Simple Summary
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cancer cells released from the primary tumor into the bloodstream, and contain cancer stem cells. The present study demonstrates the significance of a specific variant, CD44v9, in CTCs, and its combined effects with preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) values on the prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC). Analysis of the serum CEA levels and the expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTCs, followed by evaluation of their association with clinicopathological factors, showed the association of CD44v9 mRNA with liver metastasis. Furthermore, patients with CD44v9-positive CTCs showed a poorer prognosis than those with CD44v9-negative CTCs. Combining CD44v9 mRNA expression with CEA values provided more detailed prognostic information. These results suggest that CD44v9 mRNA expression in CTCs, alongside CEA levels, could serve as a valuable prognostic marker for CRC, and could potentially lead to the development of more personalized treatment strategies against CRC.
Abstract
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are cancer cells released from the primary tumor into the bloodstream, and contain cancer stem cells that influence tumor survival, recurrence, and metastasis. Here, we investigated CD44v9 expression in CTCs and impact of preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels on colorectal cancer (CRC) prognosis. We analyzed the expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTCs using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and preoperative CEA levels in blood samples obtained from 300 patients with CRC. Subsequently, we evaluated the association of CD44v9 expression and CEA levels with clinicopathological factors. CD44v9 mRNA was expressed in 31.3% of the patients, and was significantly associated with liver metastasis. Patients with positive CD44v9 expression had a lower 5-year survival rate (62.3%) than those with negative CD44v9 expression (82.8%, p < 0.001). Cox regression analysis identified CD44v9 expression and high CEA levels (≥5 ng/mL) as poor prognostic factors, while negative CD44v9 expression and low CEA levels (<5 ng/mL) were associated with favorable prognosis (hazard ratio = 0.285, p = 0.006). These results suggest that a combination of CD44v9 mRNA expression in CTCs and serum CEA levels could serve as a valuable prognostic marker for CRC, potentially enhancing the accuracy of prognosis predictions.
1. Introduction
The prevalence of colorectal cancer (CRC) has been increasing in recent years as a major global health challenge, with more than 1.8 million new cases and 881,000 deaths reported worldwide in 2018 [1]. Significant advancements have occurred in the treatment of CRC, especially progress in molecularly targeted therapies and immunotherapy, which have led to improved survival rates. However, identifying the prognostic factors remains crucial for early detection of CRC recurrence and determination of efficacy to enhance treatment outcomes [2]. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a tumor marker for CRC, recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, is widely used in clinical practice for monitoring CRC [3,4,5,6,7,8]. Elevated levels of preoperative CEA levels have been associated with poor prognosis [9]. However, its practical applicability is limited in patients with normal preoperative CEA values. Moreover, the cutoff values, sensitivity, and specificity in determining treatment efficacy vary in different reports, which limits using CEA levels as a sole indicator for monitoring treatment efficacy [10,11,12,13].
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are tumor cells that are shed from the primary or metastatic lesions and enter the peripheral bloodstream [14]. The presence of a high number of circulating tumor cells has been suggested to be significantly associated with poor progression-free survival and OS in CRC [15,16,17]. Additionally, in a study involving 430 patients with metastatic CRC, the number of CTCs before and after treatment has been identified as an independent predictor of OS [18]. They also include cancer stem cells that exhibit a self-renewal potential and resistance to anticancer drugs [19,20,21,22]. Tumors comprise a heterogeneous population of cells that exhibit or lack the ability to self-renew. Among these, cells with the ability to self-renew are known as cancer stem cells or tumor-initiating cells, which are thought to be responsible for initiating and driving tumor growth. These cells are also involved in resistance to chemotherapy, as well as in the differentiation process, through which they produce many cancer cells that lack tumor-forming ability [23,24,25,26]. Therefore, therapies targeting cancer stem cells are considered promising to prevent tumor relapse and metastasis. In CRC, several cancer stem cell-specific markers have been identified, including leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor 5, CD133, and CD44 [27,28,29]. A previous study has reported that the presence of CD133 mRNA expression in CTCs is associated with poor prognosis of CRC [30,31].
CD44 functions as a single-pass type I transmembrane protein that acts as a cell adhesion molecule to hyaluronic acid, a major component of the extracellular matrix. CD44 is involved in various physiological processes, including leukocyte homing and activation, wound healing, and cell migration [32].
CD44 is encoded by a single gene with 19 exons. The first five and the last five exons are constant, coding for the shortest isoform of CD44 with a molecular weight of 85–95 kDa, known as standard CD44 (CD44s). Variant isoforms of CD44 (CD44v) are generated through alternative splicing, resulting in a combination of the ten constant exons with any combination of the remaining nine variant exons [33,34,35,36]. Each isoform has distinct functions, and among them, CD44v8-10 binds to xCT protein on the cell membrane, which transports cystine/glutamate. This binding promotes the formation of reduced glutathione, inhibits the accumulation of reactive oxygen species in cancer cells, and suppresses the activation of oxidative stress, thereby conferring self-renewal capabilities and resistance to chemotherapy [37]. Oxidative stress has been implicated in the development, proliferation, and metastasis of colorectal cancer. We have reported that patients with colorectal cancer who have high levels of serum oxidative stress have a poor prognosis [38]. The expression of CD44v9, which has the ability to control oxidative stress, may be an effective marker for prognosis prediction, and may be a target for antibody therapy.
