Anticancer Effects of BRD4 Inhibitor in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antibodies (Abs), Media and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
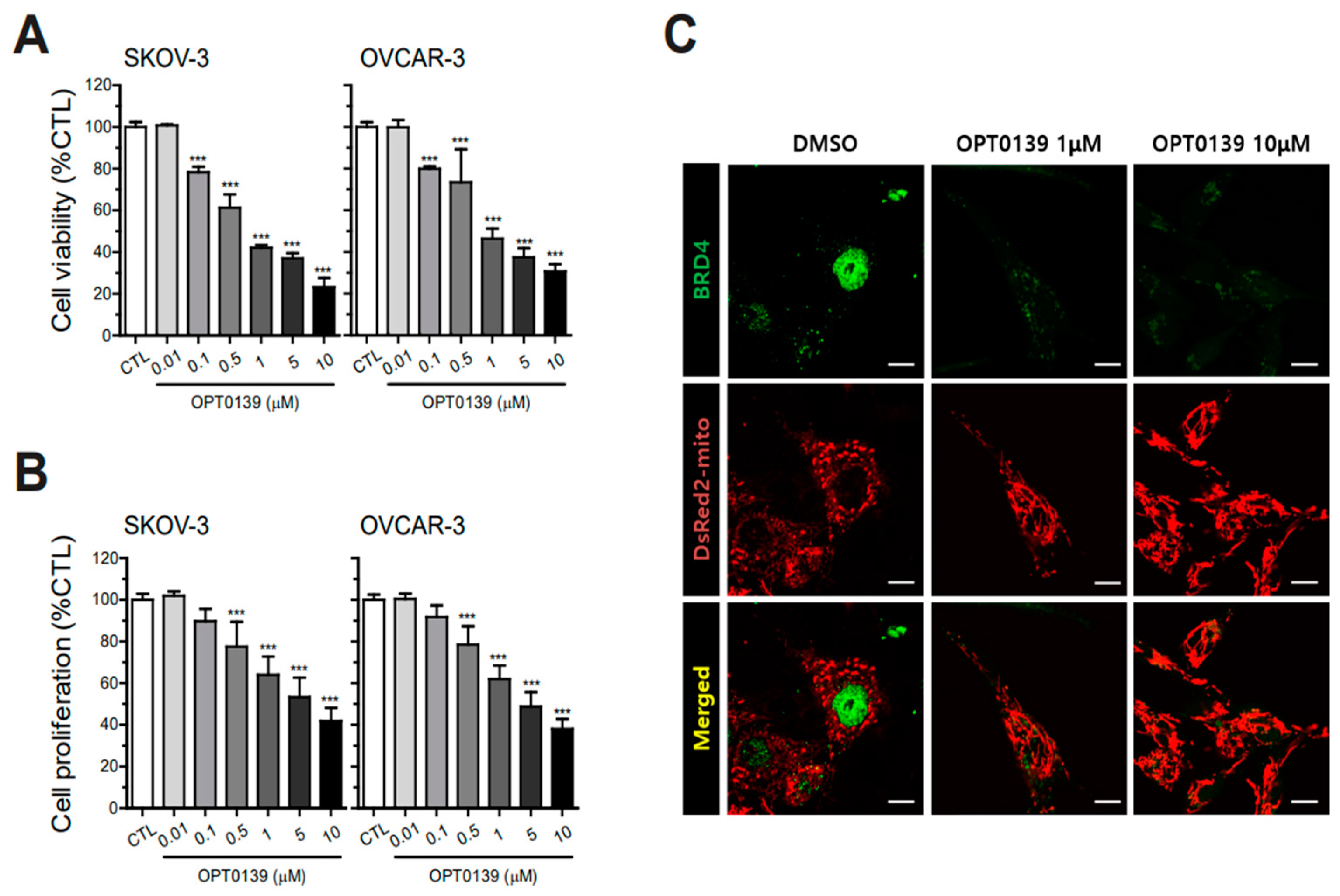
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
