Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital Invasion: A Literature Review and Modular System of Surgical Approaches
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
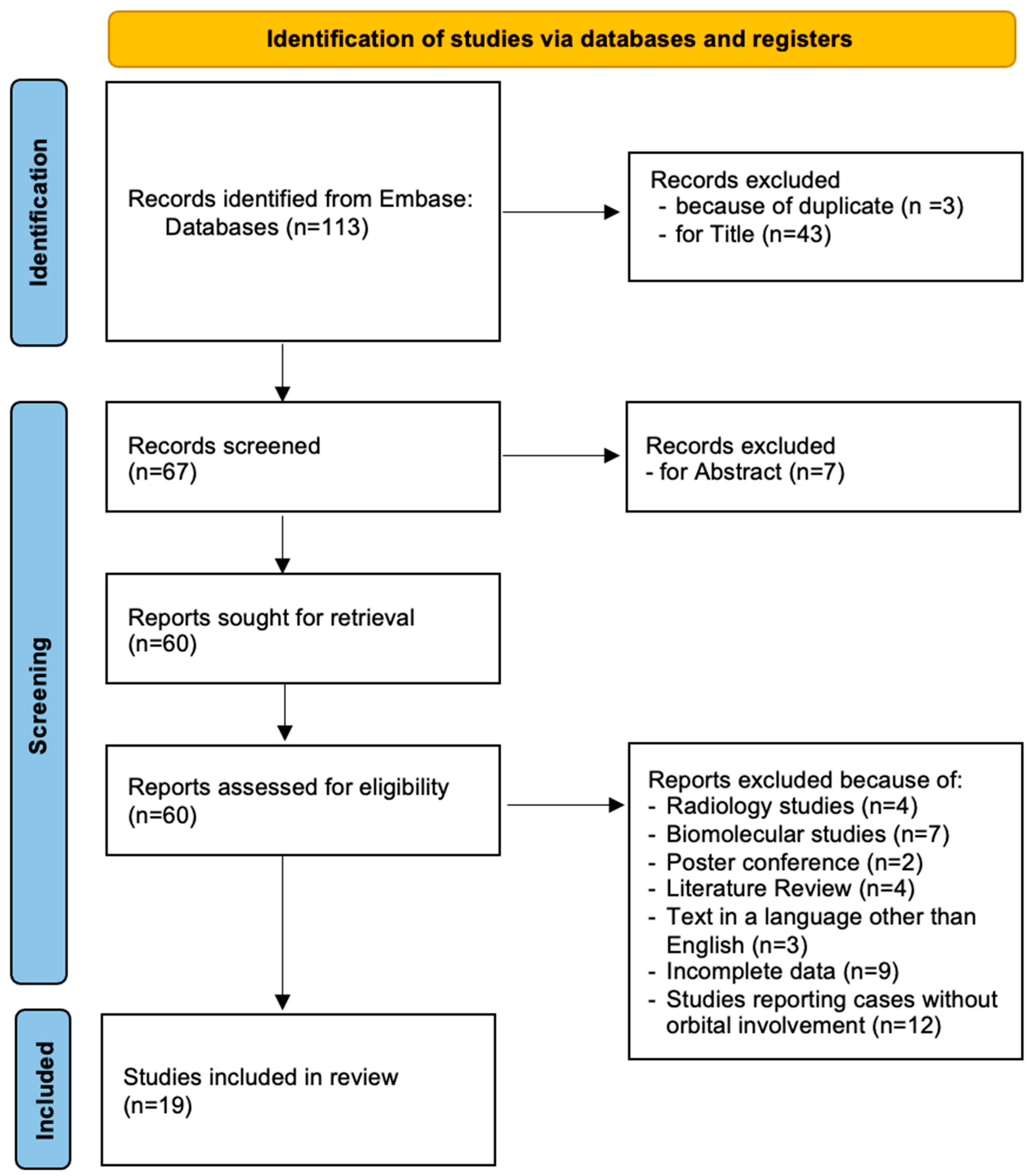
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Case
3.2. Literature Review
3.3. Demographic, Clinical, and Neuroradiological Data (Table 1 and Table 3)
3.4. Treatment and Outcome Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Treatment Strategies
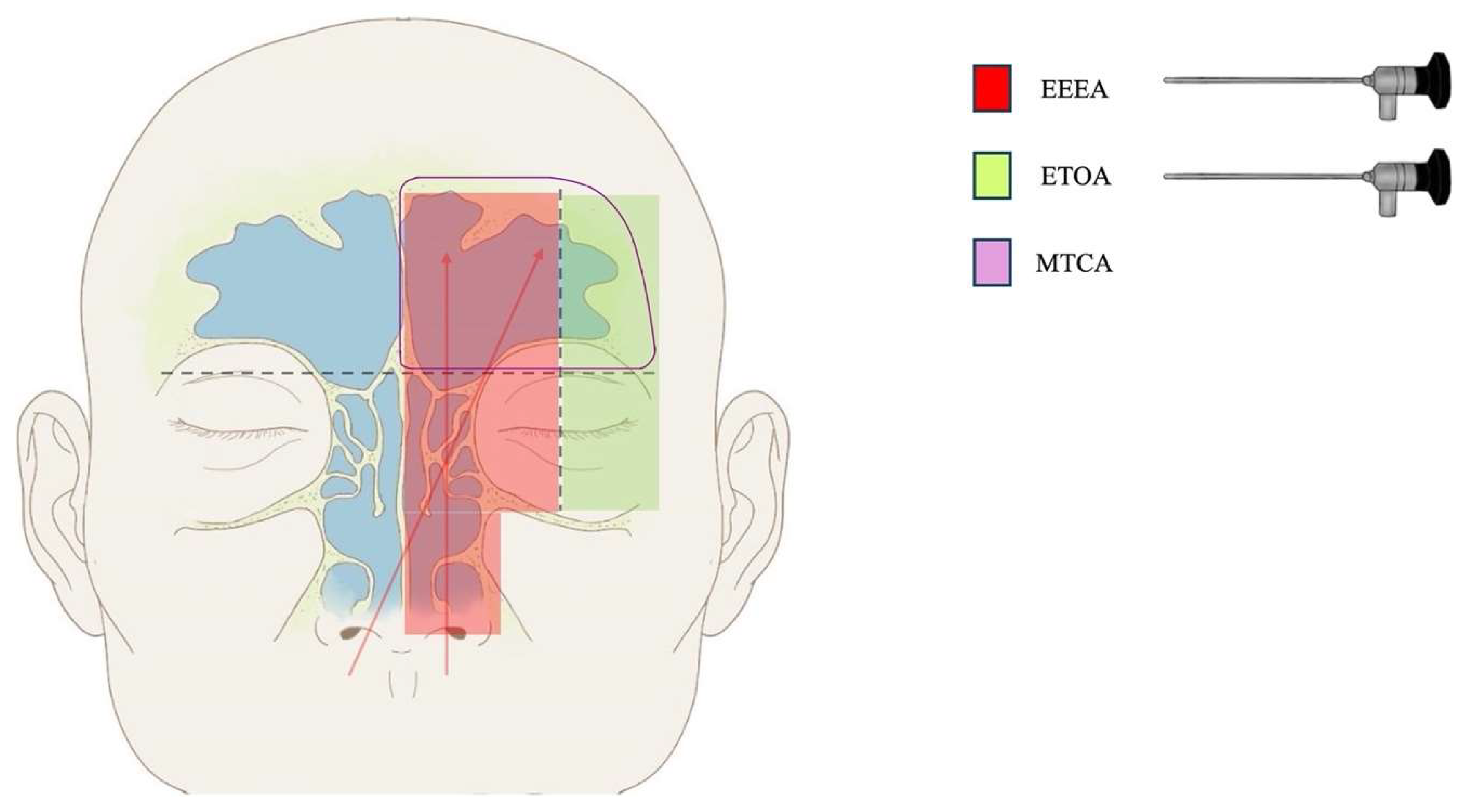
4.2. Surgical Nuances
- -
- Lesions affecting the superior–medial and inferior–medial areas, located medially to the mid-orbit meridian plane, and involving the upper nasal cavity, the ethmoid sinus, and the middle part of the frontal sinus can be accessed through an isolated EEEA (single-port strategy);
- -
- The component of the lesion extending to the superior–lateral area, located laterally to the mid-orbit meridian and into the anterior cranial fossa, can be accessed through TCA or TOA (two-port strategy: EEEA + TCA or EEEA + SETOA);
- -
- The component of the lesion extending to the inferior–lateral area, located laterally to the mid-orbit meridian and into the orbit, can be accessed through a TCA or TOA (two-port strategy: EEEA + TCA or EEEA + SETOA);
- -
- The component of the lesion extending to the superior–lateral area bilaterally can be accessed through a bilateral TCA or TOA (two-port strategy: EEEA + TCA, or three ports: EEEA + bilateral SETOA).