CD44v9, one of the splicing variants of CD44, is closely associated with tumorigenicity and several cellular processes, including cell proliferation, metastasis, and tumor invasiveness through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [25]. A previous study has shown that CD44v9 siRNA-treated cancer cells exhibit increased oxidative stress upon exposure to 5-fluorouracil, compared to the untreated control cells [39]. Furthermore, inhibition of CD44v9 was identified as a promising strategy for developing treatment strategies for CRC, with potential implications for the development of therapeutic drugs [25,39].
In a study involving 193 patients with gastric cancer, the expression of CD44v9 detected by immunostaining was shown to be significantly associated with the depth of cancer invasion, lymphatic invasion, vascular invasion, distant metastasis, and the expression of GPx2 [39]. The study also identified CD44v9 as an independent prognostic factor for poor overall (OS) and recurrence-free survival [39]. Furthermore, CD44v9 expression in tumor tissue is considered a poor prognostic factor in several carcinomas, including colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma [32,39,40,41,42]. However, reports on the characteristics and prognosis of CRC cases with CD44v9-expressing CTCs are limited. Additionally, the number of cases studied is limited, and a comprehensive approach that considers the combined effect of CD44v9-positive CTCs and preoperative CEA values is lacking. Studying both CEA levels and CD44v9-expressing CTCs together could provide a more comprehensive assessment of CRC prognosis. While elevated CEA levels may indicate a general risk of disease progression, the presence of CD44v9-expressing CTCs could identify a subset of patients with a particularly aggressive cancer phenotype. By combining these biomarkers, clinicians may be able to better stratify patients based on their risk profiles, and tailor treatment strategies accordingly, ultimately improving treatment outcomes in CRC. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to investigate the prognostic effects of the presence of CD44v9-positive CTCs and preoperative CEA levels and confirm their validity as biomarkers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sample Collection
Three hundred patients who underwent CRC resection at our institution between 2013 and 2018 were enrolled in this study. Patients with synchronous or metachronous cancers were excluded. In addition, 15 healthy donors were included as controls.
Blood samples from the patients were collected before primary tumor resection to measure the preoperative CEA levels in CTCs with or without CD44v9 expression. The normal reference value for CEA was 5 ng/mL. The first 5 mL of blood was discarded to minimize the risk of skin cell contamination. Then, 20 mL of blood was collected and separated using an OncoQuick density gradient system (Greiner Bio-One GmbH, Frickenhausen, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions, and the tumor cells were isolated through density gradient centrifugation. Subsequently, the tumor cells were resuspended in 400 μL of phosphate-buffered saline. For a negative control, blood (without epithelial cells) from healthy volunteers was collected using the OncoQuick density gradient system.
The Research Ethics Committee of the University of Fukui approved the study (Approval No. 20200058). Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this research project.
2.2. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
Total RNA was isolated from tumor cells using the ISOGEN (Wako, Tokyo, Japan) and was reverse transcribed using a Prime Script RT reagent kit (Takara, Otsu, Japan). The coding regions of CD44v9 were amplified using the following primers: forward: AGCAGAGTAATTCTCAGAGC and reverse: TGATGTCAGAGTAGAAGTTGTT [43]. The thermal cycling conditions comprised 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 55 °C for 1 min, and extension at 72 °C for 2 min. The amplification was performed using a PTC-100 Programmable Thermal Controller (NJ Research Inc., Manahawkin, NJ, USA). The PCR products were then purified using the QIAquick PCR Purification kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and analyzed using gel electrophoresis (1.2% agarose). The purified PCR products were then sequenced to confirm the presence of CD44v9.
For semi-quantitative mRNA detection, ethidium bromide staining was performed to identify CD44v9 bands in the gels. To ensure consistent results, all PCR amplifications were duplicated. The amplicons in photographed gels were quantified using densitometry.
2.3. Clinical Assessment
Data on patient demographics (age, sex), tumor characteristics (size, location, histological type, invasion depth), metastasis status (lymph node and distant metastasis), cancer stage, CEA levels, and disease-specific survival (DSS) were obtained. DSS was calculated as the time from the date of surgery to death, specifically from CRC. Histopathological and clinical staging of tumors were based on the TNM classification system.
All patients underwent follow-up assessments, including blood tests for tumor markers every 3 months, enhanced abdominal computed tomography every 6 months, and colonoscopy every 3 years.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The Kaplan–Meier method was used to analyze DSS, and comparisons between groups were performed using a log-rank test. The Cox regression model was used to assess the hazard ratio (HR). Other characteristics of the two groups were compared using the chi-square test for univariate analysis and logistic regression analysis for multivariate analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS software version 21.0 (IBM Japan, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Association between CD44v9 Expression and Clinicopathologic Features
Baseline demographic and clinicopathologic data of all patients with CRC are summarized in Table 1. The median age of the patients was 69.5 years (range: 24–91 years). Among the 300 patients, 72, 82, 85, and 61 belonged to stages I, II, III, and IV of CRC, respectively. CD44v9 was expressed in 94 of 300 cases (31.3%; Figure 1), whereas none of the healthy donors expressed CD44v9 mRNA. Stage-wise, CD44v9 mRNA expression was positive in 19 cases with stage I, 21 cases with stage II, 24 cases with stage III, and 30 cases with stage IV CRC (Figure 2). Univariate analysis revealed no correlation between CD44v9 expression and tumor size, tissue differentiation, or depth of disease, whereas it identified a significantly positive correlation between CD44v9 expression and lymph nodes, distant metastases, and advanced-stage disease. No association was observed between serum CEA levels and CD44v9 expression (Table 1). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that CD44v9 was significantly expressed in liver metastasis cases (odds ratio (OR) = 2.697, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.122–6.481, p = 0.027). However, no significant relationship with other pathological characters was observed (Table 2).

