miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Implication of miRNAs in Cancer
2.1. Genome Abnormalities
2.2. Epigenetic Alterations
2.3. miRNA Regulation at the Transcriptional Level
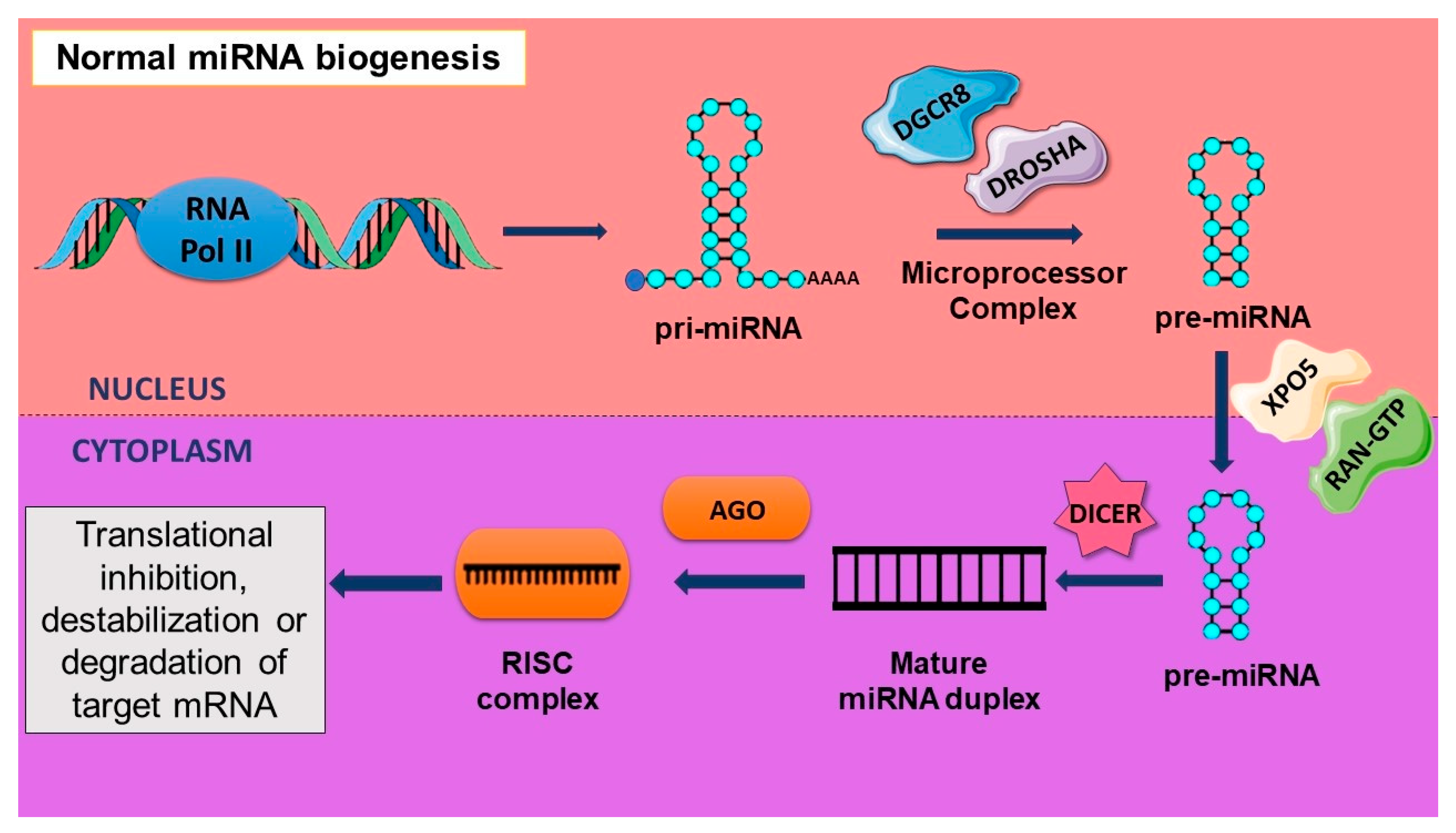
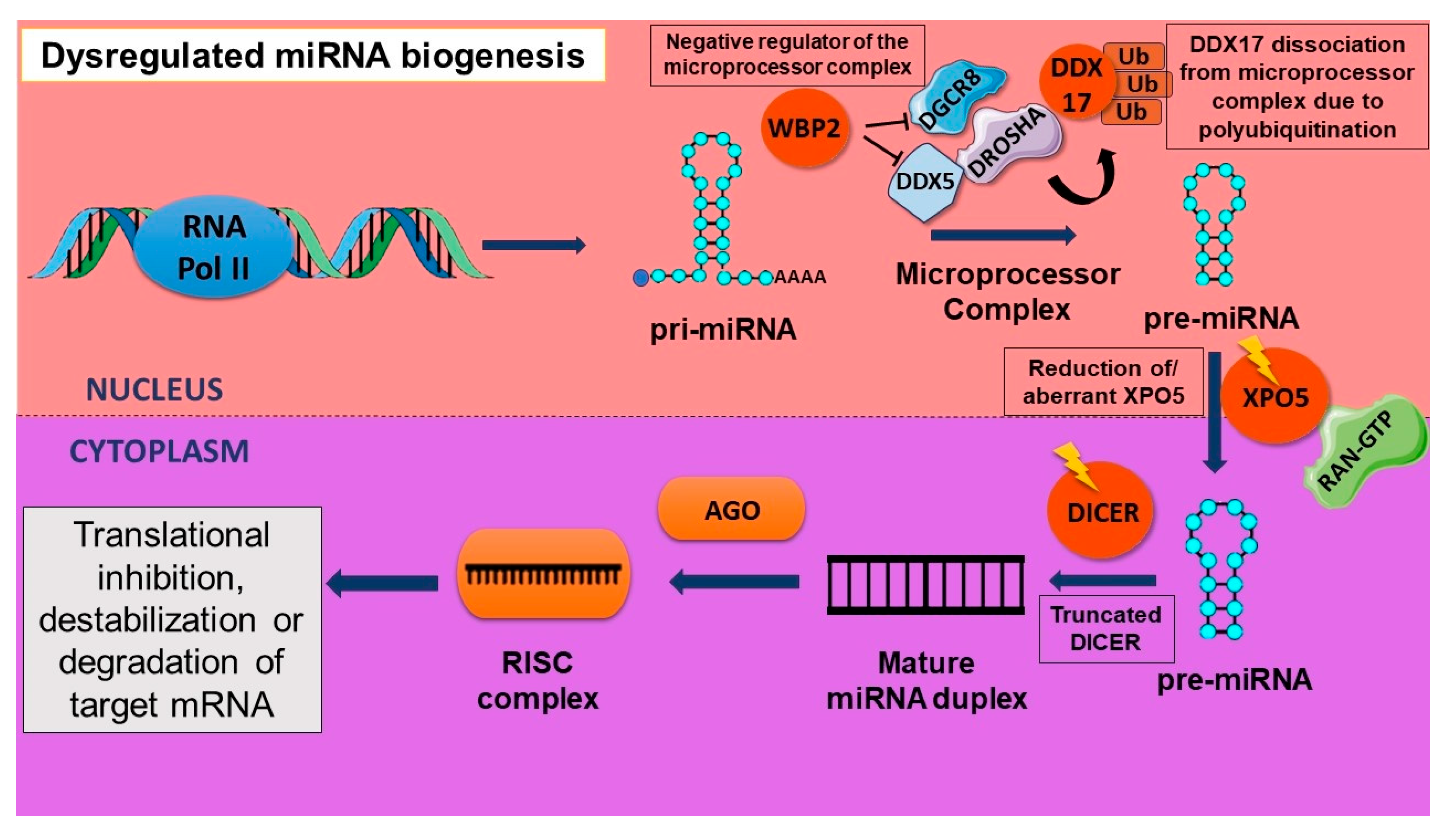
2.4. Aberrant Biogenesis of miRNA
3. How Are Stemness Properties in CSCs Related to miRNAs?
4. Eminent miRNAs in Specific Malignancies
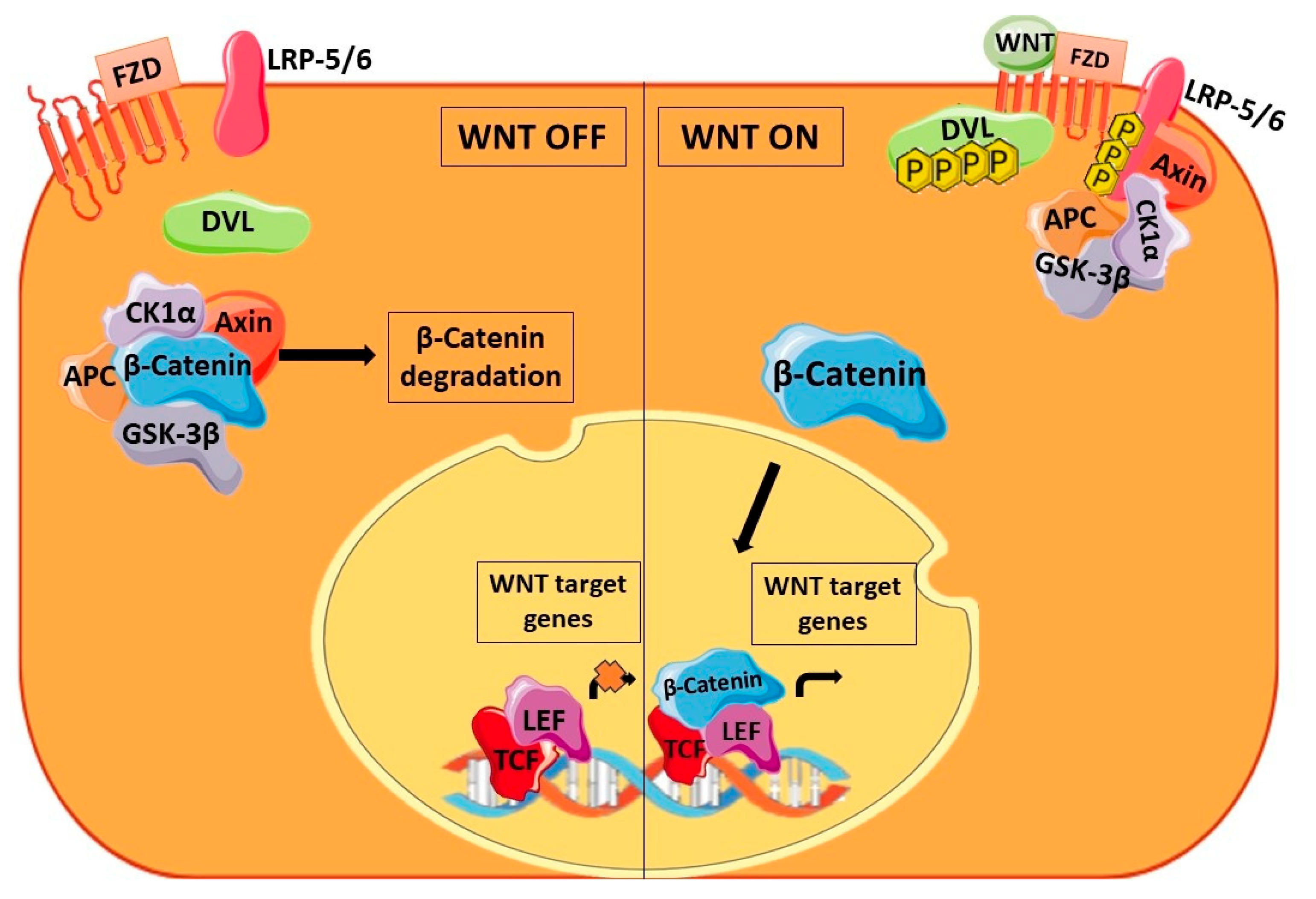
5. Prominence of miRNAs in WNT Signaling Pathway Dysregulated in CSCs
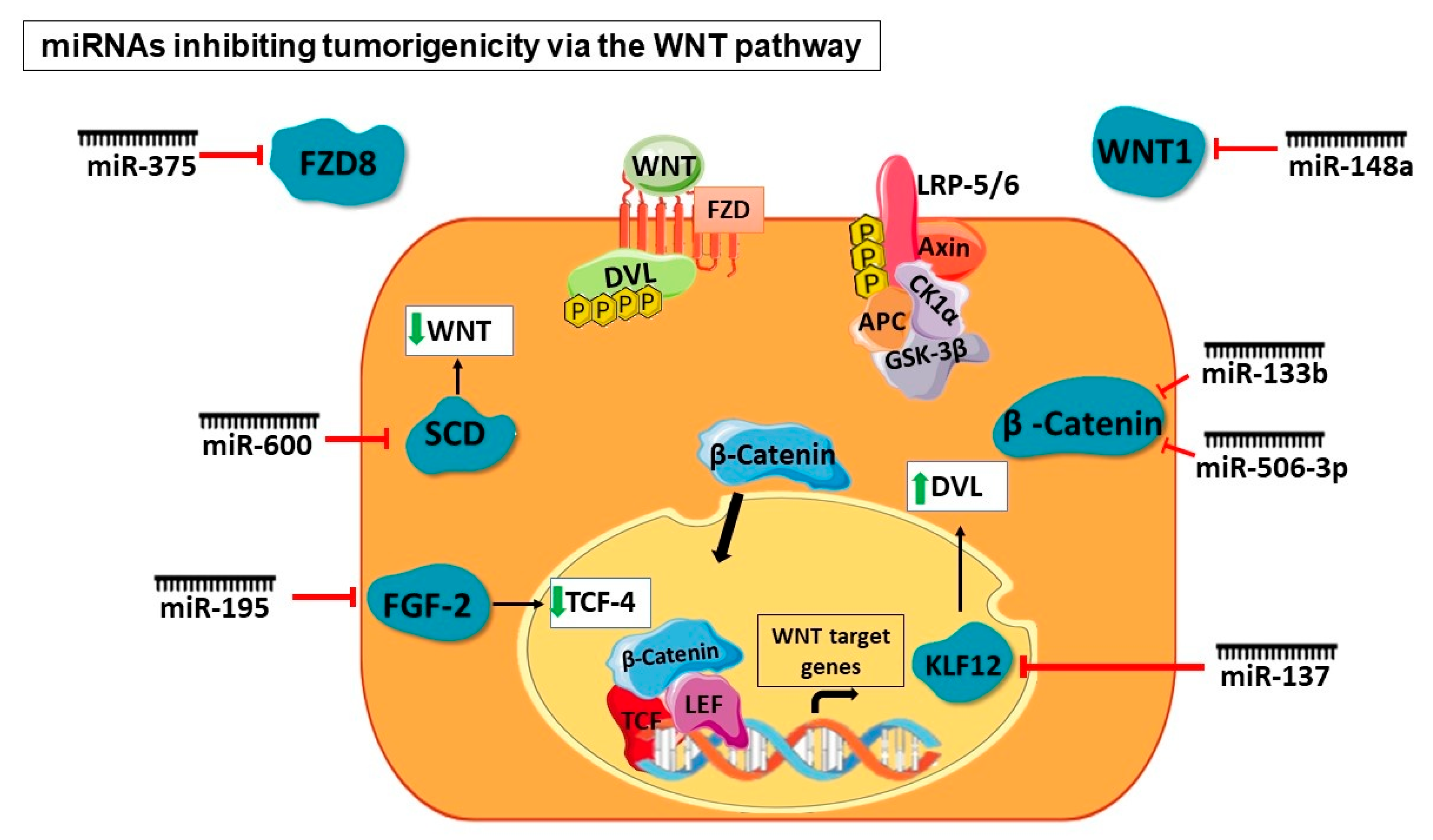
5.1. At the Extracellular Level of WNT Signaling
5.2. At the β-Catenin Level
5.3. At the Destruction Complex Level
5.4. At Transcriptional Level
6. miRNA as Druggable Compounds
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, A.Q.; Ahmed, E.I.; Elareer, N.R.; Junejo, K.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Role of MiRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human Malignancies. Cells 2019, 8, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, C.; Chin, K.-Y.; Das, S. MiRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells: Understanding the Property and the Role of MiRNA in Carcinogenesis. Tumor Biol. 2016, 10, 13039–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Jun, Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Nam, J.-S. Roles of Wnt Target Genes in the Journey of Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 8, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, B.; Qu, S.; Liang, G.; Luo, W.; Gong, C. MicroRNAs and Cancer: Key Paradigms in Molecular Therapy Review. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 2735–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Schmitz, U.; Vera, J. The Role of MicroRNAs in Cancer Biology and Therapy from a Systems Biology Perspective. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1385, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jiao, X.; Pestell, T.G.; Fan, C.; Qin, S.; Mirabelli, E.; Ren, H.; Pestell, R.G. MicroRNAs and Cancer Stem Cells: The Sword and the Shield. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4967–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cancer: Diagnostics, Monitoring and Therapeutics. A Comprehensive Review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.; Hernández-Illán, E.; Moreira, L.; Balaguer, F.; Goel, A. Epigenetics of Colorectal Cancer: Biomarker and Therapeutic Potential. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 2, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, C.W.S.; Howell, V.M.; Hahn, M.A.; Marsh, D.J. Genomic Alterations as Mediators of MiRNA Dysregulation in Ovarian Cancer: The Effect of CNVs and Snps on Mirna in Ovarian Cancer. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, B.M.; Hidayat, H.J.; Salihi, A.; Sabir, D.K.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. MicroRNA: A Signature for Cancer Progression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-S.; Su, J.-L.; Hung, M.-C. Dysregulation of MicroRNAs in Cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012, 1, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaff, E.; Aichmüller, C.; Sill, M.; Stichel, D.; Snuderl, M.; Karajannis, M.A.; Schuhmann, M.U.; Schittenhelm, J.; Hasselblatt, M.; Thomas, C.; et al. Molecular Subgrouping of Primary Pineal Parenchymal Tumors Reveals Distinct Subtypes Correlated with Clinical Parameters and Genetic Alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 2, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragomir, M.P.; Knutsen, E.; Calin, G.A. Classical and Noncanonical Functions of MiRNAs in Cancers. Trends Genet. 2022, 4, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Volinia, S.; Bonome, T.; Calin, G.A.; Greshock, J.; Yang, N.; Liu, C.-G.; Giannakakis, A.; Alexiou, P.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Genomic and Epigenetic Alterations Deregulate MicroRNA Expression in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 19, 7004–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Epigenetically Altered MiR 193a 3p Promotes HERPositive Breast Cancer Aggressiveness by Targeting GRB7. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 6, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Garzon, R.; Cimmino, A.; Liu, Z.; Zanesi, N.; Callegari, E.; Liu, S.; Alder, H.; Costinean, S.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; et al. MicroRNA-Family Reverts Aberrant Methylation in Lung Cancer by Targeting DNA Methyltransferases 3A and 3B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 40, 15805–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberti, A.; Valdes, A.F.; Torrecillas, R.; Fraga, M.F.; Fernandez, A.F. Epigenetics in Cancer Therapy and Nanomedicine. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 1, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, C.P.; Scott, H.S.; Goodall, G.J. A Network-Biology Perspective of MicroRNA Function and Dysfunction in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Shah, J. Recent Trends in Targeting MiRNAs for Cancer Therapy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 12, 1732–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. NMEIs a Master Suppressor of Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cells via Transcriptional Regulation of MiR-and Other Survival Factors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 2, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidle, U.H.; Birzele, F.; Nopora, A. MicroRNAs Promoting Growth of Gastric Cancer Xenografts and Correlation to Clinical Prognosis. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2021, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Feng, M.; Ma, X.; Tao, K.; Wang, G. Transcription Factor SP1-Induced MicroRNA-146b-3p Facilitates the Progression and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer via Regulating FAM107A. Life Sci. 2021, 119398, 119398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, A.; Falcone, E.; Garibaldi, F.; Piaggio, G. Dysregulation of MicroRNA Biogenesis in Cancer: The Impact of Mutant Pon Drosha Complex Activity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 1, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; He, J.; Pu, W.; Peng, Y. The Role of Exportin-in MicroRNA Biogenesis and Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 2, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaeian, H.; Lim, S.K.; Chu, T.; Seah, S.H.; Lim, Y.P. WBPInhibits MicroRNA Biogenesis via Interaction with the Microprocessor Complex. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 7, e202101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.S.N.; Ip, C.K.M.; Mak, A.S.C.; Wong, A.S.T. A Novel PSKinase-MicroRNA Biogenesis Axis Mediates Multicellular Spheroid Formation in Ovarian Cancer Progression. Oncotarget 2016, 25, 38064–38077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, S.-H.; Cheng, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-T.; Wu, H.-T.; Yeh, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Tsai, M.-H.; Wu, K.