Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Induces PD-L1 Expression and an Invasive Phenotype of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of OSCC Cell Lines
2.2. Western Blotting
2.3. Reverse Transcription PCR
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Scratch Assay
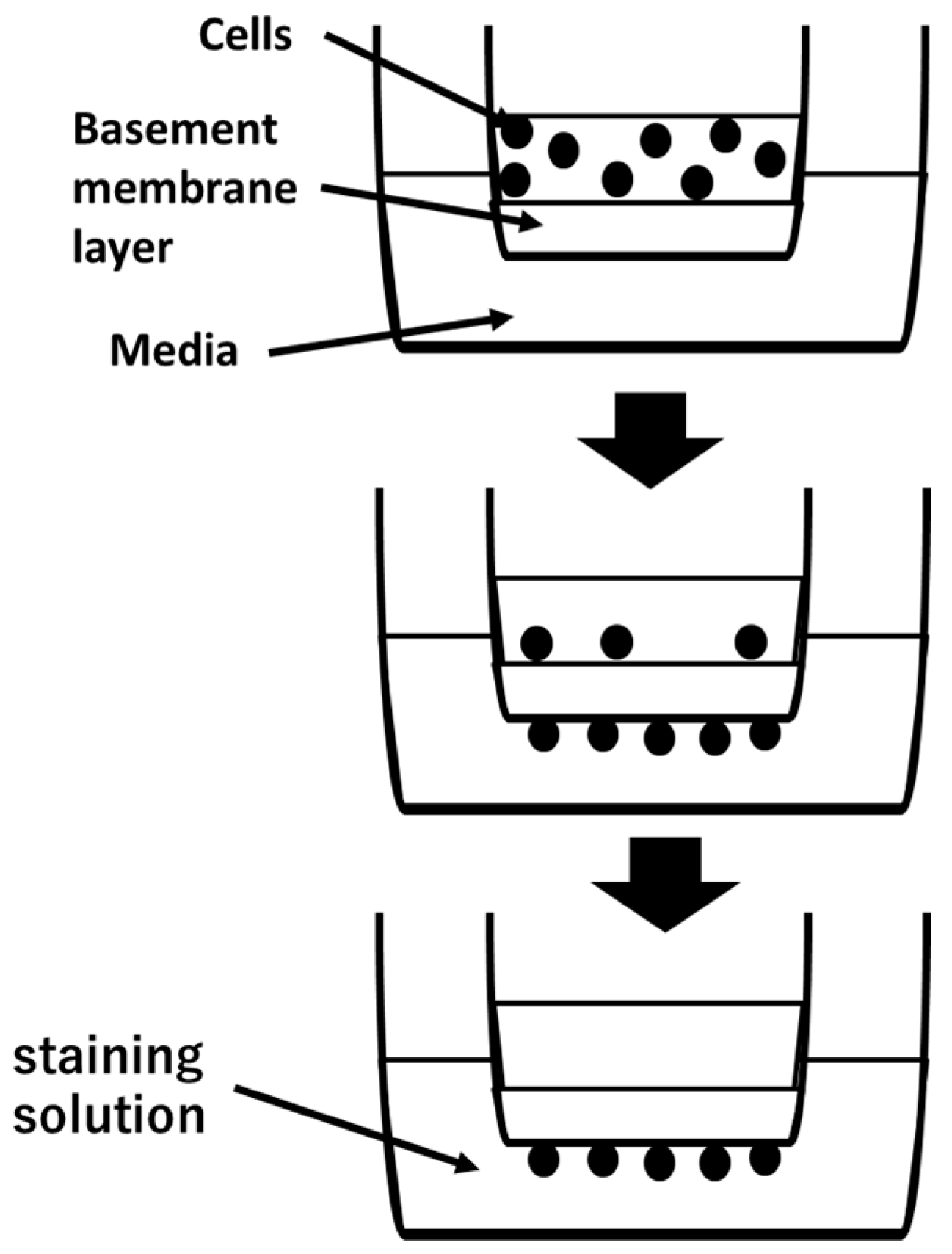
2.6. Invasion Assay
2.7. Evaluation of Cell Morphology
2.8. Evaluation of Plasticity of Cellular Changes
2.9. Isolation and Characterization of EXOs
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
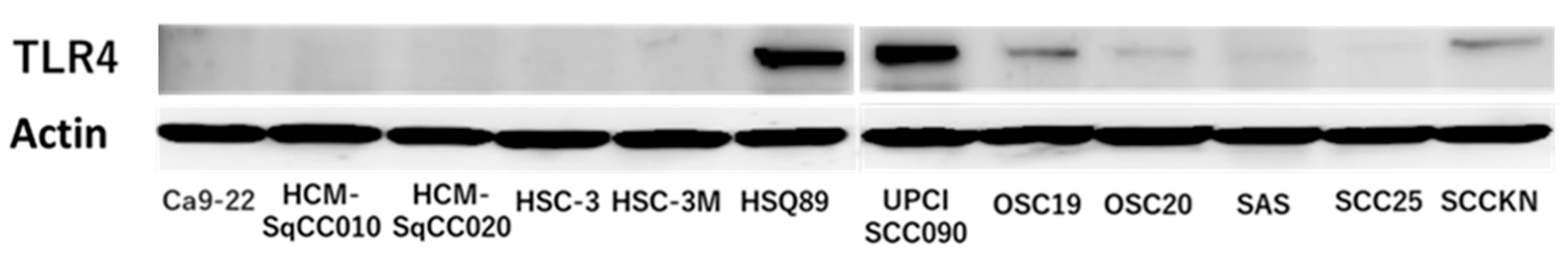
3.1. TLR4 Expression in OSCC Cells
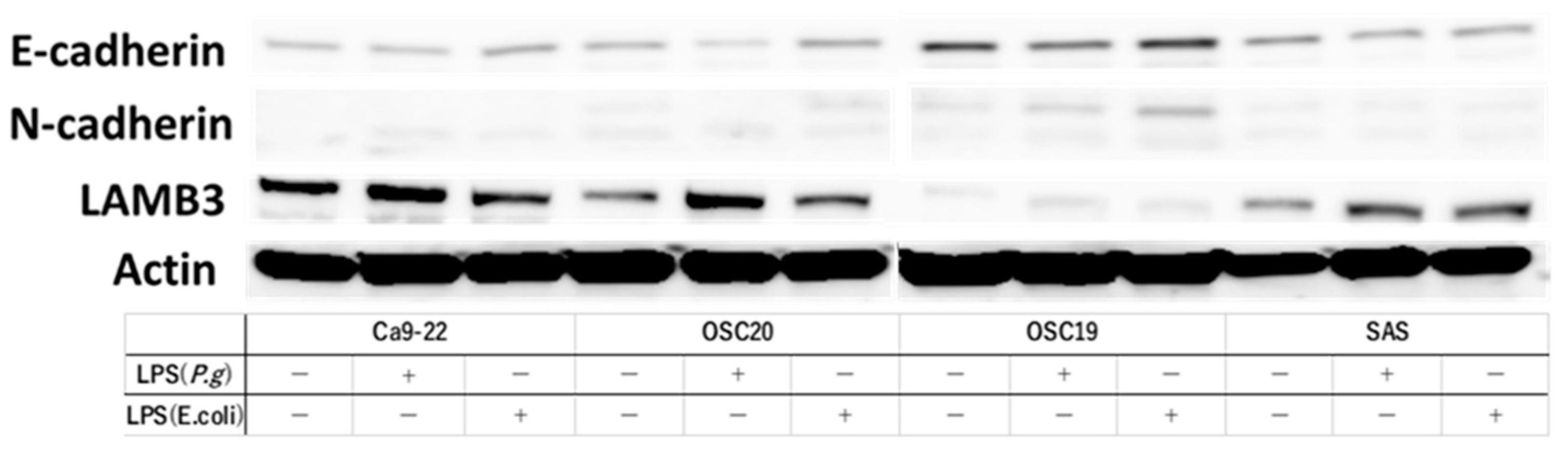
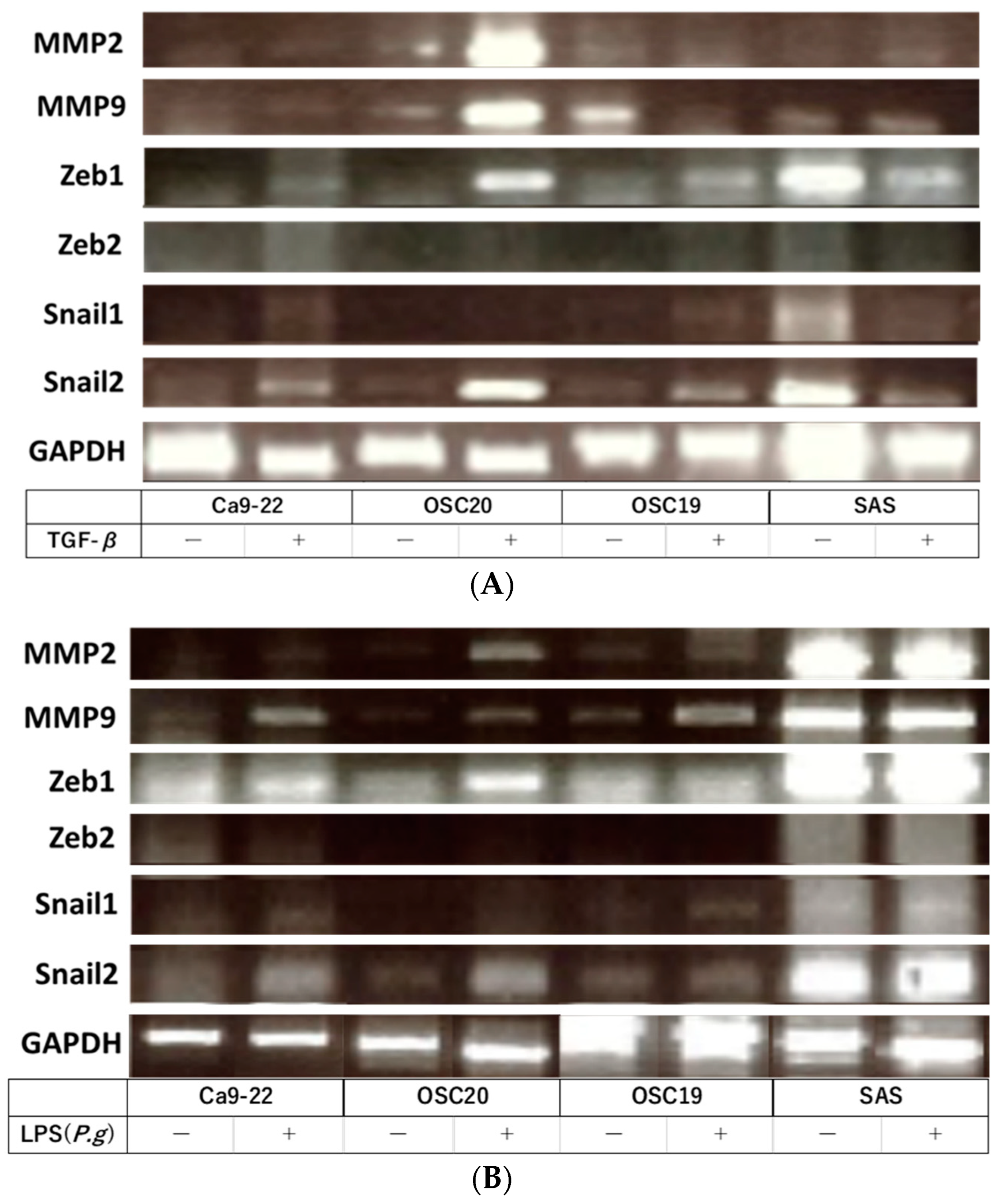
3.2. Evaluation of EMT and pEMT of OSCC Cells following LPS Addition
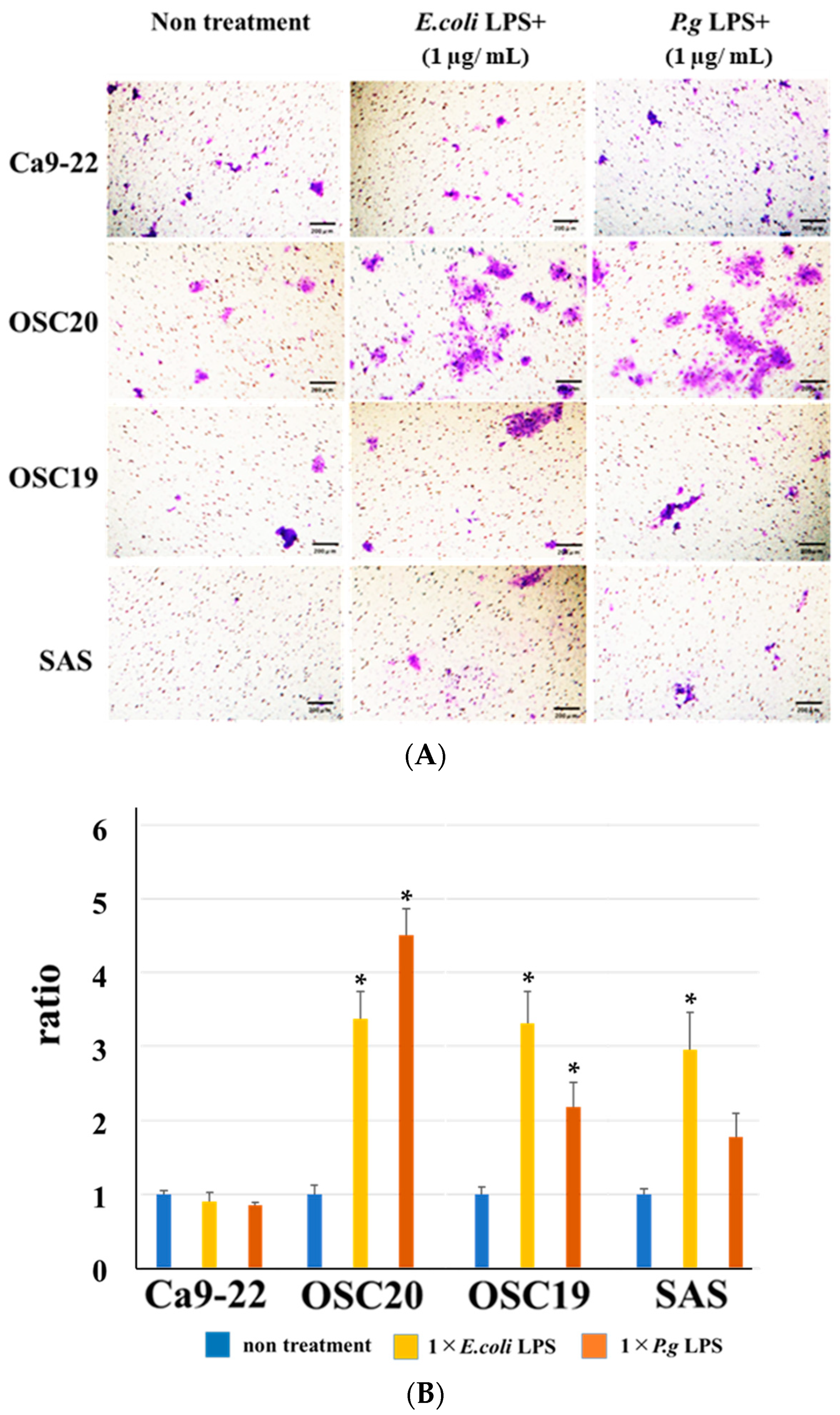
3.3. Evaluation of Cell Proliferative Ability, Migration Ability, Invasion Ability, and Cell Morphology of OSCC Cells with LPS Addition
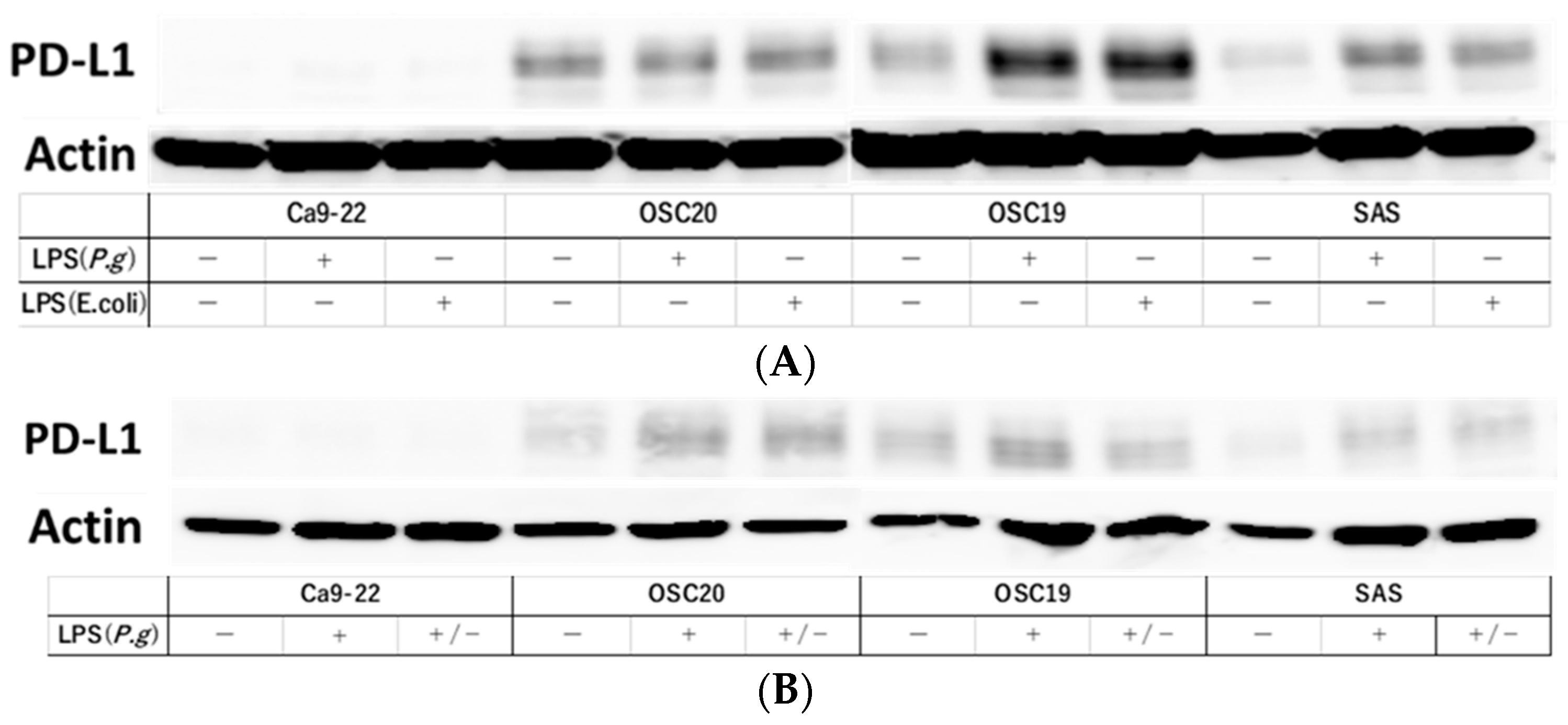
3.4. PD-L1 Expression Reversibility of OSCC Cells
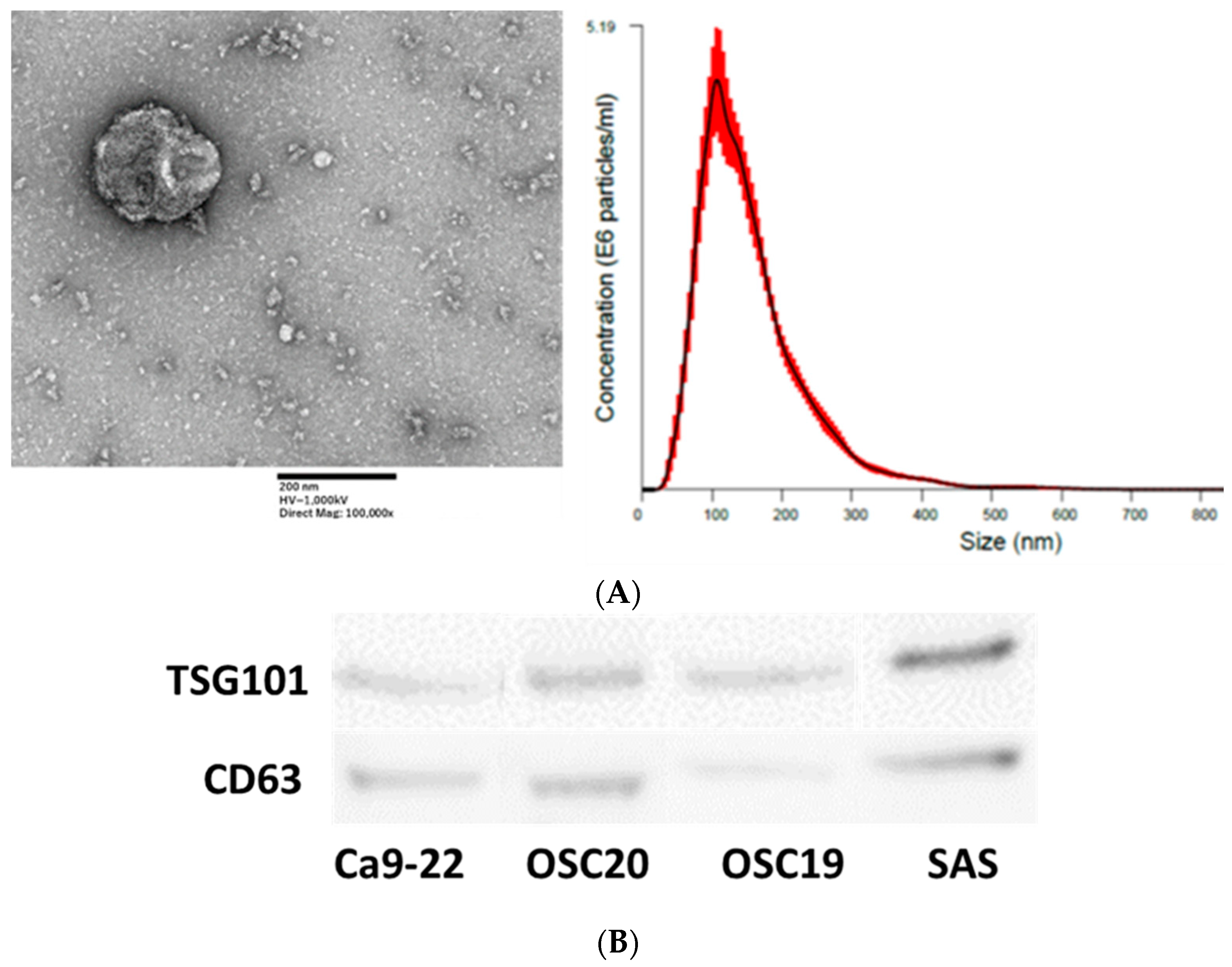
3.5. Extraction and Analysis of Exosomes from OSCC Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinn, S.B.; Myers, J.N. Oral Cavity Carcinoma: Current Management, Controversies, and Future Directions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, S.D.; Kowalski, L.P. Perineural invasion in oral cancer: Challenges, controversies and clinical impact. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cruz, A.K.; Vaish, R.; Kapre, N.; Dandekar, M.; Gupta, S.; Hawaldar, R.; Agarwal, J.P.; Pantvaidya, G.; Chaukar, D.; Deshmukh, A.; et al. Elective versus Therapeutic Neck Dissection in Node-Negative Oral Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, K.; Weinberg, R.A. Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Vanlandewijck, M.; Moustakas, A. Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, I.; Miele, L. Deadly crosstalk: Notch signaling at the intersection of EMT and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taipale, J.; Beachy, P.A. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrandah, A.M.; Chukkapalli, S.S.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Progulske-Fox, A.; Chan, E.K.L. Fusobacteria modulate oral carcinogenesis and promote cancer progression. J. Oral. Microbiol. 2020, 13, 1849493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, L.; Nicolau, M.; Giannoccaro, M.; Daidone, M.G.; Bossi, P.; Locati, L.; Licitra, L.; Canevari, S. Head and neck cancer subtypes with biological and clinical relevance: Meta-analysis of gene-expression data. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9627–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xie, N.; Liu, X.; Hou, J.; et al. Prognostic value of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastushenko, I.; Brisebarre, A.; Sifrim, A.; Fioramonti, M.; Revenco, T.; Boumahdi, S.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Brown, D.; Moers, V.; Lemaire, S.; et al. Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT. Nature 2018, 556, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscetti, M.; Quach, B.; Dadashian, E.L.; Mulholland, D.J.; Wu, H. Tracking and Functional Characterization of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Mesenchymal Tumor Cells during Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Stott, S.L.; Smas, M.E.; Ting, D.T.; Isakoff, S.J.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Wells, M.N.; Shah, A.M.; et al. Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science 2013, 339, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, R.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Beyer, I.; Persson, J.; Sova, P.; Möller, T.; Pesonen, S.; Hemminki, A.; Hamerlik, P.; et al. Analysis of epithelial and mesenchymal markers in ovarian cancer reveals phenotypic heterogeneity and plasticity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.K.; Huang, B.; Lu, M.; Mani, S.A.; Levine, H.; Ben-Jacob, E. Towards elucidating the connection between epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and stemness. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Burtness, B.; Mehra, R.; Weiss, J.; Berger, R.; Eder, J.P.; Heath, K.; McClanahan, T.; Lunceford, J.; Gause, C.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G., Jr.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.E.W.; Soulières, D.; Le Tourneau, C.; Dinis, J.; Licitra, L.; Ahn, M.J.; Soria, A.; Machiels, J.P.; Mach, N.; Mehra, R.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 393, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Fraune, C.; Blessin, N.C.; Lennartz, M.; Kluth, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Lindhorst, L.; Dahlem, R.; Fisch, M.; Eichenauer, T.; et al. Tumor cell PD-L1 expression is a strong predictor of unfavorable prognosis in immune checkpoint therapy-naive clear cell renal cell cancer. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2021, 53, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki-Maeda, H.; Kawabe, M.; Omori, Y.; Yamanegi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Noguchi, K.; Nakano, Y.; Kishimoto, H. Establishment of an oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line expressing vascular endothelial growth factor a and its two receptors. J. Dent. Sci. 2022, 17, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urade, M.; Ogura, T.; Mima, T.; Matsuya, T. Establishment of human squamous carcinoma cell lines highly and minimally sensitive to bleomycin and analysis of factors involved in the sensitivity. Cancer 1992, 15, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ory, V.; Chapman, S.; Yuan, H.; Albanese, C.; Kallakury, B.; Timofeeva, O.A.; Nealon, C.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; et al. ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kalita, P.; Patil, O.; Mohanty, S. An investigation of folic acid-protein association sites and the effect of this association on folic acid self-assembly. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 12, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, K.; Wakai, K.; Kiyono, T.; Kawabe, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Hashimoto-Tamaoki, T.