Table 1.
CD44v9 expression and clinicopathological factors analyzed using univariate analysis.
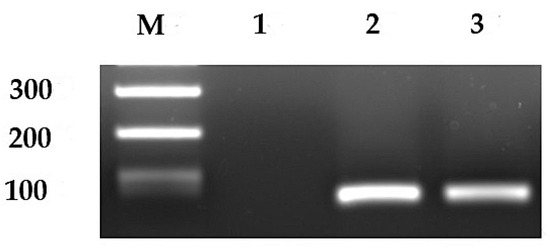
Figure 1.
Representative image of expression of CD44v9 mRNA. Lane 1, negative expression of CD44v9 mRNA; lanes 2 and 3, positive expression of CD44v9; M, DNA size marker. Original western blots are presented in Figure S5.
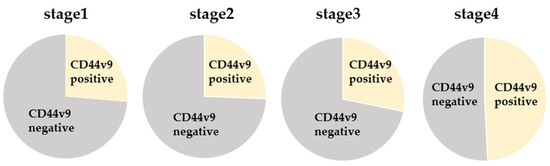
Figure 2.
Comparison of CD44v9 mRNA expression by stage.

Table 2.
CD44v9 expression and clinicopathological factors analyzed using multivariate analysis.
3.2. Association between Expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTCs and Survival Rate
The 5-year survival rate of CD44v9-positive cases was 62.3%, and that of CD44v9-negative cases was 82.8% (Figure 3). This finding indicated that CD44v9-positive cases had a significantly worse prognosis (p < 0.001). However, no significant relationship was observed between CD44v9 expression and prognosis in stage I (Figure S1a). In stage II CRC cases, the 5-year DSS rate was 86.4% for CD44v9-positive cases and 100% for CD44v9-negative cases (Figure S1b). Similarly, in patients with stage III CRC, the 5-year DSS rate was 66.2% and 87.8% for CD44v9-positive and -negative cases, respectively (Figure S1c). In stage IV CRC cases, the 2-year DSS for CD44v9-positive cases was 54.1%, whereas that for CD44v9-negative was 100% (Figure S1d). These findings indicated a significantly worse prognosis for CD44v9-positive cases in stages II (p = 0.039), III (p = 0.038), and IV (p = 0.028).
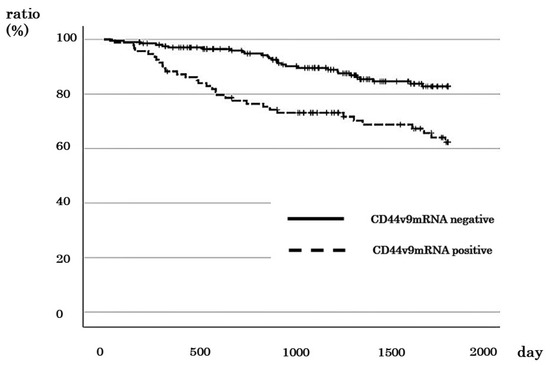
Figure 3.
Relationship between CD44v9 mRNA expression and survival rate in patients with all stages of colorectal cancer.
3.3. Association between CEA Values and Survival Rates
A total of 122 cases with CEA ≥ 5 ng/mL (high), including 12, 30, 36, and 44 cases in stages I, II, III, and IV, respectively, were identified. The 5-year survival rate for cases with high CEA was 60.0%, whereas it was 87.1% for cases with CEA < 5 ng/mL (low), indicating a significantly poorer prognosis for cases with high CEA levels (p < 0.001; Figure 4). Correlation analysis revealed no significant correlation between the CEA levels and the prognosis of patients with stages I and II CRC (Figure S2a,b). However, for stage III cases, the 5-year DSS rate was 71.5% for those with high CEA and 88.9% for cases with low CEA (Figure S2c). Similarly, the 2-year DSS rate of patients with stage IV CRC with high CEA was 51.5%, while it was 82.4% for those with low CEA (Figure S2d). These results indicate that increased CEA level is a worse prognostic factor for stage III (p = 0.041) and IV cases (p = 0.031).
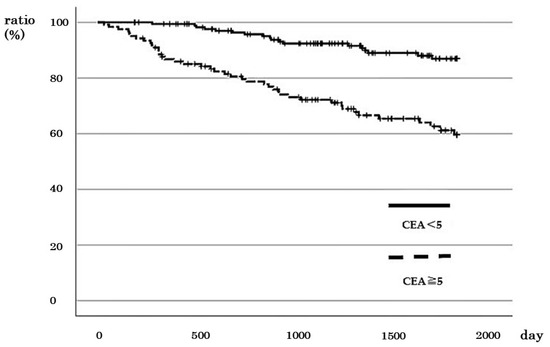
Figure 4.
