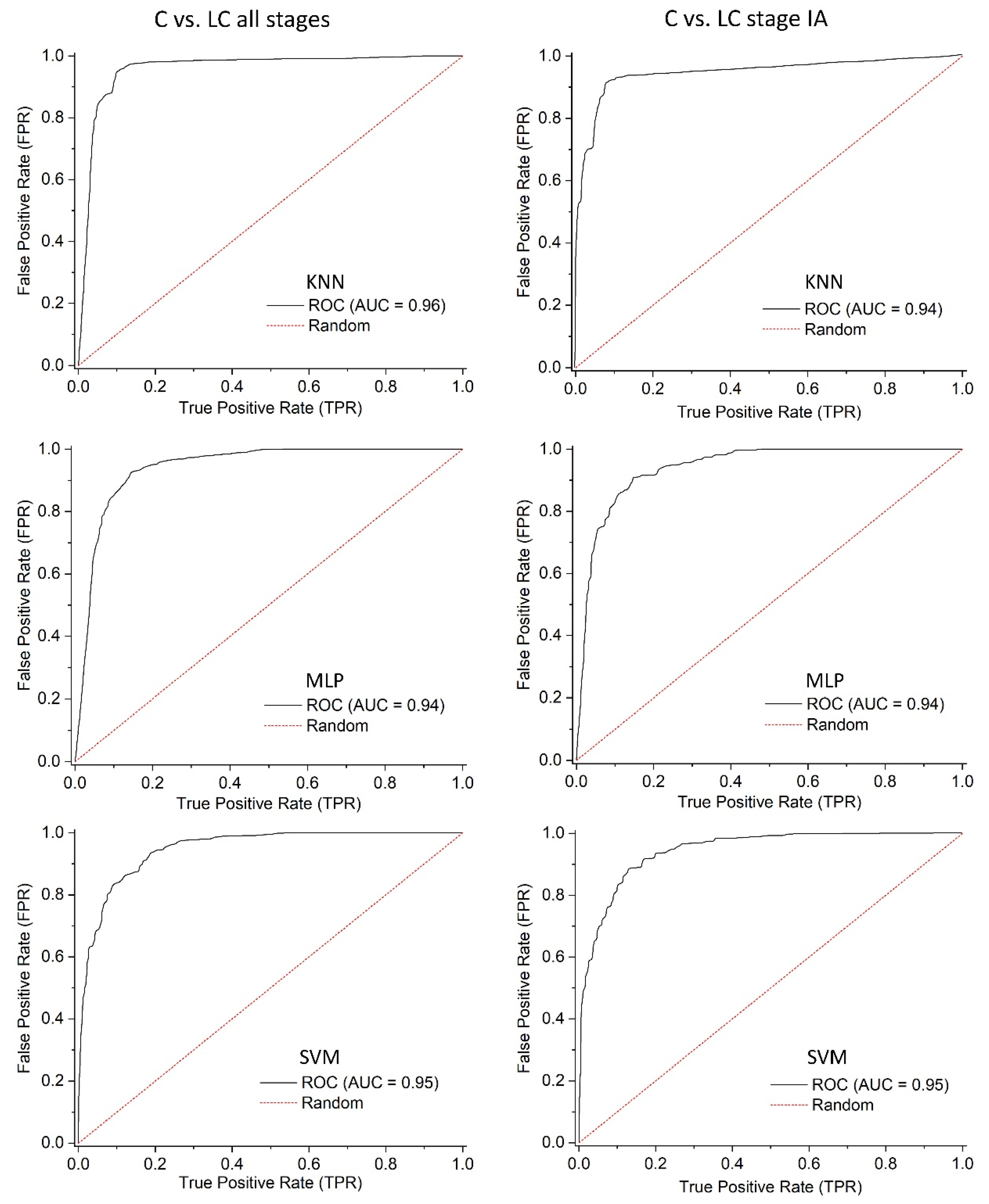
3.3. Data Processing and Machine Learning
4. Discussion
4.1. Using Exhaled Breath Profiles for Lung Cancer Screening
4.2. Study Population and Breath Test Standardization
5. Clinical Application and Future Outlook
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory (GCO) Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/15-trachea-bronchus-and-lung-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-T.; Lin, L.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-P.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yu, C.-J.; Yang, P.-C. Stage Shift Improves Lung Cancer Survival: Real-World Evidence. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 18, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, H.J.; Van Der Aalst, C.M.; De Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Center, M.M.; DeSantis, C.; Ward, E.M. Global Patterns of Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, W.C.; Gareen, I.F.; Soneji, S.S.; Sicks, J.D.; Keeler, E.B.; Aberle, D.R.; Naeim, A.; Church, T.R.; Silvestri, G.A.; Gorelick, J.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of CT Screening in the National Lung Screening Trial. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.R.; Xie, X.; de Koning, H.J.; Mali, W.P.; Vliegenthart, R.; Oudkerk, M. NELSON lung cancer screening study. Cancer Imaging 2011, 11, S79–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Cruz, C.S.D. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Research UK Early Detection and Diagnosis of Cancer: A Roadmap to the Future. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/funding-for-researchers/research-opportunities-in-early-detection-and-diagnosis/early-detection-and-diagnosis-roadmap (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- van der Schee, M.; Pinheiro, H.; Gaude, E. Breath biopsy for early detection and precision medicine in cancer. ecancermedicalscience 2018, 12, ed84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, G.B.; Boshier, P.R.; Markar, S.R.; Romano, A. Accuracy and Methodologic Challenges of Volatile Organic Compound–Based Exhaled Breath Tests for Cancer Diagnosis. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e182815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Thavasi, V.; Venkatesan, T.; Lee, P. Breath Analysis for Lung Cancer Early Detection—A Clinical Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Klieber, M.; Schwarz, K.; Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Filipiak, W.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; et al. Noninvasive detection of lung cancer by analysis of exhaled breath. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Bauer, T.L.; I Pass, H. A volatile biomarker in breath predicts lung cancer and pulmonary nodules. J. Breath Res. 2019, 13, 036013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.; Mallow, C.; Muschelli, J.; Shao, Y.; Thiboutot, J.; Lam, A.; Rule, A.M.; Crainiceanu, C.; Yarmus, L. Predictive performance of selected breath volatile organic carbon compounds in stage 1 lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Das, S.; Pan, J.; Mishra, D.C.; Fu, X.