NGS-Guided Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer and Gynecological Tumors—A Retrospective Molecular Tumor Board Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort and Workflow
2.2. Tissue Samples and DNA Extraction
2.3. Library Preparation and Next Generation Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of Genetic Variants
2.5. Variant Interpretation and Therapy Recommendations
2.6. Immunohistochemistry for PD-L1, Her2, and MMRD/MSI and Determination of Tumor Mutation Burden (TMB)
2.7. Outcome and Clinical Data Assessment
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and MTB Workflow
3.2. Characteristics of Patients Undergoing NGS Analysis
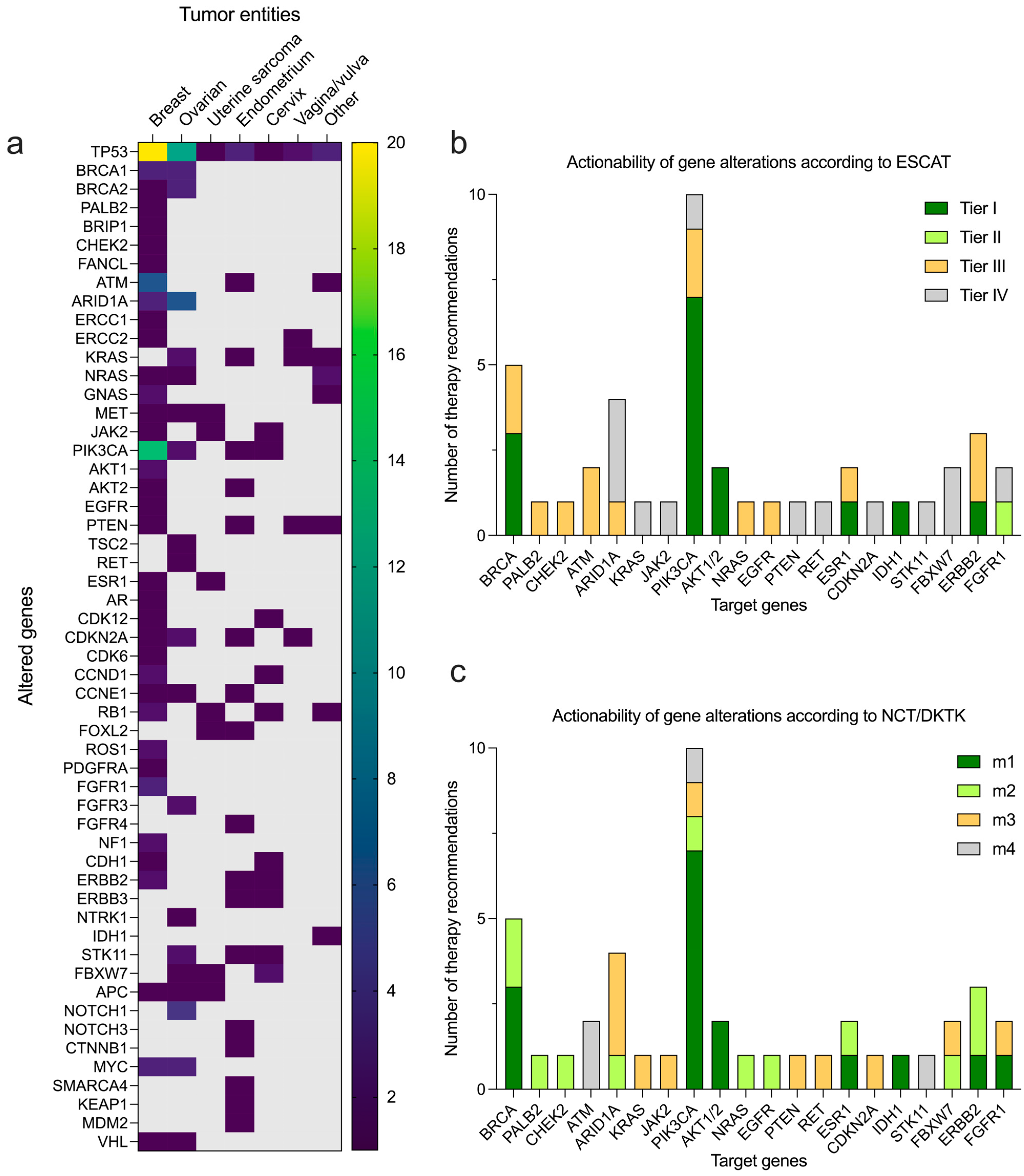
3.3. Molecular Testing and Therapeutic Suggestions
3.4. Outcomes with MTB Recommended Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mateo, J.; Steuten, L.; Aftimos, P.; André, F.; Davies, M.; Garralda, E.; Geissler, J.; Husereau, D.; Martinez-Lopez, I.; Normanno, N.; et al. Delivering precision oncology to patients with cancer. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.R.; Oliva, M.; Sabatini, P.J.B.; Stockley, T.L.; Siu, L.L. Molecular profiling for precision cancer therapies. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugger, S.A.; Platt, A.; Goldstein, D.B. Drug development in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Drilon, A.; Chakravarty, D. Precision Oncology: 2022 in Review. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.; Fletcher, P.; Popat, S.; Savage, J.; Summers, Y.; Greystoke, A.; Gilligan, D.; Cave, J.; O’Rourke, N.; Brewster, A.; et al. The National Lung Matrix Trial of personalized therapy in lung cancer. Nature 2020, 583, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner, A.; Kron, A.; van den Berg, N.; Moon, K.; Scheffler, M.; Schillinger, G.; Pelusi, N.; Hartmann, N.; Rieke, D.T.; Stephan-Falkenau, S.; et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of a nationwide precision medicine program for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Germany: A historical cohort analysis. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 36, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosinsky, A.; Ambrose, J.; Cross, W.; Turnbull, C.; Henderson, S.; Jones, L.; Hamblin, A.; Arumugam, P.; Chan, G.; Chubb, D.; et al. Insights for precision oncology from the integration of genomic and clinical data of 13,880 tumors from the 100,000 Genomes Cancer Programme. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodepeter, F.R.; Teply-Szymanski, J.; Romey, M.; Grass, A.; Erber, R.; Lebeau, A.; Mack, E.K.M.; Tarawneh, T.S.; Gremke, N.; Boekhoff, J.; et al. Clinically relevant molecular pathological diagnostics in breast cancer. Pathologie 2023, 44, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Pothuri, B.; Vergote, I.; DePont Christensen, R.; Graybill, W.; Mirza, M.R.; McCormick, C.; Lorusso, D.; Hoskins, P.; Freyer, G.; et al. Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.L.; Oza, A.M.; Lorusso, D.; Aghajanian, C.; Oaknin, A.; Dean, A.; Colombo, N.; Weberpals, J.I.; Clamp, A.; Scambia, G.; et al. Rucaparib maintenance treatment for recurrent ovarian carcinoma after response to platinum therapy (ARIEL3): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Monk, B.J.; Herrstedt, J.; Oza, A.M.; Mahner, S.; Redondo, A.; Fabbro, M.; Ledermann, J.A.; Lorusso, D.; Vergote, I.; et al. Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive, Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, J.; Harter, P.; Gourley, C.; Friedlander, M.; Vergote, I.; Rustin, G.; Scott, C.; Meier, W.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Safra, T.; et al. Olaparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, J.; Harter, P.; Gourley, C.; Friedlander, M.; Vergote, I.; Rustin, G.; Scott, C.L.; Meier, W.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Safra, T.; et al. Olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: A preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charo, L.M.; Eskander, R.N.; Sicklick, J.; Kim, K.H.; Lim, H.J.; Okamura, R.; Lee, S.; Subramanian, R.; Schwab, R.; Shatsky, R.; et al. Real-World Data From a Molecular Tumor Board: Improved Outcomes in Breast and Gynecologic Cancers Patients With Precision Medicine. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2000508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Berton-Rigaud, D.; Elez, E.; Pishvaian, M.J.; Rugo, H.S.; Puzanov, I.; Mehnert, J.M.; Aung, K.L.; Lopez, J.; et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of Pembrolizumab in Advanced Programmed Death Ligand 1-Positive Endometrial Cancer: Results From the KEYNOTE-028 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell-Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murciano-Goroff, Y.R.; Suehnholz, S.P.; Drilon, A.; Chakravarty, D. Precision Oncology: 2023 in Review. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Tourneau, C.; Delord, J.P.; Goncalves, A.; Gavoille, C.; Dubot, C.; Isambert, N.; Campone, M.; Tredan, O.; Massiani, M.A.; Mauborgne, C.; et al. Molecularly targeted therapy based on tumour molecular profiling versus conventional therapy for advanced cancer (SHIVA): A multicentre, open-label, proof-of-concept, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, D.M.; Taylor, B.S.; Baselga, J. Implementing Genome-Driven Oncology. Cell 2017, 168, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V. Perspective: The precision-oncology illusion. Nature 2016, 537, S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannock, I.F.; Hickman, J.A. Limits to Personalized Cancer Medicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultova, E.; Westphalen, C.B.; Jung, A.; Kumbrink, J.; Kirchner, T.; Mayr, D.; Rudelius, M.; Ormanns, S.; Heinemann, V.; Metzeler, K.H.; et al. NGS-guided precision oncology in metastatic breast and gynecological cancer: First experiences at the CCC Munich LMU. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 303, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzas, S.; Kuemmel, S.; Harrach, H.; Breit, E.; Ataseven, B.; Traut, A.; Ruland, A.; Kostara, A.; Chiari, O.; Dittmer-Grabowski, C.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing-Directed Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer in Routine Clinical Practice. Cancers 2021, 13, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, F.; Filleron, T.; Kamal, M.; Mosele, F.; Arnedos, M.; Dalenc, F.; Sablin, M.-P.; Campone, M.; Bonnefoi, H.; Lefeuvre-Plesse, C.; et al. Genomics to select treatment for patients with metastatic breast cancer. Nature 2022, 610, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illert, A.L.; Stenzinger, A.; Bitzer, M.; Horak, P.