The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Immunotherapy, Generalities, and Toxicity: The Dimensions That Matter
3. Clinical Evidence Concerning JAK-STAT Inhibitors and ICI Colitis
3.1. JAK Inhibitors: Generality and Classification
3.2. Contemporary Management in Accordance with Established Guidelines and Exploration of Giverse Alternatives, with Limited Emphasis on JAK Inhibitors
3.3. Navigating the Landscape: Unveiling Clinical Evidence from Pioneering Experiences to Ongoing Studies in JAK-STAT Pathway Inhibition for ICI Colitis
3.4. The Hyperactivation of T Cells as a Potential Therapeutic Target for JAK Inhibitors: General Overview with a Focus on CD8+ Resident Memory T Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Z.; Wang, Y. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Diarrhea and Colitis: A Clinical Review. JCO Oncol. Prac. 2020, 16, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Marshall, J.L.; He, A.R. Workup and Management of Immune-Mediated Colitis in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Oncologist 2020, 25, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macovei Oprescu, A.; Tulin, R.; Slavu, I.; Venter, D.P.; Oprescu, C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Gastrointestinal Toxicity: The Opinion of a Gastroenterologist. Cureus 2021, 13, e19945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, D.; Läubli, H. Mechanisms of Immune-Related Complications in Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer Immunotherapy Using Checkpoint Blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Som, A.; Mandaliya, R.; Alsaadi, D.; Farshidpour, M.; Charabaty, A.; Malhotra, N.; Mattar, M.C. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Comprehensive Review. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Sbeih, H.; Ali, F.S.; Luo, W.; Qiao, W.; Raju, G.S.; Wang, Y. Importance of Endoscopic and Histological Evaluation in the Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashash, J.G.; Francis, F.F.; Farraye, F.A. Diagnosis and Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 17, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaji, U.N.; Jeffery, L.; Gui, X.; Smith, S.C.L.; Ahmad, O.F.; Akbar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Iacucci, M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Adverse Events and Their Management. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819884196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Sbeih, H.; Wang, Y. Management Considerations for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Enterocolitis Based on Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portenkirchner, C.; Kienle, P.; Horisberger, K. Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis-A Clinical Overview of Incidence, Prognostic Implications and Extension of Current Treatment Options. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, M.; Blidner, A.G.; Choi, J.; Cooksley, T.; Glezerman, I.; Ginex, P.; Girotra, M.; Gupta, D.; Johnson, D.; Shannon, V.R.; et al. Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) 2020 Clinical Practice Recommendations for the Management of Severe Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Toxicities from Checkpoint Inhibitors. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 6129–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, M.; Wang, Y.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; Lim, J.K. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Diagnosis and Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis and Hepatitis: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, N.; Ibraheim, H.; Raine, T.; Speight, R.A.; Papa, S.; Brain, O.; Green, M.; Samaan, M.A.; Spain, L.; Yousaf, N.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology Endorsed Guidance for the Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Enterocolitis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.B.a.G.; Carbonnel, F.; Robert, C.; Kerr, K.M.; Peters, S.; Larkin, J.; Jordan, K. ESMO Guidelines Committee Management of Toxicities from Immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv119–iv142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.; Obeid, M.; Spain, L.; Carbonnel, F.; Wang, Y.; Robert, C.; Lyon, A.R.; Wick, W.; Kostine, M.; Peters, S.; et al. Management of Toxicities from Immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, M.J.; Teng, M.W. 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2018, 7, e1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljunggren, H.; Jonsson, R.; Höglund, P. Seminal Immunologic Discoveries with Direct Clinical Implications: The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine Honours Discoveries in Cancer Immunotherapy. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 88, e12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Coillie, S.; Wiernicki, B.; Xu, J. Molecular and Cellular Functions of CTLA-4. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1248, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, P.S.; Greene, J.L.; Brady, W.; Bajorath, J.; Ledbetter, J.A.; Peach, R. Human B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) Bind with Similar Avidities but Distinct Kinetics to CD28 and CTLA-4 Receptors. Immunity 1994, 1, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, P.S.; Brady, W.; Urnes, M.; Grosmaire, L.S.; Damle, N.K.; Ledbetter, J.A. CTLA-4 Is a Second Receptor for the B Cell Activation Antigen B7. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chai, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, C.W.H.; Tong, Z.; Shi, Y.; Yan, J.; Tan, S.; Gao, G.F. Remarkably Similar CTLA-4 Binding Properties of Therapeutic Ipilimumab and Tremelimumab Antibodies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67129–67139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaab, H.O.; Sau, S.; Alzhrani, R.; Tatiparti, K.; Bhise, K.; Kashaw, S.K.; Iyer, A.K. PD-1 and PD-L1 Checkpoint Signaling Inhibition for Cancer Immunotherapy: Mechanism, Combinations, and Clinical Outcome. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finger, L.R.; Pu, J.; Wasserman, R.; Vibhakar, R.; Louie, E.; Hardy, R.R.; Burrows, P.D.; Billips, L.G. The Human PD-1 Gene: Complete cDNA, Genomic Organization, and Developmentally Regulated Expression in B Cell Progenitors. Gene 1997, 197, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, G.; Laurence, A.; Amarnath, S. Programmed Cell Death-1 Receptor (PD-1)-Mediated Regulation of Innate Lymphoid Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, C.; Luong, G.; Sun, Y. A Snapshot of the PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 2735–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Current Researches in Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Iwai, Y.; Hamanishi, J.; Chamoto, K.; Honjo, T. Cancer Immunotherapies Targeting the PD-1 Signaling Pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, Y.; Ajani, J.A.; Kato, K.; Xu, J.; Wyrwicz, L.; Motoyama, S.; Ogata, T.; Kawakami, H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Adenis, A.; et al. Nivolumab Combination Therapy in Advanced Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone Versus Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castria, T.B.; Khalil, D.N.; Harding, J.J.