MR-Class: A Python Tool for Brain MR Image Classification Utilizing One-vs-All DCNNs to Deal with the Open-Set Recognition Problem
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
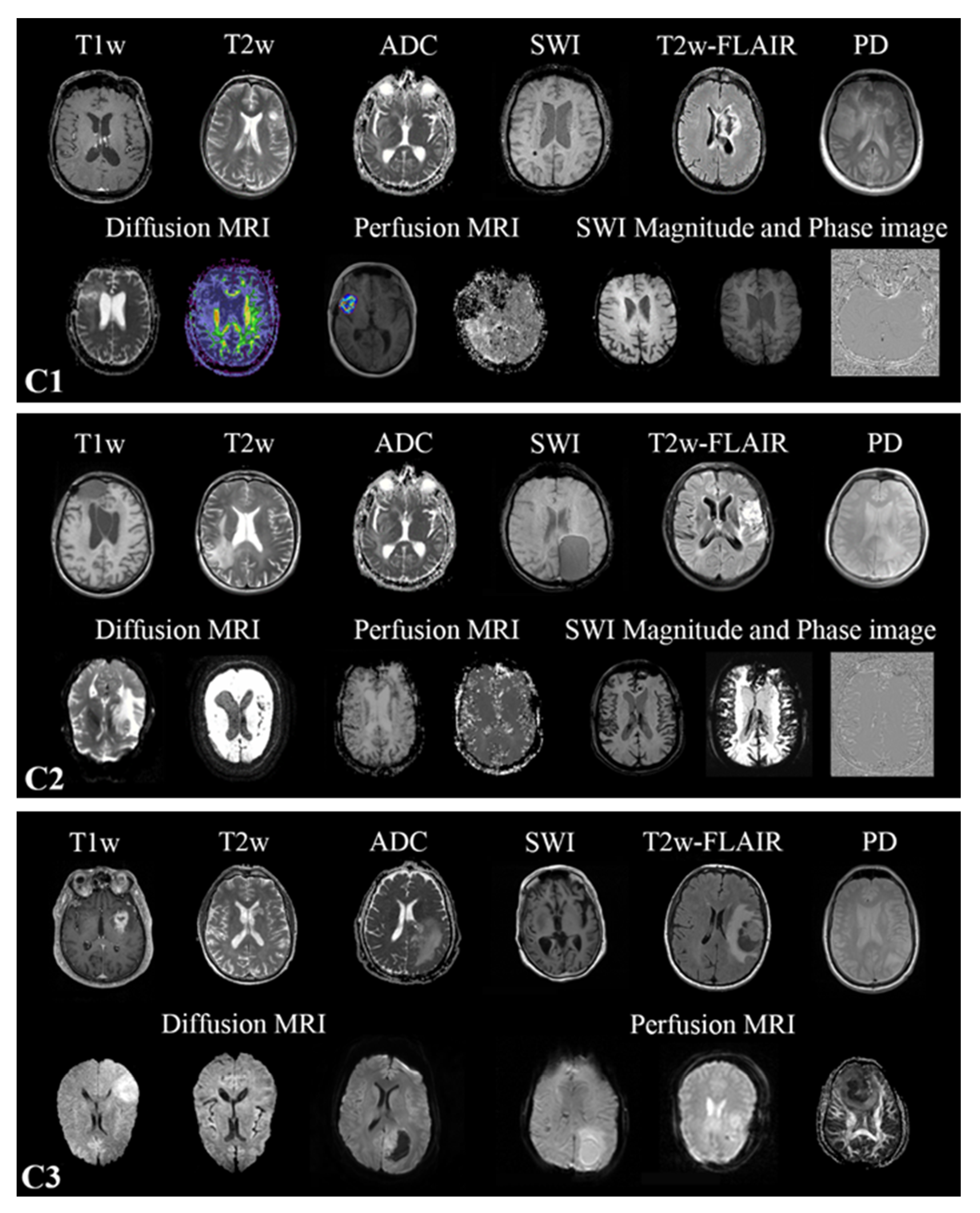
2.1. Datasets
2.2. MR Scans
2.3. DCNNs Comparison Study
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing
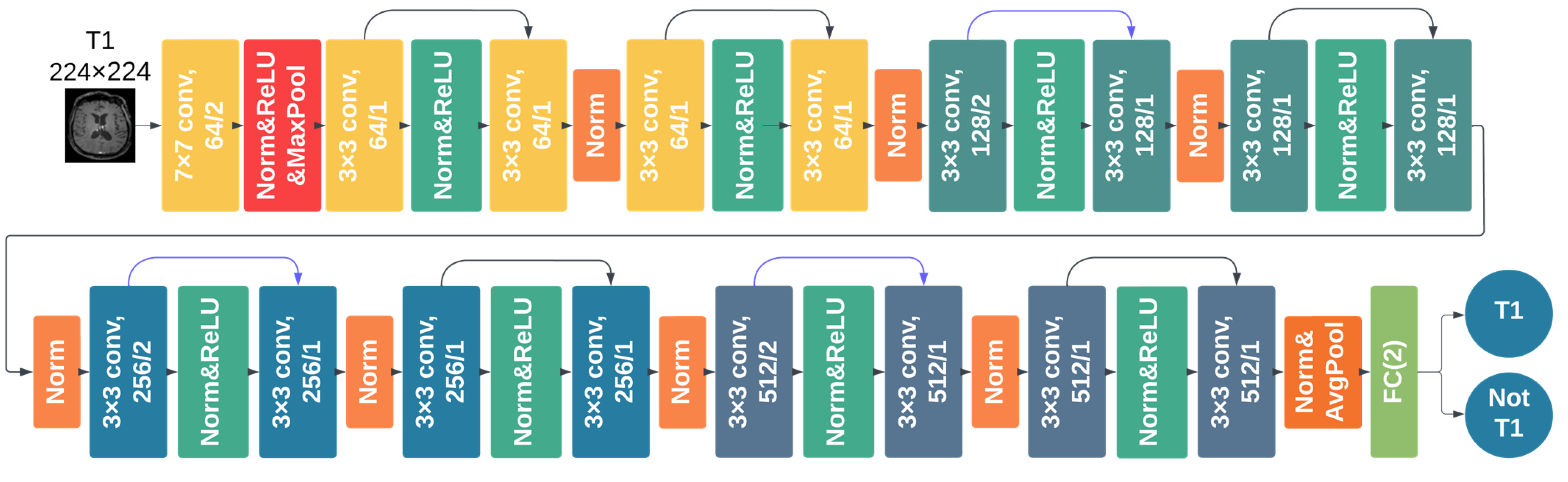
2.3.2. DCNN Training and Testing
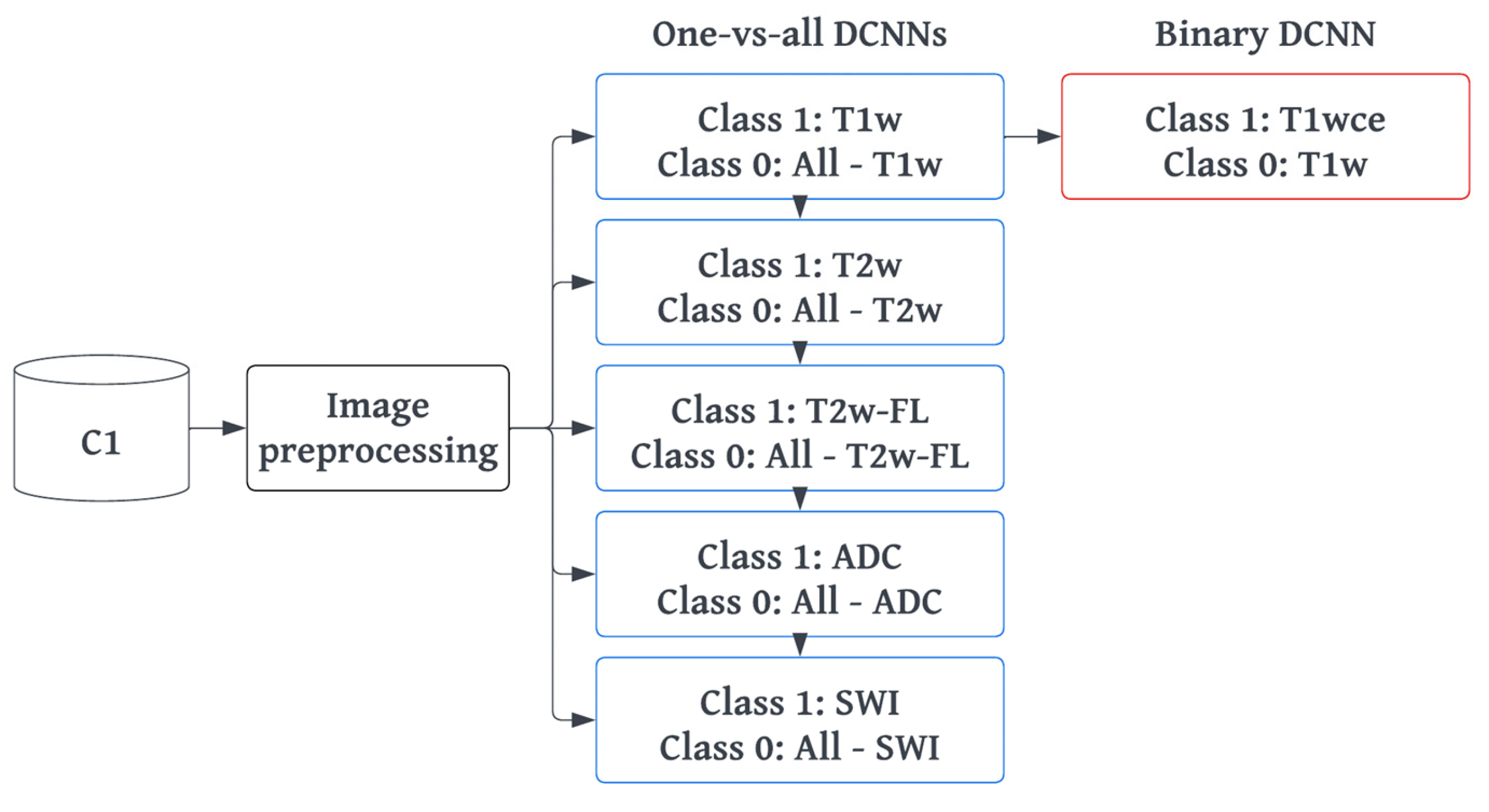
2.4. MR-Class: One-vs-All DCNNs
2.4.1. Training and Preprocessing
2.4.2. Inference and Testing
2.5. MR-Class Application: Progression-Free Survival Prediction Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Metadata Consistency
3.2. DCNN Comparison Study
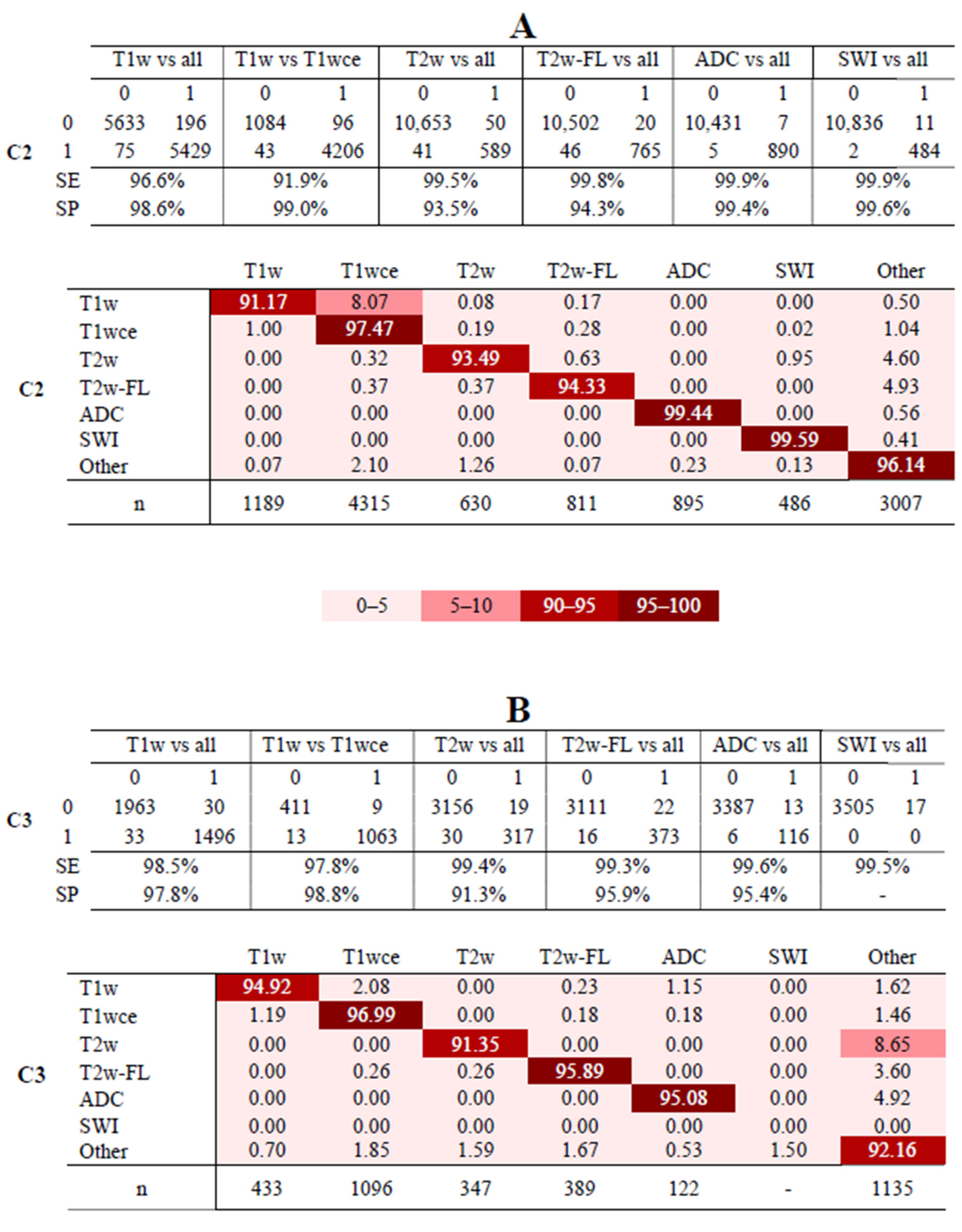
3.3. MR-Class: One-vs-All DCNNs
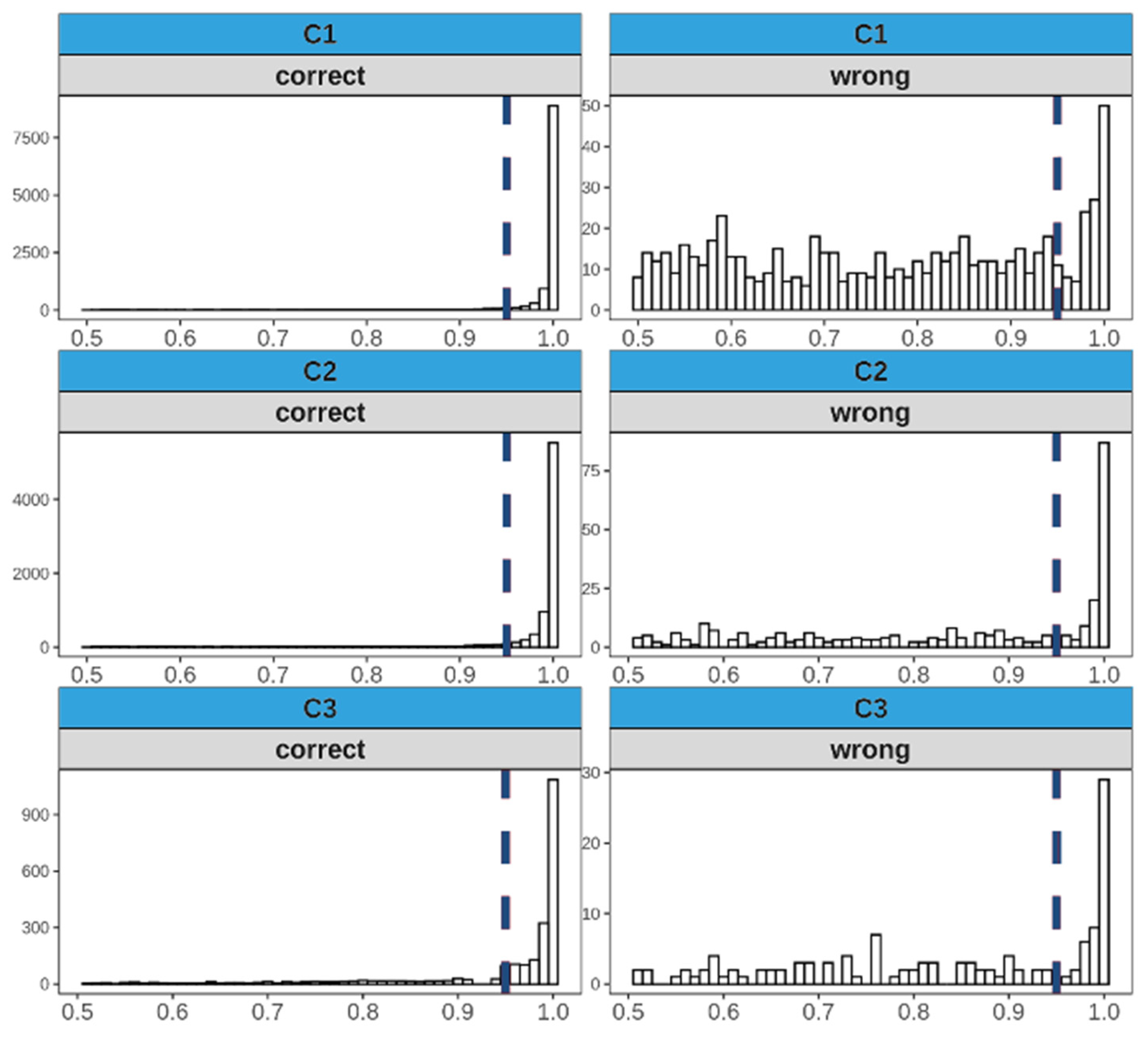
3.4. Analyses of Misclassified Images
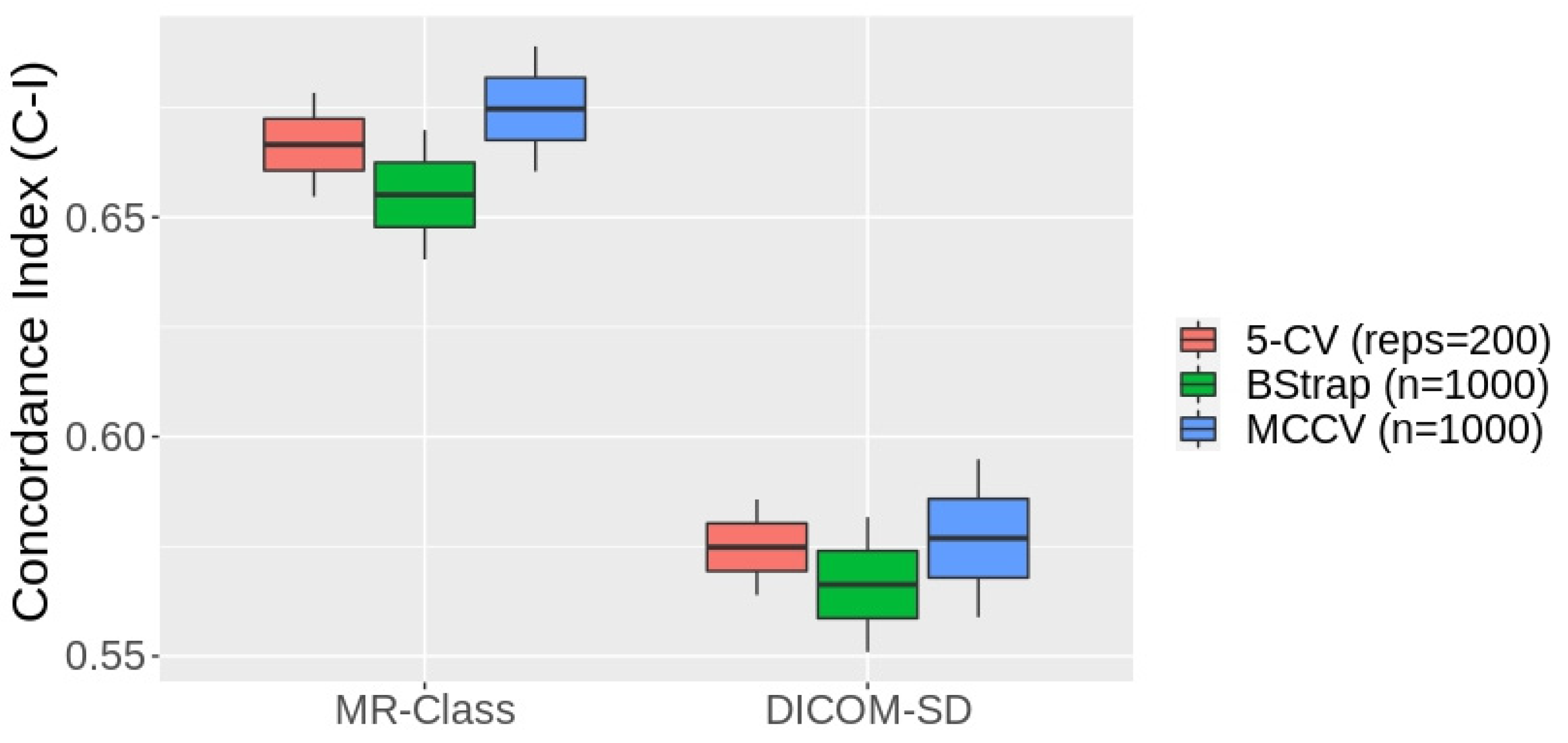
3.5. MR-Class Application: Progression-Free Survival Prediction Modeling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Westbrook, C.; Talbot, J. MRI in Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kickingereder, P.; Isensee, F.; Tursunova, I.; Petersen, J.; Neuberger, U.; Bonekamp, D.; Brugnara, G.; Schell, M.; Kessler, T.; Foltyn, M.; et al. Automated quantitative tumour response assessment of MRI in neuro-oncology with artificial neural networks: A multicentre, retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueld, M.O.; Kohnen, M.; Keysers, D.; Schubert, H.; Wein, B.B.; Bredno, J.; Lehmann, T.M. Quality of DICOM header information for image categorization. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2002: PACS and Integrated Medical Information Systems: Design and Evaluation, San Diego, CA, USA, 16 May 2002; pp. 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, H.; Glocker, B. A standardized approach for preparing imaging data for machine learning tasks in radiology. In Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Névéol, A.; Deserno, T.M.; Darmoni, S.J.; Güld, M.O.; Aronson, A.R. Natural language processing versus content-based image analysis for medical document retrieval. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, S.; Mangai, J.A.; Kumar, V.S. An improved medical image classification model using data mining techniques. In Proceedings of the 2013 7th IEEE GCC Conference and Exhibition (GCC), Doha, Qatar, 17–20 November 2013; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Varol, E.; Gaonkar, B.; Erus, G.; Schultz, R.; Davatzikos, C. Feature ranking based nested support vector machine ensemble for medical image classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Barcelona, Spain, 2–5 May 2012; pp. 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.-I. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Van Esesn, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.; Asari, V.K. The history began from alexnet: A comprehensive survey on deep learning approaches. arXiv 2018, arXiv:180301164. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Tang, W.; Xu, D.M.; Jirapatnakul, A.C.; Reeves, A.P.; Henschke, C.I.; Yankelevitz, D. Low-Dose CT Screening for Lung Cancer: Computer-aided Detection of Missed Lung Cancers. Radiology 2016, 281, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setio, A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Litjens, G.; Gerke, P.; Jacobs, C.; van Riel, S.J.; Wille, M.M.; Naqibullah, M.; Sanchez, C.I.; van Ginneken, B. Pulmonary Nodule Detection in CT Images: False Positive Reduction Using Multi-View Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Liu, K.; Hou, B.; Zhang, N. 3D multi-view convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Awais, M.; Majid, M. Medical image retrieval using deep convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 2017, 266, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyachamy, S.; Alex, V.; Khened, M.; Krishnamurthi, G. Medical image retrieval using Resnet-18. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–21 February 2019; Volume 1095410, pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Remedios, S.; Roy, S.; Pham, D.L.; Butman, J.A. Classifying magnetic resonance image modalities with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging, Houston, TX, USA, 10–15 February 2018; Volume 10575, pp. 