Relationship between CEA values and survival rate in patients with colorectal cancer with all stages.
3.4. Multivariate Cox Analysis for DSS
Table 3 shows the results of multivariate Cox analysis of age, gender, tumor size, serosa invasion, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, expression of CD44v9, and CEA value for DSS in all patients. The results revealed a significant association between DSS and lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, CD44v9 expression, and CEA value (p < 0.05 in all cases).

Table 3.
Multivariate Cox analysis for DSS in patients with different stages of CRC.
3.5. Comparison of DSS between Cases with Negative CD44v9 mRNA Expression and CEA Level
Of all cases, there was negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA in 122 cases, negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and high CEA in 84 cases, positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA in 55 cases, positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA in were 39 cases, and positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA were in 55 cases and 39 cases, respectively. The 5-year survival rates were 43.1%, 76.9%, 69.5%, and 96.1%, respectively. There was a significant difference in survival rates between groups (P < 0.001; Figure 5).
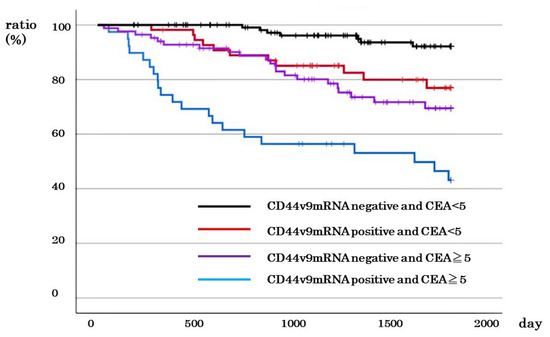
Figure 5.
Relationship between CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA level and survival rate in patients with all stages of colorectal cancer.
3.6. Comparison of DSS between Cases with Negative CD44v9 mRNA Expression and Low CEA < 5 ng/mL) and Other Cases
The number of cases with different stages of CRC with negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA was 121, including 42 of 72 cases with stage I CRC, 35 of 82 cases with stage II CRC, 36 of 85 cases with stage III, and 8 of 61 cases with stage IV CRC. The 5-year DSS of cases with negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA did not differ from that of other cases in stages I and II (96.3% vs. 95.2%; p = 0.892, and 100% vs. 92.7%; p = 0.263, respectively; Figure S3a,b). In contrast, a significantly better prognosis was observed in terms of 5-year DSS in stage III and 2-year DSS in stage IV for cases with negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA compared to other cases (100% vs. 67.9%; p = 0.001 and 100% vs. 54.1%; p = 0.028, respectively; Figure S3c,d). Furthermore, the 5-year survival rates of cases across all stages of CRC with negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA were better than those in other cases (92.1% vs. 65.4%, p < 0.001; Figure 6). Cox regression analysis revealed that lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis and negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and low CEA significantly affected prognosis (p < 0.05 in all cases; Table 4).
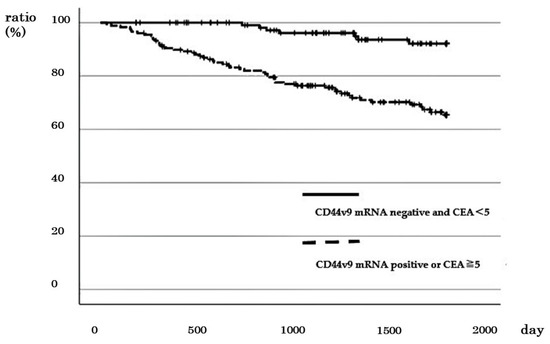
Figure 6.
Relationship between negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA < 5 and survival rate in patients with all stages of colorectal cancer.

Table 4.
Multivariate Cox analysis of different factors, including negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA < 5 ng/mL for DSS in patients with different stages of CRC.
3.7. Comparison of DSS between Cases with Positive CD44v9 mRNA Expression and High CEA (≥5 ng/mL) and Other Cases
Positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and high CEA were observed in 2 out of 72 cases with stage I, 4 out of 82 cases with stage II, 12 out of 85 cases with stage III, and 21 out of 61 cases with stage IV of CRC. No difference was observed in 5-year DSS between cases with positive CD44v9 expression and high CEA and other cases in stages I (100% vs. 95.6%, p = 0.764) and III (72.9% vs. 82.5%, p = 0.374) (Figure S4a,b). In cases with stages II and IV exhibiting positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and high CEA, a significantly worse prognosis was observed in terms of 5-year and 2-year DSS in stages II (50% vs. 98.5% p = 0.009) and IV (38.1% vs. 72.1% p = 0.007), respectively (Figure S4c,d). In addition, the comparison of 5-year survival rates across all stages of CRC revealed that cases with positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and high CEA had worse 5-year DSS compared with the other cases (43.1% vs. 81.5%, p < 0.001; Figure 7). Cox regression analysis revealed that the presence of lymph node metastasis, the presence of distant metastasis, and positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and high CEA were the factors significantly associated with worse prognosis (p < 0.05 in all cases; Table 5).
