Prognostic Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
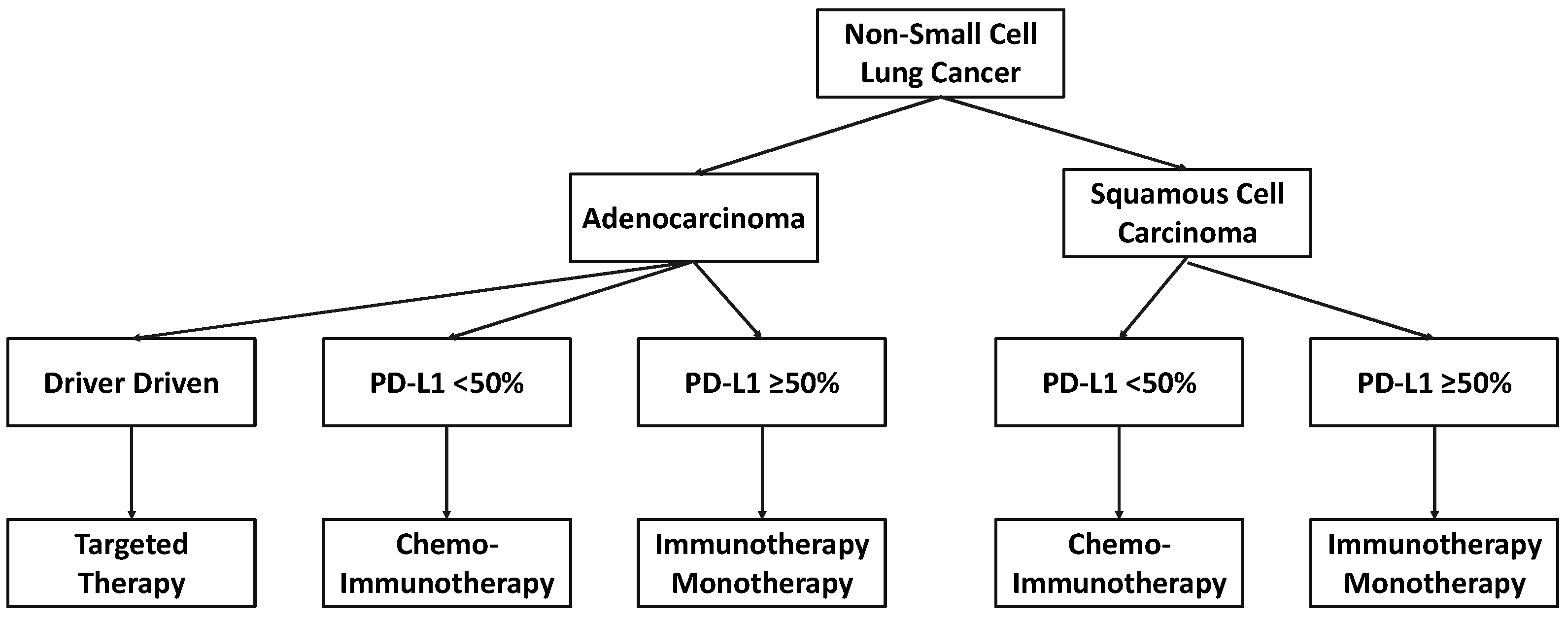
1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation
3. Leukocytes
4. Platelets and Coagulation Factors
5. Albumin
6. Non-Specific Biomarkers of Inflammation (CRP, LDH, and ESR)
7. Composite Biomarkers
8. Challenges
9. Identifying an Optimal Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation
10. Considering NSCLC as a Heterogenous Disease
11. Clinically Relevant Outcomes
12. Future Directions
13. A Minimum Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation Common Dataset
14. A Minimum Clinicopathological Common Dataset
15. Optimising Survival Endpoints
16. Discussion
17. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Lung Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/lung-cancer-statistics/ (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Cancer Research UK. Lung Cancer Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/lung-cancer (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lababede, O.; Meziane, M.A. The Eighth Edition of TNM Staging of Lung Cancer: Reference Chart and Diagrams. Oncologist 2018, 23, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postmus, P.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Oudkerk, M.; Senan, S.; Waller, D.A.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Escriu, C.; Peters, S.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv1–iv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stares, M.; Lewis, G.; Vallet, M.; Killean, A.; Tramonti, G.; Patrizio, A.; Mackean, M.; Harrow, S.; Barrie, C.; MacLennan, K.; et al. Real-World Impact of SABR on Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Outcomes at a Scottish Cancer Centre. Cancers 2023, 15, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adizie, J.B.; Khakwani, A.; Beckett, P.; Navani, N.; West, D.; Woolhouse, I.; Harden, S.V. Stage III Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Management in England. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 31, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.S.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Solomon, B.J.; et al. Non-oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 358–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.S.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Solomon, B.J.; et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet Lond. Engl. 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stares, M.; Swan, A.; Cumming, K.; Ding, T.; Leach, J.; Stratton, C.; Thomson, F.; Barrie, C.; MacLennan, K.; Campbell, S.; et al. Hypoalbuminaemia as a prognostic biomarker of first-line treatment resistance in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 734735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stares, M.; Ding, T.E.; Stratton, C.; Thomson, F.; Baxter, M.; Cagney, H.; Cumming, K.; Swan, A.; Ross, F.; Barrie, C.; et al. Biomarkers of systemic inflammation predict survival with first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, R.D.; Daly, L.E.; Simmons, C.P.; Ryan, A.M.; Sim, W.M.; Fallon, M.; Power, D.G.; Wilcock, A.; Maddocks, M.; Bennett, M.I.; et al. The Relationship between ECOG-PS, mGPS, BMI/WL Grade and Body Composition and Physical Function in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, K.; Strasser, F.; Anker, S.D.; Bosaeus, I.; Bruera, E.; Fainsinger, R.L.; Jatoi, A.; Loprinzi, C.; MacDonald, N.; Mantovani, G.; et al. Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.C.; Cook, J.; Maddocks, M.; Skipworth, R.J.E.; Fallon, M.; Laird, B.J. Combined exercise and nutritional rehabilitation in outpatients with incurable cancer: A systematic review. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 2371–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeland, E.J.; Bohlke, K.; Baracos, V.E.; Bruera, E.; Del Fabbro, E.; Dixon, S.; Fallon, M.; Herrstedt, J.; Lau, H.; Platek, M.; et al. Management of Cancer Cachexia: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2438–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caliman, E.; Fancelli, S.; Ottanelli, C.; Mazzoni, F.; Paglialunga, L.; Lavacchi, D.; Michelet, M.R.G.; Giommoni, E.; Napolitano, B.; Scolari, F.; et al. Absolute eosinophil count predicts clinical outcomes and toxicity in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immunotherapy. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2022, 32, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schernberg, A.; Mezquita, L.; Boros, A.; Botticella, A.; Caramella, C.; Besse, B.; Escande, A.; Planchard, D.; Le Péchoux, C.; Deutsch, E. Neutrophilia as prognostic biomarker in locally advanced stage III lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treffers, L.W.; Hiemstra, I.H.; Kuijpers, T.W.; van den Berg, T.K.; Matlung, H.L. Neutrophils in cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Wellenstein, M.D.; de Visser, K.E. Neutrophils in cancer: Neutral no more. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, H.; Hagerling, C.; Werb, Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: From tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1267–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, Y.-M.; Ma, L.-X. Prognostic significance of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 3098–3106. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Prasad, S.; Ma, S.J.; Yu, H.; Iovoli, A.J.; Farrugia, M.K.; Dexter, E.U.; Demmy, T.L.; Malik, N.K.; Singh, A.K. Association of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with survival in peripheral early-stage non-small cell lung cancer after stereotactic body radiation therapy. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, L.J.; Felding-Habermann, B. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, A.K.; Cedervall, J. The pro-inflammatory role of platelets in cancer. Platelets 2018, 29, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Rapoport, B.L.; Steel, H.C.; Theron, A.J. Pro-Tumorigenic and Thrombotic Activities of Platelets in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, E.; Mao, X.; Miao, S. Emerging roles of platelets in cancer biology and their potential as therapeutic targets. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 939089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Du, K. Platelet count predicts prognosis in operable non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 1351–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Cao, J.; Lin, H.; Liang, L.; Shen, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Z.; Mei, J. Prognostic role of the platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in the clinical outcomes of patients with advanced lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 962173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Prognostic value of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Pang, Z.; Shen, H.; Ni, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, Q. The Prognostic Value of PLR in Lung Cancer, a Meta-analysis Based on Results from a Large Consecutive Cohort. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, G.; Liang, C.; Xiao, F.; Yu, Q.; Wen, H.; Song, Z.; Tian, Y.; Shi, B.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D. Prognostic significance of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhan, P.; Lv, Y.; Shen, K.; Wei, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, Y. Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with systemic therapy: A meta-analysis. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Doi, T.; Hokka, D.; Maniwa, Y. Prognostic value of preoperative plasma fibrinogen levels in resected stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeroso, N.N.; Rizki Ananda, F.; Samosir, G.; Hariman, H.; Chairani Eyanoer, P. The correlation between hemostatic parameters and mortality rate in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Hematol. Rep. 2021, 13, 8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayleyegn, B.; Adane, T.; Getawa, S.; Aynalem, M.; Kifle, Z.D. Coagulation parameters in lung cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, A.F.; Greenley, S.L.; McKenzie, G.A.G.; Paton, L.W.; Johnson, M.J. Relationship between markers of malnutrition and clinical outcomes in older adults with cancer: Systematic review, narrative synthesis and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1519–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinge, M.E.; Henriksen, D.P.; Hallas, P.; Brabrand, M. Hypoalbuminemia is a strong predictor of 30-day all-cause mortality in acutely admitted medical patients: A prospective, observational, cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, B.J.; Kaasa, S.; McMillan, D.C.; Fallon, M.T.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Fayers, P.; Klepstad, P. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced cancer: A comparison of clinicopathological factors and the development of an inflammation-based prognostic system. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, P.B.; Wolfe, R.R.; Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and Clinical Significance. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2019, 43, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stares, M.; Doyle, E.; Chapple, S.; Raynes, G.; MacDonald, J.; Barrie, C.; Laird, B.; MacKean, M.; Philips, I. Prognostic value of the Scottish Inflammatory prognostic Score in patients with NSCLC expressing PD-L1 ≥ 50% progressing on first-line pembrolizumab. Lung Cancer 2024, 189, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, L.; Patel, S.H.; Lopez, G.; Grogan, M.; Li, M.; Haddad, T.; Johns, A.; Ganesan, L.P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Serum Albumin: Early Prognostic Marker of Benefit for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Monotherapy But Not Chemoimmunotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, J.; Ye, F.; Lin, Z.; Tong, L.; Liu, J. Association between albumin-to-globulin ratio and the risk of overall survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with anlotinib treatment: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Che, G. The prognostic value of serum albumin-globulin ratio in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3545–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Wei, S.; Liang, X. A Low Albumin-to-Globulin Ratio Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Patients With Metastatic Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 621592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Moon, A. C-Reactive Protein Signaling Pathways in Tumor Progression. Biomol. Ther. 2023, 31, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Galeone, C.; Gisabella, M.; Duranti, L.; Taverna, F.; Suatoni, P.; Morelli, D.; Pastorino, U. Baseline C-reactive protein level predicts survival of early-stage lung cancer: Evidence from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tumori 2016, 102, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, S.; Long, G. C-reactive protein is a significant predictor of improved survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Medicine 2019, 98, e16238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Karp, J.E.; Emadi, A. Elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) can be a marker of immune suppression in cancer: Interplay between hematologic and solid neoplastic clones and their microenvironments. Cancer Biomark. Sect. Dis. Markers 2017, 19, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serganova, I.; Cohen, I.J.; Vemuri, K.; Shindo, M.; Maeda, M.; Mane, M.; Moroz, E.; Khanin, R.; Satagopan, J.; Koutcher, J.A.; et al. LDH-A regulates the tumor microenvironment via HIF-signaling and modulates the immune response. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.W.; Elassaiss-Schaap, J.; Kefford, R.; Hwu, W.-J.; Wolchok, J.D.; Joshua, A.M.; Ribas, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; et al. Baseline Tumor Size Is an Independent Prognostic Factor for Overall Survival in Patients with Melanoma Treated with Pembrolizumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4960–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Song, Q.; Wang, G.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, S.; Wang, J. Pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase may predict outcome of advanced non small-cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, J.; Ludolph, A.C. Non-invasive ventilation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419857040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.; McMillan, D.C.; Tuck, S.; Graham, C.; McKeown, A.; Bennett, M.; O’Neill, C.; Wilcock, A.; Usborne, C.; Fearon, K.C.; et al. “How Long Have I Got?”-A Prospective Cohort Study Comparing Validated Prognostic Factors for Use in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Oncologist 2019, 24, e960–e967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score: A decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, B.J.A.; Fallon, M.; Hjermstad, M.J.; Tuck, S.; Kaasa, S.; Klepstad, P.; McMillan, D.C. Quality of Life in Patients With Advanced Cancer: Differential Association With Performance Status and Systemic Inflammatory Response. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2769–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, R.D.; Laird, B.J.A.