Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
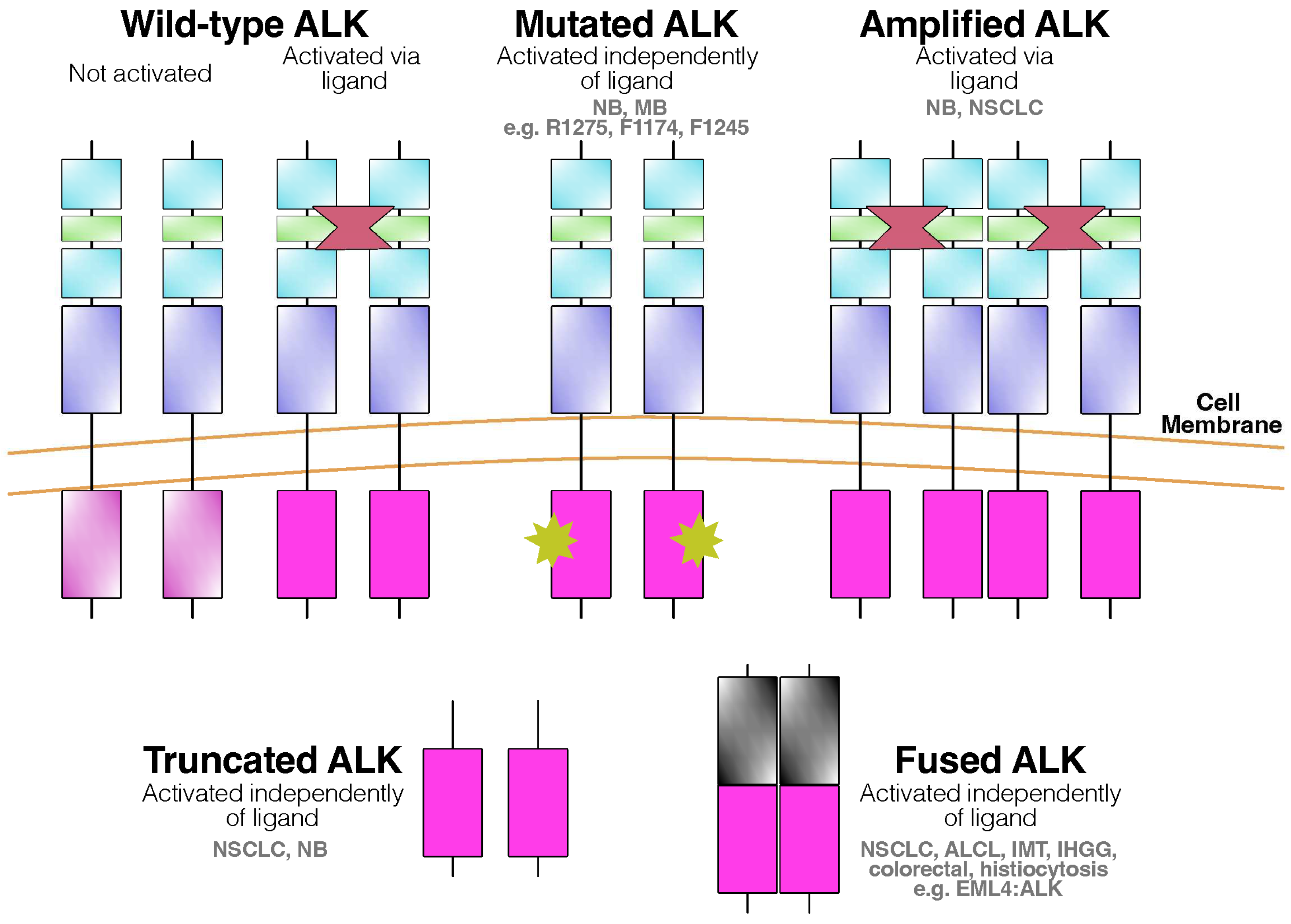
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
3. Results
| Author YOP Tumor of Interest | Study Design Number of Patients Included in Review | Age (Years) Gender (M: Male, F: Female) | Exact Location of Posterior Fossa Tumor | Therapeutic Approach Related to ALK Other Therapeutic Approaches Not Related to ALK | ALK Analysis Method with Molecular Targets | ALK Type of Pathology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahrendsen et al. 2022 [52] ALCL | Case Series 1 | 37 M | Infratentorial Compartments (including cerebellum) | - Surgery, Intrathecal Methotrexate | IHC, sequencing (447 gene exons, 191 introns across 60 genes) | ALK-positive, no genetic alterations detected |
| Geetha et al. 2014 [53] ALCL | Case Report 1 | 19 M | Right Cerebellar Hemisphere | - Surgery, Chemotherapy | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Havlioglu et al. 1995 [54] ALCL | Case Report 1 | 4.5 F | Multifocal brain, Brainstem, Spinal Cord | - Chemotherapy, Radiation | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Menon et al. 2015 [55] ALCL | Case Series 1 | 43 Μ | Multiple meningeal lesions (Right Cerebellum, Medulla involvement) | - NA | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Rudresha et al. 2017 [56] ALCL | Case Series 1 | NA NA | Cerebellum | - High-dose methotrexate, Radiation | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Strosberg et al. 2021 [57] ALCL | Case Report 1 | 29 F | Brainstem | - Chemotherapy, Methotrexate | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Hojo et al. 2023 [58] IMMT | Case Report 1 | 10 F | Left Cerebellar Hemisphere | - Surgery | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Kambe et al. 2021 [59] IMMT | Case Report 1 | 65 F | Right Cerebellar Hemisphere | - Surgery | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Kemps et al. 2022 [60] Histiocytosis | Case Series 4 | 0.75, 2.5, 3, 7 F (n = 3) M (n = 1) | Cerebellum (n = 2) Medulla (n = 2) | Alectinib (n = 1) Chemotherapy (n = 2) Corticosteroids, Surgery (n = 1) NA (n = 1) | IHC, FISH, sequencing | ALK-positive IHC (n = 4) ALK-FISH positive (n = 1) KIF5B–ALK fusion (n = 3) |
| Lucas et al. 2019 [61] Histiocytosis | Case Report 1 | 7 F | Cerebellar Vermis | - Surgery | IHC, sequencing (Sequencing: RNA assay targeting 53 genes) | KIF5B–ALK fusion |
| Swain et al. 2008 [62] IMT | Case Report 1 | 30 M | Cerebellum | - Radiation, Surgery | IHC, FISH (FISH: ALK rearrangement in 4% of tumor cells) | ALK negative IHC ALK-FISH positive |
| Coco et al. 2012 [63] MB | Case Series 4 | Pediatric NA | Cerebellum | - - | PCR, sequencing a. Sequencing for ALK exons 20–28 b. Quantitative PCR for mRNA expression | ALK mutation 3605delG in exon 23 of ALK gene (n = 1) ALK mRNA overexpression (n = 3) |
| Łastowska et al. 2017 [35] MB WNT (n = 19) SHH (n = 2) Type 3 (n = 1) Type 4 (n = 1) Not classified (n = 2) | Case Series 25 | <1–14 F (n = 13) M (n = 12) | Cerebellopontine Angle (n = 3) Cerebellar Hemisphere (n = 1) Cerebellar Midline (n = 21) | - - | IHC, sequencing | All cases: ALK-positive Additional methods: NanoString, CTNNB1 mutation (n = 9) NanoString (n = 9) CTNNB1 mutation, monosomy 6 (n = 1) Nuclear b-catenin, monosomy 6 (n = 2) MAGIC MB128 (n = 2) GAB1+, YAP1+ (n = 1) |
| Łastowska et al. 2019 [64] MB | Case Series 7 | 3–16 F (n = 4) M (n = 2) NA (n = 1) | Cerebellopontine Angle (n = 2) Cerebellar Midline (n = 4) NA (n = 1) | - - | IHC, DNA (next generation, Sanger) sequencing | ALK-positive (n = 7) APC variant detected (n = 1) |
| Trubicka et al. 2016 [65] MB | Case Report 1 | 10 M | Posterior Fossa Midline | - Surgery | IHC | ALK-positive |
| Yan et al. 2016 [34] MB WNT (n = 1) SHH (n = 1) Mixed − WNT/SHH (n = 1) | Case Series 3 | 1.8, 5.5, 12.8 F (n = 2) M (n = 1) | Posterior Fossa - 4th Ventricle (n = 2) Right Cerebellar Hemisphere (n = 1) | - Surgery, Radiation, Chemotherapy (n = 2) Surgery alone (n = 1) | IHC, DNA sequencing, FISH (DNA sequencing: ALK exons 23, 25 FISH: >15% of cells having split signals) | ALK-positive ALK-FISH negative |
4. Discussion
4.1. Medulloblastoma
