Does Breast Surgery Type Alter Incidental Axillary Irradiation? A Dosimetric Analysis of the “Sentinel Envahi et Randomisation du Curage” SERC Trial
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
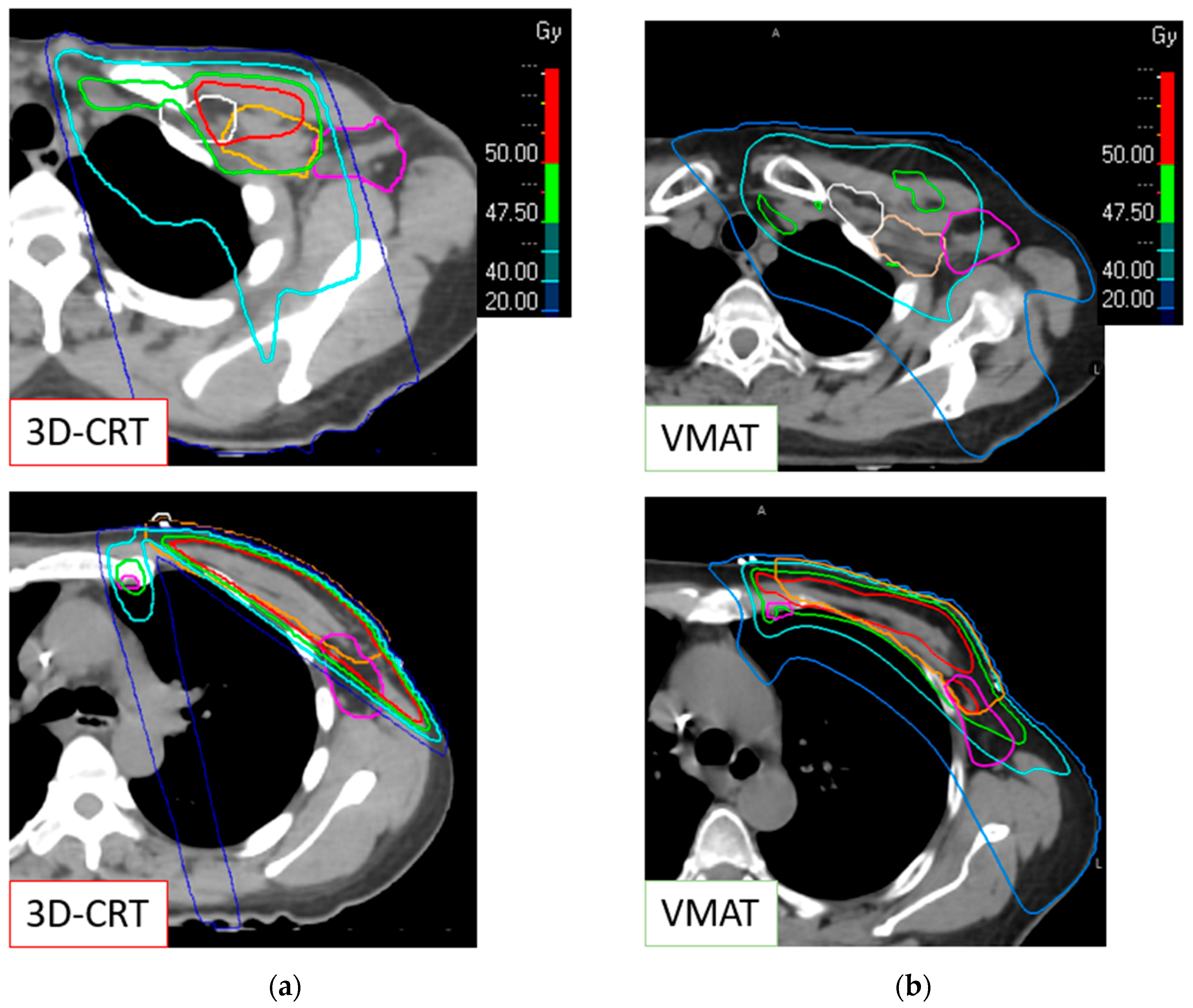
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Radiation Therapy
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galimberti, V.; Cole, B.F.; Viale, G.; Veronesi, P.; Vicini, E.; Intra, M.; Mazzarol, G.; Massarut, S.; Zgajnar, J.; Taffurelli, M.; et al. Axillary Dissection versus No Axillary Dissection in Patients with Breast Cancer and Sentinel-Node Micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): 10-Year Follow-up of a Randomised, Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Ballman, K.V.; McCall, L.; Beitsch, P.D.; Brennan, M.B.; Kelemen, P.R.; Ollila, D.W.; Hansen, N.M.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.W.; et al. Effect of Axillary Dissection vs. No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival among Women with Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solá, M.; Alberro, J.A.; Fraile, M.; Santesteban, P.; Ramos, M.; Fabregas, R.; Moral, A.; Ballester, B.; Vidal, S. Complete Axillary Lymph Node Dissection Versus Clinical Follow-up in Breast Cancer Patients with Sentinel Node Micrometastasis: Final Results from the Multicenter Clinical Trial AATRM 048/13/2000. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, A.E.; Ballman, K.; McCall, L.; Beitsch, P.; Whitworth, P.W.; Blumencranz, P.; Leitch, A.M.; Saha, S.; Morrow, M.; Hunt, K.K. Locoregional Recurrence After Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection with or Without Axillary Dissection in Patients with Sentinel Lymph Node Metastases: Long-Term Follow-up From the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (Alliance) ACOSOG Z0011 Randomized Trial. Ann. Surg. 2016, 264, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilini, O.; Botteri, E.; Leonardi, M.C.; Rotmensz, N.; Vila, J.; Peradze, N.; Thomazini, M.V.; Jereczek, B.A.; Galimberti, V.; Luini, A.; et al. Ipsilateral Axillary Recurrence after Breast Conservative Surgery: The Protective Effect of Whole Breast Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2017, 122, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, S.A.L.; Donker, M.; Poncet, C.; Sauvé, N.; Straver, M.E.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Mansel, R.E.; Blanken, C.; Orzalesi, L.; Klinkenbijl, J.H.G.; et al. Radiotherapy or Surgery of the Axilla After a Positive Sentinel Node in Breast Cancer: 10-Year Results of the Randomized Controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackstone, M.; Baldassarre, F.G.; Perera, F.E.; Cil, T.; Chavez Mac Gregor, M.; Dayes, I.S.; Engel, J.; Horton, J.K.; King, T.A.; Kornecki, A.; et al. Management of the Axilla in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Ontario Health (Cancer Care Ontario) and ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3056–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balic, M.; Thomssen, C.; Gnant, M.; Harbeck, N. St. Gallen/Vienna 2023: Optimization of Treatment for Patients with Primary Breast Cancer—A Brief Summary of the Consensus Discussion. Breast Care 2023, 18, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Moran, M.S.; Abraham, J.; Aft, R.; Agnese, D.; Allison, K.H.; Anderson, B.; Burstein, H.J.; Chew, H.; Dang, C.; et al. Breast Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2022, 20, 691–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, M.; Pin, Y.; Pflumio, C.; Mathelin, C.; Pivot, X.; Noël, G. Irradiation axillaire prophylactique « de diffusion » dans le cancer du sein—Revue de la littérature. Cancer/Radiothérapie 2021, 25, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyran, M.; Mailleux, H.; Tallet, A.; Fau, P.; Gonzague, L.; Minsat, M.; Moureau-Zabotto, L.; Resbeut, M. Volumetric-Modulated Arc Therapy for Left-Sided Breast Cancer and All Regional Nodes Improves Target Volumes Coverage and Reduces Treatment Time and Doses to the Heart and Left Coronary Artery, Compared with a Field-in-Field Technique. J. Radiat. Res. 2015, 56, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houvenaeghel, G.; Resbeut, M.; Boher, J.-M. Sentinel node invasion: Is it necessary to perform axillary lymph node dissection? Randomized trial SERC. Bull. Cancer 2014, 101, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, H.E.; Moses, L.; Stuart, K.; Nahar, N.; Tiver, K.; Wang, T.; Ward, R.; Ahern, V. Contouring Consensus Guidelines in Breast Cancer Radiotherapy: Comparison and Systematic Review of Patterns of Failure. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 63, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEC 61217:2011|IEC Webstore. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/4929 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- van Wely, B.J.; Teerenstra, S.; Schinagl, D.A.X.; Aufenacker, T.J.; de Wilt, J.H.W.; Strobbe, L.J.A. Systematic Review of the Effect of External Beam Radiation Therapy to the Breast on Axillary Recurrence after Negative Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 98, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houvenaeghel, G.; Classe, J.M.; Garbay, J.-R.; Giard, S.; Cohen, M.; Faure, C.; Charytansky, H.; Rouzier, R.; Daraï, E.; Hudry, D.; et al. Survival Impact and Predictive Factors of Axillary Recurrence after Sentinel Biopsy. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 58, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, J.K.; Armeson, K.E.; Rhome, R.; Spanos, M.; Harper, J.L. Dose to Level I and II Axillary Lymph Nodes and Lung by Tangential Field Radiation in Patients Undergoing Postmastectomy Radiation with Tissue Expander Reconstruction. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinterri, C.; Gentile, D.; Gatzemeier, W.; Sagona, A.; Barbieri, E.; Testori, A.; Errico, V.; Bottini, A.; Marrazzo, E.; Dani, C.; et al. Preservation of Axillary Lymph Nodes Compared with Complete Dissection in T1-2 Breast Cancer Patients Presenting One or Two Metastatic Sentinel Lymph Nodes: The SINODAR-ONE Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5732–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinterri, C.; Canavese, G.; Gatzemeier, W.; Barbieri, E.; Bottini, A.; Sagona, A.; Caraceni, G.; Testori, A.; Di Maria Grimaldi, S.; Dani, C.; et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy versus Axillary Lymph Node Dissection