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Moller, Y.; Beha, J.; Oner, O.; Schmitt, F.; Lassmann, S.; et al. The German Network for Personalized Medicine to enhance patient care and translational research. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, T.S.; Rodepeter, F.R.; Teply-Szymanski, J.; Ross, P.; Koch, V.; Tholken, C.; Schafer, J.A.; Gremke, N.; Mack, H.I.D.; Gold, J.; et al. Combined Focused Next-Generation Sequencing Assays to Guide Precision Oncology in Solid Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis from an Institutional Molecular Tumor Board. Cancers 2022, 14, 4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liebers, M.; Zhelyazkova, B.; Cao, Y.; Panditi, D.; Lynch, K.D.; Chen, J.; Robinson, H.E.; Shim, H.S.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Anchored multiplex PCR for targeted next-generation sequencing. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Phillips, S.M.; Kundra, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Rudolph, J.E.; Yaeger, R.; Soumerai, T.; Nissan, M.H.; et al. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.; Spies, N.C.; Krysiak, K.; McMichael, J.F.; Coffman, A.C.; Danos, A.M.; Ainscough, B.J.; Ramirez, C.A.; Rieke, D.T.; Kujan, L.; et al. CIViC is a community knowledgebase for expert crowdsourcing the clinical interpretation of variants in cancer. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, S.E.; Liu, R.; Statz, C.M.; Durkin, D.; Lakshminarayana, A.; Mockus, S.M. The clinical trial landscape in oncology and connectivity of somatic mutational profiles to targeted therapies. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrum, M.J.; Chitipiralla, S.; Brown, G.R.; Chen, C.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; Kaur, K.; Liu, C.; et al. ClinVar: Improvements to accessing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D835–D844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, P.; Griffith, M.; Danos, A.M.; Pitel, B.A.; Madhavan, S.; Liu, X.; Chow, C.; Williams, H.; Carmody, L.; Barrow-Laing, L.; et al. Standards for the classification of pathogenicity of somatic variants in cancer (oncogenicity): Joint recommendations of Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen), Cancer Genomics Consortium (CGC), and Variant Interpretation for Cancer Consortium (VICC). Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Dienstmann, R.; Jezdic, S.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Lopez-Bigas, N.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Bedard, P.L.; Tortora, G.; Douillard, J.Y.; et al. A framework to rank genomic alterations as targets for cancer precision medicine: The ESMO Scale for Clinical Actionability of molecular Targets (ESCAT). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichsenring, J.; Horak, P.; Kreutzfeldt, S.; Heining, C.; Christopoulos, P.; Volckmar, A.-L.; Neumann, O.; Kirchner, M.; Ploeger, C.; Budczies, J.; et al. Variant classification in precision oncology. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 2996–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, P.; Heining, C.; Kreutzfeldt, S.; Hutter, B.; Mock, A.; Hullein, J.; Frohlich, M.; Uhrig, S.; Jahn, A.; Rump, A.