-J. Regulation of MiRNA Biogenesis and Histone Modification by K63-Polyubiquitinated DDXControls Cancer Stem-like Features. Cancer Res. 2019, 10, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S. MicroRNA Biogenesis and Their Functions in Regulating Stem Cell Potency and Differentiation. Biol. Proced. 2016, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-S.; Lv, Z.-W.; Yu, F.; Chang, Z.-Y.; Cong, X.-L.; Zhong, X.-M.; Lu, G.-X.; Zhu, J.; Fu, D. MicroRNA-302a/d Inhibits the Self-Renewal Capability and Cell Cycle Entry of Liver Cancer Stem Cells by Targeting the E2F7/AKT Axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 1, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitarte, N.; Bandres, E.; Boni, V.; Zarate, R.; Rodriguez, J.; Gonzalez-Huarriz, M.; Lopez, I.; Javier Sola, J.; Alonso, M.M.; Fortes, P.; et al. MicroRNA-Is Involved in the Self-Renewal, Tumorigenicity, and Chemoresistance of Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2011, 11, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes Derived from Cancer Stem Cells of Gemcitabine-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer Cells Enhance Drug Resistance by Delivering MiR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 1, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, A.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M.; Haq, I.U.; Mariyam, Z.; Feng, Q. EGCG Inhibits CSC-like Properties through Targeting MiR-485/CDAxis in A549-Cisplatin Resistant Cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 12, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, L.; Ho, W.Y.; Ali, N.M.; Yeap, S.K.; Ky, H.; Chan, K.G.; Yin, W.F.; Satharasinghe, D.A.; Liew, W.C.; Tan, S.W.; et al. MiRNA Transcriptome Profiling of Spheroid-Enriched Cells with Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Human Breast MCF-Cell Line. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 4, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.C.-M.; Lun, S.W.-M.; Chung, G.T.-Y.; Chow, C.; Lo, C.; Choy, K.-W.; Lo, K.-W. MicroRNA-Suppresses Cancer Stem-like Cell Properties in EBV-Associated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-W.; Yang, S.-T.; Chien, M.-H.; Hua, K.-T.; Wu, C.-J.; Hsiao, S.M.; Lin, H.; Hsiao, M.; Su, J.-L.; Wei, L.-H. The STAT3-MiRNA-92-Wnt Signaling Pathway Regulates Spheroid Formation and Malignant Progression in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 8, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Tian, J.