Mixed Acinar Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Pancreas: Comparative Population-Based Epidemiology of a Rare and Fatal Malignancy in The United States
Abstract
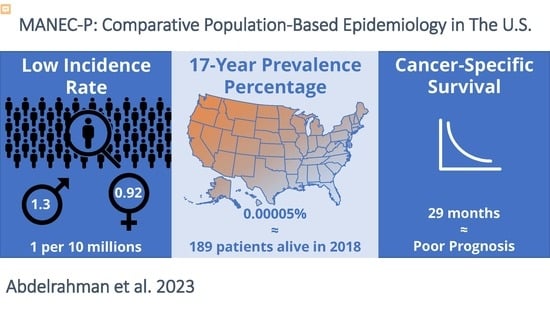
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
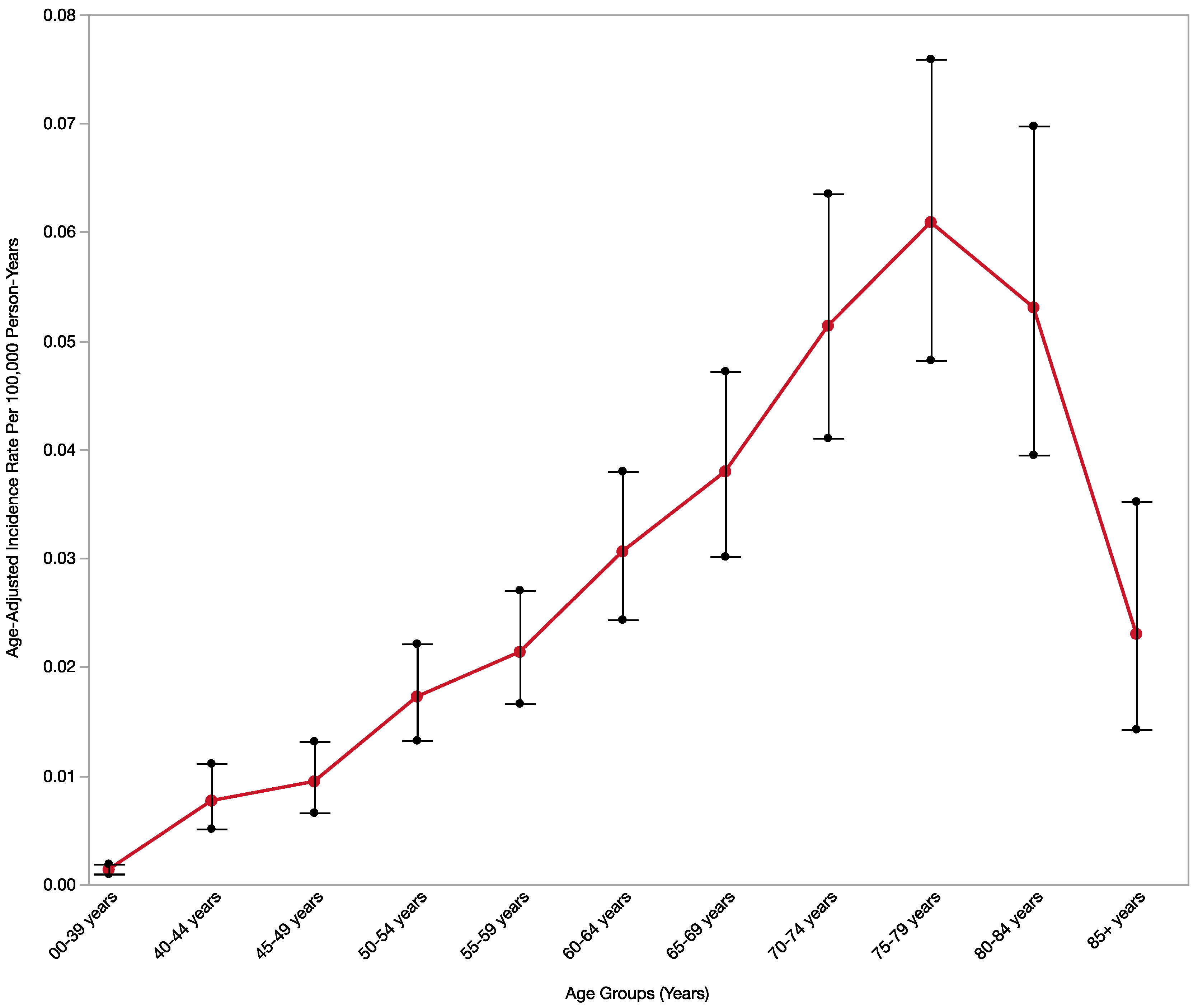
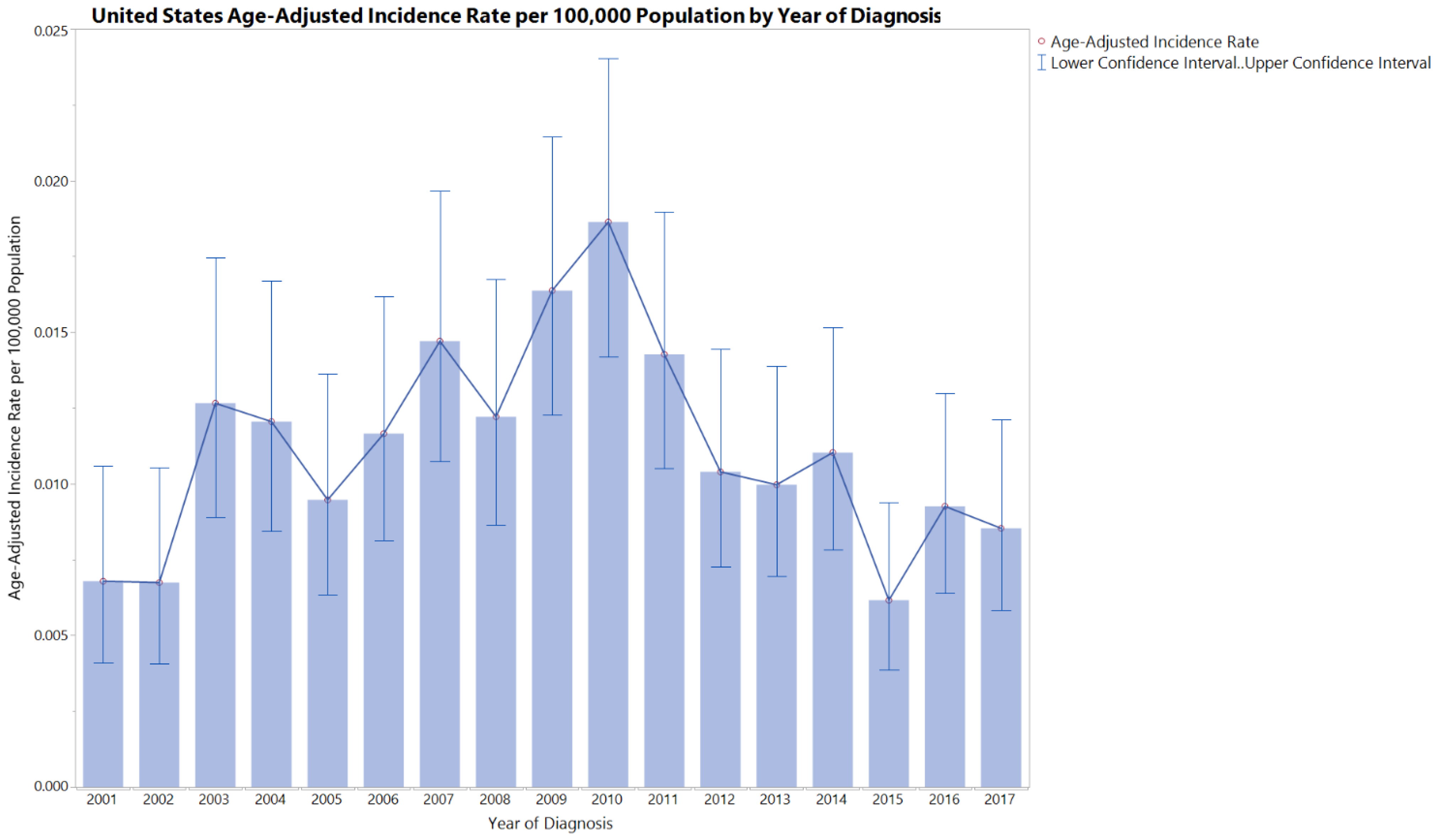
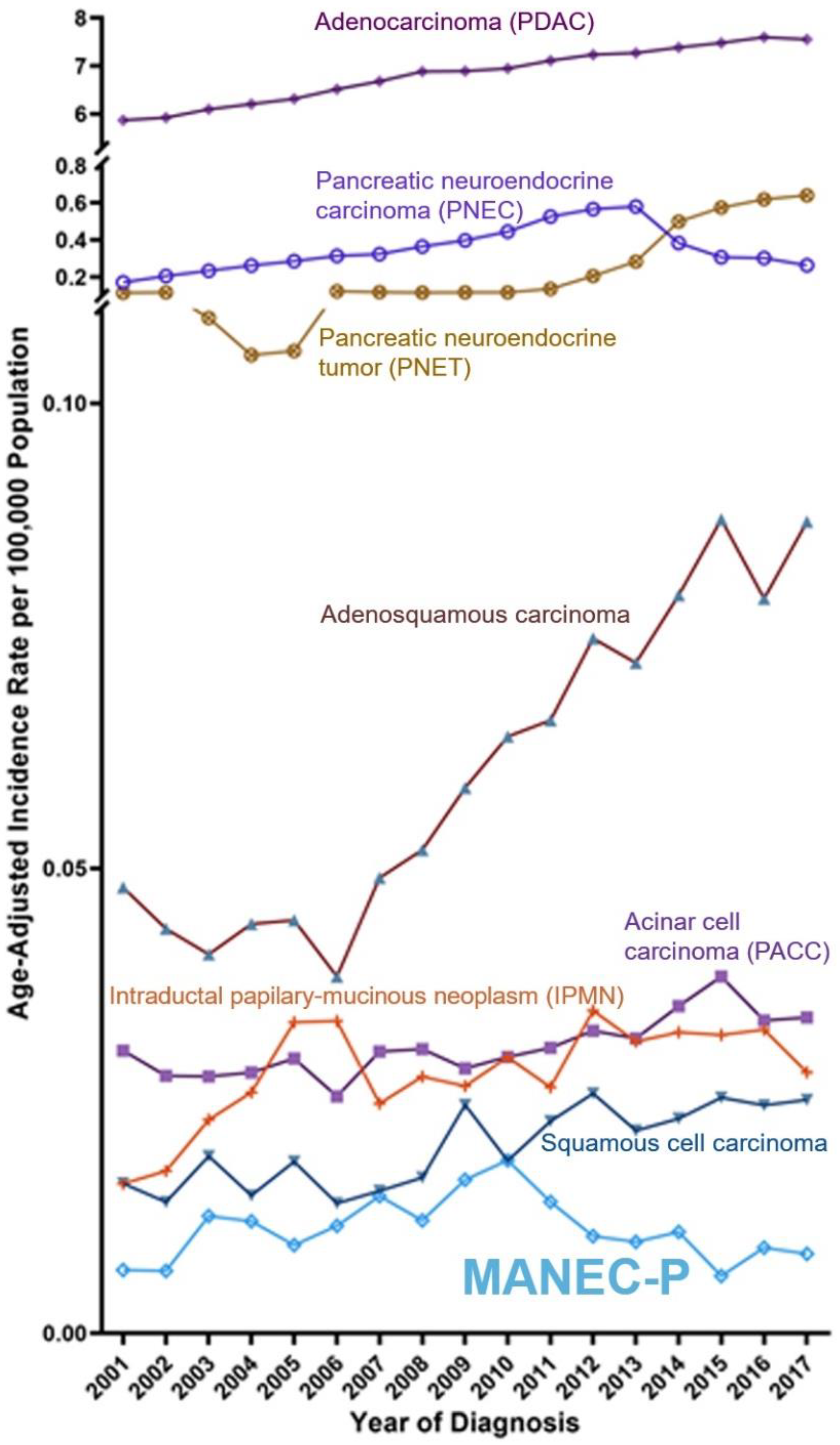
3.1. Incidence Rate
3.2. Prevalence
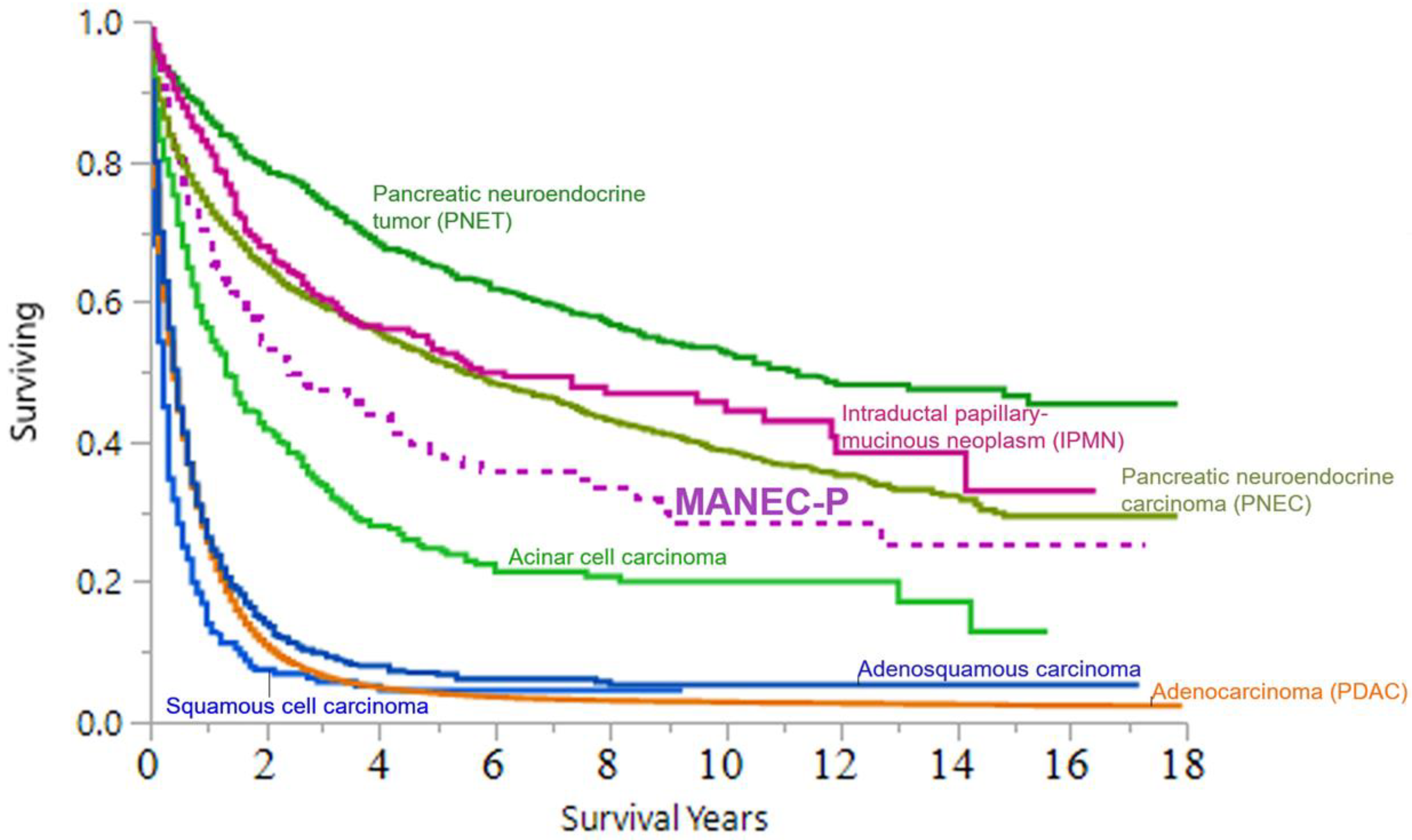
3.3. Cancer-Specific Survival (CSS)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scoazec, J.Y.; Couvelard, A. Classification of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: Changes made in the 2017 WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs and perspectives for the future. Ann. Pathol. 2017, 37, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rindi, G.; Mete, O.; Uccella, S.; Basturk, O.; La Rosa, S.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Ezzat, S.; de Herder, W.W.; Klimstra, D.S.; Papotti, M.; et al. Overview of the 2022 WHO classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms. Endocr. Pathol. 2022, 33, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokode, M.; Itai, R.; Yamashita, Y.; Zen, Y. A case report of mixed acinar-endocrine carcinoma of the pancreas treated with s-1 chemotherapy: Does it work or induce endocrine differentiation? Medicine 2017, 96, e8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niger, M.; Prisciandaro, M.; Antista, M.; Monica, M.A.T.; Cattaneo, L.; Prinzi, N.; Manglaviti, S.; Nichetti, F.; Brambilla, M.; Torchio, M.; et al. One size does not fit all for pancreatic cancers: A review on rare histologies and therapeutic approaches. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagtegaal, I.D.; Odze, R.D.; Klimstra, D.; Paradis, V.; Rugge, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Washington, K.M.; Carneiro, F.; Cree, I.A.; Board, W. The 2019 WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology 2020, 76, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulich, T.; Cheng, L.; Lewin, K.J. Acinar-endocrine cell tumor of the pancreas—Report of a pancreatic tumor containing both zymogen and neuroendocrine granules. Cancer 1982, 50, 2099–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, K. Carcinoid-tumors and the mixed (composite) glandular endocrine cell carcinomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1987, 11, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, O.; Adsay, V.; Hruban, R.H.; Yang, Z.; Giordano, T.J.; Shi, C.; Saka, B.; Klimstra, D.S. Pancreatic acinar cell carcinomas with prominent neuroendocrine differentiation: Clinicopathologic analysis of a distinct and diagnostically challenging neoplasm. Lab. Investig. 2014, 94, 447A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basturk, O.; Tang, L.; Hruban, R.H.; Adsay, V.; Yang, Z.; Krasinskas, A.M.; Vakiani, E.; La Rosa, S.; Jang, K.T.; Frankel, W.L.; et al. Poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinomas of the pancreas: A clinicopathologic analysis of 44 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yang, H.B.; Kim, H.Y. Malignant