Deciphering the Clinical Behaviour of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Defines an Aggressive Subtype
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
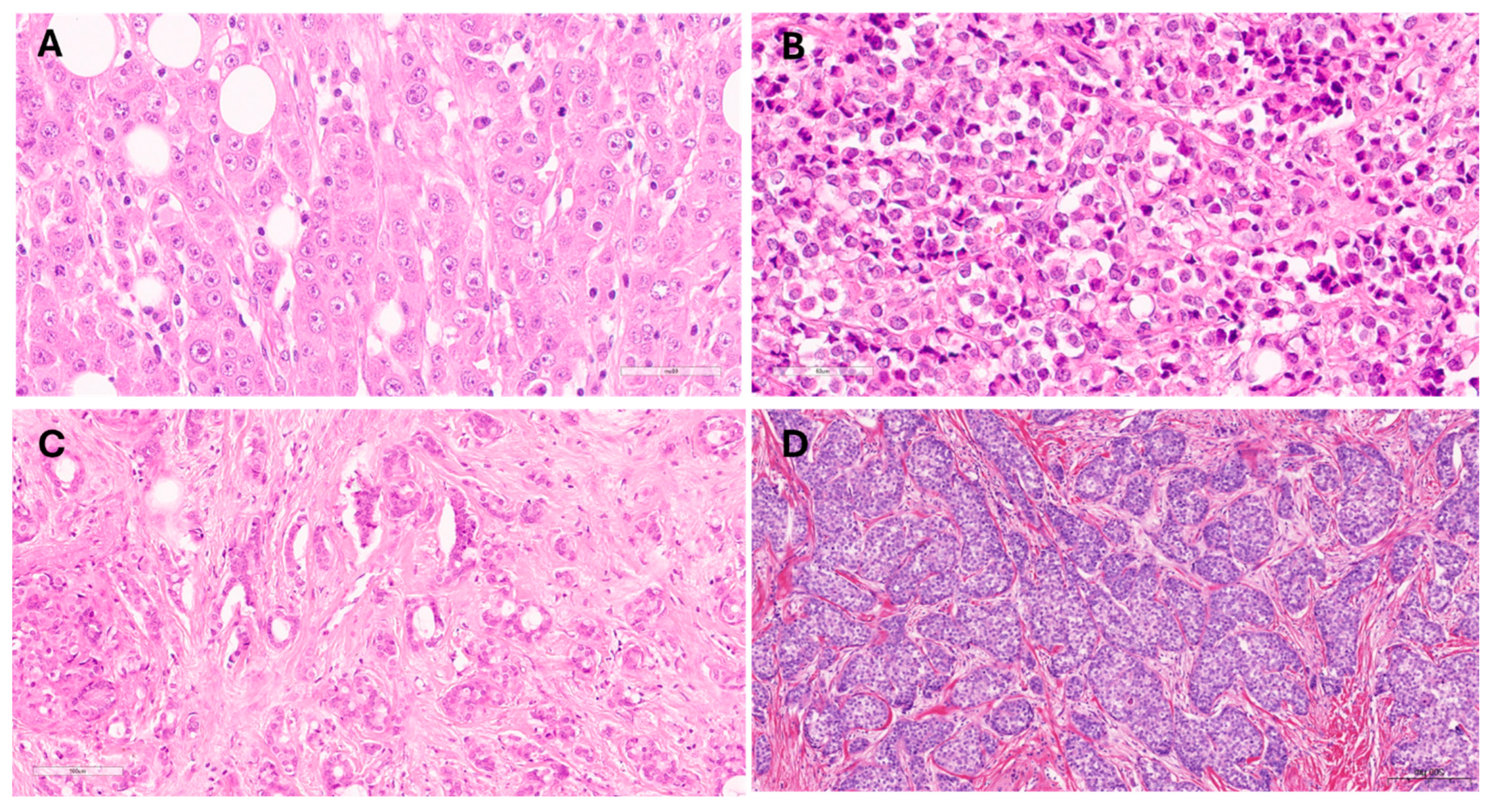
2.2. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Histological Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient and Tumour Characteristics
3.2. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Variants
3.3. Correlation between ILC Variants and Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.4. Outcome Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Fernández, A.; Lain, J.M.; Chabrera, C.; García Font, M.; Fraile, M.; Barco, I.; Torras, M.; Reñe, A.; González, S.; González, C. Comparative long-term study of a large series of patients with invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Loco-regional recurrence, metastasis, and survival. Breast J. 2015, 21, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ji, F.; Pan, W.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Yang, M.; Li, J. Comparison of overall survival between invasive lobular breast carcinoma and invasive ductal breast carcinoma: A propensity score matching study based on SEER database. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouabbi, J.A.; Hassan, A.; Lim, B.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Tripathy, D.; Layman, R.M. Invasive lobular carcinoma: An understudied emergent subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 193, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.M.; Kutasovic, J.R.; Lakhani, S.R.; Simpson, P.T. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Morphology, biomarkers and ’omics. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, E.A.; El-Sayed, M.E.; Powe, D.G.; Green, A.R.; Habashy, H.; Grainge, M.J.; Robertson, J.F.; Blamey, R.; Gee, J.; Nicholson, R.I. Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: Response to hormonal therapy and outcomes. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schepper, M.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Christgen, M.; Van Baelen, K.; Richard, F.; Tsuda, H.; Kurozumi, S.; Brito, M.J.; Cserni, G.; Schnitt, S. Results of a worldwide survey on the currently used histopathological diagnostic criteria for invasive lobular breast cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Rajagopal, P.S.; Villgran, V.; Sandhu, G.S.; Jankowitz, R.C.; Jacob, M.; Rosenzweig, M.; Oesterreich, S.; Brufsky, A. Distinct pattern of metastases in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2017, 77, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, E.; Caraceni, G.; Gentile, D.; Gavazzi, F.; Zerbi, A.; Tinterri, C. A rare case of duodenal metastasis from lobular breast cancer: From diagnosis to surgery. Case Rep. Oncol. 2023, 16, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraker, N.; Hot, S.; Akan, A.; Nayır, P. A Comparison of the Clinicopathological Features, Metastasis Sites and Survival Outcomes of Invasive Lobular, Invasive Ductal and Mixed Invasive Ductal and Lobular Breast Carcinoma. Eur. J. Breast Health 2020, 16, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.M.; Jagmohan, P.; Goh, Y.G.; Putti, T.C.; Ow, S.G.W.; Thian, Y.L.; Pillay, P. Infiltrative pattern of metastatic invasive lobular breast carcinoma in the abdomen: A pictorial review. