Melatonin and Its Role in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction: Melatonin, an Antineoplastic Molecule
2. Stages of Carcinogenesis
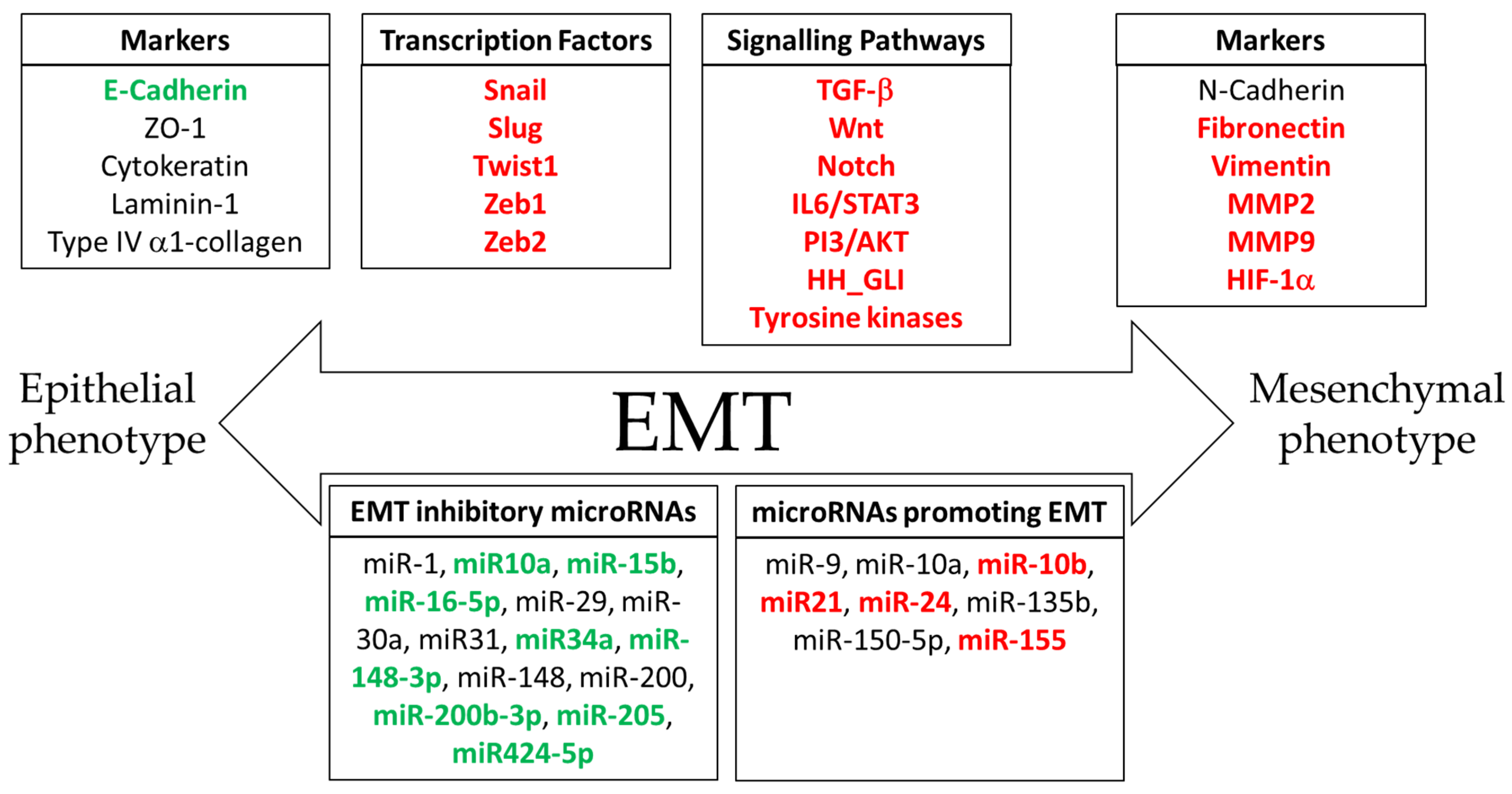
3. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Progression
5. Signaling Pathways Involved in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
6. Melatonin as an Inhibitor of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Tan, D.-X.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Qin, L.; Yang, S.-F.; Xu, K. Melatonin, a full service anti-cancer agent: Inhibition of initiation, progression and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Martínez-Campa, C. Melatonin: An Anti-Tumor Agent in Hormone-Dependent Cancers. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 3271948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Campa, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Alonso-González, C.; González, A.; Álvarez-García, V.; Cos, S. What is known about melatonin, chemotherapy and altered gene expression in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 13, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.M.; Belancio, V.P.; Dauchy, R.T.; Xiang, S.; Brimer, S.; Mao, L.; Hauch, A.; Lundberg, W.; Summers, W.; Yuan, L.; et al. Melatonin: An inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R183–R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, P.I.R.; do Carmo Neto, J.R.; Milhomem, A.C.; Machado, J.R.; Miguel, M.P. Antitumor effect of melatonin on breast cancer in experimental models: A systematic review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; González-González, A.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Cos, S.; Martínez-Campa, C. Melatonin as an Adjuvant to Antiangiogenic Cancer Treatments. Cancers 2021, 13, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulekha Suresh, D.; Guruvayoorappan, C. Molecular principles of tissue invasion and metastasis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 324, C971–C991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Miller, K.D. Exploiting the hallmarks of cancer: The future conquest of breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjiri, A. Tracing the path of cancer initiation: The AA protein-based model for cancer genesis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, J.; Xu, H. Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes: Comparative genomics and network perspectives. BMC Genom. 2015, 16 (Suppl. S7), S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland-Frei, J.; Weston, A.; Harris, C.C. Multistage Carcinogenesis. In Cancer Medicine, 6th ed.; Kufe, D.W., Pollock, R.E., Weichselbaum, R.R., Bast, R.C., Gansler, T.S., Holland, J.F., Frei, E., Eds.; BC Decker: Hamilton, ON, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malarkey, D.E.; Hoenerhoff, M.; Maronpot, R.R. Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Manifestations. In Haschek and Rousseaux’s Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 107–146. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, C. Cancer initiation, promotion, and progression and the acquisition of key behavioral traits. In Cancer: The Enemy from Within; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 25–48. ISBN 978-3-030-40650-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Morgan, D.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 6th ed.; Lewis, S.G., Zayatz, E., Eds.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V.E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genome landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, N.M.; Zolotaryova, S.Y.; Gautreau, A.M.; Denisov, E.V. Mutational drivers of cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacheck, W.J.; Zervantonakis, I.K.; Kamm, R.D. Tumor cell migration in complex microenvironments. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 1335–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.; Geetika, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Combined Interaction of Cellular and Extracellular Components Causes Genetic Cascade Activation in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Oncology 2022, 100, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, H.G.; Koh, G.Y.; Thurston, G.; Alitalo, K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jögi, A.; Vaapil, M.; Johansson, M.; Påhlman, S. Cancer cell differentiation heterogeneity and aggressive behavior in solid tumors. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 117, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.W.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Emerging Biological Principles of Metastasis. Cell 2017, 168, 670–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, M.; Sgarra, R.; Battista, S.; Cerchia, L.; Manfioletti, G. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition at the Crossroads between Metabolism and Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaya, Y.; Sheng, G. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition during gastrulation: An embryological view. Dev. Growth Differ. 