SkinLesNet: Classification of Skin Lesions and Detection of Melanoma Cancer Using a Novel Multi-Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Contributions
- The development and implementation of a cutting-edge multi-layer CNN model represents a significant contribution. The model was specifically designed for the classification and discrimination of skin lesions, and its superior performance—achieving a 96% accuracy rate—demonstrates its effectiveness, compared to established models like ResNet50 and VGG16.
- This research contributes to the field by utilizing the PAD-UFES-20 dataset, which has not been as extensively explored for skin-lesion classification. This dataset contains smartphone images rather than dermatoscopic images, which is particularly relevant to the development of smartphone applications for accessible, scalable, and cost-effective melanoma diagnosis.
- This study evaluated the proposed model on diverse datasets, including the PAD-UFES-20-Modified dataset, HAM10000, and ISIC2017. This approach enhanced the generalizability of the model, showcasing its adaptability to different datasets and real-world scenarios.
- This study’s primary contribution lies in achieving a high accuracy rate of 96% in classifying skin lesions. This is a crucial contribution, considering the complexities and challenges associated with accurate dermatological diagnoses.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
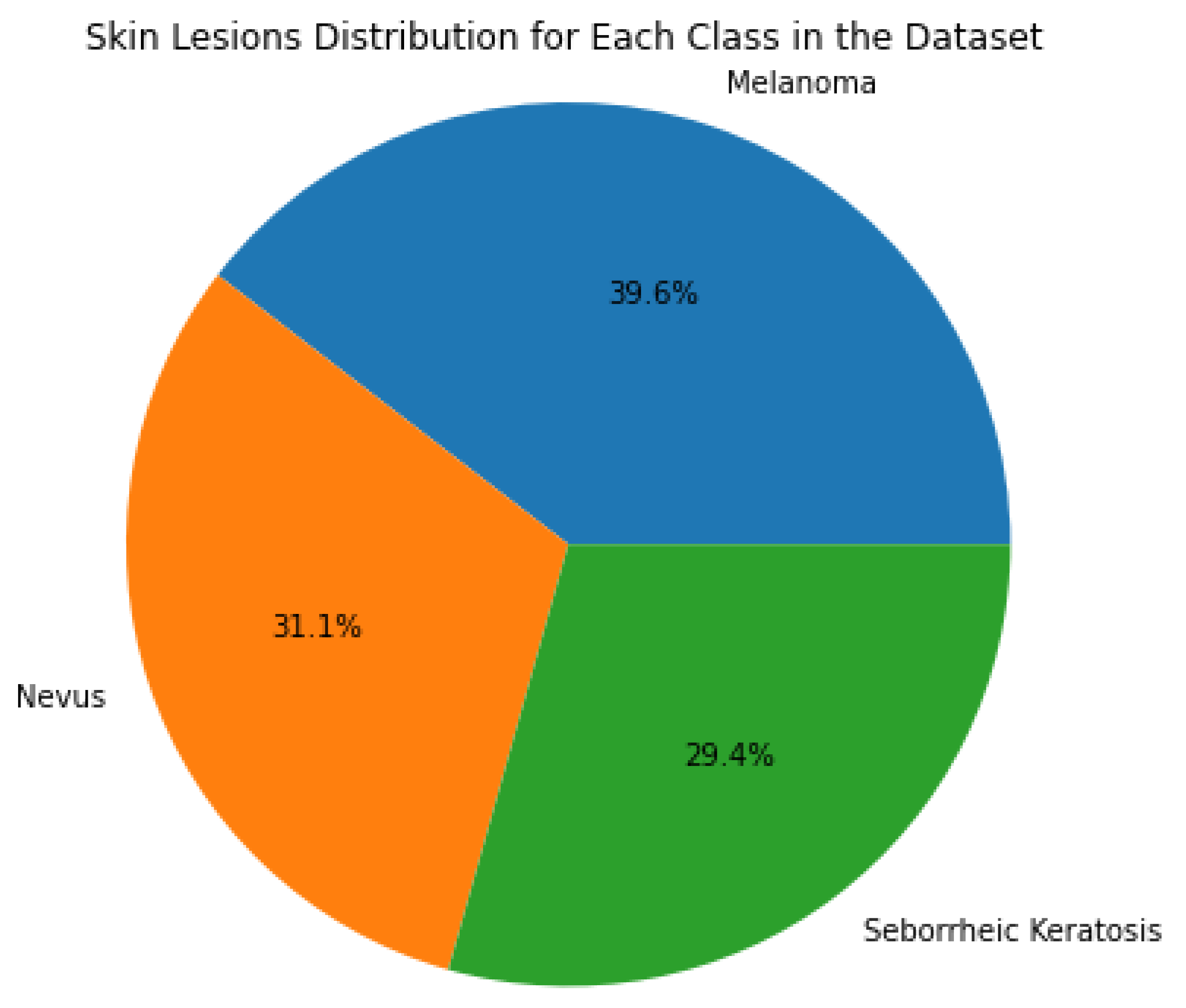
3.1. Dataset and Data Augmentation
3.2. Comparative Datasets
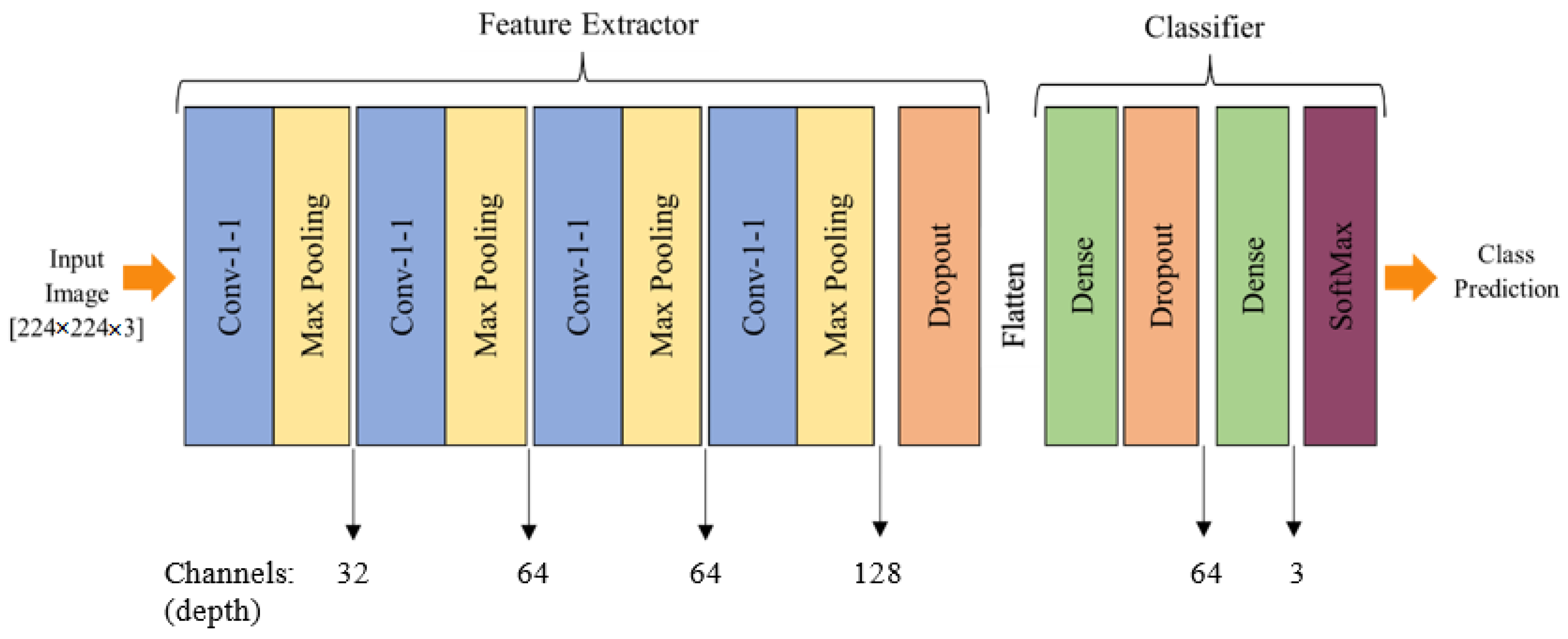
3.3. Proposed Model Architecture
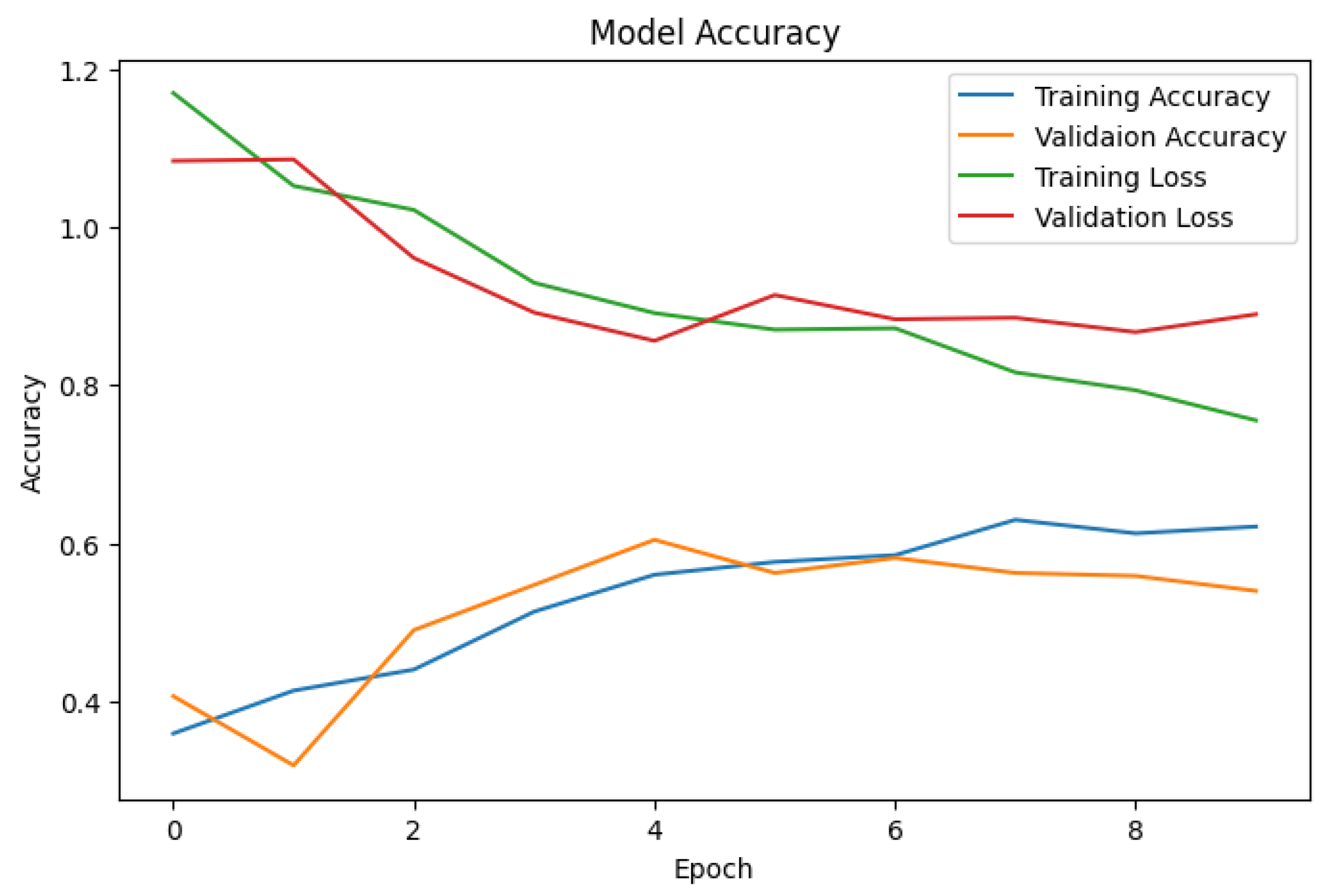
3.4. Model Training
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
GitHub Repository
References
- Khan, D.; Rahman, A.U.; Kumam, P.; Watthayu, W. A Fractional Analysis of Hyperthermia Therapy on Breast Cancer in a Porous Medium along with Radiative Microwave Heating. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, L.; Khammissa, R.; Kramer, B.; Altini, M.; Lemmer, J. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma of the head and face. Head Face Med. 2016, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulfatah, E.; Fine, S.W.; Lotan, T.L.; Mehra, R. De Novo neuroendocrine features in prostate cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 127, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, M.A.; Zakaria, A.; Nizran, P. Skin cancer. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2015, 42, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dildar, M.; Akram, S.; Irfan, M.; Khan, H.U.; Ramzan, M.; Mahmood, A.R.; Alsaiari, S.A.; Saeed, A.H.M.; Alraddadi, M.O.; Mahnashi, M.H. Skin cancer detection: A review using deep learning techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L.E.; Shalin, S.C.; Tackett, A.J. Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigel, D.S.; Carucci, J.A. Malignant melanoma: Prevention, early detection, and treatment in the 21st century. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2000, 50, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goceri, E. Evaluation of denoising techniques to remove speckle and Gaussian noise from dermoscopy images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 152, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, G.; Agrawal, S.; Raut, G.; Vishvakarma, S.K. An accurate and noninvasive skin cancer screening based on imaging technique. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, R.K.; Woods, T.N.; Cromwell, K.D.; Nelson, K.C.; Cormier, J.N. Improving outcomes in patients with melanoma: Strategies to ensure an early diagnosis. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2015, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidan, A.; Zaidan, B.; Albahri, O.; Alsalem, M.; Albahri, A.; Yas, Q.M.; Hashim, M. A review on smartphone skin cancer diagnosis apps in evaluation and benchmarking: Coherent taxonomy, open issues and recommendation pathway solution. Health Technol. 2018, 8, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachbar, F.; Stolz, W.; Merkle, T.; Cognetta, A.B.; Vogt, T.; Landthaler, M.; Bilek, P.; Braun-Falco, O.; Plewig, G. The ABCD rule of dermatoscopy: High prospective value in the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burroni, M.; Corona, R.; Dell’Eva, G.; Sera, F.; Bono, R.; Puddu, P.; Perotti, R.; Nobile, F.; Andreassi, L.; Rubegni, P. Melanoma computer-aided diagnosis: Reliability and feasibility study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, W.; Sama, N.U.; Al-Waakid, G.; Humayun, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. Detection of skin cancer based on skin lesion images using deep learning. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindewolf, T.; Stolz, W.; Albert, R.; Abmayr, W.; Harms, H. Classification of melanocytic lesions with color and texture analysis using digital image processing. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Histol. 1993, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, J.B.A.; Mishra, D.; Das, A.; Mohanty, M.N.; Sarangi, A. Skin cancer detection using machine learning techniques with ABCD features. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd Odisha International Conference on Electrical Power Engineering, Communication and Computing Technology (ODICON), Bhubaneswar, India, 11–12 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Salma, W.; Eltrass, A.S. Automated deep learning approach for classification of malignant melanoma and benign skin lesions. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 32643–32660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Javaid, S.; Khalil, R.A.; Fahim, H.; Althobaiti, T.; Alsharif, N.; Saeed, N. Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malibari, A.A.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Eltahir, M.M.; Malik, V.; Obayya, M.; Al Duhayyim, M.; Neto, A.V.L.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. Optimal deep neural network-driven computer aided diagnosis model for skin cancer. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethanan, K.; Pitakaso, R.; Srichok, T.; Khonjun, S.; Thannipat, P.; Wanram, S.; Boonmee, C.; Gonwirat, S.; Enkvetchakul, P.; Kaewta, C.; et al. Double AMIS-ensemble deep learning for skin cancer classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem Saleem, M.; Muhammad Adnan Shah, S.; Nazir, T.; Mehmood, A.; Nawaz, M.; Attique Khan, M.; Kadry, S.; Majumdar, A.; Thinnukool, O. Signet ring cell detection from histological images using deep learning. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 5985–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari, A.; Khatibi, T.; Ranjbari, S. Skin lesion detection using an ensemble of deep models: SLDED. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 10575–10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Fahim, M.A.I.; Islam, A.M.; Islam, S.; Shatabda, S. DOLG-NeXt: Convolutional neural network with deep orthogonal fusion of local and global features for biomedical image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2023, 546, 126362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Nandal, A.; Dhaka, A.; Koundal, D.; Bogatinoska, D.C.; Alyami, H. Enhanced watershed segmentation algorithm-based modified ResNet50 model for brain tumor detection. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7348344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Kim, E. Helpful or Harmful: Inter-task Association in Continual Learning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 519–535. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghvi, H.A.; Patel, R.H.; Agarwal, A.; Gupta, S.; Sawhney, V.; Pandya, A.S. A deep learning approach for classification of COVID and pneumonia using DenseNet-201. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, A.G.; Lima, G.R.; Salomao, A.S.; Krohling, B.; Biral, I.P.; de Angelo, G.G.; Alves, F.C., Jr.; Esgario, J.G.; Simora, A.C.; Castro, P.B.; et al. PAD-UFES-20: A skin lesion dataset composed of patient data and clinical images collected from smartphones. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kaluri, R.; Feng, G.; Tariq, U. Multi-modal prediction of breast cancer using particle swarm optimization with non-dominating sorting. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandris, D.; Alevizopoulos, N.; Marinos, L.; Gakiopoulou, C. Dermoscopy and novel non invasive imaging of Cutaneous Metastases. Adv. Cancer Biol.-Metastasis 2022, 6, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adla, D.; Reddy, G.V.R.; Nayak, P.; Karuna, G. Deep learning-based computer aided diagnosis model for skin cancer detection and classification. Distrib. Parallel Databases 2022, 40, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Gupta, S.; Koundal, D.; Singh, K. Fusion of U-Net and CNN model for segmentation and classification of skin lesion from dermoscopy images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 119230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Khan, M.A.; Javed, M.Y.; Tariq, U.; Kang, B.G.; Nam, Y.; Mostafa, R.R.; Sakr, R.H. Skin lesion segmentation and classification using conventional and deep learning based framework. Comput. Mater. Contin 2022, 71, 2477–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Ren, K.; Zhang, W.; Ning, H. Skin lesion classification using CNNs with grouping of multi-scale attention and class-specific loss weighting. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Elahi, H.; Sun, Z.; Khatoon, A.; Ahmad, I. Comparative analysis of AlexNet, ResNet18 and SqueezeNet with diverse modification and arduous implementation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 2397–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.D.; Bhavekar, G.S.; Chafle, P.V. Electrocardiogram signal classification using VGGNet: A neural network based classification model. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Mazher, M.; Khan, T.; Razzak, I. Semi-supervised 3D-InceptionNet for segmentation and survival prediction of head and neck primary cancers. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Li, X.; Li, K. A Dataset Auditing Method for Collaboratively Trained Machine Learning Models. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 42, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Shah, M.; Pandya, A.; Sushra, R.; Sushra, R.; Mehta, M.; Patel, K.; Patel, K. A Comprehensive Study on Skin Cancer Detection using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Clin. eHealth 2023, 6, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahar, M.A. Skin lesion classification using convolutional neural network with novel regularizer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38306–38313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, M.; Obaidellah, U.H.; Kareem, S.A. Convolutional neural network-based skin lesion classification with Variable Nonlinear Activation Functions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 83398–83414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururaj, H.; Manju, N.; Nagarjun, A.; Aradhya, V.N.M.; Flammini, F. DeepSkin: A Deep Learning Approach for Skin Cancer Classification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 50205–50214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allugunti, V.R. A machine learning model for skin disease classification using convolution neural network. Int. J. Comput. Program. Database Manag. 2022, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, M.; Vijayan, K.; Anand, O.; Raina, G. Exploration of transfer learning capability of multilingual models for text classification. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems, Shenyang, China, 28–30 July 2023; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ogudo, K.A.; Surendran, R.; Khalaf, O.I. Optimal Artificial Intelligence Based Automated Skin Lesion Detection and Classification Model. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, D.; Abdullah, M.I.; Hossain, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.S. SkinNet: An Improved Skin Cancer Classification System Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Industry 4.0 (STI), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 17–18 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan, R.; Aly, S. CU-net: A new improved multi-input color U-net model for skin lesion semantic segmentation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 15539–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, M.S.; Polat, Ö. Segmentation of Skin Lesions using U-Net with EfficientNetB7 Backbone. In Proceedings of the 2022 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference (ASYU), Antalya, Turkey, 7–9 September 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudeva, K.; Chandran, S. Classifying Skin Cancer and Acne using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2023 15th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Phuket, Thailand, 21–24 February 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jayabharathy, K.