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, H.; Mouabbi, J.A.; Ding, Q.; Sahin, A.A.; Raso, M.G. Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast: A Comprehensive Review with Translational Insights. Cancers 2023, 15, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorfida, M.; Maiorano, E.; Orvieto, E.; Maisonneuve, P.; Bottiglieri, L.; Rotmensz, N.; Montagna, E.; Dellapasqua, S.; Veronesi, P.; Galimberti, V. Invasive lobular breast cancer: Subtypes and outcome. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.P.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.; Choi, M.-Y.; Bae, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Kil, W.H.; Cho, E.Y.; Choe, J.-H. Invasive pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis compared with invasive ductal carcinoma. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 15, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmor, S.; Hui, J.Y.C.; Huang, J.L.; Kizy, S.; Beckwith, H.; Blaes, A.H.; Rueth, N.M.; Tuttle, T.M. Relative effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for invasive lobular compared with invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Cancer 2017, 123, 3015–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.; Sneige, N.; Kau, S.-W.; Broglio, K.; Theriault, R.L.; Valero, V.; Buzdar, A.U.; Kuerer, H.; Buccholz, T.A. Invasive lobular carcinoma classic type: Response to primary chemotherapy and survival outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truin, W.; Voogd, A.C.; Vreugdenhil, G.; van der Heiden-van der Loo, M.; Siesling, S.; Roumen, R.M. Effect of adjuvant chemotherapy in postmenopausal patients with invasive ductal versus lobular breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamalidou, C.; Fohlin, H.; Albertsson, P.; Arnesson, L.-G.; Einbeigi, Z.; Holmberg, E.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Nordenskjöld, B.; Karlsson, P.; Linderholm, B. Survival patterns of invasive lobular and invasive ductal breast cancer in a large population-based cohort with two decades of follow up. Breast 2021, 59, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Díaz, D.; Arce, C.; Flores-Luna, L.; Reynoso-Noveron, N.; Lara-Medina, F.; Matus, J.A.; Bargallo-Rocha, E.; Pérez, V.; Villarreal-Garza, C.; Cabrera-Galeana, P. Impact of invasive lobular carcinoma on long-term outcomes in Mexican breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, L.; Mascaro, A.; Poccia, I.; Andrich, R.; Amini, M.; Costarelli, L.; Cortese, G.; Farina, M.; Vitelli, C. Lobular breast cancer: Same survival and local control compared with ductal cancer, but should both be treated the same way? Analysis of an institutional database over a 10-year period. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, T.; Kuukasjärvi, T.; Huhtala, H.; Alarmo, E.-L.; Holli, K.; Kallioniemi, A.; Pylkkänen, L. The impact of lobular and ductal breast cancer histology on the metastatic behavior and long term survival of breast cancer patients. Breast 2013, 22, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molland, J.; Donnellan, M.; Janu, N.; Carmalt, H.; Kennedy, C.; Gillett, D. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma—A comparison of diagnosis, management and outcome with infiltrating duct carcinoma. Breast 2004, 13, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, W.; Arms, A.; Verma, V.; Hatch, S.; Butler, E.B.; Teh, B.S. Outcomes of pleomorphic lobular carcinoma versus invasive lobular carcinoma. Breast 2019, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Baimani, K.; Bazzarelli, A.; Clemons, M.; Robertson, S.J.; Addison, C.; Arnaout, A. Invasive pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Pathologic, clinical, and therapeutic considerations. Clin. Breast Cancer 2015, 15, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Van Deurzen, C.H.; Paish, E.C.; Macmillan, R.D.; Ellis, I.O.; Lee, A.H. Pleomorphic lobular carcinoma of the breast: Is it a prognostically significant pathological subtype independent of histological grade? Mod. Pathol. 2013, 26, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Baelen, K.; Geukens, T.; Maetens, M.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.; Lord, C.J.; Linn, S.; Bidard, F.-C.; Richard, F.; Yang, W.; Steele, R.E. Current and future diagnostic and treatment strategies for patients with invasive lobular breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Barni, S. Response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ductal compared to lobular carcinoma of the breast: A meta-analysis of published trials including 1764 lobular breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 142, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamtani, A.; Grabenstetter, A.; Sevilimedu, V.; Morrow, M.; Gemignani, M.L. Do non-classic invasive lobular carcinomas derive a benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 197, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; El-Sayed, M.E.; Menon, S.; Green, A.R.; Lee, A.H.; Ellis, I.O. Histologic grading is an independent prognostic factor in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 111, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, K.H.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Dowsett, M.; McKernin, S.E.; Carey, L.A.; Fitzgibbons, P.L.; Hayes, D.F.; Lakhani, S.R.; Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Perlmutter, J.; et al. Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO/CAP Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1346–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, A.; Parry, S.; Ibrahim, M.; Bartlett, J.M.; Pinder, S.; Dowsett, M.; Miller, K. Breast cancer biomarkers in clinical testing: Analysis of a UK national external quality assessment scheme for immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridisation database containing results from 199,300 patients. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2018, 4, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Somerfield, M.R.; Dowsett, M.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Hayes, D.F.; McShane, L.M.; Saphner, T.J.; Spears, P.A.; Allison, K.H. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO-College of American Pathologists Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3867–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleskandarany, M.A.; Green, A.R.; Ashankyty, I.; Elmouna, A.; Diez-Rodriguez, M.; Nolan, C.C.; Ellis, I.O.; Rakha, E. Impact of intratumoural heterogeneity on the assessment of Ki67 expression in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 158, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; Olson, J.A., Jr. Adjuvant chemotherapy guided by a 21-gene expression assay in breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Patel, A.; Powe, D.G.; Benhasouna, A.; Green, A.R.; Lambros, M.B.