MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of MR-LINACs
3. Clinical Applications of MR-LINAC
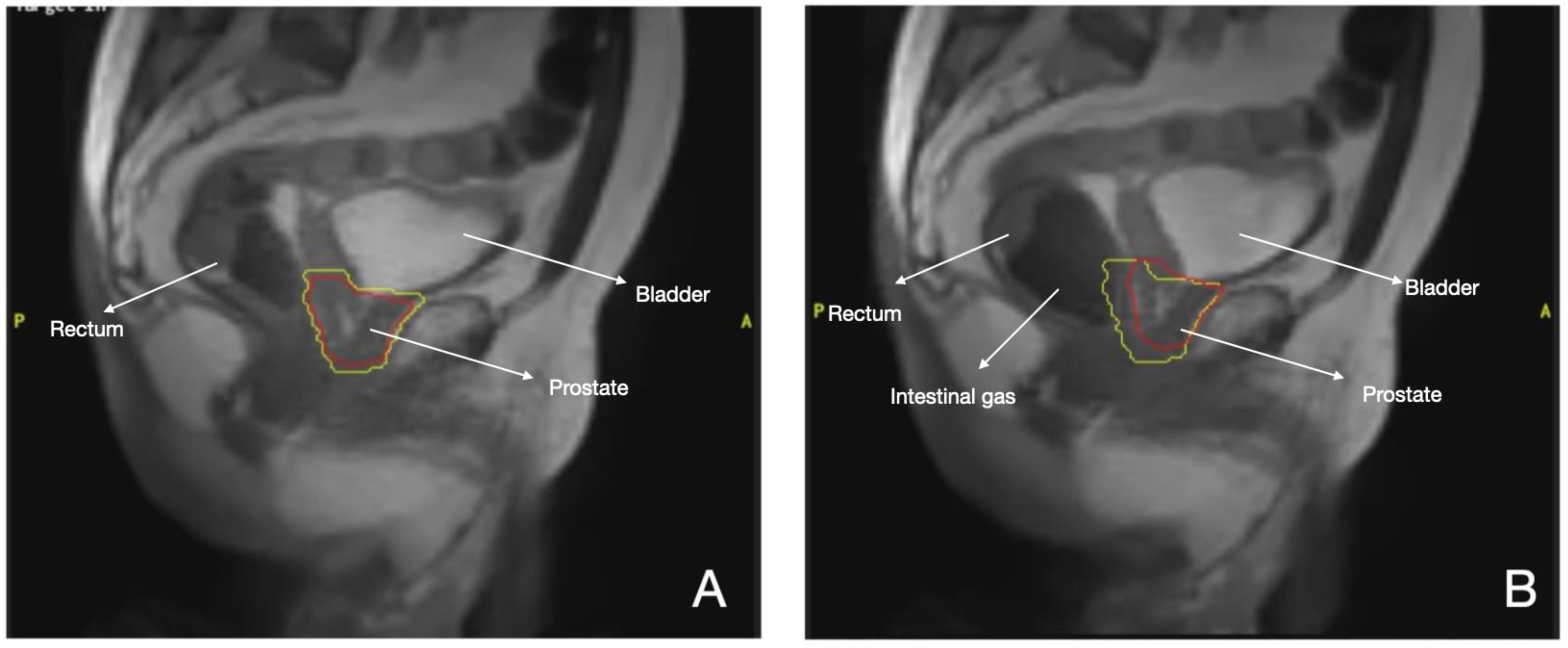
3.1. Prostate Cancer
3.2. Lung Cancer
3.3. Gastroenterological Tumors
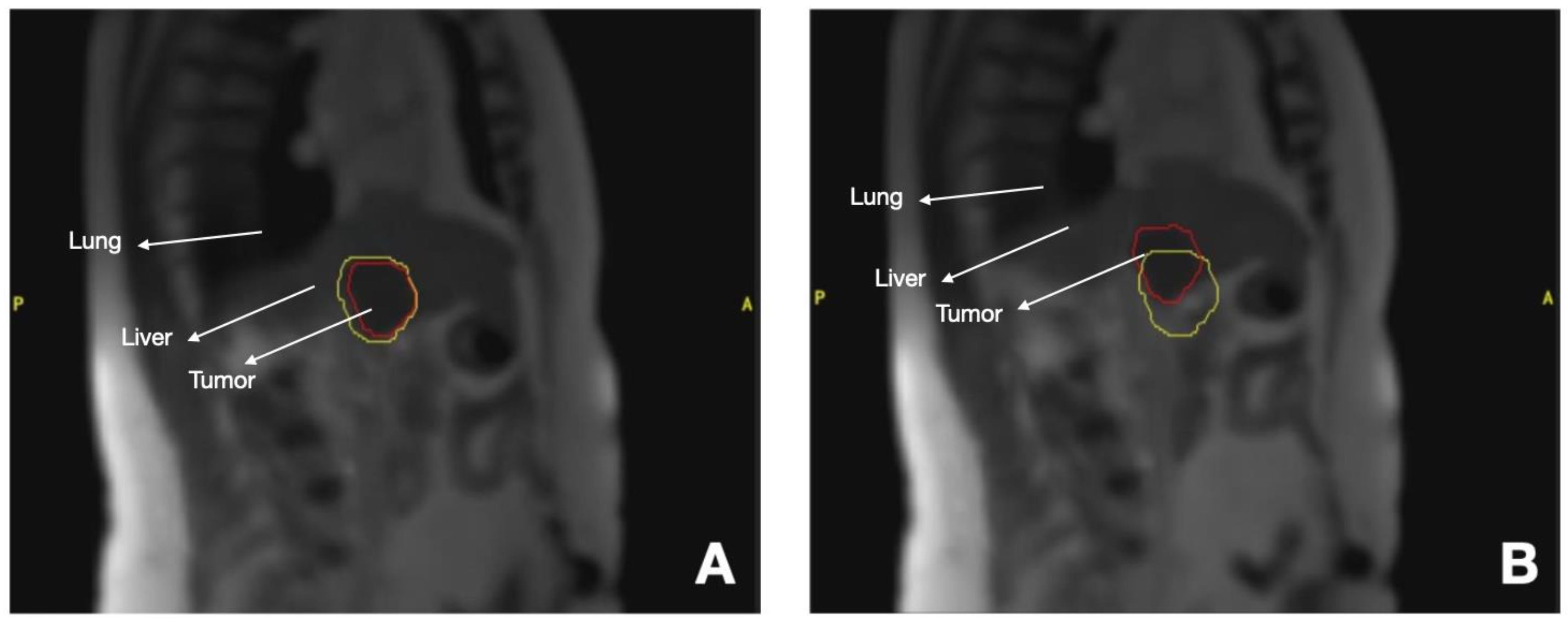
3.3.1. Liver Tumors
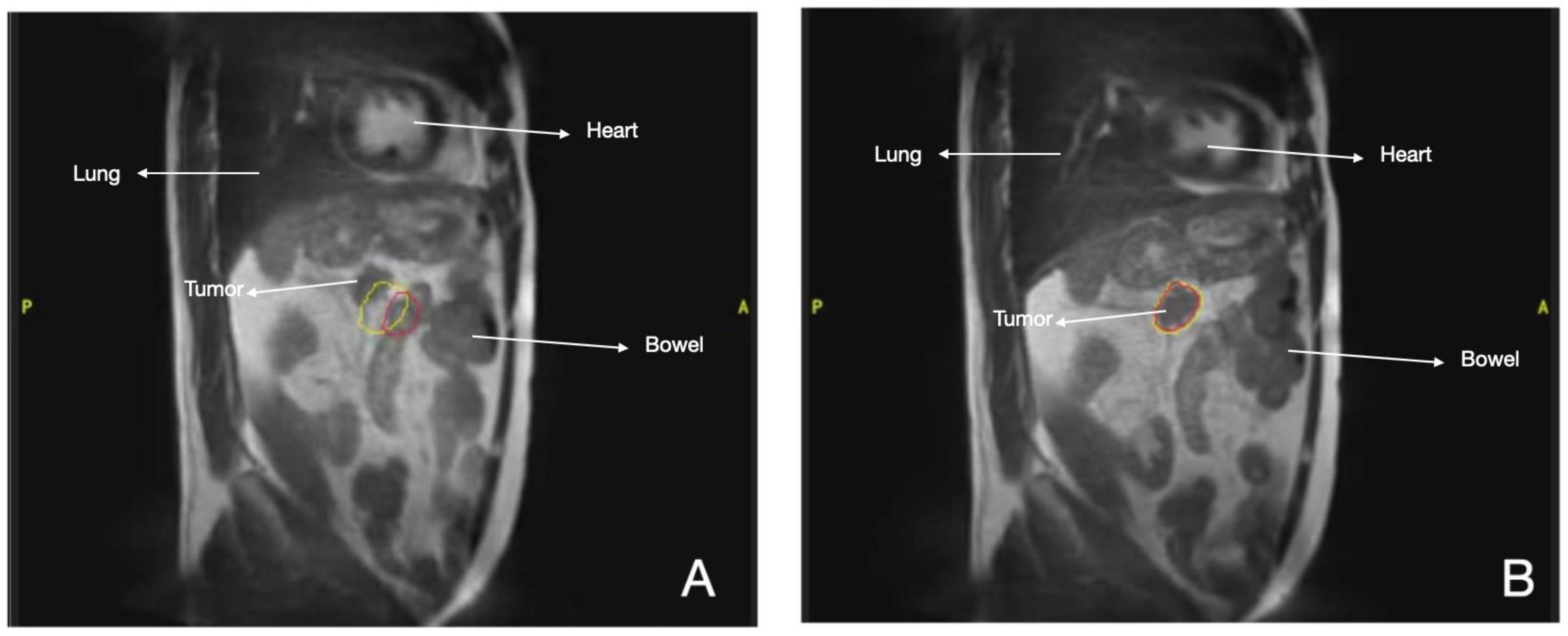
3.3.2. Pancreatic Tumors
3.3.3. Rectal Cancer
3.4. Breast Cancer
3.5. Gynecological Tumors
3.6. Kidney Tumors
3.7. Central Nervous System Tumors
3.8. Miscellanea
3.8.1. Heart Disease
3.8.2. Nodal Metastases
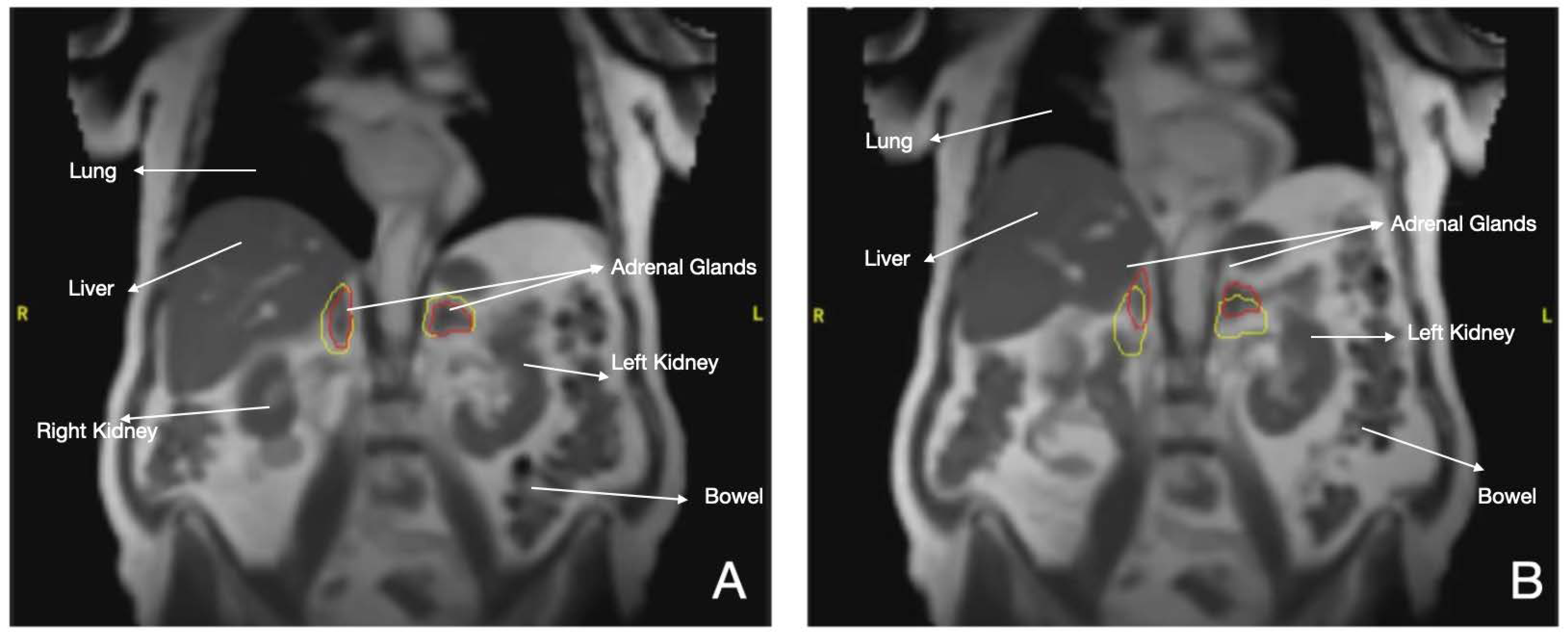
3.8.3. Adrenal Metastases
3.8.4. Spinal Metastases
3.8.5. Head and Neck
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedland, G.W.; Thurber, B.D.; Thurber, G.W.F.A.B.D.; Christner, J.A.; Kofler, J.M.; McCollough, C.H.; Johnson, T.R.C.; Donnelly, L.F.; Emery, K.H.; Brody, A.S.; et al. The birth of CT. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopp, A.H.; Yeung, A.R.; Deshmukh, S.; Gil, K.M.; Wenzel, L.; Westin, S.N.; Gifford, K.; Gaffney, D.K.; Small, W.; Thompson, S.; et al. Patient-Reported Toxicity During Pelvic Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy: NRG Oncology–RTOG 1203. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Vicini, F.; Wong, J.; Martinez, A. Adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman Minsky, N.; Saucedo Yáñez, A. Breve historia de la Resonancia Magnética Nuclear: Desde el descubrimiento hasta la aplicación en imagenología. Educ. Quím. 2019, 30, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potters, L.; Kavanagh, B.; Galvin, J.M.; Hevezi, J.M.; Janjan, N.A.; Larson, D.A.; Mehta, M.P.; Ryu, S.; Steinberg, M.; Timmerman, R.; et al. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) and American College of Radiology (ACR) Practice Guideline for the Performance of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffray, D.A. Image-guided radiotherapy: From current concept to future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammohan, N.; Randall, J.W.; Yadav, P. History of technological advancements towards MR-linac: The future of image-guided radiotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, C.E.; Parikh, P.J.; Spencer, C.R.; Green, O.L.; Hu, Y.; Mutic, S.; Olsen, J.R. Comparison of onboard low-field magnetic resonance imaging versus onboard computed tomography for anatomy visualization in radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leon, J.; Twentyman, T.; Carr, M.; Jameson, M.; Batumalai, V. Optimising the MR-Linac as a standard treatment modality. J. Med Radiat. Sci. 2023, 70, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Gregucci, F.; Pennell, R.T.; Nagar, H.; Golden, E.B.; Knisely, J.P.S.; Sanfilippo, N.J.; Formenti, S.C. MRI-LINAC: A transformative technology in radiation oncology. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1117874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagendijk, J.J.W.; Raaymakers, B.W.; van Vulpen, M. The magnetic resonance imaging–linac system. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keall, P.J.; Barton, M.; Crozier, S. The Australian magnetic resonance imaging–linac program. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallone, B.G.; Murray, B.; Rathee, S.; Stanescu, T.; Steciw, S.; Vidakovic, S.; Blosser, E.; Tymofichuk, D. First MR images obtained during megavoltage photon irradiation from a prototype integrated linac-MR system: First MR images from a prototype linac-MR system. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 2084–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutic, S.; Dempsey, J.F. The ViewRay system: Magnetic resonance–guided and controlled radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 24, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liney, G.P.; Whelan, B.; Oborn, B.; Barton, M.; Keall, P. MRI-linear accelerator radiotherapy systems. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, S.; Alongi, F.; Andratschke, N.; Azria, D.; Bohoudi, O.; Boldrini, L.; Bruynzeel, A.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Jürgenliemk-Schulz, I.; Lagerwaard, F.; et al. ESTRO-ACROP recommendations on the clinical implementation of hybrid MR-linac systems in radiation oncology. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 159, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Rannikko, A.S.; Borghi, M.; Panebianco, V.; Mynderse, L.A.; Vaarala, M.H.; Briganti, A.; Budäus, L.; Hellawell, G.; Hindley, R.G.; et al. ECISION Study Group Collaborators. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishan, A.U.; Ma, T.M.; Lamb, J.M.; Casado, M.; Wilhalme, H.; Low, D.A.; Sheng, K.; Sharma, S.; Nickols, N.G.; Pham, J.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging–guided vs computed tomography–Guided Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: The MIRAGE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, J.E.; Shin, K.; Chen, Y.; Mak, R.H.; Nguyen, P.L.; D’amico, A.V.; Martin, N.E. Acute toxicity comparison of magnetic resonance-guided adaptive versus fiducial or computed tomography-guided non-adaptive prostate stereotactic body radiotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer 2023, 129, 3044–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Archibald-Heeren, B.; Hu, Y.; Teh, A.; Beserminji, R.; Cai, E.; Liu, G.; Yates, A.; Rijken, J.; Collett, N.; et al. Varian ethos online adaptive radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Early results of contouring accuracy, treatment plan quality, and treatment time. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 23, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.M.; Ballas, L.K.; Wilhalme, H.; Sachdeva, A.; Chong, N.; Sharma, S.; Yang, T.; Basehart, V.; Reiter, R.E.; Saigal, C.; et al. Quality-of-Life Outcomes and Toxicity Profile Among Patients With Localized Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiation: The SCIMITAR Multicenter Phase 2 Trial. Endocrine 2022, 115, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciscano, A.E.; Wolfe, S.; Zhou, X.K.; Barbieri, C.E.; Formenti, S.C.; Hu, J.C.; Molina, A.M.; Nanus, D.M.; Nauseef, J.T.; Scherr, D.S.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of MRI-guided salvage radiotherapy for prostate cancer in 4 weeks versus 2 weeks (SHORTER). BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkmeijer, L.G.W.; Groen, V.H.; Pos, F.J.; Haustermans, K.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Smeenk, R.J.; Kunze-Busch, M.; de Boer, J.C.J.; Zijp, J.v.d.V.v.; van Vulpen, M.; et al. Focal Boost to the Intraprostatic Tumor in External Beam Radiotherapy for Patients With Localized Prostate Cancer: Results From the FLAME Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westley, R.L.; Biscombe, K.; Dunlop, A.; Mitchell, A.; Oelfke, U.; Nill, S.; Murray, J.; Pathmanathan, A.; Hafeez, S.; Parker, C.; et al. Interim toxicity analysis from the randomized HERMES trial of 2- and 5-fraction magnetic resonance imaging–guided adaptive prostate radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 187, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekatli, H.; Palacios, M.A.; Schneiders, F.L.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Slotman, B.J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. Local control and toxicity after magnetic resonance imaging (MR)-guided single fraction lung stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 187, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Sakyanun, P.; Mai, T.; Wong, W.; Lim, A.; Ludbrook, J.; Bettington, C.; Rezo, A.; Pryor, D.; Hardcastle, N.; et al. Long-term outcomes of TROG 13.01 SAFRON II randomized trial of single- versus multifraction stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3493–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, T.; Palacios, M.A.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Admiraal, M.A.; Spoelstra, F.O.; Bruynzeel, A.M.; Slotman, B.J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Senan, S. Stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy for peripheral lung tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Aznar, M.C.; Dubec, M.; Parker, G.J.M.; O’Connor, J.P.B. Delivering functional imaging on the MRI-linac: Current challenges and potential solutions. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.; Eccles, C.L.; McWilliam, A.; Chuter, R.; Walker, E.; Whitehurst, P.; Berresford, J.; Van Herk, M.; Hoskin, P.J.; Choudhury, A. Magnetic resonance-guided radiation therapy: A review. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 64, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Houdt, P.J.; Yang, Y.; van der Heide, U.A. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging for biological image-guided adaptive radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 615643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohri, N.; Tomé, W.A.; Romero, A.M.; Miften, M.; Haken, R.K.T.; Dawson, L.A.; Grimm, J.; Yorke, E.; Jackson, A. Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Liver Tumors. Endocrine 2018, 110, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klement, R.J.; Abbasi-Senger, N.; Adebahr, S.; Alheid, H.; Allgaeuer, M.; Becker, G.; Blanck, O.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Brunner, T.; Duma, M.; et al. The impact of local control on overall survival after stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver and lung metastases from colorectal cancer: A combined analysis of 388 patients with 500 metastases. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Krishnan, S.; Bhosale, P.R.; Javle, M.M.; Aloia, T.A.; Shroff, R.T.; Kaseb, A.O.; Bishop, A.J.; Swanick, C.W.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Ablative Radiotherapy Doses Lead to a Substantial Prolongation of Survival in Patients With Inoperable Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: A Retrospective Dose Response Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldrini, L.; Corradini, S.; Gani, C.; Henke, L.; Hosni, A.; Romano, A.; Dawson, L. MR-guided radiotherapy for liver malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 616027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, E.D.; Wu, A.; Chen, H.; Heron, D.; Kalnicki, S.; Komanduri, K.; Gerszten, K.; Burton, S.; Ahmed, I.; Shou, Z. Abdominal organ motion measured using 4D CT. Endocrine 2006, 65, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akino, Y.; Oh, R.-J.; Masai, N.; Shiomi, H.; Inoue, T. Evaluation of potential internal target volume of liver tumors using cine-MRI: Potential ITV of liver tumor. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 111704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccles, C.; Brock, K.K.; Bissonnette, J.