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic and Transcriptomic Analysis for Guiding Therapeutic Decisions in Patients with Rare Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2780–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildhaus, H.U. Predictive value of PD-L1 diagnostics. Pathologe 2018, 39, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.; Schwartz, J.N.; Hagerty, K.L.; Allred, D.C.; Cote, R.J.; Dowsett, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hanna, W.M.; Langer, A.; et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.; Hicks, D.G.; Dowsett, M.; McShane, L.M.; Allison, K.H.; Allred, D.C.; Bartlett, J.M.; Bilous, M.; Fitzgibbons, P.; et al. Recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3997–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, A.C.; Somerfield, M.R.; Dowsett, M.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; McShane, L.M.; Saphner, T.J.; Spears, P.A.; Allison, K.H. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO–College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuemmel, S.; Harrach, H.; Schmutzler, R.K.; Kostara, A.; Ziegler-Lohr, K.; Dyson, M.H.; Chiari, O.; Reinisch, M. Olaparib for metastatic breast cancer in a patient with a germline PALB2 variant. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, D.D.V.; Stephenson, J.J., Jr.; Rosen, P.; Loesch, D.M.; Borad, M.J.; Anthony, S.; Jameson, G.; Brown, S.; Cantafio, N.; Richards, D.A.; et al. Pilot Study Using Molecular Profiling of Patients’ Tumors to Find Potential Targets and Select Treatments for Their Refractory Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4877–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovich, M.; Kiel, P.J.; Nance, S.M.; Niland, E.E.; Parsley, M.E.; Ferguson, M.E.; Jiang, G.; Ammakkanavar, N.R.; Einhorn, L.H.; Cheng, L.; et al. Clinical benefit of a precision medicine based approach for guiding treatment of refractory cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56491–56500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Solomon, B.; Loong, H.H.; Park, K.; Perol, M.; Arriola, E.; Novello, S.; Han, B.; Zhou, J.; Ardizzoni, A.; et al. First-Line Selpercatinib or Chemotherapy and Pembrolizumab in RET Fusion-Positive NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrosian, I.; Somerfield, M.R.; Achatz, M.I.; Boughey, J.C.; Curigliano, G.; Friedman, S.; Kohlmann, W.K.; Kurian, A.W.; Laronga, C.; Lynce, F.; et al. Germline Testing in Patients With Breast Cancer: ASCO-Society of Surgical Oncology Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 584–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamborero, D.; Dienstmann, R.; Rachid, M.H.; Boekel, J.; Lopez-Fernandez, A.; Jonsson, M.; Razzak, A.; Braña, I.; De Petris, L.; Yachnin, J.; et al. The Molecular Tumor Board Portal supports clinical decisions and automated reporting for precision oncology. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Kahle, M.; Vo, H.H.; Baysal, M.A.; Johnson, A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Molecular tumour boards—Current and future considerations for precision oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 843–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Vicenzi, P.; Sharma, I.; Orr, K.; Teller, C.; Koentz, M.; Trinkman, H.; Vallance, K.; Ray, A. Molecular Tumor Boards: The Next Step towards Precision Therapy in Cancer Care. Hematol. Rep. 2023, 15, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, C.; Hartkopf, A.; Koch, A.; Klaumünzer, M.; Schulze, M.; Grischke, E.-M.; Taran, F.-A.; Brucker, S.; Battke, F.; Biskup, S. Sequencing for an interdisciplinary molecular tumor board in patients with advanced breast cancer: Experiences from a case series. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 3279–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelli, A.; Chiatamone Ranieri, S.; Di Giacomo, D.; Malatesta, S.; Patruno, L.V.; Tessitore, A.; Alesse, E.; Cannita, K. Role of the Molecular Tumor Board for the Personalized Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Focus on the State of the Art in Italy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.C.; Korkut, A.; Kanchi, R.S.; Hegde, A.M.; Lenoir, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, H.; Shen, H.; Ravikumar, V.; et al. A Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Molecular Study of Gynecologic and Breast Cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 690–705.e699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernas, S.; Villagrasa, P.; Vivancos, A.; Scaltriti, M.; Rodón, J.; Burgués, O.; Nuciforo, P.; Canes, J.; Paré, L.; Dueñas, M.; et al. First Nationwide Molecular Screening Program in Spain for Patients With Advanced Breast Cancer: Results From the AGATA SOLTI-1301 Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 744112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftimos, P.; Oliveira, M.; Irrthum, A.; Fumagalli, D.; Sotiriou, C.; Gal-Yam, E.N.; Robson, M.E.; Ndozeng, J.; Di Leo, A.; Ciruelos, E.M.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Analyses of Breast Cancer Primaries and Matched Metastases in AURORA, the Breast International Group (BIG) Molecular Screening Initiative. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2796–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, B.A.; Schwaederle, M.; Scur, M.D.; Boles, S.G.; Helsten, T.; Subramanian, R.; Schwab, R.B.; Kurzrock, R. Breast Cancer Experience of the Molecular Tumor Board at the University of California, San Diego Moores Cancer Center. J Oncol Pract. 2015, 11, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, I.; Mori, S.; Hayashi, N.; Hosonaga, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Wang, X.; Kawai, S.; Inagaki, L.; Ozaki, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Assessment of a cancer genomic profile test for patients with metastatic breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphalen, B.C.; Bokemeyer, C.; Buttner, R.; Frohling, S.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Glimm, H.; Hacker, U.T.; Heinemann, V.; Illert, A.L.; Keilholz, U.; et al. Conceptual framework for precision cancer medicine in Germany: Consensus statement of the Deutsche Krebshilfe working group ’Molecular Diagnostics and Therapy’. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 135, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, D.P.S.; Rini, B.I.; Khorana, A.A.; Dreicer, R.; Abraham, J.; Procop, G.W.; Saunthararajah, Y.; Pennell, N.A.; Stevenson, J.P.; Pelley, R.; et al. Prospective Clinical Study of Precision Oncology in Solid Tumors. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 108, djv332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, A.H.; Egan, J.B.; Borad, M.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Patnaik, M.M.; Ansell, S.M.; Banck, M.S.; Robinson, S.I.; et al. Experience with precision genomics and tumor board, indicates frequent target identification, but barriers to delivery. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27145–27154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massard, C.; Michiels, S.; Ferte, C.; Le Deley, M.C.; Lacroix, L.; Hollebecque, A.; Verlingue, L.; Ileana, E.; Rosellini, S.; Ammari, S.; et al. High-Throughput Genomics and Clinical Outcome in Hard-to-Treat Advanced Cancers: Results of the MOSCATO 01 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodon, J.; Soria, J.C.; Berger, R.; Miller, W.H.; Rubin, E.; Kugel, A.; Tsimberidou, A.; Saintigny, P.; Ackerstein, A.; Brana, I.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling expands precision cancer medicine: The WINTHER trial. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Velden, D.L.; Hoes, L.R.; van der Wijngaart, H.; van Berge Henegouwen, J.M.; van Werkhoven, E.; Roepman, P.; Schilsky, R.L.; de Leng, W.W.J.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Nuijen, B.; et al. The Drug Rediscovery protocol facilitates the expanded use of existing anticancer drugs. Nature 2019, 574, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, F.; Gonçalves, A.; Guille, A.; Adelaïde, J.; Garnier, S.; Carbuccia, N.; Billon, E.; Finetti, P.; Sfumato, P.; Monneur, A.; et al. Prospective high-throughput genome profiling of advanced cancers: Results of the PERMED-01 clinical trial. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Remon, J.; Mateo, J.; Westphalen, C.B.; Barlesi, F.; Lolkema, M.P.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; Robson, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N | Percentage (%) or Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 81 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 81 | (100) |
| Age | 59 (median) | 26–84 (range) |
| Tumor stage at presentation | ||
| Metastatic | 63 | (77.8) |
| Locally advanced | 16 | (19.8) |
| Localized | 2 | (2.5) |
| Initial therapeutic intent | ||
| Primary metastatic, palliative intent | 22 | (27.2) |
| Initially curative intent | 59 | (72.8) |
| Tumor type | ||
| Breast | 36 | (44.4) |
| Ovary | 21 | (25.9) |
| Uterine sarcoma | 6 | (7.4) |
| Endometrium | 4 | (4.9) |
| Cervix | 5 | (6.2) |
| Vagina/vulva | 4 | (4.9) |
| Others | 5 | (6.2) |
| Previous lines of treatment | ||
| 0 | 6 | (7.4) |
| 1 | 13 | (16.0) |
| 2 | 18 | (22.2) |
| 3 | 18 | (22.2) |
| >3 | 26 | (32.1) |
| 3 (median) | 0–14 (range) |
| Diagnosis | Fusion | Diagnostic or Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| JSCB | NTRK3-ETV6 | Molecular rationale for NTRK inhibitor (entrectinib) |
| VMM | TRIM24-BRAF | Molecular rationale for MEK1/2-targeted inhibitor (Trametinib) |
| UEC | FGFR2-TACC2 | Molecular rationale for FGFR inhibitor (pemigatinib) |
| IDC | KIF5B-RET | Molecular rationale for RET-inhibitor (selpercatinib) |
| VPDC | SYN2-PPARG | Fusion in VPDC described for the first time in literature, no evidence for direct actionability |
| UUC | YAP1-MAML2 | Fusion described for the first time in UUC, no evidence for direct actionability |
| ESS | BCOR2-ZC3H7B | Led to the very rare diagnosis of high-grade ESS with BCOR2-ZC3H7B fusion |
| Diagnosis | Therapeutic Rationale | MTB Recommendation | EL ESCAT | EL NCT/ DKTK | Label | PFS2 | PFS1 | PFSr | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPDC | TMB-H | Pembrolizumab | I-A | m1a | On | 7 | 1 | 7 | SD for 7 months |
| IDC | Her2 low (SIS 1+) | Trastuzumab–deruxtecan | I-A | m1a | On | 12 | 4 | 3 | SD for 12 months # |
| CESC | Her2 low (SIS 1+) | Trastuzumab–deruxtecan | I-C | m1c | Off | 6 | 3 | 2 | SD for 6 months # |
