The Cross-Scale Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features in Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC Patients: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Description of Cohorts
2.2. Clinical and Biological Endpoints
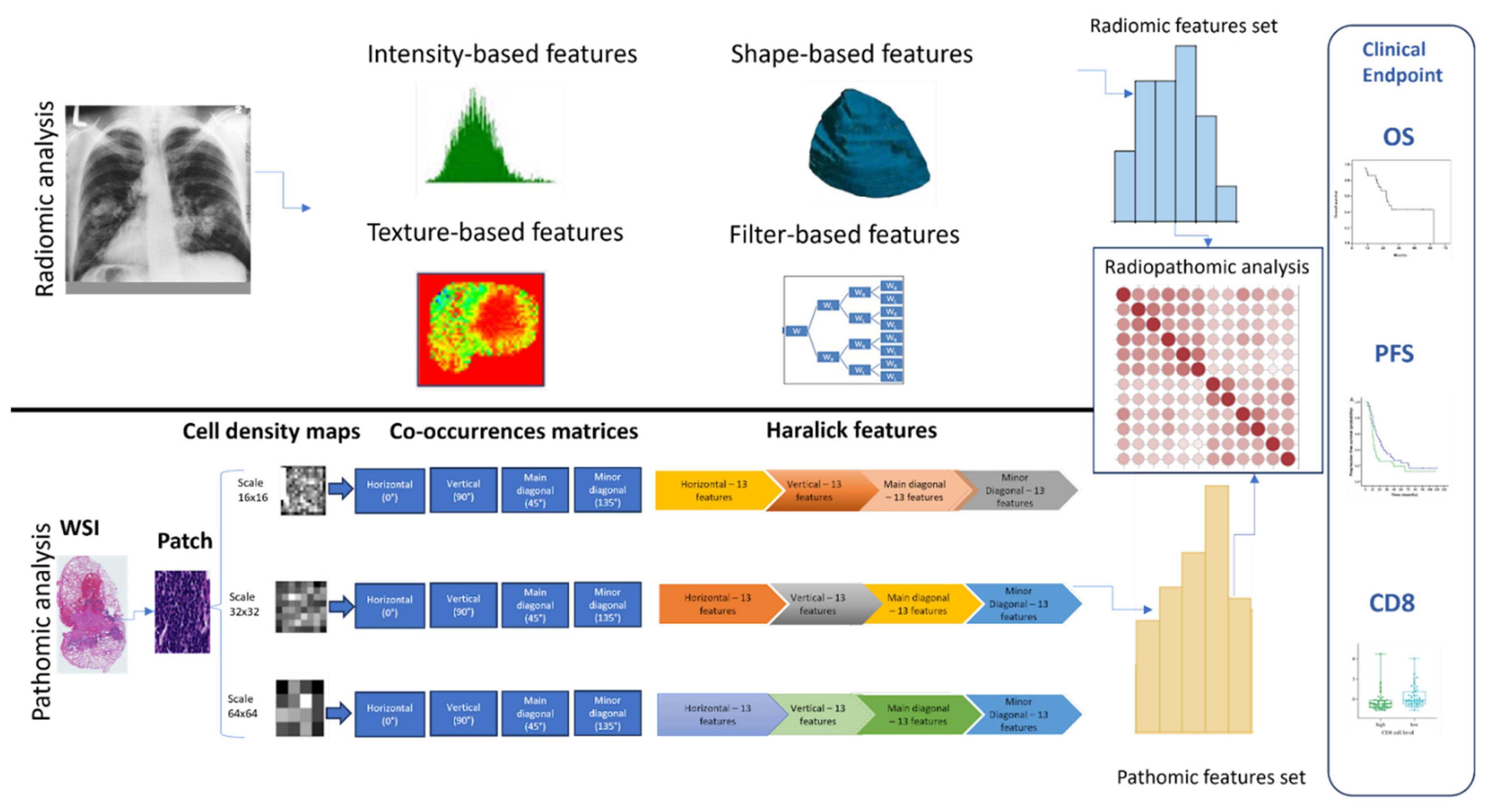
2.3. Radiomics Features Analysis
2.4. Whole Slide Image (WSI) Pre-Processing
2.5. WSI Segmentation and Patching
2.6. Extraction of Pathomics Features
2.7. Radiopathomics Analysis
2.8. Feature Reduction Analysis
2.9. Hierarchical Clustering of Features
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Feature Extraction and Reduction
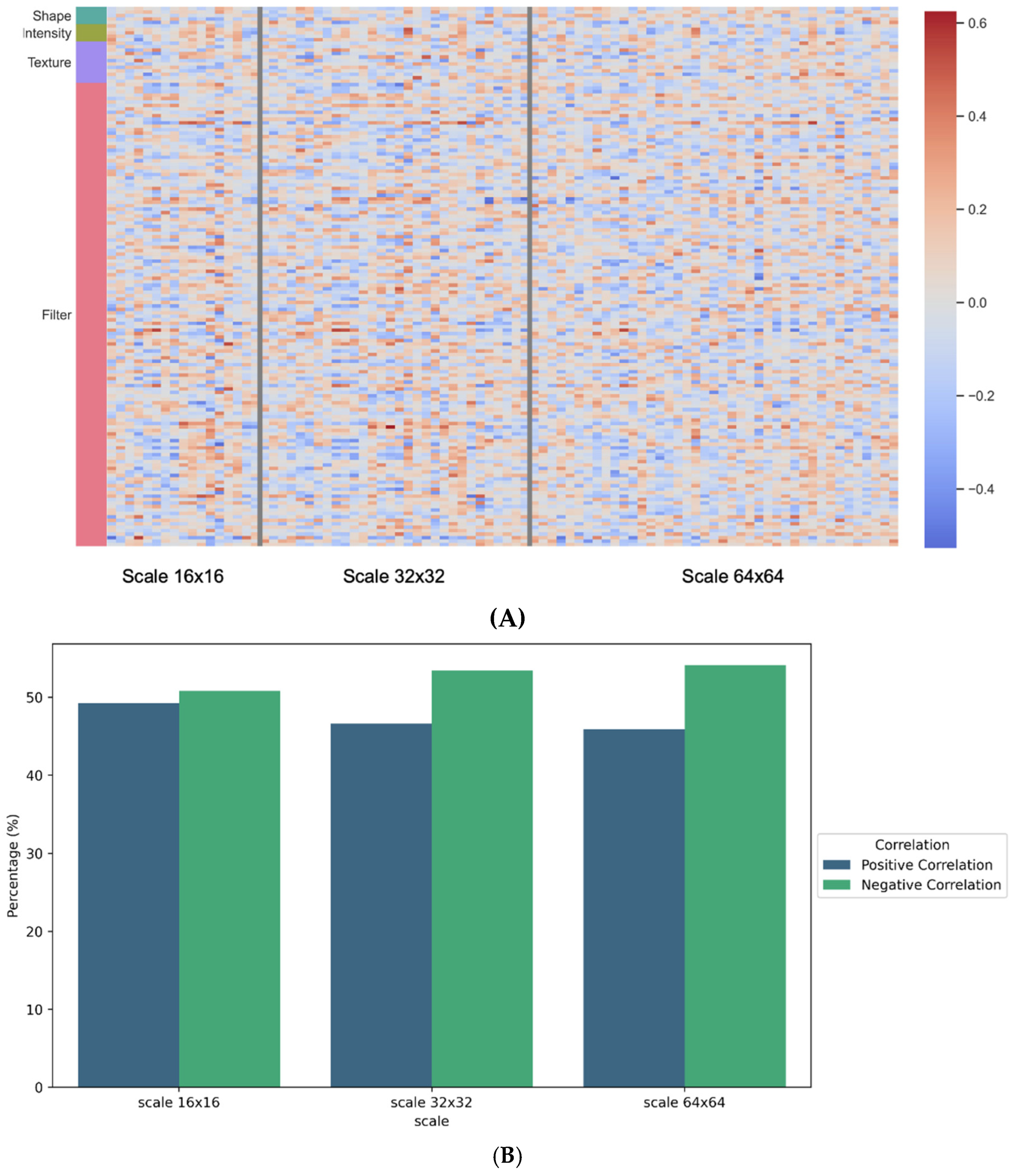
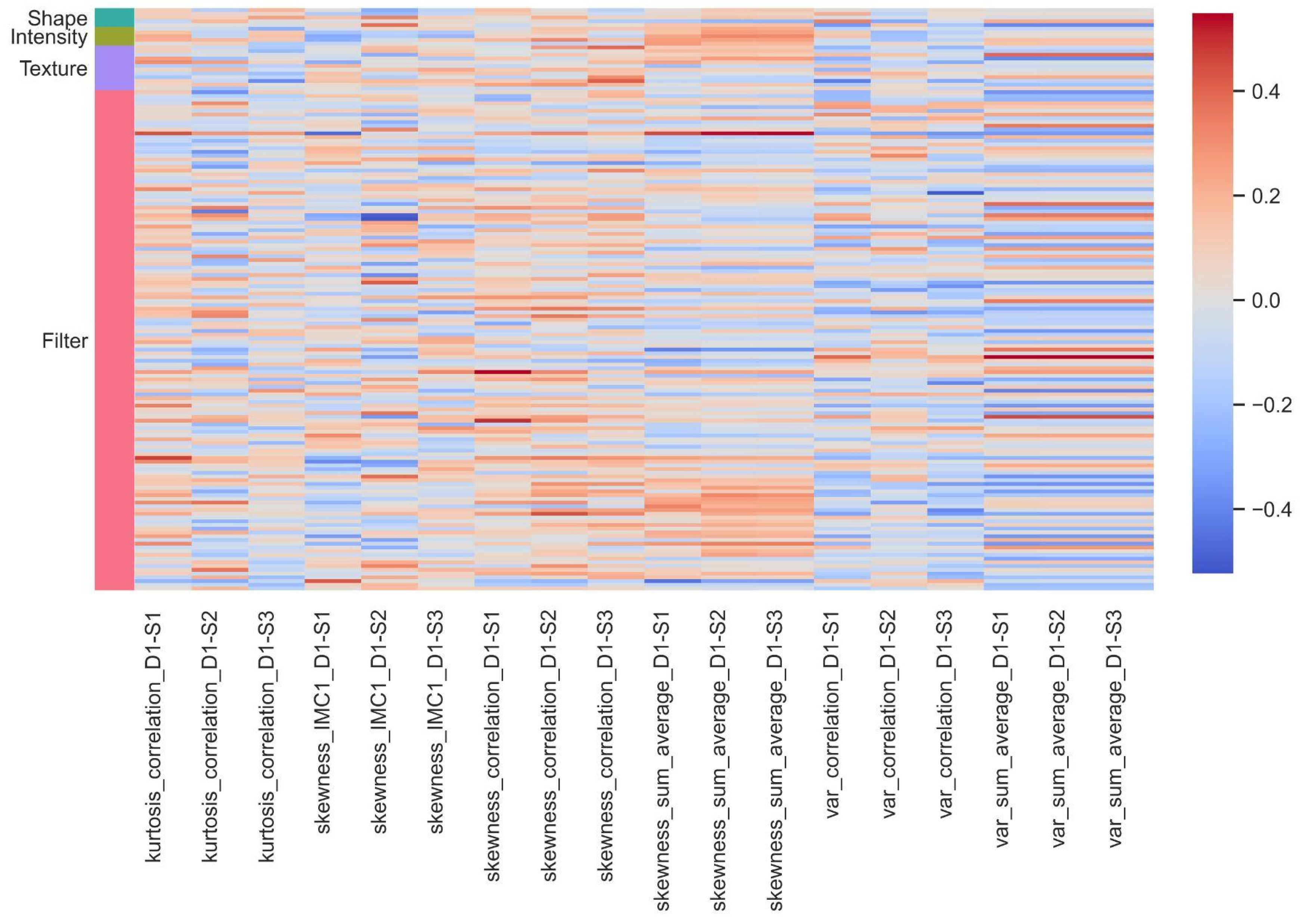
3.3. Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features
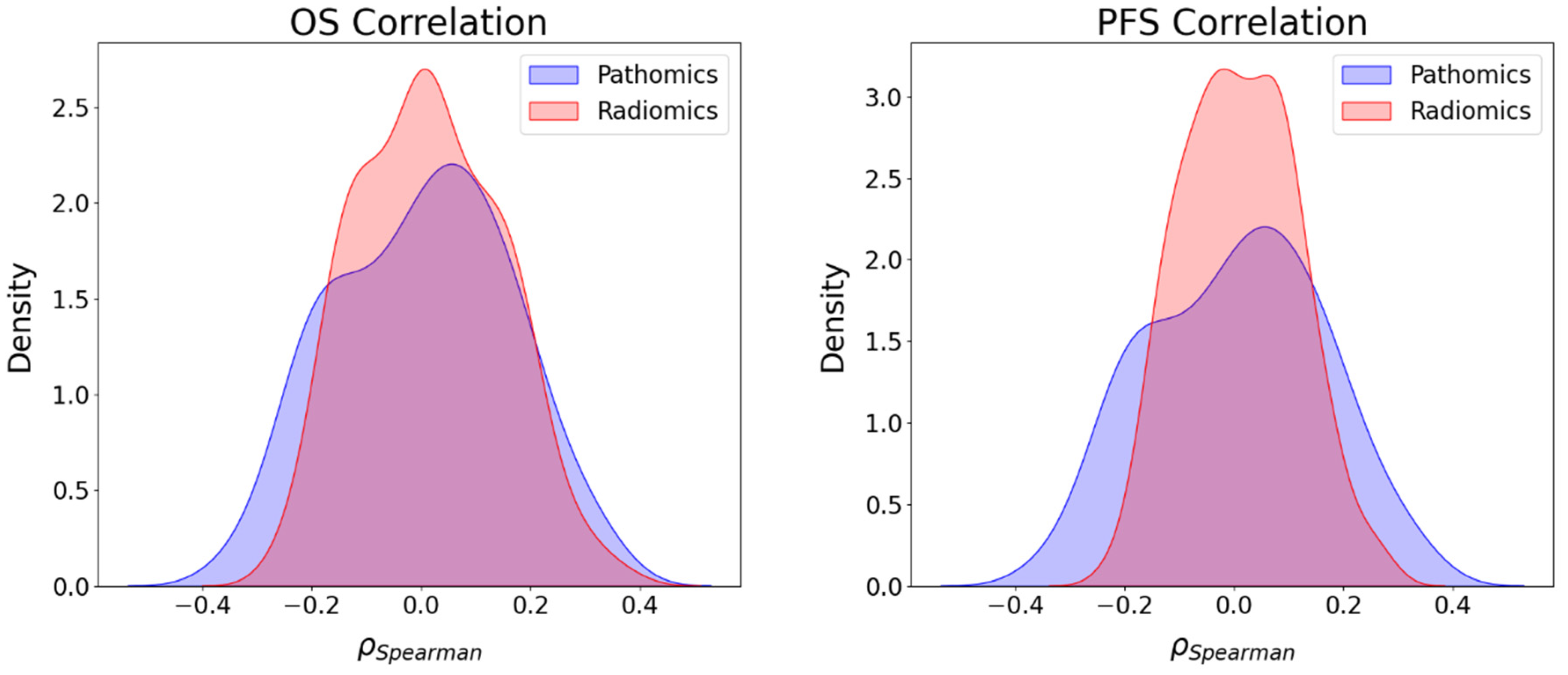
3.4. Association between Imaging Features and Survival Endpoints
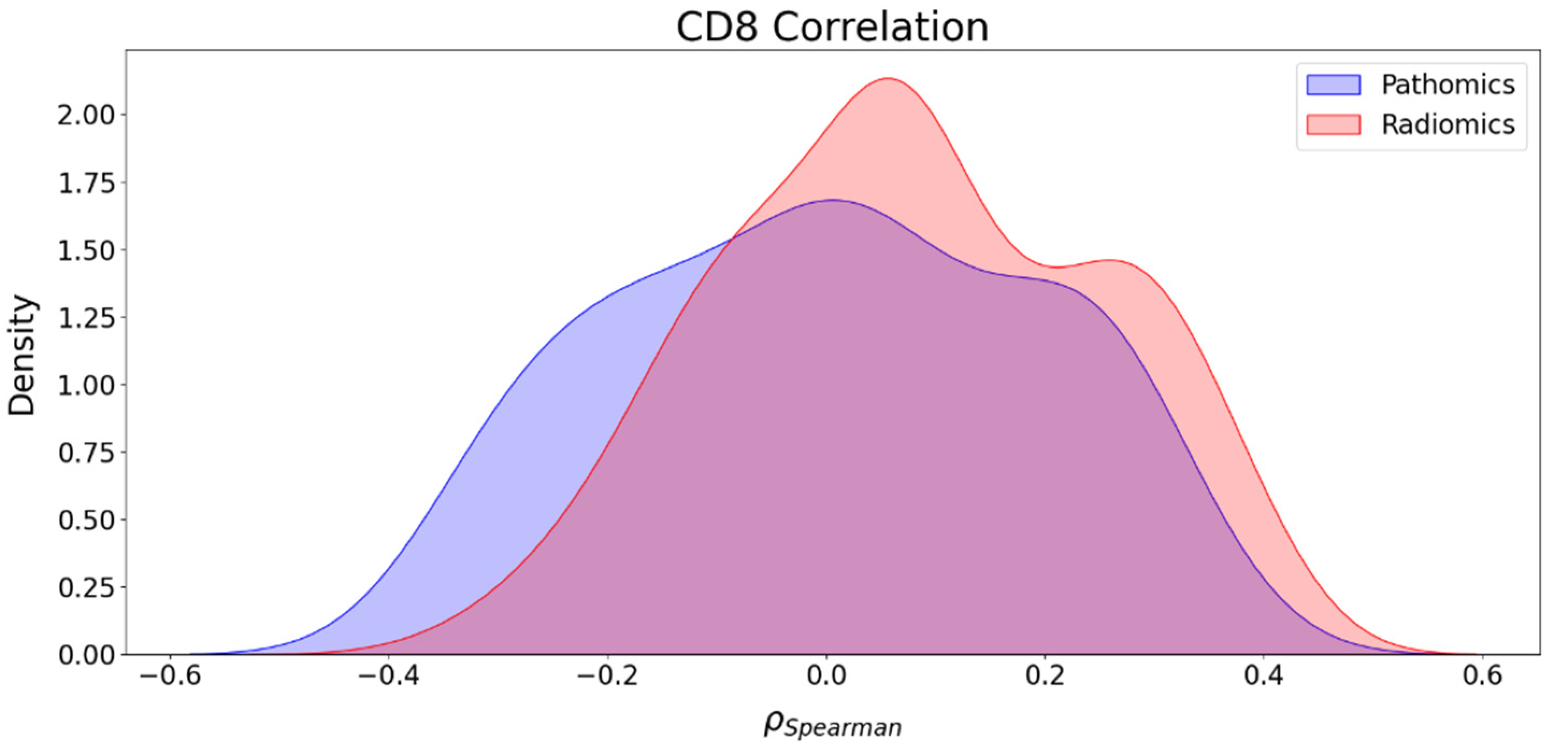
3.5. Association between Imaging Features and CD8 Counts
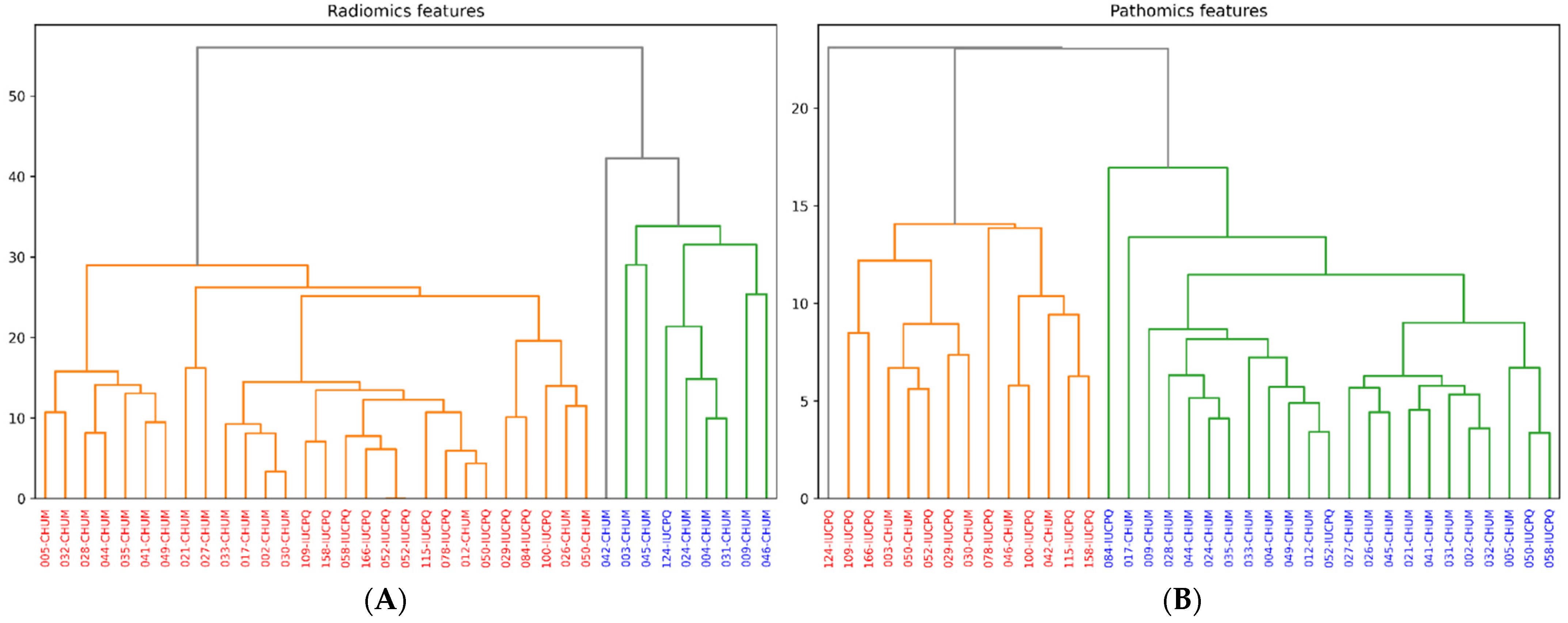
3.6. Clustering of Features
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shields, M.D.; Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Pellini, B. Immunotherapy for Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Decade of Progress. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2021, 41, e105–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punekar, S.R.; Shum, E.; Grello, C.M.; Lau, S.C.; Velcheti, V. Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Past, Present, and Future Directions. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 877594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, L.G.; Grimm, O. Integrating Digital Pathology and Mathematical Modelling to Predict Spatial Biomarker Dynamics in Cancer