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Abou-Alfa, G.K. Tremelimumab and Durvalumab in the Treatment of Unresectable, Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 3769–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, E.P.; Mooradian, M.J.; Baruch, E.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Reynolds, K.L. Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs): Diagnosis, Management, and Clinical Pearls. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, G.; Helmink, B.A.; Sharma, P.; Wargo, J.A. Hallmarks of Response, Resistance, and Toxicity to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cell 2021, 184, 5309–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Di Nucci, F.; Kwan, A.; Hammer, C.; Mariathasan, S.; Rouilly, V.; Carroll, J.; Fontes, M.; Ley Acosta, S.; Guardino, E.; et al. Polygenic Risk for Skin Autoimmunity Impacts Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Bladder Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12288–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Ding, Y.; He, J.; Wu, J. Risk of Colitis in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and in Chemotherapy/Placebo for Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 4173–4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Elias, R.; Peng, L.; Levonyak, N.; Asokan, A.; Christie, A.; Kubiliun, N.; Brugarolas, J.; Hammers, H.J. Chronic Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleiman, J.; Wei, W.; Shah, R.; Faisal, M.S.; Philpott, J.; Funchain, P. Incidence of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Diarrhea and Colitis (imDC) in Patients with Cancer and Preexisting Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Propensity Score-Matched Retrospective Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kieltyka, J.; Fleischmann, R.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. A Decade of JAK Inhibitors: What Have We Learned and What May Be the Future? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLornan, D.P.; Pope, J.E.; Gotlib, J.; Harrison, C.N. Current and Future Status of JAK Inhibitors. Lancet 2021, 398, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsky, W.; King, B.A. JAK Inhibitors in Dermatology: The Promise of a New Drug Class. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, H. JAK Inhibitors∼Overview∼. Immunol. Med. 2023, 46, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benucci, M.; Damiani, A.; Infantino, M.; Manfredi, M.; Lari, B.; Grossi, V.; Gobbi, F.L.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Cardiovascular Safety, Cancer and Jak-Inhibitors: Differences to Be Highlighted. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzik, T.; Ellul, P.; Greuter, T.; Rahier, J.F.; Verstockt, B.; Abreu, C.; Albuquerque, A.; Allocca, M.; Esteve, M.; Farraye, F.A.