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Voort, S.R.; Smits, M.; Klein, S. DeepDicomSort: An Automatic Sorting Algorithm for Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data. Neuroinformatics 2021, 19, 159–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheirer, W.J.; de Rezende Rocha, A.; Sapkota, A.; Boult, T.E. Toward open set recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1757–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpace, L.; Mikkelsen, L.; Cha, T.; Rao, S.; Tekchandani, S.; Gutman, S.; Pierce, D. Radiology Data from the Cancer Genome Atlas Glioblastoma Multiforme [TCGA-GBM] Collection. The Cancer Imaging Archive. 2016. Available online: https://www.cancerimagingarchive.net (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Ellingson, B.M.; Bendszus, M.; Boxerman, J.; Barboriak, D.; Erickson, B.J.; Smits, M.; Nelson, S.J.; Gerstner, E.; Alexander, B.; Goldmacher, G.; et al. Consensus recommendations for a standardized Brain Tumor Imaging Protocol in clinical trials. Neuro. Oncol. 2015, 17, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Combs, S.E.; Kieser, M.; Rieken, S.; Habermehl, D.; Jäkel, O.; Haberer, T.; Nikoghosyan, A.; Haselmann, R.; Unterberg, A.; Wick, W.; et al. Randomized phase II study evaluating a carbon ion boost applied after combined radiochemotherapy with te-mozolomide versus a proton boost after radiochemotherapy with temozolomide in patients with primary glioblastoma: The CLEOPATRA Trial. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.E.; Burkholder, I.; Edler, L.; Rieken, S.; Habermehl, D.; Jäkel, O.; Haberer, T.; Haselmann, R.; Unterberg, A.; Wick, W.; et al. Randomized phase I/II study to evaluate carbon ion radiotherapy versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with recurrent or progressive gliomas: The CINDERELLA trial. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyazi, M.; Adeberg, S.; Kaul, D.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Bougatf, N.; Fleischmann, D.F.; Grün, A.; Krämer, A.; Rödel, C.; Eckert, F.; et al. Independent validation of a new reirradiation risk score (RRRS) for glioma patients predicting post-recurrence survival: A multicenter DKTK/ROG analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14091556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García, F.; Sparks, R.; Ourselin, S. TorchIO: A Python library for efficient loading, preprocessing, augmentation and patch-based sampling of medical images in deep learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, S. Binomial Confidence Intervals and Contingency Tests: Mathematical Fundamentals and the Evaluation of Alter-native Methods. J. Quant. Linguist. 2013, 20, 178–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.Y.; Wei, L.J. The robust inference for the Cox proportional hazards model. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J. Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, H.; Saxe, J. Garbage in, Garbage out: How Purportedly Great ML Models can be Screwed up by Bad Data. In Proceedings of the Black Hat, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–27 July 2017; Available online: https://www.blackhat.com/us-17/call-for-papers.html#review (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Sforazzini, F.; Salome, P.; Kudak, A.; Ulrich, M.; Bougatf, N.; Debus, J.; Knoll, M.; Abdollahi, A. pyCuRT: An Automated Data Cura-tion Workflow for Radiotherapy Big Data Analysis using Pythons’ NyPipe. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, e772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Training | Validation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCNN Classifier | Targeted Class | Remaining Images | Targeted Class | Remaining Images |
| T1w-vs-all | 3152 (15.7) | 12,929 (64.3) | 788 (3.9) | 3232 (16.1) |
| T2w-vs-all | 1576 (7.9) | 14,505 (72.1) | 394 (2.0) | 3626 (18.0) |
| T2w-FL-vs-all | 1535 (7.6) | 14,546 (72.4) | 384 (1.9) | 3636 (18.1) |
| ADC-vs-all | 1550 (7.7) | 14,530 (72.3) | 388 (1.9) | 3633 (18.1) |
| SWI-vs-all | 1183 (5.9) | 14,898 (74.1) | 296 (1.5) | 3724 (18.5) |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % Error | n | % Error | n | % Error | |