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. The prognostic value of the systemic inflammatory response in randomised clinical trials in cancer: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 132, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, E.; McMillan, D.C. Towards a simple objective framework for the investigation and treatment of cancer cachexia: The Glasgow Prognostic Score. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, A.; Martin, D.; D’Cruz, L.; Fokas, E.; Rödel, C.; Fleischmann, M. C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio as Prognostic Marker in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Chemoradiotherapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Gao, X.; Sun, H.; Tian, S.; Dong, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Prognostic Parameter in NSCLC Patients Receiving EGFR-TKIs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 6688346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezquita, L.; Auclin, E.; Ferrara, R.; Charrier, M.; Remon, J.; Planchard, D.; Ponce, S.; Ares, L.P.; Leroy, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; et al. Association of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Luo, J.; Wen, J.; Jiang, M. The Relationship Between Systemic Immune Inflammatory Index and Prognosis of Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 898304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mountzios, G.; Samantas, E.; Senghas, K.; Zervas, E.; Krisam, J.; Samitas, K.; Bozorgmehr, F.; Kuon, J.; Agelaki, S.; Baka, S.; et al. Association of the advanced lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) with immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Sun, T.; Zhao, Z.; Ming, L. Preoperative Platelet to Albumin Ratio Predicts Outcome of Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 27, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Yu, H.; Lei, H.; Cao, H.; Chen, M.; Liu, S. A prognostic model using the neutrophil-albumin ratio and PG-SGA to predict overall survival in advanced palliative lung cancer. BMC Palliat. Care 2022, 21, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osugi, J.; Muto, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Suzuki, H.; Gotoh, M. Prognostic impact of the high-sensitivity modified Glasgow prognostic score in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Gao, M.-Q.; Jiang, X.-C.; Pan, X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Pang, B. Research progress and value of albumin-related inflammatory markers in the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer: A review of clinical evidence. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1294–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, X.; Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Predictive value of the prognostic nutritional index in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Xu, Q.; Yang, S.; Han, S.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y. Pretreatment systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) is an independent predictor of survival in unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy: A two-center retrospective study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigot, F.; Castanon, E.; Baldini, C.; Hollebecque, A.; Carmona, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Angevin, E.; Armand, J.-P.; Ribrag, V.; Aspeslagh, S.; et al. Prospective validation of a prognostic score for patients in immunotherapy phase I trials: The Gustave Roussy Immune Score (GRIm-Score). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 84, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkenau, H.-T.; Barriuso, J.; Olmos, D.; Ang, J.E.; de Bono, J.; Judson, I.; Kaye, S. Prospective validation of a prognostic score to improve patient selection for oncology phase I trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2692–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Ruan, G.; Wei, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; et al. The inflammatory burden index is a superior systemic inflammation biomarker for the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Tian, W.; Lin, X.; Leong, T.L.; Seki, N.; Ichiki, Y.; Su, S.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Ye, J. Association between the modified lung immune predictive index and clinical outcomes of advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 6279–6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramspek, C.L.; Jager, K.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Zoccali, C.; van Diepen, M. External validation of prognostic models: What, why, how, when and where? Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenci, E.; Cantini, L.; Pecci, F.; Cognigni, V.; Agostinelli, V.; Mentrasti, G.; Lupi, A.; Ranallo, N.; Paoloni, F.; Rinaldi, S.; et al. The Gustave Roussy Immune (GRIm)-Score Variation Is an Early-on-Treatment Biomarker of Outcome in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients Treated with First-Line Pembrolizumab. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Ihara, S.; Ikuta, S.; Komuta, K. Gustave Roussy Immune Score and Royal Marsden Hospital Prognostic Score Are Biomarkers of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Zhang, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, G.; Tang, M.; Xie, H.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Y.; et al. The advanced lung cancer inflammation index is the optimal inflammatory biomarker of overall survival in patients with lung cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, L.; Moskovitz, M.; Urban, D.; Nechushtan, H.; Keren, S.; Reinhorn, D.; Wollner, M.; Daher, S.; Rottenberg, Y.; Rovitzky, Y.; et al. dNLR-Based Score Predicting Overall Survival Benefit for the Addition of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy to Pembrolizumab in Advanced NSCLC with PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score ≥ 50. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banna, G.L.; Cortellini, A.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Tiseo, M.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Barbieri, F.; Giusti, R.; Bria, E.; Grossi, F.; Pizzutilo, P.; et al. The lung immuno-oncology prognostic score (LIPS-3): A prognostic classification of patients receiving first-line pembrolizumab for PD-L1 ≥ 50% advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, A.; Liu, A.; Tong, W.; Cao, D. Evaluation of the prognostic role of platelet-lymphocyte ratio in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 77, 105957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, M.J.; Horgan, P.G.; Talwar, D.; Fletcher, C.D.; Morrison, D.S.; McMillan, D.C. Optimization of the systemic inflammation-based Glasgow prognostic score: A Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Cancer 2013, 119, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, W.J.; Shah, N.J.; Subramaniam, D.S. Management of Brain Metastases in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Mamtani, R.; Hennessy, S. Association Between Survival and Very High Versus High PD-L1 Expression in Patients Receiving Pembrolizumab as First-line Treatment for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, E.J.; Ricciuti, B.; Gainor, J.F.; Kehl, K.L.; Kravets, S.; Dahlberg, S.; Nishino, M.; Sholl, L.M.; Adeni, A.; Subegdjo, S.; et al. Outcomes to first-line pembrolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and very high PD-L1 expression. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Nonaka, H.; Onishi, H.; Nakatani, E.; Sato, Y.; Funayama, S.; Watanabe, H.; Komiyama, T.; Kuriyama, K.; Marino, K.; et al. Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score is predictive of prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy: A retrospective study. J. Radiat. Res. 2021, 62, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Ren, G.; Yang, Q. Prognostic value of preoperative modified Glasgow prognostic score in surgical non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1094973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Deng, C.; Wen, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Han, H.; Zheng, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index is a stage-dependent prognostic factor in patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Li, W. Association of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcomes in patients with lung cancer receiving immunotherapy: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Mao, J.; Tao, P.; Chi, H.; Jia, W.; Dong, C. The relationship between NLR/PLR/LMR levels and survival prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Medicine 2022, 101, e28617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, G.; Fang, N.; Cai, L.; Du, W.; Jia, J. Platelet/lymphocyte ratio is a significant prognostic factor for targeted therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520980205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, S.; Ihara, S.; Komuta, K. Pretreatment Lung Immune Prognostic Index Is a Prognostic Marker of Chemotherapy and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banna, G.L.; Signorelli, D.; Metro, G.; Galetta, D.; De Toma, A.; Cantale, O.; Banini, M.; Friedlaender, A.; Pizzutillo, P.; Garassino, M.C.