17q Gain in Neuroblastoma: A Review of Clinical and Biological Implications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Relevance of 17q Alteration
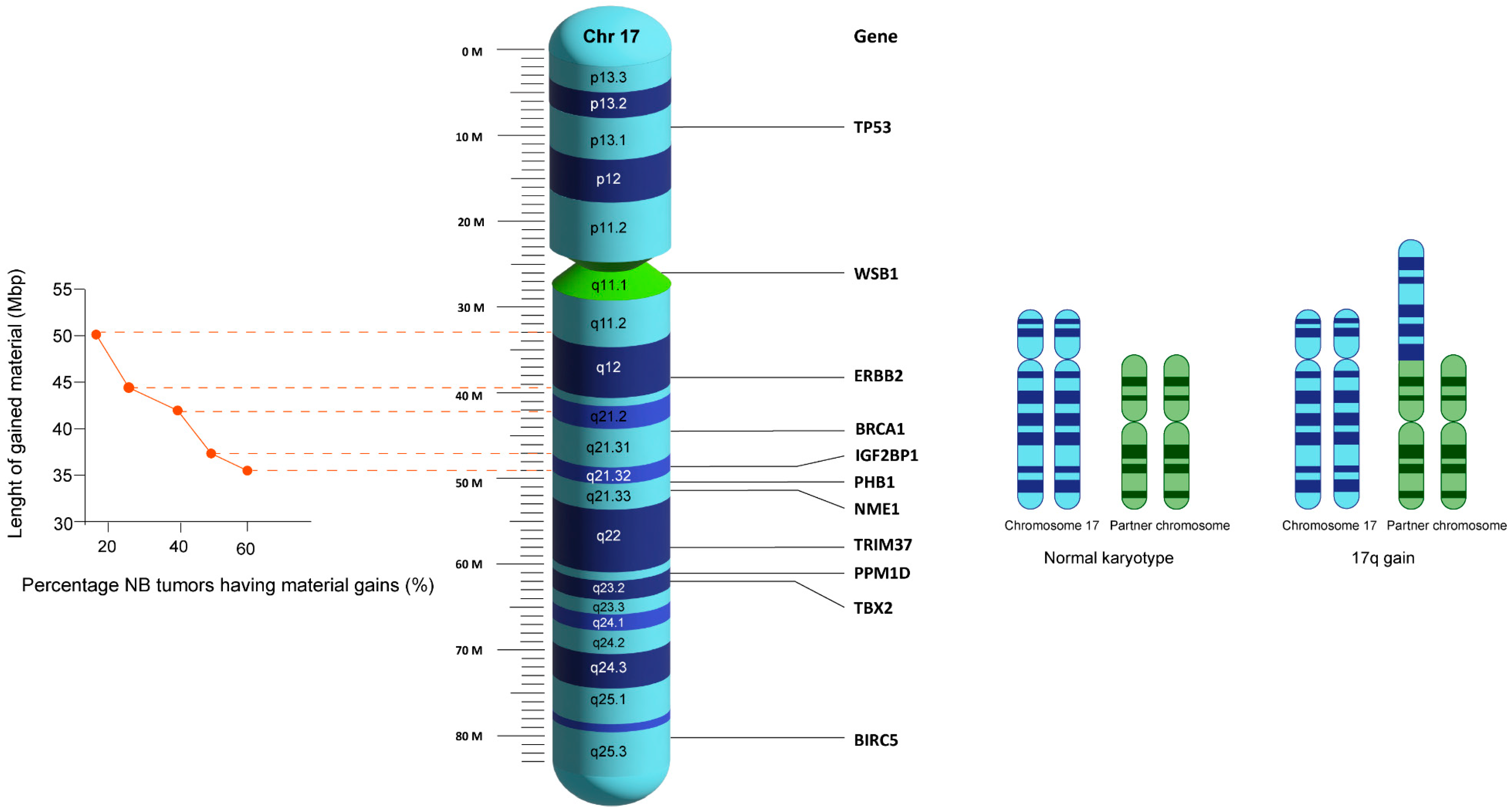
2.1. Where and How Frequently Breakpoints Occur
2.2. Where 17q Translocates to
2.3. 17q’s Associations with Other Genetic Modifications
2.4. 17q Gain’s Association with Clinically Relevant Outcomes
2.5. 17q’s Clinical Relevance in the Context of Whole-Genome Analysis
2.6. Alternative Methods for Identifying 17q Gain
3. The Biological Relevance of 17q Gain
3.1. Cellular Development of NB and 17q
3.2. Functional Gene Studies
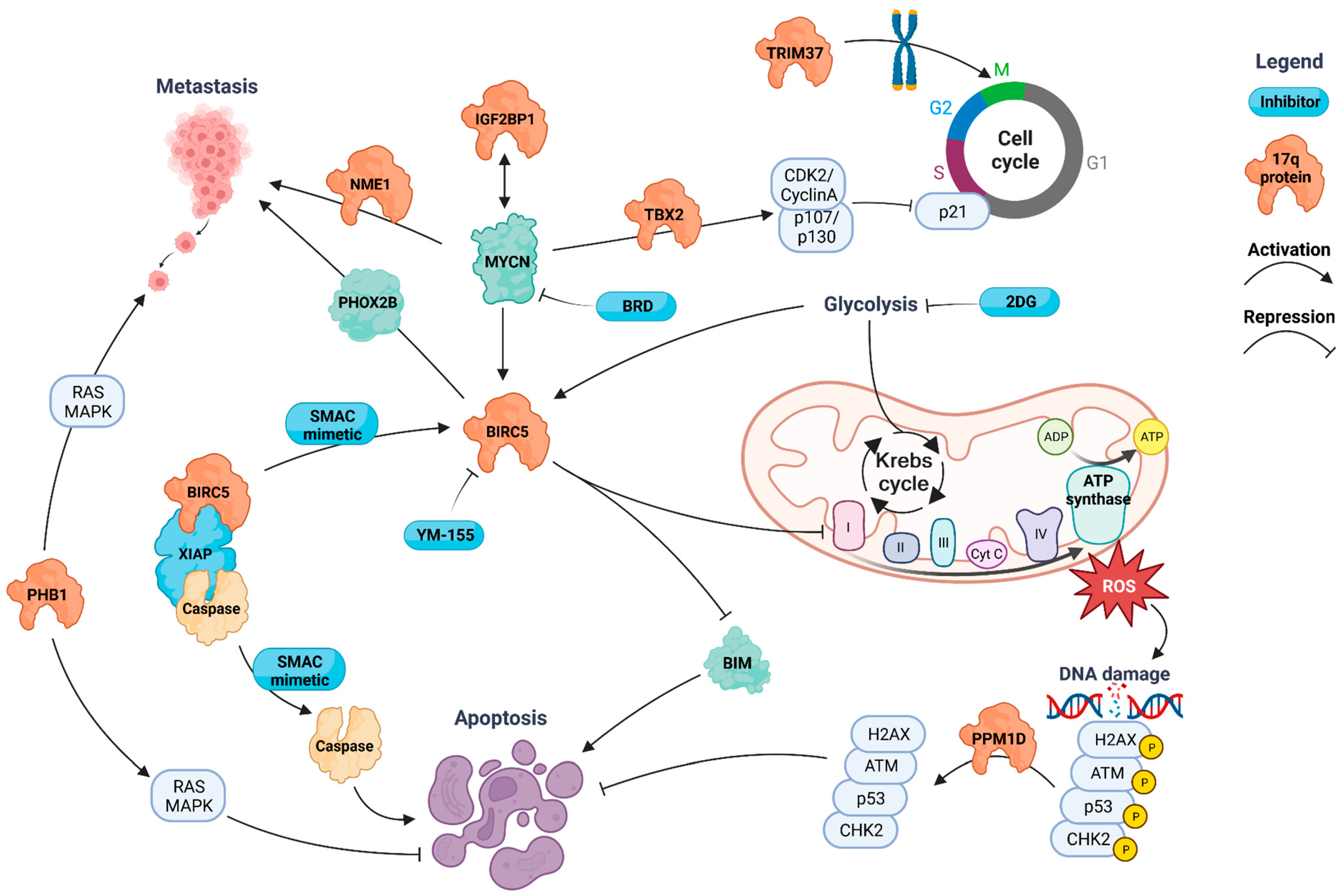
3.2.1. BIRC5 (Survivin)
3.2.2. NME1 (NM23-H1)
3.2.3. IGF2BP1
3.2.4. PPM1D
3.2.5. TBX2
3.2.6. PHB1 (Prohibitin 1)
3.2.7. TRIM37
3.2.8. Noncoding RNAs
3.2.9. BRCA1
3.2.10. ERBB2
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kholodenko, I.V.; Kalinovsky, D.V.; Doronin, I.I.; Deyev, S.M.; Kholodenko, R.V. Neuroblastoma Origin and Therapeutic Targets for Immunotherapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7394268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Qi, F.; Bian, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, M.; Tang, W. Comparison of Incidence and Outcomes of Neuroblastoma in Children, Adolescents, and Adults in the United States: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program Population Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e927218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maris, J.M.; Hogarty, M.D.; Bagatell, R.; Cohn, S.L. Neuroblastoma. Lancet 2007, 369, 2106–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthay, K.K.; Maris, J.M.; Schleiermacher, G.; Nakagawara, A.; Mackall, C.L.; Diller, L.; Weiss, W.A. Neuroblastoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yin, W.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S.; Xue, S.; Sun, G.; Wang, C. Metastasis pattern and prognosis in children with neuroblastoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolbert, V.P.; Matthay, K.K. Neuroblastoma: Clinical and biological approach to risk stratification and treatment. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, S.L.; Pearson, A.D.; London, W.B.; Monclair, T.; Ambros, P.F.; Brodeur, G.M.; Faldum, A.; Hero, B.; Iehara, T.; Machin, D.; et al. The International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) classification system: An INRG Task Force report. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakar, V.; Jurkovic Mlakar, S.; Lopez, G.; Maris, J.M.; Ansari, M.; Gumy-Pause, F. 11q deletion in neuroblastoma: A review of biological and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Feder, M.; Balaban, G.; Brangman, D.; Lurie, D.K.; Podolsky, R.; Rinaldt, V.; Vinikoor, N.; Weisband, J. Human neuroblastomas and abnormalities of chromosomes 1 and 17. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 5444–5449. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, B.S.; Balaban, G.; Boyd, J.P.; Grossman, A.; Negishi, M.; Parmiter, A.; Glick, M.C. N-myc amplification in multiple homogeneously staining regions in two human neuroblastomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3736–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, H.; Franke, F.; Bartram, C.R.; Adolph, S.; Rudolph, B.; Harbott, J.; Reiter, A.; Lampert, F. Evolution of tumor cytogenetic aberrations and N-myc oncogene amplification in a case of disseminated neuroblastoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1987, 26, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, H. Allelic loss of chromosome 1 and additional chromosome 17 material are both unfavourable prognostic markers in neuroblastoma. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 1995, 24, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastowska, M.; Van Roy, N.; Bown, N.; Speleman, F.; Lunec, J.; Strachan, T.; Pearson, A.D.; Jackson, M.S. Molecular cytogenetic delineation of 17q translocation breakpoints in neuroblastoma cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1998, 23, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, G.; Speleman, F.; Versteeg, R.; van der Drift, P.; Chan, A.; Leroy, J.; Francke, U.; Opdenakker, G.; Van Roy, N. Constitutional translocation t(1;17)(p36.31-p36.13;q11.2-q12.1) in a neuroblastoma patient. Establishment of somatic cell hybrids and identification of PND/A12M2 on chromosome 1 and NF1/SCYA7 on chromosome 17 as breakpoint flanking single copy markers. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Roy, N.; Laureys, G.; Van Gele, M.; Opdenakker, G.; Miura, R.; van der Drift, P.; Chan, A.; Versteeg, R.; Speleman, F. Analysis of 1;17 translocation breakpoints in neuroblastoma: Implications for mapping of neuroblastoma genes. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; Van Roy, N.; Van Gele, M.; Laureys, G.; Ambros, P.; Heimann, P.; Devalck, C.; Schuuring, E.; Brock, P.; Otten, J.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity of neuroblastoma studied by comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1998, 23, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastowska, M.; Cotterill, S.; Bown, N.; Cullinane, C.; Variend, S.; Lunec, J.; Strachan, T.; Pearson, A.D.; Jackson, M.S. Breakpoint position on 17q identifies the most aggressive neuroblastoma tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastowska, M.; Van Roy, N.; Bown, N.; Speleman, F.; Roberts, P.; Lunec, J.; Strachan, T.; Pearson, A.D.; Jackson, M.S. Molecular cytogenetic definition of 17q translocation breakpoints in neuroblastoma. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2001, 36, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.R.; Bilke, S.; Wei, J.S.; Greer, B.T.; Steinberg, S.M.; Westermann, F.; Schwab, M.; Khan, J. Increased WSB1 copy number correlates with its over-expression which associates with increased survival in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavarino, C.; Cheung, N.K.; Garcia, I.; Domenech, G.; de Torres, C.; Alaminos, M.; Rios, J.; Gerald, W.L.; Kushner, B.; LaQuaglia, M.; et al. Specific gene expression profiles and chromosomal abnormalities are associated with infant disseminated neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Ohara, F.; Imoto, I.; Inoue, J.; Hosoi, H.; Nakagawara, A.; Sugimoto, T.; Inazawa, J. PPM1D is a potential target for 17q gain in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schleiermacher, G.; Raynal, V.