ATF4 Transcriptionally Activates SHH to Promote Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.2. Cell Transfection
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Colony Formation
2.6. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
2.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
2.8. Xenotransplantation Experiment [27]
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
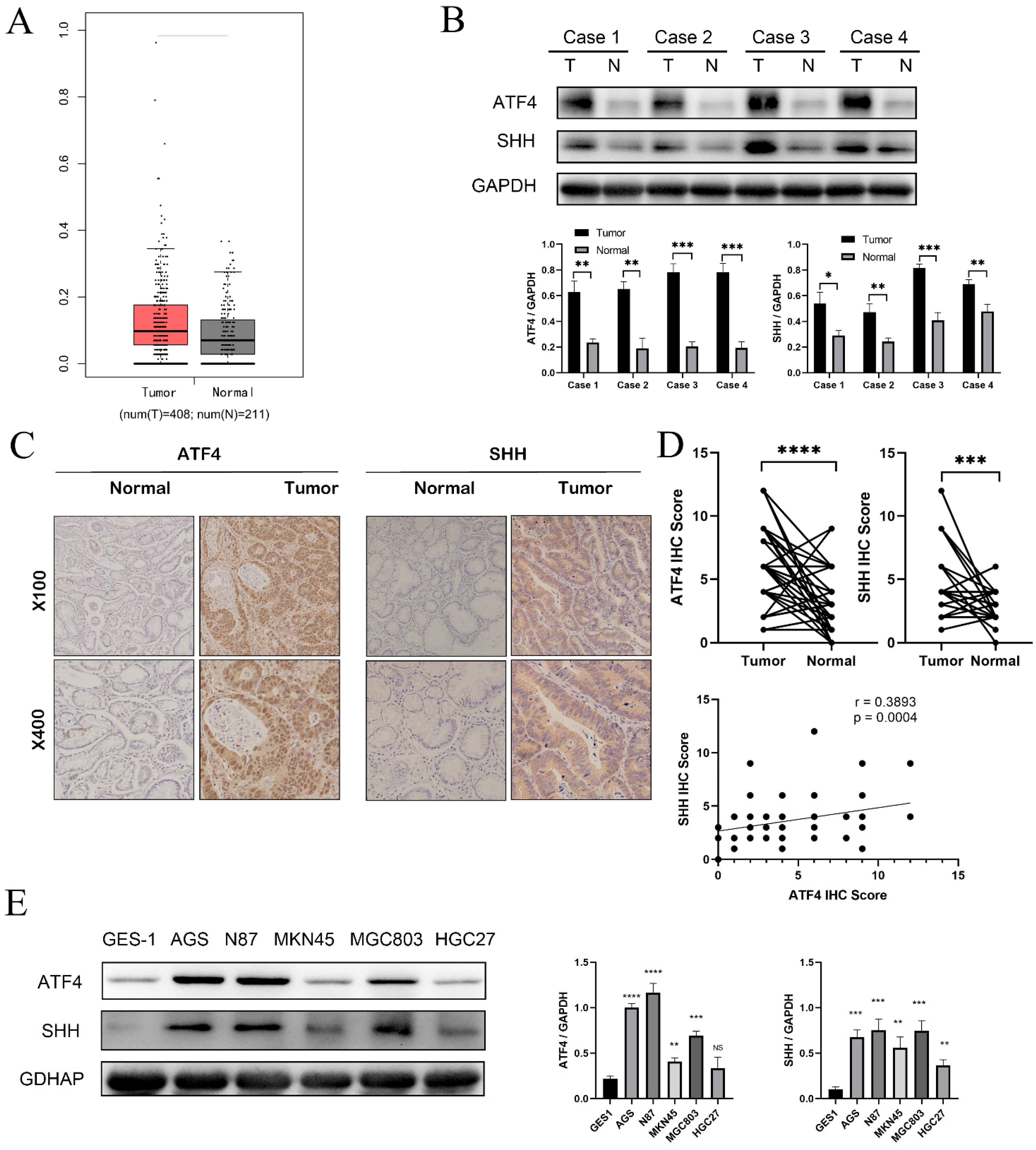
3.1. The Expression of ATF4 Is Increased in Gastric Cancer Tissues and Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
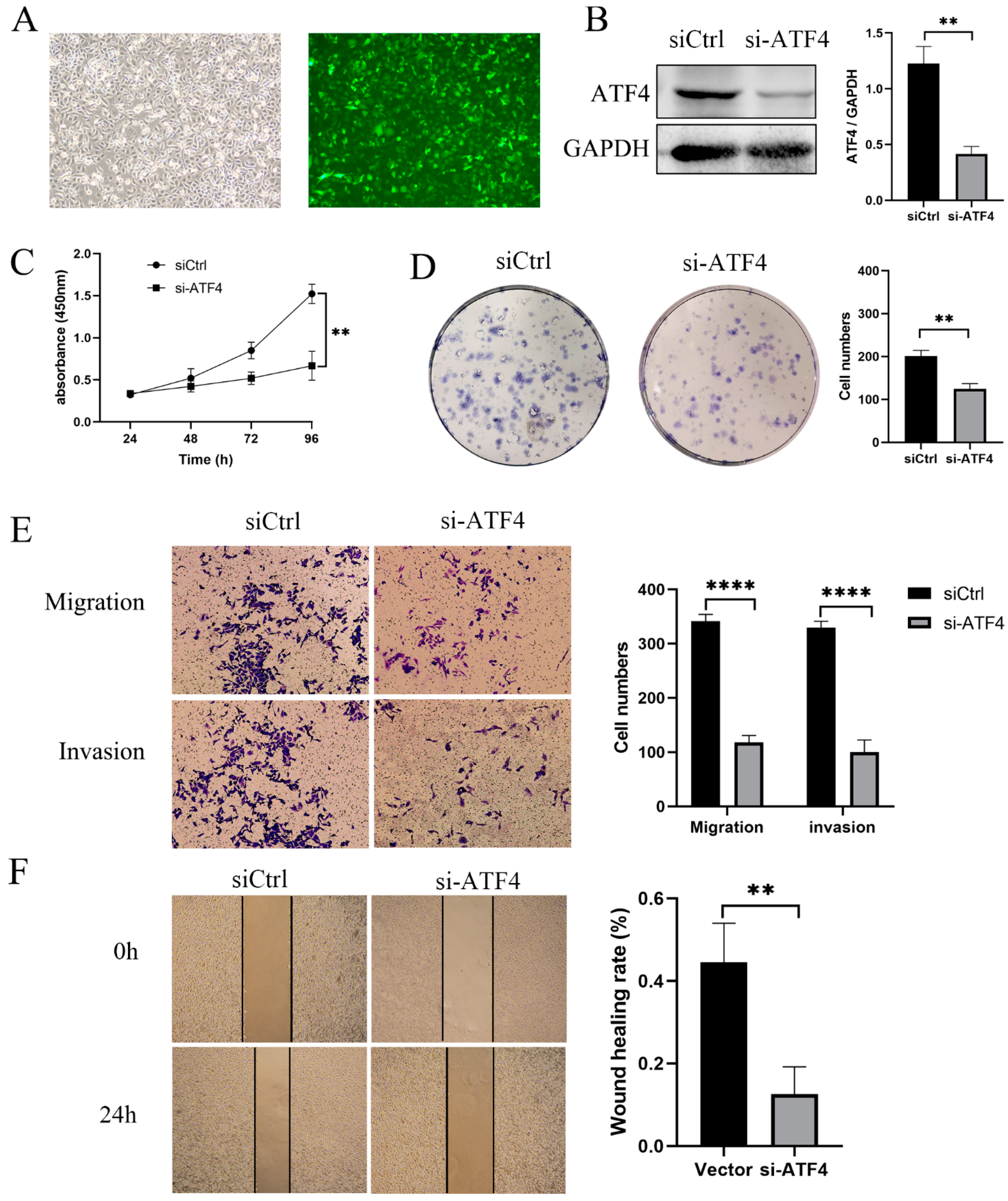
3.2. ATF4 Knockdown Strongly Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of GC Cells
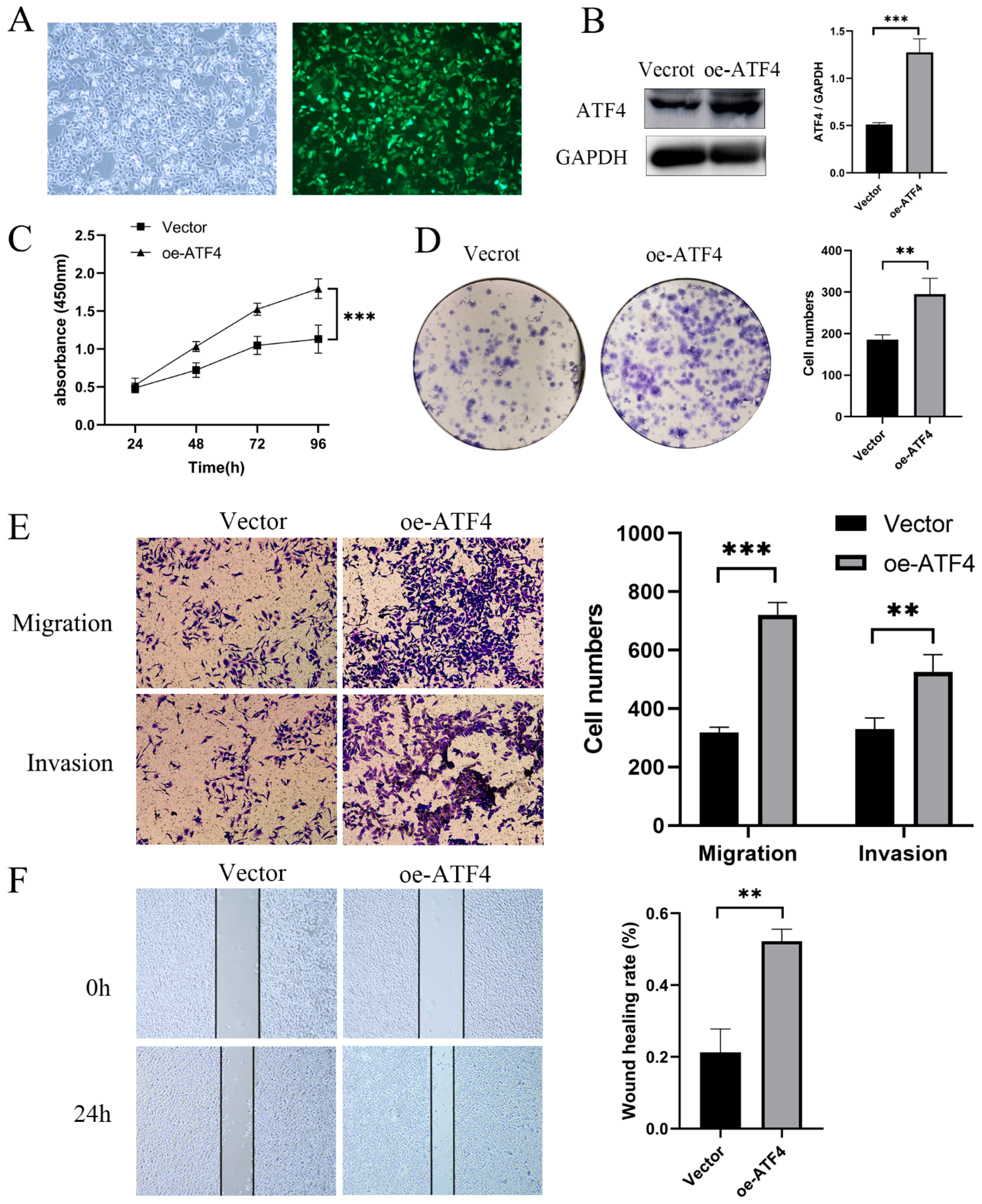
3.3. ATF4 Upregulation Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of GC Cells
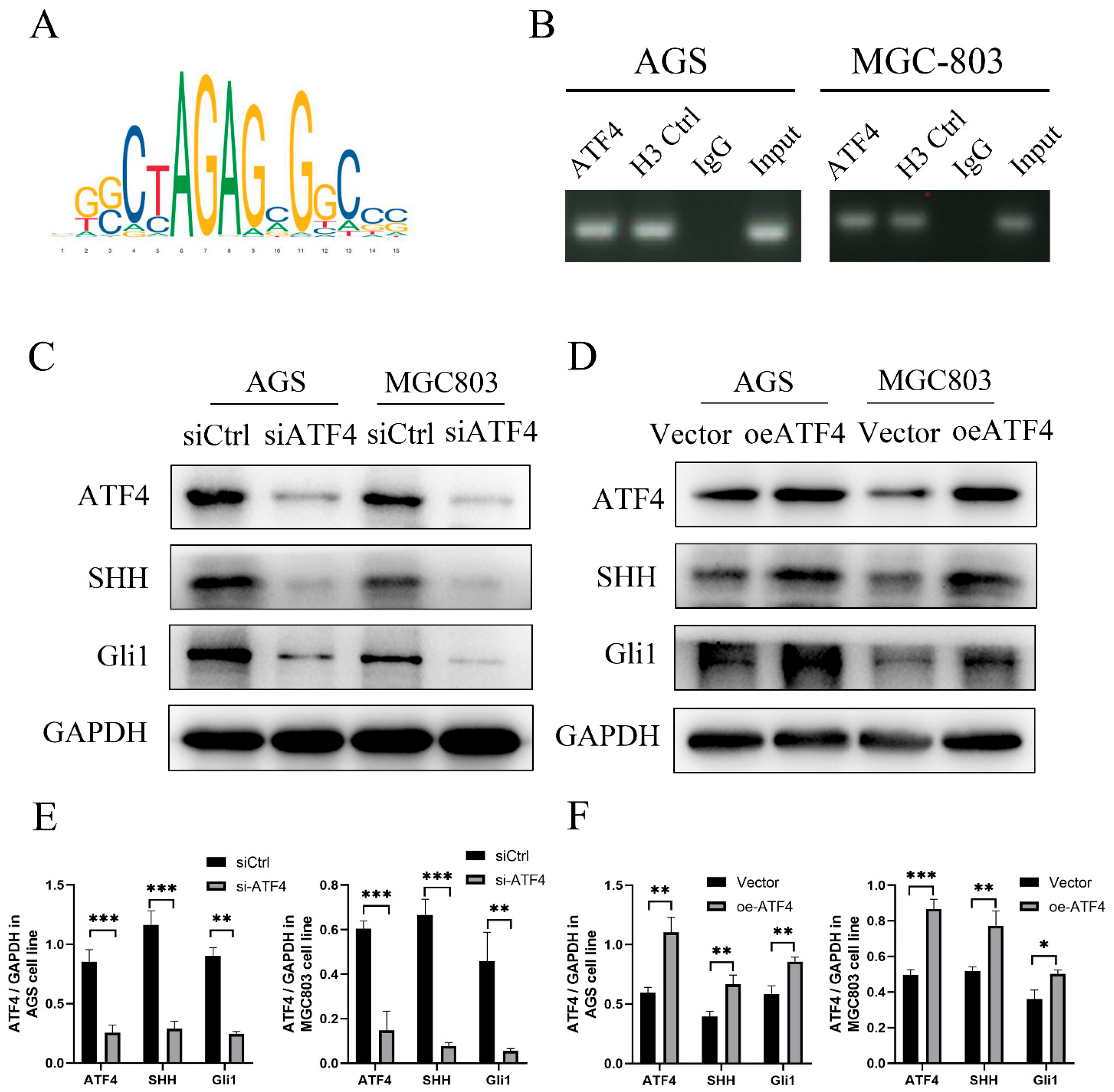
3.4. Transcription Factor ATF4 binds to the Promoter Region of SHH to Activate the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway
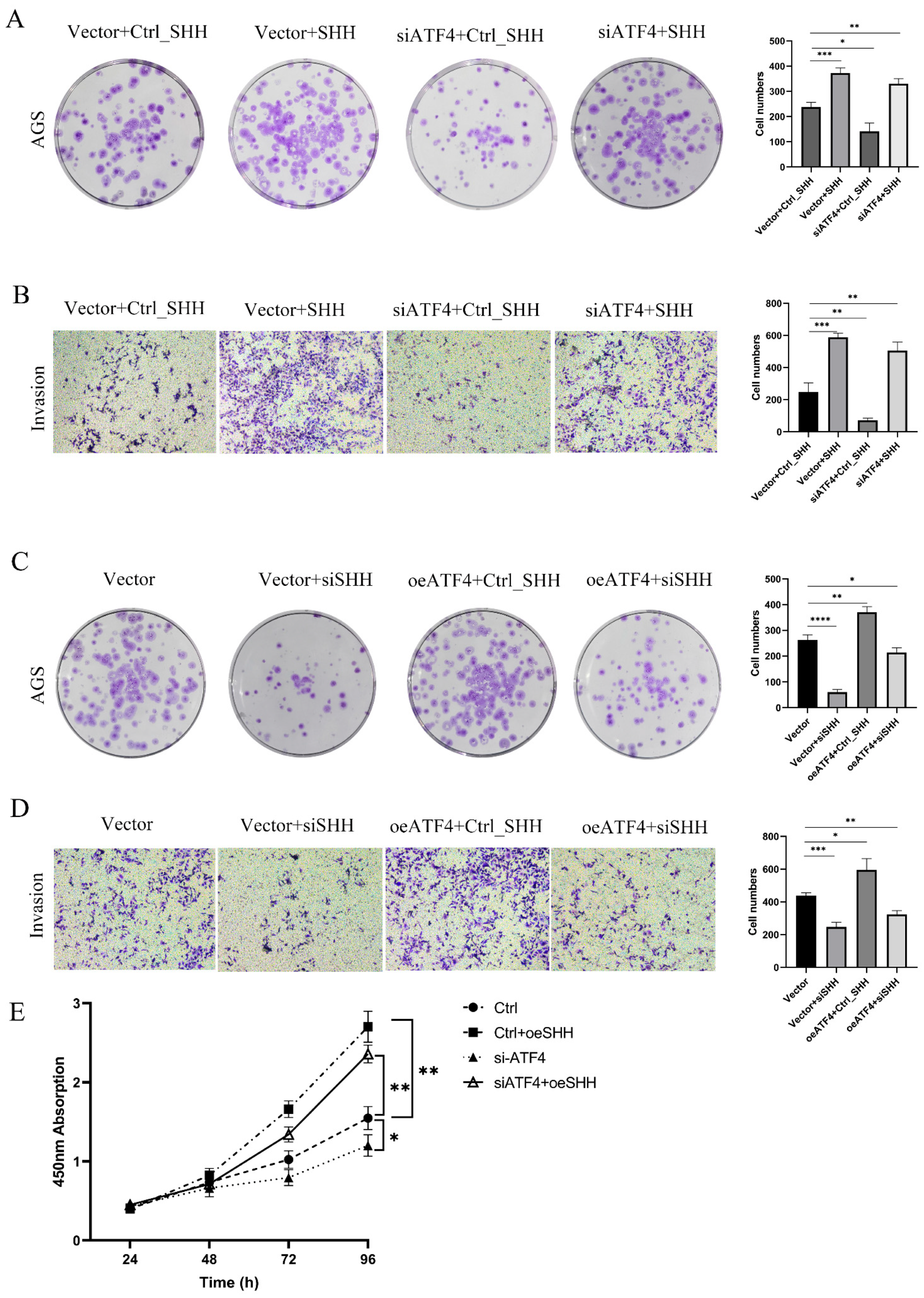
3.5. ATF4 Regulates the Proliferation and Invasive Ability of Gastric Cancer Cells through SHH
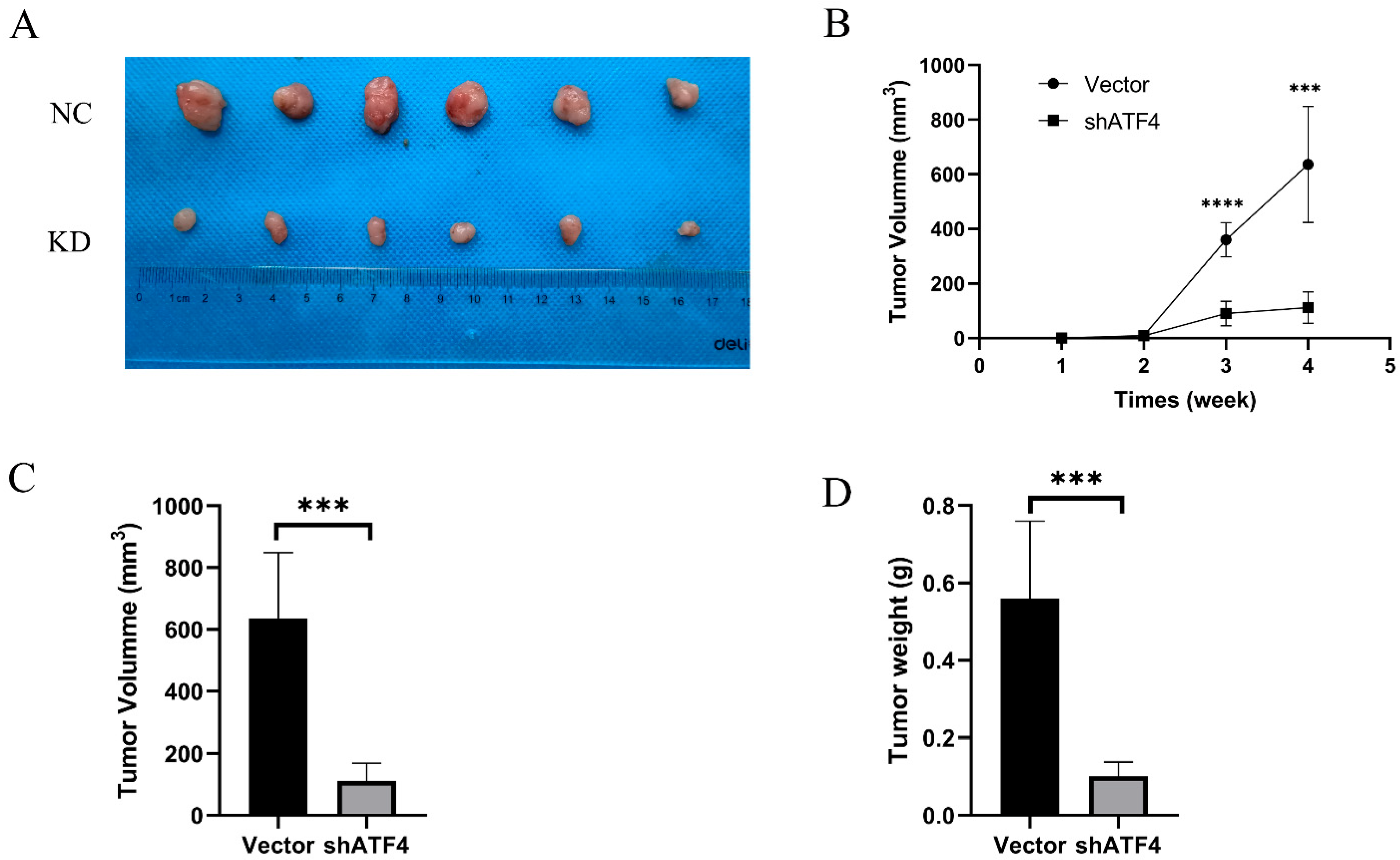
3.6. ATF4 Enhanced Tumor Formation of Gastric Cancer Cells in a Xenograft Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Chinese guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer 2018 (English version). Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 31, 707–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrift, A.P.; El-Serag, H.B. Burden of Gastric Cancer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koditz, J.; Nesper, J.; Wottawa, M.; Stiehl, D.P.; Camenisch, G.; Franke, C.; Myllyharju, J.; Wenger, R.H.; Katschinski, D.M. Oxygen-dependent ATF-4 stability is mediated by the PHD3 oxygen sensor. Blood 2007, 110, 3610–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.A.; Hai, T.Y.; SivaRaman, L.; Thimmappaya, B.; Hurst, H.C.; Jones, N.C.; Green, M.R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 8355–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, K.; Erlenbach-Wuensch, K.; Prochazka, J.; Sheraj, I.; Hampel, C.; Mrazkova, B.; Michalcikova, T.; Tureckova, J.; Iatsiuk, V.; Weissmann, A.; et al. ATF2 loss promotes tumor invasion in colorectal cancer cells via upregulation of cancer driver TROP2. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Lv, D.; Jin, G.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Fei, X. ATF-3/miR-590/GOLPH3 signaling pathway regulates proliferation of breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, R.; Romeo, M.A.; Arena, A.; Gilardini, M.M.; Di Renzo, L.; D’Orazi, G.; Cirone, M. ATF6 prevents DNA damage and cell death in colon cancer cells undergoing ER stress. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.A.; Otto, E.A.; O’Toole, J.F.; Nurnberg, G.; Kennedy, M.A.; Becker, C.; Hennies, H.C.; Helou, J.; Attanasio, M.; Fausett, B.V.; et al. The centrosomal protein nephrocystin-6 is mutated in Joubert syndrome and activates transcription factor ATF4. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ye, F.; Wen, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yu, C.; Huang, W.K.; Rojas, R.F.; Su, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, G.; et al. Structural interaction between DISC1 and ATF4 underlying transcriptional and synaptic dysregulation in an iPSC model of mental disorders. Mol. Psychiatr. 2021, 26, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsterda, A.; Asha, K.; Powrozek, O.; Repak, M.; Goswami, S.; Dunn, A.M.; Memmel, H.C.; Sharma-Walia, N. Salubrinal Exposes Anticancer Properties in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells by Manipulating the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 654940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.S.; Salji, M.J.; Rushworth, L.; Ntala, C.; Rodriguez, B.G.; Hedley, A.; Clark, W.; Peixoto, P.; Hervouet, E.; Renaude, E.; et al. SLFN5 Regulates LAT1-Mediated mTOR Activation in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3664–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zeng, C.; Zou, T.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z. Autophagy Induction by Trichodermic Acid Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Aviles, G.; Liu, Y.; Tian, R.; Unger, B.A.; Lin, Y.T.; Wiita, A.P.; Xu, K.; Correia, M.A.; Kampmann, M. Mitochondrial stress is relayed to the cytosol by an OMA1-DELE1-HRI pathway. Nature 2020, 579, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.F.; Cordes, T.; Duran, A.; Reina-Campos, M.; Valencia, T.; Ahn, C.S.; Castilla, E.A.; Moscat, J.; Metallo, C.M.; Diaz-Meco, M.T. ATF4-Induced Metabolic Reprograming Is a Synthetic Vulnerability of the p62-Deficient Tumor Stroma. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Dai, W.; Kutzler, L.; Lacko, H.A.; Jefferson, L.S.; Dennis, M.D.; Kimball, S.R. ATF4-Mediated Upregulation of REDD1 and Sestrin2 Suppresses mTORC1 Activity during Prolonged Leucine Deprivation. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kaufman, R.J. The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Hendershot, L.M. The role of the unfolded protein response in tumour development: Friend or foe? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilberg, M.S.; Shan, J.; Su, N. ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid limitation. Trends Endocrin. Met. 2009, 20, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B’Chir, W.; Maurin, A.C.; Carraro, V.; Averous, J.; Jousse, C.; Muranishi, Y.; Parry, L.; Stepien, G.; Fafournoux, P.; Bruhat, A. The eIF2alpha/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced autophagy gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 