Integration of Radiomics and Tumor Biomarkers in Interpretable Machine Learning Models
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Methods
3.1. ConRad Models and Data
3.2. Feature Engineering and Model Training
3.3. Machine Learning Classifiers
- Biomarkers + radiomics (ConRad models);
- Radiomics features;
- Biomarkers (predicted by CBM);
- CNN features;
- CNN + radiomics;
- CNN + biomarkers;
- CNN + radiomics + biomarkers (all).
4. Results
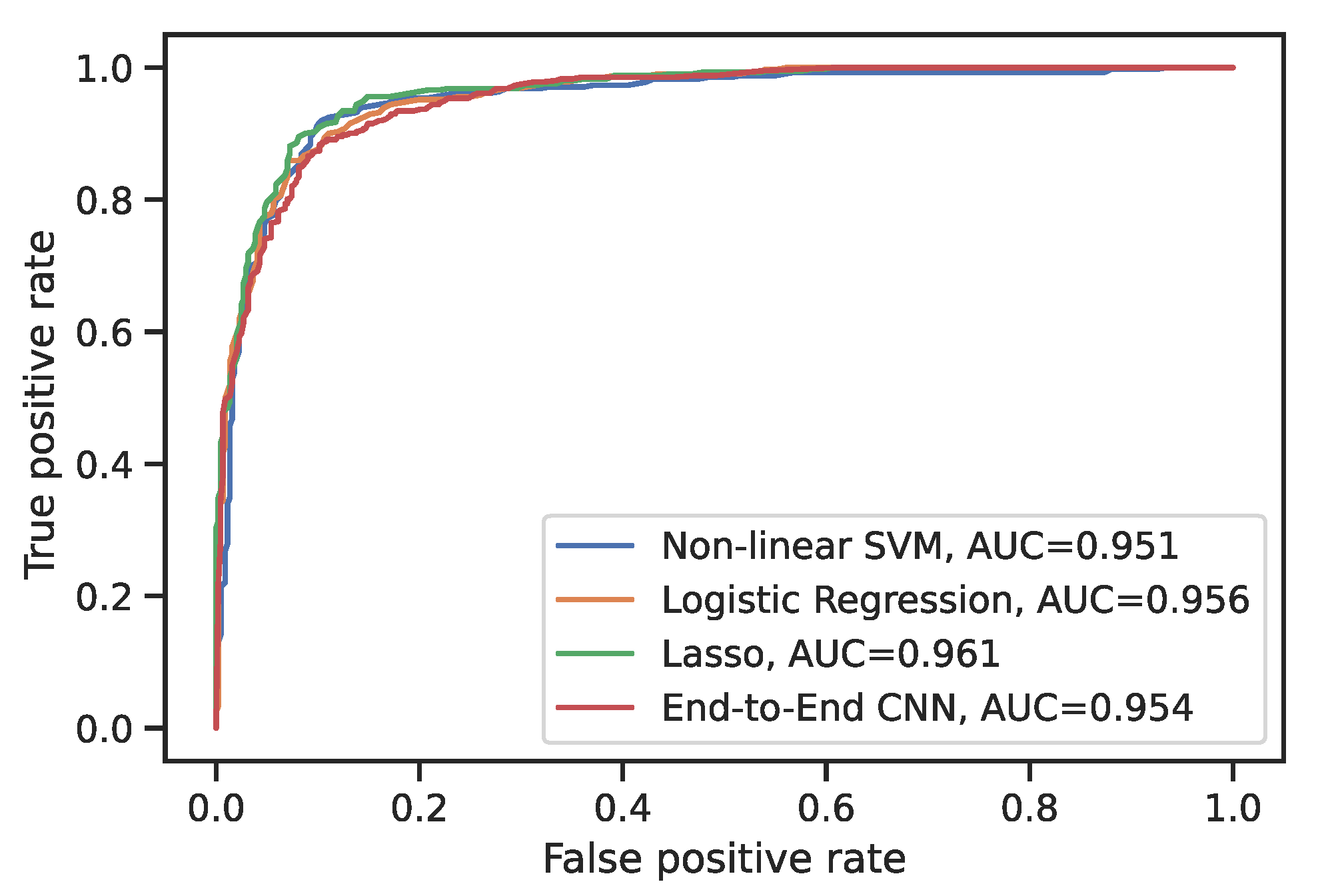
4.1. Evaluation of the ConRad Models
4.2. Comparison to CNN Models
4.3. The Lasso and Feature Selection
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNN | deep neural network |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| CBM | concept bottleneck model |
| LIDC-IDRI | Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative |
| CT | computerized tomography |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| Lasso | least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| SVM | support vector machine |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| FPR | false-positive rate |
| TPR | true-positive rate |
Appendix A
| Classifier | Features | Recall | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonlinear SVM | CNN | |||
| Radiomics | ||||
| Biomarkers | 0.900 | |||
| All | ||||
| CNN+rad | ||||
| Bio+rad | ||||
| Bio+CNN | ||||
| Linear SVM | CNN | |||
| Radiomics | ||||
| Biomarkers | ||||
| All | ||||
| CNN+rad | ||||
| Bio+rad | ||||
| Bio+cnn | ||||
| Random forest | CNN | |||
| Radiomics | ||||
| Biomarkers | ||||
| All | ||||
| CNN+rad | ||||
| Bio+rad | ||||
| Bio+cnn | ||||
| Logistic regression | CNN | |||
| Radiomics | ||||
| Biomarkers | ||||
| All | ||||
| CNN+rad | ||||
| BIO+rad | ||||
| BIO+cnn | ||||
| Logistic regression with the Lasso (feature selection) | CNN | |||
| Radiomics | ||||
| Biomarkers | ||||
| All | ||||
| CNN+rad | ||||
| Bio+rad | ||||
| Bio+cnn |
Appendix B
Appendix C

References
- World Health Organization. Cancer Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Compressed Mortality File 1999–2016 Series 20. CDC WONDER On-Line Database. Available online: https://wonder.cdc.gov/mortsql.html (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Van der Laak, J.; Litjens, G.; Ciompi, F. Deep learning in histopathology: The path to the clinic. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miotto, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Dudley, J.T. Deep learning for healthcare: Review, opportunities and challenges. Briefings Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; Semenova, L.; Zhong, C. Interpretable machine learning: Fundamental principles and 10 grand challenges. Stat. Surv. 2022, 16, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, S.S.; Aerts, H.J. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, M.; Le Rest, C.C.; Tixier, F.; Badic, B.; Schick, U.; Visvikis, D. Radiomics: Data are also images. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 38S–44S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato III, S.G.; McLennan, G.; Bidaut, L.; McNitt-Gray, M.F.; Meyer, C.R.; Reeves, A.P.; Zhao, B.; Aberle, D.R.; Henschke, C.I.; Hoffman, E.A.; et al. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): A completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, P.W.; Nguyen, T.; Tang, Y.S.; Mussmann, S.; Pierson, E.; Kim, B.; Liang, P. Concept bottleneck models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning; PMLR: Norfolk, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 5338–5348. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziugaite, G.K.; Ben-David, S.; Roy, D.M. Enforcing Interpretability and its Statistical Impacts: Trade-offs between Accuracy and Interpretability. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.13764. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, M.; Yang, F.; Yang, C.; Tian, J. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. In IPMI 2015, Proceedings of the Information Processing in Medical Imaging: 24th International Conference, Sabhal Mor Ostaig, Isle of Skye, UK, 28 June–3 July 2015; Proceedings 24; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 588–599. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Wong, A.; Clausi, D.A. Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, Halifax, NS, Canada, 3–5 June 2015; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Xie, X. Deeplung: Deep 3d dual path nets for automated pulmonary nodule detection and classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 673–681. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Lee, H.K.; Tan, M. Gated-dilated networks for lung nodule classification in CT scans. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 178827–178838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabi, M.; Shak, K.; Tan, M. ProCAN: Progressive growing channel attentive non-local network for lung nodule classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causey, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Jiang, B.; Qualls, J.A.; Politte, D.G.; Prior, F.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X. Highly accurate model for prediction of lung nodule malignancy with CT scans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Jain, A.; Mangalagiri, J.; Menon, S.; Nguyen, P.; Chapman, D.R. Lung nodule classification using biomarkers, volumetric radiomics, and 3D CNNs. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 647–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Han, S.X.; Aberle, D.R.; Bui, A.A.; Hsu, W. An interpretable deep hierarchical semantic convolutional neural network for lung nodule malignancy classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 128, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The image biomarker standardization initiative: Standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, M.; Tixier, F.; Visvikis, D.; Le Rest, C.C. Radiomics in PET/CT: More than meets the eye? J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 365–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Pesapane, F.; Bozzini, A.C.; Latronico, A.; Rotili, A.; Ferrari, F.; Signorelli, G.; Raimondi, S.; Vignati, S.; Gaeta, A.; et al. Prediction of the Malignancy of a Breast Lesion Detected on Breast Ultrasound: Radiomics Applied to Clinical Practice. Cancers 2023, 15, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnc, D.; Papp, L.; Nakuz, T.S.; Magometschnigg, H.F.; Grahovac, M.; Spielvogel, C.P.; Ecsedi, B.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Haug, A.; Karanikas, G.; et al. Breast Tumor Characterization Using [18F]FDG-PET/CT Imaging Combined with Data Preprocessing and Radiomics. Cancers 2021, 13, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.; Santinha, J.; Galvão, B.; Matos, C.; Couto, F.M.; Papanikolaou, N. Prediction of Prostate Cancer Disease Aggressiveness Using Bi-Parametric Mri Radiomics. Cancers 2021, 13, 6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.Y.; Chen, J.R.; Wang, Y.C.; Chiu, M.H.; Lin, S.P.; Mo, Y.H.; Peng, S.C.; Lu, C.F. Radiomics-Based Deep Learning Prediction of Overall Survival in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Using Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. Cancers 2022, 14, 3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Woodruff, H.C.; Rad, N.M.; Mali, S.A.; Lambin, P. From Head and Neck Tumour and Lymph Node Segmentation to Survival Prediction on PET/CT: An End-to-End Framework Featuring Uncertainty, Fairness, and Multi-Region Multi-Modal Radiomics. Cancers 2023, 15, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourbonne, V.; Schick, U.; Pradier, O.; Visvikis, D.; Metges, J.P.; Badic, B. Radiomics Approaches for the Prediction of Pathological Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Treatment in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Ready for Prime Time? Cancers 2023, 15, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, M.C.; Magnan, J.F. Lung nodule malignancy classification using only radiologist-quantified image features as inputs to statistical learning algorithms: Probing the Lung Image Database Consortium dataset with two statistical learning methods. J. Med. Imaging 2016, 3, 044504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. The regression analysis of binary sequences. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1958, 20, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; Volume 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, D.M.; Papanikolaou, N.; Bick, U.; Illing, R.; Kahn Jr, C.E.; Kalpathi-Cramer, J.; Matos, C.; Martí-Bonmatí, L.; Miles, A.; Mun, S.K.; et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cancer imaging. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato, S.G., III; Drukker, K.; Li, F.; Hadjiiski, L.; Tourassi, G.D.; Engelmann, R.M.; Giger, M.L.; Redmond, G.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.S.; et al. LUNGx Challenge for computerized lung nodule classification. J. Med. Imaging 2016, 3, 044506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
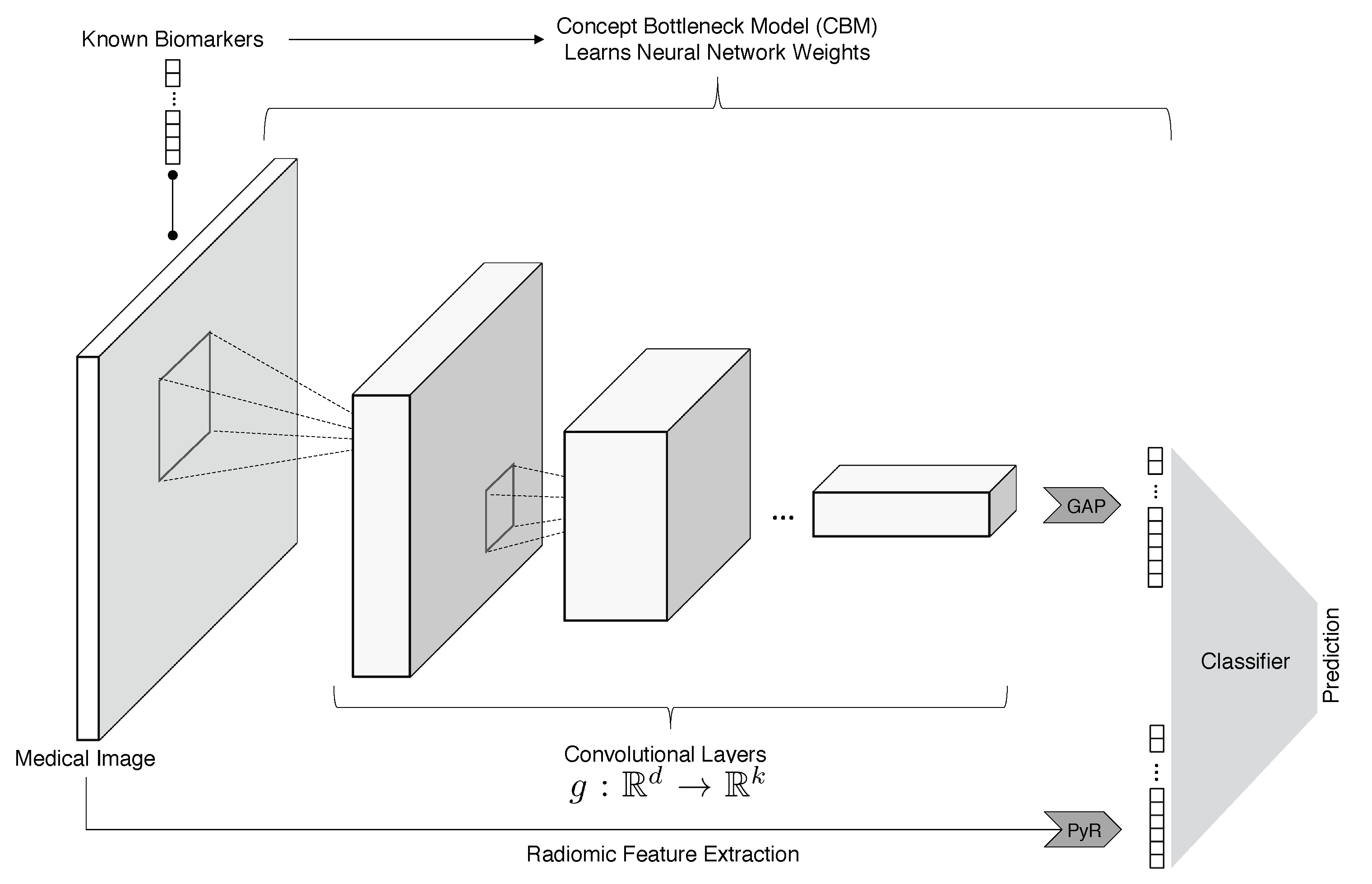

| Reference | Summary |
|---|---|
| [13] | Crops at multiple scales are fed to CNNs with shared parameters, and extracted features are concatenated for final classification |
| [18] | Radiomics features are combined with CNN features |
| [19] | Biomarkers, radiomics, and CNN features combined, and no model is trained to predict biomarkers |
| [20] | Biomarkers are predicted with a CNN, but intermediate features with no well-defined meaning are used in the final prediction |
| Final Layer Classifier | Recall | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-linear SVM | 0.886 | 0.899 | 0.897 |
| Linear SVM | 0.886 | 0.893 | 0.893 |
| Random Forest | 0.879 | 0.883 | 0.881 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.884 | 0.893 | 0.892 |
| Logistic Regression with the Lasso | 0.896 | 0.893 | 0.896 |
| Classifier | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| End-to-end CNN | 0.891 |
| Nonlinear SVM | 0.875 |
| Linear SVM | 0.87 |
| Random Forest | 0.888 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.858 |
| Logistic Regression with the Lasso | 0.891 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brocki, L.; Chung, N.C. Integration of Radiomics and Tumor Biomarkers in Interpretable Machine Learning Models. Cancers 2023, 15, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092459
Brocki L, Chung NC. Integration of Radiomics and Tumor Biomarkers in Interpretable Machine Learning Models. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092459
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrocki, Lennart, and Neo Christopher Chung. 2023. "Integration of Radiomics and Tumor Biomarkers in Interpretable Machine Learning Models" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092459
APA StyleBrocki, L., & Chung, N. C. (2023). Integration of Radiomics and Tumor Biomarkers in Interpretable Machine Learning Models. Cancers, 15(9), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092459