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Combaret, V.; Aurias, A.; Delattre, O. Variety and complexity of chromosome 17 translocations in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2004, 39, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosse, Y.P.; Greshock, J.; Margolin, A.; Naylor, T.; Cole, K.; Khazi, D.; Hii, G.; Winter, C.; Shahzad, S.; Asziz, M.U.; et al. High-resolution detection and mapping of genomic DNA alterations in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 43, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; Michels, E.; De Preter, K.; Menten, B.; Schramm, A.; Eggert, A.; Ambros, P.F.; Combaret, V.; Francotte, N.; Antonacci, F.; et al. Identification of 2 putative critical segments of 17q gain in neuroblastoma through integrative genomics. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caren, H.; Erichsen, J.; Olsson, L.; Enerback, C.; Sjoberg, R.M.; Abrahamsson, J.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. High-resolution array copy number analyses for detection of deletion, gain, amplification and copy-neutral LOH in primary neuroblastoma tumors: Four cases of homozygous deletions of the CDKN2A gene. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.; Peng, H.; Mayoh, C.; Liu, P.Y.; Atmadibrata, B.; Marshall, G.M.; Li, J.; Liu, T. Delineation of the frequency and boundary of chromosomal copy number variations in paediatric neuroblastoma. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbegall, A.P.; Villamon, E.; Piqueras, M.; Tadeo, I.; Djos, A.; Ambros, P.F.; Martinsson, T.; Ambros, I.M.; Canete, A.; Castel, V.; et al. Comparative genetic study of intratumoral heterogenous MYCN amplified neuroblastoma versus aggressive genetic profile neuroblastic tumors. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelyeva, L.; Corvi, R.; Schwab, M. Translocation involving 1p and 17q is a recurrent genetic alteration of human neuroblastoma cells. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1994, 55, 334–340. [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy, N.; Cheng, N.C.; Laureys, G.; Opdenakker, G.; Versteeg, R.; Speleman, F. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of 1;17 translocations in neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 1995, 31A, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, G.; Versteeg, R.; Speleman, F.; van der Drift, P.; Francke, U.; Opdenakker, G.; Van Roy, N. Characterisation of the chromosome breakpoints in a patient with a constitutional translocation t(1;17)(p36.31-p36.13;q11.2-q12) and neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 1995, 31A, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastowska, M.; Roberts, P.; Pearson, A.D.; Lewis, I.; Wolstenholme, J.; Bown, N. Promiscuous translocations of chromosome arm 17q in human neuroblastomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1997, 19, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConville, C.M.; Dyer, S.; Rees, S.A.; Luttikhuis, M.E.; McMullan, D.J.; Vickers, S.J.; Ramani, P.; Redfern, D.; Morland, B.J. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of two non-MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cell lines with complex t(11;17). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 130, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, B.; Jeison, M.; Bar-Am, I.; Glaser-Gabay, L.; Mardoukh, J.; Luria, D.; Feinmesser, M.; Goshen, Y.; Stein, J.; Abramov, A.; et al. Distinct cytogenetic pathways of advanced-stage neuroblastoma tumors, detected by spectral karyotyping. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, B.; Jeison, M.; Glaser-Gabay, L.; Bar-Am, I.; Mardoukh, J.; Ash, S.; Atias, D.; Stein, J.; Zaizov, R.; Yaniv, I. der(11)t(11;17): A distinct cytogenetic pathway of advanced stage neuroblastoma (NBL)—Detected by spectral karyotyping (SKY). Cancer Lett. 2003, 197, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleiermacher, G.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Combaret, V.; Derre, J.; Couturier, J.; Aurias, A.; Delattre, O. Combined 24-color karyotyping and comparative genomic hybridization analysis indicates predominant rearrangements of early replicating chromosome regions in neuroblastoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2003, 141, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallings, R.L.; Carty, P.; McArdle, L.; Mullarkey, M.; McDermott, M.; Breatnach, F.; O’Meara, A. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of recurrent unbalanced t(11;17) in neuroblastoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2004, 154, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, D.R.; Cohen, N.; Leibundgut, K.E.; Kuhne, T.; Caflisch, U.; Greiner, J.; Traktenbrot, L.; Niggli, F.K. Characterization of karyotypic events and evolution in neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2005, 44, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Penther, D.; Thioux, M.; de Cremoux, P.; Derre, J.; Ambros, P.; Vielh, P.; Benard, J.; Aurias, A.; Delattre, O. Molecular analysis of chromosome arm 17q gain in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2000, 28, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souzaki, R.; Tajiri, T.; Teshiba, R.; Kinoshita, Y.; Yosue, R.; Kohashi, K.; Oda, Y.; Taguchi, T. Correlation between the number of segmental chromosome aberrations and the age at diagnosis of diploid neuroblastomas without MYCN amplification. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 2228–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeison, M.; Ash, S.; Halevy-Berko, G.; Mardoukh, J.; Luria, D.; Avigad, S.; Feinberg-Gorenshtein, G.; Goshen, Y.; Hertzel, G.; Kapelushnik, J.; et al. 2p24 Gain region harboring MYCN gene compared with MYCN amplified and nonamplified neuroblastoma: Biological and clinical characteristics. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigliani, S.; Coco, S.; Moretti, S.; Oberthuer, A.; Fischer, M.; Theissen, J.; Gallo, F.; Garavent, A.; Berthold, F.; Bonassi, S.; et al. High genomic instability predicts survival in metastatic high-risk neuroblastoma. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzyk, A.; Booth, S.; Righolt, C.; Mathur, S.; Gartner, J.; Mai, S. MYCN overexpression is associated with unbalanced copy number gain, altered nuclear location, and overexpression of chromosome arm 17q genes in neuroblastoma tumors and cell lines. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2015, 54, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Vo, K.T.; London, W.B.; Fischer, M.; Ambros, P.F.; Nakagawara, A.; Brodeur, G.M.; Matthay, K.K.; DuBois, S.G. Identification of patient subgroups with markedly disparate rates of MYCN amplification in neuroblastoma: A report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group project. Cancer 2016, 122, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybinski, B.; Wolinsky, T.; Brohl, A.; Moerdler, S.; Reed, D.R.; Ewart, M.; Weiser, D. Multifocal primary neuroblastoma tumor heterogeneity in siblings with co-occurring PHOX2B and NF1 genetic aberrations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020, 59, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, M.M.; Piqueras, M.; Navarro, S.; Noguera, R. Aberrant copy numbers of ALK gene is a frequent genetic alteration in neuroblastomas. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungwa, J.V.; Hunt, L.P.; Ramani, P. HIF-1alpha up-regulation is associated with adverse clinicopathological and biological factors in neuroblastomas. Histopathology 2012, 61, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, O.; Handa, M.; Uehara, T.; Maseki, N.; Sakashita, A.; Sakurai, M.; Kanda, N.; Arai, Y.; Kaneko, Y. An increased NM23H1 copy number may be a poor prognostic factor independent of LOH on 1p in neuroblastomas. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Meddeb, M.; Danglot, G.; Chudoba, I.; Venuat, A.M.; Benard, J.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Vasseur, B.; Le Paslier, D.; Terrier-Lacombe, M.J.; Hartmann, O.; et al. Additional copies of a 25 Mb chromosomal region originating from 17q23.1-17qter are present in 90% of high-grade neuroblastomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1996, 17, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantaz, D.; Mohapatra, G.; Matthay, K.K.; Pellarin, M.; Seeger, R.C.; Feuerstein, B.G. Gain of chromosome 17 is the most frequent abnormality detected in neuroblastoma by comparative genomic hybridization. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Lastowska, M.; Cotterill, S.; Pearson, A.D.; Roberts, P.; McGuckin, A.; Lewis, I.; Bown, N. Gain of chromosome arm 17q predicts unfavourable outcome in neuroblastoma patients. U.K. Children’s Cancer Study Group and the U.K. Cancer Cytogenetics Group. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, N.; Lastowska, M.; Cotterill, S.; O’Neill, S.; Ellershaw, C.; Roberts, P.; Lewis, I.; Pearson, A.D.; U.K. Cancer Cytogenetics Group; the U.K. Children’s Cancer Study Group. 17q gain in neuroblastoma predicts adverse clinical outcome. U.K. Cancer Cytogenetics Group and the U.K. Children’s Cancer Study Group. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2001, 36, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkschmidt, C.; Christiansen, H.; Terpe, H.J.; Simon, R.; Lampert, F.; Boecker, W.; Dockhorn-Dworniczak, B. Distal chromosome 17 gains in neuroblastomas detected by comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) are associated with a poor clinical outcome. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2001, 36, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iehara, T.; Hamazaki, M.; Sawada, T. Cytogenetic analysis of infantile neuroblastomas by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Lett. 2002, 178, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shono, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Suita, S.; Ihara, K.; Hara, T. Quick quantitative analysis of gene dosages associated with prognosis in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2001, 166, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunsolo, C.L.; Bicocchi, M.P.; Petti, A.R.; Tonini, G.P. Numerical and structural aberrations in advanced neuroblastoma tumours by CGH analysis; survival correlates with chromosome 17 status. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abel, F.; Ejeskar, K.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. Gain of chromosome arm 17q is associated with unfavourable prognosis in neuroblastoma, but does not involve mutations in the somatostatin receptor 2(SSTR2) gene at 17q24. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- O’Neill, S.; Ekstrom, L.; Lastowska, M.; Roberts, P.; Brodeur, G.M.; Kees, U.R.; Schwab, M.; Bown, N. MYCN amplification and 17q in neuroblastoma: Evidence for structural association. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 30, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bown, N.; Cotterill, S.; Lastowska, M.; O’Neill, S.; Pearson, A.D.; Plantaz, D.; Meddeb, M.; Danglot, G.; Brinkschmidt, C.; Christiansen, H.; et al. Gain of chromosome arm 17q and adverse outcome in patients with neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, K.K.; Brisse, H.; Couanet, D.; Couturier, J.; Benard, J.; Mosseri, V.; Edeline, V.; Lumbroso, J.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Michon, J. Central nervous system metastases in neuroblastoma: Radiologic, clinical, and biologic features in 23 patients. Cancer 2003, 98, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theissen, J.; Oberthuer, A.; Hombach, A.; Volland, R.; Hertwig, F.; Fischer, M.; Spitz, R.; Zapatka, M.; Brors, B.; Ortmann, M.; et al. Chromosome 17/17q gain and unaltered profiles in high resolution array-CGH are prognostically informative in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Takimoto, T.; Nakazawa, A.; Hishiki, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Shichino, H.; Iehara, T.; Nagase, H.; Fukushima, T.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of INRG Clinical and Genomic Factors for 605 Neuroblastomas in Japan: A Report from the Japan Children’s Cancer Group Neuroblastoma Committee (JCCG-JNBSG). Biomolecules 2021, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caren, H.; Kryh, H.; Nethander, M.; Sjoberg, R.M.; Trager, C.; Nilsson, S.; Abrahamsson, J.