7683–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douard, R.; Moutereau, S.; Pernet, P.; Chimingqi, M.; Allory, Y.; Manivet, P.; Conti, M.; Vaubourdolle, M.; Cugnenc, P.H.; Loric, S. Sonic Hedgehog-dependent proliferation in a series of patients with colorectal cancer. Surgery 2006, 139, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoda, A.M.; Simovic, D.; Karin, V.; Kardum, V.; Vranic, S.; Serman, L. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. 2018, 18, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, M.; Wei, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H. Sonic hedgehog pathway contributes to gastric cancer cell growth and proliferation. Biores. Open Access 2014, 3, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqui-Salces, M.; Merchant, J.L. Hedgehog signaling and gastrointestinal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1803, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Shi, Q.; Song, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Phosphoglycerate kinase-1 is a predictor of poor survival and a novel prognostic biomarker of chemoresistance to paclitaxel treatment in breast cancer. Brit. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ali, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.N.; Zhu, X.D.; Tang, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Wang, D.R. Galectin-1 binds GRP78 to promote the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 61, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, A.; Munoz-Muela, E.; Marchal, J.A.; Cara, F.E.; Molina, M.P.; Cruz-Lozano, M.; Jimenez, G.; Verma, A.; Ramirez, A.; Qian, W.; et al. Activating Transcription Factor 4 Modulates TGFbeta-Induced Aggressiveness in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via SMAD2/3/4 and mTORC2 Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5697–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, H.; Mao, X.; Qin, Y.; Fan, C. ATF4 promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion partially through regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, L.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Fu, S.W.; Wu, Z.W.; Du, B.B.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, W.S.; Hao, X.Y.; Guo, T.K. Ribosome assembly factor URB1 contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation through transcriptional activation of ATF4. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, J.; Song, P.; Yousafzai, N.A.; Feng, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Targeting ATF4-dependent pro-survival autophagy to synergize glutaminolysis inhibition. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8464–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Y. High ATF4 Expression Is Associated With Poor Prognosis, Amino Acid Metabolism, and Autophagy in Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 