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management of Infections in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 879–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winthrop, K.L.; Cohen, S.B. Oral Surveillance and JAK Inhibitor Safety: The Theory of Relativity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, M.; Migliorisi, G.; Dal Buono, A.; Gabbiadini, R.; Mastrorocco, E.; Quadarella, A.; Repici, A.; Santoro, A.; Armuzzi, A. Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: From Pathogenesis to Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, Z.-Y.; Arslan, M.E.; Cho, D.; Lee, H. Differential Diagnosis and Management of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Comprehensive Review. World J. Exp. Med. 2021, 11, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feakins, R.; Torres, J.; Borralho-Nunes, P.; Burisch, J.; Cúrdia Gonçalves, T.; De Ridder, L.; Driessen, A.; Lobatón, T.; Menchén, L.; Mookhoek, A.; et al. ECCO Topical Review on Clinicopathological Spectrum and Differential Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Su, C.; Sands, B.E.; D’Haens, G.R.; Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Danese, S.; Feagan, B.G.; Reinisch, W.; Niezychowski, W.; et al. Tofacitinib as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, T.; Bonovas, S.; Burisch, J.; Kucharzik, T.; Adamina, M.; Annese, V.; Bachmann, O.; Bettenworth, D.; Chaparro, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Ghosh, S.; Panes, J.; Schreiber, S.; D’Haens, G.; Tanida, S.; Siffledeen, J.; Enejosa, J.; Zhou, W.; Othman, A.A.; et al. Efficacy of Upadacitinib in a Randomized Trial of Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2139–2149.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Vermeire, S.; Zhou, W.; Pangan, A.L.; Siffledeen, J.; Greenbloom, S.; Hébuterne, X.; D’Haens, G.; Nakase, H.; Panés, J.; et al. Upadacitinib as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results from Three Phase 3, Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised Trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 2113–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feagan, B.G.; Danese, S.; Loftus, E.V.; Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Ritter, T.; Fogel, R.; Mehta, R.; Nijhawan, S.; Kempiński, R.; et al. Filgotinib as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis (SELECTION): A Phase 2b/3 Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2372–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, E.V.; Panés, J.; Lacerda, A.P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; D’Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Reinisch, W.; Louis, E.; Chen, M.; Nakase, H.; et al. Upadacitinib Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1966–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Feagan, B.G.; Loftus, E.V.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Van Assche, G.; D’Haens, G.; Schreiber, S.; Colombel, J.-F.; Lewis, J.D.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in a Randomized Trial of Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2123–2138.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Petryka, R.; Kuehbacher, T.; Hebuterne, X.; Roblin, X.; Klopocka, M.; Goldis, A.; Wisniewska-Jarosinska, M.; Baranovsky, A.; et al. Clinical Remission in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease Treated with Filgotinib (the FITZROY Study): Results from a Phase 2, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.; Gamelas, V.; Saraiva, R.; Simões, G.; Saiote, J.; Ramos, J. Tofacitinib: An Option for Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis? GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 29, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenholdt, C.; Dige Ovesen, P.; Brynskov, J.; Benedict Seidelin, J. Tofacitinib for Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review. J. Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P.; García, M.J.; Chaparro, M. Rescue Therapies for Steroid-Refractory Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Review. J. Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 972–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, C.A.; Kennedy, N.A.; Raine, T.; Hendy, P.A.; Smith, P.J.; Limdi, J.K.; Hayee, B.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Parkes, G.C.; Selinger, C.; et al. British Society of Gastroenterology Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Adults. Gut 2019, 68, s1–s106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, A.S.; Andersen, M.N.; Juul-Madsen, K.; Broksø, A.D.; Skejø, C.; Schmidt, H.; Vorup-Jensen, T.; Kragstrup, T.W. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Neutralization Attenuates Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Activation of Intermediate Monocytes in Synovial Fluid Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, N.; Miyoshi, K.; Morichika, D.; Beika, Y.; Taki, T.; Mitani, R.; Okada, T.; Takata, I. Successful Treatment of Critical Coronavirus Disease 2019 in a Patient with Lung Cancer Concomitant with Pembrolizumab-Induced Arthritis by Methylprednisolone, Baricitinib, and Remdesivir. Clin. Case Rep. 2021, 9, e04459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, T.Z.; Adel, N.G.; Dang, T.-O.; Momtaz, P.; Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Carvajal, R.D.; Dickson, M.A.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Woo, K.M.; et al. Immune-Related Adverse Events, Need for Systemic Immunosuppression, and Effects on Survival and Time to Treatment Failure in Patients with Melanoma Treated with Ipilimumab at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3193–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Sbeih, H.; Ali, F.S.; Alsaadi, D.; Jennings, J.; Luo, W.; Gong, Z.; Richards, D.M.; Charabaty, A.; Wang, Y. Outcomes of Vedolizumab Therapy in Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Multi-Center Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.L.; Juhl, C.B.; Chen, I.M.; Kellermann, L.; Nielsen, O.H. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Diarrhea and Colitis: Incidence and Management. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 109, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Del Nogal, G.; Patel, N. Refractory Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis Responsive to Ustekinumab. ACG Case Rep. J. 2022, 9, e00946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.S.; Ma, W.; Wang, Y. Ustekinumab for Refractory Colitis Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirwaikar Thomas, A.; Lee, S.E.; Shatila, M.; De Toni, E.N.; Török, H.-P.; Ben Khaled, N.; Powell, N.; Weight, R.; Faleck, D.M.; Wang, Y. IL12/23 Blockade for Refractory Immune-Mediated Colitis: 2-Center Experience. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gordón Sánchez, F.M.; Gómez-Domínguez, E.; Paredes Ruiz, D.; Rodríguez Gil, Y.; Martín Algíbez, A.; Fernández Vázquez, I.; Martínez Montiel, P. Ustekinumab for Corticodependent Immune-Mediated Colitis by Pembrolizumab, an Alternative for Patients with Concomitant Liver Injury. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2022, 114, 356–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishu, S.; Melia, J.; Sharfman, W.; Lao, C.D.; Fecher, L.A.; Higgins, P.D.R. Efficacy and Outcome of Tofacitinib in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 932–934.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.; Hudson, M.; Batist, G. Tofacitinib for Refractory Immune-Related Colitis from PD-1 Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2374–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasson, S.C.; Slevin, S.M.; Cheung, V.T.F.; Nassiri, I.; Olsson-Brown, A.; Fryer, E.; Ferreira, R.C.; Trzupek, D.; Gupta, T.; Al-Hillawi, L.; et al. Interferon-Gamma–Producing CD8+ Tissue Resident Memory T Cells Are a Targetable Hallmark of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Colitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1229–1244.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstroem, R.B.; Dahl, E.K.; Helms, M.; Nielsen, H.V.; Andersen, J.B.; Bjerrum, J.T.; Svane, I.M.; Ellebaek, E.; Seidelin, J.B. Tofacitinib and Faecal Microbiota Transplantation in Treating Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Enterocolitis: Case Report. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweep, M.W.D.; Tjan, M.J.H.; Gorris, M.A.J.; Bol, K.F.; Westdorp, H. Case Report: A Severe Case of Immunosuppressant-Refractory Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Mediated Colitis Rescued by Tofacitinib. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1212432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleiman, J.; Brand, R.M.; Pai, R.; Brand, R.E.; Rhee, J.; Schwartz, M.; Davar, D. Mirroring UC Care Pathways in Refractory Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (ICI)-Mediated Colitis: Distinct Features and Common Pathways. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 16, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaguarda, E.; Hanauer, S. Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100A8/A9 in Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Okabe, M.; Kimura, Y.; Itoh, H.; Ikemoto, M. Serum S100A8/A9 as a Potentially Sensitive Biomarker for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Lab. Med. 2019, 50, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, A.J.; Mondal, A.; Dey, S.; Prendergast, G.C. IDO1 and Inflammatory Neovascularization: Bringing New Blood to Tumor-Promoting Inflammation. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1165298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.E.; Sun, L. Targeting the IDO1/TDO2-KYN-AhR Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy—Challenges and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoma, A.M.; Suo, S.; Williams, H.L.; Sharova, T.; Sullivan, K.; Manos, M.; Bowling, P.; Hodi, F.S.; Rahma, O.; Sullivan, R.J.; et al. Molecular Pathways of Colon Inflammation Induced by Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2020, 182, 655–671.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zu, L.; Cheng, G.; Hao, M.; Sun, X.; Xue, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. CXCL16/CXCR6 Chemokine Signaling Mediates Breast Cancer Progression by pERK1/2-Dependent Mechanisms. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14165–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esensten, J.H.; Helou, Y.A.; Chopra, G.; Weiss, A.; Bluestone, J.A. CD28 Costimulation: From Mechanism to Therapy. Immunity 2016, 44, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gong, R.; Zhao, C.; Lei, K.; Sun, X.; Ren, H. Human FOXP3 and Tumour Microenvironment. Immunology 2023, 168, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, B.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R. Tumor-Induced Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 Inhibits Toll-like Receptor 3 Signaling in Dendritic Cells via Binding to Tyrosine Kinase 2. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, Y.; Nakajima, H.; Suto, A.; Shimoda, K.; Saito, Y.; Nakayama, K.I.; Iwamoto, I. Enhanced Th2 Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation in Tyk2-Deficient Mice. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
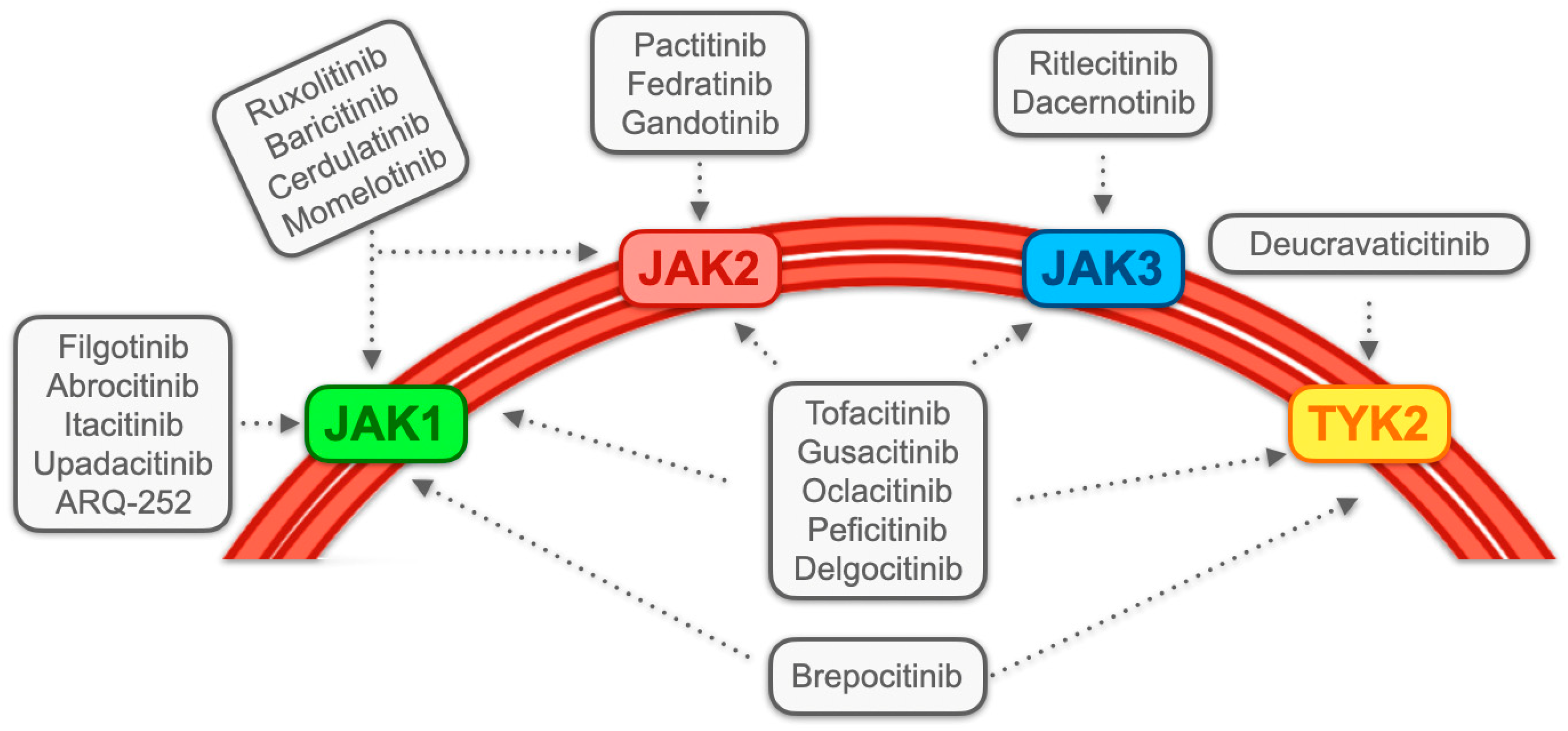
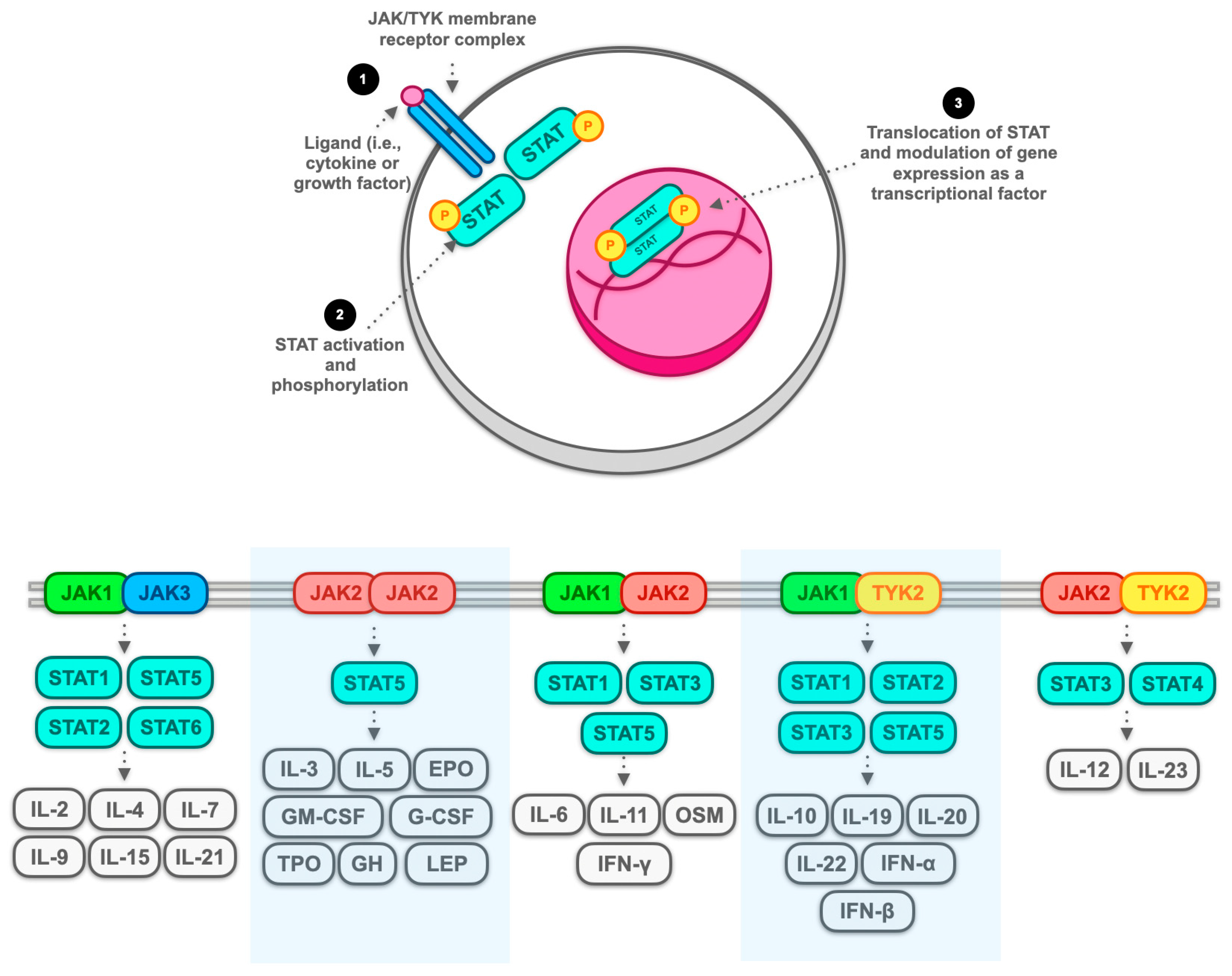

| First Author, Year, Reference | N. | Study Type | JAK Inhibitor | Cancer Treated (N.) | ICI Employed (N.) | ICI Colitis Outcome | Cancer Outcome (N.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esfahani et al., 2020 [73] | 1 | CR | Tofacitinib | Gastric cancer | Pembrolizumab | ICI colitis steroid-free remission | Cancer response |
| Bishu et al., 2020 [72] | 4 | CS | Tofacitinib | Melanoma (3); lung adenocarcinoma (1) | Ipilimumab/nivolumab (3); pembrolizumab/indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitor (1) | ICI colitis steroid-free remission | Cancer response (3); cancer progression (1). |
| Sasson et al., 2021 [74] | 1 | CR | Tofacitinib | Lung non-small-cell carcinoma | Carboplatin/pemetrexed and pembrolizumab | ICI colitis steroid-free remission | No mention concerning cancer response interference of tofacitinib |
| Holmstroem et al., 2022 [75] | 1 | CR | Tofacitinib plus FMT | Melanoma | Ipilimumab/nivolumab | ICI colitis remission | Cancer progression |
| Sweep et al., 2023 [76] | 1 | CR | Tofacitinib | Melanoma | Ipilimumab/nivolumab | Cancer response | |
| Sleiman et al., 2023 [77] | 1 | CR | Tofacitinib | Colonic adenocarcinoma | Ipilimumab/nivolumab | ICI colitis steroid-free remission | Cancer response |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Esposito, A.; Cipullo, M.; Romeo, M.; Palladino, G.; Iodice, P.; Federico, A.; Troiani, T. The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030611
Gravina AG, Pellegrino R, Esposito A, Cipullo M, Romeo M, Palladino G, Iodice P, Federico A, Troiani T. The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review. Cancers. 2024; 16(3):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030611
Chicago/Turabian StyleGravina, Antonietta Gerarda, Raffaele Pellegrino, Alfonso Esposito, Marina Cipullo, Mario Romeo, Giovanna Palladino, Patrizia Iodice, Alessandro Federico, and Teresa Troiani. 2024. "The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review" Cancers 16, no. 3: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030611
APA StyleGravina, A. G., Pellegrino, R., Esposito, A., Cipullo, M., Romeo, M., Palladino, G., Iodice, P., Federico, A., & Troiani, T. (2024). The JAK-STAT Pathway as a Therapeutic Strategy in Cancer Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Colitis: A Narrative Review. Cancers, 16(3), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030611