2008, 50, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, R.C.; Pastar, I.; Ojeh, N.; Chen, V.; Liu, S.; Garzon, K.I.; Tomic-Canic, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, G.D.; Fonticoli, L.; Rajan, T.S.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Trubiani, O.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): The Type-2 EMT in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration and Organ Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Kang, Y. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, E.D. An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 1995, 154, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Di, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhan, Q.; He, X.; Liu, S.; Zou, H.; Corpe, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. LncRNAs as epigenetic regulators of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, H.; Olmeda, D.; Cano, A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Craene, B.; Berx, G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, L.M.; da Silva, V.A.; Freire-de-Lima, L.; Previato, J.O.; Mendonça-Previato, L.; Capella, M.A. Glycosylation in Cancer: Interplay between Multidrug Resistance and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition? Front. Oncol. 2016, 126, 3219–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.E.; Nathan, V.; Osborne, J.K.; Farrow, R.K.; Deb, D.; Sullivan, J.P.; Dospoy, P.D.; Augustyn, A.; Hight, S.K.; Sato, M.; et al. ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3219–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.Y.; Hu, F.W.; Yu, C.C.; Tsai, L.L.; Yu, C.H.; Wu, B.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, P.I.; Lo, W.L. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition transcription factor ZEB1/ZEB2 co-expression predicts poor prognosis and maintains tumor-initiating properties in head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, G.; Sayan, A.E.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB proteins link cell motility with cell cycle control and cell survival in cancer. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thisse, B.; el Messal, M.; Perrin-Schmitt, F. The twist gene: Isolation of a Drosophila zygotic gene necessary for the establishment of dorsoventral pattern. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 3439–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironchik, Y.; Winnard, P.T., Jr.; Vesuna, F.; Kato, Y.; Wildes, F.; Pathak, A.P.; Kominsky, S.; Artemov, D.; Bhujwalla, Z.; Van Diest, P.; et al. Twist overexpression induces in vivo angiogenesis and correlates with chromosomal instability in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10801–10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Hui, K.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; et al. DAB2IP regulates the chemoresistance to pirarubicin and tumor recurrence of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer through STAT3/Twist1/P-glycoprotein signaling. Cell Signal 2015, 27, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, N.R.; Tran, N.L.; Rekapally, H.; Summers, C.E.; Glackin, C.; Heimark, R.L. N-cadherin gene expression in prostate carcinoma is modulated by integrin-dependent nuclear translocation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3365–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesuna, F.; van Diest, P.; Chen, J.H.; Raman, V. Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 367, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkov, C.D.; Link, A.J.; Jennings, J.L.; Plieth, D.; Inoue, T.; Nagai, K.; Xu, C.; Dimitrova, Y.N.; Rauscher, F.J.; Neilson, E.G. A proximal activator of transcription in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, P.; Steele, R.; Newhall, P.; Phillips, N.J.; Toth, K.; Ray, R.B. miRNA-29b suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Tu, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J. miR-30 inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting Snail1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siemens, H.; Jackstadt, R.; Hünten, S.; Kaller, M.; Menssen, A.; Götz, U.; Hermeking, H. miR-34 and SNAIL form a double-negative feedback loop to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 4256–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Yin, J.J.; Abou-Kheir, W.; Hynes, P.G.; Casey, O.M.; Fang, L.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Seng, V.; Sheppard-Tillman, H.; et al. MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene 2013, 32, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavadil, J.; Narasimhan, M.; Blumenberg, M.; Schneider, R.J. Transforming growth factor-beta and microRNA:mRNA regulatory networks in epithelial plasticity. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q. Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from multiple myeloma cells promote renal epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting TGF-β/SMAD7 signalling pathway. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2023, 50, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. miR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, E.; Li, X.; Lv, B.; Vikis, H.G.; Liu, P. XRN2 promotes EMT and metastasis through regulating maturation of miR-10a. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3925–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, W.; Liu, H. MicroRNA-10a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness maintenance of pancreatic cancer stem cells via upregulating the Hippo signaling pathway through WWC2 inhibition. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 4505–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Duan, X. MiR-135b improves proliferation and regulates chemotherapy resistance in ovarian cancer. J. Mol. Histol. 2022, 53, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.H.; Kuo, L.W.; Huang, M.F.; Wu, Y.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Wu, J.E.; Hsu, K.F.; Chen, Y.L.; Hong, T.M. MicroRNA-150-5p promotes cell motility by inhibiting c-Myb-mediated Slug suppression and is a prognostic biomarker for recurrent ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Yang, H.; He, L.; Zhao, J.J.; Coppola, D.; Dalton, W.S.; Cheng, J.Q. MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 6773–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Vasilaki, E.; Vorvis, C.; Iliopoulos, D.; Moustakas, A.; Kardassis, D.; Stournaras, C. Differential regulation of the two RhoA-specific GEF isoforms Net1/Net1A by TGF-β and miR-24: Role in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2862–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukerman, P.; Yamin, R.; Seidel, E.; Khawaled, S.; Schmiedel, D.; Bar-Mag, T.; Mandelboim, O. MiR-520d-5p directly targets TWIST1 and downregulates the metastamiR miR-10b. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12141–12150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, M.; Ota, M.; Rifkin, D.B. Matrix control of transforming growth factor-β function. J. Biochem. 2012, 152, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuelten, C.H.; Zhang, Y.E. Transforming Growth Factor-β: An Agent of Change in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 764727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trelford, C.B.; Dagnino, L.; Di Guglielmo, G.M. Transforming growth factor-β in tumour development. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 991612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, Y.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-β signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Mishra, L.; Deng, C.X. The role of TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakis, P. Wnt signaling in cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a008052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, S.; Hua, F.; Hu, Z.W. The regulation of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33972–33989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yook, J.I.; Li, X.Y.; Ota, I.; Fearon, E.R.; Weiss, S.J. Wnt-dependent regulation of the E-cadherin repressor snail. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11740–11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Zhao, Y.; Harris, D.C.; Zheng, G. E-cadherin/β-catenin complex and the epithelial barrier. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 567305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, D. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Maggiolini, M.; Musti, A.M. Crosstalk between Notch, HIF-1α and GPER in Breast Cancer EMT. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, K.G.; Niessen, K.; Kulic, I.; Raouf, A.; Eaves, C.; Pollet, I.; Karsan, A. Jagged1-mediated Notch activation induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Slug-induced repression of E-cadherin. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Bournazou, E.; Sansone, P.; Berishaj, M.; Gao, S.P.; Daly, L.; Wels, J.; Theilen, T.; Granitto, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. The IL-6/JAK/Stat3 feed-forward loop drives tumorigenesis and metastasis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalle, L.; Raggi, L.; Monteleone, E.; Savino, A.; Viavattene, D.; Statello, L.; Camperi, A.; Stabile, S.A.; Salemme, V.; De Marzo, N.; et al. STAT3 induces breast cancer growth via ANGPTL4, MMP13 and STC1 secretion by cancer associated fibroblasts. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cai, J.; Zuo, Z.; Li, J. Collagen facilitates the colorectal cancer stemness and metastasis through an integrin/PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Massi, D.; Hemmings, B.A.; Mandalà, M.; Hu, Z.; Wicki, A.; Xue, G. AKT-ions with a TWIST between EMT and MET. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62767–62777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Restuccia, D.F.; Lan, Q.; Hynx, D.; Dirnhofer, S.; Hess, D.; Rüegg, C.; Hemmings, B.A. Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-β signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiadomski, P.; Niedziółka, S.M.; Markiewicz, Ł.; Uśpieński, T.; Baran, B.; Chojnowska, K. Gli Proteins: Regulation in Development and Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Katoh, M. Hedgehog target genes: Mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr. Mol. Med. 2009, 9, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifas, J.M.; Pennypacker, S.; Chuang, P.T.; McMahon, A.P.; Williams, M.; Rosenthal, A.; De Sauvage, F.J.; Epstein, E.H., Jr. Activation of expression of hedgehog target genes in basal cell carcinomas. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qi, W.; Cui, Y.; Xuan, Y. GLI1 promotes cancer stemness through intracellular signaling pathway PI3K/Akt/NFκB in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 373, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Fayçal, C.; Hatat, A.S.; Gazzeri, S.; Eymin, B. Splice Variants of the RTK Family: Their Role in Tumour Progression and Response to Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Sleeman, J.P. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billottet, C.; Tuefferd, M.; Gentien, D.; Rapinat, A.; Thiery, J.P.; Broët, P.; Jouanneau, J. Modulation of several waves of gene expression during FGF-1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 104, 826–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.R.; Zhau, H.E.; Odero-Marah, V.A.; Osunkoya, A.O.; Kimbro, K.S.; Tighiouart, M.; Liu, T.; Simons, J.W.; O’Regan, R.M. Insulin-like growth factor-I-dependent up-regulation of ZEB1 drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2479–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.W.; Hsu, S.C.; Xia, W.; Cao, X.; Shih, J.Y.; Wei, Y.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Tang, M.; Geng, Z.; Zuo, L.; Song, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. VEGF Mediates Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Affecting the Expression of E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Promoting Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Gastric Cancer. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2023, 17, 11795549231175715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tordjman, S.; Chokron, S.; Delorme, R.; Charrier, A.; Bellissant, E.; Jaafari, N.; Fougerou, C. Melatonin: Pharmacology, Functions and Therapeutic Benefits. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Sharma, R.; Tan, D.X.; Huang, G.; de Almeida Chuffa, L.G.; Anderson, G. Melatonin modulates tumor metabolism and mitigates metastasis. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 18, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, S.; González, A.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Alonso-González, C.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J. Melatonin as a selective estrogen enzyme modulator. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Fuentes-Broto, L. Melatonin: A multitasking molecule. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 181, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkov, Z.A.; Velkov, Y.Z.; Galunska, B.T.; Paskalev, D.N.; Tadjer, A.V. Melatonin: Quantum-chemical and biochemical investigation of antioxidant activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2834–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: A Versatile Protector against Oxidative DNA Damage. Molecules 2018, 23, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, C.; González, A.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin as a Radio-Sensitizer in Cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blask, D.E.; Brainard, G.C.; Dauchy, R.T.; Hanifin, J.P.; Davidson, L.K.; Krause, J.A.; Sauer, L.A.; Rivera-Bermudez, M.A.; Dubocovich, M.L.; Jasser, S.A.; et al. Melatonin-depleted blood from premenopausal women exposed to light at night stimulates growth of human breast cancer xenografts in nude rats. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11174–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, K.H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Bai, J.Y.; Zhang, D.Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Ma, J.B.; Zhu, Z.J.; Wang, X.; Guo, P. Melatonin suppresses Akt/mTOR/S6K activity, induces cell apoptosis, and synergistically inhibits cell growth with sunitinib in renal carcinoma cells via reversing Warburg effect. Redox Rep. 2023, 28, 2251234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediavilla, M.D.; Cos, S.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J. Melatonin increases p53 and p21WAF1 expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in vitro. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; González-González, A.; González, A.; Cos, S.; Martínez-Campa, C. Melatonin enhances the apoptotic effects and modulates the changes in gene expression induced by docetaxel in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florido, J.; Martinez-Ruiz, L.; Rodriguez-Santana, C.; López-Rodríguez, A.; Hidalgo-Gutiérrez, A.; Cottet-Rousselle, C.; Lamarche, F.; Schlattner, U.