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Detection and classification of malignant melanoma and benign skin lesion using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Technologies and Systems for Next Generation Computing (ICSTSN), Villupuram, India, 25–26 March 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Battle, M.L.; Atapour-Abarghouei, A.; McGough, A.S. Siamese Neural Networks for Skin Cancer Classification and New Class Detection using Clinical and Dermoscopic Image Datasets. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Osaka, Japan, 17–20 December 2022; pp. 4346–4355. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, A.; Umar, A.I.; Shirazi, S.H.; Khan, Z.; Nawaz, S.; Shahzad, M. Automatic eczema classification in clinical images based on hybrid deep neural network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.H.; Abubakr, A.F.; Abdu, N.; Khalil, M.; Kamal, H.; Youssef, M.; Mohamed, H.; ElSayed, M. A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Skin Cancer Classification Using Dermoscopy Images and Metadata. Res. Sq. 2023, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedeir, R.H.; Mahmoud, R.O.; Zayed, H.H. Automated multi-class skin cancer classification through concatenated deep learning models. Iaes Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2022, 11, 764. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P.; Azam, S.; Quadir, R.; Karim, A.; Shamrat, F.; Bhowmik, S.K.; Jonkman, M.; Hasib, K.M.; Ahmed, K. SkinNet-16: A deep learning approach to identify benign and malignant skin lesions. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 931141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigar, N.; Umar, M.; Shahzad, M.K.; Islam, S.; Abalo, D. A deep learning approach based on explainable artificial intelligence for skin lesion classification. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 113715–113725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyenta, C.; Akanzawon, M. Skin Lesion Classification Based on Convolutional Neural Network. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2022, 3, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, D.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Mahbub, J.; Khan, M.M. Skin Cancer Detection using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 0169–0176. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Nazir, T.; Masood, M.; Ali, F.; Khan, M.A.; Tariq, U.; Sahar, N.; Damaševičius, R. Melanoma segmentation: A framework of improved DenseNet77 and UNET convolutional neural network. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 2137–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthakkan, A.; Anzar, S.; Jamal, S.; Mansoor, W. Concatenated Xception-ResNet50—A novel hybrid approach for accurate skin cancer prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Pandey, A.; Rakhra, M.; Singh, D.; Singh, G.; Dahiya, O. An Iris Recognition System Using CNN & VGG16 Technique. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO), Noida, India, 13–14 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mascarenhas, S.; Agarwal, M. A comparison between VGG16, VGG19 and ResNet50 architecture frameworks for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Disruptive Technologies for Multi-Disciplinary Research and Applications (CENTCON), Bengaluru, India, 19–21 November 2021; Volume 1, pp. 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Pugliesi, R.A. Deep Learning Models for Classification of Pediatric Chest X-ray Images using VGG-16 and ResNet-50. Sage Sci. Rev. Appl. Mach. Learn. 