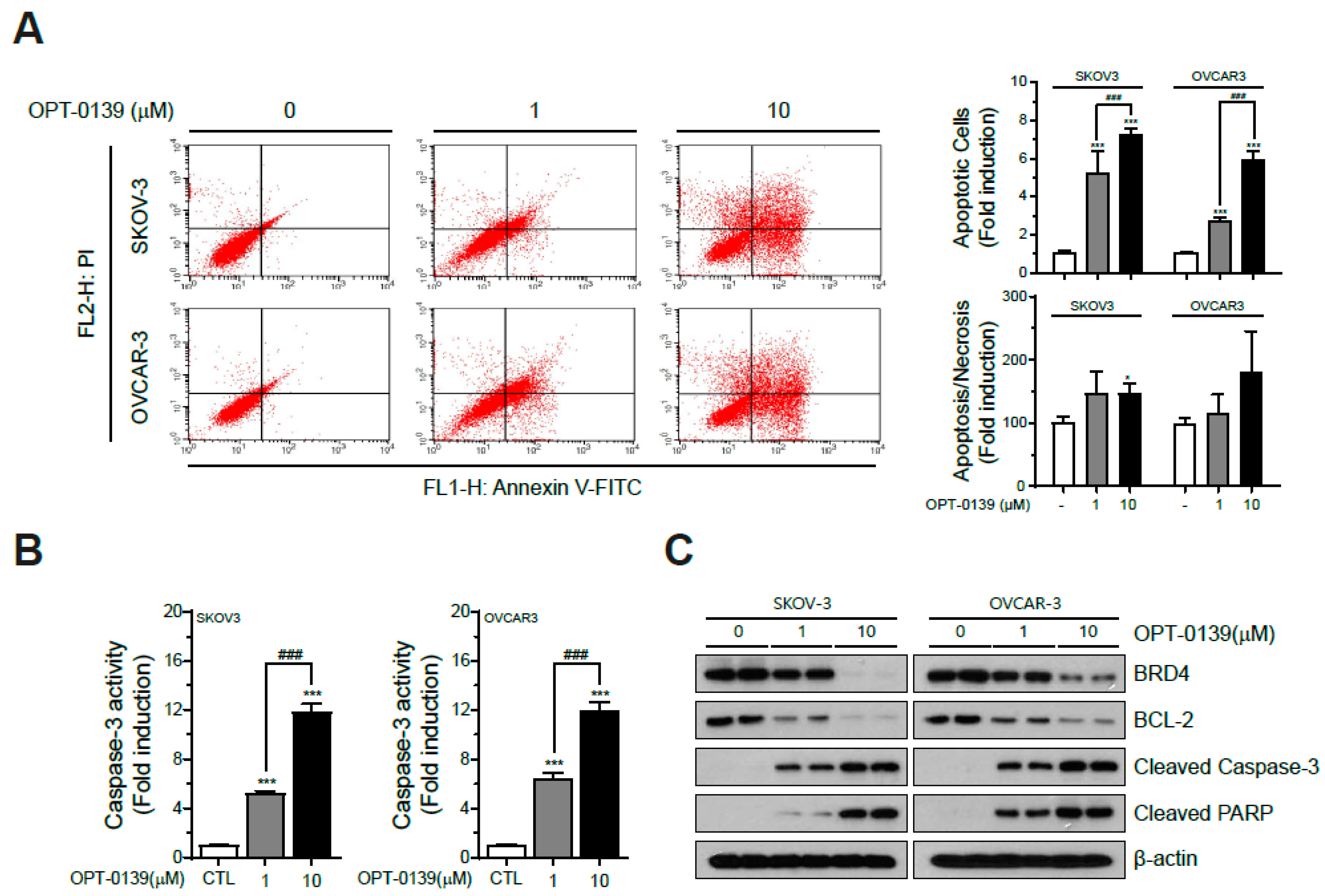
2.6. Caspase-3 Activity
2.7. Annexin V FITC and Propidium Iodide (PI) Apoptosis Detection Assay
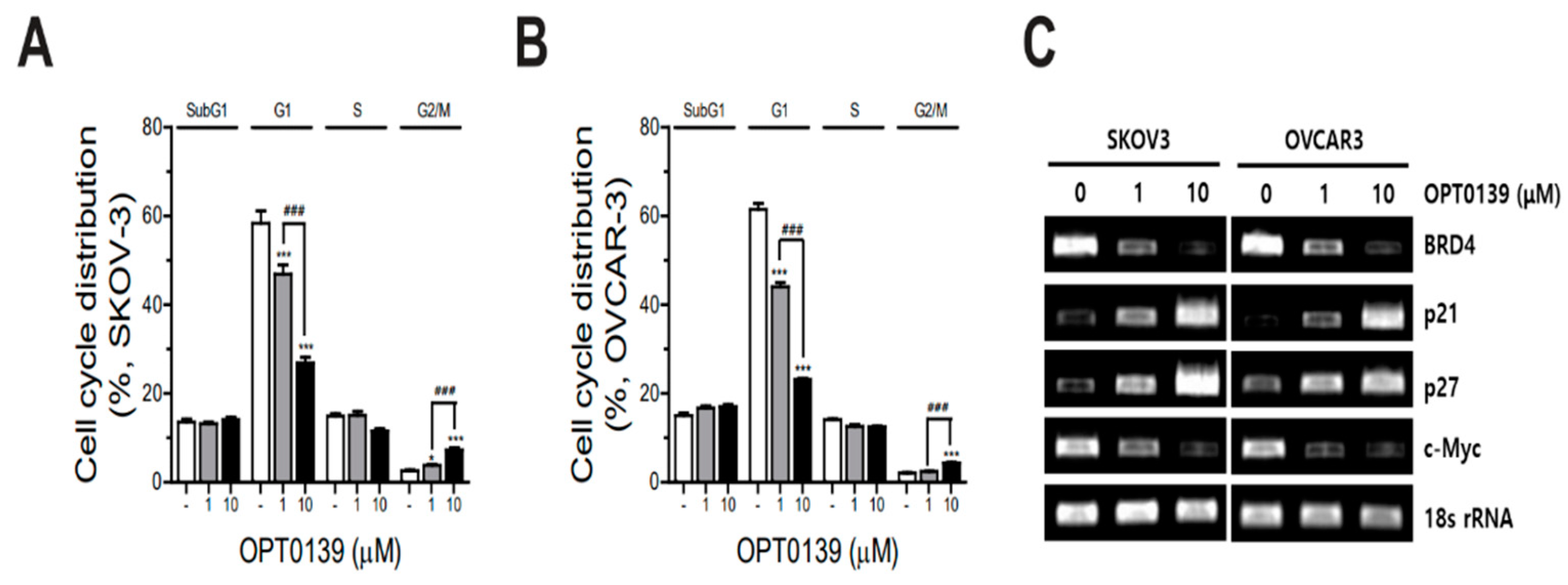
2.8. Cell Cycle Arrest
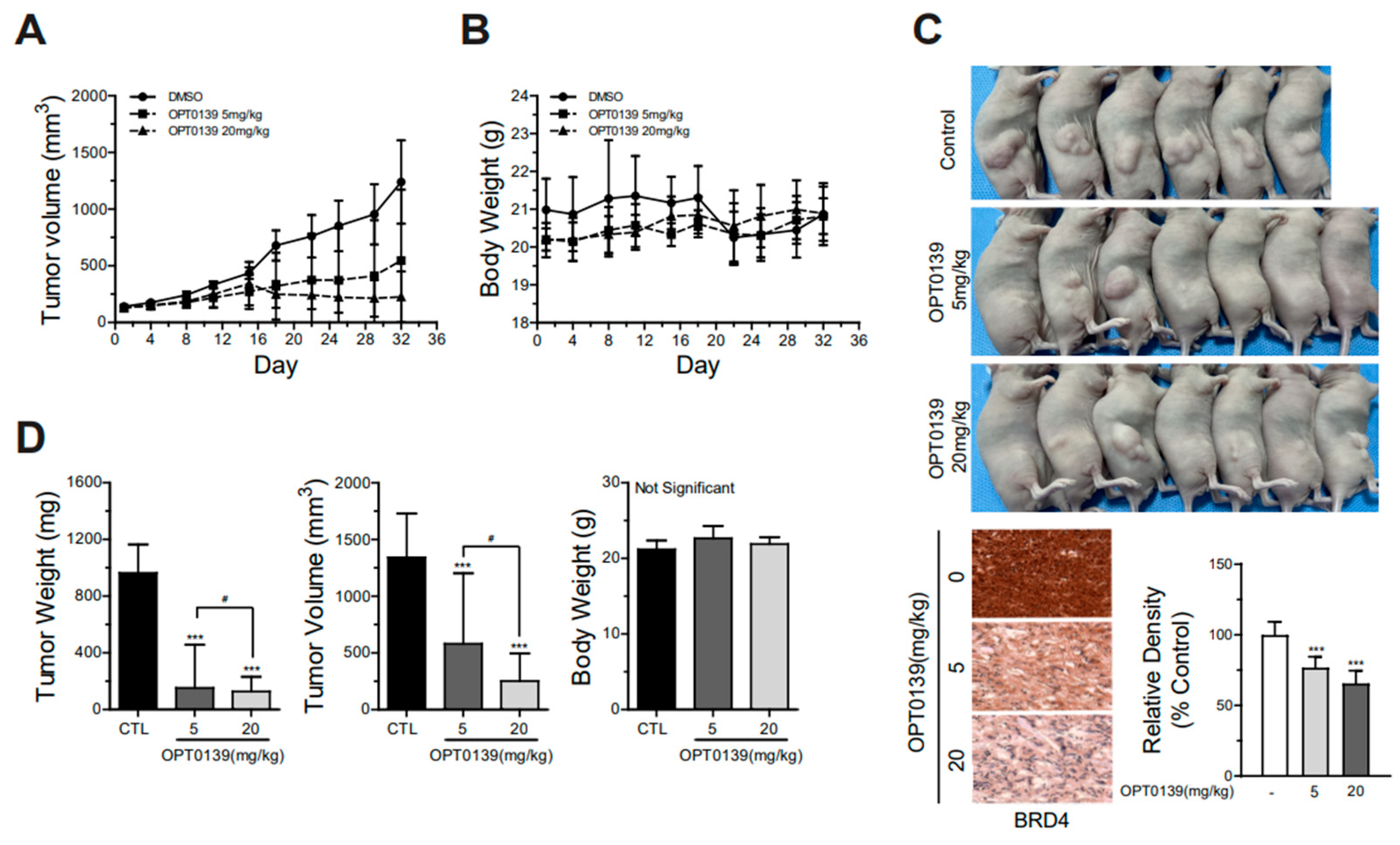
2.9. Cell-Derived Mouse Tumor Xenografts Model
- Group 1: tumor control (implanted SKOV3 cells);
- Group 2: tumor cell implantation and intravenous low-dose OPT-0139 (5 mg/kg);
- Group 3: tumor cell implantation and intravenous high-dose OPT-0139 (20 mg/kg).
- Group 1: tumor control (implanted SKOV3 cells)
- Group 2: tumor cell implantation and intravenous cisplatin (2 mg/kg);
- Group 3: tumor cell implantation and intravenous OPT-0139 (5 mg/kg);
- Group 4: tumor cell implantation and intravenous OPT-0139 and cisplatin (OPT-0139 5 mg/kg, cisplatin 2 mg/kg).