Immunotherapy. NPJ Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jimenez, C.; Sandino, A.A.; Prasanna, P.; Gupta, A.; Viswanath, S.E.; Romero, E. Identifying Cross-Scale Associations between Radiomic and Pathomic Signatures of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes: Preliminary Results. Cancers 2020, 12, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, V.; Cavaliere, C.; Garbino, N.; Isgrò, F.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. The Relationship between Radiomics and Pathomics in Glioblastoma Patients: Preliminary Results from a Cross-Scale Association Study. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1005805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Shiradkar, R.; Liu, Z. Integrating Pathomics with Radiomics and Genomics for Cancer Prognosis: A Brief Review. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 33, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in Medical Imaging—“How-To” Guide and Critical Reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawani, R.; McLane, M.; Beig, N.; Ghose, S.; Prasanna, P.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Lung Cancer: A Review for the Clinician. Lung Cancer 2018, 115, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, M.R.; Gillies, R.J. The Biological Meaning of Radiomic Features. Radiology 2021, 299, E256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolchuyeva, S.; Giacomazzi, E.; Tonneau, M.; Lamaze, F.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; Joubert, P.; et al. Radiomics Approaches to Predict PD-L1 and PFS in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multi-Institutional Study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolchuyeva, S.; Giacomazzi, E.; Tonneau, M.; Ebrahimpour, L.; Lamaze, F.C.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; et al. A Radiomics-Clinical Model Predicts Overall Survival of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy: A Multicenter Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, L.; Ma, H.; Arefan, D.