2019, 2, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Martinez, C.; Visuña, L.; Khandhar, H.; Bhatt, C.; Carretero, J. Detection and analysis of COVID-19 in medical images using deep learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijaguna, G.; Babu, J.A.; Parameshachari, B.; de Prado, R.P.; Frnda, J. Quantum Fruit Fly algorithm and ResNet50-VGG16 for medical diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 136, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izikson, L.; Sober, A.J.; Mihm, M.C.; Zembowicz, A. Prevalence of melanoma clinically resembling seborrheic keratosis: Analysis of 9204 cases. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant-Kels, J.M.; Bason, E.T.; Grin, C.M. The misdiagnosis of malignant melanoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1999, 40, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcea, F.; Serra, A.; Lamberti, F.; Morra, L. Data augmentation for medical imaging: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zephaniah, B. Comparison of Keras Applications Prebuilt Model with Extra Densely Connected Neural Layer Accuracy And Stability Using Skin Cancer Dataset of Mnist: Ham10000. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Kristen Satya Wacana, Salatiga, Indonesia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alsahafi, Y.S.; Kassem, M.A.; Hosny, K.M. Skin-Net: A novel deep residual network for skin lesions classification using multilevel feature extraction and cross-channel correlation with detection of outlier. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.M.; Shaukat, K.; Khan, W.A.; Hameed, I.A.; Almuqren, L.A.; Raza, M.A.; Aslam, M.; Luo, S. An efficient deep learning-based skin cancer classifier for an imbalanced dataset. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Luo, W.; Tang, X. Superpixel inpainting for self-supervised skin lesion segmentation from dermoscopic images. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Kolkata, India, 28–31 March 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nayef, B.H.; Abdullah, S.N.H.S.; Sulaiman, R.; Alyasseri, Z.A.A. Optimized leaky ReLU for handwritten Arabic character recognition using convolution neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 2065–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumala, K.; Markosyan, A.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Aghajanyan, A. Memorization without overfitting: Analyzing the training dynamics of large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 38274–38290. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Moon, J.; Kum, S. Application of Deep Learning Model Inference with Batch Size Adjustment. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 19–21 October 2022; pp. 2146–2148. [Google Scholar]
- Ogundokun, R.O.; Maskeliunas, R.; Misra, S.; Damaševičius, R. Improved CNN based on batch normalization and adam optimizer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Malaga, Spain, 4–7 July 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 593–604. [Google Scholar]

