Investigating the Efficacy of EGFR-TKIs and Anti-VEGFR Combination in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Assessment of the Risk of Bias
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
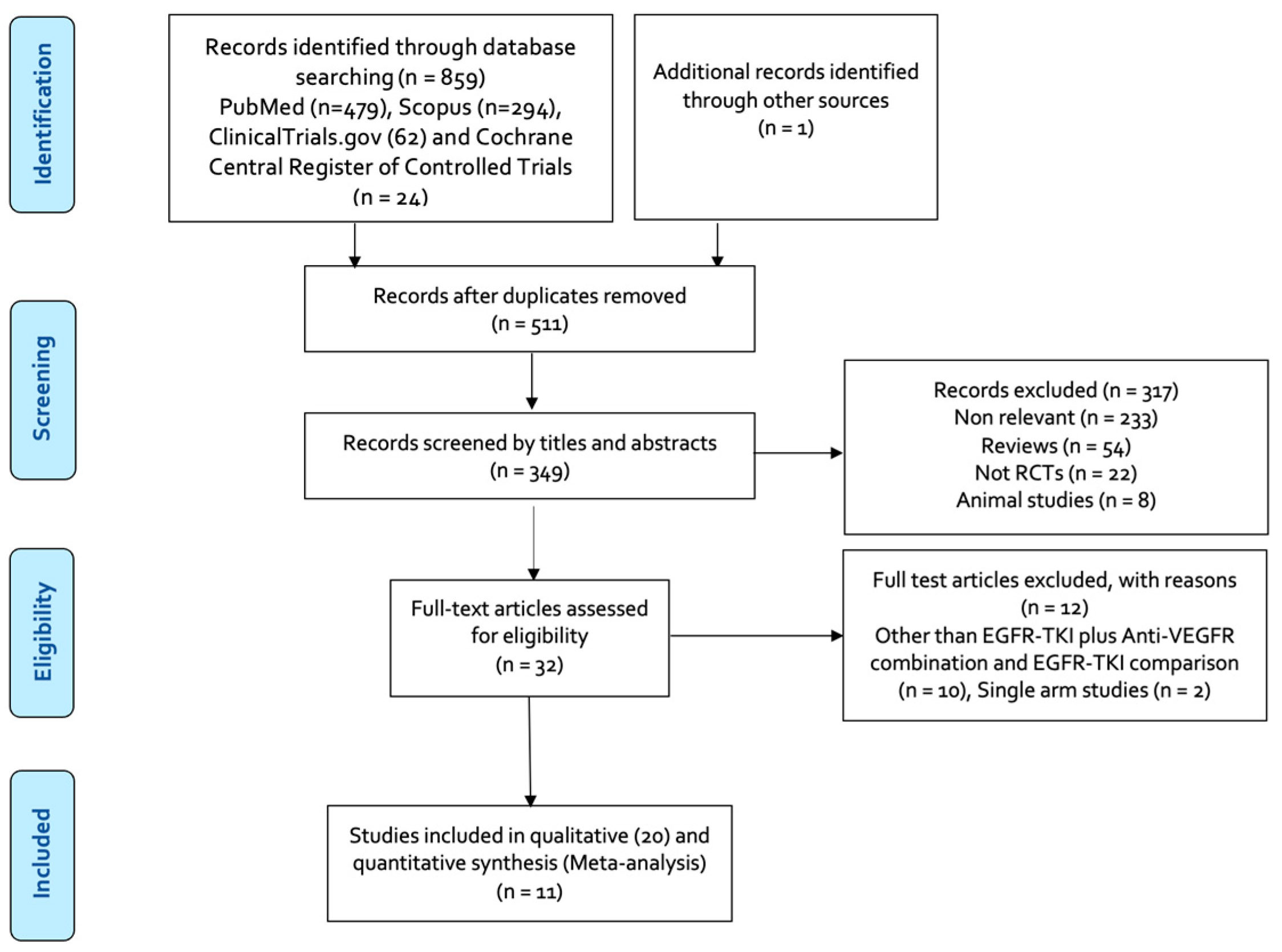
3.1. Results of the Literature Search
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
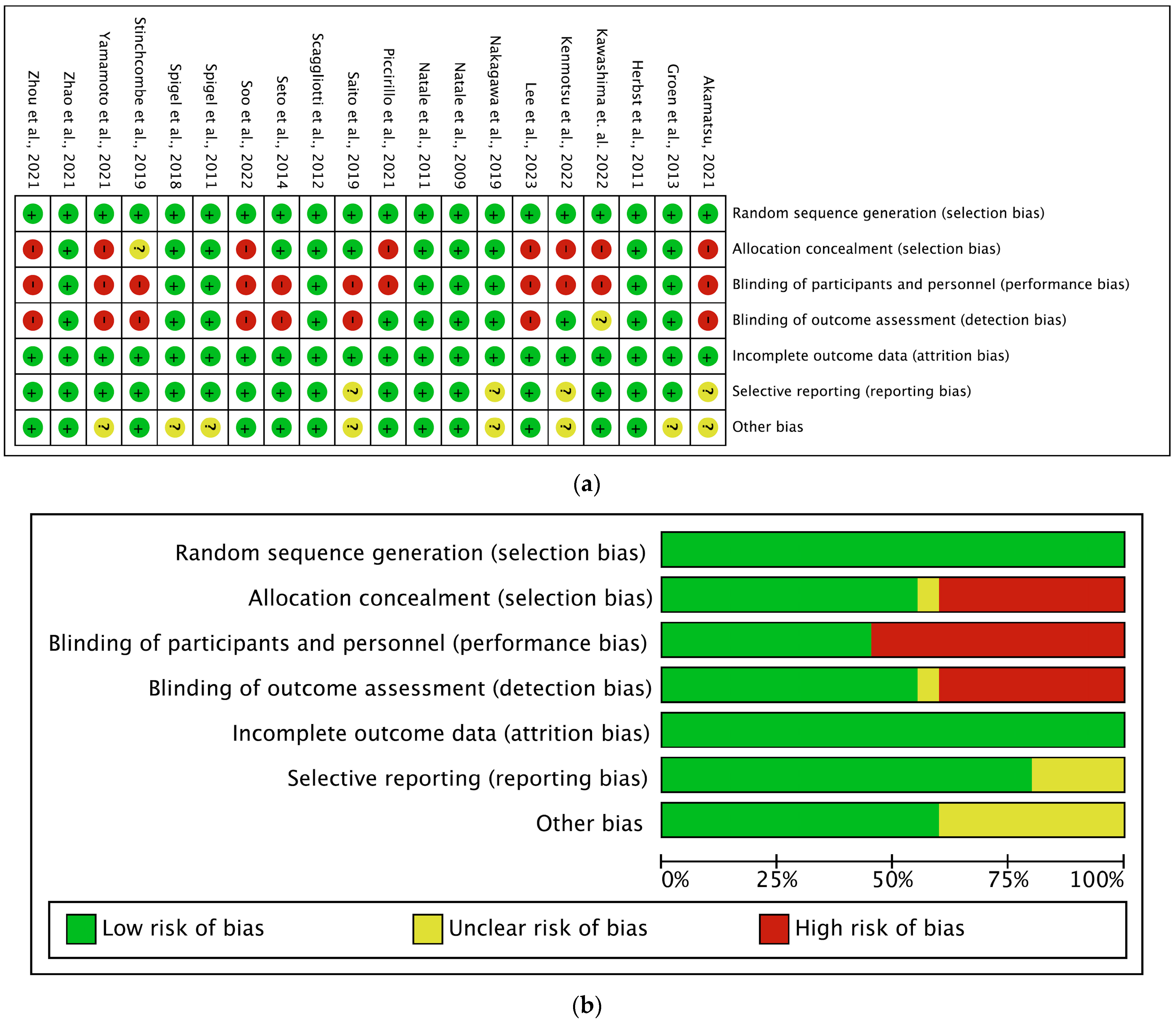
3.3. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
3.4. Meta-Analysis of Survival Outcome
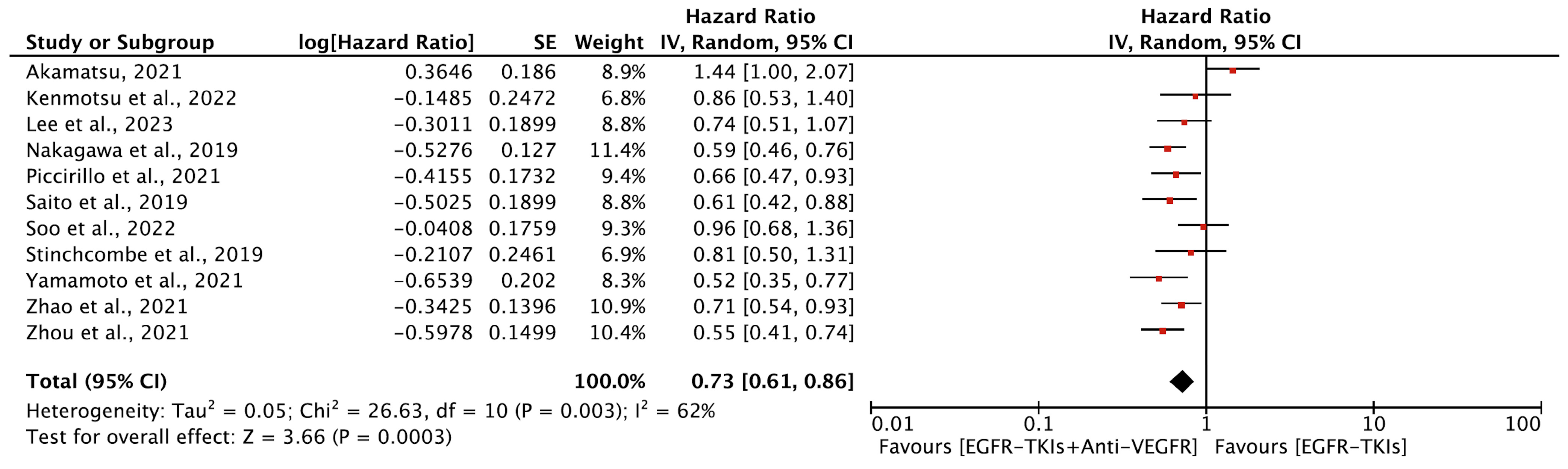
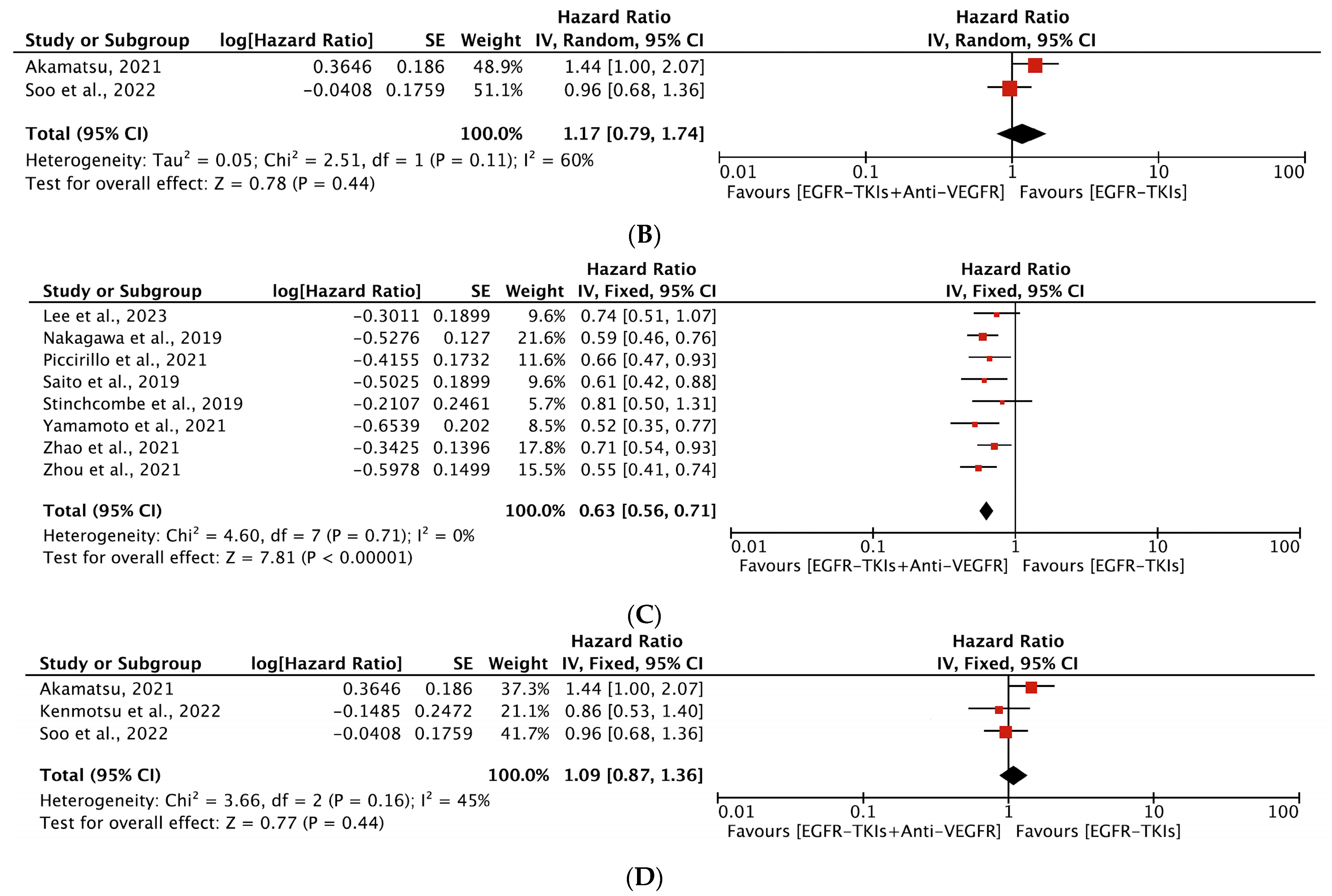
3.4.1. Progression-Free Survival
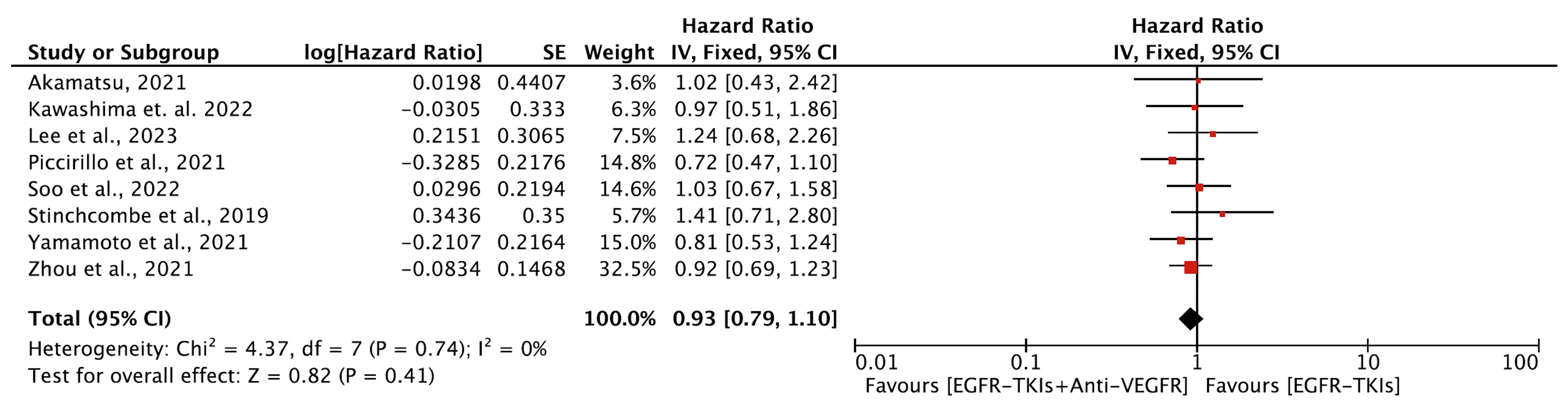
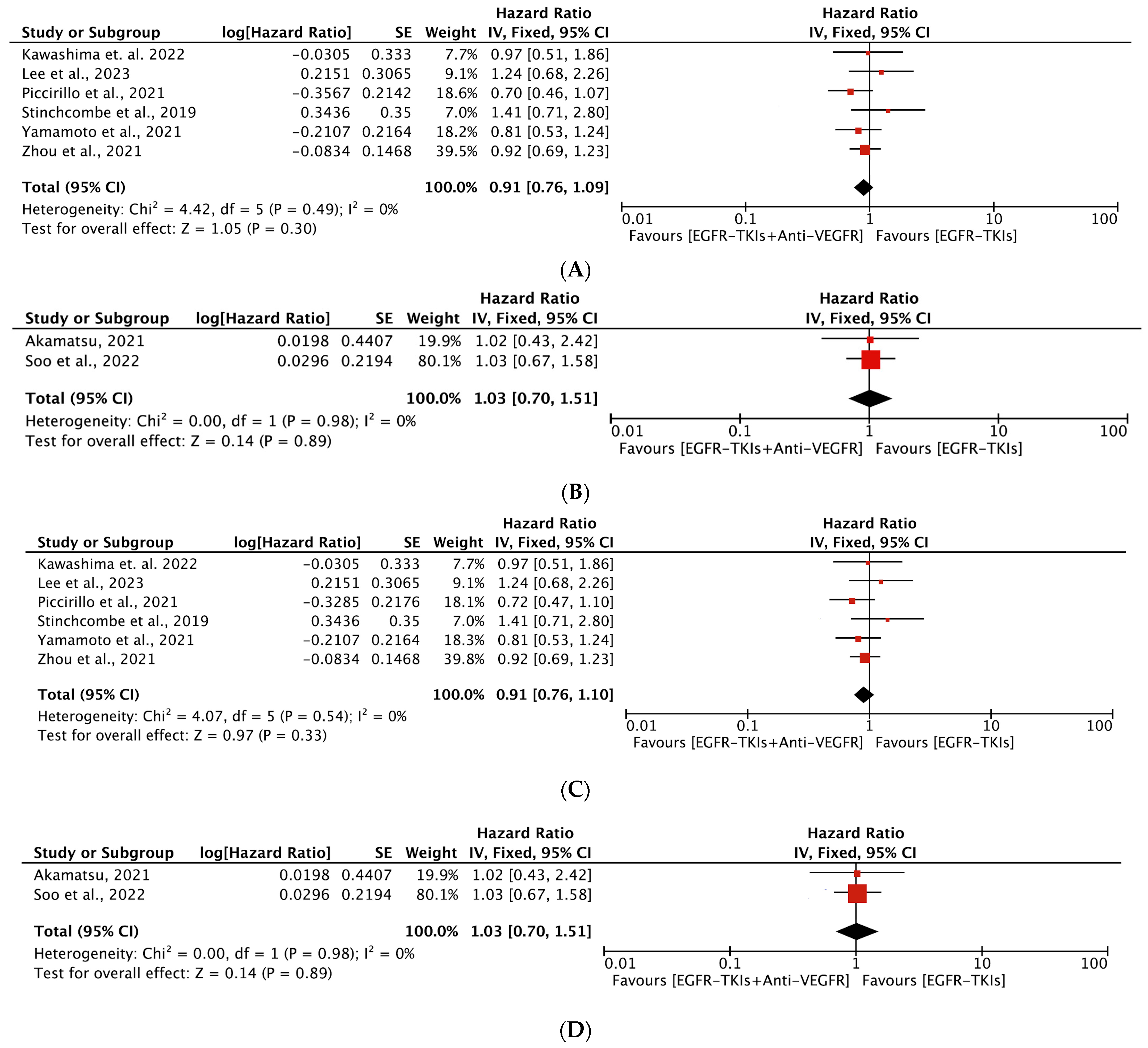
3.4.2. Overall Survival
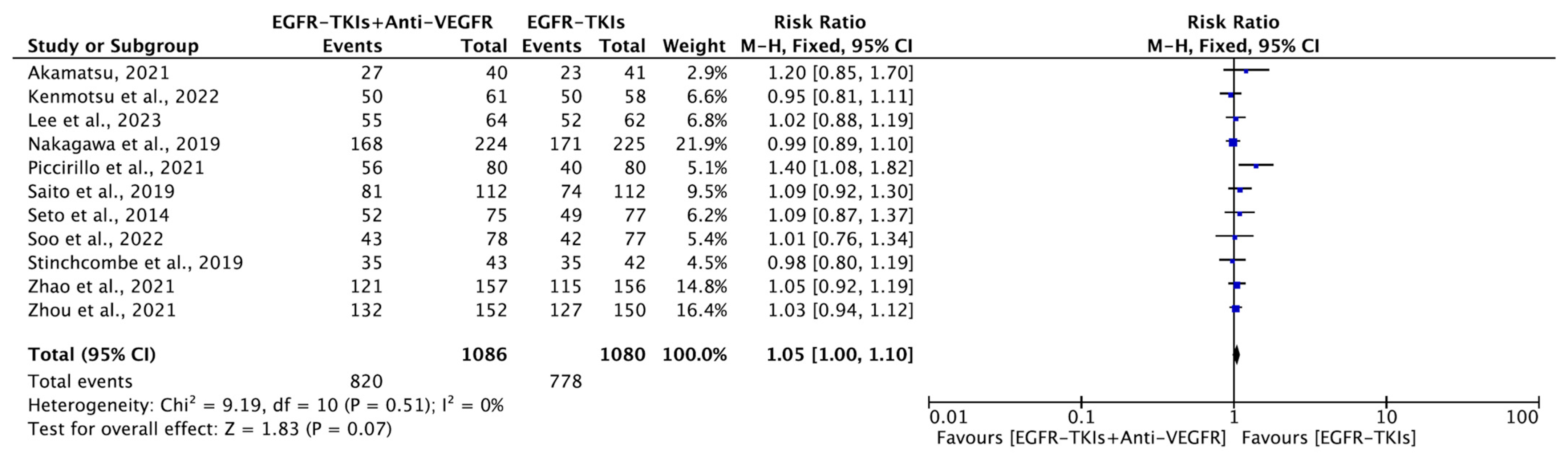
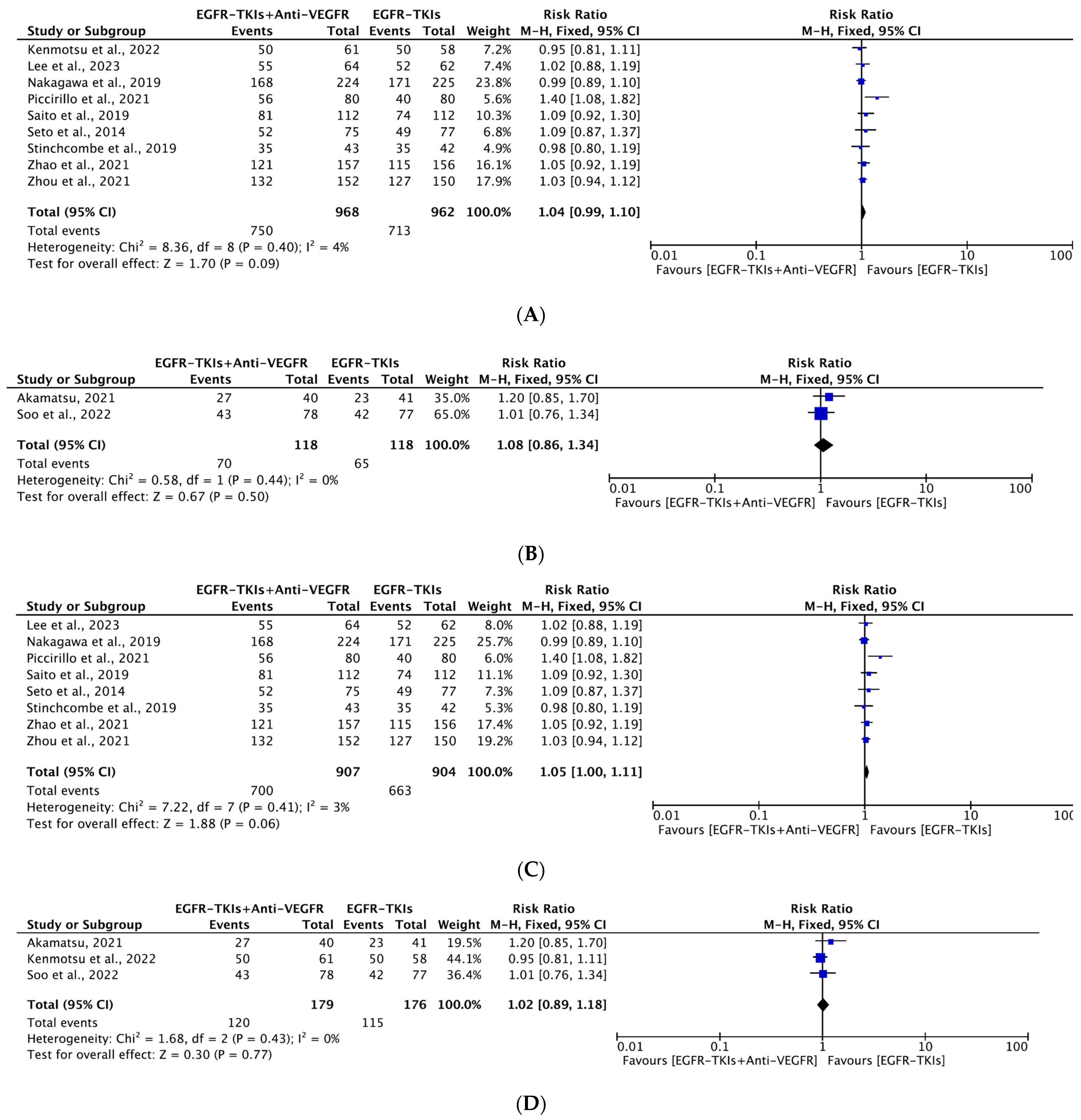
3.4.3. Objective Response Rate
3.4.4. Adverse Effects
3.5. Publication Bias
3.6. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-factsstatistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2023-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Blandin Knight, S.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, V.; Omerovic, J. Current Approaches in NSCLC Targeting K-RAS and EGFR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Lester, J.F. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Clash of the Generations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e216–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.F.; Zhu, M.L.; Liu, M.M.; Xu, Y.T.; Yuan, L.L.; Bian, J.; Xia, Y.Z.; Kong, L.Y. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: From molecular mechanisms to clinical research. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenchner, D.S.; Petrova, Z.O.; Hunihan, L.; Ashtekar, K.D.; Walther, Z.; Wilson, F.H. A destabilizing Y891D mutation in activated EGFR impairs sensitivity to kinase inhibition. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Hirsch, F.R.; Pirker, R.; Felip, E.; Valencia, C.; Smit, E.F. The role of anti-EGFR therapies in EGFR-TKI-resistant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 122, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezquita, L.; Varga, A.; Planchard, D. Safety of osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2018, 17, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, A.; Montanino, A.; Carillio, G.; Costanzo, R.; Sandomenico, C.; Normanno, N.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Daniele, G.; Perrone, F.; Rocco, G.; et al. Angiogenesis Inhibitors in NSCLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaruz, L.C.; Socinski, M.A. The role of anti-angiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer: An update. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Schmid-Bindert, G.; Zhou, C. Erlotinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An update for clinicians. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2012, 4, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Cardona, A.F.; Arrieta, O.; Aguilar, A.; Ito, M.; Pedraz, C.; Codony-Servat, J.; Santarpia, M. Coregulation of pathways in lung cancer patients with EGFR mutation: Therapeutic opportunities. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Qiao, M.; Zhou, F.; Ren, S.; Su, C.; Zhou, C. Effect of Combined Therapy Inhibiting EGFR and VEGFR Pathways in Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer on Progression-free and Overall Survival. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y. Role of Antiangiogenic Agents Combined With EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Treatment-naive Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, e70–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.P.; Heymach, J.V. ARTEMIS highlights VEGF inhibitors as effective partners for EGFR TKIs in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1178–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, M.D.F.; Moher, D.; Thombs, B.D.; McGrath, T.