4.3. Limitation of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernardo, A.; Evins, A.I.; Corvino, S. Microsurgical Anatomy of the Superior and Inferior Orbital Fissures. In Cranio-Orbital Mass Lesions; Bonavolontà, G., Maiuri, F., Mariniello, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogele, D.; Sollmann, N.; Beck, A.; Haggenmüller, B.; Schmidt, S.A.; Schmitz, B.; Kapapa, T.; Ozpeynirci, Y.; Beer, M.; Kloth, C. Orbital Tumors-Clinical, Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariniello, G.; Corvino, S.; Corazzelli, G.; de Divitiis, O.; Fusco, G.; Iuliano, A.; Strianese, D.; Briganti, F.; Elefante, A. Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: The Rationale behind the Decision-Making Process of Treatment Strategy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariniello, G.; Corvino, S.; Iuliano, A.; Maiuri, F. Spheno-orbital Meningiomas. In Cranio-Orbital Mass Lesions; Bonavolontà, G., Maiuri, F., Mariniello, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.S.; Vargas, M.I.; Ailianou, A.; Merlini, L.; Poletti, P.A.; Platon, A.; Delattre, B.M.; Rager, O.; Burkhardt, K.; Becker, M. Orbital tumours and tumour-like lesions: Exploring the armamentarium of multiparametric imaging. Insights Imaging 2016, 7, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonavolontà, G.; Strianese, D.; Grassi, P.; Comune, C.; Tranfa, F.; Uccello, G.; Iuliano, A. An analysis of 2480 space-occupying lesions of the orbit from 1976 to 2011. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasen, S.; Bishop, J.A.; Hellquist, H.; Hunt, J.; Kiss, K.; Rinaldo, A.; Skálová, A.; Willems, S.M.; Williams, M.; Ferlito, A. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: Demographics, clinicopathological characteristics, molecular features, and prognosis of a recently described entity. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelow, E.B.; Bishop, J.A. Update from the 4th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumours: Tumors of the Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses and Skull Base. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.S.; East, E.G.; McHugh, J.B. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma: A Review and Update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 1196–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.T.; Oliveira, A.M.; Nascimento, A.G.; Schembri-Wismayer, D.; Moore, E.A.; Olsen, K.D.; Garcia, J.G.; Lonzo, M.L.; Lewis, J.E. Low-grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features: A clinicopathologic analysis of 28 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, K.A.; Han, L.M.; Chiu, A.G.; Aly, F.Z. Low-grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features--diagnostic challenge and pathogenic insight. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2015, 119, e265–e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooper, L.M.; Huang, S.C.; Antonescu, C.R.; Westra, W.H.; Bishop, J.A. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: An expanded immunoprofile including consistent nuclear β-catenin positivity and absence of SOX10 expression. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.J.; Lauria, A.; Hornick, J.L.; Xiao, S.; Fletcher, J.A.; Marino-Enriquez, A. Alternate PAX3-FOXO1 oncogenic fusion in biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2016, 55, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.C.; Ghossein, R.A.; Bishop, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, T.C.; Huang, H.Y.; Antonescu, C.R. Novel PAX3-NCOA1 Fusions in Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Focal Rhabdomyoblastic Differentiation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.B.; Wiggins, R.H.; Witt, B.L.; Dundar, Y.; Johnston, T.M.; Hunt, J.P. Imaging and Outcomes for a New Entity: Low-Grade Sinonasal Sarcoma with Neural and Myogenic Features. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2017, 78, e15–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liao, B.; Han, A. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma with diffuse infiltration and intracranial extension: A case report. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 11743–11746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, A.; Rajeshwari, M.; Sakthivel, P.; Sharma, M.C.; Sharma, S.C. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: A series of six cases with evaluation of role of β-catenin immunohistochemistry in differential diagnosis. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 33, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitguppi, C.; Koszewski, I.; Collura, K.; Curtis, M.; Nyquist, G.; Rabinowitz, M.; Rosen, M. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma-Case Report and Review of Clinicopathological Features and Diagnostic Modalities. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2019, 80, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudaba, H.; Momii, Y.; Hirano, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujiki, M. Recurrence of Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Cerebral Hemorrhaging. J. Craniofac Surg. 2019, 30, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudher, S.M.; Al Zamel, H.; Bhat, I.N. A rare case of nasal biphenotypic sino-nasal sarcoma in a young female. Ann. Med. Surg. 2019, 37, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Loarer, F.; Laffont, S.; Lesluyes, T.; Tirode, F.; Antonescu, C.; Baglin, A.C.; Delespaul, L.; Soubeyran, I.; Hostein, I.; Pérot, G.; et al. Clinicopathologic and Molecular Features of a Series of 41 Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcomas Expanding Their Molecular Spectrum. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Cody, B.; Farhat, N.A.; Pool, M.D.; Katabi, N. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: Report of 3 cases with a review of literature. Hum. Pathol. 2021, 24, 200491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanbazazh, M.; Jakobiec, F.A.; Curtin, H.D.; Lefebvre, D.R. Orbital Involvement by Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with a Literature Review. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 37, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Phan, J.; DeMonte, F.; Hanna, E.Y. High-grade transformation of low-grade biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: Radiological, morphophenotypic variation and confirmatory molecular analysis. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 57, 151889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasnie, S.; Glenn, C.; Peterson, J.E.G.; El Rassi, E.T.; McKinney, K.A. High-Grade Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma: A Case Report. J. Neurol. Surg. Rep. 2022, 83, e105–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turri-Zanoni, M.; Dalfino, G.; Lechner, M.; Dallan, I.; Battaglia, P.; Facco, C.; Franzi, F.; Gravante, G.; Ferrari, M.; Terzakis, D.; et al. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma: European multicentre case-series and systematic literature review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.M.; Alruwaii, F.; Chaaban, M.; Cheng, Y.W.; Griffith, C.C. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with a Novel PAX3::FOXO6 Fusion: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2023, 17, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, A.; Mahendra, N.; Gopal Reddy, G.V. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma-A recently described entity with many mimics: A case report. Indian. J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2023, 66, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Klubíčková, N.; Mosaieby, E.; Grossmann, P.; Kalmykova, A.; Koshyk, O.; Michal, M. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma with PAX3::MAML3 fusion transforming into high-grade rhabdomyosarcoma: Report of an emerging rare phenomenon. Virchows Arch. 2023, 482, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominsky, E.; Boyke, A.E.; Madani, D.; Kamat, A.; Schiff, B.A.; Agarwal, V. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 102, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhele, S.; Chrisinger, J.S.A.; Farrell, N.F.; Van Tine, B.A.; Raptis, C.A.; Chernock, R.D. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with a Novel PAX7::PPARGC1 Fusion: Expanding the Spectrum of Gene Fusions Beyond the PAX3 Gene. Head Neck Pathol. 2023, 17, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viramontes, A.; Mueller, N.; Gocke, C.D.; Deklotz, T.R.; Ozdemirli, M. Novel PAX3::INO80D Fusion in Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma in an Adult. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 149, 849–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, E.; Kato, I.; Matsumura, M.; Arai, Y.; Suenaga, J.; Yamanaka, S.; Fujii, S. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma: A Genetically Confirmed Case Showing Bone Invasion Accompanying a Non-neoplastic Respiratory Epithelium. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 31, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, S.; Karkos, P.; Constantinidis, J. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital and Skull Base Involvement Report of 3 Cases and Systematic Review of the Literature. Indian. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 75, 3353–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitguppi, C.; Koszewski, I.; Collura, K.; Curtis, M.; Nyquist, G.; Rabinowitz, M.; Rosen, M. Biphenotypic siononasal sarcoma with acute exacerbation: A case report. Otolaryngol. Case Rep. 2020, 16, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, S.; Halderman, A.; Bishop, J.; Ryan, M.; Marple, B. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma a Newly Recognized Sinonasal Neoplasm: Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2020, 81, S1–S272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, A.; Jalisi, S.; Nishino, M.; Ivanovic, V. Biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma—Description of radiologic, intraoperative and pathologic findings. Otolaryngol. Case Rep. 2019, 11, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglani, A.; Lal, D.; Weindling, S.M.; Wood, C.P.; Hoxworth, J.M. Imaging characteristics and clinical outcomes of biphenotypic sinonasal sarcoma. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitguppi, C.; Koszewski, I.; Collura, K.; Curtis, M.; Nyquist, G.; Rabinowitz, M.; Rosen, M. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Focal Rhabdomyoblastic Differentiation: Case Report of a Newly Described Malignancy with a Review of the Literature. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2018, 79, S1–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockstein, N.G.; Dross, P.E.; Farooqui, S.; Wilhelm, I.N. Low-grade sinonasal sarcoma with neural and myogenic features. ENT-Ear Nose Throat J. 2018, 97, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Snyderman, C.H.; Mintz, A.; Gardner, P.; Carrau, R.L. Expanded endonasal approach: The rostrocaudal axis. Part I. Crista galli to the sella turcica. Neurosurg. Focus. 2005, 19, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, A.; Snyderman, C.H.; Mintz, A.; Gardner, P.; Carrau, R.L. Expanded endonasal approach: The rostrocaudal axis. Part II. Posterior clinoids to the foramen magnum. Neurosurg. Focus. 2005, 19, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardesty, D.A.; Montaser, A.; Kreatsoulas, D.; Shah, V.S.; VanKoevering, K.K.; Otto, B.A.; Carrau, R.L.; Prevedello, D.M. Complications after 1002 endoscopic endonasal approach procedures at a single center: Lessons learned, 2010–2018. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 136, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasemsiri, P.; Carrau, R.L.; Ditzel Filho, L.F.; Prevedello, D.M.; Otto, B.A.; Old, M.; de Lara, D.; Kassam, A.B. Advantages and limitations of endoscopic endonasal approaches to the skull base. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, S12–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, R.; Draf, W.; Kratzsch, B.; Hosemann, W.; Schaefer, S.D. Modern concepts of frontal sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloy, J.A.; Vázquez, A.; Liu, J.K.; Baredes, S. Endoscopic Approaches to the Frontal Sinus: Modifications of the Existing Techniques and Proposed Classification. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 49, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.S.; Bomeli, S.R.; Gross, C.W.; Han, J.K. Limits of endoscopic visualization and instrumentation in the frontal sinus. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 135, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignami, M.; Dallan, I.; Terranova, P.; Battaglia, P.; Miceli, S.; Castelnuovo, P. Frontal sinus osteomas: The window of endonasal endoscopic approach. Rhinology 2007, 45, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Papatsoutsos, E.; Kalyvas, A.; Drosos, E.; Neromyliotis, E.; Koutsarnakis, C.; Komaitis, S.; Chatzinakis, V.; Stranjalis, G.; Georgalas, C. Defining the limits and indications of the Draf III endoscopic approach to the lateral frontal sinus and maximizing visualization and maneuverability: A cadaveric and radiological study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karligkiotis, A.; Pistochini, A.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Terranova, P.; Volpi, L.; Battaglia, P.; Bignami, M.; Castelnuovo, P. Endoscopic endonasal orbital transposition to expand the frontal sinus approaches. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, G.J.; Betz, C.S.; Stelter, K.; Leunig, A. Surgical management of osteomas of the frontal recess and sinus: Extending the limits of the endoscopic approach. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 268, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turri-Zanoni, M.; Dallan, I.; Terranova, P.; Battaglia, P.; Karligkiotis, A.; Bignami, M.; Castelnuovo, P. Frontoethmoidal and intraorbital osteomas: Exploring the limits of the endoscopic approach. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 138, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, K.S.; Bergeron, C.M.; Ellenbogen, R.G. Transorbital neuroendoscopic surgery. Neurosurgery 2010, 67, ons16-28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Somma, A.; Kong, D.S.; de Notaris, M.; Moe, K.S.; Sánchez España, J.C.; Schwartz, T.H.; Enseñat, J. Endoscopic transorbital surgery levels of difficulty. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 12, 991065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Notaris, M.; Kong, D.S.; Di Somma, A.; Enseñat, J.; Hong, C.K.; Moe, K.; Schwartz, T.H. Superior eyelid transorbital approaches: A modular classification system. J. Neurosurg. 2024, 141, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, S.; Sacco, M.; Somma, T.; Berardinelli, J.; Ugga, L.; Colamaria, A.; Corrivetti, F.; Iaconetta, G.; Kong, D.S.; de Notaris, M. Functional and clinical outcomes after superior eyelid transorbital endoscopic approach for spheno-orbital meningiomas: Illustrative case and literature review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, S.; Armocida, D.; Offi, M.; Pennisi, G.; Burattini, B.; Mondragon, A.V.; Esposito, F.; Cavallo, L.M.; de Notaris, M. The anterolateral triangle as window on the foramen lacerum from transorbital corridor: Anatomical study and technical nuances. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 2407–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, S.; Guizzardi, G.; Sacco, M.; Corrivetti, F.; Bove, I.; Enseñat, J.; Colamaria, A.; Prats-Galino, A.; Solari, D.; Cavallo, L.M.; et al. The feasibility of three port endonasal, transorbital, and sublabial approach to the petroclival region: Neurosurgical audit and multiportal anatomic quantitative investigation. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvino, S.; Villanueva-Solórzano, P.; Offi, M.; Armocida, D.; Nonaka, M.; Iaconetta, G.; Esposito, F.; Cavallo, L.; de Notaris, M. A New Perspective on the Cavernous Sinus as Seen through Multiple Surgical Corridors: Anatomical Study Comparing the Transorbital, Endonasal, and Transcranial Routes and the Relative Coterminous Spatial Regions. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Notaris, M.; Sacco, M.; Corrivetti, F.; Grasso, M.; Corvino, S.; Piazza, A.; Kong, D.S.; Iaconetta, G. The Transorbital Approach, A Game-Changer in Neurosurgery: A Guide to Safe and Reliable Surgery Based on Anatomical Principles. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, S.; Kassam, A.; Piazza, A.; Corrivetti, F.; Spiriev, T.; Colamaria, A.; Cirrottola, G.; Cavaliere, C.; Esposito, F.; Cavallo, L.M.; et al. Open-door extended endoscopic transorbital technique to the paramedian anterior and middle cranial fossae: Technical notes, anatomomorphometric quantitative analysis, and illustrative case. Neurosurg. Focus. 2024, 56, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vural, A.; Carobbio, A.L.C.; Ferrari, M.; Rampinelli, V.; Schreiber, A.; Mattavelli, D.; Doglietto, F.; Buffoli, B.; Rodella, L.F.; Taboni, S.; et al. Transorbital endoscopic approaches to the skull base: A systematic literature review and anatomical description. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2857–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluzzi, A.; Gardner, P.A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tormenti, M.J.; Stefko, S.T.; Snyderman, C.H.; Maroon, J.C. “Round-the-Clock” Surgical Access to the Orbit. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2015, 76, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvino, S.; Kassam, A.; Piazza, A.; Corrivetti, F.; Esposito, F.; Iaconetta, G.; de Notaris, M. Navigating the Intersection Between the Orbit and the Skull Base: The “Mirror” McCarty Keyhole During Transorbital Approach: An Anatomic Study with Surgical Implications. Oper. Neurosurg. 2024; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Sardesai, M.G.; Ferreira, M.; Moe, K.S. Transorbital neuroendoscopic management of sinogenic complications involving the frontal sinus, orbit, and anterior cranial fossa. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2012, 73, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Berens, A.; Patel, S.A.; Humphreys, I.M.; Moe, K.S. Transorbital Approach for Improved Access in the Management of Paranasal Sinus Mucoceles. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2019, 80, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makary, C.A.; Limjuco, A.; Nguyen, J.; Ramadan, H.H. Combined Lid Crease and Endoscopic Approach to Lateral Frontal Sinus Disease with Orbital Extension. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2018, 127, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, A.D.; Coden, E.; Valentini, M.; Czaczkes, C.; Battaglia, P.; Bignami, M.; Castelnuovo, P.; Karligkiotis, A. Combined Endonasal-Transorbital Approach to Manage the Far Lateral Frontal Sinus: Surgical Technique. World Neurosurg. 2021, 151, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, N.; Kumar, P.; Goel, A. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Intracranial Extension—A Case Report with Review of Literature. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 12, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocozza, S.; Russo, C.; Pontillo, G.; Ugga, L.; Macera, A.; Cervo, A.; De Liso, M.; Di Paolo, N.; Ginocchio, M.I.; Giordano, F.; et al. Is advanced neuroimaging for neuroradiologists? A systematic review of the scientific literature of the last decade. Neuroradiology 2016, 58, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Authors/Year | Number of Cases | Sex, Mean Age (Years) | Presenting Symptoms | Anatomical Origin | Skull Base Involvement | Orbit Involvement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cannon et al. [16] 2017 | 3 | 3 F (67.6 Years) | Diplopia, facial discomfort, nasal obstruction, facial pressure | 3 FS-ES | 3 YES | 3 lamina papyracea |
| 2 | Hockstein et al. [41] 2018 | 1 | F, 79 | Asymptomatic | FS | YES | Roof |
| 3 | Koszewski et al. [40] 2018 | 1 | M, 53 | Unilateral nasal obstruction and epiphora | NC | YES (ACF) | Lamina papyracea |
| 4 | Chitguppi et al. [19] 2019 | 1 | M, 53 | n.a. | ES-NC | YES | YES |
| 5 | Alkhudher et al. [21] 2019 | 1 | F, 35 | Nasal obstruction, epistaxis | NC-MS-ES | None | Lamina papyracea |
| 6 | Miglani et al. [39] 2019 | 5 | 4 F, 1 M (56 years) | n.a. | 5 NC-ES | 5 YES (ACF) | 5 lamina papyracea |
| 7 | Le Loarer et al. [22] 2019 | 4 | 3 F, 1 M (71 years) | n.a. | 1 ES 1 ES-FS 1 NC-ES ES-FS | 2 YES | 4 YES |
| 8 | Kuhn et al. [38] 2019 | 1 | n.a. | Worsening nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, left orbital pain, proptosis, and blurry vision | NC-ES | YES (ACF) | Lamina papyracea |
| 9 | Okafor et al. [37] 2020 | 1 | M, 54 | Left-side nasal airway obstruction and anosmia | NC-MS-ES-FS | YES (ACF) | Lamina papyracea |
| 10 | Okuda et al. [36] 2020 | 1 | F, 64 | Nasal obstruction | NC-MS-ES pterygopalatine fossa | YES (MCF) | YES |
| 11 | Sethi et al. [23] 2021 | 2 | 2 F (56 years) | Nasal congestion and headaches | 2 ES-MS-FS-NC | 1 YES (ACF) | 2 YES |
| 12 | Hanbazazh et al. [24] 2021 | 1 | M, 50 | Orbital pain and pressure, diplopia, blurred vision, lateral gaze restriction | ES | YES | Lamina papyracea |
| 13 | Bell et al. [25] 2022 | 1 | M, 66 | Swelling of left eyelid, vertical diplopia, and purulent nasal discharge | NC | YES (ACF) | YES |
| 14 | Hasnie et al. [26] 2022 | 1 | F, 72 | Nasal obstruction, episodic epistaxis and facial pressure/headaches, decreased sense of smell | MS-ES-Bilateral FS-NC | YES (ACF) | Lamina papyracea |
| 15 | Ingle et al. [29] 2023 | 1 | F, 47 | Swelling of the eyelid, proptosis | NC-FS-ES-MS | None | Lamina papyracea |
| 16 | Meyer et al. [30] 2023 | 1 | M, 67 | Nasal congestion and epiphora, right-side ocular proptosis | ES-MS-FS | None | YES |
| 17 | Kominsky et al. [31] 2023 | 2 | 2 M (65 years) | Bilateral nasal congestion and blurry vision | ES-NC-FS | 2 YES | 2 lamina papyracea |
| 18 | Bhele et al. [32] 2023 | 1 | F, 22 | Vision loss, headache, hyposmia, facial pressure | NC-ES-SS-MS | YES (ACF) | Lamina papyracea |
| 19 | Anastasiadou et al. [35] 2023 | 2 | 2 F (43 years) | Exophthalmos, headaches | NC-MS | 1 YES | 2 (1 floor, 1 lamina papyracea) |
| Authors/Year | Number of Cases | Time to Treatment | Type of Treatment | Type of Surgical Approach | EOR | Peri- and Postoperative Complications | Recurrence | Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cannon et al. [16] 2017 | 3 | n.a. | 2 S 1 biopsy | 1 EEA– 1 EEA + TCA 1 EEA Biopsy | 2 GTR 1 STR | n.a. | 1/3 (17 mo.) | (Mean 25 mo.) 3 alive |
| 2 | Hockstein et al. [41] 2018 | 1 | 12 mo. | S | EEA + TCA | GTR | n.a. | None | Alive |
| 3 | Koszewski et al. [40] 2018 | 1 | 4 mo. | S + Ad.RT | n.a. | STR | n.a. | None | Alive |
| 4 | Chitguppi et al. [19] 2019 | 1 | n.a. | S + Ad-RT | TCA + ETOA | STR | n.a. | None | Alive |
| 5 | Alkhudher et al. [21] 2019 | 1 | 2 mo. | S | EEA | GTR | n.a. | None | Alive, 2 years |
| 6 | Miglani et al. [39] 2019 | 5 | n.a. | 4 S 1 S + Ad-RT | 3 TCA 2 EEA | 4 GTR 1 STR | n.a. | 2/5 (mean 31.4 mo.) | (Mean 31.4 mo.) 5 alive |
| 7 | Le Loarer et al. [22] 2019 | 4 | n.a. | 1 CHT + RT 2 S 1 S + Ad.RT | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 1/4 (after 91 mo.) | 4 Alive (mean 176 mo.) |