in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Mastectomy with One to Two Metastatic Sentinel Lymph Nodes: Sub-Analysis of the SINODAR-ONE Multicentre Randomized Clinical Trial and Reopening of Enrolment. Br. J. Surg. 2023, 110, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houvenaeghel, G.; Cohen, M.; Raro, P.; De Troyer, J.; Gimbergues, P.; Tunon de Lara, C.; Ceccato, V.; Vaini-Cowen, V.; Faure-Virelizier, C.; Marchal, F.; et al. Sentinel Node Involvement with or without Completion Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: Treatment and Pathologic Results of Randomized SERC Trial. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boniface, J.; Frisell, J.; Andersson, Y.; Bergkvist, L.; Ahlgren, J.; Rydén, L.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Sund, M.; Johansson, H.; Lundstedt, D.; et al. Survival and Axillary Recurrence Following Sentinel Node-Positive Breast Cancer without Completion Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: The Randomized Controlled SENOMAC Trial. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Mann, G.B.; Fallowfield, L.; Duley, L.; Reed, M.; Dodwell, D.; Coleman, R.E.; Fakis, A.; Newcombe, R.; Jenkins, V.; et al. POSNOC-POsitive Sentinel NOde: Adjuvant Therapy Alone versus Adjuvant Therapy plus Clearance or Axillary Radiotherapy: A Randomised Controlled Trial of Axillary Treatment in Women with Early-Stage Breast Cancer Who Have Metastases in One or Two Sentinel Nodes. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e054365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Son, S.H. Dosimetric Evaluation of Incidental Irradiation to the Axilla during Whole Breast Radiotherapy for Patients with Left-Sided Early Breast Cancer in the IMRT Era. Medicine 2016, 95, e4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Tuan, J.; Ma, J.; Mei, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shao, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. Dose Coverage of Axillary Level I-III Areas during Whole Breast Irradiation with Simplified Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy in Early Stage Breast Cancer Patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18183–18191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, T.; Bisht, S.S.; Gupta, D.; Goyal, S.; Jassal, K.; Abhishek, A.; Sharma, K.; Pareek, P.; Kumar, V.; Jain, S.; et al. Incidental Radiation to Axilla in Early Breast Cancer Treated with Intensity Modulated Tangents and Comparison with Conventional and 3D Conformal Tangents. Breast 2013, 22, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrouch, I.; Van Gestel, D.; Koshariuk, O.; Kirkove, C.; Desmet, A.; Philippson, C.; Reynaert, N.; De Caluwe, A. Unintended Dose to the Lower Axilla in Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer: Differences between Tangential Beam and VMAT. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 164, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Gaasch, A.; Schönecker, S.; Reitz, D.; Heinz, C.; Niyazi, M.; Duma, M.-N.; Alongi, F.; Belka, C.; et al. Dose Variability in Different Lymph Node Levels during Locoregional Breast Cancer Irradiation: The Impact of Deep-Inspiration Breath Hold. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2019, 195, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Kurz, S.; Rothe, T.; Serpa, M.; Scholber, J.; Erbes, T.; Gkika, E.; Baltas, D.; Verma, V.; Krug, D.; et al. Incidental Irradiation of the Regional Lymph Nodes during Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold Radiation Therapy in Left-Sided Breast Cancer Patients: A Dosimetric Analysis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borm, K.J.; Oechsner, M.; Düsberg, M.; Buschner, G.; Weber, W.; Combs, S.E.; Duma, M.-N. Irradiation of Regional Lymph Node Areas in Breast Cancer—Dose Evaluation According to the Z0011, AMAROS, EORTC 10981-22023 and MA-20 Field Design. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkacemi, Y.; Bigorie, V.; Pan, Q.; Bouaita, R.; Pigneur, F.; Itti, E.; Badaoui, H.; Assaf, E.; Caillet, P.; Calitchi, E.; et al. Breast Radiotherapy (RT) Using Tangential Fields (TgF): A Prospective Evaluation of the Dose Distribution in the Sentinel Lymph Node (SLN) Area as Determined Intraoperatively by Clip Placement. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 3758–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reznik, J.; Cicchetti, M.G.; Degaspe, B.; Fitzgerald, T.J. Analysis of Axillary Coverage during Tangential Radiation Therapy to the Breast. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagsi, R.; Chadha, M.; Moni, J.; Ballman, K.; Laurie, F.; Buchholz, T.A.; Giuliano, A.; Haffty, B.G. Radiation Field Design in the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.P.; Whelan, T.J.; Parulekar, W.R.; Chen, B.E.; Rademaker, A.W.; Helenowski, I.B.; Donnelly, E.D.; Strauss, J.B. Development and Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Lymphedema After Axillary Surgery and Radiation Therapy in Women with Breast Cancer From the NCIC CTG MA.20 Randomized Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, L.E.G.; Miller, C.L.; Horick, N.; Skolny, M.N.; Jammallo, L.S.; Sadek, B.T.; Shenouda, M.N.; O’Toole, J.A.; MacDonald, S.M.; Specht, M.C.; et al. The Impact of Radiation Therapy on the Risk of Lymphedema After Treatment for Breast Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 88, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Qi, W.-X.; Cai, G.; Xu, C.; Cai, R.; Qian, X.-F.; Shen, K.-W.; Cao, L.; Chen, J.-Y. The Influence of Axillary Surgery and Radiotherapeutic Strategy on the Risk of Lymphedema and Upper Extremity Dysfunction in Early Breast Cancer Patients. Breast 2023, 68, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 52) | 3D-CRT (n = 28) | VMAT (n = 24) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean (range)) | 55 (32–79) | 53 (33–77) | 57 (32–79) |
Side
| 28 (53.85) 24 (46.15) | 16 (57.14) 12 (42.86) | 12 (50.00) 12 (50.00) |
Clinical Tumor Stage
| 6 (11.54) 12 (23.08) 33 (63.46) 1 (1.92) | 3 (10.71) 5 (17.86) 20 (71.43) - | 3 (12.50) 7 (29.17) 13 (54.17) 1 (4.17) |
| Tumor Size (mm) (mean (range)) | 27.73 (0–150.00) | 30.33 (4.00–150.00) | 25.49 (0–65.00) |
Pathological Tumor Stage
| 1 (1.92) 1 (1.92) 17 (32.69) 29 (55.77) 4 (7.69) | 1 (3.57) 1 (3.57) 10 (35.71) 13 (46.43) 3 (10.71) | - - 7 (29.17) 16 (66.67) 1 (4.17) |
Pathological Nodal Stage
| 4 (7.69) 8 (15.38) 38 (73.08) 2 (3.85) | 3 (10.71) 4 (14.29) 19 (67.86) 2 (7.14) | 1 (4.17) 4 (16.67) 19 (77.19) - |