| IDC | PIK3CA H1047R | Alpelisib + Fulvestrant | I-A | m1a | Off | 10 | 3 | 3.3 | PR for 10 months |
| IDC | EGFR amplification | Cetuximab + Capecitabine | IV-A | m1c | Off | 10 | 2 | 5 | SD for 10 months |
| SCT * | RET Y791F | Cabozantinib | IV-A | m3 | Off | 10 | 1 | 10 | SD for 10 months |
| IDC | gPALB2 Mutation | Olaparib | III-A | m2a | Off | 22 | 10 | 2.2 | PR for 22 months |
| HGSOC | ARID1A Loss | Pembrolizumab | IV-A | m3 | Off | 6 | 1 | 6 | SD for 6 months |
| OVT | KRAS G12D GNAS R142H MET R540C | Diagnosis changed to MAAP: HIPEC + FOLFOX | n/a | n/a | On | 6 | 3 | 2 | PR for 6 months |
| UELMS | ESR1 Y537S | Fulvestant | III-A | m2a | Off | 9 | 2 | 4,5 | SD for 9 months # |
| IDC | ESR1 D538G PIK3CA H1047R | Aleplisib + Elacestrant | I-A | m1a | Off | 8 | 6 | 1.3 | SD for 8 months |
| Matched Therapy Cohort (n = 23) | Non-Matched Therapy Cohort (n = 29) | |
|---|---|---|
| Total (percentage, %) | Total (percentage, %) | |
| Tumor stage at presentation | ||
| Metastatic | 18 (78.3) | 22 (75.9) |
| Locally advanced | 4 (17.4) | 6 (20.7) |
| Localized | 1 (4.3) | 1 (3.4) |
| Initial therapeutic intent | ||
| Primary metastatic, palliative intent | 7 (30.4) | 7 (24.1) |
| Initially curative intent | 16 (69.6) | 22 (75.9) |
| Tumor type | ||
| Breast | 10 (43.5) | 14 (48.3) |
| Ovary | 8 (34.8) | 5 (17.2) |
| Uterine sarcoma | 1 (4.3) | 3 (10.3) |
| Endometrium | 2 (8.7) | 4 (13.8) |
| Cervix | 1 (4.3) | 1 (3.4) |
| Vagina/vulva | 1 (4.3) | 1 (3.4) |
| Others | 0 (0) | 1 (3.4) |
| Previous lines of treatment | ||
| 0 | 2 (8.7) | 3 (10.3) |
| 1 | 4 (17.4) | 4 (13.8) |
| 2 | 2 (8.7) | 4 (13.8) |
| 3 | 5 (21.7) | 6 (20.7) |
| >3 | 10 (43.5) | 12 (41.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gremke, N.; Rodepeter, F.R.; Teply-Szymanski, J.; Griewing, S.; Boekhoff, J.; Stroh, A.; Tarawneh, T.S.; Riera-Knorrenschild, J.; Balser, C.; Hattesohl, A.; et al. NGS-Guided Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer and Gynecological Tumors—A Retrospective Molecular Tumor Board Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081561
Gremke N, Rodepeter FR, Teply-Szymanski J, Griewing S, Boekhoff J, Stroh A, Tarawneh TS, Riera-Knorrenschild J, Balser C, Hattesohl A, et al. NGS-Guided Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer and Gynecological Tumors—A Retrospective Molecular Tumor Board Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081561
Chicago/Turabian StyleGremke, Niklas, Fiona R. Rodepeter, Julia Teply-Szymanski, Sebastian Griewing, Jelena Boekhoff, Alina Stroh, Thomas S. Tarawneh, Jorge Riera-Knorrenschild, Christina Balser, Akira Hattesohl, and et al. 2024. "NGS-Guided Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer and Gynecological Tumors—A Retrospective Molecular Tumor Board Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081561
APA StyleGremke, N., Rodepeter, F. R., Teply-Szymanski, J., Griewing, S., Boekhoff, J., Stroh, A., Tarawneh, T. S., Riera-Knorrenschild, J., Balser, C., Hattesohl, A., Middeke, M., Ross, P., Litmeyer, A.-S., Romey, M., Stiewe, T., Wündisch, T., Neubauer, A., Denkert, C., Wagner, U., & Mack, E. K. M. (2024). NGS-Guided Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer and Gynecological Tumors—A Retrospective Molecular Tumor Board Analysis. Cancers, 16(8), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081561





