Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Consolidated Therapeutic Options
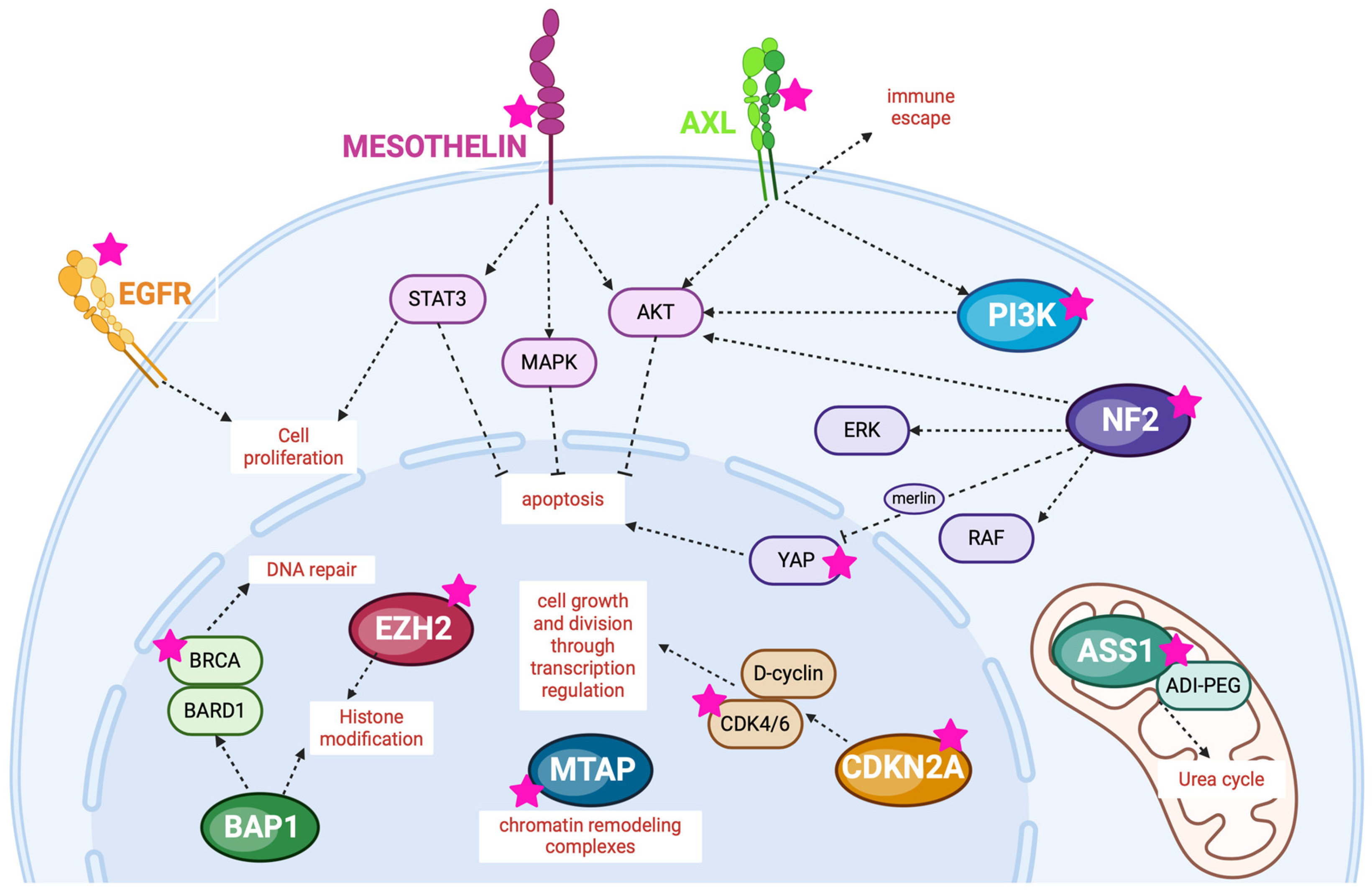
3. Potential Molecular Targets for MMs
3.1. Gene Involved in Cell Cycle Regulation
3.1.1. CDKN2A and MTAP
CDKN2A
MTAP
3.2. Gene Coding for Receptor Tyrosine Kinases
3.2.1. EGFR
3.2.2. AXL
3.3. Gene Involved in Hippo Signaling Pathway
3.3.1. NF2, YAP1/TEAD
3.3.2. PI3K
3.4. Enzyme Involved in Metabolism
3.4.1. ASS1
3.4.2. Glutamine
3.5. Surface Target
Mesothelin
3.6. Genes Involved in Responses to DNA Damage
3.6.1. BAP1 and EZH2
3.6.2. BRCA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sauter, J.L.; Bueno, R.; Dacic, S.; Gill, R.R.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Ladanyi, M.; Nowak, A.; Schmitt, F. Diffuse Pleural Mesothelioma. In WHO Classification of Tumors Editorial Board, 5th ed.; Lyon IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2021; pp. 204–219. [Google Scholar]
- Marsili, D.; Terracini, B.; Santana, V.S.; Ramos-Bonilla, J.P.; Pasetto, R.; Mazzeo, A.; Loomis, D.; Comba, P.; Algranti, E. Prevention of Asbestos-Related Disease in Countries Currently Using Asbestos. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, Y.; Loomis, D.; Guyton, K.Z.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Scoccianti, C.; Mattock, H.; et al. International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. Carcinogenicity of fluoro-edenite, silicon carbide fibres and whiskers, and carbon nanotubes. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1427–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, R.J.; Smith, N.; Cooper, W.; Lynch, G.; Patole, S.; Symonds, J.; Edey, A.; Maskell, N.A.; Bibby, A.C.; on behalf of the ASSESS-meso Collaborative group. Reflecting real-world patients with mesothelioma in research: An interim report of baseline characteristics from the ASSESS-meso cohort. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00467–02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, M.T.; Zhang, H. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: A population-based study of survival. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644, Corrected and Republished in J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; O’Brien, M.E.; Stahel, R.A.; Nackaerts, K.; Baas, P.; Karthaus, M.; Eberhardt, W.; Paz-Ares, L.; Sundstrom, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Pemetrexed plus cisplatin or pemetrexed plus carboplatin for chemonaïve patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Results of the international expanded access program. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Castagneto, B.; A Zucali, P.; Favaretto, A.; Mencoboni, M.; Grossi, F.; Cortinovis, D.; Del Conte, G.; Ceribelli, A.; Bearz, A.; et al. Pemetrexed plus carboplatin in elderly patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Combined analysis of two phase II trials. Br. J. Cancer. 2008, 99, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Gaafar, R.; Manegold, C.; Van Klaveren, R.J.; Van Marck, E.A.; Vincent, M.; Legrand, C.; Bottomley, A.; Debruyne, C.; Giaccone, G.; et al. Randomized phase III study of cisplatin with or without raltitrexed in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: An intergroup study of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lung Cancer Group and the National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6881–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalcman, G.; Mazieres, J.; Margery, J.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Molinier, O.; Corre, R.; Monnet, I.; Gounant, V.; et al. Bevacizumab for newly diagnosed pleural mesothelioma in the mesothelioma avastin cisplatin pemetrexed study (MAPS): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Baas, P.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Girard, N.; Nicholson, A.; Nowak, A.; Opitz, I.; Scherpereel, A.; Reck, M.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gooijer, C.J.; van der Noort, V.; Stigt, J.A.; Baas, P.; Biesma, B.; Cornelissen, R.; van Walree, N.; van Heemst, R.C.; Youssef-El Soud, M.; Groen, H.J.; et al. Switch-maintenance gemcitabine after first-line chemotherapy in patients with malignant mesothelioma (NVALT19): An investigator-initiated, randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Scherpereel, A.; Cornelissen, R.; Oulkhouir, Y.; Greillier, L.; Kaplan, M.A.; Talbot, T.; Monnet, I.; Hiret, S.; Baas, P.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma: 3-year outcomes from CheckMate 743. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 488499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Lesterhuis, W.J.; Kok, P.-S.; Brown, C.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Karikios, D.J.; John, T.; Kao, S.C.-H.; Leslie, C.; Cook, A.M.; et al. Durvalumab with first-line chemotherapy in previously untreated malignant pleural mesothelioma (DREAM): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial with a safety run-in. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccirillo, M.C.; Chu, Q.; Bradbury, P.; Tu, W.; Coschi, C.H.; Grosso, F.; Florescu, M.; Mencoboni, M.; Goffin, J.R.; Pagano, M.; et al. Brief Report: Canadian Cancer Trials Group IND.227: A Phase 2 Randomized Study of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (NCT02784171). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Zucali, P.A.; De Vincenzo, F.; Gianoncelli, L.; Simonelli, M.; Lorenzi, E.; Ripa, C.; Giordano, L.; Santoro, A. Retreatment with pemetrexed based chemotherapy in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2011, 72, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A. JCO, meeting abstract, 2021 ASCO annual meeting I. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maio, M.; Scherpereel, A.; Calabrò, L.; Aerts, J.; Perez, S.C.; Bearz, A.; Nackaerts, K.; Fennell, D.A.; Kowalski, D.; Tsao, A.S.; et al. Tremelimumab as second-line or third-line treatment in relapsed malignant mesothelioma (DETERMINE): A multicentre, international, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, S.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Dafni, U.; Shah, R.; O’Brien, M.; Pope, A.; Fisher, P.; Spicer, J.; Roy, A.; Gilligan, D.; et al. A multicentre randomised phase III trial comparing pembrolizumab versus single-agent chemotherapy for advanced pre-treated malignant pleural mesothelioma: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 9-15) PROMISE-meso trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1734–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.A.; Ewings, S.; Ottensmeier, C.; Califano, R.; Hanna, G.G.; Hill, K.; Danson, S.; Steele, N.; Nye, M.; Johnson, L.; et al. CONFIRM trial investigators. Nivolumab versus placebo in patients with relapsed malignant mesothelioma (CONFIRM): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabro, L.; Morra, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Amato, G.; D’Incecco, A.; Covre, A.; Lewis, A.; Rebelatto, M.C.; Danielli, R.; Altomonte, M.; et al. Tremelimumab combined with durvalumab in patients with mesothelioma (NIBIT-MESO-1): An open-label, non randomised, phase 2 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, L.; Rossi, G.; Morra, A.; Rosati, C.; Cutaia, O.; Daffinà, M.G.; Altomonte, M.