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, M. Serum MicroRNA-Expression in Patients with Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 5, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, C.; Liu, G. MicroRNA-506-3p Increases the Response to PARP Inhibitors and Cisplatin by Targeting EZH2/β-Catenin in Serous Ovarian Cancers. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 2, 100987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Helou, R.; Pinna, G.; Cabaud, O.; Wicinski, J.; Bhajun, R.; Guyon, L.; Rioualen, C.; Finetti, P.; Gros, A.; Mari, B.; et al. MiR-Acts as a Bimodal Switch That Regulates Breast Cancer Stem Cell Fate through WNT Signaling. Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 2256–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, M.; Ma, M.-T.; Wu, H.-Z.; Yu, Z.-J.; Guan, S.; Jiang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, D.-D.; Jin, F.; et al. MicroRNA-148a Inhibits Breast Cancer Migration and Invasion by Directly Targeting WNT-1. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 3, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, T.; Hisamori, S.; Hogan, D.J.; Zabala, M.; Hendrickson, D.G.; Dalerba, P.; Cai, S.; Scheeren, F.; Kuo, A.H.; Sikandar, S.S.; et al. MiR-Regulates the Tumorigenicity of Human Breast Cancer Stem Cells through the Canonical WNT Signaling Pathway. Elife 2014, 3, e01977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, D.E.; Allinson, L.M.; Al Amri, W.S.; Poulter, J.A.; Pramanik, A.; Thorne, J.L.; Verghese, E.T.; Hughes, T.A. MiR-and Its Target SEMA6D Regulate Chemoresponse in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Steele, I.; Kumar, J.D.; Dimaline, R.; Jithesh, P.V.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Reisz, Z.; Dockray, G.J.; Varro, A. Distinct MiRNA Profiles in Normal and Gastric Cancer Myofibroblasts and Significance in Wnt Signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 9, G696–G704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wen, T.; Liu, Z.; Xu, F.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Feng, G.; An, G. MicroRNA-Suppresses Human Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Frizzled 8. Oncotarget 2016, 26, 40644–40656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Yu, M.; Xie, X.; Huang, G.; Peng, Y.; Ren, D.; Lin, M.; Liu, B.; Liu, M.; Wang, W.; et al. MiR-Targeting DKKPromotes Cancer Stem Cell Properties via Activation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 4, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Ma, X.; Guan, G.