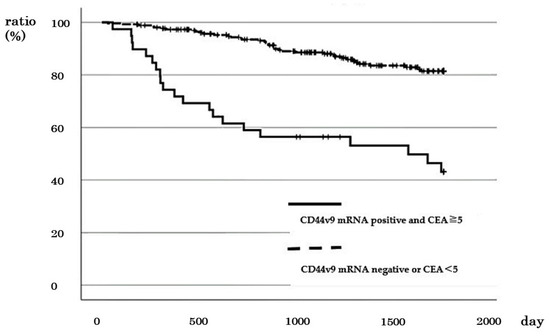
Figure 7.
Relationship between positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA ≥ 5 ng/mL and survival rate patients with all stages of colorectal cancer.

Table 5.
Multivariate Cox analysis tested for various factors, including positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA ≥ 5 ng/mL for DSS in all patients with different stages of CRC.
4. Discussion
In this study, we investigated the correlation between the expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTCs and the prognosis of CRC. Our findings revealed that in patients with CRC, the prognosis was poor when CTCs expressed CD44v9. We also showed that the expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTC was significantly higher in cases with liver metastasis. Finally, we showed that cases with negative CD44v9 expression in CTCs and normal CEA levels showed significantly better prognoses compared with other cases.
Our study is the first to investigate the association between CD44v9 mRNA expression in CTCs and the prognosis of CRC using 300 cases. Concordant with studies on other cancer stem cell markers, the CD44v9 mRNA expression in CTCs was confirmed to be significantly associated with poor prognosis. A few studies have used multivariate analysis to investigate clinicopathological factors affecting the expression of cancer stem cells in CTC. For instance, Chao et al. investigated factors affecting liver metastasis in CRC, and highlighted high CEA levels, extra nodal tumor deposits, and the expression of CD133, CD44, and CD54 in CTCs [44]. CTCs include epithelial tumor cells, tumor cells undergoing EMT, and cancer stem cells, among which cancer stem cells are considered to be involved in metastasis [45,46,47].
The hematogenous metastasis of CRC progresses in the sequence of dissociation of cancer stem cells from the primary focus, invasion into capillaries, metastasis to the whole body through the portal and systemic circulation, adhesion to the vascular endothelial cells of the target organ, extravasation, and infiltration and proliferation [48]. CD44 has been reported to be related to tumor invasion [49], and in gastric and CRCs, proteins expressed from CD44 variant exon 6 or exon 9 have been reported to be involved in hematogenous metastasis [50,51,52]. In this study, the expression of CD44v9 in CTCs was significantly higher in cases with liver metastasis, suggesting that CD44v9-expressing cancer stem cells are involved in liver metastasis. Seki used the colorectal cancer cell line HT29, which expresses CD44v9, to develop a highly metastatic cell line. By injecting these cells into the spleens of mice, they were able to create a model of liver metastasis. They reported that liver metastasis formation was inhibited when these HT29 cells were treated with an anti-CD44v9 monoclonal antibody, thus proving that CD44v9 promotes liver metastasis. Additionally, they reported that CD44v9 expression is involved in the adhesion of tumor cells to vascular endothelial cells, a critical factor for metastasis [53]. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are tumor cells that are shed from primary or metastatic tumors into the peripheral bloodstream [54], and are frequently detected in stage III and IV blood samples. Cancer stem cells such as CD44 and CD133 have also been identified in tissues from colorectal cancer liver metastases [49], and an increase in CD44v9 expression in liver metastasis cases in this study is presumed to result from shedding from the primary and metastatic sites. Cho et al. reported that the expression of CD44, CD133, and CD54 in CTCs was higher in cases with liver metastasis compared to those without, and that cases exhibiting expression of these markers had a poorer prognosis compared to those that did not [19]. We also investigated the relationship between the expression of CD44v9 in CTCs and CEA. Lin et al. [31] reported a correlation between the expression of CD133 mRNA and CEA values in univariate analysis [31]. Here, we conducted a multivariate analysis and confirmed no correlation between the expression of CD44v9 in CTCs and CEA. These findings suggest that the verification of CD44v9 mRNA expression in CTCs could be considered an effective marker different from existing tumor markers.
Preoperative CEA levels have been shown to be reliable prognostic markers, with higher preoperative CEA levels associated with poorer prognosis [55,56]. In this study, preoperative CEA was also identified as an effective predictor of prognosis. The findings indicated the potency of CD44v9 mRNA expression and serum CEA levels as CRC biomarkers. Iinuma et al. studied the impact of CD133 mRNA expression in CTCs on OS and disease-free survival in 735 cases of CRC [57]. The study revealed poor prognosis in the presence of CEA, CK, and CD133 mRNA. Another study reported that combining CTC count and CEA levels improved the accuracy of prognosis prediction for patients with CRC [58,59]. Therefore, we investigated the possibility of achieving a more accurate prognostic predictor by combining the expression of CD44v9 mRNA in CTCs with CEA levels.