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; PRISMA-DTA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: The PRISMA-DTA Statement. JAMA 2018, 319, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, H.R.; Hong, M.H.; Lee, K.H.; Park, K.U.; Lee, G.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, K.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; et al. A randomized Phase 2 study to compare erlotinib with or without bevacizumab in previously untreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutation. Cancer 2023, 129, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, C.R.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Cui, J.W.; Yang, N.; Song, Y.; Li, X.L.; Lu, S.; et al. Bevacizumab plus erlotinib in Chinese patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced NSCLC (ARTEMIS-CTONG1509): A multicenter phase 3 study. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, W.; Min, X.; Gu, K.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, J.; Miao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; et al. Apatinib Plus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Advanced EGFR-Mutant NSCLC: The Phase III ACTIVE Study (CTONG1706). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, T.; Kato, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Atagi, S.; Hosomi, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Hida, T.; Maemondo, M.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): An open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Okamoto, I.; Yamanaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Takahashi, K.; Fukuoka, M. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab vs erlotinib monotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: Survival follow-up results of the randomized JO25567 study. Lung Cancer 2021, 151, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinchcombe, T.E.; Janne, P.A.; Wang, X.; Bertino, E.M.; Weiss, J.; Bazhenova, L.; Gu, L.; Lau, C.; Paweletz, C.; Jaslowski, A.; et al. Effect of Erlotinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Erlotinib Alone on Progression-Free Survival in Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.R.