pancreatic tumor other than solid pseudopapillary tumor in pediatric patients: A single-center experience. Medicine 2021, 100, e27967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywa, C.J.; Abbott, D.E.; Matkowskyj, K.A.; Ronnekleiv-Kelly, S.M.; Winslow, E.R.; Weber, S.M.; Fisher, A.V. Natural history and treatment trends in pancreatic cancer subtypes. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, A.M.; Sharma, N.; Tsapakos, M.J.; Vaickus, L.J.; Liu, X. Pancreatic mixed acinar-neuroendocrine carcinoma, a unique diagnostic challenge on fna cytology: A small series of two cases with literature review. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2018, 46, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, A.; Schimmack, S.; Weber, T.F.; Mayer, P.; Bergmann, F.; Hinz, U.; Buchler, M.W.; Strobel, O. Presentation and outcome of mixed neuroendocrine non-neuroendocrine neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2020, 21, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Sugimura, K.; Moon, J.-H.; Omori, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Tomokuni, A.; Akita, H.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Metastatic mixed acinar-endocrine carcinoma of the pancreas treated with a multidisciplinary approach: A case report. Surg. Case Rep. 2017, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.; Bajor-Dattilo, E.B.; Das, K. Metastatic mixed acinar-neuroendocrine carcinoma of the pancreas to the liver: A cytopathology case report with review of the literature. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2013, 41, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Jih, L.; Zhai, J.; Nissen, N.N.; Colquhoun, S.; Wolin, E.; Dhall, D. Mixed acinar-endocrine carcinoma of the pancreas: New clinical and pathological features in a contemporary series. Pancreas 2013, 42, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Hamaoka, M.; Hoshino, M.; Sasaki, T.; Matsugu, Y.; Nishisaka, T.; Nakahara, H.; Itamoto, T. Mixed neuroendocrine non-neuroendocrine neoplasm: A case report and review. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohike, N.; Kosmahl, M.; Klöppel, G. Mixed acinar–endocrine carcinoma of the pancreas. A clinicopathological study and comparison with acinar-cell carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2004, 445, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Program of Cancer Registries (NPCR): About the Program. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/npcr/about.htm (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Overview of the Seer Program. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/about/overview.html (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. United States Cancer Statistics (USCS): NPCR and Seer Incidence—U.S. Cancer Statistics Public Use Databases. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/public-use/index.htm (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Icd-o-3 Coding Materials. 2020. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/icd-o-3/ (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Kim, H.J.; Fay, M.P.; Feuer, E.J.; Midthune, D.N. Permutation tests for joinpoint regression with applications to cancer rates. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Pancreatic Cancer. 2020. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Pourshams, A.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Ikuta, K.S.; Bisignano, C.; Safiri, S.; Roshandel, G.; Sharif, M.; Khatibian, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Nixon, M.R.; et al. The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.H.; Basturk, O.; Sue, J.J.; Klimstra, D.S. A practical approach to the classification of WHO grade 3 (g3) well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor (wd-net) and poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma (pd-nec) of the pancreas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosman, F.T.; Carneiro, F.; Hruban, R.H.; Theise, N.D. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.A. Challenges and Successes in Reducing Health Disparities: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- National Academies of Sciences and Medicine. Communities in action: Pathways to Health Equity; National Academies of Sciences and Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Census Bureau. 2010 Census Special Reports, Centenarians: 2010 (c2010sr-03); US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- The Administration on Aging (AoA) and The Administration for Community Living (ACL). 2019 Profile of Older Americans; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 1–26.
