Impact of Breast Cancer on Cardiometabolic Health in Spanish Women ≥50 Years with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
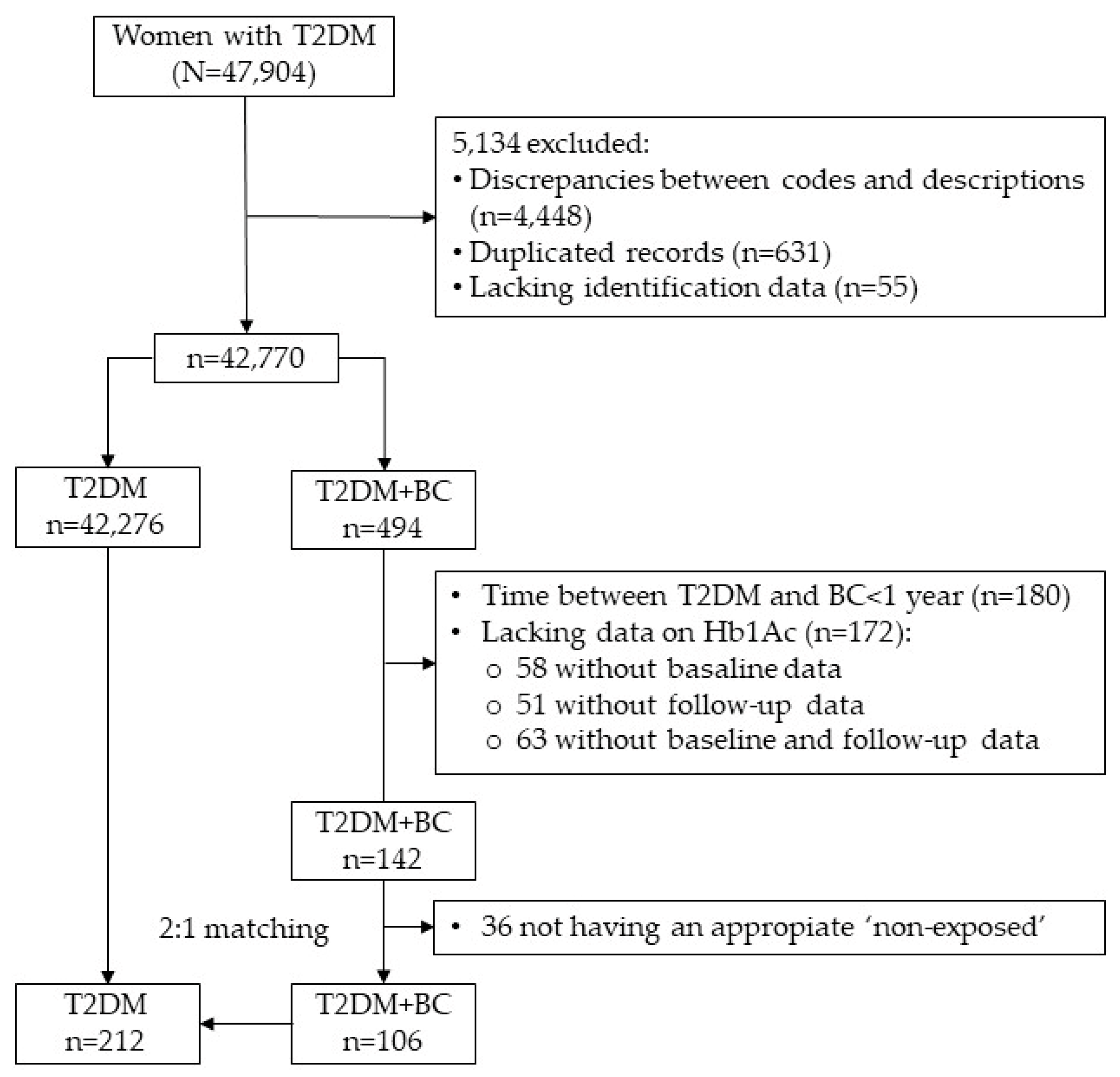
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Study Variables
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyle, P.; Boniol, M.; Koechlin, A.; Robertson, C.; Valentini, F.; Coppens, K.; Fairley, L.L.; Boniol, M.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Diabetes and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruijn, K.M.; Arends, L.R.; Hansen, B.E.; Leeflang, S.; Ruiter, R.; van Eijck, C.H. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality in breast and colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2013, 100, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, C.; Xia, J. Diabetes mellitus is associated with breast cancer: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and in silico reproduction. Panminerva Med. 2015, 57, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.J.; George, A.S.; Subrahmanyan, N.A.; Pappachan, J.M. Epidemiological link between obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and cancer. World J. Methodol. 2021, 11, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Association between diabetes mellitus and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis of the literature. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Maskarinec, G.; Fontaine, A.; Torfadottir, J.E.; Lipscombe, L.L.; Lega, I.C.; Figueroa, J.; Wild, S. The Relation of Type 2 Diabetes and Breast Cancer Incidence in Asian, Hispanic and African American Populations—A Review. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Abdollahi, S.; Aune, D.; Jayedi, A. Body mass index and cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: A dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, P.; Tripathi, V.; Nayak, A.; Kataria, S.; Lukashevich, V.; Das, A.; Parman, H. A molecular link between diabetes and breast cancer: Therapeutic potential of repurposing incretin-based therapies for breast cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2021, 21, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, I.A.; Bhatti, A.; John, P. The prognostic outcome of ‘type 2 diabetes mellitus and breast cancer’ association pivots on hypoxia-hyperglycemia axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.D.; McGee, S.L. Metabolic reprogramming in type 2 diabetes and the development of breast cancer. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 237, R35–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; de Haan-Du, J.; Sidorenkov, G.; Landman, G.W.D.; Jalving, M.; Zhang, Q.; Bock, G. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Clinicopathological Tumor Characteristics in Women Diagnosed with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Prieto, P.; Álvarez-Bañuelos, M.T.; Romero, J.M.; Córdoba, B.C.; Sampieri, C.L.; Cuevas, R.Z.; Guzmán García, R.E. Influence of type 2 diabetes mellitus on mortality in women with breast cancer: A matched case-control study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.L.; Sheu, W.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Liou, W.S. Good glycaemic control is associated with a better prognosis in breast cancer patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Summary of Revisions: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. S1), S4–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, S.S.; Ayyala, D.N. Symptoms associated with comorbid diabetes among breast cancer survivors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 189, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.Q.; Qian, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.F. Risk factors for surgical site infections after breast surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 38, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskarinec, G.; Shvetsov, Y.B.; Conroy, S.M.; Haiman, C.A.; Setiawan, V.W.; Le Marchand, L. Type 2 diabetes as a predictor of survival among breast cancer patients: The multiethnic cohort. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Arce, L.; Robles-Rodríguez, N.; Fernández-Feito, A.; Llaneza-Folgueras, A.; Encinas-Muñiz, A.I.; Lana, A. Type 2 Diabetes and all-cause mortality among Spanish women with breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control 2022, 33, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, W.R.; Hosler, A.S.; Gates Kuliszewski, M.; Leinung, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Schymura, M.J.; Boscoe, F. Impact of preexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus and antidiabetic drugs on all-cause and cause-specific mortality among Medicaid-insured women diagnosed with breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 66, 101710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Virnig, B.; Hendryx, M.; Wen, S.; Chelebowski, R.; Chen, C.; Rohan, T.; Tinker, L.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Lessin, L.; et al. Diabetes, diabetes treatment and breast cancer prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 148, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, A.E.; Visvanathan, K.; Boone, S.D.; Rifai, N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Baumgartner, R.N. Fructosamine and diabetes as predictors of mortality among Hispanic and non-Hispanic white breast cancer survivors. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, K.; Patterson, R.E.; Flatt, S.W.; Natarajan, L.; Parker, B.A.; Heath, D.D.; Laughlin, G.A.; Saquib, N.; Rock, C.L.; Pierce, J.P. Clinically defined type 2 diabetes mellitus and prognosis in early-stage breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Garza, C.; Shaw-Dulin, R.; Lara-Medina, F.; Bacon, L.; Rivera, D.; Urzua, L.; Aguila, C.; Ramirez-Morales, R.; Santamaria, J.; Bargallo, E.; et al. Impact of diabetes and hyperglycemia on survival in advanced breast cancer patients. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 732027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minicozzi, P.; Berrino, F.; Sebastiani, F.; Falcini, F.; Vattiato, R.; Cioccoloni, F.; Calagreti, G.; Fusco, M.; Vitale, M.F.; Tumino, R.; et al. High fasting blood glucose and obesity significantly and independently increase risk of breast cancer death in hormone receptor-positive disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3881–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Keating, N.L.; Bankhead, C.R. Quality of diabetes care in cancer: A systematic review. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2019, 31, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; LeRoith, D.; Gallagher, E.J. Diabetes, Obesity, and Breast Cancer. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 3801–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calip, G.S.; Hubbard, R.A.; Stergachis, A.; Malone, K.E.; Gralow, J.R.; Boudreau, D.M. Adherence to oral diabetes medications and glycemic control during and following breast cancer treatment. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2015, 24, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.I.; McFadden, E.C.; Stevens, R.J.; Valderas, J.M.; Lavery, B.A.; Khan, N.F.; Keating, N.; Bankhead, C. Quality of diabetes care in breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. J. Cancer Surviv. 