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Greco, F.A.; Shih, K.C.; Gian, V.G.; Lipman, A.J.; Daniel, D.B.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Finney, L.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Erlotinib plus either pazopanib or placebo in patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial with correlated serum proteomic signatures. Cancer 2018, 124, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Burris, H.A., 3rd; Greco, F.A.; Shipley, D.L.; Friedman, E.K.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Whorf, R.C.; Mitchell, R.B.; Daniel, D.B.; Zangmeister, J.; et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial of sorafenib and erlotinib or erlotinib alone in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, R.A.; Han, J.Y.; Dafni, U.; Cho, B.C.; Yeo, C.M.; Nadal, E.; Carcereny, E.; de Castro, J.; Sala, M.A.; Bernabe, R.; et al. A randomised phase II study of osimertinib and bevacizumab versus osimertinib alone as second-line targeted treatment in advanced NSCLC with confirmed EGFR and acquired T790M mutations: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 10-16) BOOSTER trial. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.V.; Krzakowski, M.; Szczesna, A.; Strausz, J.; Makhson, A.; Reck, M.; Wierzbicki, R.F.; Albert, I.; Thomas, M.; Miziara, J.E.; et al. Sunitinib plus erlotinib versus placebo plus erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, M.C.; Bonanno, L.; Garassino, M.C.; Esposito, G.; Dazzi, C.; Cavanna, L.; Burgio, M.A.; Rosetti, F.; Rizzato, S.; Morgillo, F.; et al. Addition of Bevacizumab to Erlotinib as First-Line Treatment of Patients With EGFR-Mutated Advanced Nonsquamous NSCLC: The BEVERLY Multicenter Randomized Phase 3 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, R.B.; Thongprasert, S.; Greco, F.A.; Thomas, M.; Tsai, C.M.