Limited Effects of Class II Transactivator-Based Immunotherapy in Murine and Human Glioblastoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Experiments
2.1.1. Glioblastoma Cells Lines: Transfection and Irradiation
2.1.2. Human Primary Cell Lines and Transfection
2.1.3. Immunohistochemistry for CIITA and HLA-DR Expression Analysis
2.1.4. CD3+ (T Lymphocyte), CD11b+ (Tumor-Associated Myeloid) and CD56+ (NK-Cell) Isolation, Expansion and Co-Culture Protocol
2.1.5. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis and qPCR Analysis
2.2. In Vivo Experiments
2.2.1. Mice
2.2.2. In Situ Syngeneic GB Xenograft Model
2.2.3. Local Vaccination
2.2.4. Subcutaneous Vaccination
2.2.5. Adoptive Cell Transfer (ACT) Experiments
2.3. RNA Sequencing Data
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Forced Expression of CIITA in Murine GL261 Cells
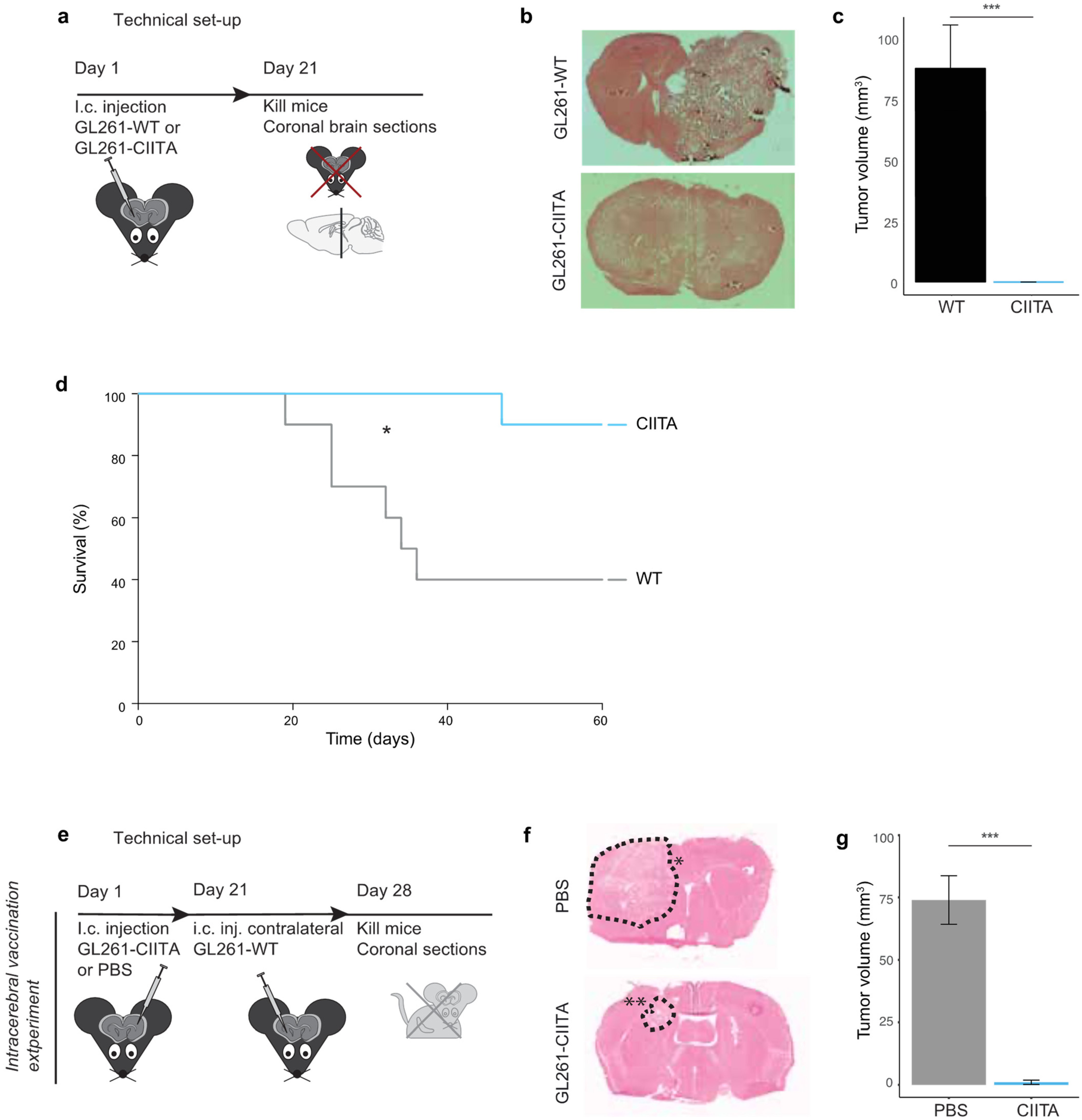
3.1.1. Tumor Growth and Animal Survival following Intracerebral Injection of CIITA-Expressing GL261 Cells in Syngeneic C57Bl/6 Mice
3.1.2. Intrastriatal Injection of CIITA-Expressing GL261 Cells Protects against a Subsequent Contralateral Wildtype Tumor Challenge
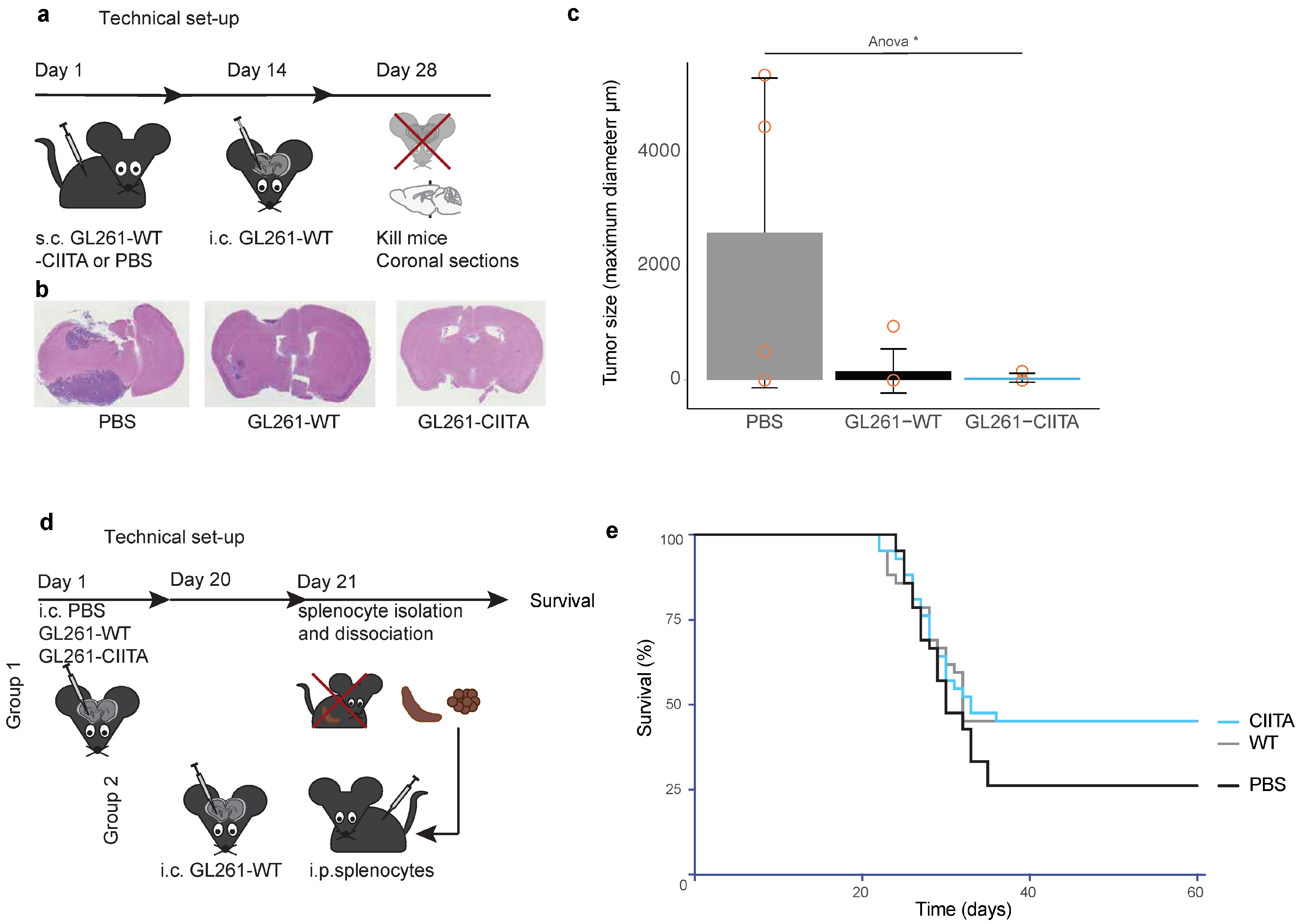
3.1.3. Subcutaneous Vaccination with GL261-CIITA or GL261-WT Cells Leads to Intracerebral Tumor Rejection in C57Bl/6 Mice
3.1.4. Adoptive Cell Transfer (ACT): Vaccination with Splenocytes of Intracerebrally Primed Mice
3.2. Forced CIITA Expression in Human Malignant Glioma Cell Lines
3.2.1. RNA Sequencing of WT and CIITA-Expressing Human Malignant Glioma Cell Lines
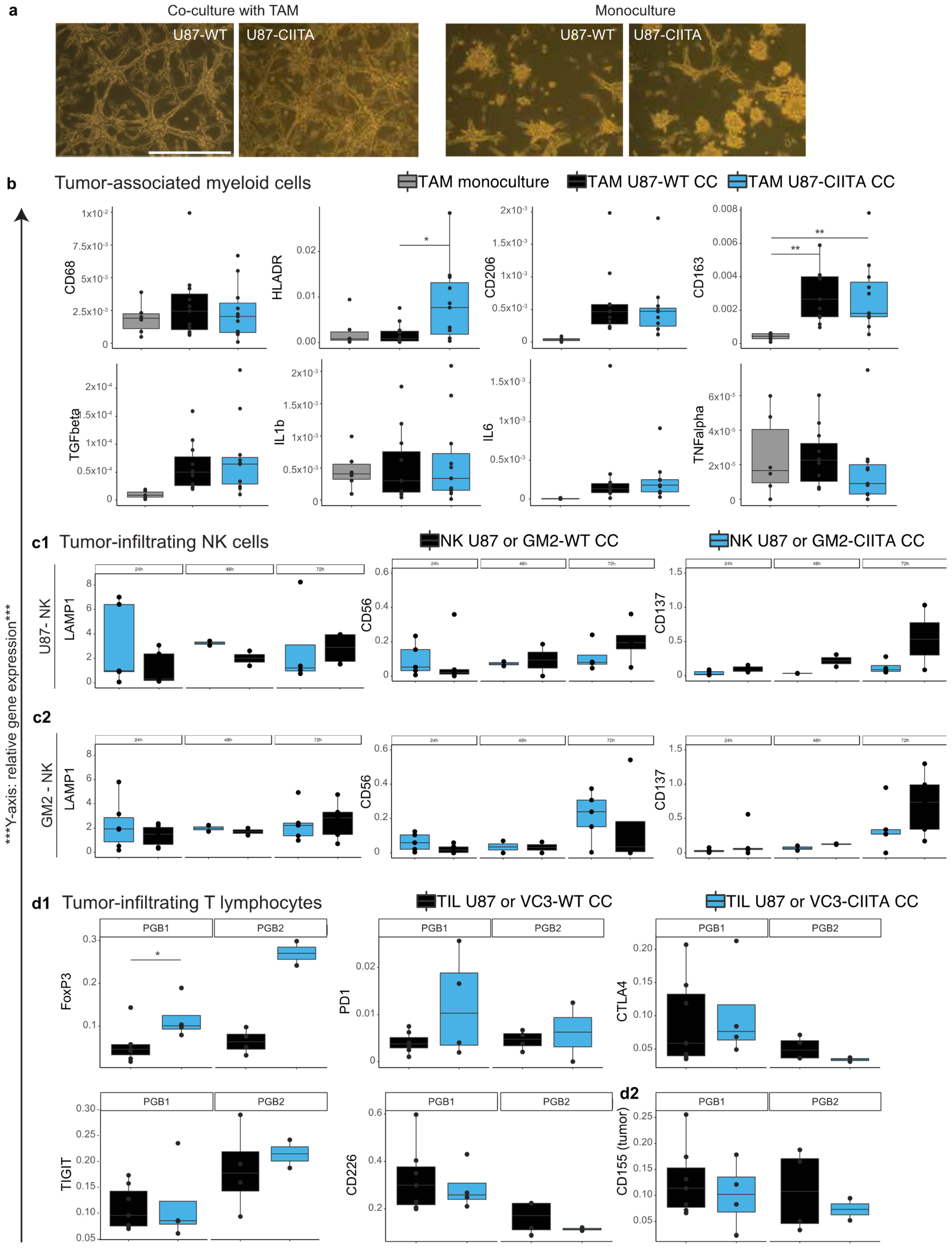
3.2.2. TAM Develop a Pro-Tumor Phenotype When Co-Cultured with U87 Cells, Regardless of Their CIITA Expression Level
3.2.3. Effects of CIITA-Expressing Glioblastoma Cells on Tumor-Infiltrating NK (CD56+) Cells
3.2.4. Syngeneic Co-Cultures of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Primary Human Glioblastoma Cells
3.3. CIITA Expression in Glioblastoma Correlates with HLA-DR Expression, but Does Not Determine Survival in Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of Radiotherapy with Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide versus Radiotherapy Alone on Survival in Glioblastoma in a Randomised Phase III Study: 5-Year Analysis of the EORTC-NCIC Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.M.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovlevs, A.; Vanags, A.; Gardovskis, J.; Strumfa, I. Molecular Classification of Diffuse Gliomas. Pol. J. Pathol. 2019, 70, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.J.; Ali, S.; Qadir, M.G.