Multidrug-Resistant Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells: Implications for Personalized Approaches with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NSCLC Tissue Samples and Establishment of Primary Cultures
2.2. Drugs and Treatments
2.3. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.4. Whole-Exome Sequencing and Variant Calling
2.5. Variant Prioritization and Pathway Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Sensitivity of Patient-Derived NSCLC Cultures to TKIs
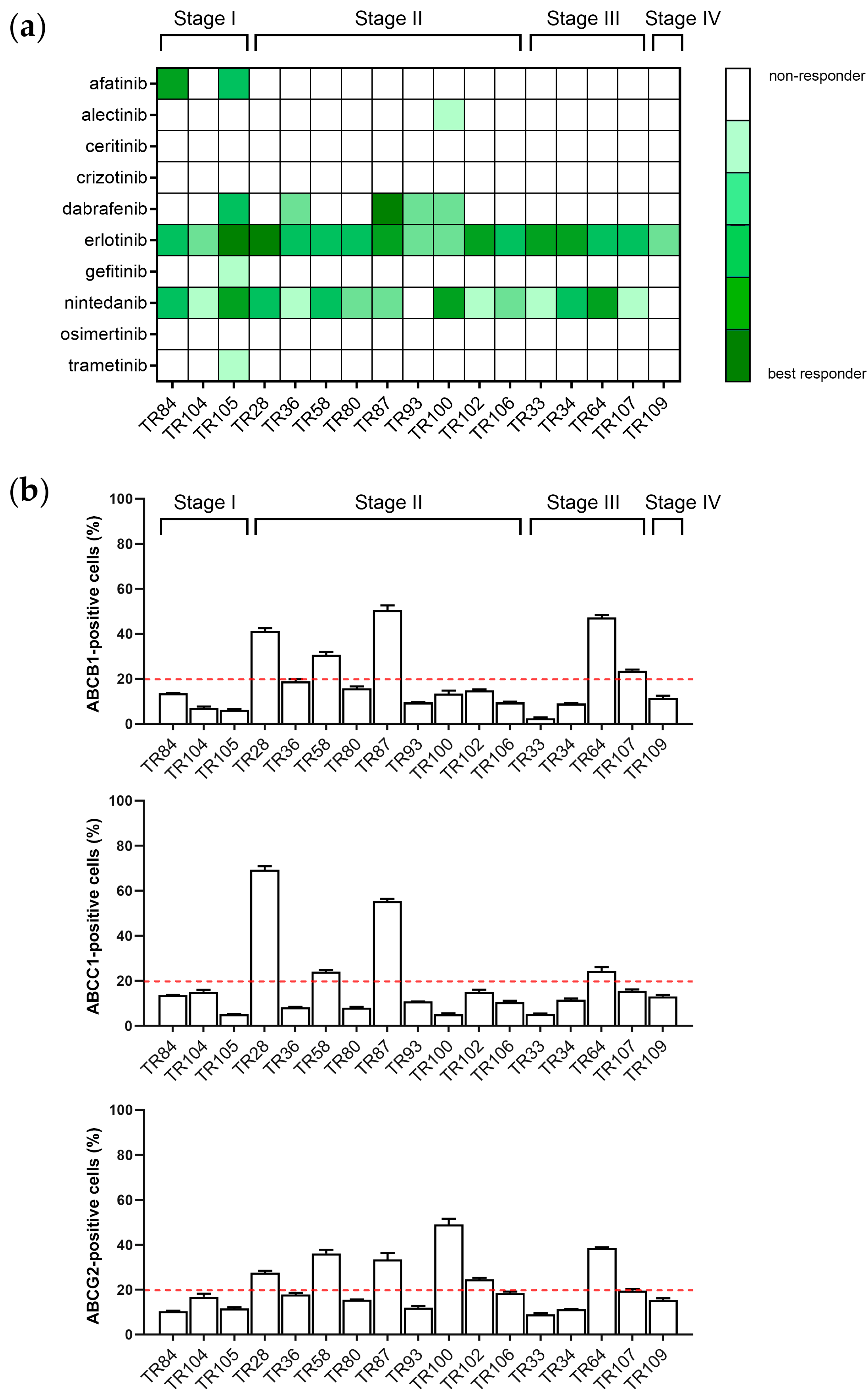
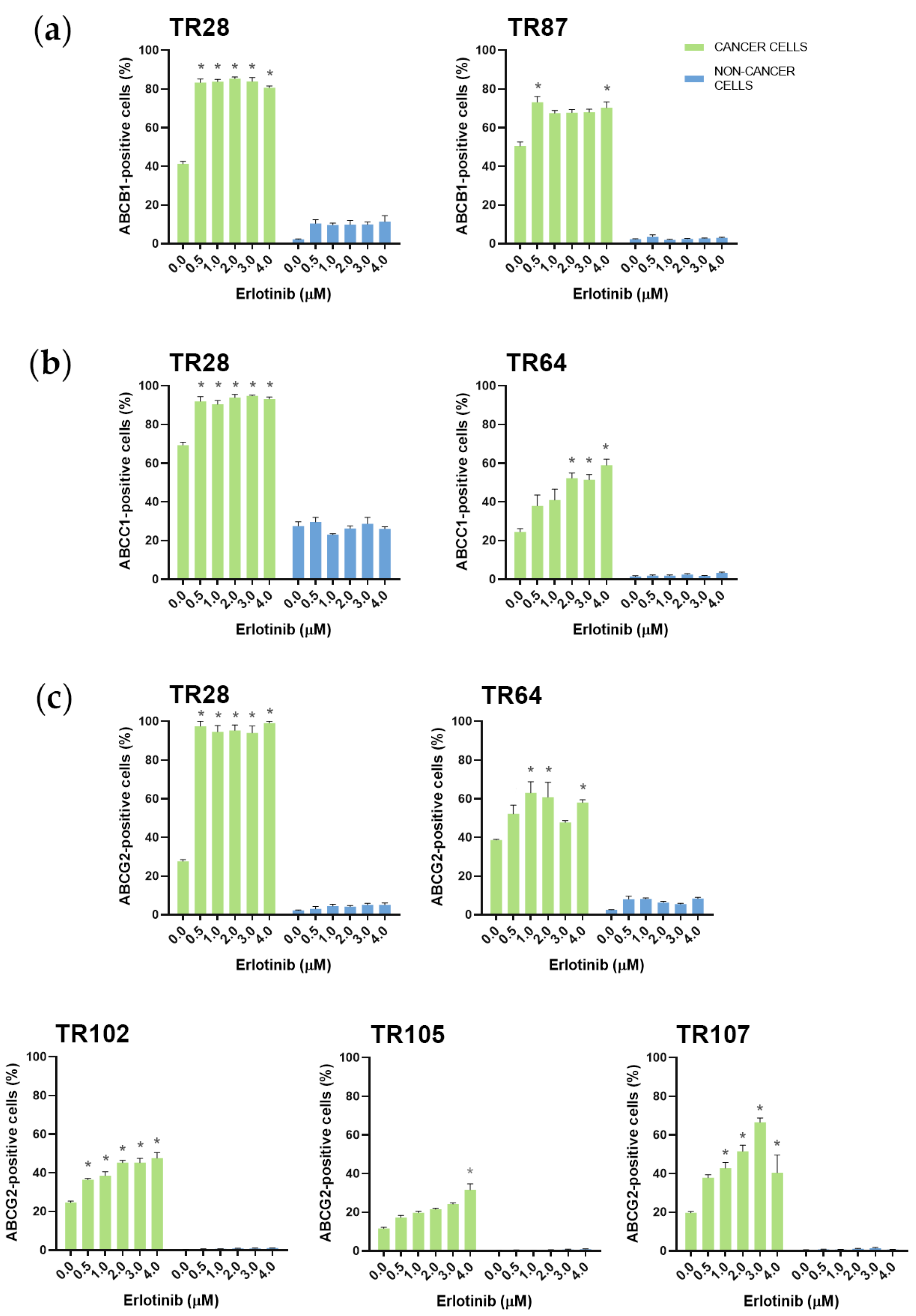
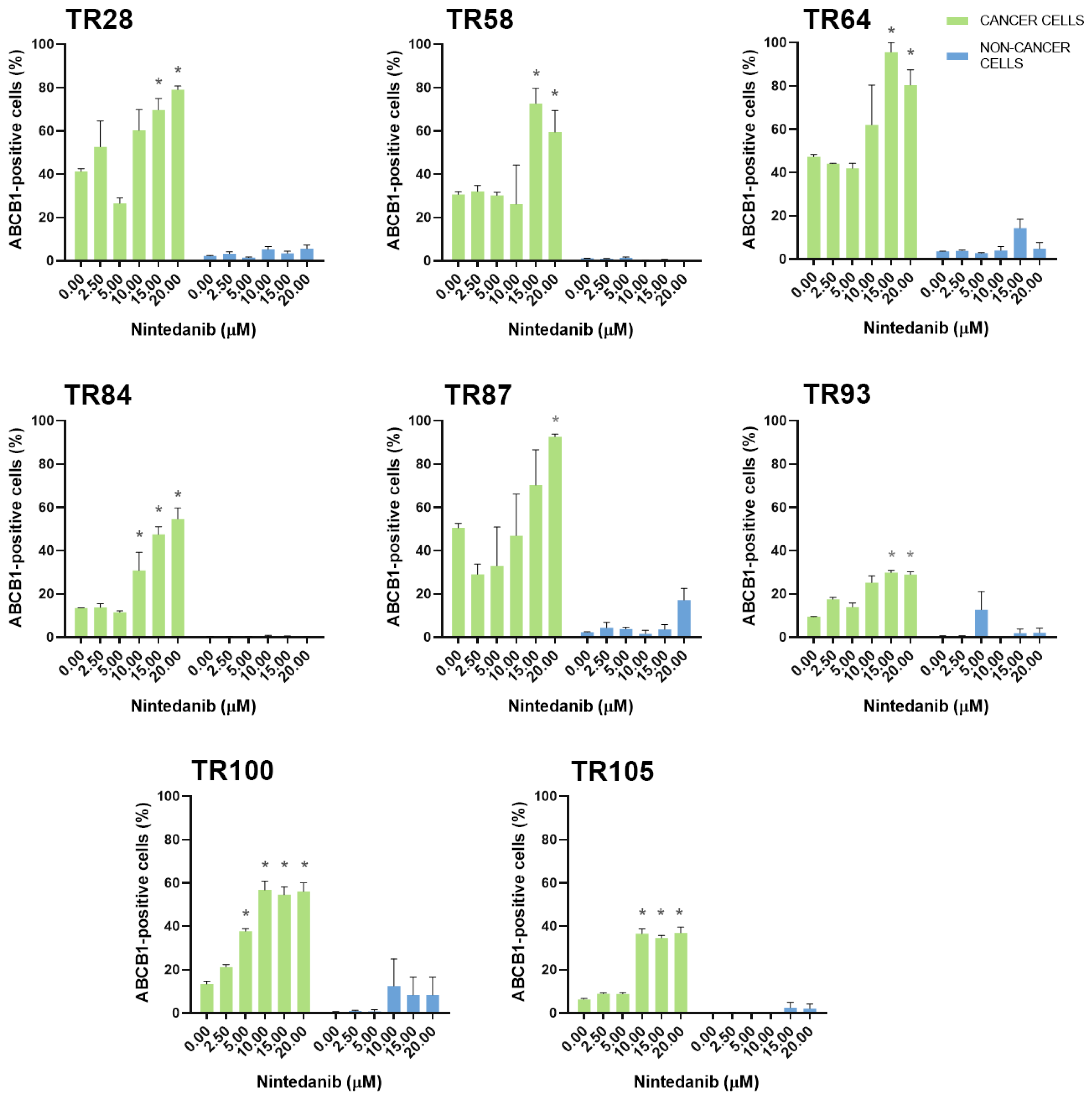
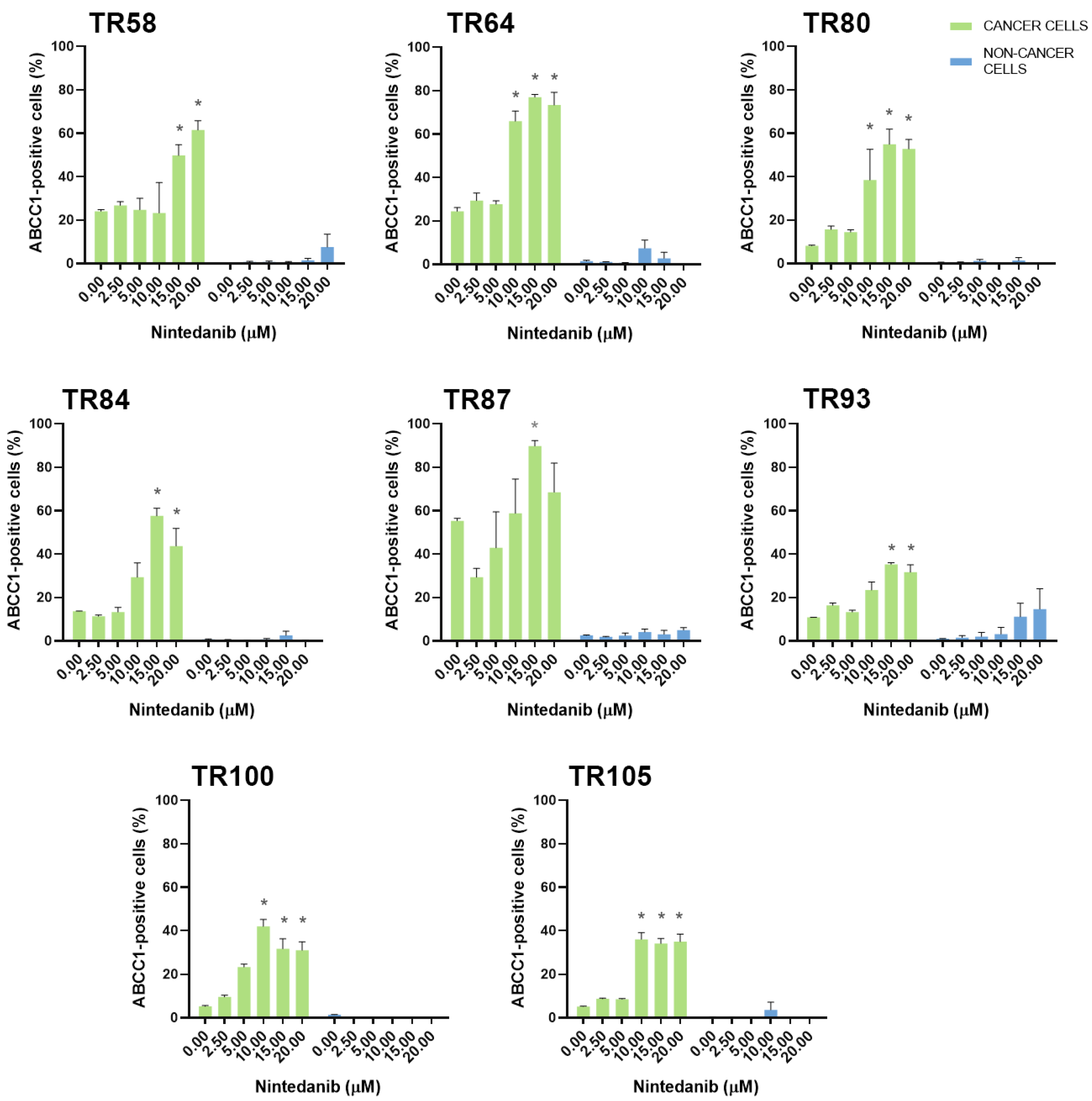
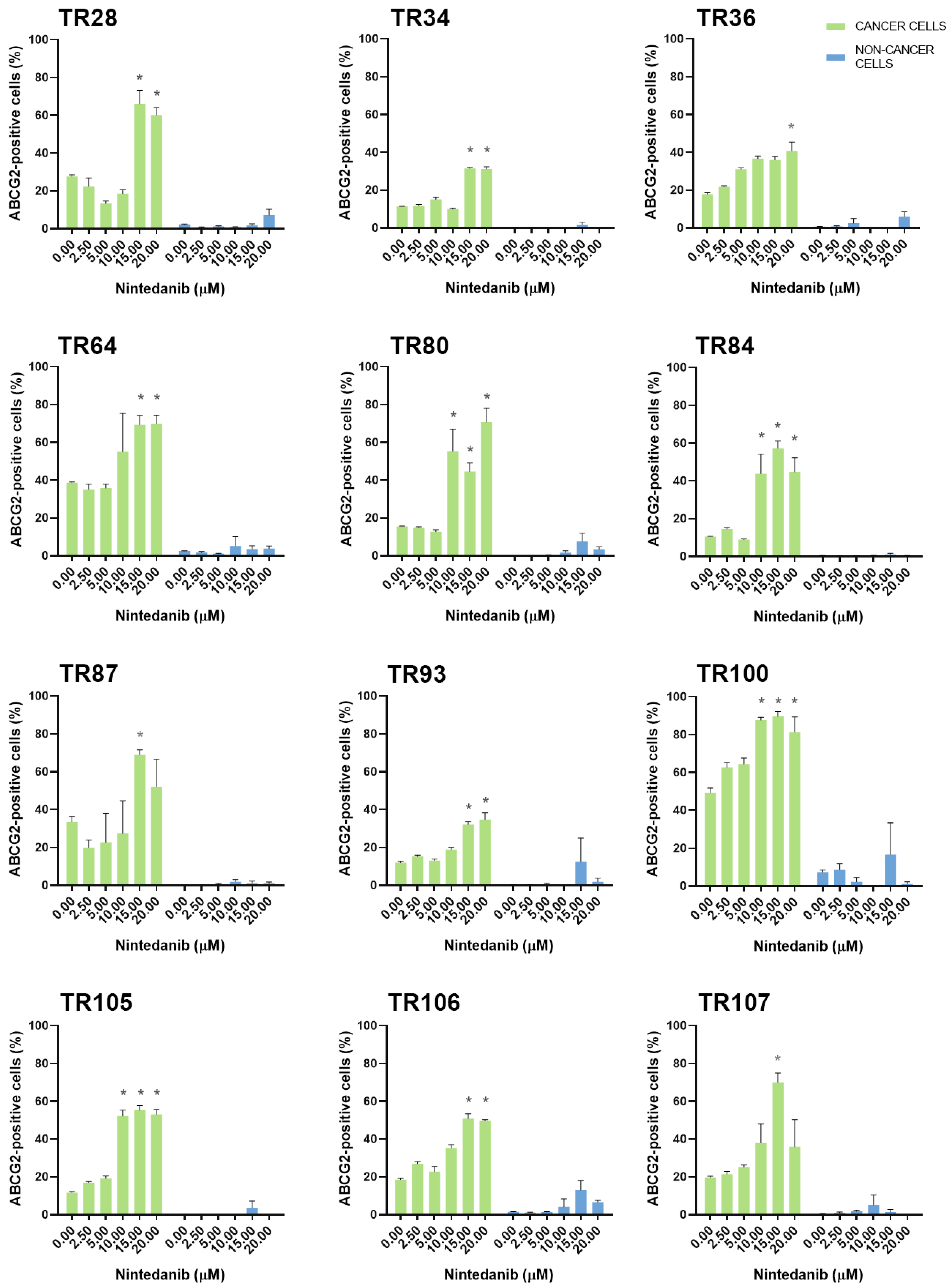
3.2. Assessment of MDR Marker Expression in Patient-Derived NSCLC Cultures after Treatment with TKIs
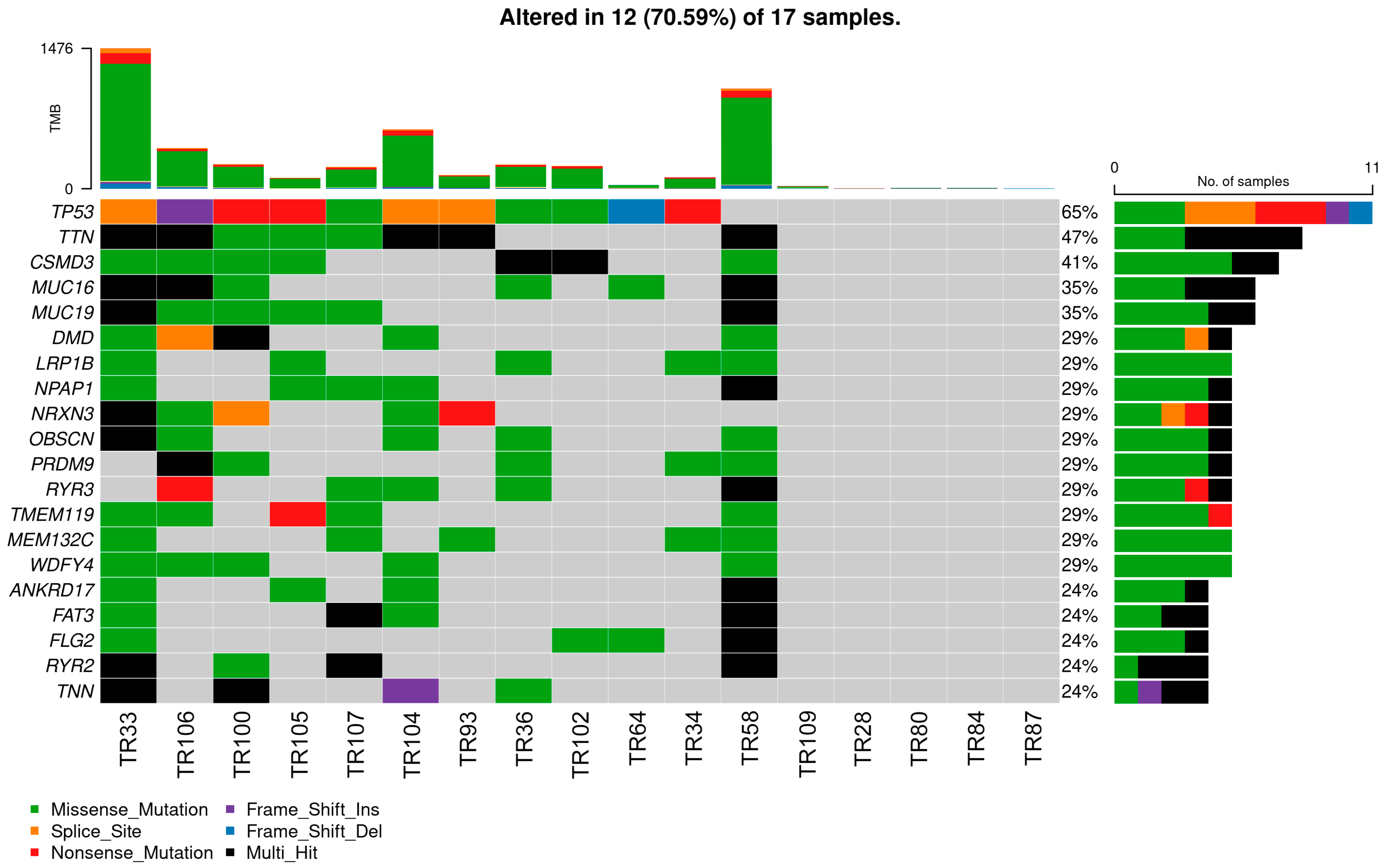
3.3. Mutational Landscape of NSCLC Patients
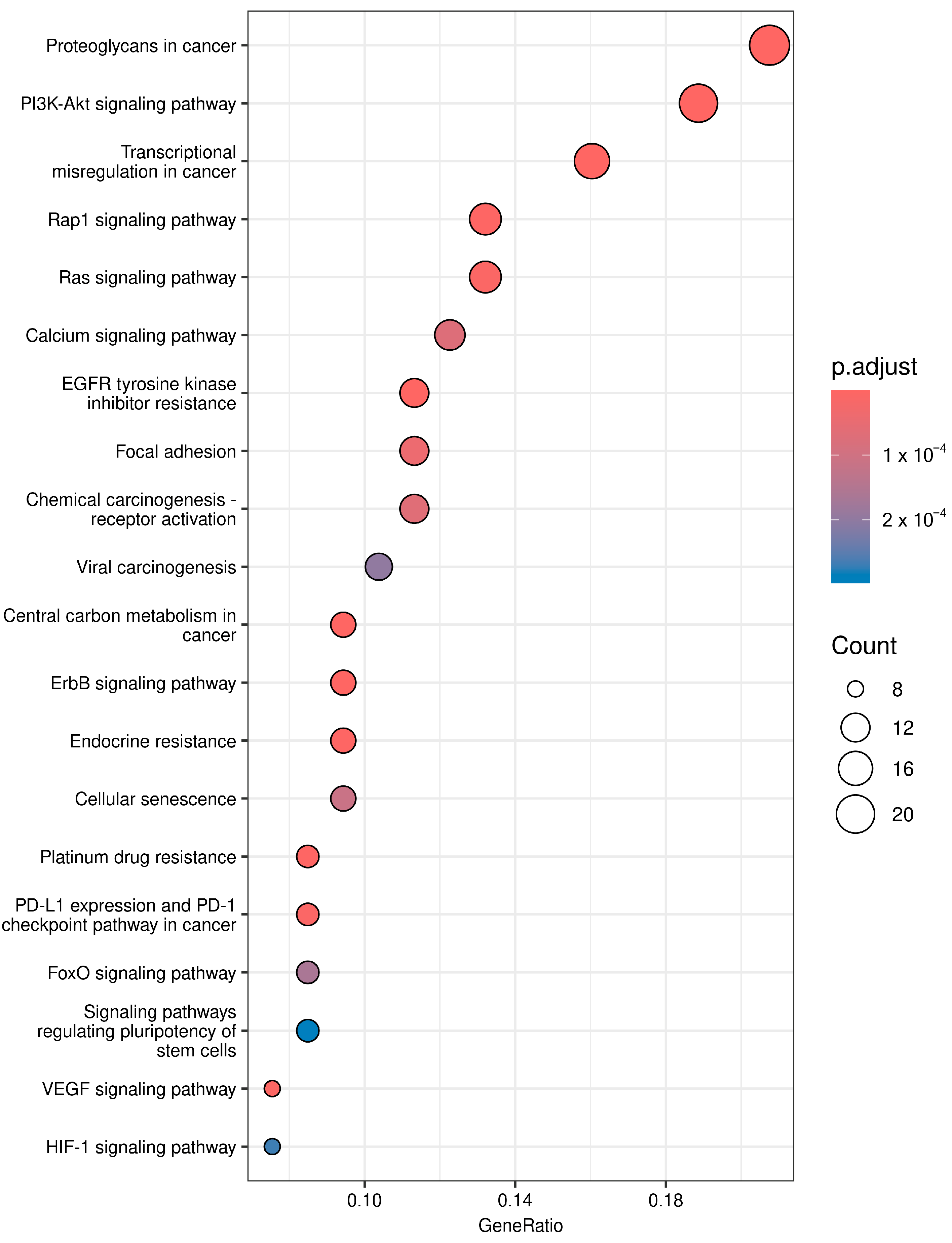
3.4. Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Q.; Wu, Z.X.; Yang, Y.; Teng, Q.X.; Li, Y.D.; Lei, Z.N.; Jani, K.A.; Kaushal, N.; Chen, Z.S. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters in cancer: A review of recent updates. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2021, 14, 232–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto Heming, C.; Muriithi, W.; Wanjiku Macharia, L.; Niemeyer Filho, P.; Moura-Neto, V.; Aran, V. P-glycoprotein and cancer: What do we currently know? Heliyon 2022, 8, e11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejendal, K.F.; Hrycyna, C.A. Multidrug resistance and cancer: The role of the human ABC transporter ABCG2. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2002, 3, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, R.J.; Moshirfar, M.; Ronquillo, Y. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Maione, P.; Sacco, P.C.; Sgambato, A.; Casaluce, F.; Rossi, A.; Gridelli, C. Overcoming resistance to targeted therapies in NSCLC: Current approaches and clinical application. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2015, 7, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakkala, S.; Ramalingam, S.S. Personalized therapy for lung cancer: Striking a moving target. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e120858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metro, G.; Crino, L. Advances on EGFR mutation for lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2012, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.; Xie, F.; Wang, F.; Fu, L. Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ye, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, X.; Han, X.; Chu, Q.