-P.; Hawkins, M.; Dawson, L.A. Reproducibility of liver position using active breathing coordinator for liver cancer radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 64, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boda-Heggemann, J.; Knopf, A.-C.; Simeonova-Chergou, A.; Wertz, H.; Stieler, F.; Jahnke, A.; Jahnke, L.; Fleckenstein, J.; Vogel, L.; Arns, A.; et al. Deep Inspiration Breath Hold—Based Radiation Therapy: A Clinical Review. Endocrine 2015, 94, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, J.S.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Bassetti, M.F. MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy for liver tumours: Visualising the future. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e74–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, W.; Timmerman, R.; Tong, L.; Abdulrahman, R.; Meyer, J.; Boike, T.; Schwarz, R.E.; Weatherall, P.; Cho, L.C. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Patients With Hepatic Metastases. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 18, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.E.; Contreras, J.A.; Green, O.L.; Cai, B.; Kim, H.; Roach, M.C.; Olsen, J.R.; Fischer-Valuck, B.; Mullen, D.F.; Kashani, R.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Image-Guided Radiotherapy (MRIgRT): A 4.5-Year Clinical Experience. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegen, P.; Zhang, K.S.; Tonndorf-Martini, E.; Weykamp, F.; Regnery, S.; Naumann, P.; Lang, K.; Ristau, J.; Körber, S.A.; Dreher, C.; et al. MR-guided adaptive versus ITV-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatic metastases (MAESTRO): A randomized controlled phase II trial. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanknebel, K.; Conlon, K.C. Advances in the surgical management of pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 2001; 7, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, M.; Redaelli, C.; Lietz, M.; A Seiler, C.; Friess, H.; Büchler, M.W. Curative resection is the single most important factor determining outcome in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 2004, 91, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Comito, T.; Ghidini, A.; Torri, V.; Scorsetti, M.; Barni, S. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and pooled analysis of 19 trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerkens, H.D.; Hall, W.A.; Li, X.A.; Knechtges, P.; Dalah, E.; Paulson, E.S.; van den Berg, C.A.T.; Meijer, G.J.; Koay, E.J.; Crane, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for MRI-based contouring of gross tumor volume and organs at risk for radiation therapy of pancreatic cancer. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 7, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, L.; Kashani, R.; Robinson, C.; Curcuru, A.; DeWees, T.; Bradley, J.; Green, O.; Michalski, J.; Mutic, S.; Parikh, P.; et al. Phase I trial of stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for the treatment of oligometastatic or unresectable primary malignancies of the abdomen. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 126, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koste, J.R.V.S.D.; Palacios, M.A.; Bruynzeel, A.M.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S.; Lagerwaard, F. MR-guided Gated Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Delivery for Lung, Adrenal, and Pancreatic Tumors: A Geometric Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong; Kirsch, C.; Herrera, R.; Rubens, M.; Gungor, G.; Schaff, E.; Dolan, J.; Kim, J.; Mittauer, K.; Kotecha, R.; et al. Long-Term Multi-Institutional Outcomes of 5-Fraction Ablative Stereotactic MR-Guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy (SMART) for Inoperable Pancreas Cancer With Median Prescribed Biologically Effective Dose of 100 Gy10. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 111, S147–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavic, M.; Niyazi, M.; Wilke, L.; Corradini, S.; Vornhülz, M.; Mansmann, U.; Al Tawil, A.; Fritsch, R.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Debus, J.; et al. MR-guided adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) of primary tumor for pain control in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (mPDAC): An open randomized, multicentric, parallel group clinical trial (MASPAC). Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Straza, M.W.; Chen, X.; Mickevicius, N.; Erickson, B.; Schultz, C.; Awan, M.; Ahunbay, E.; Li, X.A.; Paulson, E.S.W.A.; et al. Initial clinical experience of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for liver metastases, primary liver malignancy, and pancreatic cancer with 4D-MRI based online adaptation and real-time MRI monitoring using a 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong, M.D.; Bryant, J.M.; Herrera, R.; McCulloch, J.; Contreras, J.; Kotecha, R.; Romaguera, T.; Alvarez, D.; Hall, M.D.; Rubens, M.; et al. Dose-escalated magnetic resonance image–guided abdominopelvic reirradiation with continuous intrafraction visualization, soft tissue tracking, and automatic beam gating. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 7, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Small, C.; Paulson, E.; Koay, E.J.; Crane, C.; Intven, M.; Daamen, L.A.; Meijer, G.J.; Heerkens, H.D.; Bassetti, M.