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ellis, I.O. Clinical and Biological Significance of E-cadherin Protein Expression in Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board: Breast Tumours; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Lokuhetty, D.; White, V.; Watanabe, R.; Cree, I. WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Breast tumors. In WHO Classification of Tumours Series, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Rakha, E.A.; Abbas, A.; Sheeran, R. Invasive lobular carcinoma mimicking papillary carcinoma: A report of three cases. Pathobiology 2016, 83, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.T.; Yu, J.H.; Park, H.K.; Moon, B.I.; Ko, B.K.; Suh, Y.J. A comparison of the clinical outcomes of patients with invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast according to molecular subtype in a Korean population. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.S.; Yang, Q.; Haffty, B.G. The Yale University experience of early-stage invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) treated with breast conservation treatment (BCT): Analysis of clinical-pathologic features, long-term outcomes, and molecular expression of COX-2, Bcl-2, and p53 as a function of histology. Breast J. 2009, 15, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magnoni, F.; Corso, G.; Maisonneuve, P.; Bianchi, B.; Accardo, G.; Sangalli, C.; Massari, G.; Rotili, A.; Nicosia, L.; Pesapane, F. Comparison of long-term outcome between clinically high risk lobular versus ductal breast cancer: A propensity score matched study. Eclinicalmedicine 2024, 71, 102552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delon, C.; Brown, K.F.; Payne, N.W.S.; Kotrotsios, Y.; Vernon, S.; Shelton, J. Differences in cancer incidence by broad ethnic group in England, 2013–2017. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.L.; Flynn, L.W.; Murray, M.P.; Darvishian, F.; Cranor, M.L.; Fey, J.V.; King, T.A.; Tan, L.K.; Sclafani, L.M. Is pleomorphic lobular carcinoma really a distinct clinical entity? J. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 98, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.; Fan, F.; Tawfik, O. Clinicopathologic and biomarker analysis of invasive pleomorphic lobular carcinoma as compared with invasive classic lobular carcinoma: An experience in our institution and review of the literature. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 16, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, M.; Cserni, G.; Floris, G.; Marchio, C.; Djerroudi, L.; Kreipe, H.; Derksen, P.W.; Vincent-Salomon, A. Lobular breast cancer: Histomorphology and different concepts of a special spectrum of tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, P.; Reis-Filho, J.; Lambros, M.; Jones, C.; Steele, D.; Mackay, A.; Iravani, M.; Fenwick, K.; Dexter, T.; Jones, A.; et al. Molecular profiling pleomorphic lobular carcinomas of the breast: Evidence for a common molecular genetic pathway with classic lobular carcinomas. J. Pathol. 