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Outcomes of switching from crizotinib to alectinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Malik, Z. Comparison of Clinical Efficacy of Alectinib Versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 646526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Emerging paradigms in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, A.; Marinato, G.M.; Mulargiu, C.; Marino, M.; Pasello, G.; Guarneri, V.; Bonanno, L. The study of primary and acquired resistance to first-line osimertinib to improve the outcome of EGFR-mutated advanced Non-small cell lung cancer patients: The challenge is open for new therapeutic strategies. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2024, 196, 104295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Cross, D.; Janne, P.A. Kinase drug discovery 20 years after imatinib: Progress and future directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guerin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; Voegeli, A.C.; Vallat, L.; Mascaux, C.; Beau-Faller, M. Molecular Mechanism of EGFR-TKI Resistance in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Application to Biological Diagnostic and Monitoring. Cancers 2021, 13, 4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Planchard, D.; Lovly, C.M. Sequencing Therapy for Genetically Defined Subgroups of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncology. Annu. Meet. 2018, 38, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Franchina, T.; Ricciardi, G.; Battaglia, A.; Picciotto, M.; Adamo, V. Heterogeneous Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Uncommon EGFR Mutations: New Insights and Future Perspectives in this Complex Clinical Scenario. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Yan, B.; Gu, A.; Wang, W.; Huang, A.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing on Circulating Tumor Cells Explores Platinum-Drug Resistance Mutations in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 722078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, A.; Gyorffy, B. Comprehensive Outline of Whole Exome Sequencing Data Analysis Tools Available in Clinical Oncology. Cancers 2019, 11, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinic, J.; Podolski-Renic, A.; Dragoj, M.; Jovanovic Stojanov, S.; Stepanovic, A.; Lupsic, E.; Pajovic, M.; Jovanovic, M.; Petrovic Rodic, D.; Maric, D.; et al. Immunofluorescence-Based Assay for High-Throughput Analysis of Multidrug Resistance Markers in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, D.R.; Davis, M. Clinically Relevant Concentrations of Anticancer Drugs: A Guide for Nonclinical Studies. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Zhang, Q.; Larson, D.E.; Shen, D.; McLellan, M.D.; Lin, L.; Miller, C.A.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Wilson, R.K. VarScan 2: Somatic mutation and copy number alteration discovery in cancer by exome sequencing. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondka, Z.; Bamford, S.