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Casula, M.; Fazio, C.; et al. Tremelimumab plus durvalumab retreatment and 4-year outcomes in patients with mesothelioma: A follow-up of the open label, non-randomised, phase 2 NIBIT-MESO-1 study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disselhorst, M.J.; Quispel-Janssen, J.; Lalezari, F.; Monkhorst, K.; de Vries, J.F.; van der Noort, V.; Harms, E.; Burgers, S.; Baas, P. Ipilimumab and nivolumab in the treatment of recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma (INITIATE): Results of a prospective, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Mazieres, J.; Greillier, L.; Lantuejoul, S.; Dô, P.; Bylicki, O.; Monnet, I.; Corre, R.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Locatelli-Sanchez, M.; et al. Nivolumab or nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with relapsed malignant pleural mesothelioma (IFCT-1501 MAPS2): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, non-comparative, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Kasai, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Takano, M.; Morita, K.; Kadota, E.; Nonomura, A. 9p21 deletion in the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma, using fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. Pathol. Int. 2010, 60, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozitis, E.; Johnson, B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Lee, K. The Use of Immunohistochemistry, Fluorescence in situ Hybridization, and Emerging Epigenetic Markers in the Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM): A Review. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltbrunner, S.; Fleischmann, Z.; Sokol, E.S.; Zoche, M.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A. Genomic landscape of pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma tumors. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Madison, R.W.; Lennerz, J.K.; Chen, K.-T.; Hopkins, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Lester, A.; Wharton, K.A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Mesothelioma: Impact of Histologic Type and Site of Origin on Molecular Landscape. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2100422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ríos, F.; Chuai, S.; Flores, R.; Shimizu, S.; Ohno, T.; Wakahara, K.; Illei, P.B.; Hussain, S.; Krug, L.; Zakowski, M.F.; et al. Global Gene Expression Profiling of Pleural Mesotheliomas: Overexpression of Aurora Kinases and P16/CDKN2A Deletion as Prognostic Factors and Critical Evaluation of Microarray-Based Prognostic Prediction. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2970–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliagas, E.; Alay, A.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Hernández-Madrigal, M.; Cordero, D.; Gausachs, M.; Pros, E.; Saigí, M.; Busacca, S.; Sharkley, A.J.; et al. Efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors in preclinical models of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A.; King, A.; Mohammed, S.; Greystoke, A.; Anthony, S.; Poile, C.; Nusrat, N.; Scotland, M.; Bhundia, V.; Branson, A.; et al. Abemaciclib in patients with p16ink4A-deficient mesothelioma (MiST2): A single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; You, L.; Yeh, C.-C.; Chang, J.W.-C.; Zhang, F.; McCormick, F.; Jablons, D.M. Adenovirus-Mediated p14ARF Gene Transfer in Human Mesothelioma Cells. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, W.L.; Gounder, M.M.; Frank, R.; Eskens, F.; Blay, J.Y.; Cassier, P.A.; Soria, J.-C.; Chawla, S.; De Weger, V.; Wagner, A.J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the MDM2 inhibitor AMG 232 in patients with advanced P53 wild-type solid tumors or multiple myeloma. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Hida, T.; Hamasaki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sato, A.; Tsujimura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Oda, Y.; Nabeshima, K. A combination of MTAP and BAP1 immunohistochemistry in pleural effusion cytology for the diagnosis of mesothelioma. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmeljak, J.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Hoadley, K.A.; Shih, J.; Stewart, C.; Heiman, D.; Tarpey, P.; Danilova, L.; Drill, E.; Gibb, E.A.; et al. Integrative Molecular Characterization of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1548–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guccione, E.; Richard, S. The regulation, functions and clinical relevance of arginine methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, R.S.; Richard, S. Arginine Methylation: The Coming of Age. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryukov, G.V.; Wilson, F.H.; Ruth, J.R.; Paulk, J.; Tsherniak, A.; Marlow, S.E.; Vazquez, F.; Weir, B.A.; Fitzgerald, M.E.; Tanaka, M.; et al. MTAP deletion confers enhanced dependency on the PRMT5 arginine methyltransferase in cancer cells. Science 2016, 351, 1214–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrakis, K.J.; McDonald, E.R., III; Schlabach, M.R.; Billy, E.; Hoffman, G.R.; Deweck, A.; Ruddy, D.A.; Venkatesan, K.; Yu, J.; McAllister, G.; et al. Disordered methionine metabolism in MTAP/CDKN2A-deleted cancers leads to dependence on PRMT5. Science 2016, 351, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarino, M.; Cesari, D.; Bottaro, M.; Luzzi, L.; Namagerdi, A.; Bertolino, F.M.; Bellan, C.; Proietti, F.; Somma, P.; Micheli, M.; et al. PRMT5 silencing selectively affects MTAP -deleted mesothelioma: In vitro evidence of a novel promising approach. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5565–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, H.L.; Burris, H.A.; Sandler, A.B.; Oliff, I.A. A phase II multicenter study of L-alanosine, a potent inhibitor of adenine biosynthesis, in patients with MTAP-deficient cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2009, 27, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, L.D.; Aranda, R.; Waters, L.; Moya, K.; Bowcut, V.; Vegar, L.; Trinh, D.; Hebbert, A.; Smith, C.R.; Kulyk, S.; et al. MRTX1719 Is an MTA-Cooperative PRMT5 Inhibitor That Exhibits Synthetic Lethality in Preclinical Models and Patients with MTAP -Deleted Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2412–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destro, A.; Ceresoli, G.; Falleni, M.; Zucali, P.; Morenghi, E.; Bianchi, P.; Pellegrini, C.; Cordani, N.; Vaira, V.; Alloisio, M.; et al. EGFR overexpression in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2006, 51, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rena, O.; Boldorini, L.R.; Gaudino, E.; Casadio, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Prognostic correlations. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, L.L.; Rankin, C.; Gandara, D.R.; Rivkin, S.E.; Scott, K.M.; Nagle, R.B.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Testa, J.R.; Altomare, D.A.; Borden, E.C. Phase II Study of Erlotinib in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Southwest Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, D.M.; Kindler, H.L.; Yeap, B.Y.; Fidias, P.; Salgia, R.; Lucca, J.; Morse, L.K.; Ostler, P.A.