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Ferry, D.; Mulatero, C.; Whorf, R.; Thompson, J.; et al. Phase III trial of vandetanib compared with erlotinib in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, R.B.; Bodkin, D.; Govindan, R.; Sleckman, B.G.; Rizvi, N.A.; Capo, A.; Germonpre, P.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Stockman, P.K.; Kennedy, S.J.; et al. Vandetanib versus gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a two-part, double-blind, randomized phase ii study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 2523–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Wakuda, K.; Mori, K.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, S.; Kirita, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Azuma, K.; Nishino, K.; Teraoka, S.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Study of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab Versus Osimertinib for Untreated Patients with Nonsquamous NSCLC Harboring EGFR Mutations: WJOG9717L Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, Y.; Fukuhara, T.; Saito, H.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, M.; et al. Bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in Japanese patients with advanced, metastatic, EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): Overall survival analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Ansari, R.; Bustin, F.; Flynn, P.; Hart, L.; Otterson, G.A.; Vlahovic, G.; Soh, C.H.; O’Connor, P.; Hainsworth, J. Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib alone in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after failure of standard first-line chemotherapy (BeTa): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groen, H.J.; Socinski, M.A.; Grossi, F.; Juhasz, E.; Gridelli, C.; Baas, P.; Butts, C.A.; Chmielowska, E.; Usari, T.; Selaru, P.