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.A.; Dunham, I.; Forbes, S.A. The COSMIC Cancer Gene Census: Describing genetic dysfunction across all human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinVar. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Fu, L. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors enhanced the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agent in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.R.; Potukuchi, P.K.; Schuetz, E.G.; Schuetz, J.D. Beyond Competitive Inhibition: Regulation of ABC Transporters by Kinases and Protein-Protein Interactions as Potential Mechanisms of Drug-Drug Interactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2018, 46, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, K.; Shibo, L.; Xiao, Z.; Longerich, T.; Buchler, M.W.; Schemmer, P. Correlation of gene expression of ATP-binding cassette protein and tyrosine kinase signaling pathway in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goler-Baron, V.; Sladkevich, I.; Assaraf, Y.G. Inhibition of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway disrupts ABCG2-rich extracellular vesicles and overcomes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yuan, J.Q.; Wang, K.F.; Fu, X.H.; Han, X.R.; Threapleton, D.; Yang, Z.Y.; Mao, C.; Tang, J.L. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78985–78993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guerin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; Voegeli, A.C.; Vallat, L.; Mascaux, C.; Beau-Faller, M. Direct Targeting KRAS Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Ou, W.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Feng, J.; Liu, B. TP53 mutation is associated with a poor clinical outcome for non-small cell lung cancer: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uramoto, H.; Mitsudomi, T. Which biomarker predicts benefit from EGFR-TKI treatment for patients with lung cancer? Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.S.; Kobayashi, S.; Costa, D.B. Acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancers dependent on the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway. Clin. Lung Cancer 2009, 10, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, K.; Hu, S.; Dong, W.; Gong, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, C. Clinical outcomes of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with NSCLC harboring uncommon EGFR mutations: A pooled analysis of 438 patients. Lung Cancer 2022, 172, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Qian, X.; Li, Y. Efficacy of erlotinib in NSCLC harboring rare EGFR extracellular domain mutation (T263P) and common mutations: Case report and literature review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 954026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markoczy, Z.; Sarosi, V.; Kudaba, I.; Galffy, G.; Turay, U.Y.; Demirkazik, A.; Purkalne, G.; Somfay, A.; Papai-Szekely, Z.; Raso, E.; et