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Aranda-Martínez, P.; et al. Melatonin drives apoptosis in head and neck cancer by increasing mitochondrial ROS generated via reverse electron transport. J. Pineal Res. 2022, 73, e12824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, R.P.; Fernandes, P.A.; Kinker, G.S.; da Silveira Cruz-Machado, S.; Marçola, M. Immune-pineal axis—Acute inflammatory responses coordinate melatonin synthesis by pinealocytes and phagocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3239–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Reiter, R.J.; Lardone, P.J.; Herrera, J.L.; Fernández-Montesinos, R.; Guerrero, J.M.; Pozo, D. The modulatory role of melatonin on immune responsiveness. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 7, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Campa, C.M.; Alonso-González, C.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Cos, S.; González, A.; Sanchez-Barcelo, E.J. Melatonin down-regulates hTERT expression induced by either natural estrogens (17beta-estradiol) or metalloestrogens (cadmium) in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2008, 268, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-García, V.; González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Antiangiogenic effects of melatonin in endothelial cell cultures. Microvasc. Res. 2013, 87, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Chilelli, M.; Villa, S.; Cerizza, L.; Tancini, G. Five years survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy and melatonin: A randomized trial. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghal-Sadriforoush, S.; Bagheri, M.; Abdi Rad, I.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F. Melatonin Sensitizes OVCAR-3 Cells to Cisplatin through Suppression of PI3K/Akt Pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.Q.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Fernandez-Gil, B.I.; Florido, J.; García-López, S.; Martinez-Ruiz, L.; Mendivil-Perez, M.; Soto-Mercado, V.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Ortega-Arellano, H.; et al. Combination of melatonin and rapamycin for head and neck cancer therapy: Suppression of AKT/mTOR pathway activation, and activation of mitophagy and apoptosis via mitochondrial function regulation. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 64, e12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaimee, P.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Barusrux, S.; Johns, N.P. Melatonin potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Meregalli, S.; Nosetto, L.; Barni, S.; Tancini, G.; Fossati, V.; Maestroni, G. Increased survival time in brain glioblastomas by a radioneuroendocrine strategy with radiotherapy plus melatonin compared to radiotherapy alone. Oncology 1996, 53, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, N.F.; Amiri, M.; Dizaji, B.F.; Vahedian, V.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Roshanravan, N.; Haiaty, S.; Nouri, M.; Rashidi, M.R. Inhibitory effect of melatonin on hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry via suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in breast cancer stem cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 881, 173282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmler, M.P.; Eccles, R.L.; Brabletz, S.; Brabletz, T. Non-redundant functions of EMT transcription factors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.M.; Lin, W.Y.; Shen, C.C.; Pan, H.C.; Keh-Bin, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Jan, Y.J.; Lai, D.W.; Tang, S.C.; Tien, H.R.; et al. Melatonin set out to ER stress signaling thwarts epithelial mesenchymal transition and peritoneal dissemination via calpain-mediated C/EBPβ and NFκB cleavage. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Xie, J.; Hou, D.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Melatonin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells via attenuation of IL-1β/NF-κB/MMP2/MMP9 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, B.; Jia, H.; Jiao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of cell death pathways initiated by antitumor drugs melatonin and valproic acid in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Open Bio. 2017, 7, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Movassaghpour, A.A.; Ghanbari, H.; Kheirandish, M.; Fathi Maroufi, N.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Nouri, M.; Samadi, N. The potential therapeutic effect of melatonin on human ovarian cancer by inhibition of invasion and migration of cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Gu, T.; Lai, D. Melatonin suppresses chronic restraint stress-mediated metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer via NE/AKT/β-catenin/SLUG axis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, H.L.; Deng, M.J.; Wen, X.J.; Mo, Y.Y.; Chen, F.M.; Zou, C.L.; Duan, W.F.; Li, L.; Nie, X. Melatonin Inhibits Reactive Oxygen Species-Driven Proliferation, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, and Vasculogenic Mimicry in Oral Cancer. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 3510970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sokkary, G.H.; Ismail, I.A.; Saber, S.H. Melatonin inhibits breast cancer cell invasion through modulating DJ-1/KLF17/ID-1 signaling pathway. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 3945–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Zhan, W.; Kang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Hou, D.; You, R.; Huang, H. Melatonin inhibits lung metastasis of gastric cancer in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, D.; Xu, W. Melatonin suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the MG-63 cell line. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.S.; Im, E.; Lee, H.J.; Sim, D.Y.; Park, J.E.; Park, W.Y.; Park, Y.; Koo, J.; Pak, J.N.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Inhibition of TMPRSS4 mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition is critically involved in antimetastatic effect of melatonin in colorectal cancers. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4538–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Shi, X.; Zhu, P.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Yan, B.; Zhang, S. Melatonin inhibits gallbladder cancer cell migration and invasion via ERK-mediated induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, F.; Cheng, C. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals circadian rhythm disruption associated with poor prognosis and drug-resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2022, 73, e12803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Chiou, P.C.; Chen, P.C.; Liu, P.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Chao, C.C.; Tang, C.H. Melatonin reduces lung cancer stemness through inhibiting of PLC, ERK, p38, β-catenin, and Twist pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.C.; Chen, P.C.; Chiou, P.C.; Hsu, C.J.; Liu, P.I.; Yang, Y.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Yang, S.F.; Tang, C.H. Melatonin suppresses lung cancer metastasis by inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through targeting to Twist. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Hermida-Prado, F.; Granda-Díaz, R.; González, A.; García-Pedrero, J.M.; Del-Río-Ibisate, N.; González-González, A.; Cos, S.; Alonso-González, C.; Martínez-Campa, C. Deciphering the Molecular Basis of Melatonin Protective Effects on Breast Cells Treated with Doxorubicin: TWIST1 a Transcription Factor Involved in EMT and Metastasis, a Novel Target of Melatonin. Cancers 2019, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, Y.W.; Lee, Y.L.; Yu, L.Y.; Li, C.E.; Shueng, P.W.; Chiu, H.C.; Lo, C.L. Fucoidan/chitosan layered PLGA nanoparticles with melatonin loading for inducing intestinal absorption and addressing triple-negative breast cancer progression. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-SanJuan, S.; Puentes-Pardo, J.D.; Casado, J.; Escudero-Feliu, J.; Khaldy, H.; Arnedo, J.; Carazo, Á.; León, J. Agomelatine, a Melatonin-Derived Drug, as a New Strategy for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Xue, Y.; Lian, W.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Fu, Q.; Zhong, L.; Lin, N.; Lai, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Melatonin inhibits osteosarcoma stem cells by suppressing SOX9-mediated signaling. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Shin, E.A.; Kim, J.H.; Sim, D.Y.; Lee, H.; Park, J.E.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H. NEDD9 Inhibition by miR-25-5p Activation Is Critically Involved in Co-Treatment of Melatonin- and Pterostilbene-Induced Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, L. MicroRNA control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2012, 31, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, K.; Lou, T. MicroRNA-10a suppresses breast cancer progression via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5994–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğanlar, O.; Doğanlar, Z.B.; Delen, E.; Doğan, A. The role of melatonin in angio-miR-associated inhibition of tumorigenesis and invasion in human glioblastoma tumour spheroids. Tissue Cell 2021, 73, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, H. Melatonin Inhibits the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Regulating the miR-16-5p-Smad3 Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hua, L.; Huang, L. Melatonin Inhibits the Malignant Progression of Glioblastoma via Regulating miR-16-5p/PIM1. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2022, 19, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, S.; Wei, C.; Cheng, J.; Khan, M.A.; Fu, S.; Yang, L.; Tania, M.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21362–21379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, C.; González-Abalde, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; González-González, A.; Álvarez-García, V.; González-Cabeza, A.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin Modulation of Radiation-Induced Molecular Changes in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Li, X.; Hao, H. Melatonin inhibits proliferation and viability and promotes apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of the microRNA-34a/449a cluster. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, J.Z.; Ferreira, L.C.; Lopes, B.C.; Aristizábal-Pachón, A.F.; Bajgelman, M.C.; Borin, T.F.; Zuccari, D.A.P.C. Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Regulation of MiR-148a-3p and Angiogenic Factors in Breast Cancer. Microrna 2019, 8, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.C.; Orso, F.; Dettori, D.; Lacerda, J.Z.; Borin, T.F.; Taverna, D.; Zuccari, D.A.P.C. The role of melatonin on miRNAs modulation in triple-negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimalraj, S.; Saravanan, S.; Raghunandhakumar, S.; Anuradha, D. Melatonin regulates tumor angiogenesis via miR-424-5p/VEGFA signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 118011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Xu, W. Melatonin promotes apoptosis of thyroid cancer cells via regulating the signaling of microRNA-21 (miR-21) and microRNA-30e (miR-30e). Bioengineered 2022, 13, 9588–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Lu, Z.; Ji, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.T.; Li, X. Melatonin inhibits proliferation and invasion via repression of miRNA-155 in glioma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, F.; Ferraiuolo, M.; Santoro, R.; Sacconi, A.; Goeman, F.; Pallocca, M.; Pulito, C.; Korita, E.; Fanciulli, M.; Muti, P.; et al. Multitargeting activity of miR-24 inhibits long-term melatonin anticancer effects. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20532–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Wei, F.; Xia, H.; Liu, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. MicroRNA-10b mediates TGF-β1-regulated glioblastoma proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcourt, U.; Kowanetz, M.; Niimi, H.; Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell transition. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 1987–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Sun, Y.T.; Su, X.M.; He, M.; Dai, B.; Kang, J. Melatonin attenuates TGFβ1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 5567–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, Z. Melatonin attenuates hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell aggressive via Smad7/ CCL20 in glioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93580–93592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, D.; Sharda, N.; Giri, B.; Hassan, M.S.; Singh, D.; Tarasiewicz, A.; Lohr, C.; von Holzen, U.; Kristian, T.; Waddell, J.; et al. Melatonin and andrographolide synergize to inhibit the colospheroid phenotype by targeting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2022, 73, e12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Li, S.; He, K.; Kang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y. Melatonin regulates cancer migration and stemness and enhances the anti-tumour effect of cisplatin. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Yan, L.; Liu, Z.; Mu, Y.L.; Li, M.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhang, H. Melatonin inhibits 17β-estradiol-induced migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in normal and endometriotic endometrial epithelial cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Huang, C.R.; Chang, C.L.; Chiang, J.Y.; Luo, C.W.; Chen, H.H.; Yip, H.K. Jagged2 progressively increased expression from Stage I to III of Bladder Cancer and Melatonin-mediated downregulation of Notch/Jagged2 suppresses the Bladder Tumorigenesis via inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR/MMPs signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2648–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Pang, B.; Gu, G.; Gao, T.; Zhang, R.; Pang, Q.; Liu, Q. Melatonin Inhibits Glioblastoma Stem-like cells through Suppression of EZH2-NOTCH1 Signaling Axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.X.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ye, Q.L.; Xu, S.; Hong, Q.; Xing, W.Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, D.X.; Xu, D.X.; Xie, D.D. Melatonin Inhibits Migration and Invasion in LPS-Stimulated and -Unstimulated Prostate Cancer Cells Through Blocking Multiple EMT-Relative Pathways. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Zhou, J.; Sasano, H.; Suzuki, T.; Zeitoun, K.M.; Bulun, S.E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 11 secreted by malignant breast epithelial cells inhibit adipocyte differentiation by selectively down-regulating CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma: Mechanism of desmoplastic reaction. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2250–2255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-García, V.; González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin interferes in the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer by regulating cytokine production. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-González, A.; García Nieto, E.; González, A.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Cos, S.; Martínez-Campa, C. Melatonin Modulation of Radiation and Chemotherapeutics-induced Changes on Differentiation of Breast Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chang, A.