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Guided Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Advantages, Challenges, Current Approaches, and Future Directions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchelebi, L.T.; Romesser, P.B.; Feuerlein, S.; Hoffe, S.; Latifi, K.; Felder, S.; Chuong, M.D. Magnetic resonance guided radiotherapy for rectal cancer: Expanding opportunities for non-operative management. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 107327482096944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoni, P.; Fiorino, C.; Slim, N.; Ronzoni, M.; Ricci, V.; Di Palo, S.; De Nardi, P.; Orsenigo, E.; Tamburini, A.; De Cobelli, F.; et al. Feasibility of an Adaptive Strategy in Preoperative Radiochemotherapy for Rectal Cancer With Image-Guided Tomotherapy: Boosting the Dose to the Shrinking Tumor. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 87, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelt, A.L.; Pløen, J.; Harling, H.; Jensen, F.S.; Jensen, L.H.; Jørgensen, J.C.R.; Lindebjerg, J.; Rafaelsen, S.R.; Jakobsen, A. High-dose chemoradiotherapy and watchful waiting for distal rectal cancer: A prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiloiro, G.; Boldrini, L.; Meldolesi, E.; Re, A.; Cellini, F.; Cusumano, D.; Corvari, B.; Mantini, G.; Balducci, M.; Valentini, V.; et al. MR-guided radiotherapy in rectal cancer: First clinical experience of an innovative technology. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 18, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intven, M.; Otterloo, S.d.M.v.; Mook, S.; Doornaert, P.; Breugel, E.d.G.-V.; Sikkes, G.; Willemsen-Bosman, M.; van Zijp, H.; Tijssen, R. Online adaptive MR-guided radiotherapy for rectal cancer; feasibility of the workflow on a 1.5T MR-linac: Clinical implementation and initial experience. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 154, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelenkamp, H.; Boekhoff, M.R.; Verweij, M.E.; Peters, F.P.; Meijer, G.J.; Intven, M.P. Planning target volume margin assessment for online adaptive MR-guided dose-escalation in rectal cancer on a 1.5 T MR-Linac. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 162, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, M.; Blackledge, M.; White, I.; Wetscherek, A.; Lalondrelle, S.; Hafeez, S.; Bhide, S. Quantitative analysis of diffusion weighted imaging in rectal cancer during radiotherapy using a magnetic resonance imaging integrated linear accelerator. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 23, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Vicini, F.; Cecchini, R.S.; White, J.R.; Arthur, D.W.; Julian, T.B.; A Rabinovitch, R.; Kuske, R.R.; A Ganz, P.; Parda, D.S.; Scheier, M.F.; et al. Long-term primary results of accelerated partial breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A randomised, phase 3, equivalence trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, S.C.; Hsu, H.; Fenton-Kerimian, M.; Roses, D.; Guth, A.; Jozsef, G.; Goldberg, J.D.; Dewyngaert, J.K. Prone accelerated partial breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery: Five-year results of 100 patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meattini, I.; Marrazzo, L.; Saieva, C.; Desideri, I.; Scotti, V.; Simontacchi, G.; Bonomo, P.; Greto, D.; Mangoni, M.; Scoccianti, S.; et al. Accelerated Partial-Breast Irradiation Compared With Whole-Breast Irradiation for Early Breast Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Randomized Phase III APBI-IMRT-Florence Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4175–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primary Results of NSABP B-39/RTOG 0413 (NRG Oncology): A Randomized Phase III Study of Conventional Whole Breast Irradiation (WBI) versus Partial Breast Irradiation (PBI) for Women with Stage 0, I, or II Breast Cancer. cochranelibrary.com. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/es/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-01942941/full (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Whelan, T.J.; Julian, J.A.; Berrang, T.S.; Kim, D.-H.; Germain, I.; Nichol, A.M.; Akra, M.; Lavertu, S.; Germain, F.; Fyles, A.; et al. External beam accelerated partial breast irradiation versus whole breast irradiation after breast conserving surgery in women with ductal carcinoma in situ and node-negative breast cancer (RAPID): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2165–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Coles, C.; Griffin, C.L.; Kirby, A.M.; Titley, J.; Agrawal, R.K.; Alhasso, A.; Bhattacharya, I.S.; Brunt, A.M.; Ciurlionis, L.; Chan, C.; et al. Partial-breast radiotherapy after breast conservation surgery for patients with early breast cancer (UK IMPORT LOW trial): 5-year results from a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1048–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, A.; Ciérvide, R. Preoperative radio(chemo)therapy in breast cancer: Time to switch the perspective? Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 9767–9787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.; Whelan, T.J. Accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI): Where are we now? Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2020, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicini, F.A.; Kestin, L.L.; Goldstein, N.S. Defining the clinical target volume for patients with early-stage breast cancer treated with lumpectomy and accelerated partial breast irradiation: A pathologic analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Fischer-Valuck, B.W.; Mazur, T.R.; Curcuru, A.; Sona, K.; Kashani, R.; Green, O.; Ochoa, L.; Mutic, S.; Zoberi, I.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Image Guided Radiation Therapy for External Beam Accelerated Partial-Breast Irradiation: Evaluation of Delivered Dose and Intrafractional Cavity Motion. Endocrine 2016, 96, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Valuck, B.W.; Henke, L.; Green, O.; Kashani, R.; Acharya, S.; Bradley, J.D.; Robinson, C.G.; Thomas, M.; Zoberi, I.; Thorstad, W.; et al. Two-and-a-half-year clinical experience with the world’s first magnetic resonance image guided radiation therapy system. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 2, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heijst, T.C.F.; den Hartogh, M.D.; Lagendijk, J.J.W.; van den Bongard, H.J.G.D.; van Asselen, B. MR-guided breast radiotherapy: Feasibility and magnetic-field impact on skin dose. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 5917–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.H.; Shin, K.H.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Chie, E.K.; Wu, H.-G. Seroma change during magnetic resonance imaging-guided partial breast irradiation and its clinical implications. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbar, M.; Mönnich, D.; Boeke, S.; Gani, C.; Weidner, N.; Heinrich, V.; Russo, M.L.; Livi, L.; Winter, J.; Tsitsekidis, S.; et al. Partial breast irradiation with the 1.5 T MR-Linac: First patient treatment and analysis of electron return and stream effects. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 145, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charaghvandi, K.; Westeinde, T.V.; Yoo, S.; Houweling, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Verkooijen, H.; Philippens, M.; van Asselen, B.; Horton, J.; Bongard, H.v.D. Single dose partial breast irradiation using an MRI linear accelerator in the supine and prone treatment position. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Lim-Reinders, S.; McCann, C.; Ahmad, S.B.; Sahgal, A.; Lee, J.; Keller, B.M. Magnetic field dose effects on different radiation beam geometries for hypofractionated partial breast irradiation. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2017, 18, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, A.; Simmons, A.; Kim, D.N.; Leitch, M.; Haas, J.; Gu, X.; Ahn, C.; Gao, A.; Spangler, A.; Morgan, H.E.; et al. Preliminary results of multi-institutional phase 1 dose escalation trial using single-fraction stereotactic partial breast irradiation for early stage breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore-Palhares, D.; Ho, L.; Lu, L.; Chugh, B.; Vesprini, D.; Karam, I.; Soliman, H.; Symons, S.; Leung, E.; Loblaw, A.; et al. Clinical implementation of magnetic resonance imaging simulation for radiation oncology planning: 5 year experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakomy, D.S.; Yang, J.; Vedam, S.; Wang, J.; Lee, B.; Sobremonte, A.; Castillo, P.; Hughes, N.; Mohammedsaid, M.; Jhingran, A.; et al. Clinical Implementation and Initial Experience With a 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac for MR-Guided Radiation Therapy for Gynecologic Cancer: An R-IDEAL Stage 1 and 2a First in Humans Feasibility Study of New Technology Implementation. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, e296–e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavas, G.; Kuscu, U.E.; Ayhan, A.; Yavas, C.; Onal, C. The utility of 1.5 tesla MR-guided adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy for recurrent ovarian tumor—Case reports and review of the literature. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 99, 107696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelance, L.; Corradini, S.; Erickson, B.; Lalondrelle, S.; Padgett, K.; van der Leij, F.; van Lier, A.; Jürgenliemk-Schulz, I. Online Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiotherapy (oMRgRT) for Gynecological Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 628131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E.; Tang, C.; Swaminath, A.; Kerkmeijer, L.; Chu, W. Adaptive magnetic resonance-guided stereotactic body radiotherapy: The next step in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 634830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Trisler, K.; Wessels, B.W.; Knox, S.J. Radiobiologic studies of radioimmunotherapy and external beam radiotherapy in vitro and in vivo in human renal cell carcinoma xenografts. Cancer 1997, 80 (Suppl. S12), 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.; Stanfield, J.L.; Cho, L.C.; Chang, C.-H.; Forster, K.; Kabbani, W.; Cadeddu, J.A.; Hsieh, J.-T.; Choy, H.; Timmerman, R.; et al. Efficacy of Ablative High-Dose-per-Fraction Radiation for Implanted Human Renal Cell Cancer in a Nude Mouse Model. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, S.; Correa, R.J.; Warner, A.; Staehler, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Ponsky, L.; Kaplan, I.D.; Mahadevan, A.; Chu, W.; Gandhidasan, S.