al. Erlotinib as single agent first line treatment in locally advanced or metastatic activating EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CEETAC): An open-label, non-randomized, multicenter, phase IV clinical trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, B.; Hager, H.; Sorensen, B.S.; McCulloch, T.; Mellemgaard, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Nexo, E.; Meldgaard, P. EGFR mutation frequency and effectiveness of erlotinib: A prospective observational study in Danish patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; van Zandwijk, N.; Gridelli, C.; Baliko, Z.; Rischin, D.; Allan, S.; Krzakowski, M.; Heigener, D. Erlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Efficacy and safety findings of the global phase IV Tarceva Lung Cancer Survival Treatment study. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2010, 5, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezjak, A.; Tu, D.; Seymour, L.; Clark, G.; Trajkovic, A.; Zukin, M.; Ayoub, J.; Lago, S.; de Albuquerque Ribeiro, R.; Gerogianni, A.; et al. Symptom improvement in lung cancer patients treated with erlotinib: Quality of life analysis of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.21. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3831–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Rodrigues Pereira, J.; Ciuleanu, T.; Tan, E.H.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Campos, D.; Maoleekoonpiroj, S.; Smylie, M.; Martins, R.; et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Schmid-Bindert, G.; Zhou, C. Erlotinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An update for clinicians. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2012, 4, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Khan, I.; Upadhyay, S.; Lewanski, C.; Falk, S.; Skailes, G.; Marshall, E.; Woll, P.J.; Hatton, M.; Lal, R.; et al. First-line erlotinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer unsuitable for chemotherapy (TOPICAL): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2012, 13, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, S.; Shoshihara, N. Long-Term Responders to Erlotinib for Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma With Wild-Type Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: Two Case Reports and a Single-Institutional Retrospective Study. World J. Oncol. 2023, 14, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjoo, K.N.; Wakelee, H. Review of erlotinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Biol. Targets Ther. 2007, 1, 335–346. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Parmar, S.; Peng, X.X.; Shen, T.; Robey, R.W.; Bates, S.E.; Fu, L.W.; Shao, Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Zang, F.; et al. The epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 and erlotinib reverse ABCG2-mediated drug resistance. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Peng, X.X.; Kim, I.W.; Shukla, S.; Si, Q.S.; Robey, R.W.; Bates, S.E.; Shen, T.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Fu, L.W.; et al. Erlotinib (Tarceva, OSI-774) antagonizes ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 and ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2-mediated drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11012–11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbuti, A.M.; Zhang, G.-N.; Gupta, P.; Narayanan, S.; Chen, Z.-S. Chapter 1—EGFR and HER2 Inhibitors as Sensitizing Agents for Cancer Chemotherapy. In Protein Kinase Inhibitors as Sensitizing Agents for Chemotherapy; Chen, Z.-S., Yang, D.-H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Grzesk, G.; Wozniak-Wisniewska, A.; Blazejewski, J.; Gorny, B.; Wolowiec, L.; Rogowicz, D.; Nowaczyk, A. The Interactions of Nintedanib and Oral Anticoagulants-Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Ma, Z.; Wan, Q.; Peng, F. New advances in the research of clinical treatment and novel anticancer agents in tumor angiogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wind, S.; Schmid, U.; Freiwald, M.; Marzin, K.; Lotz, R.; Ebner, T.; Stopfer, P.; Dallinger, C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nintedanib. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 1131–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Adhikary, S.; Singh, V.; Gadad, S.S.; Roy, S.; Das, C. The paradigm of drug resistance in cancer: An epigenetic perspective. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20211812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Rodrigues, V.; Di Luca, A.; Mleczko, J.; Meleady, P.; Henry, M.; Pesic, M.; Cabrera, D.; van Liempd, S.; Lima, R.T.; O’Connor, R.; et al. Identification of the metabolic alterations associated with the multidrug resistant phenotype in cancer and their intercellular transfer mediated by extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, C.P.R.; Belisario, D.C.; Rebelo, R.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Giovannetti, E.; Kopecka, J.; Vasconcelos, M.H. The role of extracellular vesicles in the transfer of drug resistance competences to cancer cells. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer Chemother. 2022, 62, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.; Lima, R.T.; Lopes-Rodrigues, V.; Gonzalez, E.; Royo, F.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Different Ability of Multidrug-Resistant and -Sensitive Counterpart Cells to Release and Capture Extracellular Vesicles. Cells 2021, 10, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Andrikou, K.; Priano, I.; Cravero, P.; Pasini, L.; Urbini, M.; Delmonte, A.; Crino, L.; Bronte, G.; Ulivi, P. The Role of TP53 Mutations in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Clinical Significance and Implications for Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deben, C.; Deschoolmeester, V.; Lardon, F.