| T1w | 2023 | 15.1 | 1189 | 11.2 | 433 | 13.4 |
| T1wce | 1917 | 13.9 | 4315 | 13.4 | 1096 | 9.9 |
| T2w | 1970 | 9.3 | 630 | 11.7 | 347 | 10.3 |
| T2w-FL | 1919 | 7.2 | 811 | 10.5 | 389 | 8.2 |
| ADC | 1938 | 7.6 | 895 | 8.4 | 122 | 5.5 |
| SWI | 1479 | 6.3 | 486 | 6.6 | - | - |
| Other | 8855 | 13.1 | 3007 | 7.3 | 1135 | 12.1 |
| All | 20,101 | 11.4 | 11,333 | 10.6 | 3522 | 10.7 |
| 2D-ResNet | DeepDicomSort | Φ-Net | 3D-ResNet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1w | 98.4 | 98.8 | 97.7 | 96.5 |
| T1wce | 97.4 | 95.2 | 97.5 | 96.2 |
| T2w | 98.1 | 97.2 | 96.6 | 97.1 |
| T2w-FL | 99.7 | 99.4 | 96.5 | 98.7 |
| ADC | 99.9 | 99.3 | 98.5 | 99.2 |
| SWI | 98.2 | 98.5 | 97.5 | 98.9 |
| All | 98.6 | 98.1 | 97.4 | 97.8 |
| Classifier | Val Acc (%) | Classifier | Val Acc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1w-vs-all | 99.1 | T2wFL-vs-all | 99.4 |
| T1w-vs-T1wce | 97.7 | ADC-vs-all | 99.6 |
| T2w-vs-all | 99.3 | SWI-vs-all | 99.7 |
| Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| MR artifact-other | 146 | 26.84 |
| MR artifact-middle slice blurring | 127 | 23.35 |
| Tumor/GTV displacing ventricles | 122 | 22.43 |
| Similar content-different sequence | 80 | 14.71 |
| DWI as T2w | 76 | 13.97 |
