Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Occurrence Up to 10 Years in Advance Using Features of the Main Pancreatic Duct in Pre-Diagnostic CT Scans
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Data Description
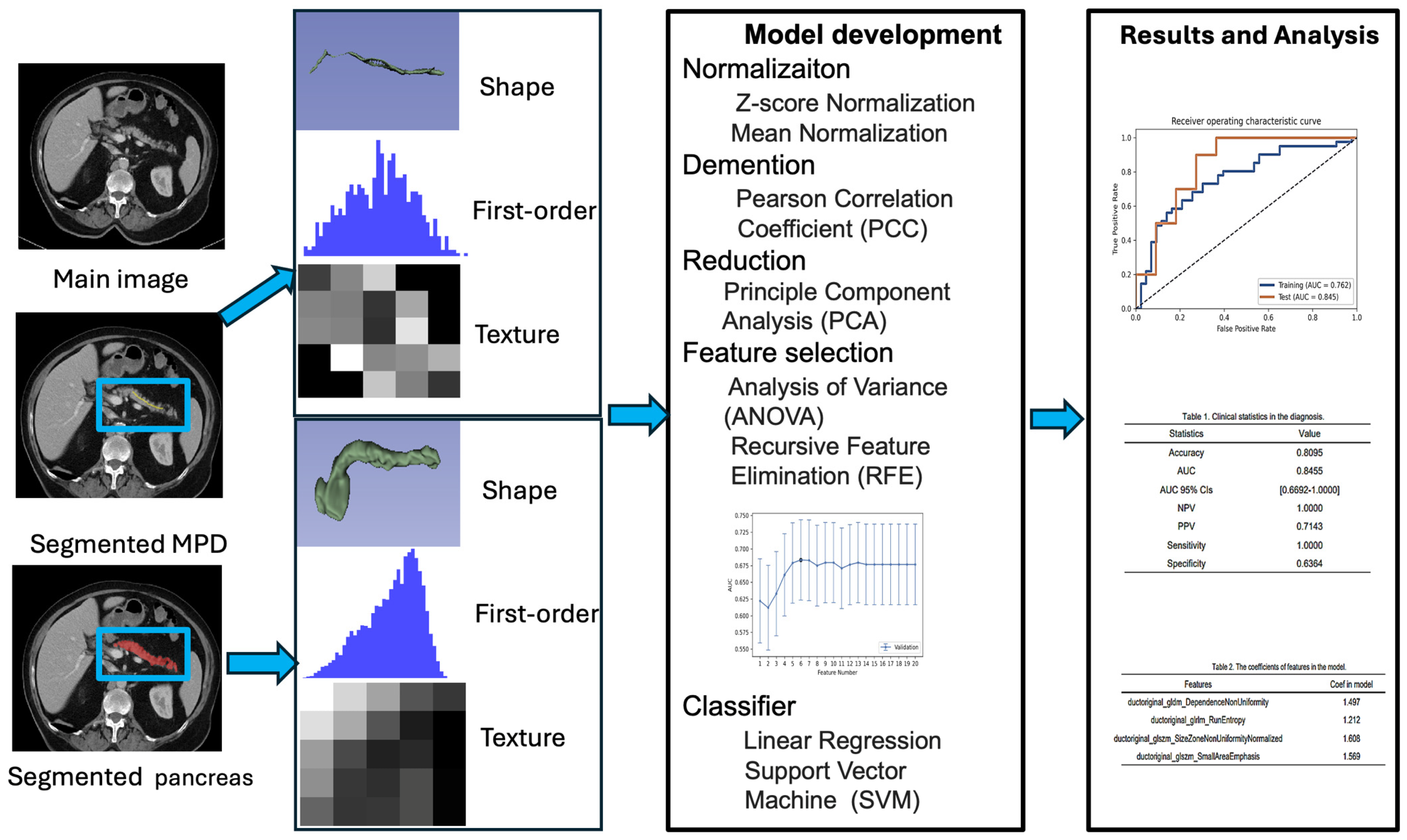
2.3. Image Segmentation and Radiomic Feature Extraction and Feature Reduction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Information
3.2. Trend of Diameters and Volumes for Control, Pre-Diagnostic, and Diagnostic Data
3.3. Performance of Radiomic Models for PDAC Prediction Across Timeframes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDAC | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| MPD | Main pancreatic duct |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRCP | Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography |
| GLCM | Gray-level co-occurrence matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-level size zone matrix |
| GLRLM | Gray-level run-length matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-level dependence matrix |
| NGTDM | Neighboring gray-tone difference matrix |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, Y.; Yonamine, N.; Fujinuma, I.; Tsunenari, T.; Takihata, Y.; Hakoda, H.; Nakazawa, A.; Iwasaki, T.; Einama, T.; Togashi, J.; et al. Impact of Preoperative Tumor Size on Prognosis of Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8621–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackford, A.L.; Canto, M.I.; Klein, A.P.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Recent trends in the incidence and survival of stage 1A pancreatic cancer: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results analysis. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Q.; Parker, R.A.; Zhou, Y.; Lustigova, E.; Wu, B.U. Risk Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With Abnormal Morphologic Findings Related to Chronic Pancreatitis: A Machine Learning Approach. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Holmes, M.V.; Chen, Z.; Kartsonaki, C. A review of lifestyle, metabolic risk factors, and blood-based biomarkers for early diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Tapper, W.J.; Collins, A.; Hamady, Z.Z.R. Predicting Pancreatic Cancer in the UK Biobank Cohort Using Polygenic Risk Scores and Diabetes Mellitus. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1665–1674.e1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Takikawa, T.; Kikuta, K.; Hamada, S.; Kume, K.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Ikeda, M.; Kataoka, F.; et al. Focal Parenchymal Atrophy of the Pancreas Is Frequently Observed on Pre-Diagnostic Computed Tomography in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koiwai, A.; Hirota, M.; Matsuura, T.; Itoh, T.; Kin, R.; Katayama, T.; Endo, K.; Takasu, A.; Kogure, T.; Murakami, K.; et al. Diffuse pancreatic parenchymal atrophy, an imaging finding predictive of the development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A case-control study. JGH Open 2023, 7, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, P.M.; Sayed, S.; Sayed, G. Hyperplastic, preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions found in 83 human pancreases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1982, 77, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, E.; Balduzzi, A.; Hijioka, S.; De Pastena, M.; Marchegiani, G.; Kato, H.; Takenaka, M.; Haba, S.; Salvia, R. Association of high-risk stigmata and worrisome features with advanced neoplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN): A systematic review. Pancreatology 2024, 24, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Jenssen, C.; Ignee, A.; Hocke, M.; Faiss, S.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Sun, S.; Dong, Y.; Dietrich, C.F. Pancreatic duct imaging during aging. Endosc. Ultrasound 2023, 12, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Butler, R.K.; Zhou, Y.; Parker, R.A.; Jeon, C.Y.; Wu, B.U. Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer Based on Imaging Features in Patients With Duct Abnormalities. Pancreas 2020, 49, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.; Dasari, V.; Jain, D. Management of Pancreatic Calculi in Chronic Pancreatitis: A Review Article. Cureus 2023, 15, e35788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, S.; Qureshi, T.A.; Deng, Z.; Wachsman, A.; Raphael, Y.; Gaddam, S.; Xie, Y.