| Ref. | Model | Dataset | Accuracy | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [38] | Deep convolutional neural network | HAM10000 | 90% | One of the main benchmark datasets was used in this paper, which produced promising results while using a CNN model. However, hyperparameters tuning is required, to increase the accuracy results. |
| [59] | Convolutional neural network (CNN) | International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) | 97.49% | A CNN model was used, which showed relatively good results, but the size of the dataset needs to be maximized. |
| [42] | ResNet50 | MNIST: HAM10000 | 91% | A State-of-the-Art model was used, which produced reasonable results on the given dataset. However, the dataset needs to be preprocessed well before training, to obtain more accurate and promising results. |
| [43] | Deep convolutional neural network | International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) | 97.8% | A CNN model was trained on an internationally recognized benchmark dataset. However, the size of the dataset was decreased, which showed good results but could lead to model overfitting. |
| [48] | U-Net | International Skin Imaging Collaboration (ISIC) | 94.9% | A State-of-the-Art model was used, which showed promising results, but more data preprocessing or augmentation is needed for accurate prediction. |
| Dataset | Train (80%) | Test (20%) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | 416 | 104 | 520 |
| Nevus | 326 | 82 | 408 |
| Seborrheic | |||
| Keratosis | 309 | 77 | 386 |
| Total | 1051 | 263 | 1314 |
| Learning Rate | Batch Size | Epochs | Optimizer | Activation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.001 | 32 | 100 | Adam | ReLU |
| Performance Metrics | VGG16 | ResNet50 | SkinLesNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 79% | 82% | 96% |
| Precision | 80% | 85% | 97% |
| Recall | 75% | 75% | 92% |
| F1-Score | 72% | 75% | 92% |
| Performance Metrics | VGG16 | ResNet50 | SkinLesNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 75% | 80% | 90% |
| Precision | 75% | 80% | 89% |
| Recall | 70% | 72% | 87% |
| F1-Score | 70% | 71% | 85% |
| Performance Metrics | VGG16 | ResNet50 | SkinLesNet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 70% | 75% | 92% |
| Precision | 70% | 75% | 80% |
| Recall | 70% | 65% | 82% |
| F1-Score | 72% | 70% | 75% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azeem, M.; Kiani, K.; Mansouri, T.; Topping, N. SkinLesNet: Classification of Skin Lesions and Detection of Melanoma Cancer Using a Novel Multi-Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Cancers 2024, 16, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010108
Azeem M, Kiani K, Mansouri T, Topping N. SkinLesNet: Classification of Skin Lesions and Detection of Melanoma Cancer Using a Novel Multi-Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzeem, Muhammad, Kaveh Kiani, Taha Mansouri, and Nathan Topping. 2024. "SkinLesNet: Classification of Skin Lesions and Detection of Melanoma Cancer Using a Novel Multi-Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network" Cancers 16, no. 1: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010108
APA StyleAzeem, M., Kiani, K., Mansouri, T., & Topping, N. (2024). SkinLesNet: Classification of Skin Lesions and Detection of Melanoma Cancer Using a Novel Multi-Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Cancers, 16(1), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010108