2008, 215, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, C.I.; Font, R.L.; Zimmerman, L.E. Metastatic mammary carcinoma in the eyelid with histiocytoid appearance. Cancer 1973, 31, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, M.J.; Livolsi, V.A. Signet ring carcinoma of the female breast: A clinicopathologic analysis of 24 cases. Cancer 1981, 48, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldulaijan, F.A.; Alsahwan, A.G.; Alsulaiman, M.H.A.; Mashhour, M.M.; Alwabari, A. Histiocytoid variant of invasive lobular breast carcinoma. A case report and literature review. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 72, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coty-Fattal, Z.; Minhas, S.; Butcher, M.; Agarwal, I.; LaBoy, C.; Blanco, L.; Novo, J. Clinicopathologic and Immunophenotypic Classification of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma with Histiocytoid Features. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 31, 10668969231189714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makower, D.; Qin, J.; Lin, J.; Xue, X.; Sparano, J.A. The 21-gene recurrence score in early non-ductal breast cancer: A National Cancer Database analysis. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsung, K.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Tu, C.; Abraham, J.; Budd, G.T.; Valente, S.A. Neoadjuvant systemic therapy in invasive lobular breast cancer: Is it indicated? Am. J. Surg. 2018, 215, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, W.; Verma, V.; Hatch, S.; Suzanne Klimberg, V.; Brian Butler, E.; Teh, B.S. Response rates and pathologic complete response by breast cancer molecular subtype following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, E.H.; Mukhtar, R.A.; Yau, C.; de Ronde, J.J.; Livasy, C.; Carey, L.A.; Loo, C.E.; Vrancken-Peeters, M.-J.T.F.D.; Sonke, G.S.; Berry, D.A.; et al. Lobular histology and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Volz, C.; Mau, C.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Hanusch, C.; Jackisch, C.; et al. Response and prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in 1051 patients with infiltrating lobular breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 144, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, P.C.; Chagpar, A.B.; Cicek, A.F.; Bossuyt, V.; Buza, N.; Mougalian, S.; Killelea, B.K.; Patel, N.; Harigopal, M. Breast cancer histopathology is predictive of low-risk Oncotype Dx recurrence score. Breast J. 2018, 24, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Bianchini, G.; Litton, J.K.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Pusztai, L. Utility of oncotype DX risk estimates in clinically intermediate risk hormone receptor-positive, HER2-normal, grade II, lymph node-negative breast cancers. Cancer 2010, 116, 5161–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, R.; Polychronopoulou, E.; Hatch, S.S.; Haque, W.; Ghani, H.A.; He, J.; Kuo, Y.f.; Gradishar, W.J.; Klimberg, V.S. Adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma and use of the 21-gene recurrence score: A National Cancer Database analysis. Cancer 2022, 128, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Characteristics | Pleomorphic Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (pILC) N (%) | Solid Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (sILC) N (%) | Classic Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (cILC) N (%) | Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, No Special Type (IDC-NST) N (%) | X2 (p-Value) a pILC vs. cILC | X2 (p-Value) b pILC vs. IDC-NST | X2 (p-Value) c sILC vs. cILC | X2 (p-Value) d sILC vs. IDC-NST | X2 (p-Value) e pILC vs. sILC | X2 (p-Value) f cILC vs. IDC-NST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years) <50 ≥50 | 27 (22) 69 (78) | 6 (14) 36 (86) | 95 (16) 503 (84) | 1366 (30) 3109 (70) | 8.6 (0.003) | 0.26 (0.6) | 0.07 (0.7) | 5.2 (0.02) | 3 (0.07) | 55.1 (<0.001) |