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, H. Radiomics-Based Features for Prediction of Histological Subtypes in Central Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Trinh, V.Q.-H.; Hasan, D.; Li, X.; Kim, T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, T.; Chinniah, K.; Maghsoudlou, S.; et al. Computational Pathology: A Survey Review and The Way Forward. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.05482. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Le, H.; Van Arnam, J.; Belinsky, D.; Hasan, M.; Samaras, D.; Kurc, T.; Saltz, J.H. Characterizing Immune Responses in Whole Slide Images of Cancer With Digital Pathology and Pathomics. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2020, 8, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Janowczyk, A.; Zhou, Y.; Thawani, R.; Fu, P.; Schalper, K.; Velcheti, V.; Madabhushi, A. Prediction of Recurrence in Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Computer Extracted Nuclear Features from Digital H&E Images. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13543. [Google Scholar]
- Barisoni, L.; Lafata, K.J.; Hewitt, S.M.; Madabhushi, A.; Balis, U.G.J. Digital Pathology and Computational Image Analysis in Nephropathology. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büllow, R.D.; Marsh, J.N.; Swamidass, S.J.; Gaut, J.P.; Boor, P. The Potential of Artificial Intelligence-Based Applications in Kidney Pathology. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2022, 31, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Seikrit, C.; Fan, N.; Bouteldja, N.; Gräbel, P.; Gadermayr, M.; Boor, P.; Merhof, D. Large-Scale Extraction of Interpretable Features Provides New Insights into Kidney Histopathology—A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Pathol. Inform. 