2.10. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.12. Immunoblot Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. BRD4 Overexpression and IC50 Value of OPT-0139 in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells
3.2. OPT-0139′s Inhibitory Effect on Cell Survival and Proliferation
3.3. OPT-0139′s Induction of Apoptotic Cell Death
3.4. OPT-0139′s Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest
3.5. OPT-0139′s Inhibition of Tumorigenesis in a Mouse Xenograft Model
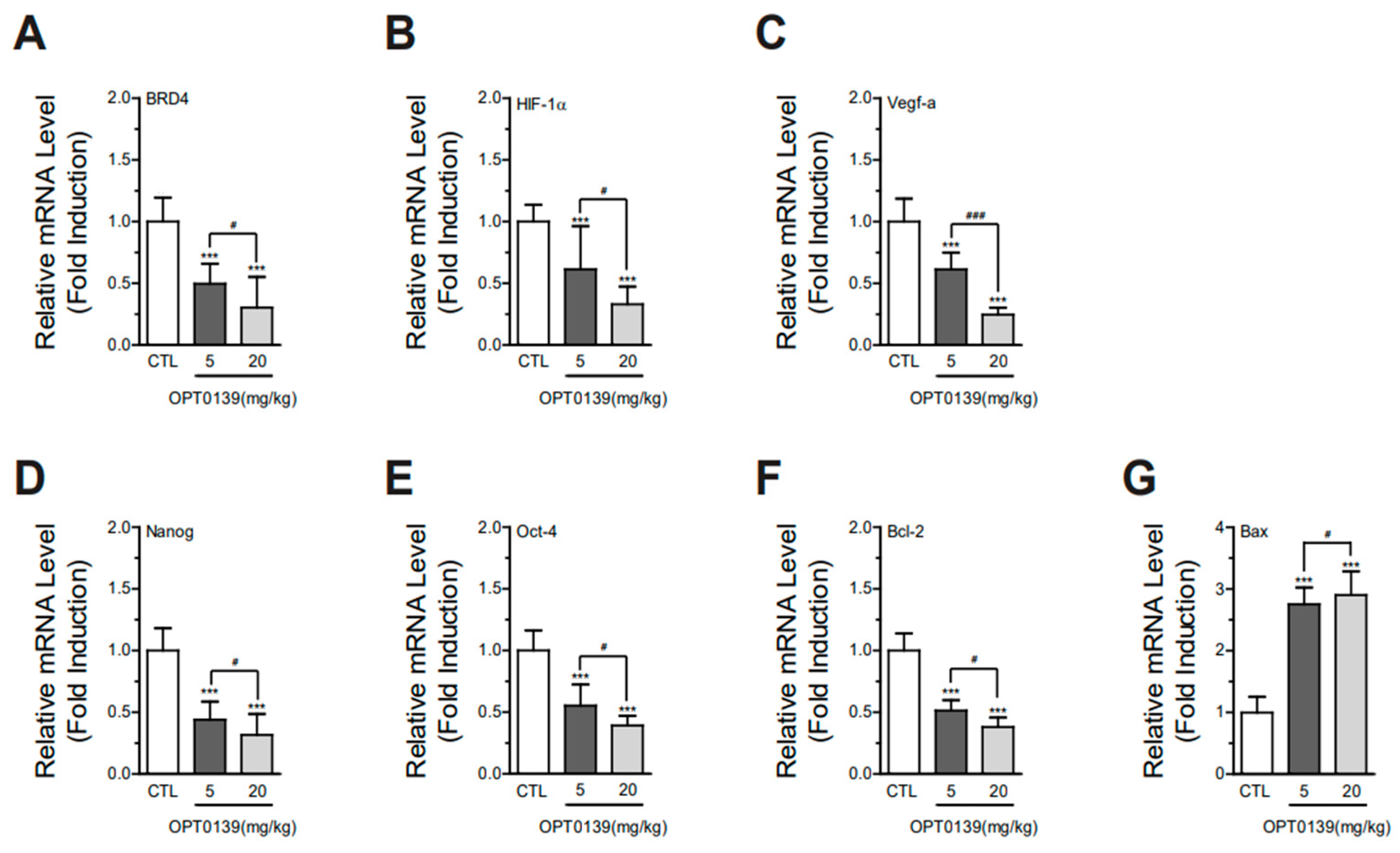
3.6. OPT-0139 Alters Hypoxia Signaling, Angiogenesis, Cancer Stemness, and Apoptosis Gene Expression Levels in Tumors
3.7. Combining OPT-0139 with Cisplatin in Ovarian Cancer Cells
3.8. Combining OPT-0139 with Cisplatin in a Mouse Xenograft Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics, K.N. Cancer Statistics 2023 (1999–2021); National Cancer Center: Goyang, Republic of Korea, 2023.