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab in previously treated patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer 2008, 113, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Kratzke, R.A.; Herndon, J.E.; Niehans, G.A.; Vollmer, R.; Watson, D.; Green, M.R.; Kindler, H.L.; on behalf of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 30101). Gefitinib in Patients with Malignant Mesothelioma: A Phase II Study by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2300–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Lind, M.J.; Cawkwell, L. Targeted epidermal growth factor receptor therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Where do we stand? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevet, M.; Shimizu, S.; Bott, M.J.; Shukla, N.; Zhou, Q.; Olshen, A.B.; Rusch, V.; Ladanyi, M. Coactivation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Malignant Mesothelioma as a Rationale for Combination Targeted Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Pavlakis, N.; Kao, S.C.; Linton, A.; Boyer, M.J.; Clarke, S.; Huynh, Y.; Chrzanowska, A.; Fulham, M.J.; Bailey, D.L.; et al. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, T.G.; Adams, T.E.; Cochran, J.R.; Hall, N.E.; Hoyne, P.A.; Olsen, M.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Rothacker, J.; Nice, E.C.; Walker, F.; et al. Identification of the Epitope for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-specific Monoclonal Antibody 806 Reveals That It Preferentially Recognizes an Untethered Form of the Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30375–30384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bent, M.; Eoli, M.; Sepulveda, J.M.; Smits, M.; Walenkamp, A.; Frenel, J.-S.; Franceschi, E.; Clement, P.M.; Chinot, O.; de Vos, F.Y.F.L.; et al. INTELLANCE 2/EORTC 1410 randomized phase II study of Depatux-M alone and with temozolomide vs temozolomide or lomustine in recurrent EGFR amplified glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2020, 22, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.-L.; Parakh, S.; Tsao, M.-S.; Pham, N.-A.; Gan, H.K.; Cao, D.; Burvenich, I.J.G.; Rigopoulos, A.; Reilly, E.B.; John, T.; et al. Targeting and Efficacy of Novel mAb806-Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Malignant Mesothelioma. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.-B.; Corson, J.M.; Flynn, D.L.; Lu, W.-P.; Wise, S.C.; Bueno, R.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Fletcher, J.A. AXL regulates mesothelioma proliferation and invasiveness. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Ke, H.; Kao, S.; Pavlakis, N. An Update on Emerging Therapeutic Options for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Lung Cancer Targets Ther. 2022, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, T.; Grabiec, A.M.; Kaur, M.; Bell, T.J.; Fujino, N.; Cook, P.C.; Svedberg, F.R.; MacDonald, A.S.; Maciewicz, R.A.; Singh, D.; et al. The Axl receptor tyrosine kinase is a discriminator of macrophage function in the inflamed lung. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, S.J.; Pan, A.; Franci, C.; Hu, Y.; Chang, B.; Li, W.; Duan, M.; Torneros, A.; Yu, J.; Heckrodt, T.J.; et al. R428, a Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of Axl Kinase, Blocks Tumor Spread and Prolongs Survival in Models of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Branson, A.; Barber, S.; Poile, C.; King, A.; Greystoke, A.; Moody, S.; Nolan, L.; Scotland, M.; Darlison, L.; et al. Bemcentinib and pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed mesothelioma: MIST3, a phase IIa trial with cellular and molecular correlates of efficacy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Oleinick, N.L.; Zhang, J. ATR/CHK1 inhibitors and cancer therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, S.; Yamada, T.; Katayama, Y.; Ishida, M.; Kawachi, H.; Matsui, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Morimoto, K.; Horinaka, M.; Sakai, T.; et al. Effects of Combined Therapeutic Targeting of AXL and ATR on Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2024, 23, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, G.A.; Merel, P.; Lutchman, M.; Sanson, M.; Zucman, J.; Marineau, C.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Demczuk, S.; Desmaze, C.; Plougastel, B.; et al. AXL and MET Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Co-Expression as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, G.A.; Merel, P.; Lutchman, M.; Sanson, M.; Zucman, J.; Marineau, C.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Demczuk, S.; Desmaze, C.; Plougastel, B.; et al. Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2. Nature 1993, 363, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, R.; Stawiski, E.W.; Goldstein, L.D.; Durinck, S.; De Rienzo, A.; Modrusan, Z.; Gnad, F.; Nguyen, T.T.; Jaiswal, B.S.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies recurrent mutations, gene fusions and splicing alterations. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quetel, L.; Meiller, C.; Assié, J.; Blum, Y.; Imbeaud, S.; Montagne, F.; Tranchant, R.; de Wolf, J.; Caruso, S.; Copin, M.; et al. Genetic alterations of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Association with tumor heterogeneity and overall survival. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1207–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiller, C.; Montagne, F.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Caruso, S.; de Wolf, J.; Bayard, Q.; Assié, J.-B.; Meunier, L.; Blum, Y.; Quetel, L.; et al. Multi-site tumor sampling highlights molecular intra-tumor heterogeneity in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, A.M.; Fernández-Valle, C. Role of Merlin/NF2 inactivation in tumor biology. Oncogene 2016, 35, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Gutmann, D.H. Merlin differentially associates with the microtubule and actin cytoskeleton. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 51, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekido, Y. Inactivation of Merlin in malignant mesothelioma cells and the Hippo signaling cascade dysregulation. Pathol. Int. 2011, 61, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClatchey, A.I.; Giovannini, M. Membrane organization and tumorigenesis--the NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin. Genes. Dev. 2005, 19, 2265–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, M.; McClatchey, A.I. Nf2/Merlin: A coordinator of receptor signalling and intercellular contact. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Sekido, Y. NF2/Merlin Inactivation and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Mesothelioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.-L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, L.; Thor, S.; Piper, M. TEAD family transcription factors in development and disease. Development 2021, 148, dev196675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lu, X.; Shi, W.-Y.; Mao, F.-J.; Yang, X.-Y.; Luo, Y.-B.; Li, W. Combined mTOR/MEK inhibition prevents proliferation and induces apoptosis in NF2-mutant tumors. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5874–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolly, S.O.; Wagner, A.J.; Bendell, J.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Krug, L.M.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Zauderer, M.G.; Lolkema, M.P.; Apt, D.; Yeh, R.-F.; et al. Phase I Study of Apitolisib (GDC-0980), Dual Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.T.; Konradi, A.W.; Feng, Y.; Peng, X.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Yu, F.-X.; Guan, K.