The Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated Using Radiotherapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Group Description
3.2. Prognostic Value of RDW and SII
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Anwar, M.; Chung, H.T. Handbook of Evidence-Based Radiation Oncology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9783319626420. [Google Scholar]
- Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J. Nowotwory Złośliwe w Polsce w 2018. Kraj. Rejestr. Nowotworów 2020, 3–4, 31–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatla, N.; Aoki, D.; Sharma, D.N.; Sankaranarayanan, R. Cancer of the Cervix Uteri. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2018, 143 (Suppl. S2), 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, J.A.; Mehta, M.P.; Ng, A.K.; Recht, A.; Tinkle, C.L.; Member, A.; Viswanathan, A.N. Gunderson & Tepper’s Clinical Radiation Oncology, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780323672467. [Google Scholar]
- Salvagno, G.L.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Picanza, A.; Lippi, G. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width: A Simple Parameter with Multiple Clinical Applications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, M.; Ding, Y.; Pu, L.; Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Cabanero, M.; Li, J.; Xiang, R.; Xiong, S. Prognostic Value of RDW in Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16027–16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, A.; Giamouzis, G.; Dimos, A.; Skoularigki, E.; Starling, R.C.; Skoularigis, J.; Triposkiadis, F. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology, Prognostic Role, Controversies and Dilemmas. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.; Nath, P.; Satpathy, S.K.; Panda, B.; Patro, S. Comparing Prognostic Scores and Inflammatory Markers in Predicting the Severity and Mortality of Acute Pancreatitis. Cureus 2023, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liao, B.; Cao, T.; Ji, T.; Huang, J.; Ma, K. Diagnostic Value of RDW for the Prediction of Mortality in Adult Sepsis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 997853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhai, E.T.; Yuan, Y.J.; Wu, K.M.; Xu, J.B.; Peng, J.J.; Chen, C.Q.; He, Y.L.; Cai, S.R. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index for Predicting Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6261–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lin, H. Prognostic Value of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Patients with Urologic Cancers: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Patients with Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartl, T.; Bekos, C.; Postl, M.; Alexander, R.; Polterauer, S.; Stefanie, A.; Richard, S. The Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) Is an Independent Prognostic Parameter of Survival in Patients with Invasive Vulvar Cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1–10.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleko, M.; Pitynski, K.; Pluta, E.; Czerw, A.; Sygit, K.; Karakiewicz, B.; Banas, T. Role of Systemic Inflammatory Reaction in Female Genital Organ Malignancies—State of the Art. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 5491–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Xie, J.; Chang, L. Elevated Red Blood Cell Distribution Width Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3611–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.Y.; Lau, H.C.; Li, S.; Tao, L.; Zhang, M.; Gong, H.; Zhou, L. Pretreatment Level of Red Cell Distribution Width as a Prognostic Indicator for Survival in a Large Cohort Study of Male Laryngeal Squamous Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yan, W.; Liang, J.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Hao, J.; Wan, Q.; Liu, J.; Luo, C.; Chen, Y. Nomogram Based on Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index to Predict Survival of Tongue Cancer Patients Who Underwent Cervical Dissection. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, M.; Uysal, S.; Altinişik, U.; Cevizci, S.; Güçlü, O.; Dereköy, F.S. The Pre-Treatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width Predict Prognosis in Patients with Laryngeal Carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraez, I.; Bento, L.; Del Campo, R.; Sas, A.; Ramos, R.; Ibarra, J.; Mestre, F.; Alemany, R.; Bargay, J.; Sampol, A.; et al. Prognostic Role of the Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW)in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.P.; Kang, K.; Lin, Q.; Hai, J. Prognostic Significance of Preoperative Systemic Cellular Inflammatory Markers in Gliomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Therapy, E.; Program, C.; Chase, F. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms and Consequences. Immunity 2020, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cervix Uteri. In AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 649–659. [Google Scholar]