Histology type
| 37 (71.15) 11 (21.15) 2 (3.85) 2 (3.85) | 23 (82.14) 2 (7.14) 1 (3.57) 2 (7.14) | 14 (58.33) 9 (37.50) 1 (4.17) - |
SBR Grade
| 14 (26.92) 21 (40.38) 17 (32.69) | 8 (28.57) 10 (35.71) 10 (35.71) | 6 (25) 11 (45.83) 7 (29.17) |
LVI
| 20 (38.46) 29 (55.77) 3 (5.77) | 11 (39.29) 15 (53.57) 2 (7.14) | 9 (37.50) 14 (58.33) 1 (4.17) |
Endocrine receptors status
| 44 (84.62) 7 (13.46) 1 (1.92) | 25 (89.29) 2 (7.14) 1 (3.57) | 19 (79.2) 5 (20.8) - |
HER2 status
| 9 (17.31) 42 (80.77) 1 (1.92) | 5 (17.86) 22 (78.57) 1 (3.57) | 4 (16.67) 20 (83.33) - |
| cALND | 22 (42.31) | 12 (42.86) | 10 (41.67) |
| NSN+ $ | 5 (22.73) | 2 (16.67) | 3 (30) |
Extracapsular invasion
| 13 (25) 38 (73.08) 1 (1.92) | 4 (14.29) 23 (82.14) 1 (3.57) | 9 (37.5) 15 (62.5) - |
Lymph node area target
| 51 (98) 49 (94) 49 (94) 51 (98) | 27 (96) 25 (89) 25 (89) 27 (96) | 24 (100) 24 (100) 24 (100) 24 (100) |
| Total (n = 52) | 3D-CRT (n = 28) | VMAT (n = 24) | p-Value t-Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dmean | 37.2 Gy (SD = 8.5 Gy) | 34.8 Gy (SD = 8.6 Gy) | 43.6 Gy (SD = 3.1 Gy) | <0.001 |
| V95% | 54.6% (SD = 19.0%) | 49.4% (SD = 20.7%) | 60.8% (SD = 15.2%) | 0.027 |
| V40Gy | 67.0% (SD = 21.6%) | 55.5% (SD = 22.3%) | 80.4% (SD = 10.3%) | <0.001 |
| D50% | 41.5 Gy (SD = 9.9 Gy) | 37.8 Gy (SD = 12.3 Gy) | 45.8 Gy (SD = 2.1 Gy) | 0.002 |
| D95% | 18.6 Gy (SD = 13.8 Gy) | 7.3 Gy (SD = 6.7 Gy) | 31.8 Gy (SD = 5.8 Gy) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolas, C.; Petit, C.; Tallet, A.; Boher, J.-M.; Varela Cagetti, L.; Favrel, V.; Gonzague Casabianca, L.; Guenole, M.; Mailleux, H.; Darreon, J.; et al. Does Breast Surgery Type Alter Incidental Axillary Irradiation? A Dosimetric Analysis of the “Sentinel Envahi et Randomisation du Curage” SERC Trial. Cancers 2024, 16, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061198
Nicolas C, Petit C, Tallet A, Boher J-M, Varela Cagetti L, Favrel V, Gonzague Casabianca L, Guenole M, Mailleux H, Darreon J, et al. Does Breast Surgery Type Alter Incidental Axillary Irradiation? A Dosimetric Analysis of the “Sentinel Envahi et Randomisation du Curage” SERC Trial. Cancers. 2024; 16(6):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061198
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolas, Camille, Claire Petit, Agnès Tallet, Jean-Marie Boher, Leonel Varela Cagetti, Veronique Favrel, Laurence Gonzague Casabianca, Morgan Guenole, Hugues Mailleux, Julien Darreon, and et al. 2024. "Does Breast Surgery Type Alter Incidental Axillary Irradiation? A Dosimetric Analysis of the “Sentinel Envahi et Randomisation du Curage” SERC Trial" Cancers 16, no. 6: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061198
APA StyleNicolas, C., Petit, C., Tallet, A., Boher, J.-M., Varela Cagetti, L., Favrel, V., Gonzague Casabianca, L., Guenole, M., Mailleux, H., Darreon, J., Bannier, M., Cohen, M., Sabiani, L., Tallet, C., Teyssandier, C., Gonçalves, A., De Nonneville, A., Lopez Almeida, L., Coste, N., ... Houvenaeghel, G. (2024). Does Breast Surgery Type Alter Incidental Axillary Irradiation? A Dosimetric Analysis of the “Sentinel Envahi et Randomisation du Curage” SERC Trial. Cancers, 16(6), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061198