2018, 12, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Kubatka, P.; Triggle, C.R.; Büsselberg, D. Metformin: The Answer to Cancer in a Flower? Current Knowledge and Future Prospects of Metformin as an Anti-Cancer Agent in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Metformin and Its Benefits for Various Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershey, D.S.; Tipton, J.; Given, B.; Davis, E. Perceived impact of cancer treatment on diabetes self-management. Diabetes Educ. 2012, 38, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, R.I.; Valderas, J.M.; McFadden, E.C.; Bankhead, C.R.; Lavery, B.A.; Khan, N.F.; Stevens, R.; Keating, N. Outcomes of preexisting diabetes mellitus in breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer. J. Cancer Surviv. 2017, 11, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaioli, G.; Schäfer, W.L.A.; Boerma, W.G.W.; Spreeuwenberg, P.M.M.; Schellevis, F.G.; Groenewegen, P.P. Communication between general practitioners and medical specialists in the referral process: A cross-sectional survey in 34 countries. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelby, R.A.; Dorfman, C.S.; Arthur, S.S.; Bosworth, H.B.; Corsino, L.; Sutton, L.; Owen, L.; Erkali, A.; Keefe, F.; Corbett, C.; et al. Improving health engagement and lifestyle management for breast cancer survivors with diabetes. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2020, 92, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.S.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; Sharp, S.J.; Ong, K.K.; Khaw, K.T.; Ardanaz, E.; Amiano, P.; Boeing, H.; Maria-Dolores, C.; et al. Age at menopause, reproductive life span, and type 2 diabetes risk: Results from the EPIC-InterAct study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T2DM (n = 212) | T2DM+BC (n = 106) | p-Value a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 79.1 (9.71) | 79.3 (9.59) | 0.887 | |
| ≥65 years, n (%) | 23 (89.2) | 10 (90.6) | 0.696 | |
| Urban residential area, n (%) | 112 (52.8) | 56 (52.8) | 1.000 | |
| Age at T2DM diagnosis, years | 63.6 (10.1) | 64.6 (9.84) | 0.389 | |
| Duration of T2DM, years | 15.5 (4.52) | 14.6 (5.33) | 0.127 | |
| Visits/year to PHC providers | 23.3 (13.6) | 22.4 (10.4) | 0.523 | |
| Adequate therapeutic adherence, n (%) | 172 (81.1) | 88 (83.0) | 0.681 | |
| Self-monitoring of blood glucose, n (%) | 117 (55.2) | 67 (63.2) | 0.172 | |
| Health advice, n (%) | ||||
| On alcohol | 136 (64.2) | 76 (71.7) | 0.178 | |
| On tobacco | 128 (60.4) | 72 (67.9) | 0.189 | |
| On food | 200 (94.3) | 97 (91.5) | 0.338 | |
| On physical activity | 203 (95.8) | 99 (93.4) | 0.364 | |
| Morbidity, n (%) | ||||
| Cardiovascular | 47 (22.2) | 27 (25.5) | 0.511 | |
| Stroke | 11 (5.2) | 7 (6.6) | 0.607 | |
| Hypertension | 137 (64.6) | 69 (65.1) | 0.934 | |
| Dyslipemia | 81 (38.2) | 45 (42.5) | 0.466 | |
| Mental | 69 (32.6) | 40 (37.7) | 0.358 | |
| Osteoporosis | 36 (17.0) | 12 (11.3) | 0.134 | |
| T2DM (n = 212) | T2DM+BC (n = 106) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Follow-Up | p-Value a | Baseline | Follow-Up | p-Value a | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 31.2 (5.4) | 30.5 (5.3) | <0.001 | 31.3 (5.3) | 30.9 (4.9) | 0.024 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 137 (13.8) | 138 (13.7) | 0.272 | 137 (12.5) | 136 (12.2) | 0.346 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 77.8 (7.4) | 76.4 (6.7) | <0.001 | 76.5 (7.7) | 74.5 (7.6) | 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 207 (43.8) | 194 (39.9) | <0.001 | 198 (39.2) | 187 (35.1) | <0.001 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 123 (32.6) | 112 (32.6) | <0.001 | 116 (35.3) | 105 (32.3) | <0.001 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 52.2 (14.4) | 53.3 (12.6) | 0.073 | 55.8 (25.6) | 54.6 (23.5) | 0.205 |