-L.; Post, L. Small Molecule Inhibitors of TEAD Auto-palmitoylation Selectively Inhibit Proliferation and Tumor Growth of NF2-deficient Mesothelioma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Huang, B.; Shim, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, S.-J.; Anders, R.A.; Liu, J.O.; Pan, D. Genetic and pharmacological disruption of the TEAD-YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Adhikary, G.; Rorke, E.A.; Friedberg, J.S.; Mickle, M.B.; Alexander, H.R.; Eckert, R.L. The YAP1 Signaling Inhibitors, Verteporfin and CA3, Suppress the Mesothelioma Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Kwiatkowski, D.J.; Desai, J.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Millward, M.; Kindler, H.L.; Tolcher, A.W.; Frentzas, S.; Thurston, A.W.; Post, L.; et al. First-in-class, first-in-human phase 1 trial of VT3989, an inhibitor of yes-associated protein (YAP)/transcriptional enhancer activator domain (TEAD), in patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors enriched for malignant mesothelioma and other tumors with neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) mutations. Cancer Res. 2023, 83 (Suppl. 8), CT006. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Abu-Eid, R.; Shrimali, R.; Webb, M.; Verma, V.; Doroodchi, A.; Berrong, Z.; Samara, R.; Rodriguez, P.C.; Mkrtichyan, M.; et al. Differential PI3Kδ Signaling in CD4+ T-cell Subsets Enables Selective Targeting of T Regulatory Cells to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1892–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Kannan, A.; Zhao, S.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Ejadi, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Barreto, J.C.; Zhao, H.; Gao, L. Inhibition of PI3K by copanlisib exerts potent antitumor effects on Merkel cell carcinoma cell lines and mouse xenografts. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedrés, S.; Montero, M.A.; Martinez, P.; Martinez, A.; Rodríguez-Freixinós, V.; Torrejon, D.; Gabaldon, A.; Salcedo, M.; Ramon, Y.C.S.; Felip, E. Exploratory analysis of activation of PTEN-PI3K pathway and downstream proteins in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalla, C.; Ott, G.; Finotello, F.; Niewola-Staszkowska, K.; Di Conza, G.; Lahn, M.; van der Veen, L.; Schüler, J.; Falkenstern-Ge, R.; Kopecka, J.; et al. The highly selective and oral phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3K-δ) inhibitor roginolisib induces apoptosis in mesothelioma cells and increases immune effector cell composition. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 43, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: Are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.A.; Digiacomo, G.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R.; Quaini, F.; Falco, A.; Madeddu, D.; La Monica, S.; Cretella, D.; Ravelli, A.; et al. Combined Inhibition of CDK4/6 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathways Induces a Synergistic Anti-Tumor Effect in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauderer, M.G.; Alley, E.W.; Bendell, J.; Capelletto, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Callies, S.; Szpurka, A.M.; Kang, S.; Willard, M.D.; Wacheck, V.; et al. Phase 1 cohort expansion study of LY3023414, a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, in patients with advanced mesothelioma. Investig. New Drugs. 2021, 39, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Klabatsa, A.; Pallaska, A.; Sheaff, M.; Smith, P.; Crook, T.; Grimshaw, M.J.; Steele, J.P.; Rudd, R.M.; Balkwill, F.R.; et al. In vivo Loss of Expression of Argininosuccinate Synthetase in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Is a Biomarker for Susceptibility to Arginine Depletion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7126–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, R.; Campbell, E.; Wheatley, D.N. Arginine deprivation, growth inhibition and tumour cell death: 2. Enzymatic degradation of arginine in normal and malignant cell cultures. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Steele, J.P.; Nolan, L.; Gilligan, D.; Taylor, P.; Spicer, J.; Lind, M.; Mitra, S.; Shamash, J.; Phillips, M.M.; et al. Arginine Deprivation With Pegylated Arginine Deiminase in Patients With Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1–Deficient Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beddowes, E.; Spicer, J.; Chan, P.Y.; Khadeir, R.; Corbacho, J.G.; Repana, D.; Steele, J.P.; Schmid, P.; Szyszko, T.; Cook, G.; et al. Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Study of Pegylated Arginine Deiminase, Cisplatin, and Pemetrexed in Patients With Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1–Deficient Thoracic Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Phillips, M.M.; Pavlyk, I.; Steele, J.; Shamash, J.; Spicer, J.; Kumar, S.; Pacey, S.; Feng, X.; Johnston, A.; et al. Expansion Phase 1 Study of Pegargiminase Plus Pemetrexed and Cisplatin in Patients With Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1–Deficient Mesothelioma: Safety, Efficacy, and Resistance Mechanisms. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Creelan, B.; Sarkodie, T.; Nolan, L.; Taylor, P.; Olevsky, O.; Grosso, F.; Cortinovis, D.; Chitnis, M.; Roy, A.; et al. Abstract CT007: Phase 2-3 trial of pegargiminase plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in patients with non-epithelioid pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, CT007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Agnihotri, N.; Kumar, S. Targeting fuel pocket of cancer cell metabolism: A focus on glutaminolysis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 198, 114943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.N.; Ngwa, V.M.; Wang, S.; Shiuan, E.; Brantley-Sieders, D.M.; Kim, L.C.; Reynolds, A.B.; Chen, J.; White, A.D.; Peña, K.A.; et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 promotes glutamine metabolism in tumors by activating the transcriptional coactivators YAP and TAZ. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaan4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, G.; Shrestha, S.; Naselsky, W.; Newland, J.J.; Chen, X.; Xu, W.; Emadi, A.; Friedberg, J.S.; Eckert, R.L. Mesothelioma cancer cells are glutamine addicted and glutamine restriction reduces YAP1 signaling to attenuate tumor formation. Mol. Carcinog. 2023, 62, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, E.L.; Colovos, C.; Rodriguez, L.; Bograd, A.J.; Nitadori, J.-I.; Sima, C.; Rusch, V.W.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Mesothelin overexpression promotes mesothelioma cell invasion and MMP-9 secretion in an orthotopic mouse model and in epithelioid pleural mesothelioma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2478–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argani, P.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Ryu, B.; Rosty, C.; Goggins, M.; Wilentz, R.E.; Murugesan, S.R.; Leach, S.D.; Jaffee, E.; Yeo, C.J.; et al. Mesothelin is overexpressed in the vast majority of ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas: Identification of a new pancreatic cancer marker by serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE). Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 3862–3868. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.-F.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chang, M.-C.; Hu, Y.