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. High-risk neuroblastoma tumors with 11q-deletion display a poor prognostic, chromosome instability phenotype with later onset. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4323–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiermacher, G.; Michon, J.; Huon, I.; d’Enghien, C.D.; Klijanienko, J.; Brisse, H.; Ribeiro, A.; Mosseri, V.; Rubie, H.; Munzer, C.; et al. Chromosomal CGH identifies patients with a higher risk of relapse in neuroblastoma without MYCN amplification. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiermacher, G.; Mosseri, V.; London, W.B.; Maris, J.M.; Brodeur, G.M.; Attiyeh, E.; Haber, M.; Khan, J.; Nakagawara, A.; Speleman, F.; et al. Segmental chromosomal alterations have prognostic impact in neuroblastoma: A report from the INRG project. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitz, R.; Hero, B.; Ernestus, K.; Berthold, F. Gain of distal chromosome arm 17q is not associated with poor prognosis in neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, J.; Gerald, W.L.; Qin, J.; Cheung, N.K. Evolving significance of prognostic markers associated with treatment improvement in patients with stage 4 neuroblastoma. Cancer 2002, 94, 2756–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzolo, A.; Rossi, E.; Gimelli, S.; Parodi, F.; Negri, F.; Conte, M.; Pistorio, A.; Sementa, A.; Pistoia, V.; Zuffardi, O.; et al. Presence of 1q gain and absence of 7p gain are new predictors of local or metastatic relapse in localized resectable neuroblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Son, M.H.; Hyun, J.K.; Cho, H.W.; Ju, H.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Yoo, K.H.; Sung, K.W.; Koo, H.H. Clinical Significance of Segmental Chromosomal Aberrations in Patients with Neuroblastoma: First Report in Korean Population. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebire, N.J. Histopathological features of pretreatment neuroblastoma are of limited clinical significance following adjustment for clinical and biological marker status. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastowska, M.; Cullinane, C.; Variend, S.; Cotterill, S.; Bown, N.; O’Neill, S.; Mazzocco, K.; Roberts, P.; Nicholson, J.; Ellershaw, C.; et al. Comprehensive genetic and histopathologic study reveals three types of neuroblastoma tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3080–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; Speleman, F.; Van Roy, N.; Laureys, G.; Brinskchmidt, C.; Christiansen, H.; Lampert, F.; Lastowska, M.; Bown, N.; Pearson, A.; et al. Multicentre analysis of patterns of DNA gains and losses in 204 neuroblastoma tumors: How many genetic subgroups are there? Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 2001, 36, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosse, Y.P.; Diskin, S.J.; Wasserman, N.; Rinaldi, K.; Attiyeh, E.F.; Cole, K.; Jagannathan, J.; Bhambhani, K.; Winter, C.; Maris, J.M. Neuroblastomas have distinct genomic DNA profiles that predict clinical phenotype and regional gene expression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2007, 46, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, T.; Shono, K.; Tanaka, S.; Suita, S. Evaluation of genetic heterogeneity in neuroblastoma. Surgery 2002, 131, S283–S287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajiri, T.; Tanaka, S.; Higashi, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tatsuta, K.; Suita, S. Biological diagnosis for neuroblastoma using the combination of highly sensitive analysis of prognostic factors. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006, 41, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, R.; Oberthuer, A.; Zapatka, M.; Brors, B.; Hero, B.; Ernestus, K.; Oestreich, J.; Fischer, M.; Simon, T.; Berthold, F. Oligonucleotide array-based comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) of 90 neuroblastomas reveals aberration patterns closely associated with relapse pattern and outcome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006, 45, 1130–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaruffi, P.; Coco, S.; Cifuentes, F.; Albino, D.; Nair, M.; Defferrari, R.; Mazzocco, K.; Tonini, G.P. Identification and characterization of DNA imbalances in neuroblastoma by high-resolution oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 177, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uryu, K.; Nishimura, R.; Kataoka, K.; Sato, Y.; Nakazawa, A.; Suzuki, H.; Yoshida, K.; Seki, M.; Hiwatari, M.; Isobe, T.; et al. Identification of the genetic and clinical characteristics of neuroblastomas using genome-wide analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107513–107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morowitz, M.; Shusterman, S.; Mosse, Y.; Hii, G.; Winter, C.L.; Khazi, D.; Wang, Q.; King, R.; Maris, J.M. Detection of single-copy chromosome 17q gain in human neuroblastomas using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combaret, V.; Brejon, S.; Iacono, I.; Schleiermacher, G.; Pierron, G.; Ribeiro, A.; Bergeron, C.; Marabelle, A.; Puisieux, A. Determination of 17q gain in patients with neuroblastoma by analysis of circulating DNA. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 56, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Takita, J.; Morio, T.; Takagi, M. Copy number alteration analysis for neuroblastoma using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr. Int. 2021, 63, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumer, S.; Altungoz, O.; Bagci, O.; Olgun, H.N. The Detection of Genetic Parameters for Prognostic Stratification of Neuroblastoma Using Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification Technique. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2016, 20, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, J.; Bown, N.P.; Case, M.C.; Hall, A.G.; Lunec, J.; Tweddle, D.A. High-resolution analysis of allelic imbalance in neuroblastoma cell lines by single nucleotide polymorphism arrays. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 172, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gele, M.; Van Roy, N.; Jauch, A.; Laureys, G.; Benoit, Y.; Schelfhout, V.; De Potter, C.R.; Brock, P.