-A. Multigroup prediction in lung cancer patients and comparative controls using signature of volatile organic compounds in breath samples. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0277431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Loukides, S.; Sterk, P.J.; Högman, M.; Olin, A.-C.; Amann, A.; Antus, B.; Baraldi, E.; Bikov, A.; et al. A European Respiratory Society technical standard: Exhaled biomarkers in lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guillou, I. Chemistry World. Available online: https://www.chemistryworld.com/features/how-the-power-of-smell-could-identify-new-medical-tests/4014075.article (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Keogh, R.J.; Riches, J.C. The Use of Breath Analysis in the Management of Lung Cancer: Is It Ready for Primetime? Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7355–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolinska, A.; Hauschild, A.-C.; Fijten, R.R.R.; Dallinga, J.W.; Baumbach, J.; van Schooten, F.J. Current breathomics—a review on data pre-processing techniques and machine learning in metabolomics breath analysis. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doupe, P.; Faghmous, J.; Basu, S. Machine Learning for Health Services Researchers. Value Heal. 2019, 22, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, G.A.; Wakelee, H. Lung Cancer in Never Smokers. In Lung Cancer and Personalized Medicine; Ahmad, A., Gadgeel, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 893, pp. 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M.; Linhas, R.; Campainha, S.; Conde, S.; Barroso, A. Lung cancer in never-smokers – what are the differences? Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Vonder, M.; Pelgrim, G.J.; Rook, M.; Kramer, G.; Groen, H.J.; de Bock, G.H.; Vliegenthart, R. Distribution of Solid Lung Nodules Presence and Size by Age and Sex in a Northern European Nonsmoking Population. Radiology 2024, 312, e231436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiry, F.; Barham, A.; Zhu, J. Analyses of lung cancer-derived volatiles in exhaled breath and in vitro models. Exp. Biol. Med. 2022, 247, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.; Kohlbrenner, D.; Malesevic, S.; Huang, A.; Klein, S.D.; Puhan, M.A.; Kohler, M. Mapping the landscape of lung cancer breath analysis: A scoping review (ELCABA). Lung Cancer 2022, 175, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pal, M. Review—Non-Invasive Monitoring of Human Health by Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, T.; I Baumbach, J.; Kreuer, S. Ion mobility spectrometry in breath research. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinhas, M.; Leitão, P.M.; Raimundo, B.S.; Gil, N.; Vaz, P.D.; Luis-Ferreira, F. AI Applied to Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Profiles from Exhaled Breath Air for Early Detection of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, R.A.; Weinberg, R.A. The Biology of Cancer; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 9781136977381. [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts, B.; Spira, A.; Massion, P.; Walser, T.; Wistuba, I.; Minna, J.; Dubinett, S. Evolving Concepts in Lung Carcinogenesis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 32, 032–043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Phillips, M.; Amann, A.; Haick, H. Volatile Organic Compounds of Lung Cancer and Possible Biochemical Pathways. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5949–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Kabeer, A.; Abbas, Z.; Siddiqui, H.A.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C. Interplay of oxidative stress, cellular communication and signaling pathways in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Díaz, B.; García-Botello, D.R.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Reyes-Soto, G.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; Herrera-Montalvo, L.A. Tumor microenvironment differences between primary tumor and brain metastases. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, P. Rebuilding the microenvironment of primary tumors in humans: A focus on stroma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 527–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochalski, P.; King, J.; Klieber, M.; Unterkofler, K.; Hinterhuber, H.; Baumann, M.; Amann, A. Blood and breath levels of selected volatile organic compounds in healthy volunteers. Analyst 2013, 138, 2134–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipiak, W.; Filipiak, A.; Sponring, A.; Schmid, T.; Zelger, B.; Ager, C.; Klodzinska, E.; Denz, H.; Pizzini, A.; Lucciarini, P.; et al. Comparative analyses of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from patients, tumors and transformed cell lines for the validation of lung cancer-derived breath markers. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWeerdt, S. Could rats and dogs detect disease better than the finest lab equipment? Nature 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S.M.; Szidon, J.P.; Krotoszynski, B.K.; Gibbons, R.D.; O’Neill, H.J. Volatile organic compounds in exhaled air from patients with lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahed, H.; Feng, X.; Sheikh, M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Ginsburg, O.; Shiels, M.; Robbins, H. EP01.01-24 Median Age at Lung Cancer Diagnosis in 60 Countries: An International Comparative Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S422–S423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.; Godbeer, L.; Ball, M.L. Establishing breath as a biomarker platform—take home messages from the Breath Biopsy Conference 2023. J. Breath Res. 2024, 18, 030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Lung Cancer Patients | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 73 (37.2) | 123 (62.8) | |
| Age (years) | |||
| Median (range) | 66 (41–86) | 40 (20–78) | |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Female | 46 (63.0) | 93 (75.6) | |
| Male | 27 (37.0) | 30 (24.4) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||
| Current smoker | 23 (31.5) | 39 (31.7) | |
| Former smoker | 28 (38.4) | 17 (13.8) | |
| Never smoker | 22 (30.1) | 67 (54.5) | |
| Lung cancer type, n (%) | – | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 49 (67.1) | ||