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. The Role of Bevacizumab in the Treatment of Glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 133, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Weller, M.; Chiocca, E.A. Current State of Immune-Based Therapies for Glioblastoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2016, 35, e132–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medikonda, R.; Dunn, G.; Rahman, M.; Fecci, P.; Lim, M. A Review of Glioblastoma Immunotherapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 151, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherm, A.; Ippen, F.M.; Hau, P.; Baurecht, H.; Wick, W.; Gempt, J.; Knüttel, H.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Seliger, C. Targeted Therapies in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma—A Systematic Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weenink, B.; French, P.J.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.E.; Debets, R.; Geurts, M. Immunotherapy in Glioblastoma: Current Shortcomings and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.F.; Carter, T.J.; Ottaviani, D.; Mulholland, P. Harnessing the Immune System in Glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accolla, R.S.; Ramia, E.; Tedeschi, A.; Forlani, G. CIITA-Driven MHC Class II Expressing Tumor Cells as Antigen Presenting Cell Performers: Toward the Construction of an Optimal Anti-Tumor Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Bergers, G. Glioblastoma: Defining Tumor Niches. Trends Cancer 2015, 1, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, D.; Balça-Silva, J.; da Graça, G.C.; Wanjiru, C.M.; Macharia, L.W.; Nascimento, C.P.; Roque, N.R.; Coelho-Aguiar, J.M.; Pereira, C.M.; Dos Santos, M.F.; et al. Microglia/Astrocytes–Glioblastoma Crosstalk: Crucial Molecular Mechanisms and Microenvironmental Factors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M.D.; Dahlrot, R.H.; Boldt, H.B.; Hansen, S.; Kristensen, B.W. Tumour-Associated Microglia/Macrophages Predict Poor Prognosis in High-Grade Gliomas and Correlate with an Aggressive Tumour Subtype. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Pelz, A.; Feng, X.; Synowitz, M.; Markovic, D.; Langmann, T.; Holtman, I.R.; Wang, X.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M.; et al. Glioma-Associated Microglia/Macrophages Display an Expression Profile Different from M1 and M2 Polarization and Highly Express Gpnmb and Spp1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Rhodin, K.; Kemeny, H.; Dechant, C.; Farber, S.H.