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for ≥T1b Primary Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report From the International Radiosurgery Oncology Consortium for Kidney (IROCK). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 108, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; Bresel, M.; Sidhom, M.; Sridharan, S.; Vanneste, B.; Davey, R.; Ruben, J.; Foroudi, F.; Higgs, B.G.; Lin, C.; et al. TROG 15.03/ANZUP International Multicenter Phase II Trial of Focal Ablative STereotactic RAdiotherapy for Cancers of the Kidney (FASTRACK II). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusumano, D.; Dhont, J.; Boldrini, L.; Chiloiro, G.; Romano, A.; Votta, C.; Longo, S.; Placidi, L.; Azario, L.; De Spirito, M.; et al. Reliability of ITV approach to varying treatment fraction time: A retrospective analysis based on 2D cine MR images. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusumano, D.; Dhont, J.; Boldrini, L.; Chiloiro, G.; Teodoli, S.; Massaccesi, M.; Fionda, B.; Cellini, F.; Azario, L.; Vandemeulebroucke, J.; et al. Predicting tumour motion during the whole radiotherapy treatment: A systematic approach for thoracic and abdominal lesions based on real time MR. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 129, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudra, S.; Fischer-Valuck, B.; Pachynski, R.; Daly, M.; Green, O. Magnetic Resonance Image Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy to the Primary Renal Mass in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetar, S.U.; Bohoudi, O.; Senan, S.; Palacios, M.A.; Oei, S.S.; Wel, A.M.v.d.; Slotman, B.J.; Moorselaar, R.J.A.v.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E. The Role of Daily Adaptive Stereotactic MR-Guided Radiotherapy for Renal Cell Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziero, D.; Straza, M.W.; Ford, J.C.; Bovi, J.A.; Diwanji, T.; Stoyanova, R.; Paulson, E.S.; Mellon, E.A. MR-guided radiotherapy for brain and spine tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 626100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.; Sahgal, A.; Zadeh, M.M.; Moazen, B.; Jabehdar Maralani, P.; Breen, S.; Lau, A.; Binda, S.; Keller, B.; Husain, Z.; et al. Empirical planning target volume modeling for high precision MRI guided intracranial radiotherapy. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 39, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.K.; Dooley, S.; Maziero, D.; Ford, J.C.; Stoyanova, R.; Goryawala, M.; Diwanji, T.; Mellon, E. MRI-Guided Radiotherapy Identifies Early Pseudoprogression of Glioblastoma. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, B.; Cullison, K.; Maziero, D.; Azzam, G.A.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Brown, K.; Valderrama, A.; Meshman, J.; Breto, A.; Ford, J.C.; et al. Simulated Adaptive Radiotherapy for Shrinking Glioblastoma Resection Cavities on a Hybrid MRI–Linear Accelerator. Cancers 2023, 15, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, A.; Mittauer, K.E.; Rzepczynski, A.E.; Chuong, M.D.; Kutuk, T.; Bassiri, N.; McAllister, N.C.; Hall, M.D.; McCulloch, J.; Alvarez, D.; et al. Treatment of glioblastoma using MRIdian® A3i BrainTxTM: Imaging and treatment workflow demonstration. Med. Dosim. 2023, 48, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-L.; Chen, H.; Stewart, J.; Lau, A.Z.; Chan, R.W.; Lawrence, L.S.P.; Myrehaug, S.; Soliman, H.; Detsky, J.; Lim-Fat, M.J.; et al. High grade glioma radiation therapy on a high field 1.5 Tesla MR-Linac—Workflow and initial experience with daily adapt-to-position (ATP) MR guidance: A first report. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1060098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Kenjo, M.; Doi, Y.; Ueda, T.; Nakao, M.; Ozawa, S.; Nagata, Y. Effect of Target Changes on Target Coverage and Dose to the Normal Brain in Fractionated Stereotactic Radiation Therapy for Metastatic Brain Tumors. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, P.; Peng, K.; He, H.; Zhou, R.; et al. An exploratory analysis of MR-guided fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 40, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, S.; Alongi, F.; Andratschke, N.; Belka, C.; Boldrini, L.; Cellini, F.; Debus, J.; Guckenberger, M.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; et al. MR-guidance in clinical reality: Current treatment challenges and future perspectives. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawlani, V.; Davies, N.; Patel, M.; Flintham, R.; Fong, C.; Heyes, G.; Cruickshank, G.; Steven, N.; Peet, A.; Hartley, A.; et al. Evaluation of response to stereotactic radiosurgery in brain metastases using multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and a review of the literature. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seravalli, E.; Sierts, M.; Brand, E.; Maspero, M.; David, S.; Philippens, M.E.; Voormolen, E.H.; Verhoeff, J.J. Dosimetric feasibility of direct post-operative MR-Linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery for resection cavities of brain metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 179, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussani, R.; De-Giorgio, F.; Abbate, A.; Silvestri, F. Cardiac metastases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.J.; Palm, R.F.; DeLozier, K.B.; Feygelman, V.; Latifi, K.; Redler, G.; Washington, I.R.; Wuthrick, E.J.; Rosenberg, S.A. MR-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy for intracardiac and pericardial metastases. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 25, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabani, P.; Fischer-Valuck, B.W.; Robinson, C.G.; Wilson, D.B.; Michalski, J.M. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for the treatment of primary cardiac angiosarcoma causing hemodynamic instability. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 9, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladbury, C.; Amini, A.; Schwer, A.; Liu, A.; Williams, T.; Lee, P. Clinical applications of magnetic resonance-guided radiotherapy: A narrative review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuculich, P.S.; Schill, M.R.; Kashani, R.; Mutic, S.; Lang, A.; Cooper, D.; Faddis, M.; Gleva, M.; Noheria, A.; Smith, T.W.; et al. Noninvasive Cardiac Radiation for Ablation of Ventricular Tachycardia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, D.; Zaman, A.; Eidinger, L.; Grehn, M.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Rudic, B.; Mehrhof, F.; Boldt, L.H.; Hohmann, S.; Merten, R.; et al. Radiosurgery for ventricular tachycardia (RAVENTA): Interim analysis of a multicenter multiplatform feasibility trial. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2023, 199, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccia, F.; Rigo, M.; Gurrera, D.; Nicosia, L.; Mazzola, R.; Figlia, V.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Ricchetti, F.; Attinà, G.; Pastorello, E.; et al. Mitigation on bowel loops daily variations by 1.5-T MR-guided daily-adaptive SBRT for abdomino-pelvic lymph-nodal oligometastases. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 3269–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.M.; Luterstein, E.; Chu, F.; Cao, M.; Lamb, J.; Agazaryan, N.; Low, D.; Raldow, A.; Steinberg, M.L.; Lee, P. Clinical outcomes of stereotactic magnetic resonance image-guided adaptive radiotherapy for primary and metastatic tumors in the abdomen and pelvis. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 5897–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buergy, D.; Würschmidt, F.; Gkika, E.; Hörner-Rieber, J.; Knippen, S.; Gerum, S.; Balermpas, P.; Henkenberens, C.; Voglhuber, T.; Kornhuber, C.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy of adrenal metastases—A dose-finding study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegen, P.; Katsigiannopulos, E.; Buchele, C.; Regnery, S.; Weykamp, F.; Sandrini, E.; Ristau, J.; Liermann, J.; Meixner, E.; Forster, T.; et al. Stereotactic magnetic resonance-guided online adaptive radiotherapy of adrenal metastases combines high ablative doses with optimized sparing of organs at risk. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 39, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztek, M.A.; A Mayr, N.; Mossa-Basha, M.; Nyflot, M.; A Sponseller, P.; Wu, W.; Hofstetter, C.P.; Saigal, R.; Bowen, S.R.; Hippe, D.S.; et al. The Dancing Cord: Inherent Spinal Cord Motion and Its Effect on Cord Dose in Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redler, G.; Stevens, T.; Cammin, J.; Malin, M.; Green, O.; Mutic, S.; Pitroda, S.; Aydogan, B. Dosimetric Feasibility of Utilizing the ViewRay Magnetic Resonance Guided Linac System for Image-guided Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Cureus 2019, 11, e6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.M.; Hsu, S.; Lamb, J.; Yang, Y.; Agazaryan, N.; Steinberg, M.L.; Low, D.A.; Cao, M. MRI-guided radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: Initial clinical experience. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 20, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MRIdian | Unity | |
|---|---|---|
| Magnet design | Split magnet | Single magnet design |
| Magnet | 0.35 T * | 1.5 T * |
| Intrafraction management | Automatic | Non-automatic |
| Image | TRUFI **, T1, T2 | Variety of image sequences |
| Tracking | Real-time tracking | Real-time tracking |
| Gating | Automatic | Non-automatic |
| Gantry | Maximum rotation speed 0.5 rpm *** | Maximum rotation speed 6 rpm *** |
| Study Name | Tumor Type | Study Type | Intervention | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose de-escalation in prostate radiotherapy using the MRL (DESTINATION) NCT05709496 | Prostate cancer | Phase II | Radiotherapy to the prostate which will be given in 30 Gy in 5 fractions to the whole prostate and 45 Gy in 5 fractions to the dominant lesion. | The goal of this feasibility study is to learn about dose de-escalation in the treatment of men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. |
| Randomized trial of five or two MRI-Guided adaptive radiotherapy treatments for prostate cancer (FORT) NCT04984343 | Prostate cancer | Phase II | Patients will receive 25 Gy in two radiotherapy treatments vs. 37.5 Gy in 5 fractions. | To demonstrate that two treatments of radiotherapy does not significantly increase patient-reported gastrointestinal (GI) and genitourinary (GU) symptoms compared to five treatments of radiotherapy 2 years after treatment completion. |