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in combination with PD-L1 or lactate dehydrogenase as biomarkers for high PD-L1 non-small cell lung cancer treated with first-line pembrolizumab. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-L.; Wu, Y.-M.; Chen, J.-T.; Chang, K.-Y.; Cherng, Y.-G.; Lin, S.-P.; Tsou, M.-Y.; Tai, Y.-H. A comparison of inflammation markers for predicting oncological outcomes after surgical resection of non-small-cell lung cancer: A validated analysis of 2066 patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, Y.M.; Ojara, F.W.; Pérez-Pitarch, A.; Geiger, K.; Huisinga, W.; Hartung, N.; Michelet, R.; Holdenrieder, S.; Joerger, M.; Kloft, C. C-Reactive Protein as an Early Predictor of Efficacy in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Tumor Dynamics-Biomarker Modeling Framework. Cancers 2023, 15, 5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kang, B.-H.; Kim, H.J.; Wu, H.-G.; Lee, J.H. Predictors of Post-chemoradiotherapy Pulmonary Complication in Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioulbasanis, I.; Pallis, A.; Vlachostergios, P.J.; Xyrafas, A.; Giannousi, Z.; Perdikouri, I.-E.; Makridou, M.; Kakalou, D.; Georgoulias, V. The Glasgow Prognostic Score (GPS) predicts toxicity and efficacy in platinum-based treated patients with metastatic lung cancer. Lung Cancer Amst. Neth. 2012, 77, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte ratio as a predictor for immune-related adverse events in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1234142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, A.; Toyokawa, G.; Koutake, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kawamata, Y.; Fukuishi, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Takeo, S. Association between pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and immune-related adverse events due to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chennamadhavuni, A.; Abushahin, L.; Jin, N.; Presley, C.J.; Manne, A. Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Practical Guide to Identifying High-Risk Patients and Rechallenging Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 779691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynes, G.; Stares, M.; Low, S.; Haron, D.; Sarwar, H.; Abhi, D.; Barrie, C.; Laird, B.; Caledonian Cachexia Collaborative; Phillips, I.; et al. Immune-Related Adverse Events, Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation, and Survival Outcomes in Patients Receiving Pembrolizumab for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShane, L.M.; Altman, D.G.; Sauerbrei, W.; Taube, S.E.; Gion, M.; Clark, G.M.; Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics. REporting recommendations for tumour MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Cancer Institue; National Human Genome Research Institute. The Cancer Genome Atlas Homepage. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- DataLoch. DataLoch Homepage. Available online: https://dataloch.org (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Cancer Research UK. Unleashing the Power of Data to Beat Cancer: Our Research Data Strategy. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/sites/default/files/cancer_research_uk_-_research_data_strategy.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Alaa, A.M.; Gurdasani, D.; Harris, A.L.; Rashbass, J.; Van Der Schaar, M. Machine learning to guide the use of adjuvant therapies for breast cancer. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.C.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test Item | Reference Range | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Haemoglobin | 115–165 (female) 130–180 (male) | g/L |
| Haematocrit | 0.40–0.52 | Ratio |
| Red Cell Count | 4.5–6.5 | ×1012/L |
| Mean Cell Volume | 78–98 | g/L |
| White Cell Count | 4.0–11.0 | ×109/L |
| Neutrophil Count | 2.0–7.5 | ×109/L |
| Lymphocyte Count | 1.5–4.5 | ×109/L |
| Monocyte Count | 0.2–0.8 | ×109/L |
| Basophil Count | 0.01–0.10 | ×109/L |
| Eosinophil Count | 0.04–0.40 | ×109/L |
| Platelet Count | 150–400 | ×109/L |
| Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time | 21.0–28.0 | Seconds |
| Prothrombin Time | 9.0–22.0 | Seconds |
| International Normalised Ratio | 0.9–1.2 | Ratio |
| Fibrinogen | 1.5–4.0 | g/L |
| Urea | 2.5–6.6 | mmol/L |