4.2. Histiocytosis
4.3. Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphomas (ALCL)
4.4. Intracranial Mesenchymal Tumors That Are FET::CREB-Fusion-Positive
4.5. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors
4.6. Therapeutic Considerations
4.7. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, K.; Lamant, L.; Morris, S.W.; Butler, L.H.; Wood, K.M.; Stroud, D. Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Nucleolar pro- Tein Nucleophosmin (NPM)–ALK Proteins in Normal and Neoplastic Cells with the Monoclonal Antibody ALK1. Blood 1997, 89, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Naeve, C.W.; Mathew, P.; James, P.L.; Kirstein, M.N.; Cui, X.; Witte, D.P. ALK, the Chromosome 2 Gene Locus Altered by the t(2;5) in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Encodes a Novel Neural Receptor Tyrosine Kinase That Is Highly Related to Leukocyte Tyrosine Kinase (LTK). Oncogene 1997, 14, 2175–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahara, T.; Fujimoto, J.; Wen, D.; Cupples, R.; Bucay, N.; Arakawa, T.; Mori, S.; Ratzkin, B.J.; Yamamoto, T. Molecular Characterization of ALK, a Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Expressed Specifically in the Nervous System. Oncogene 1997, 14, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK): Structure, Oncogenic Activation, and Pharmacological Inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 68, 68–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.C.; Jia, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, X.; Ng, K.; Ambing, E. Crystal Structure of the ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase) Catalytic Domain. Biochem. J. 2010, 430, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossi, R.T.; Saccardo, M.B.; Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Rusconi, L.; Magnaghi, P. Crystal Structures of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Complex with ATP Competitive Inhibitors. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6813–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Pinera, P.; Zhang, W.; Chang, Y.; Vega, J.A.; Deuel, T.F. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Is Acti- Vated through the Pleiotrophin/Receptor Protein- Tyrosine Phosphatase Beta/Zeta Signaling Pathway: An Alternative Mechanism of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28683–28690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, G.E.; Kuo, A.H.; Powers, C.; Bowden, E.T.; Sale, E.B.; Riegel, A.T.; Wellstein, A. Midkine Binds to Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and Acts as a Growth Factor for Different Cell Types. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35990–35998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Viscardi, G.; Di Liello, R.; Fasano, M.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Role and Targeting of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Pao, L.I.; Zhou, A.; Brace, A.D.; Halenbeck, R.; Hsu, A.W.; Bray, T.L.; Hestir, K.; Bosch, E.; Lee, E.; et al. Deorphanization of the Human Leukocyte Tyrosine Kinase (LTK) Receptor by a Signaling Screen of the Extracellular Proteome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15741–15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnyak, A.V.; Murray, P.B.; Shi, X.; Mo, E.S.; Mohanty, J.; Tome, F.; Bai, H.; Gunel, M.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Augmentor α and β (FAM150) Are Ligands of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinases ALK and LTK: Hierarchy and Specificity of Ligand-Receptor Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15862–15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a Kinase Gene, ALK, to a Nucleolar Protein Gene, NPM, in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiota, M.; Fujimoto, J.; Semba, T.; Satoh, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Mori, S. Hyperphosphorylation of a Novel 80 kDa Protein-Tyrosine Kinase Similar to Ltk in a Human Ki-1 Lymphoma Cell Line, AMS3. Oncogene 1994, 9, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.H.; Vernersson, E.; Grabbe, C.; Hallberg, B. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase: Signalling in Development and Disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 420, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzec, M.; Zhang, Q.; Goradia, A.; Raghunath, P.N.; Liu, X.; Paessler, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Wysocka, M.; Cheng, M.; Ruggeri, B.A.; et al. Oncogenic Kinase NPM/ALK Induces through STAT3 Expression of Immunosuppressive Protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20852–20857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaud, C.; Knörr, F.; Brugières, L.; Woessmann, W. Diagnosis and Management of ALK-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2023, 36, 101444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm-Welk, C.; Klapper, W.; Oschlies, I.; Gesk, S.; Röttgers, S.; Bradtke, J.; Siebert, R.; Reiter, A.; Woessmann, W. Distribution of NPM1-ALK and X-ALK Fusion Transcripts in Paediatric Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Molecular–Histological Correlation. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 146, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, C.A.; Hawkins, A.L.; Dvorak, C.; Henkle, C.T.; Ellingham, T.; Perlman, E.J. Recurrent Involvement of 2p23 in Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2776–2780. [Google Scholar]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S. Identification of the Transforming EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global Survey of Phosphotyrosine Signaling Identifies Oncogenic Kinases in Lung Cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirks, W.G.; Fähnrich, S.; Lis, Y.; Becker, E.; MacLeod, R.A.F.; Drexler, H.G. Expression and Functional Analysis of the Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Gene in Tumor Cell Lines. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 100, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, C.; Aigner, A.; Stoica, G.E.; McDonnell, K.; Wellstein, A. Pleiotrophin Signaling through Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Is Rate-Limiting for Glioblastoma Growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14153–14158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carén, H.; Abel, F.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. High Incidence of DNA Mutations and Gene Amplifications of the ALK Gene in Advanced Sporadic Neuroblastoma Tumours. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takita, J. The Role of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Pediatric Cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, J.; Takita, J.; Chen, Y.; Oki, K.; Nishimura, R.; Kato, M.; Sanada, M.; Hiwatari, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Aberrant Activation of ALK Kinase by a Novel Truncated Form ALK Protein in Neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4667–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreenivas, A.; Janku, F.; Gouda, M.A.; Chen, H.-Z.; George, B.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. ALK Fusions in the Pan-Cancer Setting: Another Tumor-Agnostic Target? NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, T.R.; Slavish, J.; George, R.E.; Look, A.T.; Xue, L.; Jiang, Q.; Cui, X.; Rentrop, W.B.; Morris, S.W. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase: Role in Cancer Pathogenesis and Small-Molecule Inhibitor Development for Therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2009, 9, 331–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamant, L.; Pulford, K.; Bischof, D.; Morris, S.W.; Mason, D.Y.; Delsol, G. Expression of the ALK Tyrosine Kinase Gene in Neuroblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Bigerna, B.; Fizzotti, M.; Pulford, K.; Pileri, S.; Delsol, G.; Carbone, A.; Paulli, M.; Magrini, U.; Menestrina, F.; et al. ALK Expression Defines a Distinct Group of T/Null Lymphomas (“ALK Lymphomas”) with a Wide Morphological Spectrum. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cessna, M.H.; Zhou, H.; Sanger, W.G.; Perkins, S.L.; Tripp, S.R.; Pickering, D.L.; Daines, C.; Coffin, C.M. Expression of ALK1 and P80 in Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor and Its Mesenchymal Mimics: A Study of 135 Cases. Mod. Pathol. 