| MR-LINAC Guided Ultra-hypofractionated RT for Prostate Cancer (NCT05183074) | Prostate cancer | Phase II | Ultra-hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients with low-, intermediate, and high-risk prostate cancer. | To investigate the tolerability of MR-LINAC based stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (MRL-SBRT) for patients with localized prostate cancer. |
| Magnetic Resonance Guided Adaptive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Lung Tumors in Ultracentral Location (MAGELLAN) NCT04925583 | Lung cancer | Phase I | Patients will receive 50 Gy in 5 fractions; 55 Gy in 5 fractions; 60 Gy in 5 fractions; or 65 Gy in 5 fractions. | To identify the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of MRI-guided SBRT to ultracentral lung tumors. |
| Magnetic Resonance-Guided Hypofractionated Adaptive Radiation Therapy With Concurrent Chemotherapy and Consolidation Durvalumab for Inoperable Stage IIB, IIIA, and Select IIIB and IIIC Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT03916419 | Lung cancer | Phase II | Patients will receive 60 Gy in 15 fractions. | Safety of hypofractionated MRI-guided adaptive radiotherapy. |
| Magnetic Resonance-guided Adaptive Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Hepatic Metastases (MAESTRO) NCT05027711 | Liver metastases | Phase I | SBRT with MRI-LINAC BED ≥ 100 Gy with ITV vs. SBRT with LINAC ITV ≥ 100 Gy vs. SBRT with MRI-LINAC to the highest possible dose to the ITV. | Treatment-related toxicity. |
| Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Treated With ABLAtivE Stereotactic MRI-guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy (LAP-ABLATE) NCT05585554 | Pancreatic cancer | Phase I–II | Induction chemotherapy + MR-LINAC 50 Gy vs. induction chemotherapy alone. | To demonstrate superior 2-year overall survival from date of randomization in ablative MRIdian SMART versus no ablative MRIdian SMART in locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients without disease progression after induction chemotherapy. |
| Chemotherapy Combined With High-dose Radiotherapy for Low Rectal Cancer Using MR Guided Linear Accelerator NCT05338866 | Rectal cancer | Phase II | CT-RT in LINAC (50 Gy in 25 fractions) + Boost in MR-LINAC 16–20 Gy in 8–10 fractions vs. CT-RT in LINAC (50 Gy in 25 fractions) + Boost in MR-LINAC 30 Gy in 15 fractions. | Three-year progression-free survival rate. |
| MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Early-Stage Kidney Cancer, the MRI-MARK Trial NCT04580836 | Kidney cancer | Phase II | Treatment (MRI-guided SBRT). | To evaluate local control following magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-guided stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for primary kidney cancer, as defined by no growth by imaging at 24 months following SBRT. |
| UNITED (UNIty-Based MR-Linac Guided AdapTive RadiothErapy for High GraDe Glioma: A Phase 2 Trial (UNITED) NCT04726397 | Glioblastoma multiforme | Phase II | Radiation: adaptative radiotherapy with reduced margins (CTV 5 mm) | Tumor recurrence detected by imaging at the edge of the radiation volume. |
| UNITy-BasED MR-Linac Adaptive Simultaneous Integrated Hypofractionationed Boost Trial for High Grade Glioma in the Elderly (UNITED2) NCT05565521 | Glioblastoma multiforme, adult IDH-mutant glioblastoma | Phase II | Radiation: dose escalation + adaptative radiotherapy with reduced margins. | Progression-free survival at 6 months after chemoradiation. |
| A Prospective, Phase II Study of MR-Linac Guided Adaptive Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases From Non-small Cell Lung Cancer NCT04946019 | 1–10 BM non-small cell lung cancer | Phase II | Combined product: FSRT guided by Unity-based MR-LINAC FSRT (30 Gy in five fractions). | Intracranial progression-free survival at 1 year. |
| A Master Protocol of Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance Guided Adaptive Radiation Therapy (SMART) NCT04115254 | All/multiple sites (including BM) | Phase I–II | MRI-guided LINAC. | Phase I: radiation will be administered in an MRI-LINAC. Phase II: Improvement in local control. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ocanto, A.; Torres, L.; Montijano, M.; Rincón, D.; Fernández, C.; Sevilla, B.; Gonsalves, D.; Teja, M.; Guijarro, M.; Glaría, L.; et al. MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape. Cancers 2024, 16, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020270
Ocanto A, Torres L, Montijano M, Rincón D, Fernández C, Sevilla B, Gonsalves D, Teja M, Guijarro M, Glaría L, et al. MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020270
Chicago/Turabian StyleOcanto, Abrahams, Lisselott Torres, Miguel Montijano, Diego Rincón, Castalia Fernández, Beatriz Sevilla, Daniela Gonsalves, Macarena Teja, Marcos Guijarro, Luis Glaría, and et al. 2024. "MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape" Cancers 16, no. 2: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020270
APA StyleOcanto, A., Torres, L., Montijano, M., Rincón, D., Fernández, C., Sevilla, B., Gonsalves, D., Teja, M., Guijarro, M., Glaría, L., Hernánz, R., Zafra-Martin, J., Sanmamed, N., Kishan, A., Alongi, F., Moghanaki, D., Nagar, H., & Couñago, F. (2024). MR-LINAC, a New Partner in Radiation Oncology: Current Landscape. Cancers, 16(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020270