- Holub, K.; Biete, A. Impact of Systemic Inflammation Biomarkers on the Survival Outcomes of Cervical Cancer Patients. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, S.; Yang, G.; Hosseinifard, H.; Imani, S.; Yang, L.; Maghsoudloo, M.; Fu, S.Z.; Wen, Q.L.; Liu, Q. Prognostic Value of Systemic Hemato-Immunological Indices in Uterine Cervical Cancer: A Systemic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression of Observational Studies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 160, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Pan, B.; Xiang, H.; Zheng, M. Pretreatment Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Can Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Cervical Cancer at Stages IB2-IIB. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, J.; Lin, L.; Guo, J.; Ye, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Y. Predictive Value of Hematological Markers of Systemic Inflammation for Managing Cervical Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44824–44832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, P.S.V.; Mantoani, P.T.S.; Murta, E.F.C.; Nomelini, R.S. Laboratory Parameters as Predictors of Prognosis in Uterine Cervical Neoplasia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021, 256, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferioli, M.; Benini, A.; Malizia, C.; Forlani, L.; Medici, F.; Laghi, V.; Ma, J.; Galuppi, A.; Cilla, S.; Buwenge, M.; et al. Classical Prognostic Factors Predict Prognosis Better than Inflammatory Indices in Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer: Results of a Comprehensive Observational Study Including Tumor-, Patient-, and Treatment-Related Data (ESTHER Study). J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Feng, S.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Lin, X.; Yuan, L.; Sheng, X.; Li, D. Prognostic Value of Body Composition and Systemic Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer Following Chemoradiotherapy. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 5145–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Huang, X.; Jin, C.; Zhuang, X.; Ye, L.; Zheng, F.; Lin, F. Preoperative Platelet Count Improves the Prognostic Prediction of the FIGO Staging System for Operable Cervical Cancer Patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 473, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G. Clinical Utility of Red Blood Cell Distribution Width for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
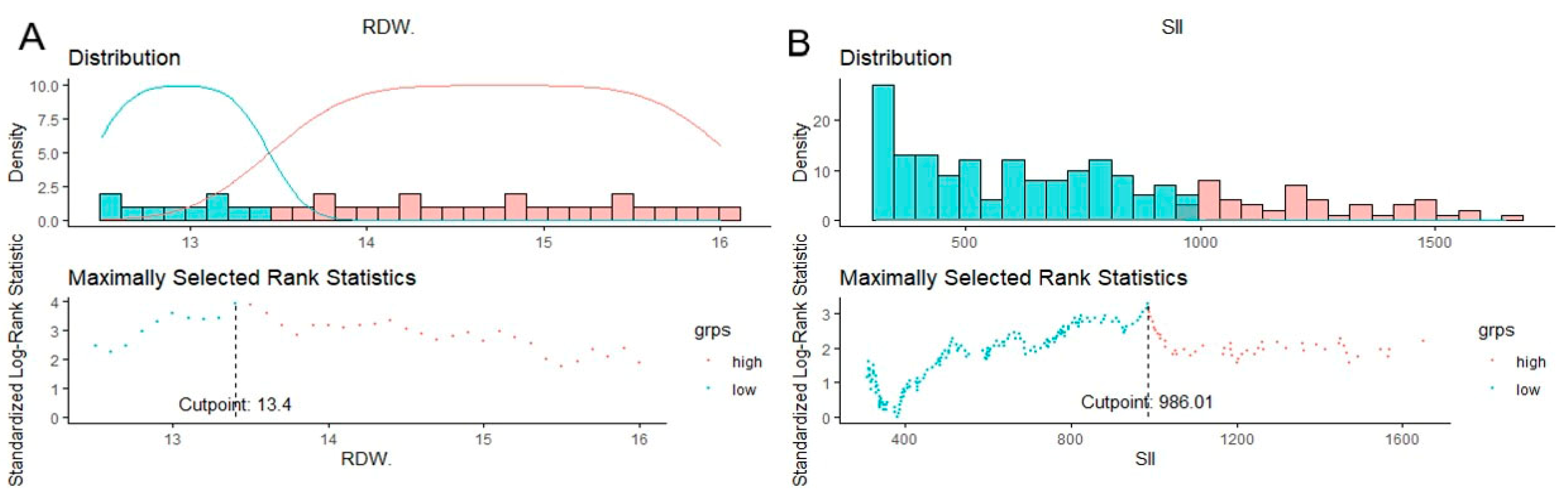
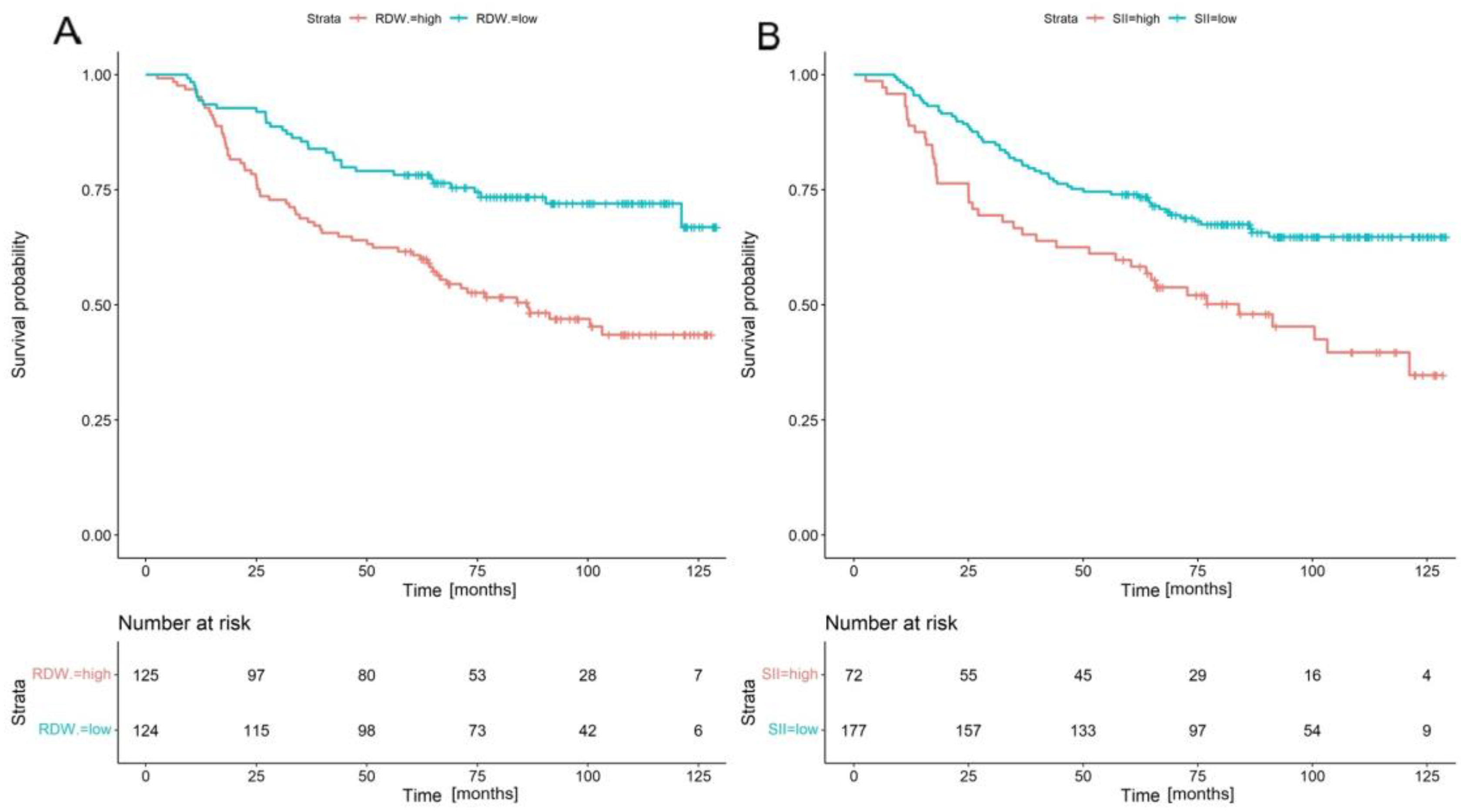
| RDW | SII | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Low ≤ 13.4% n = 124 (%) | High > 13.4% n = 125 (%) | Low ≤ 986.01 n = 177 (%) | High > 986.01 n = 72 (%) |
| Age [years] | 57.8 (51.5–64) | 56.9 (48.5–65.4) | 58.6 (52.1–65.5) | 51.8 (44.1–58.9) |
| Histopathology | ||||