The analysis of survival involving 300 patients with CRC in this study revealed that the expression of CD44v9 showed an HR of 1.817 (p = 0.029). However, in cases exhibiting CD44v9 expression with high CEA levels, the HR was 1.771 (p = 0.047). Conversely, in cases with negative CD44v9 expression and low CEA, the HR was 0.285 (p = 0.006). These results indicated that evaluating the expression of CD44v9 alone can sufficiently predict poor prognosis. However, considering the expression of CD44v9 along with CEA values could be more effective in predicting the prognosis. This strategy can play a supportive role when considering the application of adjuvant chemotherapy in cases with poor general conditions or elderly patients with stage II or III disease. In addition to CEA, which we reported on, Sialyl Lex (SLX) has been reported as a factor related to the expression of CD44v9 that affects the prognosis of colorectal cancer cases. SLX is known to play an important role in the adhesion between tumor cells and endothelial cells. It has been reported that if both are expressed in the immunostaining of colorectal cancer tissues, the prognosis is poor, whereas if neither is expressed, the prognosis is good [60].
Sulfasalazine, used for inflammatory diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, is considered to specifically inhibit cystine transport via xCT, thereby selectively controlling the proliferation of cancer cells expressing CD44v [61]. Based on these studies, clinical research is also being conducted, suggesting the potential development of therapies targeting CD44v9 [39,62,63,64].
The study has some limitations. Firstly, the low number of deaths in stages II and III cases made it challenging to perform a multivariate analysis to assess the impact of CD44v9 expression in CTCs on the prognosis of these cases. However, the univariate analysis indicated that CD44v9 expression could be a potential risk factor for poor prognosis. Secondly, when examining OS in stage IV cases, it is important to consider that the prognosis for stage IV CRC has significantly improved with the advancements in chemotherapy approaches and the introduction of molecular-targeted drugs.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the present study highlights the significance of CD44v9-positive CTCs and preoperative CEA levels as prognostic markers in CRC. Furthermore, no correlation between CEA and CD44v9 mRNA in CTC suggests that these two markers serve as a unique tumor marker, while their combination is more effective in identifying cases with a favorable prognosis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers16081556/s1, Figure S1: Relationship between CD44v9 mRNA expression and survival rate in patients with colorectal cancer. (a) Stage I, (b) stage II, (c) stage III, (d) stage IV; Figure S2: Relationship between CEA values and survival rate in patients with colorectal cancer. (a) Stage I, (b) stage II, (c) stage III, (d) stage IV; Figure S3: Relationship between negative CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA < 5 ng/mL and survival rate in patients with colorectal cancer. (a) Stage I, (b) stage III, (c) stage II, (d) stage IV; Figure S4: Relationship between positive CD44v9 mRNA expression and CEA ≥ 5 ng/mL and survival rate in patients with colorectal cancer. (a) Stage I, (b) stage II, (c) stage III, (d) stage IV. Figure S5: Original western blots.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, K.S. and Y.K.; Investigation, K.S.; Data curation, K.S.; Writing—original draft, K.S.; Supervision, K.K.; Project administration, T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no external funding was received for this study.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol for this research project was approved by a suitable Institutional Ethics Committee and conformed to the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki. The Research Ethics Committee of the University of Fukui approved the study (Approval No. 20200058, approval date 1 April 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from participants prior to the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Masae Saitoh for their assistance in patient data collection and administrative support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baidoun, F.; Elshiwy, K.; Elkeraie, Y.; Merjaneh, Z.; Khoudari, G.; Sarmini, M.T.; Gad, M.; Al-Husseini, M.; Saad, A. Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology: Recent Trends and Impact on Outcomes. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, P.W.; Ruff, S.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Update on Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; van Dalen, A.; Haglund, C.; Hansson, L.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Klapdor, R.; Lamerz, R.; Peltomaki, P.; Sturgeon, C.; Topolcan, O. Tumour markers in colorectal cancer: European Group on Tumour Markers (EGTM) guidelines for clinical use. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locker, G.Y.; Hamilton, S.; Harris, J.; Jessup, J.M.; Kemeny, N.; Macdonald, J.S.; Somerfield, M.R.; Hayes, D.F.; Bast, R.C. ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.; Venook, A.P.; Al-Hawary, M.M.; Arain, M.A.; Chen, Y.J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.; Farkas, L.; et al. Colon Cancer, Version 2.2021. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 329–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, U.; Primrose, J.N.; Finan, P.J.; Perren, T.J.; Selby, P.; Purves, D.A.; Cooper, E.H. The use of tumour markers CEA, CA-195 and CA-242 in evaluating the response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preketes, A.P.; King, J.; Caplehorn, J.R.M.; Clingan, P.R.; Ross, W.B.; Morris, D.L. Cea reduction after cryotherapy for liver metastases from colon-cancer predicts survival. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1994, 64, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; Verweij, J.; Van Glabbeke, M.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T.; Shimada, Y.; Hsu, M.; Tufts, L.; Jimenez-Rodriguez, R.; Cercek, A.; Yaeger, R.; Saltz, L.; Smith, J.J.; Nash, G.M.; et al. Association of Preoperative and Postoperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Colon Cancer Outcome. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Jung, E.J.; Ryu, C.G.; Hwang, D.Y. Usefulness of Carcinoembryonic Antigen for Monitoring Tumor Progression during Palliative Chemotherapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.E.; Yang, J.