740120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten, H.A.; Bektas, N.; von Serenyi, S.; Losen, I.; Arweiler, E.C.; Hartmann, A.; Knuchel, R.; Dahl, E. Expression of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog (GLI) 1 in human breast cancer is associated with unfavourable overall survival. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Wang, Q.S.; Zhao, W.M.; Xiang, L. Expression of smoothened protein in colon cancer and its prognostic value for postoperative liver metastasis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4001–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.; Fritz, S.; Bolm, L.; Wellner, U.F.; Fernandez-Del-Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Liss, A.S. Hedgehog signaling promotes angiogenesis directly and indirectly in pancreatic cancer. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, K.A.; Krauss, R.S. Murine models of holoprosencephaly. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2008, 84, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, M.; Ohta, M.; Asaoka, Y.; Ikenoue, T.; Tada, M.; Miyabayashi, K.; Mohri, D.; Tanaka, Y.; Ijichi, H.; Tateishi, K.; et al. Regulation of the hedgehog signaling by the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in gastric cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, J.L. Hedgehog signalling in gut development, physiology and cancer. J. Physiol.-Lond. 2012, 590, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, J.L.; Ding, L. Hedgehog Signaling Links Chronic Inflammation to Gastric Cancer Precursor Lesions. Cell. Mol. Gastroenter. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, G.R.; Hardwick, J.C.; Nielsen, C.; Xu, C.; Ten, K.F.; Glickman, J.; van Deventer, S.J.; Roberts, D.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Sonic hedgehog expression correlates with fundic gland differentiation in the adult gastrointestinal tract. Gut 2002, 51, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ali, M.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Tang, D.; Wang, D. ATF4 Transcriptionally Activates SHH to Promote Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051429
Wang Y, Ali M, Zhang Q, Sun Q, Ren J, Wang W, Tang D, Wang D. ATF4 Transcriptionally Activates SHH to Promote Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051429
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yang, Muhammad Ali, Qi Zhang, Qiannan Sun, Jun Ren, Wei Wang, Dong Tang, and Daorong Wang. 2023. "ATF4 Transcriptionally Activates SHH to Promote Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051429
APA StyleWang, Y., Ali, M., Zhang, Q., Sun, Q., Ren, J., Wang, W., Tang, D., & Wang, D. (2023). ATF4 Transcriptionally Activates SHH to Promote Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells. Cancers, 15(5), 1429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051429