| Tumour size (cm) <2 ≥2 | 29 (30) 67 (70) | 20 (48) 22 (52) | 344 (57) 254 (43) | 2672 (60) 1797 (40) | 24.8 (<0.001) | 34.0 (<0.001) | 1.6 (0.2) | 2.6 (0.1) | 3.9 (0.04) | 1.1 (0.2) |
| Tumour grade 1 2 3 | 0 52 (54) 44 (46) | 0 33 (79) 9 (21) | 55 (9) 543 (91) 0 | 320 (7) 1659 (37) 2496 (56) | 295.9 (<0.001) | 15.9 (<0.001) | 38.8 (<0.001) | 7.9 (0.005) | 7.4 (0.007) | 687.4 (<0.001) |
| Mitotic count 1 2 3 | 52 (54) 28 (29) 16 (17) | 26 (62) 7 (17) 9 (21) | 563 (94) 35 (6) 0 | 1612 (36) 957 (21) 1906 (43) | 156.7 (<0.001) | 26.2 (<0.001) | 95.5 (<0.001) | 12.5 (0.002) | 2.3 (0.2) | 734.8 (<0.001) |
| Nuclear pleomorphism 1 2 3 | 0 0 96 (100) | 0 42 (100) 0 | 30 (5) 568 (95) 0 | 14 (1) 1066 (23) 3395 (76) | 522.9 (<0.001) | 29.8 (<0.001) | 2 (0.1) | 122.1 (<0.001) | 138 (<0.001) | 1412.1 (<0.001) |
| Tubule formation 1 2 3 | 0 0 96 (100) | 0 0 42 (100) | 6 (1) 40 (7) 552 (92) | 88 (2) 1120 (25) 3267 (73) | 7.2 (0.007) | 32.6 (<0.001) | 3.2 (0.07) | 14.3 (<0.001) | - | 106.3 (<0.001) |
| Nottingham Prognostic Index Good Prognostic Group Moderate Prognostic Group Poor Prognostic Group | 19 (20) 52 (54) 25 (26) | 15 (36) 25 (59) 2 (5) | 317 (53) 239 (40) 41 (7) | 1288 (29) 2453 (55) 719 (16) | 54.2 (<0.001) | 8.4 (0.01) | 2.4 (0.1) | 4.2 (0.1) | 9.9 (0.007) | 149.5 (<0.001) |
| Axillary nodal status * Negative Positive | 51 (53) 45 (47) | 31 (74) 11 (26) | 411 (69) 186 (31) | 2886 (65) 1580 (35) | 9.1 (0.002) | 5.4 (0.02) | 0.5 (0.5) | 1.5 (0.2) | 5.2 (0.02) | 4.1 (0.04) |
| Lymph node stage 1 (Negative) 2 (1–3 positive) 3 (>3 positive) | 51 (53) 29 (30) 16 (17) | 31 (74) 9 (21) 2 (5) | 411 (69) 131 (22) 55 (9) | 2886 (65) 1206 (27) 374 (8) | 10.0 (0.007) | 9.8 (0.007) | 0.8 (0.3) | 1.7 (0.1) | 6 (0.04) | 6.9 (0.03) |
| Lymphovascular invasion Negative Positive | 67 (70) 29 (30) | 34 (81) 8 (19) | 536 (90) 62 (10) | 3241 (72) 1234 (28) | 28.6 (<0.001) | 0.33 (0.5) | 2.6 (0.1) | 1.6 (0.2) | 1.9 (0.1) | 82.1 (<0.001) |
| Distant metastasis site ** Common Uncommon | 34 (97) 1 (3) | 8 (89) 1 (11) | 96 (91) 10 (9) | 947 (98) 18 (2) | 1.9 (0.1) | 0.16 (0.6) | 0.02 (0.8) | 1.9 (0.1) | 0.9 (0.3) | 14.1 (<0.001) |
| Oestrogen receptor Negative Positive | 13 (13) 83 (87) | 0 42 (100) | 12 (2) 576 (98) | 1297 (30) 3103 (70) | 31 (<0.001) | 11.6 (<0.001) | 1.7 (0.1) | 17.5 (<0.001) | 6.3 (0.01) | 201.7 (<0.001) |
| Progesterone receptor Negative Positive | 34 (37) 59 (63) | 8 (20) 31 (80) | 135 (25) 413 (75) | 1834 (44) 2318 (56) | 5.8 (0.01) | 2.1 (0.1) | 0.3 (0.5) | 8.8 (0.003) | 3 (0.07) | 75.9 (<0.001) |
| Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 Negative Positive | 81 (91) 8 (9) | 38 (97) 1 (3) | 542 (99) 8 (1) | 3359 (81) 766 (19) | 17.8 (<0.001) | 5.3 (0.02) | 0.3 (0.6) | 6.6 (0.1) | 2.0 (0.1) | 102.9 (<0.001) |
| Ki67 index Low (≤14%) High (>14%) | 28 (54) 24 (46) | 7 (29) 17 (71) | 220 (79) 60 (21) | 744 (35) 1394 (65) | 14.2 (<0.001) | 8.1 (0.005) | 28.5 (<0.001) | 0.3 (0.5) | 4.0 (0.04) | 197.9 (<0.001) |