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakano, Y. Molecular analysis of keratocystic odontogenic tumor cell lines derived from sporadic and basal cell nevus syndrome patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Kanda, S.; Yoshida, K.; Funaoka, Y.; Yamanegi, K.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Nakano, Y. Establishment of a patient-derived mucoepidermoid carcinoma cell line with the CRTC1-MAML2 fusion gene. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Riordan, S.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Escherichia coli K12 Upregulates Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Gamma Interferon-Sensitized Intestinal Epithelial Cells via the NF-κB Pathway. Infect. Immun. 2020, 89, e00618-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.L. In vitro scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, S.E.; Quinley, C.; Kim, H.; Herdman, S.; Corr, M.; Raz, E. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) protein suppresses adenoma-to-carcinoma transition in Apcmin/+ mice via regulation of Snail-1 (SNAI) protein stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18182–18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wen, G. The TLR4/ERK/PD-L1 axis may contribute to NSCLC initiation. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J. TGFβ signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Duan, L.; Tong, Z.; Tan, S.; Zhang, H.; Saw, P.E.; et al. Tumor cell-intrinsic PD-1 receptor is a tumor suppressor and mediates resistance to PD-1 blockade therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6640–6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; de Castro, G., Jr.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Zheng, X.; Niu, M.; Zhu, S.; Ge, H.; Wu, K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current advances and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B.; Du, X.; Poltorak, A. Identification of Toll like receptor 4 (Tlr4) as the aole conduit for LPS sifnal transduction: Genetic and evolutionary studies. J. Endotoxin Res. 2001, 7, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebek, G.; Bennett, K.L.; Funchain, P.; Campbell, R.; Seth, R.; Scharpf, J.; Burkey, B.; Eng, C. Microbiomic subprofiles and MDR1 promoter methylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Delgado, R.Z.R.; Frias-Lopez, J. The Oral Microbiome and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezal, M.; Sullivan, M.A.; Reid, M.E.; Marshall, J.R.; Hyland, A.; Loree, T.; Lillis, C.; Hauck, L.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Scannapieco, F.A. Chronic periodontitis and the risk of tongue cancer. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezal, M.; Sullivan, M.A.; Hyland, A.; Marshall, J.R.; Stoler, D.; Reid, M.E.; Loree, T.R.; Rigual, N.R.; Merzianu, M.; Hauck, L.; et al. Chronic periodontitis and the incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, S.G.; Katz, J. The association between periodontal disease and cancer: A review of the literature. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Yamanaka, R.; Yokoi, A.; Ekuni, D.; Tomofuji, T.; Mizukawa, N.; Onoda, T.; Eguchi, M.; Morita, M. Relationship between serum albumin concentration and periodontal condition in patients with head and neck cancer. J. Periodontol. 2012, 83, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Segers, S.; Hayes, R.B. Periodontal disease, Porphyromonas gingivalis serum antibody levels and orodigestive cancer mortality. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaba, H.; Sugita, H.; Kuboniwa, M.; Iwai, S.; Hamada, M.; Noda, T.; Morisaki, I.; Lamont, R.J.; Amano, A. Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma through induction of proMMP9 and its activation. Cell Microbiol. 2014, 16, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, C.F.; Ge, X.; Li, D.M.; Wen, Y.Y.; Sun, H.R.; Pan, M.H.; Li, W.; et al. Downregulation of miR-218 contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis in lung cancer by targeting Slug/ZEB2 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Alečković, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; García-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: Communication from a distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELAndaloussi, S.; Mager, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.W.; Chan, L.C.; Wei, Y.; Hsu, J.M.; Xia, W.; Cha, J.H.; Hou, J.; Hsu, J.L.; Sun, L.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 harbors active defense function to suppress T cell killing of breast cancer cells and promote tumor growth. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omori, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Kitamura, M.; Makihara, Y.; Omae, T.; Hanawa, S.; Yoshikawa, K.; Takaoka, K.; Kishimoto, H. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Induces PD-L1 Expression and an Invasive Phenotype of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020343
Omori Y, Noguchi K, Kitamura M, Makihara Y, Omae T, Hanawa S, Yoshikawa K, Takaoka K, Kishimoto H. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Induces PD-L1 Expression and an Invasive Phenotype of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020343
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmori, Yuji, Kazuma Noguchi, Mizuha Kitamura, Yuna Makihara, Takayuki Omae, Soutaro Hanawa, Kyohei Yoshikawa, Kazuki Takaoka, and Hiromitsu Kishimoto. 2024. "Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Induces PD-L1 Expression and an Invasive Phenotype of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells" Cancers 16, no. 2: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020343
APA StyleOmori, Y., Noguchi, K., Kitamura, M., Makihara, Y., Omae, T., Hanawa, S., Yoshikawa, K., Takaoka, K., & Kishimoto, H. (2024). Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide Induces PD-L1 Expression and an Invasive Phenotype of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cancers, 16(2), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020343