| Creatinine | 64–111 | mmol/L |
| Sodium | 135–145 | mmol/L |
| Potassium | 3.6–5.0 | mmol/L |
| Phosphate | 0.8–1.4 | mmol/L |
| Magnesium | 0.7–1.0 | mmol/L |
| Bilirubin | 3–21 | U/L |
| Alanine Transaminase | 10–50 | U/L |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | 40–125 | U/L |
| Calcium | 2.20–2.60 | mmol/L |
| Adjusted Calcium | 2.20–2.60 | mmol/L |
| Albumin | 36–47 | g/L |
| C-Reactive Protein | 0–10 | mg/L |
| Lactate Dehydrogenase | 125–220 | U/L |
| Name | Abbreviation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio [65] | NLR | NC ÷ LC |
| Derived Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio [66] | dNLR | NC ÷ (WCC − LC) |
| Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio [33] | PLR | Platelets ÷ LC |
| Monocyte to Lymphocyte Ratio [67] | MLR | MC ÷ LC |
| Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index [68] | ALI | Body mass index × (albumin ÷ NLR) |
| Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index [67] | SII | Platelets × NLR |
| CRP to Albumin Ratio [64] | CAR | CRP ÷ albumin |
| Platelet to Albumin Ratio [69] | PAR | Platelets ÷ albumin |
| Neutrophil to Albumin Ratio [70] | NAR | NC ÷ albumin |
| Albumin to Globulin Ratio [50] | AGR | Albumin ÷ serum globulin |
| Glasgow Prognostic Score [44] | GPS | 1 point each for albumin < 35 g/L, CRP > 10 mg/L; total score 0: low, 1: intermediate, 2: poor |
| Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score [60] | mGPS | 0 = any albumin and CRP ≤ 10 mg/L 1 = albumin ≥ 35 g/L and CRP > 10 mg/L 2 = albumin <35 g/L and CRP > 10 mg/L |
| High-Sensitivity Glasgow Prognostic Score [71] | HS-mGPS | 0 = any albumin and CRP ≤ 3 mg/L 1 = albumin ≥ 35 g/L and CRP > 3 mg/L 2 = albumin < 35 g/L and CRP > 3 mg/L |
| Adjusted Glasgow Prognostic Score [72] | A-mGPS | 0 = any albumin and CRP ≤ 3 mg/L 1 = albumin ≥ 39 g/L and CRP > 3 mg/L 2 = albumin < 39 g/L and CRP > 3 mg/L |
| Scottish Inflammatory Prognostic Index [15] | SIPS | 1 point each for albumin < 35 g/L, NC > 7.5 × 109/L; total score 0: low, 1: intermediate, 2: poor |
| Prognostic Nutritional Index [73] | PNI | Albumin + (5 × LC) |
| Systemic Inflammation Response Index [74] | SIRI | NC × MLR |
| Gustave Roussy Immune Score [75] | GRim | 1 point each for: LDH > ULN, albumin < 35 g/L, NLR > 6; score 0–1: low risk; score 2–3: high risk |
| Royal Marsden Hospital Prognostic Score [76] | RMH | 1 point each for: LDH > ULN, albumin < 35 g/L, number of metastatic sites > 2; score 0–1: low risk; score 2–3: high risk |
| CRP/Albumin/Lymphocyte Ratio [77] | CALLY | (Albumin × LC) ÷ (CRP × 104) |
| Inflammatory Burden Index [77] | IBI | CRP × NLR |
| Lung Immune Prognostic Score [66] | LIPI | 1 point each for dNLR > 3, LDH > ULN, ECOG PS 1 or 2; total score—0: low, 1: intermediate, 2: poor |
| Modified Lung Immune Prognostic Score [78] | mLIPI | 1 point each for dNLR > 3, LDH > ULN, ECOG PS 1 or 2; total score—0: low, 1: intermediate, 2: poor, 3: very poor |
| EPSILoN Score [79] | EPSILoN | 1 point each for NLR > 4, LDH > 400 mg/dL, liver metastases, smoking < 43 pack-years, ECOG PS ≥ 2; total score—0: low, 1–2: intermediate, 3–5: poor |
| Result | Prognosis | Median Overall Survival | |
|---|---|---|---|
| White Cell Count (≤11 × 109/L, >11 × 109/L) | 11.0 | Favourable | 16.8 months |
| Neutrophil Count (≤7.5 × 109/L, >7.5 × 109/L) | 7.67 | Poor | 6.8 months |
| Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio (≤5, >5) | 3.18 | Favourable | 20.5 months |
| Platelet/Lymphocyte Ratio (≤180, >180) | 194 | Poor | 9.9 months |
| Prognostic Nutritional Index (≥45, <45) | 41 | Favourable | 28.7 months |
| Albumin (<35 g/L, ≥35 g/L) | 29 | Poor | 7.7 months |
| Scottish Inflammatory Prognostic Score (0, 1, 2) | 2 | Very Poor | 5.1 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stares, M.; Brown, L.R.; Abhi, D.; Phillips, I. Prognostic Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers 2024, 16, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081508
Stares M, Brown LR, Abhi D, Phillips I. Prognostic Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081508
Chicago/Turabian StyleStares, Mark, Leo R. Brown, Dhruv Abhi, and Iain Phillips. 2024. "Prognostic Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081508
APA StyleStares, M., Brown, L. R., Abhi, D., & Phillips, I. (2024). Prognostic Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review of Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers, 16(8), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081508