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-A. High mesothelin correlates with chemoresistance and poor survival in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Tsunoda, T.; Riku, M.; Ito, H.; Inoko, A.; Murakami, H.; Ebi, M.; Ogasawara, N.; Pastan, I.; Kasugai, K.; et al. Diffuse mesothelin expression leads to worse prognosis through enhanced cellular proliferation in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.R.; Xian, R.R.; Ziober, A.; Conejo-Garcia, J.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; June, C.H.; Zhang, P.J.; Tchou, J. Mesothelin expression is associated with poor outcomes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastan, I.; Hassan, R. Discovery of mesothelin and exploiting it as a target for immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2907–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Pastan, I. Molecular cloning of mesothelin, a differentiation antigen present on mesothelium, mesotheliomas, and ovarian cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.K.; Pastan, I. Mesothelin is not required for normal mouse development or reproduction. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 2902–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, L.; Riedel, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Dinu, C.Z.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mesothelin promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumorigenicity of human lung cancer and mesothelioma cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiu, O.; Stebbing, J.; Lombardo, Y.; Bracci, E.; Uehara, N.; Bonotti, A.; Cristaudo, A.; Foddis, R.; Mutti, L.; Barale, R.; et al. MSLN gene silencing has an anti-malignant effect on cell lines overexpressing mesothelin deriving from malignant pleural mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Remaley, A.T.; Sampson, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Cox, D.D.; Pingpank, J.; Alexander, R.; Willingham, M.; Pastan, I.; Onda, M. Detection and quantitation of serum mesothelin, a tumor marker for patients with mesothelioma and ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Phung, Y.; Gao, W.; Kawa, S.; Hassan, R.; Pastan, I.; Ho, M. New high affinity monoclonal antibodies recognize non-overlapping epitopes on mesothelin for monitoring and treating mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, O.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Hansen, J.K.; Hassan, R.; Lee, B.; Ho, M. A binding domain on mesothelin for CA125/MUC16. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rump, A.; Morikawa, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Minami, S.; Umesaki, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Miyajima, A. Binding of ovarian cancer antigen CA125/MUC16 to mesothelin mediates cell adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9190–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, J.A.; Belisle, J.; Onda, M.; Rancourt, C.; Migneault, M.; Ho, M.; Bera, T.K.; Connor, J.; Sathyanarayana, B.K.; Lee, B.; et al. Mesothelin-MUC16 binding is a high affinity, N-glycan dependent interaction that facilitates peritoneal metastasis of ovarian tumors. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ramírez, C.; Casjens, S.; Juárez-Pérez, C.A.; Raiko, I.; Del Razo, L.M.; Taeger, D.; Calderón-Aranda, E.S.; Rihs, H.-P.; Acosta-Saavedra, L.C.; Weber, D.G.; et al. Mesothelin, Calretinin, and Megakaryocyte Potentiating Factor as Biomarkers of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Lung 2019, 197, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Level of mesothelin expression can indicate the prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 7479–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaya, D.; Farahmand, B.; Walter, A.O.; Kneip, C.; Jöhrens, K.; Tukiainen, M.; Schmitz, A.A. Prognosis of patients with malignant mesothelioma by expression of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and mesothelin in a contemporary cohort in Finland. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2020, 25, 100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaguma, S.; Wang, Z.; Lasota, J.; Onda, M.; Czapiewski, P.; Langfort, R.; Rys, J.; Szpor, J.; Waloszczyk, P.; Okoń, K.; et al. Comprehensive immunohistochemical study of mesothelin (MSLN) using different monoclonal antibodies 5B2 and MN-1 in 1562 tumors with evaluation of its prognostic value in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26744–26754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zeng, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Lai, Y.; Wang, M.; Che, G. Prognostic significance of soluble mesothelin in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46425–46435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goricar, K.; Kovac, V.; Dodic-Fikfak, M.; Dolzan, V.; Franko, A. Evaluation of soluble mesothelin-related peptides and MSLN genetic variability in asbestos-related diseases. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollevoet, K.; Nackaerts, K.; Thas, O.; Thimpont, J.; Germonpré, P.; De Vuyst, P.; Bosquée, L.; Legrand, C.; Kellen, E.; Kishi, Y.; et al. The effect of clinical covariates on the diagnostic and prognostic value of soluble mesothelin and megakaryocyte potentiating factor. Chest 2012, 141, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.I.; Roshkovan, L.; Berger, I.; Friedberg, J.S.; Alley, E.W.; Simone, C.B.; Haas, A.R.; Cengel, K.A.; Sterman, D.H.; Albelda, S.M. Serum soluble mesothelin-related protein (SMRP) and fibulin-3 levels correlate with baseline malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) tumor volumes but are not useful as biomarkers of response in an immunotherapy trial. Lung Cancer 2021, 154, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonotti, A.; Simonini, S.; Pantani, E.; Giusti, L.; Donadio, E.; Mazzoni, M.R.; Chella, A.; Marconi, L.; Ambrosino, N.; Lucchi, M.; et al. Serum mesothelin, osteopontin and vimentin: Useful markers for clinical monitoring of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int. J. Biol. Mark. 2017, 32, e126–e131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ryan, B.M.; Thomas, A.; Morrow, B.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Z.; Zingone, A.; Onda, M.; Hassan, R.; Pastan, I.; et al. Elevated Serum Megakaryocyte Potentiating Factor as a Predictor of Poor Survival in Patients with Mesothelioma and Primary Lung Cancer. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2018, 3, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriu, B.D.; Chahine, B.; Vachani, A.; Gey, T.; Conti, M.; Sterman, D.H.; Marchandise, G.; Porte, H.; Albelda, S.M.; Scherpereel, A. Kinetics of soluble mesothelin in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma during treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.; Feng, M.; Fisher, R.J.; Rader, C.; Pastan, I. A novel high-affinity human monoclonal antibody to mesothelin. Int. J. Cancer. 2011, 128, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Thomas, A.; Alewine, C.; Le, D.T.; Jaffee, E.M.; Pastan, I. Mesothelin Immunotherapy for Cancer: Ready for Prime Time? J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Ho, M. Mesothelin targeted cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Yang, H.; He, Z.; Liu, X.; Qin, W.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Modified CAR T cells targeting membrane-proximal epitope of mesothelin enhances the antitumor function against large solid tumor. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Cohen, S.J.; Phillips, M.; Pastan, I.; Sharon, E.; Kelly, R.J.; Schweizer, C.; Weil, S.; Laheru, D. Phase I Clinical Trial of the Chimeric Anti-Mesothelin Monoclonal Antibody MORAb-009 in Patients with Mesothelin-Expressing Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6132–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Kindler, H.L.; Jahan, T.; Bazhenova, L.; Reck, M.; Thomas, A.; Pastan, I.; Parno, J.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Fatato, P.; et al. Phase II Clinical Trial of Amatuximab, a Chimeric Antimesothelin Antibody with Pemetrexed and Cisplatin in Advanced Unresectable Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5927–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfier, S.; Kopitz, C.; Kahnert, A.; Heisler, I.; Schatz, C.A.; Stelte-Ludwig, B.; Mayer-Bartschmid, A.; Unterschemmann, K.; Bruder, S.; Linden, L.; et al. Anetumab ravtansine: A novel mesothelin-targeting antibody-drug conjugate cures tumors with heterogeneous target expression favored by bystander effect. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, H.L.; Novello, S.; Bearz, A.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Aerts, J.G.J.; Spicer, J.; Taylor, P.; Nackaerts, K.; Greystoke, A.; Jennens, R.; et al. Anetumab Ravtansine versus Vinorelbine in Patients with Relapsed, Mesothelin-Positive Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (ARCS-M): A Randomised, Open-Label Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Wang, D.; Wrangle, J.; Thomas, A.; Byars, A.; Asschert, L.; Atienza, R.; Rajagopalan, P.; Walter, A.; Zhang, J.; et al. Abstract A095: Phase Ib Study of Anetumab Ravtansine in Combination with Pemetrexed and Cisplatin in Patients with Mesothelin-Expressing Epithelial Mesothelioma or Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, A095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottey, S.; Clarke, J.; Aung, K.; Machiels, J.-P.; Markman, B.; Heinhuis, K.M.; Millward, M.; Lolkema, M.; Patel, S.P.; de Souza, P.; et al. Phase I/IIa Trial of BMS-986148, an Anti-mesothelin Antibody-drug Conjugate, Alone or in Combination with Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, U.B.; Ellingsen, C.; Schuhmacher, J.; Kristian, A.; Mobergslien, A.; Cruciani, V.; Wickstroem, K.; Schatz, C.A.; Kneip, C.; Golfier, S.; et al. Mesothelin-Targeted Thorium-227 Conjugate (MSLN-TTC): Preclinical Evaluation of a New Targeted Alpha Therapy for Mesothelin-Positive Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4723–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Sharon, E.; Thomas, A.; Zhang, J.; Ling, A.; Miettinen, M.; Kreitman, R.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Hollevoet, K.; Pastan, I. Phase 1 study of the antimesothelin immunotoxin SS1P in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin for front-line therapy of pleural mesothelioma and correlation of tumor response with serum mesothelin, megakaryocyte potentiating factor, and cancer antigen 125. Cancer 2014, 120, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Miller, A.C.; Sharon, E.; Thomas, A.; Reynolds, J.C.; Ling, A.; Kreitman, R.J.; Miettinen, M.M.; Steinberg, S.M.; Fowler, D.H.; et al. Major cancer regressions in mesothelioma after treatment with an anti-mesothelin immunotoxin and immune suppression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 208ra147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Alewine, C.; Mian, I.; Spreafico, A.; Siu, L.L.; Gomez-Roca, C.; Delord, J.-P.; Italiano, A.; Lassen, U.; Soria, J.-C.; et al. Phase 1 study of the immunotoxin LMB-100 in patients with mesothelioma and other solid tumors expressing mesothelin. Cancer 2020, 126, 4936–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Ghafoor, A.; Mian, I.; Rathkey, D.; Thomas, A.; Alewine, C.; Sengupta, M.; Ahlman, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Morrow, B.; et al. Enhanced efficacy of mesothelin-targeted immunotoxin LMB-100 and anti-PD-1 antibody in patients with mesothelioma and mouse tumor models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, C.-D.; Wu, X.-H. Therapeutic cancer vaccines: From initial findings to prospects. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockstedt, D.G.; Giedlin, M.A.; Leong, M.L.; Bahjat, K.S.; Gao, Y.; Luckett, W.; Liu, W.; Cook, D.N.; Portnoy, D.A.; Dubensky, T.W. Listeria-based cancer vaccines that segregate immunogenicity from toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13832–13837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Brockstedt, D.G.; Nir-Paz, R.; Hampl, J.; Mathur, S.; Nemunaitis, J.; Sterman, D.H.; Hassan, R.; Lutz, E.; Moyer, B.; et al. A live-attenuated Listeria vaccine (ANZ-100) and a live-attenuated Listeria vaccine expressing mesothelin (CRS-207) for advanced cancers: Phase I studies of safety and immune induction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Alley, E.; Kindler, H.; Antonia, S.; Jahan, T.; Honarmand, S.; Nair, N.; Whiting, C.C.; Enstrom, A.; Lemmens, E.; et al. Clinical Response of Live-Attenuated, Listeria monocytogenes Expressing Mesothelin (CRS-207) with Chemotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5787–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Chang, M.-C.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-W.; Sun, N.-Y.; Chen, C.-A.; Sun, W.-Z.; Cheng, W.-F. Immuno-modulators enhance antigen-specific immunity and anti-tumor effects of mesothelin-specific chimeric DNA vaccine through promoting DC maturation. Cancer Lett. 2018, 425, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelletti, L.; Yeo, D.; van Zandwijk, N.; Rasko, J.E.J. Anti-Mesothelin CAR T cell therapy for malignant mesothelioma. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenito, C.; Milone, M.C.; Hassan, R.; Simonet, J.C.; Lakhal, M.; Suhoski, M.M.; Varela-Rohena, A.; Haines, K.M.; Heitjan, D.F.; Albelda, S.M.; et al. Control of large, established tumor xenografts with genetically retargeted human T cells containing CD28 and CD137 domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Moon, E.; Carpenito, C.; Paulos, C.M.; Liu, X.; Brennan, A.L.; Chew, A.; Carroll, R.G.; Scholler, J.; Levine, B.L.; et al. Multiple Injections of Electroporated Autologous T Cells Expressing a Chimeric Antigen Receptor Mediate Regression of Human Disseminated Tumor. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9053–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, G.L.; Haas, A.R.; Maus, M.V.; Torigian, D.A.; Soulen, M.C.; Plesa, G.; Chew, A.; Zhao, Y.; Levine, B.L.; Albelda, S.M.; et al. Mesothelin-specific chimeric antigen receptor mRNA-engineered T cells induce anti-tumor activity in solid malignancies. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, A.R.; Tanyi, J.L.; O’hara, M.H.; Gladney, W.L.; Lacey, S.F.; Torigian, D.A.; Soulen, M.C.; Tian, L.; McGarvey, M.; Nelson, A.M.; et al. Phase I Study of Lentiviral-Transduced Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells Recognizing Mesothelin in Advanced Solid Cancers. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Cherkassky, L.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Colovos, C.; Servais, E.; Plotkin, J.; Jones, D.R.; Sadelain, M. Regional delivery of mesothelin-targeted CAR T cell therapy generates potent and long-lasting CD4-dependent tumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 261ra151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rusch, V.W.; O’Cearbhaill, R.; Zhu, A.; Ngai, D.; McGee, E.; Chintala, N.; Messinger, J.; Cheema, W.; et al. Regional delivery of mesothelin-targeted CAR T cells for pleural cancers: Safety and preliminary efficacy in combination with anti-PD-1 agent. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, P.S.; Zauderer, M.G.; Rivière, I.; Solomon, S.B.; Rusch, V.W.; O’Cearbhaill, R.E.; Zhu, A.; Cheema, W.; Chintala, N.K.; Halton, E.; et al. A phase I trial of regional mesothelin-targeted CAR T-cell therapy in patients with malignant pleural disease, in combination with the anti-PD-1 agent pembrolizumab. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2748–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Johnson, M.; Tanyi, J.L.; MacMullen, L.; Tighe, R.; Jalbert, L.; Muzithras, V.P.; Zikaras, K.; Cardama, A.Q.; Hassan, R. Preliminary safety and efficacy of gavocabtagene autoleucel (gavo-cel, TC-210), a T cell receptor fusion construct (TRuC™), in patients with treatment refractory mesothelin overexpressing solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81 (Suppl. S13), CT105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFave, L.M.; Béguelin, W.; Koche, R.; Teater, M.; Spitzer, B.; Chramiec, A.; Papalexi, E.; Keller, M.D.; Hricik, T.; Konstantinoff, K.; et al. Loss of BAP1 function leads to EZH2-dependent transformation. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1344–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, S.A.; Abou Gabal, H.H. Diagnostic Utility of BAP1, EZH2 and Survivin in Differentiating Pleural Epithelioid Mesothelioma and Reactive Mesothelial Hyperplasia: Immunohistochemical Study. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 600073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A Novel Target for Cancer Treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.; Lu, X.; Song, B.; Fong, K.-W.; Cao, Q.; Licht, J.D.; Zhao, J.C.; Yu, J. Polycomb- and Methylation-Independent Roles of EZH2 as a Transcription Activator. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2808–2820.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Ushiku, T.; Morita, S.; Anraku, M.; Nakajima, J.; Fukayama, M. Diagnostic Utility of BAP1 and EZH2 Expression in Malignant Mesothelioma. Histopathology 2017, 70, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Lenzini, A.; Aprile, V.; Alì, G.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. New Insights in Pleural Mesothelioma Classification Update: Diagnostic Traps and Prognostic Implications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zauderer, M.G.; Szlosarek, P.W.; Le Moulec, S.; Popat, S.; Taylor, P.; Planchard, D.; Scherpereel, A.; Koczywas, M.; Forster, M.; Cameron, R.B.; et al. EZH2 inhibitor tazemetostat in patients with relapsed or refractory, BAP1-inactivated malignant pleural mesothelioma: A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhai, J.; Landman, N.; Pandey, G.K.; Song, J.-Y.; Hulsman, D.; Krijgsman, O.; Chandrasekaran, G.; Berns, A.; van Lohuizen, M. Combined Inhibition of EZH2 and FGFR is Synergistic in BAP1-deficient Malignant Mesothelioma. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, N.; Hulsman, D.; Badhai, J.; Kopparam, J.; Puppe, J.; Pandey, G.K.; van Lohuizen, M. Combination of EZH2 and ATM inhibition in BAP1-deficient mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennishi, D.; Takata, K.; Béguelin, W.; Duns, G.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Bashashati, A.; Saberi, S.; Boyle, M.; Meissner, B.; et al. Molecular and Genetic Characterization of MHC Deficiency Identifies EZH2 as Therapeutic Target for Enhancing Immune Recognition. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Khatib, M.O.; Pinton, G.; Moro, L.; Porta, C. Benefits and Challenges of Inhibiting EZH2 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2023, 15, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Wu, W.; Koike, A.; Kojima, R.; Gomi, H.; Fukuda, M.; Ohta, T. BRCA1-associated protein 1 interferes with BRCA1/BARD1 RING heterodimer activity. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. PARP inhibitors: Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science 2017, 355, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Akatsuka, S.; Motooka, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Mashimo, T.; Imaoka, T.; Toyokuni, S. BRCA1 haploinsufficiency impairs iron metabolism to promote chrysotile-induced mesothelioma via ferroptosis resistance. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchert, S.; Wessolly, M.; Schmeller, J.; Mairinger, E.; Kollmeier, J.; Hager, T.; Mairinger, T.; Herold, T.; Christoph, D.C.; Walter, R.F.H.; et al. Gene expression profiling of homologous recombination repair pathway indicates susceptibility for olaparib treatment in malignant pleural mesothelioma in vitro. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xu, D.; Gao, Y.; Schmid, R.A.; Peng, R.-W. The Association of BAP1 Loss-of-Function With the Defect in Homologous Recombination Repair and Sensitivity to PARP-Targeted Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, e88–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrotta, R.; Okonska, A.; Ronner, M.; Weder, W.; Stahel, R.; Penengo, L.; Felley-Bosco, E. A Novel BRCA1-Associated Protein-1 Isoform Affects Response of Mesothelioma Cells to Drugs Impairing BRCA1-Mediated DNA Repair. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, D.A.; King, A.; Mohammed, S.; Branson, A.; Brookes, C.; Darlison, L.; Dawson, A.G.; Gaba, A.; Hutka, M.; Morgan, B.; et al. MiST1 study group. Rucaparib in patients with BAP1-deficient or BRCA1-deficient mesothelioma (MiST1): An open-label, single-arm, phase 2a clinical trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, A.; Mian, I.; Wagner, C.; Mallory, Y.; Agra, M.G.; Morrow, B.; Wei, J.S.; Khan, J.; Thomas, A.; Sengupta, M.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Olaparib in Malignant Mesothelioma and Correlation of Efficacy With Germline or Somatic Mutations in BAP1 Gene. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladanyi, M.; Vega, F.S.; Zauderer, M. Loss of BAP1 as a candidate predictive biomarker for immunotherapy of mesothelioma. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelidou, C.; Sonzogni, O.; De Oliveria Taveira, M.; Mehta, A.K.; Kothari, A.; Wang, D.; Visal, T.; Li, M.K.; Pinto, J.; Castrillon, J.A.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Efficacy Depends on CD8+ T-cell Recruitment via Intratumoral STING Pathway Activation in BRCA-Deficient Models of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passiglia, F.; Righi, L.; Bironzo, P.; Listì, A.; Farinea, G.; Capelletto, E.; Novello, S.; Merlini, A.; Scagliotti, G.V. Niraparib plus Dostarlimab in Pleural Mesothelioma or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring HRR Mutations: Interim Results of the UNITO-001 Phase II Prospective Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, I.; Abdullaev, Z.; Morrow, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Gao, S.; Miettinen, M.; Schrump, D.S.; Zgonc, V.; Wei, J.S.; Khan, J.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Gene Rearrangement in Children and Young Adults With Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, J.L.; Peters, G.; Szaumkessel, M.; Leong, T.; Asadi, K.; Rivalland, G.; Do, H.; Senko, C.; Mitchell, P.L.; Quing, C.Z.; et al. NTRK and ALK rearrangements in malignant pleural mesothelioma, pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours and non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüschoff, J.H.; Gradhand, E.; Kahraman, A.; Rees, H.; Ferguson, J.L.