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Sciot, R.; et al. Sensitive and reliable detection of genomic imbalances in human neuroblastomas using comparative genomic hybridisation analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 1979–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combaret, V.; Iacono, I.; Brejon, S.; Schleiermacher, G.; Pierron, G.; Couturier, J.; Bergeron, C.; Blay, J.Y. Analysis of genomic alterations in neuroblastoma by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification and array comparative genomic hybridization: A comparison of results. Cancer Genet. 2012, 205, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomioka, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Kageyama, H.; Ohira, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Sasaki, F.; Todo, S.; Nakagawara, A.; Kaneko, Y. Chromosomes that show partial loss or gain in near-diploid tumors coincide with chromosomes that show whole loss or gain in near-triploid tumors: Evidence suggesting the involvement of the same genes in the tumorigenesis of high- and low-risk neuroblastomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 36, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson, S.; Ostensson, M.; Djos, A.; Javanmardi, N.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. Estimation of copy number aberrations: Comparison of exome sequencing data with SNP microarrays identifies homozygous deletions of 19q13.2 and CIC in neuroblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, K.W.; Kim, J.S. Comparison of Next-Generation Sequencing and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for Detection of Segmental Chromosomal Aberrations in Neuroblastoma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suita, S.; Tajiri, T.; Higashi, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kinoshita, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tatsuta, K. Insights into infant neuroblastomas based on an analysis of neuroblastomas detected by mass screening at 6 months of age in Japan. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 17, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiermacher, G.; Bourdeaut, F.; Combaret, V.; Picrron, G.; Raynal, V.; Aurias, A.; Ribeiro, A.; Janoueix-Lerosey, I.; Delattre, O. Stepwise occurrence of a complex unbalanced translocation in neuroblastoma leading to insertion of a telomere sequence and late chromosome 17q gain. Oncogene 2005, 24, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisselsson, D.; Lundberg, G.; Ora, I.; Hoglund, M. Distinct evolutionary mechanisms for genomic imbalances in high-risk and low-risk neuroblastomas. J. Carcinog. 2007, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masecchia, S.; Coco, S.; Barla, A.; Verri, A.; Tonini, G.P. Genome instability model of metastatic neuroblastoma tumorigenesis by a dictionary learning algorithm. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krona, C.; Caren, H.; Sjoberg, R.M.; Sandstedt, B.; Laureys, G.; Kogner, P.; Martinsson, T. Analysis of neuroblastoma tumour progression; loss of PHOX2B on 4p13 and 17q gain are early events in neuroblastoma tumourigenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, V.; Villamon, E.; Canete, A.; Navarro, S.; Ruiz, A.; Melero, C.; Herrero, A.; Yanez, Y.; Noguera, R. Neuroblastoma in adolescents: Genetic and clinical characterisation. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2010, 12, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbegall, A.P.; Villamon, E.; Tadeo, I.; Martinsson, T.; Canete, A.; Castel, V.; Navarro, S.; Noguera, R. Neuroblastoma after childhood: Prognostic relevance of segmental chromosome aberrations, ATRX protein status, and immune cell infiltration. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Dickson, B.C.; Marrano, P.; Thorner, P.S.; Chung, C.T. Adult-onset neuroblastoma: Report of seven cases with molecular genetic characterization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2020, 59, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocco, K.; Defferrari, R.; Sementa, A.R.; Garaventa, A.; Longo, L.; De Mariano, M.; Esposito, M.R.; Negri, F.; Ircolo, D.; Viscardi, E.; et al. Genetic abnormalities in adolescents and young adults with neuroblastoma: A report from the Italian Neuroblastoma group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2015, 62, 1725–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.; Cheung, N.K.; Juan, G.; Illei, P.; Cheung, I.; Akram, M.; Chi, S.; Ladanyi, M.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Gerald, W.L. Neuroblastic and Schwannian stromal cells of neuroblastoma are derived from a tumoral progenitor cell. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6892–6898. [Google Scholar]
- Angelini, P.; London, W.B.; Cohn, S.L.; Pearson, A.D.; Matthay, K.K.; Monclair, T.; Ambros, P.F.; Shimada, H.; Leuschner, I.; Peuchmaur, M.; et al. Characteristics and outcome of patients with ganglioneuroblastoma, nodular subtype: A report from the INRG project. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, L.; McDermott, M.; Purcell, R.; Grehan, D.; O’Meara, A.; Breatnach, F.; Catchpoole, D.; Culhane, A.C.; Jeffery, I.; Gallagher, W.M.; et al. Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of gene expression in neuroblastoma displaying loss of chromosome 11q. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, P.; Baruchel, S.; Marrano, P.; Irwin, M.S.; Thorner, P.S. The neuroblastoma and ganglion components of nodular ganglioneuroblastoma are genetically similar: Evidence against separate clonal origins. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewoestyne, M.; Kumps, C.; Swerts, K.; Menten, B.; Lammens, T.; Philippe, J.; De Preter, K.; Laureys, G.; Van Roy, N.; Speleman, F.; et al. Isolation of disseminated neuroblastoma cells from bone marrow aspirates for pretreatment risk assessment by array comparative genomic hybridization. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, P.; Somerville, M.S.; May, M.T. Podoplanin lymphatic density and invasion correlate with adverse clinicopathologic and biological factors and survival in neuroblastomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piqueras, M.; Navarro, S.; Canete, A.; Castel, V.; Noguera, R. Prognostic value of partial genetic instability in neuroblastoma with ≤50% neuroblastic cell content. Histopathology 2011, 59, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panarello, C.; Morerio, C.; Russo, I.; Pasquali, F.; Rapella, A.; Corrias, M.V.; Morando, A.; Rosanda, C. Full cytogenetic characterization of a new neuroblastoma cell line with a complex 17q translocation. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2000, 116, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureys, G. The neuroblastoma, “enfant terrible” among pediatric tumors. Verh. K. Acad. Voor Geneeskd. Belg. 2003, 65, 5–23; discussion 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lastowska, M.; Viprey, V.; Santibanez-Koref, M.; Wappler, I.; Peters, H.; Cullinane, C.; Roberts, P.; Hall, A.G.; Tweddle, D.A.; Pearson, A.D.; et al. Identification of candidate genes involved in neuroblastoma progression by combining genomic and expression microarrays with survival data. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7432–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Gout, A.M.; Hagiwara, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Macias, M.; Chen, X.; Easton, J.; et al. Pan-neuroblastoma analysis reveals age- and signature-associated driver alterations. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, P.; Nash, R.; Sowa-Avugrah, E.; Rogers, C. High levels of polo-like kinase 1 and phosphorylated translationally controlled tumor protein indicate poor prognosis in neuroblastomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 125, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, P.; Sowa-Avugrah, E.; May, M.T. High proliferation index, as determined by immunohistochemical expression of Aurora kinase B and geminin, indicates poor prognosis in neuroblastomas. Virchows Arch. 2015, 467, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.L.Y.; Wong, M.R.E.; Kuick, C.H.; Saffari, S.E.; Wong, M.K.; Tan, S.H.; Merchant, K.; Chang, K.T.E.; Thangavelu, M.; Periyasamy, G.; et al. Integrated Genomic Profiling and Drug Screening of Patient-Derived Cultures Identifies Individualized Copy Number-Dependent Susceptibilities Involving PI3K Pathway and 17q Genes in Neuroblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 709525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, C.S.; Hodgson, J.G.; Law, M.E.; Fridlyand, J.; Osoegawa, K.; de Jong, P.J.; Nowak, N.J.; Pinkel, D.; Albertson, D.G.; Jain, A.; et al. Genome-wide array CGH analysis of murine neuroblastoma reveals distinct genomic aberrations which parallel those in human tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5266–5273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lastowska, M.; Chung, Y.J.; Cheng Ching, N.; Haber, M.; Norris, M.D.; Kees, U.R.; Pearson, A.D.; Jackson, M.S. Regions syntenic to human 17q are gained in mouse and rat neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2004, 40, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, R.R.; Otero, J.H.; Garcia-Lopez, J.; Wallace, K.; Finkelstein, D.; Rehg, J.E.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.D.; Freeman, K.W. MYCN induces neuroblastoma in primary neural crest cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5075–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.J.; Cheng, N.C.; Ford, J.; Smith, J.; Murray, J.E.; Flemming, C.; Lastowska, M.; Jackson, M.S.; Hackett, C.S.; Weiss, W.A.; et al. Cell lines from MYCN transgenic murine tumours reflect the molecular and biological characteristics of human neuroblastoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heukamp, L.C.; Thor, T.; Schramm, A.; De Preter, K.; Kumps, C.; De Wilde, B.; Odersky, A.; Peifer, M.; Lindner, S.; Spruessel, A.; et al. Targeted expression of mutated ALK induces neuroblastoma in transgenic mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 141ra191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogev, O.; Almeida, G.S.; Barker, K.T.; George, S.L.; Kwok, C.; Campbell, J.; Zarowiecki, M.; Kleftogiannis, D.; Smith, L.M.; Hallsworth, A.; et al. In Vivo Modeling of Chemoresistant Neuroblastoma Provides New Insights into Chemorefractory Disease and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5382–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, W.P. Radiology for back pain. Clin. Radiol. 1989, 40, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thole, T.M.; Toedling, J.; Sprussel, A.; Pfeil, S.; Savelyeva, L.; Capper, D.; Messerschmidt, C.; Beule, D.; Groeneveld-Krentz, S.; Eckert, C.; et al. Reflection of neuroblastoma intratumor heterogeneity in the new OHC-NB1 disease model. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, P.; Parisatto, B.; Rampazzo, E.; Persano, L.; Frasson, C.; Di Meglio, A.; Leslz, A.; Santoro, L.; Cafferata, B.; Zin, A.; et al. Patient-derived organoids (PDOs) as a novel in vitro model for neuroblastoma tumours. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate-Eya, L.T.; Ebus, M.E.; Koster, J.; den Hartog, I.J.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Schild, L.; van der Ploeg, I.; Dolman, M.E.; Caron, H.N.; Versteeg, R.; et al. Newly-derived neuroblastoma cell lines propagated in serum-free media recapitulate the genotype and phenotype of primary neuroblastoma tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Kageyama, H.; Takada, N.; Kawamoto, T.; Takayasu, H.; Isogai, E.; Ohira, M.; Hashizume, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Kaneko, Y.; et al. High expression of Survivin, mapped to 17q25, is significantly associated with poor prognostic factors and promotes cell survival in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2000, 19, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, F.; Schild, L.; Koster, J.; Versteeg, R.; Caron, H.N.; Molenaar, J.J. Targeted BIRC5 silencing using YM155 causes cell death in neuroblastoma cells with low ABCB1 expression. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, M.; Voges, Y.; Rothweiler, F.; Weipert, F.; Zia-Ahmad, A.; Cinatl, J.; von Deimling, A.; Westermann, F.; Rodel, F.; Wass, M.N.; et al. Testing of the Survivin Suppressant YM155 in a Large Panel of Drug-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Cancers 2020, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, F.; van der Ploeg, I.; Schild, L.; Ebus, M.E.; Koster, J.; Hansen, B.R.; Koch, T.; Versteeg, R.; Caron, H.N.; Molenaar, J.J. Knockdown of survivin (BIRC5) causes apoptosis in neuroblastoma via mitotic catastrophe. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuchner, J.; Kuznetsov, A.V.; Obexer, P.; Ausserlechner, M.J. BIRC5/Survivin enhances aerobic glycolysis and drug resistance by altered regulation of the mitochondrial fusion/fission machinery. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4748–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuchner, J.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Obexer, P.; Ausserlechner, M.J. BIRC5/Survivin as a target for glycolysis inhibition in high-stage neuroblastoma. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenbuchner, J.; Oberacher, H.; Arnhard, K.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Ausserlechner, M.J. Modulation of Respiration and Mitochondrial Dynamics by SMAC-Mimetics for Combination Therapy in Chemoresistant Cancer. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4909–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfried, M.B.; Veenstra, M.; v Sluis, P.; Boon, K.; v Asperen, R.; Hermus, M.C.; v Schaik, B.D.; Voute, T.P.; Schwab, M.; Versteeg, R.; et al. The N-myc and c-myc downstream pathways include the chromosome 17q genes nm23-H1 and nm23-H2. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentijn, L.J.; Koster, J.; Versteeg, R. Read-through transcript from NM23-H1 into the neighboring NM23-H2 gene encodes a novel protein, NM23-LV. Genomics 2006, 87, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, K.; Lesperance, J.; Hunter, T.; Zage, P.E. The Potential Functional Roles of NME1 Histidine Kinase Activity in Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentijn, L.J.; Koppen, A.; van Asperen, R.; Root, H.A.; Haneveld, F.; Versteeg, R. Inhibition of a new differentiation pathway in neuroblastoma by copy number defects of N-myc, Cdc42, and nm23 genes. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3136–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.L.; Turlapati, R.; Liu, T.; Schulte, J.H.; Huttelmaier, S. IGF2BP1 harbors prognostic significance by gene gain and diverse expression in neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, S.; Misiak, D.; Bell, J.L.; Fuchs, T.; Lederer, M.I.; Bley, N.; Hammerle, M.; Ghazy, E.; Sippl, W.; Schulte, J.H.; et al. IGF2BP1 induces neuroblastoma via a druggable feedforward loop with MYCN promoting 17q oncogene expression. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamdhere, M.R.; Gowda, C.P.; Singh, V.; Liu, Z.; Carruthers, N.; Grant, C.N.; Sharma, A.; Dovat, S.; Sundstrom, J.M.; Wang, H.G.; et al. IGF2BP1 regulates the cargo of extracellular vesicles and promotes neuroblastoma metastasis. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.S.; Bao, B.; Sarkar, F.H. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: A comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortzel, I.; Dror, S.; Kenific, C.M.; Lyden, D. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, M.; Dayaram, T.; Gilmartin, A.G.; Ganji, G.; Pemmasani, S.K.; Van Der Key, H.; Shohet, J.M.; Donehower, L.A.; Kumar, R. WIP1 phosphatase as a potential therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogan, K.; Bernstein, M.; Leclerc, J.M.; Brisson, L.; Brossard, J.; Brodeur, G.M.; Pelletier, J.; Gros, P. Absence of p53 gene mutations in primary neuroblastomas. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar]
- Milosevic, J.; Treis, D.; Fransson, S.; Gallo-Oller, G.; Sveinbjornsson, B.; Eissler, N.; Tanino, K.; Sakaguchi, K.; Martinsson, T.; Wickstrom, M.; et al. PPM1D Is a Therapeutic Target in Childhood Neural Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakar, V.; Jurkovic Mlakar, S.; Lesne, L.; Marino, D.; Rathi, K.S.; Maris, J.M.; Ansari, M.; Gumy-Pause, F. PRIMA-1(MET)-induced neuroblastoma cell death is modulated by p53 and mycn through glutathione level. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaesteker, B.; De Preter, K.; Speleman, F. DREAM target reactivation by core transcriptional regulators supports neuroblastoma growth. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 6, 1565470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decaesteker, B.; Denecker, G.; Van Neste, C.; Dolman, E.M.; Van Loocke, W.; Gartlgruber, M.; Nunes, C.; De Vloed, F.; Depuydt, P.; Verboom, K.; et al. TBX2 is a neuroblastoma core regulatory circuitry component enhancing MYCN/FOXM1 reactivation of DREAM targets. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlakar, V.; Morel, E.; Mlakar, S.J.; Ansari, M.; Gumy-Pause, F. A review of the biological and clinical implications of RAS-MAPK pathway alterations in neuroblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalingam, K.; Wunder, C.; Brinkmann, V.; Churin, Y.; Hekman, M.; Sievers, C.; Rapp, U.R.; Rudel, T. Prohibitin is required for Ras-induced Raf-MEK-ERK activation and epithelial cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, I.C.; Bei, Y.; Garcia, H.D.; Ortiz, M.V.; Toedling, J.; Klironomos, F.; Rolff, J.; Eggert, A.; Schulte, J.H.; Kentsis, A.; et al. Prohibitin promotes de-differentiation and is a potential therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e127130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meitinger, F.; Ohta, M.; Lee, K.Y.; Watanabe, S.; Davis, R.L.; Anzola, J.V.; Kabeche, R.; Jenkins, D.A.; Shiau, A.K.; Desai, A.; et al. TRIM37 controls cancer-specific vulnerability to PLK4 inhibition. Nature 2020, 585, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Ohira, M.; Li, Y.; Niizuma, H.; Oo, M.L.; Zhu, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Isogai, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Koda, T.; et al. High expression of ncRAN, a novel non-coding RNA mapped to chromosome 17q25.1, is associated with poor prognosis in neuroblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, T.; Juvvuna, P.K.; Kirkeby, A.; Mitra, S.; Kosalai, S.T.; Traxler, L.; Hertwig, F.; Wernig-Zorc, S.; Miranda, C.; Deland, L.; et al. Sense-Antisense lncRNA Pair Encoded by Locus 6p22.3 Determines Neuroblastoma Susceptibility via the USP36-CHD7-SOX9 Regulatory Axis. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 417–434.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Zheng, S.; Huse, J.T.; Bae, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Yoo, K.H.; Koo, H.H.; Kyung, S.; Park, W.Y.; et al. ARID1B alterations identify aggressive tumors in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45943–45950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Varkhedi, M.; Barker, V.R.; Eakins, R.A.; Blanck, G. CNV assessments associated with outcome distinctions for adult and pediatric cancers: Loss of BRCA1 in neuroblastoma associates with a lower survival probability. Gene 2022, 836, 146673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, D.; Solvie, D.; Baluapuri, A.; Endres, T.; Ha, S.A.; Herold, S.; Kalb, J.; Giansanti, C.; Schulein-Volk, C.; Ade, C.P.; et al. MYCN recruits the nuclear exosome complex to RNA polymerase II to prevent transcription-replication conflicts. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 159–176.e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Kalb, J.; Buchel, G.; Ade, C.P.; Baluapuri, A.; Xu, J.; Koster, J.; Solvie, D.; Carstensen, A.; Klotz, C.; et al. Recruitment of BRCA1 limits MYCN-driven accumulation of stalled RNA polymerase. Nature 2019, 567, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Crawley, C.D.; Garofalo, A.; Nichols, J.W.; Campbell, P.A.; Khramtsova, G.F.; Olopade, O.I.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Yamini, B. p50 mono-ubiquitination and interaction with BARD1 regulates cell cycle progression and maintains genome stability. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Yu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, W.; Chu, P.; Tai, J.; Chen, F.; et al. Functional Polymorphisms in BARD1 Association with Neuroblastoma in a regional Han Chinese Population. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, S.W.; Jia, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, S.B.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, F.H.; Xia, H.; He, J.; et al. BARD1 Gene Polymorphisms Confer Nephroblastoma Susceptibility. eBioMedicine 2017, 16, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wouwer, M.; Couzinie, C.; Serrano-Palero, M.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, O.; Galmes-Varela, C.; Menendez-Antoli, P.; Grau, L.; Villalobo, A. Activation of the BRCA1/Chk1/p53/p21(Cip1/Waf1) pathway by nitric oxide and cell cycle arrest in human neuroblastoma NB69 cells. Nitric Oxide 2012, 26, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Morozova, O.; Attiyeh, E.F.; Asgharzadeh, S.; Wei, J.S.; Auclair, D.; Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Hanna, M.; Kiezun, A.; et al. The genetic landscape of high-risk neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepoele, K.; Andries, V.; Van Roy, N.; Staes, K.; Vandesompele, J.; Laureys, G.; De Smet, E.; Berx, G.; Speleman, F.; van Roy, F. A constitutional translocation t(1;17)(p36.2;q11.2) in a neuroblastoma patient disrupts the human NBPF1 and ACCN1 genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Roy, N.; Vandesompele, J.; Berx, G.; Staes, K.; Van Gele, M.; De Smet, E.; De Paepe, A.; Laureys, G.; van der Drift, P.; Versteeg, R.; et al. Localization of the 17q breakpoint of a constitutional 1;17 translocation in a patient with neuroblastoma within a 25-kb segment located between the ACCN1 and TLK2 genes and near the distal breakpoints of two microdeletions in neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 35, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Xu, X.; Ye, M.; Sheng, B.; Zhu, X. The prognostic value of HER2 in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrisch, C.; Piccart, M. An overview of HER2. Semin. Oncol. 2001, 28, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambini, C.; Sementa, A.R.; Boni, L.; Marino, C.E.; Croce, M.; Negri, F.; Pistoia, V.; Ferrini, S.; Corrias, M.V. Expression of HER2/neu is uncommon in human neuroblastic tumors and is unrelated to tumor progression. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2003, 52, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izycka-Swieszewska, E.; Wozniak, A.; Kot, J.; Grajkowska, W.; Balcerska, A.; Perek, D.; Dembowska-Baginska, B.; Klepacka, T.; Drozynska, E. Prognostic significance of HER2 expression in neuroblastic tumors. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wilzen, A.; Krona, C.; Sveinbjornsson, B.; Kristiansson, E.; Dalevi, D.; Ora, I.; De Preter, K.; Stallings, R.L.; Maris, J.; Versteeg, R.; et al. ERBB3 is a marker of a ganglioneuroblastoma/ganglioneuroma-like expression profile in neuroblastic tumours. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, T.; Kizmazoglu, D.; Aktas, S.; Erol, A.; Serinan, E.; Gokbayrak, O.; Ozdemir, S.M.; Altun, Z.; Ozer, E.; Cecen, E.; et al. Unraveling the Mystery: Next Generation Sequencing Sheds Light on Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis and Targeted Therapies. Front. Biosci. 2023, 28, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, B.O.P.; de Andrade, W.P.; Fialho, S.L.; Silva, L.M. Markers to sensibility and relapse on IMR-32 neuroblastoma cell line cultured in monolayer (2D) and neurosphere (3D) models cisplatin-treated. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mlakar, V.; Dupanloup, I.; Gonzales, F.; Papangelopoulou, D.; Ansari, M.; Gumy-Pause, F. 17q Gain in Neuroblastoma: A Review of Clinical and Biological Implications. Cancers 2024, 16, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020338
Mlakar V, Dupanloup I, Gonzales F, Papangelopoulou D, Ansari M, Gumy-Pause F. 17q Gain in Neuroblastoma: A Review of Clinical and Biological Implications. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020338
Chicago/Turabian StyleMlakar, Vid, Isabelle Dupanloup, Fanny Gonzales, Danai Papangelopoulou, Marc Ansari, and Fabienne Gumy-Pause. 2024. "17q Gain in Neuroblastoma: A Review of Clinical and Biological Implications" Cancers 16, no. 2: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020338
APA StyleMlakar, V., Dupanloup, I., Gonzales, F., Papangelopoulou, D., Ansari, M., & Gumy-Pause, F. (2024). 17q Gain in Neuroblastoma: A Review of Clinical and Biological Implications. Cancers, 16(2), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020338