2022, 13, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolini, A.; Bussola, N.; Arbitrio, E.; Amgad, M.; Jurman, G.; Furlanello, C. Histolab: A Python Library for Reproducible Digital Pathology Preprocessing with Automated Testing. SoftwareX 2022, 20, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, A.G.; Orchard, W.R.; Gehrung, M.; Markowetz, F. SliDL: A Toolbox for Processing Whole-Slide Images in Deep Learning. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussola, N.; Xu, J.; Wu, L.; Gorini, L.; Zhang, Y.; Furlanello, C.; Tong, W. A Weakly Supervised Deep Learning Framework for Whole Slide Classification to Facilitate Digital Pathology in Animal Study. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, A.G.; Orchard, W.R.; Gehrung, M.; Markowetz, F. PathML: A Unified Framework for Whole-Slide Image Analysis with Deep Learning. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.S.; Toro, P.; Corredor, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Madabhushi, A. The State of the Art for Artificial Intelligence in Lung Digital Pathology. J. Pathol. 2022, 257, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.T.; Ismail, M.; Hossain, I.; Wang, Z.; Prasanna, P.; Madabhushi, A.; Tiwari, P.; Viswanath, S.E. RADIomic Spatial TexturAl Descriptor (RADISTAT): Quantifying Spatial Organization of Imaging Heterogeneity Associated With Tumor Response to Treatment. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 2627–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, K.M.; Khosravi, P.; Vanguri, R.; Gao, J.; Shah, S.P. Harnessing Multimodal Data Integration to Advance Precision Oncology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Leo, H.; Frederick, K.; Wojciech, S.; Klaus-Robert, M.; Emmanuel, D.; Sonja, S.; Sylvia, H.; Ina, K.; Jörg, A.; Liron, P.; et al. Imaging Bridges Pathology and Radiology. J. Pathol. Inform. 