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Cui, X.; Koyama, S.; Jackson, C.; et al. T-Cell Exhaustion Signatures Vary with Tumor Type and Are Severe in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.I.; Rhodin, K.E.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Keith, K.A.; Fecci, P.E. T-Cell Dysfunction in Glioblastoma: Applying a New Framework. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.; Fecci, P.E. T-Cell Exhaustion in Glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35287–35288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filley, A.C.; Henriquez, M.; Dey, M. Recurrent Glioma Clinical Trial, CheckMate-143: The Game Is Not over Yet. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91779–91794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuro, A.; Vlahovic, G.; Lim, M.; Sahebjam, S.; Baehring, J.; Cloughesy, T.; Voloschin, A.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Latek, R.; et al. Nivolumab with or without Ipilimumab in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma: Results from Exploratory Phase I Cohorts of CheckMate 143. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickler, J.H.; Hanks, B.A.; Khasraw, M. Tumor Mutational Burden as a Predictor of Immunotherapy Response: Is More Always Better? Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlani, G.; Michaux, J.; Pak, H.; Huber, F.; Marie Joseph, E.L.; Ramia, E.; Stevenson, B.J.; Linnebacher, M.; Accolla, R.S.; Bassani-Sternberg, M. CIITA-Transduced Glioblastoma Cells Uncover a Rich Repertoire of Clinically Relevant Tumor-Associated HLA-II Antigens. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagzag, D.; Salnikow, K.; Chiriboga, L.; Yee, H.; Lan, L.; Ali, M.A.; Garcia, R.; Demaria, S.; Newcomb, E.W. Downregulation of Major Histocompatibility Complex Antigens in Invading Glioma Cells: Stealth Invasion of the Brain. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaseki, T.; Ikeda, H.; Takamura, Y.; Toyota, M.; Hirohashi, Y.; Tokino, T.; Himi, T.; Sato, N. Histone Deacetylation, But Not Hypermethylation, Modifies Class II Transactivator and MHC Class II Gene Expression in Squamous Cell Carcinomas. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4980–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.C.; Spangler, W.E.; Boss, J.M. Methylation of Class II Trans-Activator Promoter IV: A Novel Mechanism of MHC Class II Gene Control. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4143–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamura, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Kanaseki, T.; Toyota, M.; Tokino, T.; Imai, K.; Houkin, K.; Sato, N. Regulation of MHC Class II Expression in Glioma Cells by Class II Transactivator (CIITA). Glia 2004, 45, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Stoep, N.; Biesta, P.; Quinten, E.; van den Elsen, P.J. Lack of IFN-Gamma-Mediated Induction of the Class II Transactivator (CIITA) through Promoter Methylation Is Predominantly Found in Developmental Tumor Cell Lines. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soos, J.M.; Krieger, J.I.; Stüve, O.; King, C.L.; Patarroyo, J.C.; Aldape, K.; Wosik, K.; Slavin, A.J.; Nelson, P.A.; Antel, J.P.; et al. Malignant Glioma Cells Use MHC Class II Transactivator (CIITA) Promoters III and IV to Direct IFN-γ-Inducible CIITA Expression and Can Function as Nonprofessional Antigen Presenting Cells in Endocytic Processing and CD4+ T-Cell Activation. Glia 2001, 36, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Nasser Eddine, F.; Forlani, G.; Lombardo, L.; Tedeschi, A.; Tosi, G.; Accolla, R.S. CIITA-Driven MHC Class II Expressing Tumor Cells Can Efficiently Prime Naive CD4+ TH Cells in Vivo and Vaccinate the Host against Parental MHC-II-Negative Tumor Cells. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1261777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meazza, R.; Comes, A.; Orengo, A.M.; Ferrini, S.; Accolla, R.S. Tumor Rejection by Gene Transfer of the MHC Class II Transactivator in Murine Mammary Adenocarcinoma Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celesti, F.; Gatta, A.; Shallak, M.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; Cerati, M.; Sessa, F.; Accolla, R.S.; Forlani, G. Protective Anti-Tumor Vaccination against Glioblastoma Expressing the MHC Class II Transactivator CIITA. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1133177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmari, T.; Lumniczky, K.; Desaknai, S.; Trajcevski, S.; Hidvegi, E.J.; Hamada, H.; Safrany, G. Detailed Characterization of the Mouse Glioma 261 Tumor Model for Experimental Glioblastoma Therapy. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekkirala, C.R.; Cappello, P.; Accolla, R.S.; Giovarelli, M.; Romero, I.; Garrido, C.; Garcia-Lora, A.M.; Novelli, F. Class II Transactivator-Induced MHC Class II Expression in Pancreatic Cancer Cells Leads to Tumor Rejection and a Specific Antitumor Memory Response. Pancreas 2014, 43, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artesi, M.; Kroonen, J.; Bredel, M.; Nguyen-Khac, M.; Deprez, M.; Schoysman, L.; Poulet, C.; Chakravarti, A.; Kim, H.; Scholtens, D.; et al. Connexin 30 Expression Inhibits Growth of Human Malignant Gliomas but Protects Them against Radiation Therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2015, 17, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robe, P.A.