2002, 15, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pinera, P.; Chang, Y.; Astudillo, A.; Mortimer, J.E.; Deuel, T.F. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Is Expressed in Different Subtypes of Human Breast Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duijkers, F.A.M.; Gaal, J.; Meijerink, J.P.P.; Admiraal, P.; Pieters, R.; de Krijger, R.R.; van Noesel, M.M. High Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Immunohistochemical Staining in Neuroblastoma and Ganglioneuroblastoma Is an Independent Predictor of Poor Outcome. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Kuick, C.H.; Lim, M.; Yong, M.H.; Lee, C.K.; Low, S.Y.Y.; Low, D.C.Y.; Lim, D.; Soh, S.Y.; Chang, K.T.E. Characterization of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Medulloblastomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 120–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łastowska, M.; Trubicka, J.; Niemira, M.; Paczkowska-Abdulsalam, M.; Karkucińska-Więckowska, A.; Kaleta, M.; Drogosiewicz, M.; Tarasińska, M.; Perek-Polnik, M.; Krętowski, A.; et al. ALK Expression Is a Novel Marker for the WNT-Activated Type of Pediatric Medulloblastoma and an Indicator of Good Prognosis for Patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capper, D.; Reifenberger, G.; French, P.J.; Schweizer, L.; Weller, M.; Touat, M.; Niclou, S.P.; Euskirchen, P.; Haberler, C.; Hegi, M.E.; et al. EANO Guideline on Rational Molecular Testing of Gliomas, Glioneuronal, and Neuronal Tumors in Adults for Targeted Therapy Selection. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiełbowski, K.; Żychowska, J.; Becht, R. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibitors-a Review of Anticancer Properties, Clinical Efficacy, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1285374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.L.; Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. ALK-Positive Lung Cancer: A Moving Target. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Xia, Q.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z. New Perspectives for Targeting Therapy in ALK-Positive Human Cancers. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şeker, A.; Rhoton, A.L. The Anatomy of the Posterior Cranial Fossa. In Posterior Fossa Tumors in Children; Özek, M.M., Cinalli, G., Maixner, W., Sainte-Rose, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 75–99. ISBN 978-3-319-11274-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, A.O.M. New Germline Syndrome with Brainstem Abnormalities and Neuroblastoma, Caused by ALK Mutation. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pontual, L.; Kettaneh, D.; Gordon, C.T.; Oufadem, M.; Boddaert, N.; Lees, M.; Balu, L.; Lachassinne, E.; Petros, A.; Mollet, J.; et al. Germline Gain-of-Function Mutations of ALK Disrupt Central Nervous System Development. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.; Sung, W.-S.; Shaya, M.; Patwardhan, R.; Willis, B.; Smith, D.; Nanda, A. Complications of Posterior Cranial Fossa Surgery--an Institutional Experience of 500 Patients. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emara, M.; Mamdouh, A.-E.; Elmaghrabi, M.M. Surgical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumours: A Benha Experience. Egypt. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 35, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.R.; Wani, M.A.; Kirmani, A.R. Histopathological Pattern and Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumors in Children and Adults—A 20-Year Experience. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2020, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabozzi, F.; Margoni, S.; Andreozzi, B.; Musci, M.S.; Del Baldo, G.; Boccuto, L.; Mastronuzzi, A.; Carai, A. Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome: From Pathophysiology to Rehabilitation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1082947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catsman-Berrevoets, C.; Patay, Z. Cerebellar Mutism Syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 155, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.L.; Leigh, L. Survivors of Pediatric Posterior Fossa Tumors: Cognitive Outcome, Intervention, and Risk-Based Care. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2009, 13, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Yu, Z.-W.; Jiang, T.; Shao, L.-W.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, Y.-F.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.-Y.; Zhang, M.; et al. SNCA, a Novel Biomarker for Group 4 Medulloblastomas, Can Inhibit Tumor Invasion and Induce Apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendsen, J.T.; Ta, R.; Li, J.; Weinberg, O.K.; Ferry, J.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Meredith, D.M.; Varma, H.; Sadigh, S.; Michaels, P.D. Primary Central Nervous System Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma, ALK Positive. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 158, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, N.; Sreelesh, K.P.; Nair, R.; Mathews, A. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Presenting as a Cerebellar Mass. Hematol./Oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 2014, 7, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlioglu, N.; Manepalli, A.; Galindo, L.; Sotelo-Avila, C.; Grosso, L. Primary Ki-1 (Anaplastic Large Cell) Lymphoma of the Brain and Spinal Cord. Am J Clin Pathol 1995, 103, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.P.; Nicolae, A.; Meeker, H.; Raffeld, M.; Xi, L.; Jegalian, A.G.; Miller, D.C.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. Primary CNS T-Cell Lymphomas: A Clinical, Morphologic, Immunophenotypic, and Molecular Analysis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudresha, A.H.; Chaudhuri, T.; Lakshmaiah, K.C.; Babu, G.; Lokesh, K.N.; Rajeev, L.K. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma in Immunocompetent Patients: A Regional Cancer Center Experience. South Asian J Cancer 2017, 06, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, C.; Sagatys, E.M. Primary Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma of the CNS as Initial Presentation of HIV Infection: A Case Report. Hum. Pathol. Case Rep. 2021, 24, 200513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, K.; Furuta, T.; Komaki, S.; Yoshikane, Y.; Kikuchi, J.; Nakamura, H.; Ide, M.; Shima, S.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Araki, J.; et al. Systemic Inflammation Caused by an Intracranial Mesenchymal Tumor with a EWSR1::CREM Fusion Presenting Associated with IL -6/STAT3 Signaling. Neuropathology 2023, 43, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, A.; Kuwamoto, S.; Shimizu, T.; Amisaki, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Inagaki, H.; Kurosaki, M. A Case of Intracranial Myxoid Mesenchymal Tumor with EWSR1:CREM Fusion in an Adult Female: Extensive Immunohistochemical Evaluation. Neuropathology 2021, 41, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemps, P.G.; Picarsic, J.; Durham, B.H.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Hiemcke-Jiwa, L.; van den Bos, C.; van de Wetering, M.D.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; van Laar, J.A.M.; Verdijk, R.M.; et al. ALK-Positive Histiocytosis: A New Clinicopathologic Spectrum Highlighting Neurologic Involvement and Responses to ALK Inhibition. Blood 2022, 139, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.G.; Gilani, A.; Solomon, D.A.; Liang, X.; Maher, O.M.; Chamyan, G.; Kleinschmidt-Demasters, B.K.; Perry, A. ALK-Positive Histiocytosis with KIF5B-ALK Fusion in the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, R.S.; Tihan, T.; Horvai, A.E.; Di Vizio, D.; Loda, M.; Burger, P.C.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kim, G.E. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Central Nervous System and Its Relationship to Inflammatory Pseudotumor. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, S.; De Mariano, M.; Valdora, F.; Servidei, T.; Ridola, V.; Andolfo, I.; Oberthuer, A.; Tonini, G.P.; Longo, L. Identification of ALK Germline Mutation (3605delG) in Pediatric Anaplastic Medulloblastoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łastowska, M.; Trubicka, J.; Karkucińska-Więckowska, A.; Kaleta, M.; Tarasińska, M.; Perek-Polnik, M.; Sobocińska, A.A.; Dembowska-Bagińska, B.; Grajkowska, W.; Matyja, E. Immunohistochemical Detection of ALK Protein Identifies APC Mutated Medulloblastoma and Differentiates the WNT-Activated Medulloblastoma from Other Types of Posterior Fossa Childhood Tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2019, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubicka, J.; Szperl, M.; Grajkowska, W.; Karkucińska-Więckowska, A.; Tarasińska, M.; Falana, K.; Dembowska-Bagińska, B.; Łastowska, M. Identification of a Novel Inherited ALK Variant M1199L in the WNT Type of Medulloblastoma. Folia Neuropathol. 2016, 54, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Dasgupta, A.; Shirsat, N.; Epari, S.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Gupta, T. WNT-Pathway Medulloblastoma: What Constitutes Low-Risk and How Low Can One Go? Oncotarget 2023, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mynarek, M.; Milde, T.; Padovani, L.; Janssens, G.O.; Kwiecien, R.; Mosseri, V.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Rutkowski, S. SIOP PNET5 MB Trial: History and Concept of a Molecularly Stratified Clinical Trial of Risk-Adapted Therapies for Standard-Risk Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Aubart, F.; Idbaih, A.; Emile, J.-F.; Amoura, Z.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Durham, B.H.; Haroche, J.; Diamond, E.L. Histiocytosis and the Nervous System: From Diagnosis to Targeted Therapies. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroche, J.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Rollins, B.J.; Donadieu, J.; Charlotte, F.; Idbaih, A.; Vaglio, A.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Emile, J.-F.; Amoura, Z. Histiocytoses: Emerging Neoplasia behind Inflammation. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e113–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emile, J.-F.; Cohen-Aubart, F.; Collin, M.; Fraitag, S.; Idbaih, A.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Rollins, B.J.; Donadieu, J.; Haroche, J. Histiocytosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersey, Z.C.; Zheng, I.; Bregy, A.; Agarwal, N.; Komotar, R.J. Intracranial Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: A Review. Interdiscip. Neurosurg. 2020, 21, 100729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.; Naushahi, M.; Bernard, A.; Campbell, R. Epidemiology of Paediatric Central Nervous System Tumours in Queensland, Australia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 92, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Wen, Y.; Pan, Z.; Lian, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; et al. Systemic Juvenile Xanthogranuloma Has a Higher Frequency of ALK Translocations than BRAFV600E Mutations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullangi, S.; Lekkala, M.R. CNS Lymphoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Grommes, C.; DeAngelis, L.M. Primary CNS Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseb, H.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R.; Rajasurya, V. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Berge, R.; Oudejans, J.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Pulford, K.; Willemze, R.; Falini, B.; Chott, A.; Meijer, C. ALK Expression in Extranodal Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Favours Systemic Disease with (Primary) Nodal Involvement and a Good Prognosis and Occurs before Dissemination. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 53, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumerai, J.D.; Rosenthal, A.; Harkins, S.; Duffy, J.; Mecca, C.; Wang, Y.; Grewal, R.K.; El-Jawahri, A.R.; Liu, H.; Menard, C.; et al. Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Are Highly Active in ALK-Positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkizilkaya, H.I.; Johnson, J.M.; O’Brien, B.J.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Prabhu, S.S.; Ghia, A.J.; Fuller, G.N.; Huse, J.T.; Ballester, L.Y. Intracranial Mesenchymal Tumor, FET::CREB Fusion-Positive in the Lateral Ventricle. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, E.A.; Chiang, J.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Alexandrescu, S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Wang, W.; Mafra, M.; Ud Din, N.; Carr-Boyd, E.; Watson, M.; et al. Intracranial Mesenchymal Tumor with FET-CREB Fusion—A Unifying Diagnosis for the Spectrum of Intracranial Myxoid Mesenchymal Tumors and Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma-like Neoplasms. Brain Pathol. 2021, 31, e12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Nozaki, Y.; Kohashi, K.; Kinoshita, I.; Oda, Y. Diagnostic Utility of Pan-Trk Immunohistochemistry for Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumours. Histopathology 2020, 76, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, L.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Jones, R.L.; Digklia, A. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour: State of the Art. Cancers 2022, 14, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Chang, K.-H.; Suh, Y.-L.; Jung, H.W.; Park, S.-H. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Central Nervous System: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 10 Cases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clarke, A.J.; Jacques, T.S.; Galloway, M.J.; Thom, M.; Kitchen, N.D.; Plant, G.T. ALK Positive Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumour of the Pineal Region. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 58, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoste-Collin, L.; Roux, F.-E.; Gomez-Brouchet, A.; Despeyroux, M.-L.; Uro-Coste, E.; Coindre, J.-M.; Delisle, M.-B. Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor: A Spinal Case with Aggressive Clinical Course and ALK Overexpression. Case Report. J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, A.D.J.; Barry, E.; Mossé, Y.P.; Ligas, F.; Bird, N.; de Rojas, T.; Zimmerman, Z.F.; Wilner, K.; Woessmann, W.; Weiner, S.; et al. Second Paediatric Strategy Forum for Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibition in Paediatric Malignancies: ACCELERATE in Collaboration with the European Medicines Agency with the Participation of the Food and Drug Administration. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöffski, P.; Sufliarsky, J.; Gelderblom, H.; Blay, J.-Y.; Strauss, S.J.; Stacchiotti, S.; Rutkowski, P.; Lindner, L.H.; Leahy, M.G.; Italiano, A.; et al. Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced, Inoperable Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumours with and without Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Gene Alterations (European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer 90101 CREATE): A Multicentre, Single-Drug, Prospective, Non-Randomised Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennouf, A.; Arslanian, E.; Roberge, D.; Berthelet, F.; Bojanowski, M.; Bahary, J.-P.; Masucci, L.; Belanger, K.; Florescu, M.; Wong, P. Efficiency of Crizotinib on an ALK-Positive Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Central Nervous System: A Case Report. Cureus 2017, 9, e1068. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-Line Crizotinib versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesinger, F.; Roeper, J.; Pöttgen, C.; Willborn, K.C.; Eberhardt, W.E.E. Brain Metastases in ALK-Positive NSCLC—Time to Adjust Current Treatment Algorithms. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35181–35194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgeel, S.; Peters, S.; Mok, T.; Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Pérol, M.; Wrona, A.; Novello, S.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Treatment-Naive Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive (ALK+) Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: CNS Efficacy Results from the ALEX Study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokihara, H.; Hida, T.; Kondo, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Azuma, K.; Seto, T.; Takiguchi, Y.; Nishio, M.; Yoshioka, H.; Imamura, F.; et al. Alectinib (ALC) versus Crizotinib (CRZ) in ALK-Inhibitor Naive ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ALK+ NSCLC): Primary Results from the J-ALEX Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Ahn, J.S.; De Petris, L.; Govindan, R.