2023, 14, 100298. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, A.; Guddati, A.K. Clinical Endpoints in Oncology—A Primer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.; Liu, X.; Jomier, J.; Marion, C.; Ibanez, L. ITK: Enabling Reproducible Research and Open Science. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, M.; Molinari, F.; Acharya, U.R.; Molinaro, L.; Meiburger, K.M. Impact of Stain Normalization and Patch Selection on the Performance of Convolutional Neural Networks in Histological Breast and Prostate Cancer Classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. Update 2021, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manik, S.; Saini, L.M.; Vadera, N. Counting and Classification of White Blood Cell Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN). In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES), Delhi, India, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahasan, R.; Ratul, A.U.; Bakibillah, A.S.M. White Blood Cells Nucleus Segmentation from Microscopic Images of Strained Peripheral Blood Film during Leukemia and Normal Condition. In Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 13–14 May 2016; pp. 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Shahriar Sazzad, T.M.; Armstrong, L.J.; Tripathy, A.K. An Automated Ovarian Tissue Detection Approach Using Type P63 Non-Counter Stained Images to Minimize Pathology Experts Observation Variability. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences (IECBES), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Rajyalakshmi, U.; Rao, S.K.; Prasad, K.S. Supervised Classification of Breast Cancer Malignancy Using Integrated Modified Marker Controlled Watershed Approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Hyderabad, India, 5–7 January 2017; pp. 584–589. [Google Scholar]