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Niu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Bian, C.; Zang, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-Promotes Cancer Progression by Targeting NR3Cin Hepatocellular Carcinoma. FASEB J. 2019, 1, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Ng, K.-Y.; Tong, M.; Lau, E.Y.; Lee, T.K.; Chan, K.W.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Cheung, T.-T.; Cheung, S.-T.; Wang, X.-Q.; et al. Octamer 4/MicroRNA-Signaling Axis Drives Wnt/β-Catenin Activation in Liver Cancer Stem Cells. Hepatology 2016, 6, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, S.; Zhu, C.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. MicroRNA-Reduces Stemness Features of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Targeting KLF12. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 1, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, H. MicroRNA-133b Represses the Progression of Lung Cancer through Inhibiting SOX9/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 9, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Asadzadeh, Z.; Mansoori, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Aghajani, M.; Haji-Asgarzadeh, K.; Safarzadeh, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Baradaran, B. MicroRNAs in Cancer Stem Cells: Biology, Pathways, and Therapeutic Opportunities. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 7, 10002–10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Wang, D.; Lu, Y. MicroRNA-Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cells Proliferation via Targeting FGFand Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 11, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Abba, M.L.; Patil, N.; Leupold, J.H.; Moniuszko, M.; Utikal, J.; Niklinski, J.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNAs as Novel Targets and Tools in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2017, 387, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.F.; Cerqueira, L.; Figueiredo, C.; Oliveira, C.; Azevedo, N.F. Anti-MiRNA Oligonucleotides: A Comprehensive Guide for Design. RNA Biol. 2018, 3, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.; Gamit, N.; Dharmarajan, A.; Sethi, G.; Warrier, S. Identification of a Novel Wnt Antagonist Based Therapeutic and Diagnostic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease Using a Stem Cell-Derived Model. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-N.; Ren, C.-C.; Yang, L.; Nai, M.-M.; Xu, Y.-M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA Let 7d 5p Rescues Ovarian Cancer Cell Apoptosis and Restores Chemosensitivity by Regulating the PSignaling Pathway via HMGA1. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 5, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Li, C.; Duan, W.; Du, S.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Xing, J. MicroRNA-Represses Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion through Targeting Frizzled7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 3, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, M.; Slack, F.J. Challenges Identifying Efficacious MiRNA Therapeutics for Cancer. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 9, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging Concepts of MiRNA Therapeutics: From Cells to Clinic. Trends Genet. 2022, 6, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.P.; Dwyer, R.M. Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 2, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, M.; Lampis, A.; Ghidini, M.; Salati, M.; Mirchev, M.B.; Valeri, N.; Hahne, J.C. MicroRNAs MiRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs LncRNAs as New Tools for Cancer Therapy: First Steps from Bench to Bedside. Target. Oncol. 2020, 3, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cancer Type | miRNA | Type of miRNA | Pathway Involved | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia | miR-15, miR16 | Tumor suppressor | Apoptosis | [11,12] |
| Epithelial ovarian cancer | miR-34b | Tumor suppressor | Apoptosis, senescence in cells, and cell cycle arrest | [11,15] |
| miR-92a | Oncogenic | Tumor initiation and metastasis | [36,37] | |
| miR-506-3p | Tumor suppressor | Chemoresistance | [38] | |
| Breast cancer | miR-193a-3p | Tumor suppressor | Migration, invasion, and proliferation of cells | [16] |
| miR-600 | Oncogenic | Proliferation of cells | [39] | |
| miR-148a | Tumor suppressor | Migration and invasion | [40] | |