| DICOM corrupted images | 69 | 12.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salome, P.; Sforazzini, F.; Brugnara, G.; Kudak, A.; Dostal, M.; Herold-Mende, C.; Heiland, S.; Debus, J.; Abdollahi, A.; Knoll, M. MR-Class: A Python Tool for Brain MR Image Classification Utilizing One-vs-All DCNNs to Deal with the Open-Set Recognition Problem. Cancers 2023, 15, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061820
Salome P, Sforazzini F, Brugnara G, Kudak A, Dostal M, Herold-Mende C, Heiland S, Debus J, Abdollahi A, Knoll M. MR-Class: A Python Tool for Brain MR Image Classification Utilizing One-vs-All DCNNs to Deal with the Open-Set Recognition Problem. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061820
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalome, Patrick, Francesco Sforazzini, Gianluca Brugnara, Andreas Kudak, Matthias Dostal, Christel Herold-Mende, Sabine Heiland, Jürgen Debus, Amir Abdollahi, and Maximilian Knoll. 2023. "MR-Class: A Python Tool for Brain MR Image Classification Utilizing One-vs-All DCNNs to Deal with the Open-Set Recognition Problem" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061820
APA StyleSalome, P., Sforazzini, F., Brugnara, G., Kudak, A., Dostal, M., Herold-Mende, C., Heiland, S., Debus, J., Abdollahi, A., & Knoll, M. (2023). MR-Class: A Python Tool for Brain MR Image Classification Utilizing One-vs-All DCNNs to Deal with the Open-Set Recognition Problem. Cancers, 15(6), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061820







