The Role of Microbiota in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
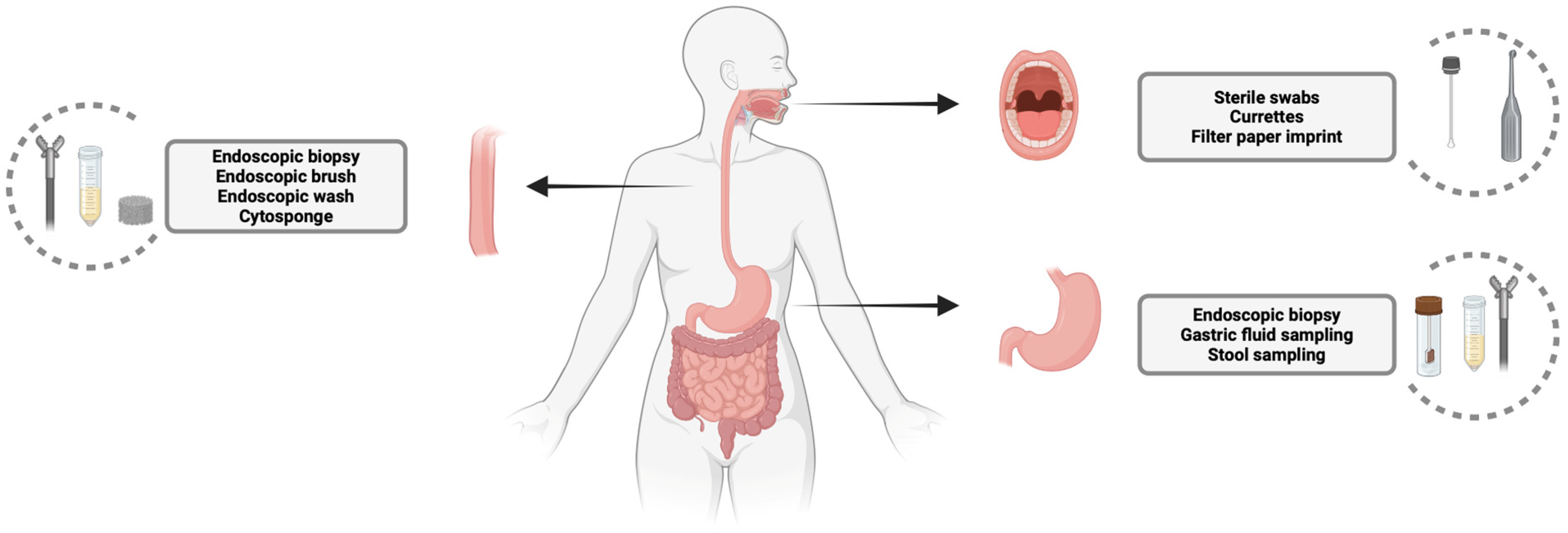
2. Sampling of Oral, Esophageal, and Gastric Microbiota: Techniques and Relevance
2.1. Oral Microbiota Sampling
2.2. Esophageal Microbiota Sampling
2.3. Gastric Microbiota Sampling
3. Microbiota in Esophageal Cancer
3.1. Microbial Alterations in Barrett’s Esophagus
3.2. Microbial Alterations in Esophageal Cancer
3.3. Microbiota and Esophageal Cancer Screening and Prognosis
3.4. Microbiota Modulation in Esophageal Cancer
4. Microbiota in Gastric Cancer
4.1. Microbiota in Gastric Cancer
4.2. Non-Helicobacter Pylori Microbiota Alteration in Gastric Cancer
4.3. Microbiota and Gastric Cancer Screening and Prognosis
4.4. Microbiota Modulation in Gastric Cancer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smyth, E.C.; Lagergren, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Lordick, F.; Shah, M.A.; Lagergren, P.; Cunningham, D. Oesophageal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, G.; Tropini, C. The Gut Microbiota and Its Biogeography. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Ando, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Maeda, O.; Watanabe, O.; Funasaka, K.; Nakamura, M.; Miyahara, R.; Ohmiya, N.; Goto, H. Characterization of Bacterial Biota in the Distal Esophagus of Japanese Patients with Reflux Esophagitis and Barrett’s Esophagus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radani, N.; Metwaly, A.; Reitmeier, S.; Baumeister, T.; Ingermann, J.; Horstmann, J.; Anand, A.; Gatz, I.; Kohlmayer, F.; Janssen, K.P.; et al. Analysis of Fecal, Salivary, and Tissue Microbiome in Barrett’s Esophagus, Dysplasia, and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, S.; Luan, S.; Xiao, X.; Yang, Y.; Mao, C.; Chen, L.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Gut Microbiota for Esophageal Cancer: Role in Carcinogenesis and Clinical Implications. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 71242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.B.; Coburn, S.B.; Lam, J.R.; Taylor, P.R.; Schneider, J.L.; Corley, D.A. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Risks in a Large US Barrett’s Oesophagus Cohort. Gut 2018, 67, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P. Barrett Esophagus. JAMA 2022, 328, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, X.; Nossa, C.W.; Francois, F.; Peek, R.M.; Pei, Z. Inflammation and Intestinal Metaplasia of the Distal Esophagus Are Associated with Alterations in the Microbiome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, W.; Peng, L.; Yan, B.; Li, Z.; Pan, F. Human Microbiota in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 791214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Compres, G.; Freedberg, D.E.; Giddins, M.J.; Khiabanian, H.; Lightdale, C.J.; Nobel, Y.R.; Toussaint, N.C.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Abrams, J.A. Barrett’s Esophagus Is Associated with a Distinct Oral Microbiome. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Goh, K.L.; Fock, K.M.; Mitchell, H.M.; Kaakoush, N.O. Dysbiosis of the Microbiome in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.D.; Gadalla, S.M.; Anderson, L.A.; Rabkin, C.S.; Cardwell, C.R.; Song, M.; Camargo, M.C. Autoimmune Conditions and Gastric Cancer Risk in a Population-Based Study in the United Kingdom. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Yu, H.T.; Kuo, C.L.; Chang, Y.Y.; Meng, F.T.; Wu, Y.X.; Hsiao, J.L.; Chen, M.J.; Lin, K.P.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Incidence of Gastric Cancer Between 1980 and 2022. Gastroenterology 2024, 166, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Perez Perez, G.I. Is There a Role for the Non-Helicobacter Pylori Bacteria in the Risk of Developing Gastric Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Q.; Miao, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, C.; Guan, W. Gastric Microbiota: An Emerging Player in Gastric Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1130001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Weng, W.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Increases Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells and Tumor Development in Mice by Activating Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling to Nuclear Factor-ΚB, and Up-Regulating Expression of MicroRNA-21. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 851–866.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, M.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Hao, Y.; Cai, G.; Han, Y.W. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Promotes Colorectal Carcinogenesis by Modulating E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Signaling via Its FadA Adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, C.; Ibrahim, Y.; Isaacson, B.; Yamin, R.; Abed, J.; Gamliel, M.; Enk, J.; Bar-On, Y.; Stanietsky-Kaynan, N.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; et al. Binding of the Fap2 Protein of Fusobacterium Nucleatum to Human Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Protects Tumors from Immune Cell Attack. Immunity 2015, 42, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, C.; Alkhateeb, A.A.; Deanhardt, B.K.; Macdonald, J.K.; Chi, D.L.; Wang, J.R.; Wolfgang, M.C. Saliva Sampling Method Influences Oral Microbiome Composition and Taxa Distribution Associated with Oral Diseases. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, F. The Sampling Strategy of Oral Microbiome. iMeta 2022, 1, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; Fabbri, C.; D’Accolti, M.; Soffritti, I.; Bassi, C.; Mazzacane, S.; Franchi, M. Defining the Oral Microbiome by Whole-Genome Sequencing and Resistome Analysis: The Complexity of the Healthy Picture. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzychczy-Sroka, B.; Talaga-Ćwiertnia, K.; Sroka-Oleksiak, A.; Gurgul, A.; Zarzecka-Francica, E.; Ostrowski, W.; Kąkol, J.; Drożdż, K.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Zarzecka, J. Standardization of the Protocol for Oral Cavity Examination and Collecting of the Biological Samples for Microbiome Research Using the Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Own Experience with the COVID-19 Patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanen, P.; Siikala, E.; Uittamo, J.; Richardson, M.; Rautemaa, R. A Novel Method for Sampling the Microbiota from the Oral Mucosa. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2009, 13, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, J. A Comparative Study of Sampling Methods in the Detection of Esophageal Cancer-Related Microbiota. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0038924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Gail, M.H.; Shi, J.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Paster, B.J.; Dye, B.A.; Wang, G.Q.; Wei, W.Q.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; et al. Association between Upper Digestive Tract Microbiota and Cancer Predisposing States in the Esophagus and Stomach. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yip, H.C.; Cheung, M.K.; Chan, H.C.; Ng, C.; Lau, E.H.L.; Yeung, Z.W.C.; Wong, E.W.Y.; Leung, L.; Qu, X.; et al. Convergent Dysbiosis of Upper Aerodigestive Microbiota between Patients with Esophageal and Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillon, S.A.; Harris, J.K.; Wagner, B.D.; Kelly, C.J.; Stevens, M.J.; Moore, W.; Fang, R.; Schroeder, S.; Masterson, J.C.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Novel Device to Sample the Esophageal Microbiome—The Esophageal String Test. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijimaya, T.; Tahara, T.; Yamazaki, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Tomiyama, T.; Fukui, T.; Shibata, T.; et al. Microbiome of Esophageal Endoscopic Wash Samples Is Associated with Resident Flora in the Esophagus and Incidence of Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.R.F.; Walker, A.W.; O’Donovan, M.; Parkhill, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C. A Non-Endoscopic Device to Sample the Oesophageal Microbiota: A Case-Control Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januszewicz, W.; Tan, W.K.; Lehovsky, K.; Debiram-Beecham, I.; Nuckcheddy, T.; Moist, S.; Kadri, S.; di Pietro, M.; Boussioutas, A.; Shaheen, N.J.; et al. Safety and Acceptability of Esophageal Cytosponge Cell Collection Device in a Pooled Analysis of Data From Individual Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 647–656.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Jin, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Current Sampling Methods for Gut Microbiota: A Call for More Precise Devices. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 493817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalon, D.; Culver, R.N.; Grembi, J.A.; Folz, J.; Treit, P.V.; Shi, H.; Rosenberger, F.A.; Dethlefsen, L.; Meng, X.; Yaffe, E.; et al. Profiling the Human Intestinal Environment under Physiological Conditions. Nature 2023, 617, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Article, O.; Sung, J.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.; Jo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Nam, R.H.; Seok, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, D.H.; et al. Comparison of Gastric Microbiota Between Gastric Juice and Mucosa by Next Generation Sequencing Method. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Mira, A.; Suárez, A.; Mayo, B. Microbiological Survey of the Human Gastric Ecosystem Using Culturing and Pyrosequencing Methods. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Seo, H.; Kang, C.S.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, J.W.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, Y.K. Dysbiotic Change in Gastric Microbiome and Its Functional Implication in Gastric Carcinogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandsberg, N.K.; Moro, G.; Ghavami, M.; Andersen, S.B.; de Visser, E.N.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Mortensen, M.S.; Licht, T.R.; Boisen, A. Ingestible Device for Gastric Fluid Sampling. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 9, 2400434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hoang, M.C.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Multiple Sampling Capsule Robot for Studying Gut Microbiome. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2300625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermannová, R.; Alsina, M.; Cervantes, A.; Leong, T.; Lordick, F.; Nilsson, M.; van Grieken, N.C.T.; Vogel, A.; Smyth, E.C. Oesophageal Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Feng, L.; Cai, X.; Qian, Y.; Xu, L. Esophageal Microflora in Esophageal Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1145791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendra, S.; Wang, B.; Snow, E.T.; Sharma, P.; Pavey, D.; Merrett, N.; Ball, M.J.; Brain, T.; Fernando, R.; Robertson, I.K. Transcriptionally Active Human Papillomavirus Is Strongly Associated with Barrett’s Dysplasia and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1082–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norder Grusell, E.; Dahlén, G.; Ruth, M.; Ny, L.; Quiding-Järbrink, M.; Bergquist, H.; Bove, M. Bacterial Flora of the Human Oral Cavity, and the Upper and Lower Esophagus. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 26, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, A.; Fero, J.; McCoy, C.; Claywell, B.C.; Sanchez, C.A.; Blount, P.L.; Li, X.; Vaughan, T.L.; Matsen, F.A.; Reid, B.J.; et al. Bacterial Composition of the Human Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiome Is Dynamic and Associated with Genomic Instability in a Barrett’s Esophagus Cohort. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopetuso, L.R.; Severgnini, M.; Pecere, S.; Ponziani, F.R.; Boskoski, I.; Larghi, A.; Quaranta, G.; Masucci, L.; Ianiro, G.; Camboni, T.; et al. Esophageal Microbiome Signature in Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, N.P.; Riordan, S.M.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Wilkins, M.R.; Kaakoush, N.O. Signatures within the Esophageal Microbiome Are Associated with Host Genetics, Age, and Disease. Microbiome 2018, 6, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okereke, I.C.; Miller, A.L.; Jupiter, D.C.; Hamilton, C.F.; Reep, G.L.; Krill, T.; Andersen, C.R.; Pyles, R.B. Microbiota Detection Patterns Correlate With Presence and Severity of Barrett’s Esophagus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 555072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackett, K.L.; Siddhi, S.S.; Cleary, S.; Steed, H.; Miller, M.H.; MacFarlane, S.; MacFarlane, G.T.; Dillon, J.F. Oesophageal Bacterial Biofilm Changes in Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease, Barrett’s and Oesophageal Carcinoma: Association or Causality? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, S.; García-Zaragozá, E.; Hernández, C.; Quintana, E.; Felipo, V.; Esplugues, J.V.; Barrachina, M.D. Downregulation of NNOS and Synthesis of PGs Associated with Endotoxin-Induced Delay in Gastric Emptying. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G1360–G1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.R.; Jiang, Y.; Villalta, P.W.; Stornetta, A.; Boudreau, P.D.; Carrá, A.; Brennan, C.A.; Chun, E.; Ngo, L.; Samson, L.D.; et al. The Human Gut Bacterial Genotoxin Colibactin Alkylates DNA. Science 2019, 363, eaar7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Nadeem, M.; Naseem, K.; Amjad, W.; Zahid, R.; Haider, M.; Farooq, U.; Sohail, A. S464 Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Risk of Esophageal Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 116, S205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.L.; Duan, R.Q.; Duan, L.P. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Barrett’s Esophagus: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shrestha, P.; Qiu, Z.; Harman, D.G.; Teoh, W.C.; Al-Sohaily, S.; Liem, H.; Turner, I.; Ho, V. Distinct Microbiota Dysbiosis in Patients with Non-Erosive Reflux Disease and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tözün, N.; Vardareli, E. Gut Microbiome and Gastrointestinal Cancer Les Liaisons Dangereuses. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 50, S191–S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, C.H.; Jia, M.; Xing, X.; Gao, L.; Tsai, H.T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Yeung, S.C.J.; et al. Tumor-Associated Microbiota in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, C.; Yadlapati, R.; Shah, S.; Knight, R.; Curtius, K. Challenges in Determining the Role of Microbiome Evolution in Barrett’s Esophagus and Progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shao, D.; Fan, Z.; Qin, J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, C.; et al. Non-Invasive Early Detection on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Precancerous Lesions by Microbial Biomarkers Combining Epidemiological Factors in China. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, K.; Izumi, D.; Kandimalla, R.; Sonohara, F.; Baba, Y.; Yoshida, N.; Kodera, Y.; Baba, H.; Goel, A. Intratumoral Fusobacterium Nucleatum Levels Predict Therapeutic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6170–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-F.; Lu, M.-S.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Chen, W.-C. Porphyromonas Gingivalis Promotes Tumor Progression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 44, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X.-E.; He, F.; Liu, S.; Yan, S.; Huang, L.; Lu, W.; et al. Streptococcus and Prevotella Are Associated with the Prognosis of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiecka, A.; Szczepanik, M. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Induced Gut Dysbiosis and Immunomodulation: Current Knowledge and Potential Restoration by Probiotics. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Compres, G.; Freedberg, D.E.; Khiabanian, H.; Nobel, Y.R.; Stump, S.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Lightdale, C.J.; Abrams, J.A. Alterations to the Esophageal Microbiome Associated with Progression from Barrett’s Esophagus to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, I.; Konikoff, F.M.; Oppenheim, M.; Gophna, U.; Half, E.E. Gastric Microbiota Is Altered in Oesophagitis and Barrett’s Oesophagus and Further Modified by Proton Pump Inhibitors. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sohda, M.; Kim, M.; Saito, H.; Ubukata, Y.; Nakazawa, N.; Kuriyama, K.; Hara, K.; Sano, A.; Sakai, M.; et al. Preoperative Evaluation of Oral Hygiene May Predict the Overall Survival of Patients with Esophageal Cancer. Esophagus 2023, 20, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, G.; Liu, X. Dietary Fiber Intake Reduces Risk for Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Cancer. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobel, Y.R.; Snider, E.J.; Compres, G.; Freedberg, D.E.; Khiabanian, H.; Lightdale, C.J.; Toussaint, N.C.; Abrams, J.A. Increasing Dietary Fiber Intake Is Associated with a Distinct Esophageal Microbiome. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2018, 9, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; Fu, X. Gastric Microbiota Dysbiosis and Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1153269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.M.; Pereira-Marques, J.; Pinto-Ribeiro, I.; Costa, J.L.; Carneiro, F.; MacHado, J.C.; Figueiredo, C. Gastric Microbial Community Profiling Reveals a Dysbiotic Cancer-Associated Microbiota. Gut 2018, 67, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Infection Is Prevalent in Human Colorectal Carcinoma. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Song, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Xu, Z.Z. Meta-Analysis Reveals Helicobacter Pylori Mutual Exclusivity and Reproducible Gastric Microbiome Alterations during Gastric Carcinoma Progression. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2197835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.F.; Lindberg, M.; Jakobsson, H.; Bäckhed, F.; Nyrén, P.; Engstrand, L. Comparative Analysis of Human Gut Microbiota by Barcoded Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Meek, B.; Doi, Y.; Muramatsu, M.; Chiba, T.; Honjo, T.; Fagarasan, S. Aberrant Expansion of Segmented Filamentous Bacteria in IgA-Deficient Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B.N.; Ijaz, U.Z.; D’Amore, R.; Burkitt, M.D.; Eccles, R.; Lenzi, L.; Duckworth, C.A.; Moore, A.R.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Varro, A.; et al. Comparison of the Human Gastric Microbiota in Hypochlorhydric States Arising as a Result of Helicobacter Pylori-Induced Atrophic Gastritis, Autoimmune Atrophic Gastritis and Proton Pump Inhibitor Use. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.H.; Lin, J.T.; Ho, H.J.; Lai, Z.L.; Wang, C.B.; Tang, S.L.; Wu, C.Y. Gastric Microbiota and Predicted Gene Functions Are Altered after Subtotal Gastrectomy in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.Y.; Tung, S.Y.; Pan, H.Y.; Yen, C.W.; Xu, H.W.; Lin, Y.J.; Deng, Y.F.; Hsu, W.T.; Wu, C.S.; Li, C. Increased Abundance of Clostridium and Fusobacterium in Gastric Microbiota of Patients with Gastric Cancer in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, H.; Xia, M.; Chen, X.-L.; Kudriashov, V.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.-H.; Jiang, H.; et al. Distinct Oral-Associated Gastric Microbiota and Helicobacter Pylori Communities for Spatial Microbial Heterogeneity in Gastric Cancer. mSystems 2024, 9, e0008924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloliqi, A.A. Towards Identification of Therapeutics against Multi-Infections and Cancers Causing Propionibacterium Acnes: Molecular Modeling and Dynamics Simulation Investigation. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 415, 126373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Ji, F.; Mei, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, F.; Yan, C.; Li, L.; Ling, Z. Alterations of Gastric Mucosal Microbiota across Different Stomach Microhabitats in a Cohort of 276 Patients with Gastric Cancer. eBioMedicine 2018, 40, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoul, P.; Maccauro, V.; Cintoni, M.; Scarpellini, E.; Ianiro, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C.; Rinninella, E. Microbiota–Gastric Cancer Interactions and the Potential Influence of Nutritional Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Potentiates Intestinal Tumorigenesis and Modulates the Tumor-Immune Microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.Y.; Tung, S.Y.; Pan, H.Y.; Chang, T.S.; Wei, K.L.; Chen, W.M.; Deng, Y.F.; Lu, C.K.; Lai, Y.H.; Wu, C.S.; et al. Fusobacterium Nucleatum Colonization Is Associated with Decreased Survival of Helicobacter Pylori-Positive Gastric Cancer Patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7311–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicksved, J.; Lindberg, M.; Rosenquist, M.; Enroth, H.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. Molecular Characterization of the Stomach Microbiota in Patients with Gastric Cancer and in Controls. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.A.; Garrett, W.S. Fusobacterium Nucleatum—Symbiont, Opportunist and Oncobacterium. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 17, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertpiriyapong, K.; Whary, M.T.; Muthupalani, S.; Lofgren, J.L.; Gamazon, E.R.; Feng, Y.; Ge, Z.; Wang, T.C.; Fox, J.G. Gastric Colonisation with a Restricted Commensal Microbiota Replicates the Promotion of Neoplastic Lesions by Diverse Intestinal Microbiota in the Helicobacter Pylori INS-GAS Mouse Model of Gastric Carcinogenesis. Gut 2014, 63, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Han, M.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Dong, Y.; Sun, T.; Xu, J. Intratumoral and Fecal Microbiota Reveals Microbial Markers Associated with Gastric Carcinogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1397466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Gao, X.; Wu, L.