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Ro, S.; Lee, M.A. Clinical significance of changes in systemic inflammatory markers and carcinoembryonic antigen levels in predicting metastatic colorectal cancer prognosis and chemotherapy response. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Lee, J.E.; Yang, J.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Ro, S.; Oh, S.T.; Kim, J.G.; Choi, M.H.; Lee, M.A. Clinical Significance of Discordance between Carcinoembryonic Antigen Levels and RECIST in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haas, R.J.; Wicherts, D.A.; Flores, E.; Ducreux, M.; Levi, F.; Paule, B.; Azoulay, D.; Castaing, D.; Lemoine, A.; Adam, R. Tumor Marker Evolution: Comparison with Imaging for Assessment of Response to Chemotherapy in Patients with Colorectal Liver Metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Hayashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Ito, S.; Eguchi, H.; Mimori, K. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C. Relationship among circulating tumor cells, CEA and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2708–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, U.; Rahbari, N.N.; Schölch, S.; Reissfelder, C.; Kahlert, C.; Büchler, M.W.; Weitz, J.; Koch, M. Circulating tumour cells and outcome in non-metastatic colorectal cancer: A prospective study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Fan, C.W.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.R.; Meng, W.T.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, J.K.; Li, Y.; Mo, X.M.; et al. Prognostic value of CD133+CD54+CD44+ circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer with liver metastasis. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2850–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaks, V.; Koopman, C.D.; Werb, Z. Circulating Tumor Cells. Science 2013, 341, 1186–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Bos, P.D.; Massague, J. Metastasis: From dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, U265–U274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, T.; Nagano, O.; Yae, T.; Tamada, M.; Motohara, T.; Oshima, H.; Oshima, M.; Ikeda, T.; Asaba, R.; Yagi, H.; et al. CD44 Variant Regulates Redox Status in Cancer Cells by Stabilizing the xCT Subunit of System xc- and Thereby Promotes Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Sheng, W.Q.; Du, X. CD133: A cancer stem cells marker, is used in colorectal cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2603–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannakul, N.; Ma, N.; Midorikawa, K.; Oikawa, S.; Kobayashi, H.; He, F.; Kawanishi, S.; Murata, M. CD44v9 Induces Stem Cell-Like Phenotypes in Human Cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, L.T.H.; Sari, I.N.; Yang, Y.G.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, N.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kwon, H.Y. Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) in Drug Resistance and their Therapeutic Implications in Cancer Treatment. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 5416923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalerba, P.; Dylla, S.J.; Park, I.K.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.H.; Cho, R.W.; Hoey, T.; Gurney, A.; Huang, E.H.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N.; Ridgway, R.A.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; Danenberg, E.; Clarke, A.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Clevers, H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009, 457, U119–U608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilati, P.; Mocellin, S.; Bertazza, L.; Galdi, F.; Briarava, M.; Mammano, E.; Tessari, E.; Zavagno, G.; Nitti, D. Prognostic Value of Putative Circulating Cancer Stem Cells in Patients Undergoing Hepatic Resection for Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.H.; Hassan, M.; Li, Y.N.; Zhao, H.; Nooka, A.; Sorenson, E.; Xie, K.P.; Champlin, R.; Wu, X.F.; Li, D.H. Elevated circulating endothelial progenitor marker CD133 messenger RNA levels predict colon cancer recurrence. Cancer 2007, 110, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakehashi, A.; Ishii, N.; Sugihara, E.; Gi, M.; Saya, H.; Wanibuchi, H. CD44 variant 9 is a potential biomarker of tumor initiating cells predicting survival outcome in hepatitis C virus-positive patients with resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, O.; Saya, H. Mechanism and biological significance of CD44 cleavage. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.J.; Karnad, A.; Freeman, J.W. The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Goi, T.; Naruse, T.; Ueda, Y.; Kurebayashi, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Kimura, Y.; Hirono, Y.; Yamaguchi, A. Cancer Stem Cell Marker in Circulating Tumor Cells: Expression of CD44 Variant Exon 9 Is Strongly Correlated to Treatment Refractoriness, Recurrence and Prognosis of Human Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ziranu, P.; Aimola, V.; Pretta, A.; Dubois, M.; Murru, R.; Liscia, N.; Cau, F.; Persano, M.; Deias, G.; Palmas, E.; et al. New Horizons in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Prognostic Role of CD44 Expression. Cancers 2023, 15, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Goi, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Hirono, Y.; Katayama, K.; Urano, T.; Yamaguchi, A. CD44variant exon 9 plays an important role in colon cancer initiating cells. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sawai, K.; Goi, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Matsunaka, T.; Maegawa, N.; Koneri, K. Oxidative stress as a biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. Oncology 2022, 100, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogo, T.; Oki, E.; Nakanishi, R.; Ando, K.; Nakashima, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Saeki, H.; Oda, Y.; Maehara, Y.; Mori, M. Expression of CD44 variant 9 induces chemoresistance of gastric cancer by controlling intracellular reactive oxygen spices accumulation. Gastric Cancer 2021, 24, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Urano, T.; Goi, T.; Saito, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Hirose, K.; Nakagawara, G.; Shiku, H.; Furukawa, K. Expression of a CD44 variant containing exons 8 to 10 is a useful independent factor for the prediction of prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 1996, 14, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Ji, M.; Wu, J.; Jiang, J.T.; Wu, C.P. Clinical significance of CD44 variants expression in colorectal cancer. Tumori 2013, 99, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, K.; Suzuki, H.; Imaeda, H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Tsugawa, H.; Nagano, O.; Asakura, K.; Saya, H.; Hibi, T. CD44 variant 9 expression in primary early gastric cancer as a predictive marker for recurrence. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, K.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. CD44v/CD44s expression patterns are associated with the survival of pancreatic carcinoma patients. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Fan, C.W.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.R.; Meng, W.T.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Peng, Z.H.; Hu, J.K.; Li, Y.; et al. CD133+CD54+CD44+ circulating tumor cells as a biomarker of treatment selection and liver metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 77389–77403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, P.K.; Cummins, A.G.; Price, T.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Hardingham, J.E. Circulating tumour cells: The evolving concept and the inadequacy of their enrichment by EpCAM-based methodology for basic and clinical cancer research. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarz-Knoll, N.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Plasticity of disseminating cancer cells in patients with epithelial malignancies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Stolpe, A.; Pantel, K.; Sleijfer, S.; Terstappen, L.W.; den Toonder, J.M.J. Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Diagnostics: Toward Routine Clinical Use. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5955–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 1996, 86, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellizzi, A.; Sebastian, S.; Ceglia, P.; Centonze, M.; Divella, R.; Manzillo, E.F.; Azzariti, A.; Silvestris, N.; Montemurro, S.; Caliandro, C.; et al. Co-expression of CD133(+)/CD44(+) in human colon cancer and liver metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goi, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Takeuchi, K.; Nakagawa, G.; Yamashiro, S.; Furukawa, K.; Urano, T.; Shiku, H. CD44 with variant exons 8-10 in colorectal tumors: Expression analysis by a variant exon 9-specific monoclonal antibody. Int. J. Oncol. 1996, 8, 657–662. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Goi, T.; Yu, J.R.; Hirono, Y.; Ishida, M.; Iida, A.; Kimura, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Katayama, K.; Hirose, K. Expression of CD44v6 in advanced gastric cancer and its relationship to hematogenous metastasis and long-term prognosis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2002, 79, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.I.; Li, Y.; Graham, D.Y.; Cen, P.T. The Role of CD44 in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy of Gastric Cancer. Gut Liver 2011, 5, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Goi, T.; Nakagawara, G.; Matsukawa, S.; Urano, T.; Furukawa, K. Inhibition of liver metastasis formation by anti-CD44 variant exon 9 monoclonal antibody. Int. J. Oncol. 1997, 11, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, J.M. Clinical and biological significance of circulating tumor cells, circulating tumor DNA, and exosomes as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 55632–55645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanebo, H.J.; Rao, B.; Pinsky, C.M.; Hoffman, R.G.; Stearns, M.; Schwartz, M.K.; Oettgen, H.F. Preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen level as a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 299, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grem, J. The prognostic importance of tumor markers in adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 1997, 9, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iinuma, H.; Watanabe, T.; Mimori, K.; Adachi, M.; Hayashi, N.; Tamura, J.; Matsuda, K.; Fukushima, R.; Okinaga, K.; Sasako, M.; et al. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells, Including Cancer Stem-Like Cells, in Peripheral Blood for Recurrence and Prognosis in Patients with Dukes’ Stage B and C Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Yeh, P.H.; Hsu, C.J.; Chang, L.W.; Chan, W.J.; Lin, C.P.; Lyu, Y.Y.; Wu, W.C.; Lee, C.W.; et al. Highly Correlated Recurrence Prognosis in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer by Synergistic Consideration of Circulating Tumor Cells/Microemboli and Tumor Markers CEA/CA19-9. Cells 2021, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.Y.; Lu, L.S.; Cho, W.; Wu, S.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Yang, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Jiang, J.K.; Tseng, F.G. Enumerating Circulating Tumor Cells with a Self-Assembled Cell Array (SACA) Chip: A Feasibility Study in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Goi, T.; Seki, K.; Ohtaki, N.; Maehara, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Niimoto, S.; Katayama, K.; Hirose, K.; Nakagawara, G.; et al. Clinical significance of combined immunohistochemical detection of CD44v and sialyl lex expression for colorectal cancer patients undergoing curative resection. Oncology 1998, 55, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.S.; Song, Y.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Tong, T.; Li, Y.; Fu, M.; Guo, X.L.; Dong, L.J.; He, X.; Qiao, H.X.; et al. Disruption of xCT inhibits cancer cell metastasis via the caveolin-1/beta-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2009, 28, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Doi, T.; Nagano, O.; Imamura, C.K.; Ozeki, T.; Ishii, Y.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Nakajima, T.E.; Hironaka, S.; et al. Dose-escalation study for the targeting of CD44v(+) cancer stem cells by sulfasalazine in patients with advanced gastric cancer (EPOC1205). Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Doi, T.; Nagano, O.; Fukutani, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Nomura, S.; Sato, A.; Kuwata, T.; Asai, K.; Einaga, Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of sulfasalazine and cisplatin for patients with CD44v-positive gastric cancer refractory to cisplatin (EPOC1407). Gastric Cancer 2017, 20, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsubo, K.; Nosaki, K.; Imamura, C.K.; Ogata, H.; Fujita, A.; Sakata, S.; Hirai, F.; Toyokawa, G.; Iwama, E.; Harada, T.; et al. Phase I study of salazosulfapyridine in combination with cisplatin and pemetrexed for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).