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Bonif, M.; Rogister, B.; Deprez, M.; Haddada, H.; Khac, M.-T.N.; Jolois, O.; Erkmen, K.; Merville, M.-P.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Activity of the Nuclear Factor-ΚB Inhibitor Sulfasalazine in Human Glioblastomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5595–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneeboer, M.A.M.; Snijders, G.J.L.J.; Berdowski, W.M.; Fernández-Andreu, A.; van Mierlo, H.C.; Berdenis van Berlekom, A.; Litjens, M.; Kahn, R.S.; Hol, E.M.; de Witte, L.D. Microglia in Post-Mortem Brain Tissue of Patients with Bipolar Disorder Are Not Immune Activated. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingemann, H.-G.; Martinson, J. Ex Vivo Expansion of Natural Killer Cells for Clinical Applications. Cytotherapy 2004, 6, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausman, J.; Shapiro, W.; Rall, D. Studies on the chemotherapy of experimental brain tumors: Development of an experimental model Studies on the Chemotherapy of Experimental Brain Tumors: Development of an Experimental Model. Cancer Res. 1970, 30, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.; Fakurnejad, S.; Sayegh, E.T.; Clark, A.J.; Ivan, M.E.; Sun, M.Z.; Safaee, M.; Bloch, O.; James, C.D.; Parsa, A.T. Immunocompetent Murine Models for the Study of Glioblastoma Immunotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Georganaki, M.; Conze, L.L.; Laviña, B.; van Hooren, L.; Vemuri, K.; van de Walle, T.; Ramachandran, M.; Zhang, L.; Pontén, F.; et al. ELTD1 Deletion Reduces Vascular Abnormality and Improves T-Cell Recruitment after PD-1 Blockade in Glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollis, P.M.; Ebert, L.M.; Toubia, J.; Bastow, C.R.; Ormsby, R.J.; Poonnoose, S.I.; Lenin, S.; Tea, M.N.; Pitson, S.M.; Gomez, G.A.; et al. Characterising Distinct Migratory Profiles of Infiltrating T-Cell Subsets in Human Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 850226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackstein, R.; Schatton, T.; Barthel, S.R. T-Lymphocyte Homing: An Underappreciated yet Critical Hurdle for Successful Cancer Immunotherapy. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 669–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golán, I.; Rodríguez de la Fuente, L.; Costoya, J. NK Cell-Based Glioblastoma Immunotherapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kang, W.Y.; Yoon, Y.; Jin, J.Y.; Song, H.J.; Her, J.H.; Kang, S.M.; Hwang, Y.K.; Kang, K.J.; Joo, K.M.; et al. Natural Killer (NK) Cells Inhibit Systemic Metastasis of Glioblastoma Cells and Have Therapeutic Effects against Glioblastomas in the Brain. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felices, M.; Lenvik, A.J.; McElmurry, R.; Chu, S.; Hinderlie, P.; Bendzick, L.; Geller, M.A.; Tolar, J.; Blazar, B.R.; Miller, J.S. Continuous Treatment with IL-15 Exhausts Human NK Cells via a Metabolic Defect. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 3, e96219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaim, H.; Shanley, M.; Basar, R.; Daher, M.; Gumin, J.; Zamler, D.B.; Uprety, N.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; et al. Targeting the Av Integrin/TGF-β Axis Improves Natural Killer Cell Function against Glioblastoma Stem Cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puigdelloses, M.; Garcia-Moure, M.; Labiano, S.; Laspidea, V.; Gonzalez-Huarriz, M.; Zalacain, M.; Marrodan, L.; Martinez-Velez, N.; De la Nava, D.; Ausejo, I.; et al. CD137 and PD-L1 Targeting with Immunovirotherapy Induces a Potent and Durable Antitumor Immune Response in Glioblastoma Models. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, A.K.; Henry, A.; Goffart, N.; van Logtestijn, S.; Bours, V.; Hol, E.M.; Robe, P.A. Limited Effects of Class II Transactivator-Based Immunotherapy in Murine and Human Glioblastoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010193
Tan AK, Henry A, Goffart N, van Logtestijn S, Bours V, Hol EM, Robe PA. Limited Effects of Class II Transactivator-Based Immunotherapy in Murine and Human Glioblastoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010193
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, A. Katherine, Aurelie Henry, Nicolas Goffart, Sofie van Logtestijn, Vincent Bours, Elly M. Hol, and Pierre A. Robe. 2024. "Limited Effects of Class II Transactivator-Based Immunotherapy in Murine and Human Glioblastoma" Cancers 16, no. 1: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010193
APA StyleTan, A. K., Henry, A., Goffart, N., van Logtestijn, S., Bours, V., Hol, E. M., & Robe, P. A. (2024). Limited Effects of Class II Transactivator-Based Immunotherapy in Murine and Human Glioblastoma. Cancers, 16(1), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010193