| Squamous cell | 6 (8.2) | ||
| Small cell | 5 (6.9) | ||
| Other | 13 (17.8) | ||
| Clinical stage, n (%) | – | ||
| 0 | 5 (6.8) | ||
| IA and IB | 37 (50.7) | ||
| IIA and IIB | 3 (4.1) | ||
| IIIA | 10 (13.7) | ||
| IIIB and IIIC | 3 (4.1) | ||
| IVA | 11 (15.1) | ||
| IVB | 4 (5.5) |
| Parameter/Method | SVM | MLP | KNN |
|---|---|---|---|
| C vs. LC all stages | |||
| Sensitivity | 88% | 84% | 87% |
| Specificity | 86% | 90% | 92% |
| Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | 77% | 85% | 88% |
| Negative Predictive Value (NPV) | 93% | 90% | 92% |
| Accuracy | 87% | 88% | 90% |
| C vs. LC stage IA | |||
| Sensitivity | 87% | 75% | 80% |
| Specificity | 90% | 94% | 93% |
| Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | 57% | 77% | 70% |
| Negative Predictive Value (NPV) | 98% | 93% | 96% |
| Accuracy | 89% | 90% | 90% |
| Adenocarcinoma vs. Other Histology | |||
| Sensitivity | 71% | 77% | 75% |
| Specificity | 72% | 78% | 75% |
| Positive Predictive Value (PPV) | 77% | 81% | 79% |
| Negative Predictive Value (NPV) | 65% | 73% | 72% |
| Accuracy | 71% | 77% | 75% |
| Method | AUC (“C vs. LC All Stages”) | AUC (“C vs. LC Stage IA”) |
|---|---|---|
| KNN | 0.9486 (0.9327–0.9636) | 0.9253 (0.8950–0.9532) |
| MLP | 0.9331 (0.9163–0.9493) | 0.9325 (0.9069–0.9547) |
| SVM | 0.9428 (0.9274–0.9565) | 0.9428(0.9229–0.9603) |
| Benchmarking | p-Value (“C vs. LC All Stages”) | p-Value (“C vs. LC Stage IA”) |
|---|---|---|
| KNN vs. MLP | 0.9792 | 0.9880 |
| KNN vs. SVM | 0.9920 | 0.9713 |
| MLP vs. SVM | 0.9873 | 0.9832 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raimundo, B.S.; Leitão, P.M.; Vinhas, M.; Pires, M.V.; Quintas, L.B.; Carvalheiro, C.; Barata, R.; Ip, J.; Coelho, R.; Granadeiro, S.; et al. Breath Insights: Advancing Lung Cancer Early-Stage Detection Through AI Algorithms in Non-Invasive VOC Profiling Trials. Cancers 2025, 17, 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101685
Raimundo BS, Leitão PM, Vinhas M, Pires MV, Quintas LB, Carvalheiro C, Barata R, Ip J, Coelho R, Granadeiro S, et al. Breath Insights: Advancing Lung Cancer Early-Stage Detection Through AI Algorithms in Non-Invasive VOC Profiling Trials. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101685
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaimundo, Bernardo S., Pedro M. Leitão, Manuel Vinhas, Maria V. Pires, Laura B. Quintas, Catarina Carvalheiro, Rita Barata, Joana Ip, Ricardo Coelho, Sofia Granadeiro, and et al. 2025. "Breath Insights: Advancing Lung Cancer Early-Stage Detection Through AI Algorithms in Non-Invasive VOC Profiling Trials" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101685
APA StyleRaimundo, B. S., Leitão, P. M., Vinhas, M., Pires, M. V., Quintas, L. B., Carvalheiro, C., Barata, R., Ip, J., Coelho, R., Granadeiro, S., Simões, T. S., Gonçalves, J., Baião, R., Rocha, C., Alves, S., Fidalgo, P., Araújo, A., Matos, C., Simões, S., ... Vaz, P. D. (2025). Breath Insights: Advancing Lung Cancer Early-Stage Detection Through AI Algorithms in Non-Invasive VOC Profiling Trials. Cancers, 17(10), 1685. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101685