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Hughes, B.; Lena, H.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Bearz, A.; Ramirez, S.V.; et al. Alectinib in Crizotinib-Refractory ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase II Global Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Gandhi, L.; Gadgeel, S.; Riely, G.J.; Cetnar, J.; West, H.; Camidge, D.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Chiappori, A.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Alectinib in ALK-Positive, Crizotinib-Resistant, Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Group, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, S.; Mazières, J.; Oh, I.-J.; de Castro, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; Helland, Å.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Griesinger, F.; Kotb, A.; Zeaiter, A.; et al. Alectinib versus Chemotherapy in Crizotinib-Pretreated Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase III ALUR Study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.Y.; Friboulet, L.; Kodack, D.P.; Engstrom, L.D.; Li, Q.; West, M.; Tang, R.W.; Wang, H.; Tsaparikos, K.; Wang, J.; et al. PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 Inhibitor, Overcomes Resistance to 1st and 2nd Generation ALK Inhibitors in Pre-Clinical Models. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.W.; Richardson, P.F.; Bailey, S.; Brooun, A.; Burke, B.J.; Collins, M.R.; Cui, J.J.; Deal, J.G.; Deng, Y.-L.; Dinh, D.; et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-Amino-12-Fluoro-2,10,16-Trimethyl-15-Oxo-10,15,16,17-Tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(Metheno)Pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-Benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-Carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a Macrocyclic Inhibitor of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) and c-Ros Oncogene 1 (ROS1) with Preclinical Brain Exposure and Broad-Spectrum Potency against ALK-Resistant Mutations. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4720–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Bauer, T.M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Liu, G.; Mazieres, J.; de Marinis, F.; Goto, Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Jassem, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Lorlatinib versus Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced, ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Analysis of Data from the Phase 3, Randomised, Open-Label CROWN Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.M.; Shaw, A.T.; Johnson, M.L.; Navarro, A.; Gainor, J.F.; Thurm, H.; Pithavala, Y.K.; Abbattista, A.; Peltz, G.; Felip, E. Brain Penetration of Lorlatinib: Cumulative Incidences of CNS and Non-CNS Progression with Lorlatinib in Patients with Previously Treated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Target Oncol. 2020, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mousa, D.-P.V.; Mavrovounis, G.; Argyropoulos, D.; Stranjalis, G.; Kalamatianos, T. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers 2024, 16, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030650
Mousa D-PV, Mavrovounis G, Argyropoulos D, Stranjalis G, Kalamatianos T. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers. 2024; 16(3):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030650
Chicago/Turabian StyleMousa, Danai-Priskila V., Georgios Mavrovounis, Dionysios Argyropoulos, George Stranjalis, and Theodosis Kalamatianos. 2024. "Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives" Cancers 16, no. 3: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030650
APA StyleMousa, D.-P. V., Mavrovounis, G., Argyropoulos, D., Stranjalis, G., & Kalamatianos, T. (2024). Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Posterior Cranial Fossa Tumors: A Scoping Review of Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cancers, 16(3), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030650