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D. Segmentation of Pancreatic Subregions in Computed Tomography Images. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, S.; Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Wachsman, A.M.; Chen, W.; Asadpour, V.; Jeon, C.Y.; Wu, B. Risk prediction of pancreatic cancer using AI analysis of pancreatic subregions in computed tomography images. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1007990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Xia, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, X.; Lambert, L.; Zhang, T.; Tang, W.; Jin, G.; Jiang, H.; Fang, X.; et al. Large-scale pancreatic cancer detection via non-contrast CT and deep learning. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Wen, K.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Huang, M.; Ma, L.; Liu, H.; et al. Clinical-radiomics nomogram using contrast-enhanced CT to predict histological grade and survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1218128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.C.; Park, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Zinreich, E.S.; Graves, J.S.; Horton, K.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Yuille, A.L.; et al. Utility of CT Radiomics Features in Differentiation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma From Normal Pancreatic Tissue. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, W.; Zhao, R.; Qiu, W.; Duan, S.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of Texture Analysis for the Differential Diagnosis of Mass-Forming Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma on Contrast-Enhanced CT Images. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, K.; Gu, X.; Duan, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. Diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced CT texture analysis to differentiate mass-forming pancreatitis from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, J.; Su, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Xia, Q. Epitranscriptomics in liver disease: Basic concepts and therapeutic potential. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezawa, K.; Fukuda, J.; Nakao, M.; Nakano, Y.; Higashi, C.; Chagi, M.; Nakaya, Y.; Ohkawa, K. Correlation between main pancreatic duct diameter measurements: Special pancreatic ultrasonography versus magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Medicine 2024, 103, e37283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaji, R.; Yamada, Y.; Shimada, R.; Matsumoto, S.; Daa, T.; Endo, Y.; Inomata, M.; Asayama, Y. Retrospective evaluation of venous phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography images in patients who developed pancreatic adenocarcinomas after treatment for nonpancreatic primary cancer. BJR Open 2021, 3, 20200069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Hou, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yao, Y.F.; Yang, G. FeAture Explorer (FAE): A tool for developing and comparing radiomics models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Mori, N.; Hirasawa, M.; Hamada, S.; Mugikura, S.; Masamune, A.; Takase, K. Abnormal Findings on “T1WI or DWI or MRCP:” An Effective Boolean Interpretation Model in Discriminating Small Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Control Group. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Nakaizumi, A.; Ioka, T.; Oshikawa, O.; Uehara, H.; Nakao, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishikawa, O.; Ohigashi, H.; Kitamra, T. Main Pancreatic Duct Dilatation: A Sign of High Risk for Pancreatic Cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 32, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Song, L.J.; Xiao, B. Chronic pancreatitis: Pain and computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging findings. World J. Radiol. 2024, 16, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.M.; Chu, L.C.; Javed, A.A.; Yasrab, M.; Blanco, A.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Kawamoto, S. Hidden in plain sight: Commonly missed early signs of pancreatic cancer on CT. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 3599–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.A.; Zhou, Y.; Puttock, E.J.; Chen, W.; Lustigova, E.; Wu, B.U. Early features of pancreatic cancer on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A case-control study. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegård, J.; Mortensen, F.V.; Cronin-Fenton, D. Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol 2017, 112, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Chen, Q.; Yu, W.; Dong, E.Y.; Chung, J.; Pandol, S.J.; Yadav, D.; Conwell, D.L.; Wu, B.U. Identification of Individuals at Increased Risk for Pancreatic Cancer in a Community-Based Cohort of Patients With Suspected Chronic Pancreatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, M.; Nakai, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Fukukura, Y.; Sato, K.; Kameda, A.; Tashiro, Y.; Kageyama, S.; Sofue, K.; Nakano, T.; et al. Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the pancreas: Clinical and radiological features compared to those of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; Koay, E.J.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A. Early detection of pancreatic cancer in high-risk individuals: Where do we go from here? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wachsman, A.M.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Asadpour, V.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Pandol, S.J.; et al. Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Asadpour, V.; Parker, R.A.; Puttock, E.J.; Lustigova, E.; Wu, B.U. Quantitative Radiomic Features from Computed Tomography Can Predict Pancreatic Cancer up to 36 Months before Diagnosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, A.; Khasawneh, H.; Korfiatis, P.; Rajamohan, N.; Suman, G.; Majumder, S.; Panda, A.; Johnson, M.P.; Larson, N.B. Radiomics-based machine-learning models can detect pancreatic cancer on prediagnostic computed tomography scans at a substantial lead time before clinical diagnosis. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1435–1446.e1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Chatterjee, A.; Lui, J.; Nehra, A.K.; Bell, M.G.; Lennon, R.J.; Kassmeyer, B.A.; Graham, R.P.; Nagayama, H.; Schulte, P.J.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes and Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. JAMA Network Open 2023, 6, e2337799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Park, S.H.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.S. Progression of Unresected Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas to Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1509–1520.e1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.; Ansary-Moghaddam, A.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Barzi, F.; Woodward, M. Type-II diabetes and pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis of 36 studies. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chu, L.C.; Hruban, R.H.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Yuille, A.L.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Ghandili, S.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Differentiating autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with CT radiomics features. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yachida, S.; Jones, S.; Bozic, I.; Antal, T.; Leary, R.; Fu, B.; Kamiyama, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Eshleman, J.R.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gukovsky, I.; Li, N.; Todoric, J.; Gukovskaya, A.; Karin, M. Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: Common features in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1199–1209.e1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Control | Pre-Diagnostic | Diagnostic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subjects (CT scans) | 117 | 104 | 100 |
| Median age (range), in years | 63 y (40–90 y) | 66 y (41–93 y) | 69 y (44–96 y) |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 58 | 52 | 50 |
| Male | 59 | 52 | 50 |
| Duratio n between pre-diagnostic and diagnostic scan | Mean 3.02 years (0.60–10 years) | ||
| 6 months–3 years | 51 cases (49.0%) | ||
| 3–6 years | 32 cases (30.8%) | ||
| 6–10 years | 21 cases (20.2%) | ||
| Class | Sample Size | Max Ductal Diameter (mm) | Min Ductal Diameter (mm) | Mean Ductal Diameter (mm) | Standard Deviation | Ductal Volume (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 117 | 1.94 ± 0.80 | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 1.10 ± 0.25 | 0.31 ± 0.29 | 1017.41 ± 446.58 |