| Oncotype Dx recurrence score Low Intermediate High | 2 (22) 6 (67) 1 (1) | 4 (36) 6 (55) 1 (9) | 5 (11) 37 (82) 3 (7) | 44 (16) 160 (56) 80 (28) | 0.2 (0.6) | 1.2 (0.2) | 2.0 (0.1) | 4.0 (0.1) | 0.5 (0.7) | 12.0 (0.003) |
| Breast surgery Breast-conserving Mastectomy | 35 (36) 61 (64) | 23 (55) 19 (45) | 279 (47) 319 (53) | 2354 (53) 2121 (47) | 3.5 (0.06) | 9.8 (0.002) | 1.0 (0.3) | 0.08 (0.7) | 4.0 (0.04) | 7.5 (0.006) |
| Endocrine therapy No Yes | 24 (25) 72 (75) | 4 (10) 38 (90) | 161 (27) 433 (73) | 1727 (39) 2711 (61) | 0.19 (0.6) | 7.7 (0.006) | 6.3 (0.01) | 15.2 (<0.001) | 4.3 (0.03) | 31.7 (<0.001) |
| Chemotherapy No Yes | 61 (64) 35 (36) | 38 (90) 4 (10) | 504 (84) 94 (16) | 2849 (64) 1625 (36) | 23.5 (<0.001) | 0.001 (0.9) | 1.2 (0.2) | 13 (<0.001) | 10.5 (0.001) | 99.9 (<0.001) |
| Characteristics | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis (years) | |
| <50 | 29 (28) |
| ≥50 | 76 (72) |
| Tumour size (cm) <2 ≥2 | 33 (31) 72 (69) |
| Tumour grade | |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 52 (50) |
| 3 | 53 (50) |
| Mitotic count | |
| 1 | 52 (49) |
| 2 | 28 (27) |
| 3 | 25 (24) |
| Nuclear pleomorphism | |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 9 (9) |
| 3 | 96 (91) |
| Tubule formation | |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 100 (100) |
| Nottingham Prognostic Index | |
| Good Prognostic Group | 19 (18) |
| Moderate Prognostic Group | 60 (57) |
| Poor Prognostic Group | 26 (25) |
| Lymph node stage | |
| 1 (Negative) | 57 (54) |
| 2 (1–3 positive) | 31 (30) |
| 3 (>3 positive) | 17 (16) |
| Lymphovascular invasion | |
| Negative | 74 (70) |
| Positive | 31 (30) |
| Oestrogen receptor | |
| Negative | 13 (12) |
| Positive | 92 (88) |
| Progesterone receptor | |
| Negative | 34 (34) |
| Positive | 67 (66) |
| HER2 | |
| Negative | 89 (92) |
| Positive | 8 (8) |
| Ki67 index | |
| Low (≤14%) | 28 (48) |
| High (>14%) | 30 (52) |
| Oncotype Dx recurrence score | |
| Low | 2 (20) |
| Intermediate | 6 (60) |
| High | 2 (20) |
| Breast surgery | |
| Breast-conserving | 39 (37) |
| Mastectomy | 66 (63) |
| Endocrine therapy | |
| No | 24 (23) |
| Yes | 81 (77) |
| Chemotherapy | |
| No | 69 (66) |
| Yes | 36 (34) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Makhlouf, S.; Atallah, N.M.; Polotto, S.; Lee, A.H.S.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A. Deciphering the Clinical Behaviour of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Defines an Aggressive Subtype. Cancers 2024, 16, 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101893
Makhlouf S, Atallah NM, Polotto S, Lee AHS, Green AR, Rakha EA. Deciphering the Clinical Behaviour of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Defines an Aggressive Subtype. Cancers. 2024; 16(10):1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101893
Chicago/Turabian StyleMakhlouf, Shorouk, Nehal M. Atallah, Susanna Polotto, Andrew H. S. Lee, Andrew R. Green, and Emad A. Rakha. 2024. "Deciphering the Clinical Behaviour of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Defines an Aggressive Subtype" Cancers 16, no. 10: 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101893
APA StyleMakhlouf, S., Atallah, N. M., Polotto, S., Lee, A. H. S., Green, A. R., & Rakha, E. A. (2024). Deciphering the Clinical Behaviour of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Defines an Aggressive Subtype. Cancers, 16(10), 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101893