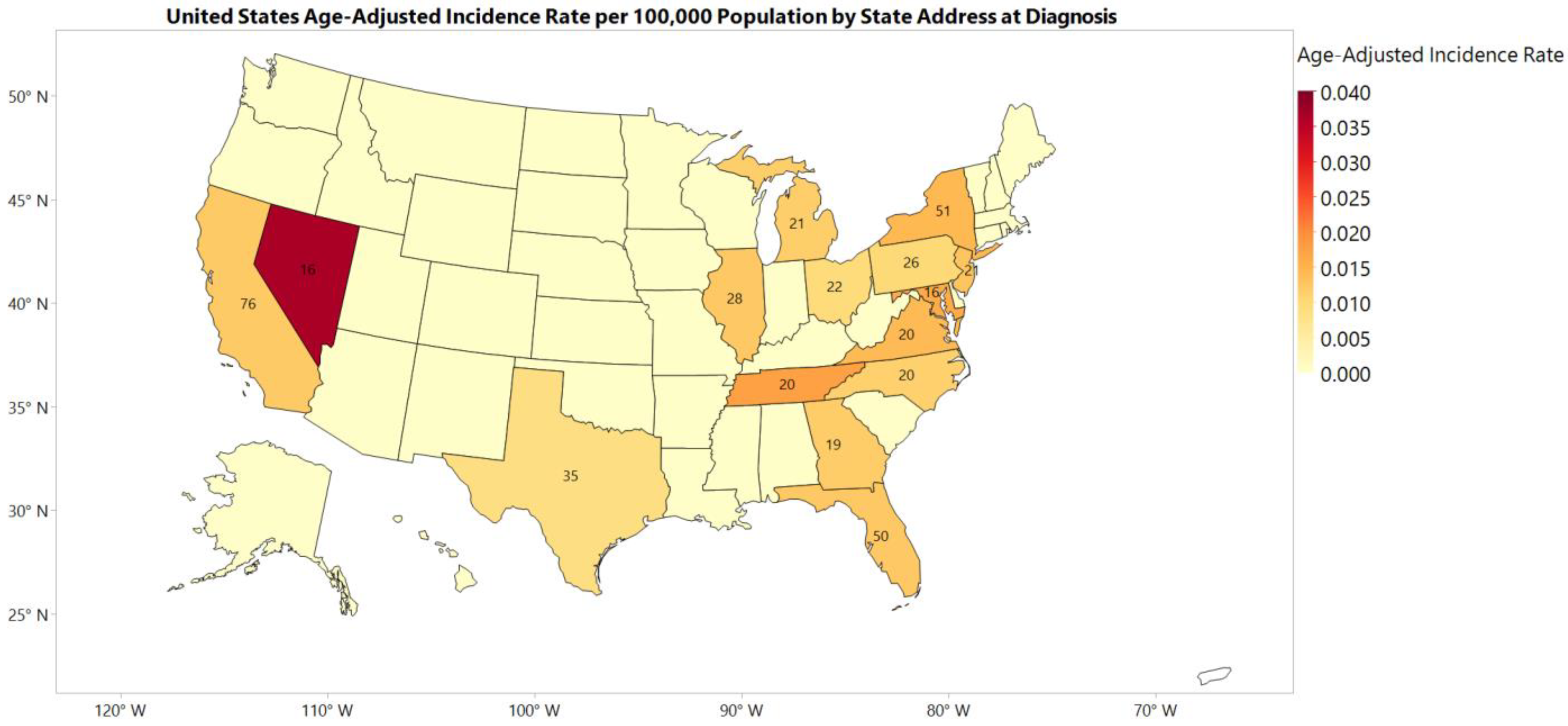
| Variable | Level | MANEC-P Cases, n (%) | Age-Adjusted Incidence Rate per 10,000,000 (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Program | NPCR | 611 (96.98) | 1.13 (1.04–1.23) | Reference |
| SEER | 19 (3.02) | 0.98 (0.58–1.54) | 0.64 | |
| Age, years | 00–39 years | 37 (5.87) | 0.14 (0.1–0.19) | Reference |
| 40–44 years | 28 (4.44) | 0.77 (0.51–1.11) | <0.05 | |
| 45–49 years | 35 (5.56) | 0.95 (0.66–1.32) | <0.05 | |
| 50–54 years | 62 (9.84) | 1.73 (1.32–1.73) | <0.05 | |
| 55–59 years | 69 (10.95) | 2.14 (1.66–2.14) | <0.05 | |
| 60–64 years | 82 (13.02) | 3.06 (2.44–3.06) | <0.05 | |
| 65–69 years | 81 (12.86) | 3.80 (3.02–3.8) | <0.05 | |
| 70–74 years | 85 (13.49) | 5.14 (4.11–5.14) | <0.05 | |
| 75–79 years | 97 (15.40) | 6.09 (4.82–6.09) | <0.05 | |
| 80–84 years | 51 (8.10) | 5.31 (3.95–5.31) | <0.05 | |
| 85+ years | 21 (3.33) | 2.30 (1.43–2.30) | <0.05 | |
| Sex | Male | 357 (56.67) | 1.30 (1.25–1.55) | Reference |
| Female | 273 (43.33) | 0.92 (0.81–1.04) | <0.05 | |
| Age, years; and Sex | ||||
| 00–39 years | Female | 18 (48.65) | 0.13 (0.08–0.21) | Reference |
| Male | 19 (51.35) | 0.14 (0.08–0.22) | 1 | |
| 40–44 years | Female | ^ | ^ | ^ |
| Male | ^ | ^ | ^ | |
| 45–49 years | Female | ^ | ^ | Reference |
| Male | 20 | 1.09 (0.67–1.69) | ^ | |
| 50–54 years | Female | 24 (38.71) | 1.31 (0.84–1.95) | Reference |
| Male | 38 (61.29) | 2.16 (1.53–2.96) | 0.07 | |
| 55–59 years | Female | 31 (44.93) | 1.87 (1.27–2.65) | Reference |
| Male | 38 (55.07) | 2.43 (1.72–3.33) | 0.33 | |
| 60–64 years | Female | 34 (41.46) | 2.43 (1.69–3.40) | Reference |
| Male | 48 (58.54) | 3.75 (2.76–4.97) | 0.07 | |
| 65–69 years | Female | 33 (40.74) | 2.92 (2.01–4.10) | Reference |
| Male | 48 (59.26) | 4.79 (3.53–6.35) | 0.04 | |
| 70–74 years | Female | 39 (45.88) | 4.33 (3.08–5.92) | Reference |
| Male | 46 (54.12) | 6.11 (4.47–8.14) | 0.14 | |
| 75–79 years | Female | 34 (43.04) | 4.62 (3.20–6.45) | Reference |
| Male | 45 (56.96) | 8.03 (5.85–0.74) | 0.02 | |
| 80–84 years | Female | 25 (49.02) | 4.32 (2.80–6.38) | Reference |