| Pre-diagnostic | 104 | 2.59 ± 1.24 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 1.41 ± 0.70 | 0.48 ± 0.43 | 1296.21 ± 1061.06 |
| Diagnostic | 100 | 4.67 ± 2.49 | 0.97 ± 0.31 | 2.63 ± 1.46 | 1.07 ± 0.67 | 2583.22 ± 2335.84 |
| p-value (ANOVA) | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 0 vs. 1 | 0.009 | 0.961 | 0.032 | 0.023 | 0.334 | |
| 0 vs. 2 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 1 vs. 2 | 0.000 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Model | ACC | AUC | AUC (95% CIs) | SE | SP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 months–3 years | Diameter + volume | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.59–1 | 0.80 | 0.91 |
| MPD | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.73–1 | 0.90 | 0.82 | |
| Pancreas | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.65–1 | 1 | 0.73 | |
| MPD + pancreas | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.89–1 | 1 | 0.91 | |
| 3–6 years | Diameter + volume | 0.86 | 0.77 | 0.46–1 | 0.83 | 0.88 |
| MPD | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.58–1 | 0.83 | 0.75 | |
| Pancreas | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.56–1 | 0.83 | 0.75 | |
| MPD + pancreas | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.82–1 | 1 | 0.75 | |
| 6–10 years | Diameter + volume | 0.75 | 0.69 | 0.25–1 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| MPD | 0.87 | 0.75 | 0.26–1 | 0.75 | 1 | |
| Pancreas | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.35–1 | 0.75 | 0.75 | |
| MPD + pancreas | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.53–1 | 0.75 | 1 | |
| 6 months–10 years | Diameter + volume | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.56–0.87 | 0.62 | 0.83 |
| MPD | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.56–0.87 | 0.71 | 0.70 | |
| Pancreas | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.62–0.91 | 0.90 | 0.65 | |
| MPD + pancreas | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.70–0.96 | 0.86 | 0.70 |
| Delong Test | p Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 6 months–3 years | Diameter vs. MPD | 0.02 |
| MPD vs. pancreas | 0.38 | |
| MPD vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.010 | |
| Pancreas vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.000 | |
| 3–6 years | Diameter vs. MPD | 0.08 |
| MPD vs. pancreas | 0.34 | |
| MPD vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.002 | |
| Pancreas vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.01 | |
| 6–10 years | Diameter vs. MPD | 0.45 |
| MPD vs. pancreas | 0.65 | |
| MPD vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.05 | |
| Pancreas vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.05 | |
| 6 months–10 years | Diameter vs. MPD | 0.76 |
| MPD vs. pancreas | 0.000 | |
| MPD vs. MPD+ pancreas | 0.000 | |
| Pancreas vs. MPD + pancreas | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Qureshi, T.A.; Xie, Y.; Gaddam, S.; Azab, L.; Wu, C.; He, Y.; Deng, Z.; Javed, S.; et al. Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Occurrence Up to 10 Years in Advance Using Features of the Main Pancreatic Duct in Pre-Diagnostic CT Scans. Cancers 2025, 17, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111886
Wang L, Shi Y, Qureshi TA, Xie Y, Gaddam S, Azab L, Wu C, He Y, Deng Z, Javed S, et al. Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Occurrence Up to 10 Years in Advance Using Features of the Main Pancreatic Duct in Pre-Diagnostic CT Scans. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111886
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lixia, Yu Shi, Touseef Ahmad Qureshi, Yibin Xie, Srinivas Gaddam, Linda Azab, Chaowei Wu, Yimeng He, Zengtian Deng, Sehrish Javed, and et al. 2025. "Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Occurrence Up to 10 Years in Advance Using Features of the Main Pancreatic Duct in Pre-Diagnostic CT Scans" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111886
APA StyleWang, L., Shi, Y., Qureshi, T. A., Xie, Y., Gaddam, S., Azab, L., Wu, C., He, Y., Deng, Z., Javed, S., Diwan, G., Vendrami, C. L., Rodriguez, A., Specht, K., Jeon, C. Y., Chaudhry, H., Buxbaum, J. L., Pisegna, J. R., Yaghmai, V., ... Li, D. (2025). Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Occurrence Up to 10 Years in Advance Using Features of the Main Pancreatic Duct in Pre-Diagnostic CT Scans. Cancers, 17(11), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111886