| SCC | 117 (94.4%) | 120 (96%) | 169 (95.5%) | 68 (94.4%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 7 (5.6%) | 5 (4%) | 8 (4.5%) | 4 (5.6%) |
| FIGO stage * | ||||
| IB1 | ||||
| IB2 | 1 (0.8%) | 1 (0.6%) | ||
| IB3 | ||||
| IIA1 | ||||
| IIA2 | 1 (0.8%) | 1 (0.6%) | ||
| IIB | 18 (14.5%) | 15 (12%) | 31 (17.5%) | 2 (2.8%) |
| IIIA | ||||
| IIIB | 51 (41.1%) | 44 (35.2%) | 75 (42.4%) | 20 (27.8%) |
| IIIC1 | 55 (44.4%) | 58 (46.4%) | 66 (37.3%) | 47 (65.3%) |
| IIIC2 | 3 (2.4%) | 3 (1.7%) | ||
| IVA | 3 (2.4%) | 3 (4.2%) | ||
| TNM stage * | ||||
| IB1 | 6 (4.8%) | 2 (1.6%) | 7 (4%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| IB2 | 2 (1.6%) | 1 (0.6%) | 1 (1.4%) | |
| IIA1 | 11 (8.9%) | 10 (8%) | 19 (10.7%) | 2 (2.8%) |
| IIA2 | 21 (16.9%) | 20 (16%) | 25 (14.1%) | 16 (22.2%) |
| IIB | 63 (50.8%) | 70 (56%) | 99 (55.9%) | 34 (47.2%) |
| IIIA | 4 (3.2%) | 3 (1.7%) | 1 (1.4%) | |
| IIIB | 8 (6.5%) | 12 (9.6%) | 12 (6.8%) | 8 (11.1%) |
| IV | 9 (7.3%) | 11 (8.8%) | 11 (6.2%) | 9 (12.5%) |
| ECOG | ||||
| 0 | 94 (75.8%) | 93 (74.4%) | 135 (76.3%) | 52 (72.2%) |
| 1 | 28 (22.6%) | 30 (24%) | 40 (22.6%) | 18 (25%) |
| 2 | 2 (1.6%) | 2 (1.6%) | 2 (1.1%) | 2 (2.8%) |
| Positive nodal status | 55 (44.4%) | 63 (50.4%) | 69 (39%) | 49 (68.1%) |
| Radiation modality | ||||
| EBRT | 1 (0.8%) | 2 (1.6%) | 2 (1.1%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| EBRT + BT | 123 (99.2%) | 123 (98.4%) | 175 (98.9%) | 71 (98.6%) |
| Concurrent chemotherapy | 115 (92.7%) | 110 (88%) | 159 (89.8%) | 66 (91.7%) |
| Number of cycles | ||||
| 0 | 9 (7.3%) | 15 (12%) | 18 (10.2%) | 6 (8.3%) |
| 1 | 2 (1.6%) | 3 (2.4%) | 4 (2.3%) | 1 (1.4%) |
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | 6 (4.8%) | 3 (2.4%) | 7 (4%) | 2 (2.8%) |
| 4 | 10 (8.1%) | 9 (7.2%) | 15 (8.5%) | 4 (5.6%) |
| 5 | 26 (21%) | 31 (24.8%) | 41 (23.2%) | 16 (22.2%) |
| 6 | 71 (57.3%) | 64 (51.2%) | 92 (52%) | 43 (59.7%) |
| RDW [%] | 12.9 (12.6–13.2) | 14.4 (13.9–15.7) | 13.3 (12.8–14.1) | 14.1 (13.2–15.9) |
| NLR | 2.38 (1.7–3.35) | 2.65 (1.71–3.73) | 2.05 (1.53–2.63) | 3.96 (3.3–4.84) |
| PLR | 131.76 (106.14–177.6) | 160.07 (112.9–218.12) | 122.62 (96.65–154.12) | 216.78 (172.66–261.29) |
| SII | 602.82 (392.04–868.02) | 766.83 (391.64–1187.58) | 497.32 (337.39–741.41) | 1394.39 (1120.5–1777.18) |
| RBC [106/μL] | 4.45 (4.2–4.7) | 4.44 (4.18–4.63) | 4.49 (4.26–4.74) | 4.22 (3.99–4.53) |
| HGB [g/dL] | 13.7 (12.95–14.2) | 13 (11.2–13.9) | 13.7 (12.98–14.3) | 11.9 (10.6–13.2) |
| WBC [103/μL] | 7.44 (5.89–9.16) | 7.36 (6.12–9.27) | 6.89 (5.66–8.21) | 9.56 (7.73–11.87) |
| LYMPH [103/μL] | 1.91 (1.5–2.36) | 1.85 (1.56–2.27) | 1.96 (1.63–2.35) | 1.72 (1.43–2.2) |