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P. TP53 and MDM2 genetic alterations in non-small cell lung cancer: Evaluating their prognostic and predictive value. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2016, 99, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.G.; Sikic, B.I. Molecular pathways: Regulation and therapeutic implications of multidrug resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.W.; Pouliot, L.M.; Hall, M.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Cisplatin resistance: A cellular self-defense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Tsuboi, M.; He, J.; John, T.; Grohe, C.; Majem, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.W.; Kato, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Resected EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 3. 2024. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1450 (accessed on 19 March 2024).

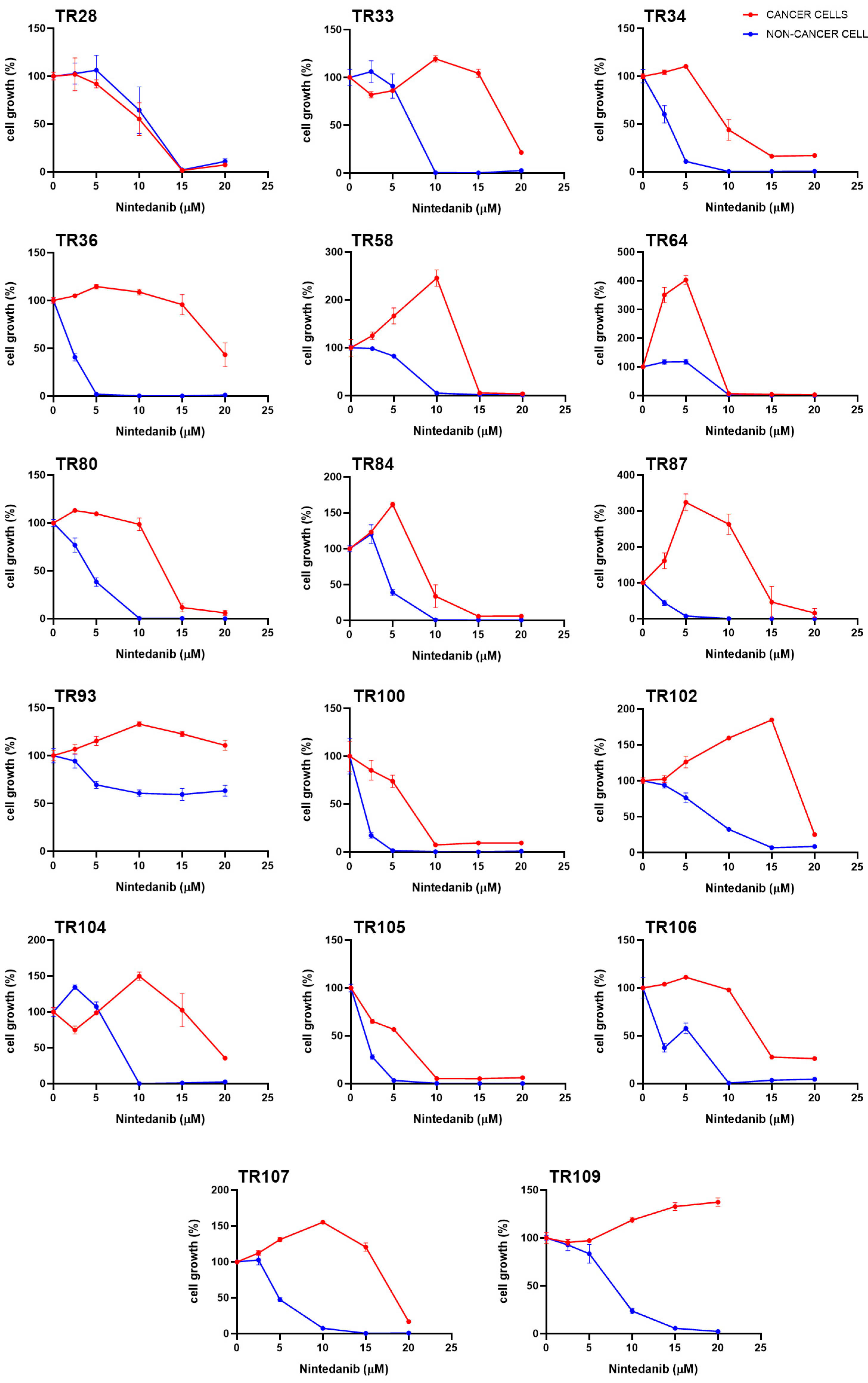
| NSCLC Cultures | IC50 (µM) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer Cells (CK8/18+) | Afatinib | Alectinib | Ceritinib | Crizotinib | Dabrafenib | Erlotinib | Gefitinib | Nintedanib | Osimertinib | Trametinib | |
| Stage I | TR84 | 0.0447 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 2.430 | >0.4 [22] | 12.851 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR104 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 3.250 | >0.4 | 17.525 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR105 | 0.0293 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | 2.595 | 0.456 | 0.399 | 3.240 | >0.15 | 0.024 | |
| Stage II | TR28 | >0.05 | N/A * | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 0.240 | >0.4 | 8.685 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR36 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | 4.381 | 2.288 | >0.4 | 19.315 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR58 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 1.829 | >0.4 [22] | 13.631 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR80 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 3.276 | >0.4 | 18.125 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR87 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | 0.608 | 1.297 | >0.4 [22] | 15.869 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR93 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 3.291 | >0.4 | >20 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR100 | >0.05 | 1.391 | >1.5 | >1 | 4.299 | 2.630 | >0.4 | 4.939 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR102 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 0.916 | >0.4 | 17.862 