- Win, K.Y.; Choomchuay, S. Automated Segmentation of Cell Nuclei in Cytology Pleural Fluid Images Using OTSU Thresholding. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology (ICDAMT), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 1–4 March 2017; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Petushi, S.; Garcia, F.U.; Haber, M.M.; Katsinis, C.; Tozeren, A. Large-Scale Computations on Histology Images Reveal Grade-Differentiating Parameters for Breast Cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 2006, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veta, M.; van Diest, P.J.; Kornegoor, R.; Huisman, A.; Viergever, M.A.; Pluim, J.P.W. Automatic Nuclei Segmentation in H&E Stained Breast Cancer Histopathology Images. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70221. [Google Scholar]
- Kornilov, A.S.; Safonov, I.V. An Overview of Watershed Algorithm Implementations in Open Source Libraries. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, C.F.W.; Übelhör, C.; Mes, S.W.; Martens, R.; Koopman, T.; de Graaf, P.; van Velden, F.H.P.; Boellaard, R.; Castelijns, J.A.; te Beest, D.E.; et al. Stable Prediction with Radiomics Data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.11696. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, L.; Sun, Z.; Peng, W.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zou, S.; et al. Selecting Candidates for Organ-Preserving Strategies after Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for Rectal Cancer: Development and Validation of a Model Integrating MRI Radiomics and Pathomics. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Qiu, X.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Z. Application of Radiomics-Based Multiomics Combinations in the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Prognosis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age [mean ± SD] | 67 ± 7.2 |