| NEU [103/μL] | 4.63 (3.54–5.91) | 4.67 (3.35–6.12) | 3.89 (3.17–4.99) | 6.6 (5.46–8.51) |
| PLT [103/μL] | 263 (219–305) | 283 (230–358) | 248 (208.8–284.3) | 361 (308–437) |
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age [years] | 0.99 (0.973–1.008) | 0.270 | 0.997 (0.978–1.016) | 0.607 |
| Histopathology (SCC vs. adenocarcinoma) | 0.953 (0.388–2.344) | 0.917 | 1.14 (0.46–2.84) | 0.897 |
| Positive nodal status | 1.514 (1.018–2.251) | 0.041 | 1.26 (0.82–1.92) | 0.361 |
| ECOG status (1 vs. 0) | 0.95 (0.58–1.57) | 0.852 | 0.91 (0.55–1.50) | 0.781 |
| ECOG status (2 vs. 0) | 4.25 (1.54–11.71) | 0.005 | 4.55 (1.61–12.85) | 0.023 |
| FIGO stage (III and IV vs. I and II) | 2.184 (1.059–4.505) | 0.034 | 1.68 (0.78–3.63) | 0.177 |
| TNM stage (III and IV vs. I and II) | 1.589 (0.969–2.541) | 0.067 | ||
| RBC [106/μL] | 0.666 (0.43–1.031) | 0.069 | ||
| RDW | 1.183 (1.082–1.294) | <0.001 | 2.04 (1.32–3.16) | 0.001 |
| HGB [g/dL] | 0.866 (0.77–0.975) | 0.017 | 0.89 (0.78–1.02) | 0.909 |
| WBC [103/μL] | 1.112 (1.05–1.179) | <0.001 | ||
| NEU [103/μL] | 1.138 (1.063–1.219) | <0.001 | ||
| LYMPH [103/μL] | 1.08 (0.802–1.454) | 0.611 | ||
| PLT [103/μL] | 1.002 (1–1.004) | 0.107 | ||
| NLR | 1.243 (1.082–1.428) | 0.002 | ||
| PLR | 1.002 (0.999–1.004) | 0.199 | ||
| SII | 1 (1–1.001) | 0.001 | 1.42 (0.89–2.25) | 0.138 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Staniewska, E.; Grudzien, K.; Stankiewicz, M.; Raczek-Zwierzycka, K.; Rembak-Szynkiewicz, J.; Nowicka, Z.; Tarnawski, R.; Miszczyk, M. The Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated Using Radiotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081542
Staniewska E, Grudzien K, Stankiewicz M, Raczek-Zwierzycka K, Rembak-Szynkiewicz J, Nowicka Z, Tarnawski R, Miszczyk M. The Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated Using Radiotherapy. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081542
Chicago/Turabian StyleStaniewska, Emilia, Karolina Grudzien, Magdalena Stankiewicz, Katarzyna Raczek-Zwierzycka, Justyna Rembak-Szynkiewicz, Zuzanna Nowicka, Rafal Tarnawski, and Marcin Miszczyk. 2024. "The Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated Using Radiotherapy" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081542
APA StyleStaniewska, E., Grudzien, K., Stankiewicz, M., Raczek-Zwierzycka, K., Rembak-Szynkiewicz, J., Nowicka, Z., Tarnawski, R., & Miszczyk, M. (2024). The Prognostic Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index (SII) and Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) in Patients with Cervical Cancer Treated Using Radiotherapy. Cancers, 16(8), 1542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081542