| miR-142 | Oncogenic | Metastasis | [41] | |
| miR-150 | Oncogenic | Cellular proliferation | [41] | |
| miR-195 | Oncogenic | Chemoresistance and metastasis | [42] | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | miR-29 | Tumor suppressor | Inhibition of cancer progression | [17,18] |
| Gastric cancer | miR-100 | Oncogenic | Apoptosis | [21] |
| miR-181d | Oncogenic | Proliferation and migration | [43] | |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-146b-3p | Oncogenic | Invasion, migration, and proliferation | [22] |
| miR-451 | Tumor suppressor | Tumor initiation, self-renewal, and resistance to chemotherapy | [31] | |
| miR-375 | Tumor suppressor | Migration and invasion | [44] | |
| Liver cancer | miRNA-302a/d | Tumor suppressor | Cell proliferation and tumor sphere formation | [30] |
| miR-217 | Oncogenic | Cell proliferation, chemoresistance, and metastasis | [45] | |
| miR-766 | Oncogenic | Metastasis and proliferation of cells | [46] | |
| miR-1246 | Oncogenic | Chemoresistance, self-renewal, and metastasis | [47] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | miR-210 | Oncogenic | Chemoresistance | [32] |
| miR-137 | Tumor suppressor | Cell proliferation and invasion | [48] | |
| Non-small-cell lung cancer | miR-485 | Tumor suppressor | Chemoresistance | [33] |
| miR-133b | Tumor suppressor | Cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis | [49] | |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | miR-183 | Tumor suppressor | Cell proliferation, self-renewal and chemoresistance | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhagtaney, L.; Dharmarajan, A.; Warrier, S. miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment. Cancers 2024, 16, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050957
Bhagtaney L, Dharmarajan A, Warrier S. miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050957
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhagtaney, Lekha, Arun Dharmarajan, and Sudha Warrier. 2024. "miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment" Cancers 16, no. 5: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050957
APA StyleBhagtaney, L., Dharmarajan, A., & Warrier, S. (2024). miRNA on the Battlefield of Cancer: Significance in Cancer Stem Cells, WNT Pathway, and Treatment. Cancers, 16(5), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050957