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y. Salivary Microbiota for Gastric Cancer Prediction: An Exploratory Study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 640309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ding, X.; Song, Q.; Zhao, G.; Han, L.; Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Hao, X.; Li, H. Alterations in Mucosa-Associated Microbiota in the Stomach of Patients with Gastric Cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.K.; Park, J.C.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.J.; Jeong, H.; Oh, Y.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Human Gastric Microbiota Transplantation Recapitulates Premalignant Lesions in Germ-Free Mice. Gut 2021, 71, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.Q.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, S.S.; Chen, L.; Hu, Y.; Yu, L.M.; Xu, J.M.; Lyu, B. Impact of Helicobacter Pylori Eradication on the Gastric Microbiome. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Rocco, G.; Zaccari, P.; Porowska, B.; Mascellino, M.T.; Severi, C. Helicobacter Pylori Infection and Gastric Dysbiosis: Can Probiotics Administration Be Useful to Treat This Condition? Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 6237239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Leung, W.K. Long-Term Use of Proton-Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Gastric Cancer: A Review of the Current Evidence. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819834511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xiao, S.; Li, S.; Suo, B.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, L. The Impact of Helicobacter Pylori Infection, Eradication Therapy, and Probiotics Intervention on Gastric Microbiota in Young Adults. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, T. Effects of Probiotics on Gastric Cancer-Related Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, R.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. Probiotics in Helicobacter Pylori Eradication Therapy: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Zheng, C.; Xu, X.; Jin, R.; Huang, F.; Shi, M.; He, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Clostridium Butyricum Potentially Improves Inflammation and Immunity through Alteration of the Microbiota and Metabolism of Gastric Cancer Patients after Gastrectomy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1076245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gong, M.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Mackay, C.R.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolites Facilitate Anticancer Therapy Efficacy by Modulating Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cell Immunity. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 988–1000.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Gou, H.; Lau, H.C.H.; Yu, J. Stomach Microbiota in Gastric Cancer Development and Clinical Implications. Gut 2024, 73, 2062–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marasco, G.; Colecchia, L.; Salvi, D.; Bruni, A.; Capelli, C.; Dajti, E.; Barbaro, M.R.; Cremon, C.; Stanghellini, V.; Barbara, G. The Role of Microbiota in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancers 2025, 17, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101719
Marasco G, Colecchia L, Salvi D, Bruni A, Capelli C, Dajti E, Barbaro MR, Cremon C, Stanghellini V, Barbara G. The Role of Microbiota in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancers. 2025; 17(10):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101719
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarasco, Giovanni, Luigi Colecchia, Daniele Salvi, Angelo Bruni, Cecilia Capelli, Elton Dajti, Maria Raffaella Barbaro, Cesare Cremon, Vincenzo Stanghellini, and Giovanni Barbara. 2025. "The Role of Microbiota in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers" Cancers 17, no. 10: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101719
APA StyleMarasco, G., Colecchia, L., Salvi, D., Bruni, A., Capelli, C., Dajti, E., Barbaro, M. R., Cremon, C., Stanghellini, V., & Barbara, G. (2025). The Role of Microbiota in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancers, 17(10), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17101719