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Cao, J.; Gu, W.; Tang, R. Melatonin synergizes BRAF-targeting agent dabrafenib for the treatment of anaplastic thyroid cancer by inhibiting AKT/hTERT signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12119–12130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhu, P.; Chen, W.; Luo, K.; Shi, X.J.; Zhai, W. Melatonin inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion by inducing ROS-mediated apoptosis via suppression of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in gallbladder cancer cells. Aging 2021, 13, 22502–22515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Godoy, B.L.V.; Moschetta-Pinheiro, M.G.; Chuffa, L.G.A.; Pondé, N.F.; Reiter, R.J.; Colombo, J.; Zuccari, D.A.P.C. Synergistic actions of Alpelisib and Melatonin in breast cancer cell lines with PIK3CA gene mutation. Life Sci. 2023, 324, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hao, B.; Zhang, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Lin, S.; Zheng, T.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Yue, L.; Abay, B.; et al. Melatonin enhances radiofrequency-induced NK antitumor immunity, causing cancer metabolism reprogramming and inhibition of multiple pulmonary tumor development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Arbab, A.S.; Ferreira, L.C.; Borin, T.F.; Varma, N.R.; Iskander, A.S.; Shankar, A.; Ali, M.M.; de Campos Zuccari, D.A. Effect of melatonin on tumor growth and angiogenesis in xenograft model of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Yu, M.; Peng, X.; Dong, L.; Yang, Z. Melatonin prevents human pancreatic carcinoma cell PANC-1-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-García, V.; González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by melatonin in human breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, A.; González, A.; Rueda, N.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez, J.M.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Mitola, S.; Cos, S. Usefulness of melatonin as complementary to chemotherapeutic agents at different stages of the angiogenic process. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-González, A.; González, A.; Rueda, N.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin Enhances the Usefulness of Ionizing Radiation: Involving the Regulation of Different Steps of the Angiogenic Process. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Su, Y.; Choi, W.S. Melatonin Suppresses Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Migration and Invasion through Blocking FGF19/FGFR 4 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Tumor | Cell Lines | In Vivo | [Mel] | Upregulated Genes | Downregulated Genes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric cancer | AG5, MKN45 | 0.1 μM–2 mM | E-cadherin | MMP2, MMP9, NF-κB, Snail | [115] | |
| Gastric cancer | MGC80-3, SGC790 | 0.1–1.5 mM | E-cadherin | Snail, Slug, Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB | [116] | |
| Gastric cancer | MGC80-3 | In vivo lung metastasis | 100 mg/Kg/day | E-cadherin | MMP2, MMP9, NF-κB, Snail, Slug, Fibronectin | [122] |
| Ovarian cancer | SK-OV-3 | 3.4 mM | ZEB1, ZEB2, Snail, Vimentin | [118] | ||
| Ovarian cancer | SK-OV-3 | Tumor-bearing mouse model | 200 μg/100 g/day | Akt, β-catenin, Slug | [119] | |
| Bladder cancer | UC3 | 1 μM | E-cadherin | N-cadherin, Fibronectin, Snail, Slug | [117] | |
| Oral cancer | SCC25, SCC9, Tca8113, Cal27, FaDu | 1 mM | Akt, Snail, Vimentin | [120] | ||
| Breast cancer | MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 | 1 nM | E-cadherin | Snail | [121] | |
| Breast cancer | MCF-7 | 1 nM | Twist1, Slug, Akt | [129] | ||
| Osteosarcoma | MG-63 | 200 nM | E-cadherin | N-cadherin, Snail, MMP-9 | [123] | |
| Colorrectal cancer | HCT-15 SW620 | 1–2 mM | E-cadherin | Snail | [124] | |
| Gallbladder cancer | GBC-SD | 0.1–2 mM | E-cadherin | N-cadherin, Snail, Vimentin | [125] | |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | H1299 | 0.1 mM | Snail, Twist1 | [126] | ||
| Lung cancer | A549, CL1-5 | 1 mM | Twist1 | [127] | ||
| Lung cancer | CL1-5 | 1 mM | Slug, Twist1, β-catenin | [128] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Campa, C.; Álvarez-García, V.; Alonso-González, C.; González, A.; Cos, S. Melatonin and Its Role in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050956
Martínez-Campa C, Álvarez-García V, Alonso-González C, González A, Cos S. Melatonin and Its Role in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050956
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Campa, Carlos, Virginia Álvarez-García, Carolina Alonso-González, Alicia González, and Samuel Cos. 2024. "Melatonin and Its Role in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 5: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050956
APA StyleMartínez-Campa, C., Álvarez-García, V., Alonso-González, C., González, A., & Cos, S. (2024). Melatonin and Its Role in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Cancer. Cancers, 16(5), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050956