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, phase II study of erlotinib with or without sunitinib for the second-line treatment of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2382–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, H.; Toi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, D.; Tachihara, M.; Furuya, N.; Otani, S.; Shimizu, J.; Katakami, N.; Azuma, K.; et al. Efficacy of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab vs Osimertinib in Patients with EGFR T790M-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Previously Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: West Japan Oncology Group 8715L Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author, Year | EGFR-TKI | Anti-VEGFR Agent | Phase | Study Region | Trial Name | EGFR Mutation | Line of Treatment | Prior Treatment | Patients (N) | Age (yrs.) (Median) | Female, (%) | % Asian | ITT Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akamatsu, 2021 [38] | Osimertinib | Bevacizumab | II | Asia | WJOG8715L | T790M EGFR | Second-line | EGFR-TKI | 81 | 68 | 59 | 100 | + |
| a Kawashima et. al., 2022 [35] a Saito et al., 2019 [34] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | III | Asia | NEJ026 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 224 | 67 | 64 | 100 | + |
| Kenmotsu et al., 2022 [33] | Osimertinib | Bevacizumab | II | Asia | WJOG9717L | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 122 | 67 | 61 | 100 | + |
| Nakagawa et al., 2019 [32] | Erlotinib | Ramucirumab | III | Global | RELAY | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 449 | 64 | 63 | 77 | + |
| Piccirillo et al., 2022 [29] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | III | Europe | BEVERLY | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 160 | 67 | 64 | 0 | + |
| Soo et al., 2022 [27] | Osimertinib | Bevacizumab | II | Global | BOOSTER | T790M EGFR | Second line | EGFR-TKI | 155 | 67 | 62 | 41 | + |
| Stinchcombe et al., 2019 [24] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | II | US | NCT01532089 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 88 | 63 | 70 | 3 | + |