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR106 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 2.123 | >0.4 | 20.174 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| Stage III | TR33 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 0.969 | >0.4 | 16.706 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR34 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 1.385 | >0.4 | 10.901 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR64 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 2.765 | >0.4 [22] | 10.596 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR107 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 2.070 | >0.4 | 17.625 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| Stage IV | TR109 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 3.028 | >0.4 | >20 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| Non-Cancer Cells (CK8/18−) | Afatinib | Alectinib | Ceritinib | Crizotinib | Dabrafenib | Erlotinib | Gefitinib | Nintedanib | Osimertinib | Trametinib | |
| Stage I | TR84 | >0.05 s | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 [22] | 4.161 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR104 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 7.481 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR105 | >0.05 s | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 s | >4 s | >0.4 s | 0.618 | >0.15 | >0.025 s | |
| Stage II | TR28 | >0.05 | N/A * | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 10.624 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR36 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | 0.726 | 1.044 | >4 s | >0.4 | 0.909 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR58 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | 3.205 s | >0.4 [22] | 5.215 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR80 | >0.05 | 1.447 | >1.5 | 0.404 | 4.531 | >4 s | >0.4 | 2.732 | 0.133 | >0.025 | |
| TR87 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | 0.927 | 0.229 | >4 s | 0.188 [22] | 1.069 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR93 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | >20 | >0.15 | 0.005 | |
| TR100 | >0.05 | 0.403 | 0.358 | 0.176 | 0.787 | >4 s | >0.4 | 0.357 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR102 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 6.559 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR106 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 2.112 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| Stage III | TR33 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 6.682 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| TR34 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | 0.921 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 1.568 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR64 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 [22] | 7.360 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| TR107 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 4.150 | >0.15 | >0.025 | |