| Male | 26 (50.98) | 6.80 (4.44–9.96) | 0.14 | |
| 85+ years | Female | ^ | ^ | Reference |
| Male | 16 | 5.39 (3.08–8.76) | ^ | |
| Ethnicity | Spanish-Hispanic-Latino | 41 (6.51) | 0.80 (0.56–1.09) | Reference |
| Non-Spanish-Hispanic-Latino | 589 (93.49) | 1.16 (1.07–1.26) | 0.021 | |
| Race | White | 525 (83.33) | 1.12 (1.02–1.22) | Reference |
| Black | 78 (12.38) | 1.30 (1.02–1.64) | 0.24 | |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 20 (3.17) | 0.89 (0.54–1.39) | 0.38 | |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | ^ | ^ | ^ | |
| Other/Unknown | ^ | ^ | ^ | |
| Primary site, pancreas | Head | 245 (38.83) | 0.44 (0.38–0.50) | Reference |
| Body, tail, and duct | 249 (39.62) | 0.45 (0.40–0.51) | 0.87 | |
| IOL | 16 (2.54) | 0.03 (0.02–0.04) | <0.01 | |
| Other specified parts and overlapping lesions | 44 (6.97) | 0.07 (0.06–0.10) | <0.01 | |
| NOS | 76 (12.04) | 0.14 (0.11–0.17) | <0.01 | |
| Grade | Grade I | 117 (18.57) | 0.21 (0.17–0.25) | Reference |
| Grade II | 126 (20.00) | 0.22 (0.18–0.26) | 0.80 | |
| Grade III | 123 (19.52) | 0.22 (0.18–0.26) | 0.76 | |
| Grade IV | 19 (3.02) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | <0.01 | |
| Unknown | 245 (38.89) | 0.44 (0.39–0.50) | <0.01 | |
| Historical Staging | In situ/Localized disease | 123 (19.52) | 0.23 (0.19–0.27) | Reference |
| Regional, direct extension only | 96 (15.24) | 0.17 (0.14–0.21) | 0.06 | |
| Regional, regional lymph nodes only | 52 (8.25) | 0.09 (0.14–0.21) | <0.01 | |
| Regional direct extension and regional lymph nodes | 122 (19.37) | 0.22 (0.18–0.26) | 0.78 | |
| Regional, NOS | ^ | ^ | ^ | |
| Distant site(s)/node(s) involved | 219 (34.76) | 0.39 (0.34–0.45) | <0.01 | |
| Not applicable | ^ | ^ | ^ | |
| Unknown/unstaged/unspecific | 18 (2.86) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | <0.01 | |
| Multiple primary sites | One primary only | 475 (75.40) | 0.85 (0.78–0.93) | Reference |
| 1st of 2 or more primaries | 46 (7.30) | 0.08 (0.06–0.11) | <0.01 | |
| 2nd of 2 of more primaries | 89 (14.13) | 0.16 (0.13–0.19) | <0.01 | |