| b Yamamoto et al., 2021 [23] b Seto et al. 2014 [22] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | II | Asia | JO25567 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 152 | 67 | 63 | 100 | |
| Zhao et al., 2021 [21] | Gefitinib | Apatinib | III | Asia | ACTIVE CTONG 1706 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First line | None | 313 | 59 | 59 | 100 | + |
| Zhou et al., 2021 [20] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | III | Asia | ARTEMIS CTOG1509 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 311 | 58 | 62 | 100 | + |
| Lee et al., 2023 [19] | Erlotinib | Bevacizumab | II | Asia | NCT03126799 | L858R or del19 EGFR | First-line | None | 127 | 63 | 66 | 100 | + |
| Author, Year | ORR—Comb | Patient— Comb (N) | ORR—Mono | Patients— Mono (N) | ORR—p-Value | Comb—PFS (Months) | Mono—PFS (Months) | PFS—HR, (95% CI) | Comb—OS (Months) | Mono—OS (Months) | OS—HR, (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akamatsu, 2021 [38] | 27 | 40 | 23 | 41 | 0.2 | 9.4 | 13.5 | 1.44 [1.00–2.08] | 8.2 | 7.6 | 1.02 [0.43, 2.44] |
| a Kawashima et. al., 2022 [35] | 50.7 | 46.2 | 0.970 [0.505–1.866] | ||||||||
| a Saito et al., 2019 [34] | 81 | 112 | 74 | 112 | 0.31 | 16.9 | 13.3 | 0.61 [0.42–0.88] | |||
| Kenmotsu et al., 2022 [33] | 50 | 61 | 50 | 58 | 0.786 | 22.1 | 20.2 | 0.862 [0.531–1.397] | |||
| Nakagawa et al., 2019 [32] | 168 | 224 | 171 | 225 | 19.4 | 12.4 | 0.59 [0.46–0.76] | ||||
| Piccirillo et al., 2022 [29] | 56 | 80 | 40 | 80 | 0.01 | 15.4 | 9.6 | 0.66 [0.47–0.92] | 33.3 | 22.8 | 0.72 [0.47–1.10] |
| Soo et al., 2022 [27] | 43 | 78 | 42 | 77 | 0.93 | 15.4 | 12.3 | 0.96 [0.68–1.37] | 24 | 24.3 | 1.03 (0.67–1.56) |
| Stinchcombe et al., 2019 [24] | 35 | 43 | 35 | 42 | 0.81 | 17.9 | 13.5 | 0.81 [0.50–1.31] | 32.4 | 50.6 | 1.41 [0.71–2.81] |
| b Yamamoto et al., 2021 [23] | 16.4 | 9.8 | 0.52 (0.35–0.76) | 47 | 47.4 | 0.81 [0.53–1.23] | |||||
| b Seto et al., 2014 [22] | 52 | 75 | 49 | 77 | 0.49 | ||||||
| Zhao et al., 2021 [21] | 121 | 157 | 115 | 156 | 0.56 | 13.7 | 10.2 | 0.71 [0.54–0.95] | |||