| Stage IV | TR109 | >0.05 | >1.5 | >1.5 | >1 | >5 | >4 s | >0.4 | 6.010 | >0.15 | >0.025 |
| CK8/18+ Cells | ABCB1 * Expression Increased | ABCC1 * Expression Increased | ABCG2 * Expression Increased |
|---|---|---|---|
| TR28 | erlotinib, nintedanib | erlotinib | erlotinib, nintedanib |
| TR33 | / | / | / |
| TR34 | / | / | nintedanib |
| TR36 | / | / | nintedanib |
| TR58 | nintedanib | nintedanib | / |
| TR64 | nintedanib | erlotinib, nintedanib | erlotinib, nintedanib |
| TR80 | / | dabrafenib, nintedanib | nintedanib |
| TR84 | gefitinib, nintedanib | gefitinib [22], nintedanib | gefitinib, nintedanib |
| TR87 | ceritinib, erlotinib, nintedanib | afatinib, nintedanib | ceritinib, gefitinib, nintedanib |
| TR93 | nintedanib | nintedanib | nintedanib |
| TR100 | nintedanib | nintedanib | nintedanib |
| TR102 | / | / | erlotinib |
| TR104 | / | / | / |
| TR105 | nintedanib | nintedanib | erlotinib, nintedanib |
| TR106 | / | / | nintedanib |
| TR107 | / | / | alectinib, ceritinib, dabrafenib, erlotinib, nintedanib |
| TR109 | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dinić, J.; Dragoj, M.; Jovanović Stojanov, S.; Stepanović, A.; Lupšić, E.; Pajović, M.; Mohr, T.; Glumac, S.; Marić, D.; Ercegovac, M.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells: Implications for Personalized Approaches with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers 2024, 16, 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111984
Dinić J, Dragoj M, Jovanović Stojanov S, Stepanović A, Lupšić E, Pajović M, Mohr T, Glumac S, Marić D, Ercegovac M, et al. Multidrug-Resistant Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells: Implications for Personalized Approaches with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111984
Chicago/Turabian StyleDinić, Jelena, Miodrag Dragoj, Sofija Jovanović Stojanov, Ana Stepanović, Ema Lupšić, Milica Pajović, Thomas Mohr, Sofija Glumac, Dragana Marić, Maja Ercegovac, and et al. 2024. "Multidrug-Resistant Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells: Implications for Personalized Approaches with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" Cancers 16, no. 11: 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111984
APA StyleDinić, J., Dragoj, M., Jovanović Stojanov, S., Stepanović, A., Lupšić, E., Pajović, M., Mohr, T., Glumac, S., Marić, D., Ercegovac, M., Podolski-Renić, A., & Pešić, M. (2024). Multidrug-Resistant Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patient-Derived Cells: Implications for Personalized Approaches with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancers, 16(11), 1984. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111984