| 8 | Kuhn et al. [38] 2019 | 1 | n.a | S | TCA | GTR | None | n.a. | n.a. |
| 9 | Okafor et al. [37] 2020 | 1 | 5 mo. | 2 S | 2 EEA | 1 STR 1 GTR | None | n.a. | n.a. |
| 10 | Okuda et al. [36] 2020 | 1 | REC after 2 mo. | S + Ad.CHT | TCA | GTR | None | YES (after 2 mo.) | Dead after 8 mo. due to tumor progression |
| 11 | Sethi et al. [23] 2021 | 2 | n.a. | 1 S + Ad.RT 1 S | 2 EEA | 2 GTR | None | None | 1/2 * alive (32 mo.) |
| 12 | Hanbazazh et al. [24] 2021 | 1 | 36 mo. | 1 biopsy 1S 1S + Ad.RT | Biopsy EEA TOA TCA | 3 STR | None | None | Alive |
| 13 | Bell et al. [25] 2022 | 1 | REC after 15 years | 1 S + Ad.RT | TCA | GTR | None | No further | Alive, 10 mo. |
| 14 | Hasnie et al. [26] 2022 | 1 | 24 mo. | S | EEA + TCA | GTR | Infection pericranial flap, pneumocephal | None | Death due to other causes |
| 15 | Ingle et al. [29] 2023 | 1 | 2 mo. | S | EEA + TCA | GTR | n.a. | None | Alive, 3 mo. |
| 16 | Meyer et al. [30] 2023 | 1 | 36 mo. | S + RT, CHT | EEA | STR | n.a. | Progression | Death after 15 mo. due to tumor progression |
| 17 | Kominsky et al. [31] 2023 | 2 | 3 weeks (1) | 2 S | 2 EEA | 2 GTR | n.a. | None | 2 alive (mean 13 mo.) |
| 18 | Bhele et al. [32] 2023 | 1 | 8 mo. | Neo-CHT, S, Ad-PB | TCA + EEA | STR | n.a. | None | Alive, 10 mo. |
| 19 | Anastasiadou et al. [35] 2023 | 2 | n.a. | 1S, 1S + Ad.RT | 2 EEA | 2 GTR | 1 CSF leak | None | 2 alive (mean 78 mo.) |
| Covariates | Overall Sample 31 (%) | Statistical Analysis (p Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Demographic and clinical data | ||
| Sex | 30/31 * (96.7%) | p = 0.66 |
| 20/30 (66.7%) | |
| 10/30 (33.3%) | |
| Age range (Median) | 22–84 years (55.2 years old) | S-W = 0.79; p = 0.04 |
| Main presenting symptoms | 21/31 * (67.7%) | p = 0.47 |
| 14/21 (66.6%) | |
| 11/21 (52.4%) | |
| 6/21 (28.5%) | |
| 2/21 (9.5%) | |
| Radiological data | ||
| Anatomical origin | 31/31 * (100%) | p = 0.23 |
| 26/31 (83.9%) | |
| 22/31 (71%) | |
| 14/31 (45.1%) | |
| 11/31 (35.4%) | |
| 1/31 (3.2%) | |
| Skull base involvement | 31/31 * (100%) | p = 0.15 |
| 25/31 (80.6%) | |
| 6/31 (19.4%) | |
| Covariates | Overall Sample 31 (%) | Statistical Analysis (p Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment data | ||
| Time to treatment (Mean ± SD) | 10/31 * (32.3%) 24 ± 48.5 mo. | S-W = 0.52; p < 0.01 |
| Type of treatment | 34 * | p = 0.21 |
| 20/34 (59%) | |
| 8/34 (23.5%) | |
| 2/34 (5.9%) | |
| 1/34 (2.9%) | |
| 2/34 (5.9%) | |
| 1/34 (2.9%) | |
| Type of surgical approach | 29/33 * (87.9%) | p = 0.13 |
| 15/29 (51.7%) | |
| 7/29 (24.1%) | |
| 1/29 (3.4%) | |
| 6/29 (20.7%) | |
| EOR | 30/33 * (91%) | p = 0.35 |
| 20/30 (66.7%) | |
| 10/30 (33.3%) | |
| Peri- and postoperative complications | 12/33 * (36.4%) | p = 0.12 |
| 2/12 (16.6%) | |
| 10/12 (83.4%) | |
| Outcome | ||
| Recurrence | 31/31 * (100%) | p = 0.6 |
| 6/31(19.3%) | |
| 25/31 (80.7%) | |
| Status | 28/31 * (90.3%) | p = 0.88 |
| 25/28 (89.3%) | |
| 3/28 (10.7%) | |
| Follow-up (Mean ± SD) | 50.48 ± 58.71 | S-W = 0.66; p < 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corvino, S.; de Divitiis, O.; Iuliano, A.; Russo, F.; Corazzelli, G.; Cohen, D.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Palmiero, C.; Pontillo, G.; Staibano, S.; et al. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital Invasion: A Literature Review and Modular System of Surgical Approaches. Cancers 2024, 16, 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193316
Corvino S, de Divitiis O, Iuliano A, Russo F, Corazzelli G, Cohen D, Di Crescenzo RM, Palmiero C, Pontillo G, Staibano S, et al. Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital Invasion: A Literature Review and Modular System of Surgical Approaches. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193316
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorvino, Sergio, Oreste de Divitiis, Adriana Iuliano, Federico Russo, Giuseppe Corazzelli, Dana Cohen, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Carmela Palmiero, Giuseppe Pontillo, Stefania Staibano, and et al. 2024. "Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital Invasion: A Literature Review and Modular System of Surgical Approaches" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193316
APA StyleCorvino, S., de Divitiis, O., Iuliano, A., Russo, F., Corazzelli, G., Cohen, D., Di Crescenzo, R. M., Palmiero, C., Pontillo, G., Staibano, S., Strianese, D., Elefante, A., & Mariniello, G. (2024). Biphenotypic Sinonasal Sarcoma with Orbital Invasion: A Literature Review and Modular System of Surgical Approaches. Cancers, 16(19), 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193316