| Zhou et al., 2021 [20] | 132 | 152 | 127 | 150 | 0.56 | 17.9 | 11.2 | 0.55 [0.41–0.73] | 36.2 | 31.6 | 0.92 [0.69, 1.23] |
| Lee et al., 2023 [19] | 55 | 64 | 52 | 62 | 0.48 | 17.5 | 12.4 | 0.74 [0.51, 1.08] | 1.24 [0.68, 2.26] |
| Adverse Drug Events | EGFR-TKIs + Anti-VEGFR Event/Total | EGFR-TKIs Event/Total | RR (95% CI) | p-Value | Heterogeneity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 | p-Value | |||||
| Grade 3 AEs | 537/1086 (49.4%) | 154/1088 (14.2%) | 3.27 (2.25, 4.75) | <0.00001 | 82% | <0.00001 |
| Skin rash | 154/1.010 (15.2%) | 132/1011 (13.1%) | 1.17 (0.99, 1.37) | 0.06 | 39% | 0.10 |
| Hypertension | 282/1.086 (25.9%) | 47/1088 (4.3%) | 5.11 (2.93, 8.89) | <0.00001 | 62% | 0.003 |
| Diarrhea | 57/1086 (5.2%) | 25/1088 (2.3%) | 2.25 (1.43, 3.54) | 0.0005 | 25% | 0.20 |
| Proteinuria | 88/1086 (8.1%) | 4/1088 (0.4%) | 12.22 (5.83, 25.60) | <0.00001 | 0% | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakharkar, P.; Kurup, S.; Deb, S.; Assaad, K.; Gesinski, D.; Gayle, E.J. Investigating the Efficacy of EGFR-TKIs and Anti-VEGFR Combination in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061188
Sakharkar P, Kurup S, Deb S, Assaad K, Gesinski D, Gayle EJ. Investigating the Efficacy of EGFR-TKIs and Anti-VEGFR Combination in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(6):1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061188
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakharkar, Prashant, Sonali Kurup, Subrata Deb, Kaitlin Assaad, Dayna Gesinski, and Erysa J. Gayle. 2024. "Investigating the Efficacy of EGFR-TKIs and Anti-VEGFR Combination in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 6: 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061188
APA StyleSakharkar, P., Kurup, S., Deb, S., Assaad, K., Gesinski, D., & Gayle, E. J. (2024). Investigating the Efficacy of EGFR-TKIs and Anti-VEGFR Combination in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(6), 1188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16061188