| Sex [n (%)] Male Female | 13 (36%) 23 (64%) |
| BMI [mean ± SD] | 25.7 ± 5.3 |
| Smoking habit [n (%)] Current Former Never | 9 (25%) 26 (72%) 2 (3%) |
| Progression [n (%)] Yes No | 28 (76%) 8 (24%) |
| OS [n (%)] ≤12 months >12 months | 8 (23%) 28 (77%) |
| PFS [n (%)] ≤12 months >12 months | 26 (61%) 14 (39%) |
| CD8 [mean ± SD] | 7.6 ± 6.9 |
| Radiomic Feature Name | Pathomics Feature Name | Correlation | Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| wavelet.HLL_glszm_GrayLevelVariance | kurtosis_IMC1_D3 | −0.644 | 64 × 64 |
| wavelet.HLH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | var_sum_average_D1 | 0.578 | 64 × 64 |
| wavelet.LHL_firstorder_Mean | skewness_IMC2_D2 | −0.568 | 64 × 64 |
| wavelet.LLH_glszm_SmallAreaEmphasis | skewness_correlation_D3 | −0.526 | 64 × 64 |
| original_glszm_SmallAreaEmphasis | skewness_correlation_D3 | −0.502 | 64 × 64 |
| wavelet.HLL_gldm_DependenceEntropy | kurtosis_IMC1_D3 | −0.500 | 64 × 64 |
| wavelet.HLH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | var_sum_average_D1 | 0.578 | 32 × 32 |
| wavelet.HLH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | kurtosis_IMC2_D3 | −0.572 | 32 × 32 |
| wavelet.LHH_firstorder_Mean | skewness_IMC1_D3 | −0.537 | 32 × 32 |
| wavelet.LHH_firstorder_Mean | skewness_contrast_D4 | −0.527 | 32 × 32 |
| original_ngtdm_Busyness | median_sum_variance_D2 | −0.604 | 16 × 16 |
| wavelet.HLH_gldm_DependenceEntropy | kurtosis_IMC2_D3 | −0.551 | 16 × 16 |
| wavelet.LHH_firstorder_Mean | var_IMC2_D1 | 0.521 | 16 × 16 |
| Clusters Based on Pathomics Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | Cluster Size | Number (%) of Patients with PFS > 12 Months | Number (%) of Patients with OS > 12 Months | Number (%) of Patients with CD8 > Median |