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Zoche, M.; Moch, H.; Vrugt, B. STRN-ALK Rearranged Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma With Dramatic Response Following Ceritinib Treatment. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.19.00048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, F.; Fu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, D.; Du, N.; Lizaso, A.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Acquired multiple mutations ALK I1171N, L1196M and G1202R mediate lorlatinib resistance in EML4-ALK-rearranged malignant pleural mesothelioma: A case report. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2020, 14, 1753466620935770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiante, L.; Alcala, N.; Sexton-Oates, A.; Di Genova, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Khandekar, A.; Bergstrom, E.N.; Kim, J.; Liu, X.; Blazquez-Encinas, R.; et al. Multiomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma identifies molecular axes and specialized tumor profiles driving intertumor heterogeneity. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NCT Identifier | Phase | Drud(S) Class | Population | Treatment Arms | Status | Primary Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03054298 | I | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | MSLN-expressing tumors | HuCART-meso | Active, not Recruiting | Number of participants with treatment-related AEs |
| NCT02414269 | I/II | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | MPM Lung cancer Breast cancer | Genetic: iCasp9M28z T cell infusions Drug: pembrolizumab | Active, not Recruiting | Phase I: composite measure of severity and number of AE changes Phase II: clinical benefit rate |
| NCT03907852 | I/II | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | MM, cholangiocarcinoma, ovarian cancer, NSCLC | Biological: gavo-cel Drug: fludarabine/cyclophosphamide /nivolumab/ipilimumab | Active, not Recruiting | Phase I: DLTs within 28 days post-treatment Phase II: ORR at 3 months; DCR based on ORR + SD lasting at least 8 weeks |
| NCT06256055 | I | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | Colorectal cancer MM Bile duct cancer Rectal cancer Ovarian cancer Pancreatic cancer Breast cancer | UCMYM802 injection | Active, recruiting | Treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) Treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) Adverse events of special interest (AESI) Incidence of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) |
| NCT05795595 | I/II | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma Cervical carcinoma Esophageal sarcinoma Pancreatic carcinoma MPM | CTX131 | Active, recruiting | Phase I: incidence of AEs Phase II: ORR |
| NCT06051695 | I/II | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | Solid tumor Colorectal cancer NSCLC Pancreatic cancer Colorectal adenocarcinoma Ovarian cancer MM | A2B694 | Active, recruiting | Phase I: rate of adverse events and DLTs by dose level + recommended phase II dose Phase II: ORR |
| NCT04577326 | I | Anti-MSLN CAR T cells | MPM | Drug: cyclophosphamide Biological: CAR T cells | Active, recruiting | MTD |
| NCT02637531 | I | PI3K inhibitor | Advanced solid tumors, for part G: relapsed MM, any histology | IPI-549 | Active, recruiting | Antitumor activity |
| NCT05627960 | I | PI3K inhibitor | Triple-negative breast cancer Hormone-resistant breast cancer Non-small cell lung cancer, MM | AG01 | Active, recruiting | DLT and antitumor activity |
| NCT05245500 | I/II | PRMT5-MTA inhibitors | Advanced solid tumors with homozygous MTAP deletion | MRTX1719 | Active, recruiting | Phase I: number of patients who experience dose-limiting toxicity and TRAE Phase II: ORR, DOR, PFS, and OS |
| NCT05275478 | I/II | PRMT5-MTA inhibitors | Advanced solid tumors with homozygous MTAP deletion | TNG908 | Active, recruiting | Phase I: MTD and dosing schedule of TNG908 Phase II: efficacy by RECIST or mRECIST v1.1 or modified RANO criteria |
| NCT05732831 | I/II | PRMT5-MTA inhibitor | MTAP-deleted solid tumors | TNG462 | Active, recruiting | Phase I: MTD and dosing schedule Phase II: antineoplastic activity |
| NCT05455424 | II | PARPi | Relapsed or refractory MM | Niraparib vs. active symptom control | Active, not recruiting | PFS |
| NCT04940637 | II | PARPi + anti-PD-1 | Relapsed or refractory MM | Niraparib + dostarlimab | Active, recruiting | PFS |
| NCT04515836 | II | PARPi | Relapsed MM with BAP1 loss or mutations in cells that disrupt protein function | Olaparib | Active, recruiting | ORR |
| NCT04665206 | I | YAP/TEAD inhibitor | Relapsed MM or solid tumors NF2-mutated | VT3989 | Active, recruiting | DLT and occurrence of general toxicity |
| NCT04857372 | I | YAP/TEAD inhibitor | Relapsed MM or solid tumors NF2-mutated or with YAP/TAZ fusion | IAG933 | Active, recruiting | DLT, number of SAE, and number of patients with dose interruption/changes |
| NCT05765084 | I/II | PD-L1 inhibitor + WT1/DC vaccination | I line epithelioid MPM | Atezolizumab + WT1/DC vaccines + platinum/pemetrexed | Active, recruiting | Proportion of patients that experienced (S)AEs, number and grade of AEs and SAEs, and proportion of patients who completed study treatment schedule |
| NCT03126630 | I/II | Anti-MSLN + anti-PD-1 | MSLN + MPM | Anetumab ravtansine + pembrolizumab | Active, not recruiting | Phase I: safety dose of anetumab ravtansine Phase II: ORR combination vs. pembrolizumab |
| NCT04287829 | II | Anti-VEGFR + anti-PD-1 | II and III line MPM | Lenvatinib + pembrolizumab | Active, recruiting | ORR |
| NCT05425576 | II | TGF-b2 inhibitor + anti-PD-1 | MPM failing to respond to checkpoint inhibition | OT-101 + pembrolizumab | Active, not recruiting | ORR |
| NCT06031636 | II | Oncolytic virus + anti-PD-1 | Advanced MPM resistant to advanced PD-1 inhibitors | Oncolytic adenovirus H101 + pembrolizumab | Active, recruiting | ORR, DCR |
| NCT04013334 | II | Cancer vaccine + anti-PD-1 | Relapsed MM | MTG201 (intratumoral injection) + nivolumab | Active, not recruiting | ORR |
| NCT04040231 | I | Cancer vaccine + anti-PD-1 | WT1-expressing MPM | Galinpepimut-S + nivolumab | Active, not recruiting | MTD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertoli, E.; De Carlo, E.; Bortolot, M.; Stanzione, B.; Del Conte, A.; Spina, M.; Bearz, A. Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way. Cancers 2024, 16, 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111971
Bertoli E, De Carlo E, Bortolot M, Stanzione B, Del Conte A, Spina M, Bearz A. Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111971
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertoli, Elisa, Elisa De Carlo, Martina Bortolot, Brigida Stanzione, Alessandro Del Conte, Michele Spina, and Alessandra Bearz. 2024. "Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way" Cancers 16, no. 11: 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111971
APA StyleBertoli, E., De Carlo, E., Bortolot, M., Stanzione, B., Del Conte, A., Spina, M., & Bearz, A. (2024). Targeted Therapy in Mesotheliomas: Uphill All the Way. Cancers, 16(11), 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111971