| 3rd of 3 or more primaries | 16 (2.54) | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | <0.01 | |
| Regions | Northeast | 132 (20.95) | 1.25 (1.04–1.49) | Reference |
| Midwest | 110 (17.46) | 0.88 (0.72–1.06) | <0.01 | |
| South | 250 (39.68) | 1.21 (1.06–1.37) | 0.82 | |
| West | 138 (21.91) | 1.13 (0.95–1.34) | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrahman, A.M.; Yin, J.; Alva-Ruiz, R.; Yonkus, J.A.; Leiting, J.L.; Lynch, I.T.; Fogliati, A.; Campbell, N.A.; Carlson, D.M.; Roberts, L.R.; et al. Mixed Acinar Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Pancreas: Comparative Population-Based Epidemiology of a Rare and Fatal Malignancy in The United States. Cancers 2023, 15, 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030840
Abdelrahman AM, Yin J, Alva-Ruiz R, Yonkus JA, Leiting JL, Lynch IT, Fogliati A, Campbell NA, Carlson DM, Roberts LR, et al. Mixed Acinar Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Pancreas: Comparative Population-Based Epidemiology of a Rare and Fatal Malignancy in The United States. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):840. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030840
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrahman, Amro M., Jun Yin, Roberto Alva-Ruiz, Jennifer A. Yonkus, Jennifer L. Leiting, Isaac T. Lynch, Alessandro Fogliati, Nellie A. Campbell, Danielle M. Carlson, Lewis R. Roberts, and et al. 2023. "Mixed Acinar Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Pancreas: Comparative Population-Based Epidemiology of a Rare and Fatal Malignancy in The United States" Cancers 15, no. 3: 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030840
APA StyleAbdelrahman, A. M., Yin, J., Alva-Ruiz, R., Yonkus, J. A., Leiting, J. L., Lynch, I. T., Fogliati, A., Campbell, N. A., Carlson, D. M., Roberts, L. R., Gores, G. J., Smoot, R. L., Graham, R. P., Halfdanarson, T. R., & Truty, M. J. (2023). Mixed Acinar Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Pancreas: Comparative Population-Based Epidemiology of a Rare and Fatal Malignancy in The United States. Cancers, 15(3), 840. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030840