| Blood glucose, mg/dL | 154 (54.6) | 141 (39.4) | <0.001 | 137 (34.5) | 141 (37.0) | 0.072 |
| Hb1Ac, % | 7.17 (1.78) | 7.15 (1.35) | 0.889 | 6.74 (1.23) | 7.17 (1.20) | 0.009 |
| Hb1Ac, mmol/mol | 54.9 (19.4) | 54.6 (14.8) | 0.889 | 50.2 (13.5) | 54.8 (13.1) | 0.009 |
| T2DM (n = 212) | T2DM+BC (n = 106) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI ≥ 30 | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.48 (0.64–3.41) | 0.357 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.06 (0.38–3.01) | 0.908 | |
| SBP ≥ 130 mm Hg | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.64 (0.35–1.19) | 0.158 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.74 (0.36–1.53) | 0.415 | |
| DBP ≥ 80 mm Hg | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.60 (0.32–1.14) | 0.122 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.65 (0.31–1.38) | 0.261 | |
| Total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.88 (0.50–1.57) | 0.661 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.96 (0.49–1.86) | 0.894 | |
| LDL ≥ 100 mg/dL | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.32 (0.72–2.40) | 0.365 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.40 (0.72–2.73) | 0.325 | |
| HDL < 40 mg/dL | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.72 (0.32–1.60) | 0.419 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 0.79 (0.29–2.20) | 0.656 | |
| Blood glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.82 (1.08–3.07) | 0.024 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.85 (1.01–3.41) | 0.048 | |
| Hb1Ac ≥ 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) | ||||
| Model 1 a, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 1.98 (1.14–3.46) | 0.016 | |
| Model 2 b, OR (95% CI) | 1.00 | 2.48 (1.23–4.99) | 0.011 | |
| T2DM (n = 212) | T2DM+BC (n = 106) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retinopathy, n (%) | 9 (4.2) | 1 (0.9) | 0.112 |
| Diabetic foot ulcer, n (%) | 21 (9.9) | 7 (6.6) | 0.327 |
| Nephropathy, n (%) | 19 (9.0) | 9 (8.5) | 0.889 |
| Neuropathy, n (%) | 5 (2.4) | 4 (3.8) | 0.473 |
| Hyperuricemia, n (%) | 7 (3.3) | 5 (4.7) | 0.532 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Arce, L.; Robles-Rodríguez, N.; Fernández-Feito, A.; Fernández-Iglesias, R.; Fernández-Álvarez, M.d.M.; Lana, A. Impact of Breast Cancer on Cardiometabolic Health in Spanish Women ≥50 Years with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers 2024, 16, 2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162853
Fernández-Arce L, Robles-Rodríguez N, Fernández-Feito A, Fernández-Iglesias R, Fernández-Álvarez MdM, Lana A. Impact of Breast Cancer on Cardiometabolic Health in Spanish Women ≥50 Years with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162853
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Arce, Lucía, Nena Robles-Rodríguez, Ana Fernández-Feito, Rocío Fernández-Iglesias, María del Mar Fernández-Álvarez, and Alberto Lana. 2024. "Impact of Breast Cancer on Cardiometabolic Health in Spanish Women ≥50 Years with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162853
APA StyleFernández-Arce, L., Robles-Rodríguez, N., Fernández-Feito, A., Fernández-Iglesias, R., Fernández-Álvarez, M. d. M., & Lana, A. (2024). Impact of Breast Cancer on Cardiometabolic Health in Spanish Women ≥50 Years with Pre-Existing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cancers, 16(16), 2853. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162853