- Garzon, S.; Lagana, A.S.; Casarin, J.; Raffaelli, R.; Cromi, A.; Franchi, M.; Barra, F.; Alkatout, I.; Ferrero, S.; Ghezzi, F. Secondary and tertiary ovarian cancer recurrence: What is the best management? Gland. Surg. 2020, 9, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignata, S.; Cecere, S.C.; Du Bois, A.; Harter, P.; Heitz, F. Treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, viii51–viii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.; Wilson, A.J.; Hirst, J.; Roby, K.F.; Fadare, O.; Crispens, M.A.; Beeghly-Fadiel, A.; Khabele, D. CCNE1 and BRD4 co-amplification in high-grade serous ovarian cancer is associated with poor clinical outcomes. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 157, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Pothuri, B. Appropriate Selection of PARP Inhibitors in Ovarian Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2022, 23, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, A.J.; Tudrej, P.; Kujawa, K.A.; Lisowska, K.M. Advances in ovarian cancer therapy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, B.; Edwards, R.P. Diagnosis and Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 32, 943–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Guan, Y.; Qin, W.; Zhai, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, H. Targeting Brd4 for cancer therapy: Inhibitors and degraders. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, B.; Lorenzini, E.; Ciarrocchi, A. BRD4 and Cancer: Going beyond transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, S.S.; Kouchaki, S.; Salimian, Z.; Sotoudeh, M.; Mousavi, A.S.; Alimoghaddam, K.; Ghaffari, H.S. Overexpression of Bromodomain and Extraterminal Domain is Associated with Progression, Metastasis and Unfavorable Outcomes: Highlighting Prognostic and Therapeutic Value of the BET Protein Family in Gastric Cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Tian, L.; Su, Q.; An, P.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Du, J.; Shan, H.; et al. Inhibition of BRD4 suppresses the malignancy of breast cancer cells via regulation of Snail. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Weng, X.; Guo, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Inhibition of BRD4 suppresses tumor growth in prostate cancer via the enhancement of FOXO1 expression. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2503–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ye, F.; Xiong, H.; Peng, L.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, F.; Cui, M.; Wei, C.; Wang, X.; et al. BRD4 inhibitor inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1928–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dulak, A.M.; Hattersley, M.M.; Willis, B.S.; Nikkila, J.; Wang, A.; Lau, A.; Reimer, C.; Zinda, M.; Fawell, S.E.; et al. BRD4 facilitates replication stress-induced DNA damage response. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3763–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ucar, D.; Lin, D.I. Amplification of the bromodomain-containing protein 4 gene in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma is associated with worse prognosis and survival. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumond-Bock, A.L.; Bieniasz, M. The role of distinct BRD4 isoforms and their contribution to high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma pathogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; You, L.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Fan, J. Synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and BRD4 inhibitor in multiple models of ovarian cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, M.E.; Faraahi, Z.; McCormick, A.; Edmondson, R.J. DNA damage repair in ovarian cancer: Unlocking the heterogeneity. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.E. Carrot and stick: HIF-alpha engages c-Myc in hypoxic adaptation. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Guo, Y.; Hu, R.; Cai, W.L.; Li, Y.; Pei, S.; Sun, H.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; et al. Potent BRD4 inhibitor suppresses cancer cell-macrophage interaction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Z. Safety and Efficacy of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Inhibitors for the Treatment of Hematological Malignancies and Solid Tumors: A Systematic Study of Clinical Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 621093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asangani, I.A.; Dommeti, V.L.; Wang, X.; Malik, R.; Cieslik, M.; Yang, R.; Escara-Wilke, J.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Dhanireddy, S.; Engelke, C.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of BET bromodomain proteins in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 2014, 510, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordan, J.D.; Thompson, C.B.; Simon, M.C. HIF and c-Myc: Sibling rivals for control of cancer cell metabolism and proliferation. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-González, J.M.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E. c-MYC and Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 601512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, E.; Rappaport, A.R.; Herrmann, H.; Sison, E.A.; Magoon, D.; Qi, J.; Blatt, K.; Wunderlich, M.; et al. RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2011, 478, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, J.F.; Ho, F.; Robertson, E.S.; You, J. Bromodomain-Containing Protein BRD4 Is Hyperphosphorylated in Mitosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarraj, J.; Hunter, K.W. Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4: A Dynamic Regulator of Breast Cancer Metastasis through Modulation of the Extracellular Matrix. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 2012, 670632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretones, G.; Delgado, M.D.; León, J. Myc and cell cycle control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W.; Adami, G.R.; Wei, N.; Keyomarsi, K.; Elledge, S.J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993, 75, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, K.; Kato, J.Y.; Solomon, M.J.; Sherr, C.J.; Massague, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Koff, A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes. Dev. 1994, 8, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmider-Ross, A.; Pirsig, O.; Gottschalk, E.; Denkert, C.; Lichtenegger, W.; Reles, A. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors CIP1 (p21) and KIP1 (p27) in ovarian cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 132, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, B.; Cui, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Lu, F.; Qin, T.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Guo, E.; et al. BRD4 inhibition impairs DNA mismatch repair, induces mismatch repair mutation signatures and creates therapeutic vulnerability to immune checkpoint blockade in MMR-proficient tumors. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2023, 11, e006070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhyasen, G.W.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dulak, A.; Castriotta, L.; Jacques, K.; Zhao, W.; Gharahdaghi, F.; Hattersley, M.M.; Lyne, P.D.; et al. BRD4 amplification facilitates an oncogenic gene expression program in high-grade serous ovarian cancer and confers sensitivity to BET inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetry, M.; Bhandari, A.; Lin, Y. Prognostic role of overexpressed Bromodomain and extra-terminal family in ovarian cancer. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Choucair, K.; Ashraf, M.; Hammouda, D.M.; Alloghbi, A.; Khan, T.; Senzer, N.; Nemunaitis, J. Bromodomain and extra-terminal motif inhibitors: A review of preclinical and clinical advances in cancer therapy. Future Sci. OA 2019, 5, Fso372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaufort, C.M.; Helmijr, J.C.; Piskorz, A.M.; Hoogstraat, M.; Ruigrok-Ritstier, K.; Besselink, N.; Murtaza, M.; van IJcken, W.F.; Heine, A.A.; Smid, M.; et al. Ovarian cancer cell line panel (OCCP): Clinical importance of in vitro morphological subtypes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Feng, G.; Yuan, L. GANT61 elevates chemosensitivity to cisplatin through regulating the Hedgehog, AMPK and cAMP pathways in ovarian cancer. Future Med. Chem. 2022, 14, 479–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.J.; Lalani, A.S.; Wass, E.; Saskowski, J.; Khabele, D. Romidepsin (FK228) combined with cisplatin stimulates DNA damage-induced cell death in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 127, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakashev, S.; Zhang, R.G. Mouse models of epithelial ovarian cancer for preclinical studies. Zool. Res. 2021, 42, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Park, W.-H.; Suh, D.-H.; Kim, K.; No, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-B. Anticancer Effects of BRD4 Inhibitor in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050959
Kim Y, Park W-H, Suh D-H, Kim K, No J-H, Kim Y-B. Anticancer Effects of BRD4 Inhibitor in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050959
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeorae, Wook-Ha Park, Dong-Hoon Suh, Kidong Kim, Jae-Hong No, and Yong-Beom Kim. 2024. "Anticancer Effects of BRD4 Inhibitor in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 5: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050959
APA StyleKim, Y., Park, W.-H., Suh, D.-H., Kim, K., No, J.-H., & Kim, Y.-B. (2024). Anticancer Effects of BRD4 Inhibitor in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancers, 16(5), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050959