| 0 | 24 | 11 (46%) | 18 (75%) | 12 (50%) |
| 1 | 12 | 3 (25%) | 10 (83%) | 6 (50%) |
| Clusters based on radiomics features | ||||
| 0 | 9 | 3 (33%) | 8 (89%) | 3 (33%) |
| 1 | 27 | 11 (41%) | 20 (74%) | 15 (56%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dia, A.K.; Ebrahimpour, L.; Yolchuyeva, S.; Tonneau, M.; Lamaze, F.C.; Orain, M.; Coulombe, F.; Malo, J.; Belkaid, W.; Routy, B.; et al. The Cross-Scale Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features in Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC Patients: A Preliminary Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020348
Dia AK, Ebrahimpour L, Yolchuyeva S, Tonneau M, Lamaze FC, Orain M, Coulombe F, Malo J, Belkaid W, Routy B, et al. The Cross-Scale Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features in Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC Patients: A Preliminary Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020348
Chicago/Turabian StyleDia, Abdou Khadir, Leyla Ebrahimpour, Sevinj Yolchuyeva, Marion Tonneau, Fabien C. Lamaze, Michèle Orain, Francois Coulombe, Julie Malo, Wiam Belkaid, Bertrand Routy, and et al. 2024. "The Cross-Scale Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features in Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC Patients: A Preliminary Study" Cancers 16, no. 2: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020348
APA StyleDia, A. K., Ebrahimpour, L., Yolchuyeva, S., Tonneau, M., Lamaze, F. C., Orain, M., Coulombe, F., Malo, J., Belkaid, W., Routy, B., Joubert, P., Després, P., & Manem, V. S. K. (2024). The Cross-Scale Association between Pathomics and Radiomics Features in Immunotherapy-Treated NSCLC Patients: A Preliminary Study. Cancers, 16(2), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020348








